Muslim Conquest Of The Levant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Muslim conquest of the Levant ( ar, فَتْحُ الشَّام, translit=Feth eş-Şâm), also known as the Rashidun conquest of Syria, occurred in the first half of the 7th century, shortly after the rise of Islam."Syria." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 20 October 200
Syria – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
/ref> As part of the larger military campaign known as the early Muslim conquests, the
Syria – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
During the Roman period, beginning after the fall of Jerusalem in the year 70, the entire region (
Ghassan (ancient kingdom, Arabia) – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
/ref> During the last of the Roman-Persian Wars, beginning in 603, the
Iran – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
/ref> Thus, on the eve of the Muslim conquests the Romans (or Byzantines as modern Western historians conventionally refer to Romans of this period) were still in the process of rebuilding their authority in these territories, which in some areas had been lost to them for almost twenty years. Politically, the Syrian region consisted of two provinces: Syria proper stretched from
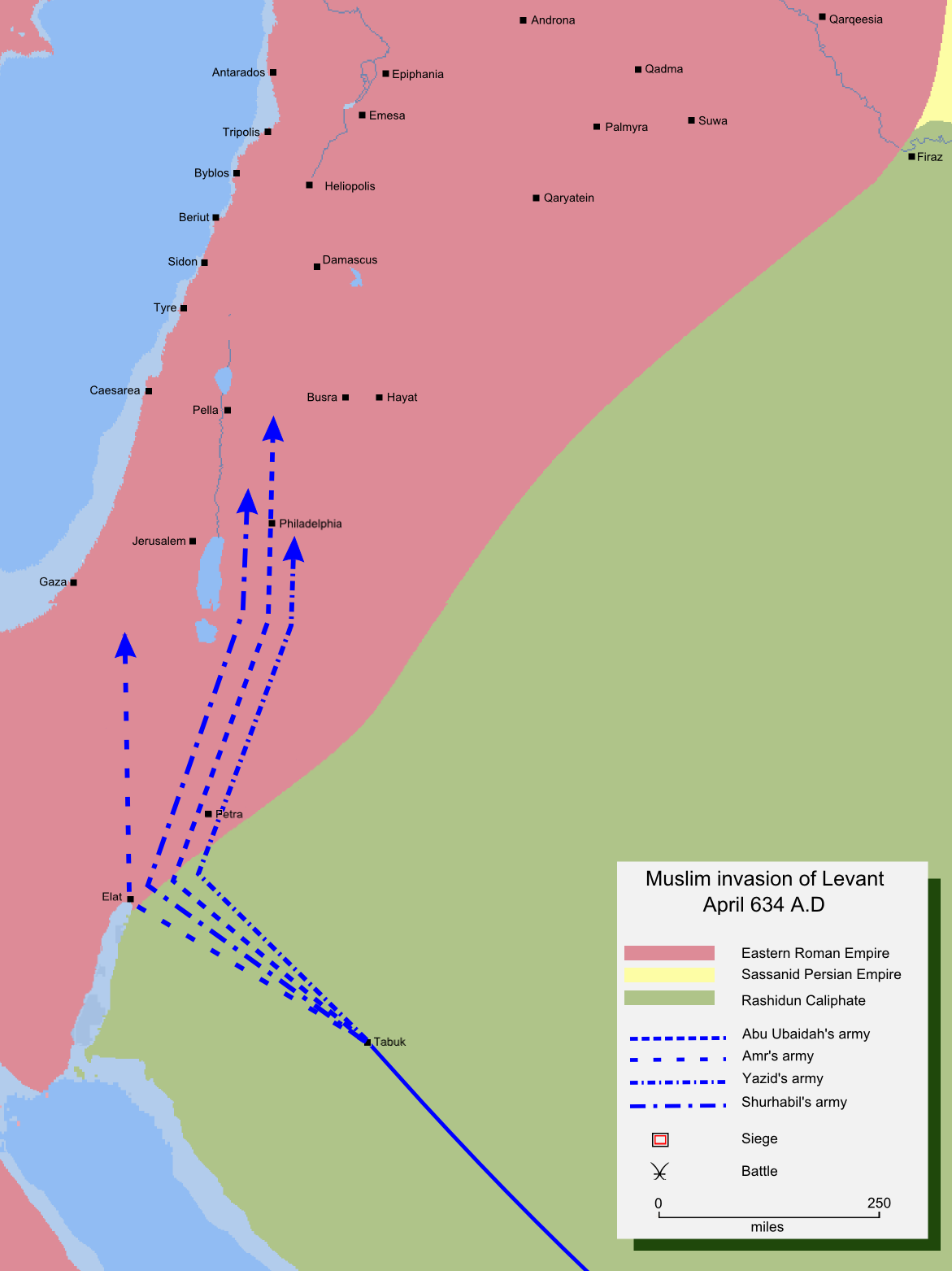 After successful campaigns against the Sassanids and the ensuing conquest of
After successful campaigns against the Sassanids and the ensuing conquest of

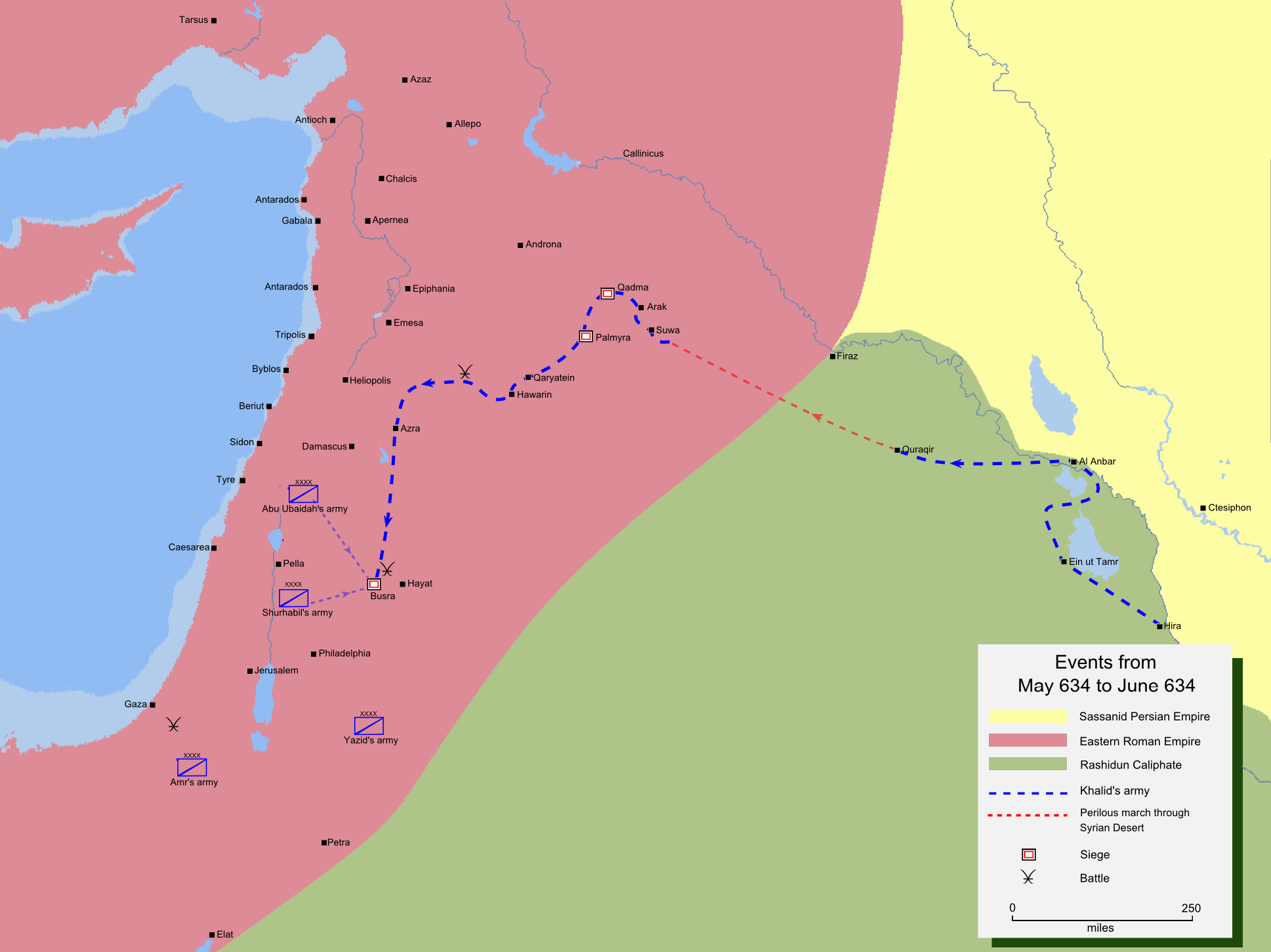 Khalid immediately set out for Syria from Al-Hirah, in
Khalid immediately set out for Syria from Al-Hirah, in
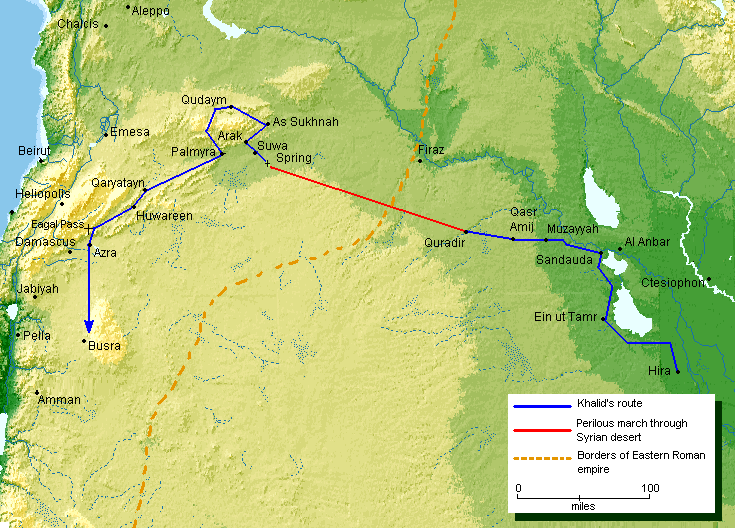 Here Khalid took over the command of the Muslim armies in Syria from Abu Ubaidah, according to the instructions of the Caliph. Massive Byzantine armies were concentrating at Ajnadayn to push the invading armies back to the desert. Early Muslim sources claim the Byzantine strength to have been 90,000, although most modern historians doubt the figures, yet consider this battle to be the key to breaking Byzantine power in Syria. On Khalid's instructions, all Muslim corps concentrated at Ajnadayn, where they won a decisive battle against the Byzantines on 30 July.
This defeat left Syria vulnerable to the Muslim invaders. Khalid decided to capture Damascus, the Byzantine stronghold. At Damascus, Thomas, son-in-law of Emperor Heraclius, was in charge. Having received intelligence of Khalid's march towards Damascus, he prepared for its defence, writing to Emperor Heraclius in Emesa for reinforcements. Moreover, Thomas, in order to get more time for preparation of a siege, sent armies to delay or, if possible, halt Khalid's march to Damascus. One of these armies was defeated at the Battle of Yaqusa in mid-August near Lake Tiberias, 145 kilometres (90 mi) from Damascus. Another was defeated in the Battle of Maraj as Saffer on 19 August. These engagements had the desired effect, delaying Khalid long enough to prepare for a siege. However, by the time Heraclius' reinforcements had reached the city Khalid had begun his siege, having reached Damascus on 20 August. To isolate the city from the rest of the region Khalid placed detachments south on the road to Palestine and in the north at the Damascus-Emesa route, and several other smaller detachments on routes towards Damascus. Heraclius' reinforcements were intercepted and routed at the Battle of Sanita-al-Uqab, 30 kilometres (20 mi) from Damascus. Khalid's forces withstood three Roman sallies that tried to break the siege. Khalid finally attacked and conquered Damascus on 18 September after 30 days, although, according to some sources, the siege had in fact lasted for four or six months. Heraclius, having received the news of the fall of Damascus, left for
Here Khalid took over the command of the Muslim armies in Syria from Abu Ubaidah, according to the instructions of the Caliph. Massive Byzantine armies were concentrating at Ajnadayn to push the invading armies back to the desert. Early Muslim sources claim the Byzantine strength to have been 90,000, although most modern historians doubt the figures, yet consider this battle to be the key to breaking Byzantine power in Syria. On Khalid's instructions, all Muslim corps concentrated at Ajnadayn, where they won a decisive battle against the Byzantines on 30 July.
This defeat left Syria vulnerable to the Muslim invaders. Khalid decided to capture Damascus, the Byzantine stronghold. At Damascus, Thomas, son-in-law of Emperor Heraclius, was in charge. Having received intelligence of Khalid's march towards Damascus, he prepared for its defence, writing to Emperor Heraclius in Emesa for reinforcements. Moreover, Thomas, in order to get more time for preparation of a siege, sent armies to delay or, if possible, halt Khalid's march to Damascus. One of these armies was defeated at the Battle of Yaqusa in mid-August near Lake Tiberias, 145 kilometres (90 mi) from Damascus. Another was defeated in the Battle of Maraj as Saffer on 19 August. These engagements had the desired effect, delaying Khalid long enough to prepare for a siege. However, by the time Heraclius' reinforcements had reached the city Khalid had begun his siege, having reached Damascus on 20 August. To isolate the city from the rest of the region Khalid placed detachments south on the road to Palestine and in the north at the Damascus-Emesa route, and several other smaller detachments on routes towards Damascus. Heraclius' reinforcements were intercepted and routed at the Battle of Sanita-al-Uqab, 30 kilometres (20 mi) from Damascus. Khalid's forces withstood three Roman sallies that tried to break the siege. Khalid finally attacked and conquered Damascus on 18 September after 30 days, although, according to some sources, the siege had in fact lasted for four or six months. Heraclius, having received the news of the fall of Damascus, left for
 Soon after the appointment of Abu-Ubaidah as commander in chief, he sent a small detachment to the annual fair held at Abu-al-Quds, modern day Ablah, near Zahlé east of Beirut. There was a Byzantine and Christian Arab garrison nearby, but the size of the garrison was miscalculated by the Muslim informants. The garrison quickly encircled the small Muslim detachment, but before it was completely destroyed, Khalid came to the rescue of the Muslim army. Abu Ubaidah, having received new intelligence, had sent Khalid. Khalid reached the battlefield and defeated the garrison on 15 October and returned with tons of looted booty from the fair and hundreds of Roman prisoners.
By capturing central Syria, the Muslims had given a decisive blow to the Byzantines. The communication between Northern Syria and Palestine was now cut off. Abu Ubaidah decided to march to Fahl, which is about 150 metres (500 ft) below sea level, where a strong Byzantine garrison and survivors of the Battle of Ajnadayn were present. The region was crucial because from here the Byzantine army could strike eastwards and cut Muslim communications with Arabia. Moreover, with this large garrison at their rear Palestine could not be invaded.
Khalid, commanding the advance guard, reached Fahl first and found that the Byzantines had flooded the plains by blocking the
Soon after the appointment of Abu-Ubaidah as commander in chief, he sent a small detachment to the annual fair held at Abu-al-Quds, modern day Ablah, near Zahlé east of Beirut. There was a Byzantine and Christian Arab garrison nearby, but the size of the garrison was miscalculated by the Muslim informants. The garrison quickly encircled the small Muslim detachment, but before it was completely destroyed, Khalid came to the rescue of the Muslim army. Abu Ubaidah, having received new intelligence, had sent Khalid. Khalid reached the battlefield and defeated the garrison on 15 October and returned with tons of looted booty from the fair and hundreds of Roman prisoners.
By capturing central Syria, the Muslims had given a decisive blow to the Byzantines. The communication between Northern Syria and Palestine was now cut off. Abu Ubaidah decided to march to Fahl, which is about 150 metres (500 ft) below sea level, where a strong Byzantine garrison and survivors of the Battle of Ajnadayn were present. The region was crucial because from here the Byzantine army could strike eastwards and cut Muslim communications with Arabia. Moreover, with this large garrison at their rear Palestine could not be invaded.
Khalid, commanding the advance guard, reached Fahl first and found that the Byzantines had flooded the plains by blocking the
 After capturing Emesa, Khalid moved north to capture Northern Syria, using his cavalry as an advance guard and raiding force. At Shaizar, Khalid intercepted a convoy taking provisions for Chalcis. The prisoners were interrogated and informed him about Emperor Heraclius' ambitious plan to take back Syria with an army possibly two hundred thousand (200,000) strong. Khalid immediately ended the raid.
After his past experiences, Heraclius now avoided pitched battle with the Muslim army. His plans were to send massive reinforcements to all the major cities, isolate the Muslim corps from each other, and then separately encircle and destroy the Muslim armies.
Part of his plan was to coordinate his attacks with those of Yazdgerd III, the
After capturing Emesa, Khalid moved north to capture Northern Syria, using his cavalry as an advance guard and raiding force. At Shaizar, Khalid intercepted a convoy taking provisions for Chalcis. The prisoners were interrogated and informed him about Emperor Heraclius' ambitious plan to take back Syria with an army possibly two hundred thousand (200,000) strong. Khalid immediately ended the raid.
After his past experiences, Heraclius now avoided pitched battle with the Muslim army. His plans were to send massive reinforcements to all the major cities, isolate the Muslim corps from each other, and then separately encircle and destroy the Muslim armies.
Part of his plan was to coordinate his attacks with those of Yazdgerd III, the
 With Emesa already in hand, Abu Ubaidah and Khalid moved towards
With Emesa already in hand, Abu Ubaidah and Khalid moved towards
 After the devastating defeat at Yarmouk, the remainder of the Byzantine empire was left vulnerable. With few military resources left, it was no longer in a position to attempt a military comeback in Syria. To gain time to prepare a defense of the rest of his empire, Heraclius needed the Muslims occupied in Syria. He thus sought help from the Christians (some of whom were Arabs) of Jazirah, mainly from Circesium and Hīt, who mustered a large army and marched against Emesa, Abu Ubaidah's headquarters. Abu Ubaidah withdrew all his forces from northern Syria to Emesa, and the Christians laid in a siege. Khalid was in favor of an open battle outside the fort, but Abu Ubaidah referred the matter to Umar, who sent a detachment from Iraq to invade Jazirah from three different routes. Another detachment was sent to Emesa from Iraq under Qa’qa ibn Amr, a veteran of Yarmouk, who had originally been sent to Iraq for the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. Umar himself marched from Medina with 1,000 men.
In 638, Muslims attacked Hīt, which they found to be well fortified; thus, they left a fraction of the army to impose a siege on the city, while the rest went after Circesium. When the Christians received the news of the Muslim invasion of their homeland, they abandoned the siege and hastily withdrew there. At this point Khalid and his mobile guard came out of the fort and devastated their army by attacking them from the rear.
On the orders of Umar, Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas, commander of the Muslim army in Iraq, sent an army under Iyad ibn Ghanm to conquer the region between the Tigris and the Euphrates up to
After the devastating defeat at Yarmouk, the remainder of the Byzantine empire was left vulnerable. With few military resources left, it was no longer in a position to attempt a military comeback in Syria. To gain time to prepare a defense of the rest of his empire, Heraclius needed the Muslims occupied in Syria. He thus sought help from the Christians (some of whom were Arabs) of Jazirah, mainly from Circesium and Hīt, who mustered a large army and marched against Emesa, Abu Ubaidah's headquarters. Abu Ubaidah withdrew all his forces from northern Syria to Emesa, and the Christians laid in a siege. Khalid was in favor of an open battle outside the fort, but Abu Ubaidah referred the matter to Umar, who sent a detachment from Iraq to invade Jazirah from three different routes. Another detachment was sent to Emesa from Iraq under Qa’qa ibn Amr, a veteran of Yarmouk, who had originally been sent to Iraq for the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. Umar himself marched from Medina with 1,000 men.
In 638, Muslims attacked Hīt, which they found to be well fortified; thus, they left a fraction of the army to impose a siege on the city, while the rest went after Circesium. When the Christians received the news of the Muslim invasion of their homeland, they abandoned the siege and hastily withdrew there. At this point Khalid and his mobile guard came out of the fort and devastated their army by attacking them from the rear.
On the orders of Umar, Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas, commander of the Muslim army in Iraq, sent an army under Iyad ibn Ghanm to conquer the region between the Tigris and the Euphrates up to
 The conquest of Jazirah was completed by 640 CE, after which Abu Ubaidah sent Khalid and Iyad ibn Ghanm (conqueror of Jazirah) to invade Byzantine territory north of there. They marched independently and captured
The conquest of Jazirah was completed by 640 CE, after which Abu Ubaidah sent Khalid and Iyad ibn Ghanm (conqueror of Jazirah) to invade Byzantine territory north of there. They marched independently and captured
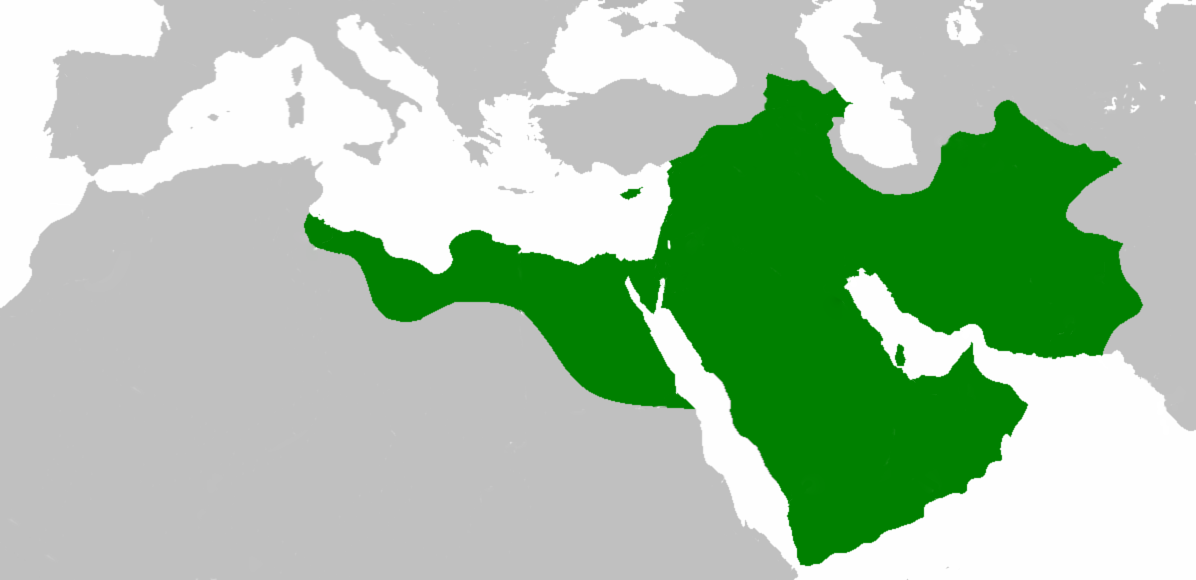 During the reign of
During the reign of
Last accessed 20 Oct 2006
A full-scale invasion was planned and a large force was sent to reconquer Syria. Muawiyah I, the governor of Syria, called for reinforcements and Uthman ordered the governor of
The Islamic World to 1600: Tutorial Outline
* Edward Gibbon
Chapter 51 * Bishop John Nikio
Chapters CXVI-CXXI {{DEFAULTSORT:Muslim Conquest Of Levant Arab–Byzantine wars History of the Levant 630s in the Byzantine Empire 630s conflicts 634 635 636 637 Heraclius
Syria – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
/ref> As part of the larger military campaign known as the early Muslim conquests, the
Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology an ...
was brought under the rule of the Rashidun Caliphate and developed into the provincial region of Bilad al-Sham. The presence of Arab Muslim troops on the southern Levantine borders of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
had occurred during the lifetime of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
, with the Battle of Muʿtah in 629 formally marking the start of the Arab–Byzantine wars. However, the actual conquest did not begin until 634, two years after Muhammad's death. It was led by the first two Rashidun caliphs who succeeded Muhammad: Abu Bakr and Umar ibn al-Khattab. During this time, Khalid ibn al-Walid was the most important leader of the Rashidun army
The Rashidun army () was the core of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century. The army is reported to have maintained a high level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization, gran ...
.
Roman Syria
Syria had been under Roman rule for seven centuries prior to the Arab Muslim conquest and had been invaded by theSassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Name ...
Persians on a number of occasions during the 3rd, 6th and 7th centuries; it had also been subject to raids by the Sassanids' Arab allies, the Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capit ...
."Syria." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 20 October 200Syria – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
During the Roman period, beginning after the fall of Jerusalem in the year 70, the entire region (
Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous south ...
, Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first ...
, and the Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Gali ...
) was renamed '' Palaestina'', subdivided into Diocese I and II. The Romans also renamed an area of land including the Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
, Sinai, and the west coast of the Arabian Peninsula as '' Palaestina Salutaris'', sometimes called ''Palaestina III'' or ''Palaestina Tertia''.Kaegi, 1995, p. 41. Part of the area was ruled by the Arab vassal state of the Ghassanids' ''symmachos''."Ghassan." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 18 October 200Ghassan (ancient kingdom, Arabia) – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
/ref> During the last of the Roman-Persian Wars, beginning in 603, the
Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
under Khosrau II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩, Husrō), also known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian king ( shah) of Iran, ruling ...
had succeeded in occupying Syria, Palestine and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
for over a decade before being forced by the victories of Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
to conclude the peace of 628."Iran." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 20 October 200Iran – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
/ref> Thus, on the eve of the Muslim conquests the Romans (or Byzantines as modern Western historians conventionally refer to Romans of this period) were still in the process of rebuilding their authority in these territories, which in some areas had been lost to them for almost twenty years. Politically, the Syrian region consisted of two provinces: Syria proper stretched from
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
and Aleppo in the north to the top of the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
. To the west and south of the Dead Sea lay the province of Palestine.
Syria was mostly made up of Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
speakers with a partly Arab population, especially in its eastern and southern parts. The Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
of Syria were people of no consequence until the migration of the powerful Ghassanid tribe from Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
to Syria, who converted to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
and thereafter ruled a semi-autonomous state with their own king under Roman vassalage. The Ghassanid Dynasty became one of the honoured princely dynasties of the Empire, with the Ghassanid king ruling over the Arabs in Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Ri ...
and Southern Syria from his capital at Bosra. The last of the Ghassanid kings, who ruled at the time of the Muslim invasion, was Jabalah ibn al-Aiham.
The Byzantine Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
, after re-capturing Syria from the Sassanians, set up new defense lines from Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip Lebanon
* Ghazzeh, a village in ...
to the south end of the Dead Sea. These lines were only designed to protect communications from bandits, and the bulk of the Byzantine defenses were concentrated in Northern Syria facing the traditional foes, the Sassanid Persians. The drawback of this defense line was that it enabled the Muslims, advancing from the desert in the south, to reach as far north as Gaza before meeting regular Byzantine troops.
The 7th century was a time of rapid military change in the Byzantine Empire. The empire was certainly not in a state of collapse when it faced the new challenge from Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
after being exhausted by recent Roman–Persian Wars, but utterly failed to tackle the challenge effectively.
Demographics of Roman Syria
Prior to the Muslim conquest, the demographic structure of theLevant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology an ...
was made up of a population base which included Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
, Samaritans
Samaritans (; ; he, שומרונים, translit=Šōmrōnīm, lit=; ar, السامريون, translit=as-Sāmiriyyūn) are an ethnoreligious group who originate from the ancient Israelites. They are native to the Levant and adhere to Samarit ...
, Aramaeans, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in Italy, ...
. During the 2nd century AD, Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
started to replace the previously spoken Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant a ...
throughout the region, incorporating local features from previous local languages such as Phoenician and Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
. Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
was spoken in the Hellenized urban centers and coastal cities, while Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
was fully spoken as a language only in Roman Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
. Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
was also spoken inland and Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
formed a significant portion of the populations in Petra, Bosra and Hauran
The Hauran ( ar, حَوْرَان, ''Ḥawrān''; also spelled ''Hawran'' or ''Houran'') is a region that spans parts of southern Syria and northern Jordan. It is bound in the north by the Ghouta oasis, eastwards by the al-Safa field, to the ...
in the south, Palmyra and Emesa in the center and Qinnasrin and Aleppo in the north.
Rise of the Caliphate
Military confrontations with theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
began during the lifetime of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
. The Battle of Mu'tah was fought in September 629 near the village of Mu'tah, east of the Jordan River and Karak Karak may refer to:
Places
* Al-Karak or Kerak, city and Crusader castle in Jordan
** Karak Governorate, Jordan
* al-Karak, Syria, city in Syria's Daraa Governorate
* Karak Nuh, village in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon
* Karak, Iran (disambiguation) ...
in Karak Governorate, between the forces of the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets a ...
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
and the forces of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
and their Arab Christian Ghassanid vassals. In Islamic historical sources, the battle is usually described as the Muslims' attempt to take retribution against the Ghassanids
The Ghassanids ( ar, الغساسنة, translit=al-Ġasāsina, also Banu Ghassān (, romanized as: ), also called the Jafnids, were an Arab tribe which founded a kingdom. They emigrated from southern Arabia in the early 3rd century to the Levan ...
after a Ghassanid official executed Muhammad's emissary who was en route to Bosra. During the battle the Muslim army was routed. After three Muslim leaders were killed, the command was given to Khalid ibn al-Walid and he succeeded in saving the rest of the forces. The surviving Muslim forces retreated to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
.
After the Farewell Pilgrimage in 632, the Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
appointed Usama ibn Zayd as the commander of an expeditionary force which was to invade the region of Balqa in the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
. This expedition was known as the Expedition of Usama bin Zayd and its stated aim was to avenge the Muslim losses at the Battle of Mu'tah, in which Usama's father and Muhammad's former adopted son, Zayd ibn Harithah, had been killed. Usama's expedition in May/June 632 was successful and his army was the first Muslim force to successfully invade and raid Byzantine territory.
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
died in June 632, and Abu Bakr was appointed Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
and political successor at Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
. Soon after Abu Bakr's succession, several Arab tribes revolted against him in the '' Ridda wars'' (Arabic for the Wars of Apostasy). The Campaign of the Apostasy was fought and completed during the eleventh year of the Hijri. The year 12 Hijri dawned, on 18 March 633, with Arabia united under the central authority of the Caliph at Medina.
Whether Abu Bakr intended a full-out imperial conquest or not is hard to say; he did, however, set in motion a historical trajectory that in just a few short decades would lead to one of the largest empires in history
Several empires in human history have been contenders for the largest of all time, depending on definition and mode of measurement. Possible ways of measuring size include area, population, economy, and power. Of these, area is the most commonly ...
, starting with a confrontation with the Persian Empire under the general Khalid ibn al-Walid.
Expedition to Syria
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Khalid established his stronghold in Iraq. While engaged with Sassanid forces, he also confronted the Ghassanids, Arab clients of the Byzantines. Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
soon recruited tribal contingents from all over the Arabian peninsula. Only those who had rebelled during the Ridda wars were excluded from the summons and remained excluded from Rashidun armies until 636, when Caliph Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphat ...
fell short of manpower for the Battle of Yarmouk and the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. The tradition of raising armies from tribal contingents remained in use until 636, when Caliph Umar organised the army as a state department.
Abu Bakr organised the army into four corps, each with its own commander and objective.
* Amr ibn al-A'as
( ar, عمرو بن العاص السهمي; 664) was the Arab commander who led the Muslim conquest of Egypt and served as its governor in 640–646 and 658–664. The son of a wealthy Qurayshite, Amr embraced Islam in and was assigned import ...
: Objective Palestine. Move on Elat
Eilat ( , ; he, אֵילַת ; ar, إِيلَات, Īlāt) is Israel's southernmost city, with a population of , a busy port and popular resort at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on what is known in Israel as the Gulf of Eilat and in Jordan ...
route, then across Valley of Arabah.
* Yazid ibn Abu Sufyan: Objective Damascus. Move on Tabuk route.
* Shurahbil ibn Hasana: Objective Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Ri ...
. Move on Tabuk route after Yazid.
* Abu Ubaidah ibn al-Jarrah: Objective Emesa. Move on Tabuk route after Shurahbil.
Not knowing the precise position of the Byzantine army, Abu Bakr ordered that all corps should remain in touch with each other so that they could render assistance if the Byzantines were able to concentrate their army in any operational sector. In case the corps had to concentrate for one major battle, Abu Ubaidah was appointed Commander-in-Chief of the entire army.The Sword of Allah: Khalid bin al-Waleed, His Life and Campaigns: page no:576 by Lieutenant-General Agha Ibrahim Akram, Nat. Publishing. House, Rawalpindi (1970) .
In the first week of April 634, the Muslim forces began to move from their camps outside Medina. The first to leave was Yazid's corps, followed by Shurahbil, Abu Ubaidah and Amr, each a day's march from the other.
Abu Bakr walked for a short distance by the side of each corps commander. His parting words which he repeated to each of the corps commanders, were as follows:
Conquest of Syria

Initial phase
Moving to their assigned target beyond Tabouk, Yazid's corps made contact with a small Christian Arab force that was retreating after a skirmish with the Muslim advance guard, after which Yazid made for the Valley of Arabah where it meets the southern end of theDead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
.
As the main Byzantine defence line started from the coastal regions near Ghazahh, Yazid arrived at the Valley of Araba at about the same time as Amr bin Al Aas reached Elat
Eilat ( , ; he, אֵילַת ; ar, إِيلَات, Īlāt) is Israel's southernmost city, with a population of , a busy port and popular resort at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on what is known in Israel as the Gulf of Eilat and in Jordan ...
. The two forward detachments sent by the Byzantine army to prevent the entry of Yazid's and Amr's corps, respectively, into Palestine, were easily defeated by them, though they did prevent the Rashidun forces from reaching their assigned objective. Abu Ubaidah and Shurhabil, on the other hand, continued their march, and by early May 634 they reached the region between Bosra and Jabiya. The Emperor Heraclius, having received intelligence of the movements of the Muslim armies from his Arab clients, began to plan countermeasures. Upon Heraclius' orders, Byzantine forces from different garrisons in the north started moving to gather at Ayjnadyn. From here they could engage Amr's corps and maneuver against the flank or rear of the rest of the Muslim corps that were in Jordan and Southern Syria. The strength of the Byzantine forces, according to rough estimates, was about 100,000. Abu Ubaidah informed the Caliph about the preparations made by the Byzantines in the third week of May 634. Because Abu Ubaida didn't have experience as a commander of military forces in such major operations, especially against the powerful Roman Army, Abu Bakr decided to send Khalid ibn Walid to assume command. According to early Muslim chronicles, Abu Bakr said, "By Allah, I shall destroy the Romans and the friends of Satan with Khalid Ibn Al Walid."
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, in early June, taking with him half his army, about 8000 strong. There were two routes towards Syria from Iraq: one was via Daumat-ul-Jandal, and the other was through Mesopotamia, passing through Raqqa. The Muslim armies in Syria were in need of urgent reinforcement, so Khalid avoided the conventional route to Syria via Daumat ul Jandal, as it was the longer route, and would take weeks to reach Syria. Khalid avoided the Mesopotamian route because of the presence of Roman garrisons there and in Northern Syria. To engage them at a time when Muslim armies were being outflanked in Syria was not a wise idea. Khalid selected a shorter route to Syria, an unconventional route passing through the Syrian Desert. It is recorded that his soldiers marched for two days without a single drop of water, before reaching a predetermined water source at an oasis. Khalid thus entered Northern Syria and caught the Byzantines on their right flank. According to modern historians, this ingenious strategic maneuver unhinged the Byzantine defences in Syria.
Southern Syria
Ain Tamer, Quraqir, Suwa, Arak, and the historical city of Tadmur were first to fall to Khalid. Sukhnah, al-Qaryatayn andHawarin
Huwwarin ( ar, حوارين, also spelled Hawarin, Huwarin or Hawarine) is a village in central Syria, administratively part of the Homs Governorate, south of Homs. Situated in the Syrian Desert, the village is adjacent to the larger town of Mahin ...
were captured after the Battle of al-Qaryatayn and the Battle of Hawarin. After dealing with all these cities, Khalid moved towards Damascus through a mountain pass which is now known as Sanita-al-Uqab (Uqab Pass) after the name of Khalid's army standard. From here he moved away from Damascus, towards Bosra, the capital of the Ghassanids. He ordered other Muslim commanders to concentrate their armies, still near the Syrian-Arabian border, at Bosra. At Maraj-al-Rahab, Khalid defeated a Ghassanid army in a quick battle, called the Battle of Marj-al-Rahit. Meanwhile, Abu Ubaida ibn al-Jarrah, the supreme commander of the Muslim armies in Syria, had ordered Shurhabil ibn Hasana to attack Bosra. The latter laid siege to Bosra with his small army of 4000. The Roman and Ghassanid Arab garrison, realizing that this might be the advance guard of the larger Muslim army to come, sallied out of the fortified city and attacked Shurhabil, surrounding him from all sides; however, Khalid reached the arena with his cavalry and saved Shurhabil. The combined forces of Khalid, Shurhabil, and Abu Ubaidah then resumed the siege of Bosra, which surrendered some time in mid-July 634 CE, effectively ending the Ghassanid Dynasty.
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
from Emesa. The citizens were granted peace on the promise of annual tribute and the Byzantine army was given three days to go as far as they could. After three days, Khalid took a cavalry force, caught up to the Romans using an unknown shortcut, and attacked them at the Battle of Maraj-al-Debaj
Battle of Marj-ud-Debaj ( ar, معركة مرج الديباج) was fought between the Byzantine army, survivors from the conquest of Damascus, and the Rashidun Caliphate army in September 634. It was a successful raid after three days of armi ...
, north of Damascus.
Conquest under Caliph Umar
Dismissal of Khalid from command
On 22 August, Abu Bakr, the first caliph, died, having made Umar his successor. Umar's first move was to relieve Khalid from command and appoint Abu Ubaidah ibn al-Jarrah as the new commander-in-chief of the Islamic army. Abu Ubaidah got the letter memorializing this during the siege, but he delayed the announcement until the city had been conquered. Later on, Khalid pledged his loyalty to the new Caliph and continued to serve as an ordinary commander under Abu Ubaidah. He is reported to have said, "If Abu Bakr is dead and Umar is Caliph, then we listen and obey." Abu Ubaidah moved more slowly and steadily, which had a concomitant effect on military operations in Syria. Abu Ubaidah, being an admirer of Khalid, made him commander of the cavalry and relied heavily on his advice during the whole campaign.Conquest of the Central Levant
River Jordan
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Shariea ...
. The Byzantine army was eventually defeated at the Battle of Fahl on 23 January 635.
Conquest of Palestine
Next, the Muslim armies consolidated their conquest of the Levant as Shurhabil and Amr went deeper into Palestine. Bet She'an surrendered after a little resistance followed by the surrender of Tiberias in February. Umar, after having learned of the position and strength of the Byzantine army in Palestine, wrote detailed instructions to his corps commanders there and ordered Yazid to capture theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
coast. Amr and Shurhabil accordingly marched against the strongest Byzantine garrison and defeated them in the Second Battle of Ajnadyn. The two corps then separated, with Amr moving to capture Nablus, Amawas
Imwas or Emmaus ( ar, عِمواس), known in classical times as Nicopolis ( gr, Νικόπολις, lit=City of Victory), was a Palestinian Arab village located southeast of the city of Ramla and from Jerusalem in the Latrun salient of the We ...
, Jaffa, Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropoli ...
, Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip Lebanon
* Ghazzeh, a village in ...
and Yubna
Yibna ( ar, يبنى; ''Jabneh'' or ''Jabneel'' in Biblical times; ''Jamnia'' in Roman times; '' Ibelin'' to the Crusaders), or Tel Yavne is an archaeological site and depopulated Palestinian town. The ruins are located immediately southeast of ...
in order to complete the conquest of all Palestine, while Shurahbil moved against the coastal towns of Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial and US customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square ...
and Tyre. Yazid advanced from Damascus to capture the ports of Sidon
Sidon ( ; he, צִידוֹן, ''Ṣīḏōn'') known locally as Sayda or Saida ( ar, صيدا ''Ṣaydā''), is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located in the South Governorate, of which it is the capital, on the Mediterranean coast ...
, Arqa, Byblos and Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
. By 635 CE, Palestine, Jordan and Southern Syria, with the exception of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and Caesarea, were in Muslim hands. On the orders of Umar, Yazid next besieged Caesarea, which, barring a suspension around the time of the Battle of Yarmouk, lasted until the port fell in 640.
According to lexicographer David ben Abraham al-Fasi (died before 1026 CE), the Muslim conquest of Palestine brought relief to the country's Jewish citizens, who had previously been barred by the Byzantines from praying on the Temple Mount.
Battles for Emesa and Second Battle of Damascus
After the battle, which proved to be the key to Palestine and Jordan, the Muslim armies split up. Shurhabil and Amr's corps moved south to capture Palestine, while Abu Ubaidah and Khalid, with a relatively larger corps, moved north to conquer Northern Syria. While the Muslims were occupied at Fahl, Heraclius, sensing an opportunity, quickly sent an army under General Theodras to recapture Damascus, where a small Muslim garrison was left. Shortly thereafter, the Muslims, having just won the Battle of Fahl, were on their way to Emesa. In the meantime, the Byzantine army split in two, one deployed at Maraj al Rome ( Beqaa Valley) led by Schinos; the other, commanded by Theodras, stationed to the west of Damascus ( Al-Sabboura region). During the night, Theodras advanced to Damascus to launch a surprise attack. Khalid's spy informed him about the move and Khalid, having received permission from Abu Ubaidah, galloped towards Damascus with his mobile guard. While Abu Ubaidah fought and defeated the Roman army in theBattle of Marj ar-Rum
The Battle of Marj ar-Rum ('), also known as the Battle of Marj Dimashq ('), was a conflict between the Rashidun caliphate and the Byzantine Empire. The battle occurred shortly after the Battle of Fahl when the Byzantines attempted to recapture ...
, Khalid moved to Damascus with his cavalry and attacked and defeated Theodras there. A week later, Abu Ubaida himself moved towards Heliopolis, where the great Temple of Jupiter stood.
In May 636, Heliopolis surrendered to the Muslims after little resistance and agreed to pay tribute. Abu Ubaidah sent Khalid straight towards Emesa.
Emesa and Chalcis
Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida ( Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved f ...
offered a peace treaty for a year. Abu Ubaidah accepted the offer and, rather than invading districts of Emesa and Chalcis, he consolidated his rule in conquered land and captured Hamah, and Maarrat al-Nu'man
, timezone = EET
, utc_offset = +3
, timezone_DST = EEST
, utc_offset_DST = +2
, blank_name = Climate
, blank_info = BSk
, coordinates=
, e ...
. Having mustered sizeable armies at Antioch, Heraclius sent them to reinforce strategically important areas of Northern Syria, like Emesa and Chalcis. The Byzantine reinforcement of Emesa violated the treaty, and Abu Ubaidah and Khalid accordingly marched there. A Byzantine army that halted Khalid's advance guard was defeated. The Muslims besieged Emesa which was finally conquered in March 636 CE after two months.
Battle of Yarmouk
Sassanid emperor
The Sasanian monarchs were the rulers of Iran after their victory against their former suzerain, the Parthian Empire, at the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224. At its height, the Sasanian Empire spanned from Turkey and Rhodes in the west to Pakistan in ...
. In 635 Yazdgerd III had sought an alliance with Heraclius, marrying the latter's daughter (or granddaughter, according to tradition) Manyanh. While Heraclius prepared for a major offense in the Levant, Yazdegerd was supposed to mount a well-coordinated counterattack on his front in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, while Heraclius attacked in the Levant. However, it was not meant to be. Umar probably had intelligence of this alliance, and started peace negotiations with Yazdegerd III, apparently inviting him to join Islam. When Heraclius launched his offensive in May 636, Yazdegerd, probably owing to the exhaustion of his government, could not coordinate with the Heraclian offensive, frustrating the plan.
Five massive armies were launched in June to recapture Syria. Khalid, having grasped Heraclius' plan, feared that the Muslim armies would become isolated and then destroyed piecemeal. He thus suggested to Abu Ubaidah in a council of war that he consolidate all the Muslim armies at one place to force a decisive battle with the Byzantines. Abu Ubaidah agreed, and concentrated them at Jabiya. This maneuver delivered a decisive blow to Heraclius' plan, since the latter did not wish to engage his troops in open battle with the Muslim light cavalry. From Jabiya, again on Khalid's suggestion, Abu Ubaidah ordered the Muslim troops to withdraw to the Plain of the Yarmouk River, where the cavalry could be used effectively. While the Muslim armies were gathering at Yarmouk, Khalid intercepted and routed the Byzantine advance guard, ensuring a safe path of retreat.
The Muslim armies reached the plain in July. A week or two later, around mid-July, the Byzantine army arrived. The Byzantine commander-in-chief, Vahan, sent Ghassanid forces, under their king, Jabala, to gauge the Muslim strength. Khalid's mobile guard defeated and routed them, the last action before the battle started. For one month negotiations continued between the two armies and Khalid went to meet Vahan in person at the Byzantine camp. Meanwhile, Muslim reinforcements arrived from Umar.
Abu Ubaidah, in another council of war, transferred field command of the Muslim army to Khalid. Finally, on 15 August, the Battle of Yarmouk was fought, lasting six days and ending in a major defeat for the Byzantines. This battle and subsequent clean-up engagements forever ended Byzantine domination of the Levant.
Meanwhile, Umar occupied Yazdegerd III in a grand deception. Yazdegerd III lost his army at the Battle of Qadisiyyah in November, three months after Yarmouk, ending Sassanid control west of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
.
Capturing Jerusalem
With the Byzantine army routed, the Muslims quickly recaptured the territory they had conquered prior to Yarmouk. Abu Ubaida held a meeting with his high commanders, including Khalid, and decided to conquerJerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. The Siege of Jerusalem lasted four months, after which the city agreed to surrender, but only to Umar personally. Amr-bin al-Aas suggested that Khalid should be sent to impersonate the caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
, due to his very strong resemblance. However, Khalid was recognized and Umar had to come himself to accept the surrender of Jerusalem in April 637.
Umar appointed his close advisor Ali to hold the lieutenancy of Medina. After Jerusalem, the Muslim armies broke up once again. Yazid's corps went to Damascus and then captured Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
. Amr and Shurhabil's corps left to conquer the rest of Palestine, while Abu Ubaidah and Khalid, at the head of a 17,000-strong army, moved north to conquer Northern Syria.
Conquest of northern Syria
Chalcis
Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida ( Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved f ...
, which was strategically the most significant Byzantine fort. Through Chalcis the Byzantines would be able to guard Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
, Heraclius' homeland of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
, and the regional capital, Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
. Abu Ubaidah sent Khalid with his mobile guard towards Chalcis. The virtually impregnable fort was guarded by Greek troops under Menas, reportedly second in prestige only to the Emperor himself. Menas, diverting from conventional Byzantine tactics, decided to face Khalid and destroy the leading elements of Muslim army before the main body could join them at Hazir 5 kilometres (3 mi) east of Chalcis. The resulting Battle of Hazir even reportedly forced Umar to praise Khalid's military genius, saying, "Khalid is truly the commander. May Allah have mercy upon Abu Bakr. He was a better judge of men than I have been."
Abu Ubaidah soon joined Khalid at Chalcis, which surrendered some time in June. With this strategic victory, the territory north of Chalcis lay open to the Muslims. Khalid and Abu Ubaidah continued their march northward and laid siege to Aleppo, which was captured after fierce resistance from desperate Byzantine troops in October. Before marching towards Antioch, Khalid and Abu Ubaidah decided to isolate the city from Anatolia. They accordingly sent detachments north to eliminate all possible Byzantine forces and captured the garrison town of Azaz, 50 kilometres (30 mi) from Aleppo; from there Muslims attacked Antioch from the eastern side, resulting in the Battle of Iron bridge. The Byzantine army, composed of the survivors of Yarmouk and other Syrian campaigns, was defeated, retreating to Antioch, whereupon the Muslims besieged the city. Having little hope of help from the Emperor, Antioch surrendered on 30 October, on the condition that all Byzantine troops would be given safe passage to Constantinople. Abu Ubaidah sent Khalid towards the north and he himself marched to the south and captured Latakia, Jablah, Tartus, and the coastal areas west of the Anti-Lebanon Mountains. Khalid moved north and raided territory up to as far as Kızılırmak River in Anatolia. Emperor Heraclius had already left Antioch for Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city ('' polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Os ...
before the Muslims arrived. He then arranged for the necessary defenses in Jazirah and Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
and left for Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. On the way, he had a narrow escape when Khalid, who had just captured Marash, was heading south towards Manbij. Heraclius hastily took the mountainous path and, on passing through the Cilician gate
The Cilician Gates or Gülek Pass is a pass through the Taurus Mountains connecting the low plains of Cilicia to the Anatolian Plateau, by way of the narrow gorge of the Gökoluk River. Its highest elevation is about 1000m.
The Cilician Gates hav ...
s, is reported to have said, "Farewell, a long farewell to Syria, my fair province. Thou art an infidel's (enemy's) now. Peace be with you, O, Syria – what a beautiful land you will be for the enemy hands."
Byzantine counterattack
 After the devastating defeat at Yarmouk, the remainder of the Byzantine empire was left vulnerable. With few military resources left, it was no longer in a position to attempt a military comeback in Syria. To gain time to prepare a defense of the rest of his empire, Heraclius needed the Muslims occupied in Syria. He thus sought help from the Christians (some of whom were Arabs) of Jazirah, mainly from Circesium and Hīt, who mustered a large army and marched against Emesa, Abu Ubaidah's headquarters. Abu Ubaidah withdrew all his forces from northern Syria to Emesa, and the Christians laid in a siege. Khalid was in favor of an open battle outside the fort, but Abu Ubaidah referred the matter to Umar, who sent a detachment from Iraq to invade Jazirah from three different routes. Another detachment was sent to Emesa from Iraq under Qa’qa ibn Amr, a veteran of Yarmouk, who had originally been sent to Iraq for the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. Umar himself marched from Medina with 1,000 men.
In 638, Muslims attacked Hīt, which they found to be well fortified; thus, they left a fraction of the army to impose a siege on the city, while the rest went after Circesium. When the Christians received the news of the Muslim invasion of their homeland, they abandoned the siege and hastily withdrew there. At this point Khalid and his mobile guard came out of the fort and devastated their army by attacking them from the rear.
On the orders of Umar, Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas, commander of the Muslim army in Iraq, sent an army under Iyad ibn Ghanm to conquer the region between the Tigris and the Euphrates up to
After the devastating defeat at Yarmouk, the remainder of the Byzantine empire was left vulnerable. With few military resources left, it was no longer in a position to attempt a military comeback in Syria. To gain time to prepare a defense of the rest of his empire, Heraclius needed the Muslims occupied in Syria. He thus sought help from the Christians (some of whom were Arabs) of Jazirah, mainly from Circesium and Hīt, who mustered a large army and marched against Emesa, Abu Ubaidah's headquarters. Abu Ubaidah withdrew all his forces from northern Syria to Emesa, and the Christians laid in a siege. Khalid was in favor of an open battle outside the fort, but Abu Ubaidah referred the matter to Umar, who sent a detachment from Iraq to invade Jazirah from three different routes. Another detachment was sent to Emesa from Iraq under Qa’qa ibn Amr, a veteran of Yarmouk, who had originally been sent to Iraq for the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. Umar himself marched from Medina with 1,000 men.
In 638, Muslims attacked Hīt, which they found to be well fortified; thus, they left a fraction of the army to impose a siege on the city, while the rest went after Circesium. When the Christians received the news of the Muslim invasion of their homeland, they abandoned the siege and hastily withdrew there. At this point Khalid and his mobile guard came out of the fort and devastated their army by attacking them from the rear.
On the orders of Umar, Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas, commander of the Muslim army in Iraq, sent an army under Iyad ibn Ghanm to conquer the region between the Tigris and the Euphrates up to Urfa
Urfa, officially known as Şanlıurfa () and in ancient times as Edessa, is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of Şanlıurfa Province. Urfa is situated on a plain about 80 km east of the Euphrates River. Its climate features e ...
. In 639–640, Raqqa fell into Muslim hands, followed by most of Jazirah, the last base of the Eastern Roman Empire in the region, which surrendered peacefully and agreed to pay Jizya.
Campaigns in Armenia and Anatolia
Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city ('' polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Os ...
, Amida, Melitene (Malatya) and the whole of Armenia up to Ararat
Ararat or in Western Armenian Ararad may refer to:
Personal names
* Ararat ( hy, Արարատ), a common first name for Armenian males (pronounced Ararad in Western Armenian)
* Ararat or Araratian, a common family name for Armenians (pronounced A ...
and raided northern and central Anatolia. Heraclius had already abandoned all the forts between Antioch and Tartus to create a buffer zone between the Muslim controlled areas and Anatolia.
Umar then called a halt to the expedition and ordered Abu Ubaidah, now governor of Syria, to consolidate his rule there. This decision can be explained by the dismissal of Khalid from the army, which ended his military career, and a drought followed by a plague the year after.
Under Caliph Uthman's reign
Caliph Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic prophe ...
, Constantine III Constantine III may refer to:
* Constantine III (Western Roman Emperor), self-proclaimed western Roman Emperor 407–411
* Heraclius Constantine, Byzantine Emperor in 641
* Constans II, Byzantine emperor 641–668, sometimes referred to under this ...
decided to recapture the Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology an ...
, which had been lost to the Muslims during Umar's reign."Umar (634–644)", ''The Islamic World to 1600'' Multimedia History Tutorials by the Applied History Group, University of Calgary.Last accessed 20 Oct 2006
A full-scale invasion was planned and a large force was sent to reconquer Syria. Muawiyah I, the governor of Syria, called for reinforcements and Uthman ordered the governor of
Kufa
Kufa ( ar, الْكُوفَة ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000. Currently, Kufa and Naja ...
to send a contingent, which, together with the local garrison, defeated the Byzantine army in Northern Syria.
In 645–646, Sufyan bin Mujib Al-Azdi, appointed by Muawiyah, managed to seize Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
*Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in t ...
to eventually capture the last Byzantine stronghold on the Levantine coast.
Uthman gave permission to Muawiyah to build a navy. From their base in Syria, the Muslims used this fleet to capture Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
in 649, Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cypru ...
, and Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
. Annual raids into western Anatolia dissuaded the Byzantines from further attempts to recapture Syria. In 654–655, Uthman ordered the preparation of an expedition to capture Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, but, due to unrest in the caliphate that resulted in his assassination in 655, the expedition was delayed for decades, only to be attempted unsuccessfully under the Ummayad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
s.
Administration under the Rashidun Caliphate
The new rulers divided Syria into four districts (''junds''): Jund Dimashq (Damascus), Jund Hims, Jund al-Urdunn (Jordan), and Jund Filastin (Palestine) (to which a fifth, Jund Qinnasrin, was later added) Yaqut al-Hamawi as cited in and the Arab garrisons were kept apart in camps, and life went on much as before for the local population. The Muslims tolerated the Jews and Christians; indeed, Nestorian and Jacobite Christians were treated better under the Muslims than under the Byzantines. The taxes instituted were the ''kharaj
Kharāj ( ar, خراج) is a type of individual Islamic tax on agricultural land and its produce, developed under Islamic law.
With the first Muslim conquests in the 7th century, the ''kharaj'' initially denoted a lump-sum duty levied upon the ...
'', which landowners and peasants paid according to the productivity of their fields, and the '' jizya'', paid by non-Muslims in return for state protection and exemption from military service. The Byzantine civil service was retained until a new system could be instituted; therefore, Greek remained the administrative language in the new Muslim territories for over 50 years after the conquests.
Rise of the Umayyads
When the firstcivil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polic ...
broke out in the Muslim empire as a result of the murder of Uthman and the nomination of Ali as caliph, the Rashidun Caliphate was succeeded by the Umayyad dynasty, with Syria as its core and Damascus its capital for the next century to come.
See also
* Spread of Islam * Muslim conquests * Byzantine-Arab Wars *Ghassanids
The Ghassanids ( ar, الغساسنة, translit=al-Ġasāsina, also Banu Ghassān (, romanized as: ), also called the Jafnids, were an Arab tribe which founded a kingdom. They emigrated from southern Arabia in the early 3rd century to the Levan ...
* Iudaea Province
* Umayyad conquest of North Africa
*
* History of Lebanon
* History of Syria
* History of Jordan
* History of Palestine
* History of the Levant
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * * * *External links
* Multimedia History Tutorials by the Applied History Group, ''The Islamic World to 1600'', University of Calgary.The Islamic World to 1600: Tutorial Outline
* Edward Gibbon
Chapter 51 * Bishop John Nikio
Chapters CXVI-CXXI {{DEFAULTSORT:Muslim Conquest Of Levant Arab–Byzantine wars History of the Levant 630s in the Byzantine Empire 630s conflicts 634 635 636 637 Heraclius