As part of the
early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests (), also known as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the founder of Islam. He established the first Islamic state in Medina, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia that ...
, which were initiated by
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
in 622, the
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
conquered the
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
between 632 and 654. This event led to the decline of
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
, which had been the official religion of
Persia (or Iran) since the time of the
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
. The
persecution of Zoroastrians
The persecution of Zoroastrians is a significant aspect of the later part of the community's history. It is speculated that religious strife existed between Zoroastrianism, Zoroastrians and early Christians, particularly within the context ...
by the
early Muslims
From 613 to 619 Common Era, CE, the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad gathered in his hometown of Mecca a small following of those who embraced his message of Islam and thus became Muslims. The first person who professed ...
during and after this conflict prompted many of them to flee eastward to
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, where they were
granted refuge by various kings.
While
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
was experiencing the rise of
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
in the 7th century, Persia was struggling with unprecedented levels of political, social, economic, and military weakness; the
Sasanian army had greatly exhausted itself in the
Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628
The Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628, also called the Last Great War of Antiquity, was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire. It was the final and most devastating conflict of the Roman–Persian wars (54 BCAD&n ...
. Following the execution of Sasanian shah
Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 ...
in 628, Persia's internal political stability began deteriorating at a rapid pace. Subsequently, ten new royal claimants were enthroned within the next four years.
[The Muslim Conquest of Persia By A.I. Akram. Ch: 1 ] Shortly afterwards, Persia was further devastated by the
Sasanian Interregnum, a large-scale civil war that began in 628 and resulted in the government's decentralization by 632.
Amidst Persia's turmoil, the first Rashidun invasion of Sasanian territory took place in 633, when the
Rashidun army
The Rashidun army () was the core of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century. The army is reported to have maintained a high level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization, grantin ...
conquered parts of
Asoristan, which was the Sasanians' political and economic centre in
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. Later, the regional Rashidun army commander
Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arabs, Arab military commander. He initially led campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career ...
was transferred to oversee the
Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant (; ), or Arab conquest of Syria, was a 634–638 CE invasion of Byzantine Syria by the Rashidun Caliphate. A part of the wider Arab–Byzantine wars, the Levant was brought under Arab Muslim rule and develope ...
, and as the Rashidun army became increasingly focused on the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, the newly conquered Mesopotamian territories were retaken by the Sasanian army. The second Rashidun invasion began in 636, under
Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas
Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas ibn Wuhayb al-Zuhri () was an Arabs, Arab Muslims, Muslim commander. He was the founder of Kufa and served as its governor under Umar, Umar ibn al-Khattab. He played a leading role in the Muslim conquest of Persia and was a cl ...
, when a key victory at the
Battle of al-Qadisiyyah
The Battle of al-Qadisiyyah ( ; ) took place between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Empire in November 636. It resulted in a decisive victory for the Rashidun army and is considered to be one of the most significant engagements of the ...
permanently ended all Sasanian control to the west of modern-day
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. For the next six years, the
Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
, a natural barrier, marked the political boundary between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Empire. In 642,
Umar ibn al-Khattab
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muh ...
, eight years into his reign as Islam's second
caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
, ordered a full-scale invasion of the rest of the
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
. Directing the war from the city of
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
in Arabia, Umar's quick conquest of Persia in a series of coordinated and multi-pronged attacks became his greatest triumph, contributing to his reputation as a great military and political strategist.
In 644, however, he was assassinated by the Persian craftsman
Abu Lu'lu'a Firuz
(, from Middle Persian: ''Pērōz''), also known in modern Persian-language sources as () or (), was a Sasanian Persian slave who assassinated Umar ibn al-Khattab (), the second Islamic caliph, in November 644.
After having been capture ...
, who had been captured by Rashidun troops and brought to Arabia as a slave.
Some Iranian historians have defended their forebears by using Arab sources to illustrate that "contrary to the claims of some historians, Iranians, in fact, fought long and hard against the invading Arabs." By 651, most of the urban centres in Iranian lands, with the notable exception of the provinces along the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
(i.e., in
Tabaristan
Tabaristan or Tabarestan (; ; from , ), was a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. It corresponded to the present-day province of Mazandaran, which became the predominant name of the area from the 11th-century onward ...
and
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
), had come under Muslim domination. Many localities fought against the invaders; although the Rashidun army had established hegemony over most of the country, many cities rose in rebellion by killing their Arab governors or attacking their garrisons. Eventually, military reinforcements quashed the Iranian insurgencies and imposed complete control. The
Islamization of Iran
The Islamization of Iran began with the Muslim conquest of Iran, when the Rashidun Caliphate annexed the Sasanian Empire. It was a long process by which Islam, though initially rejected, eventually spread among the Persians and the other Irania ...
was gradual and incentivized in various ways over a period of centuries, though some Iranians never converted and there is widespread evidence of
Zoroastrian scriptures and all other pre-Islamic being systematically burnt and
Zoroastrian priests being executed, particularly in areas that were centers of resistance. Islam had become Iran's predominant religion by the
Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
; the majority of Iranians were
Sunni Muslims
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Musli ...
until the
Safavids forcefully converted Iran to Shia Islam in the 16th century.
This was the first time since the collapse of the
Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
in 539 BC with the
Battle of Opis
The Battle of Opis was the last major military engagement between the Achaemenid Empire and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, which took place in September 539 BC, during the Persian invasion of Mesopotamia. At the time, Babylonia was the last major ...
, that Mesopotamia was ruled again by
Semitic-speaking people, after centuries of Persian (
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the large ...
,
Parthian and
Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign ...
empires), and Roman-Greek (
Macedonian,
Seleucid, and
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
empires) ruling periods.
Historiography and recent scholarship
When Western academics first investigated the
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
conquest of
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, they relied solely on the accounts of the
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
bishop
Sebeos, and accounts in Arabic written some time after the events they describe. The most significant work was probably that of
Arthur Christensen, and his ''L’Iran sous les Sassanides'', published in
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
and
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
in 1944.
Recent scholarship has begun to question the traditional narrative:
Parvaneh Pourshariati, in her ''Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire: The Sasanian-Parthian Confederacy and the Arab Conquest of Iran'', published in 2008, provides both a detailed overview of the problematic nature of trying to establish exactly what happened, and a great deal of original research that questions fundamental facts of the traditional narrative, including the timeline and specific dates.
Pourshariati's central thesis is that contrary to what was commonly assumed, the Sassanian Empire was highly decentralized, and was in fact a "confederation" with the
Parthians, who themselves retained a high level of independence.
[Parvaneh Pourshariati, ''Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire'', (I.B.Tauris, 2009), 3.] Despite their recent victories over the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, the Parthians unexpectedly withdrew from the confederation, and the Sassanians were thus ill-prepared and ill-equipped to mount an effective and cohesive defense against the
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
armies.
[Parvaneh Pourshariati, ''Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire: The Sasanian-Parthian Confederacy and the Arab Conquest of Iran'', I.B. Tauris, 2008.] Moreover, the powerful northern and eastern Parthian families, the kust-i khwarasan and kust-i adurbadagan, withdrew to their respective strongholds and made peace with the Arabs, refusing to fight alongside the
Sassanians.
Another important theme of Pourshariati's study is a re-evaluation of the traditional timeline. Pourshariati argues that the
Arab conquest of Mesopotamia
The Arab conquest of Mesopotamia was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 638 AD. The Arab Muslim forces of Caliph Umar first attacked Sasanian territory in 633, when Khalid ibn al-Walid invaded Mesopotamia (then known as the Sasa ...
"took place, not, as has been conventionally believed, in the years 632–634, after the accession of the last Sasanian king
Yazdgerd III (632–651) to power, but in the period from 628 to 632."
[Parvaneh Pourshariati, ''Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire: The Sasanian-Parthian Confederacy and the Arab Conquest of Iran'', I.B. Tauris, 2008. (p. 4)] An important consequence of this change in timeline means that the
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
conquest started precisely when the Sassanians and Parthians were engaged in internecine warfare over succession to the Sassanian throne.
Sasanian Empire before the conquest
Since the
1st century BC
The 1st century Before Christ, BC, also known as the last century BC and the last century Common Era , BCE, started on the first day of 100 BC, 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC, 1 BC. The Anno Domini, AD/BC notation does not ...
, the border between the
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
(later
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
) and
Parthian (later
Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign ...
) empires had been the
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
River. The border was constantly contested. Most battles, and thus most fortifications, were concentrated in the hilly regions of the north, as the vast Arabian or
Syrian Desert
The Syrian Desert ( ''Bādiyat Ash-Shām''), also known as the North Arabian Desert, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badiya, is a region of desert, semi-desert, and steppe, covering about of West Asia, including parts of northern Saudi Arabia, ea ...
(Roman Arabia) separated the rival empires in the south. The only dangers expected from the south were occasional raids by nomadic
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
tribesmen. Both empires therefore allied themselves with small, semi-independent Arab principalities, which served as buffer states and protected Byzantium and Persia from
Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
attacks. The Byzantine clients were the
Ghassanid
The Ghassanids, also known as the Jafnids, were an Arab tribe. Originally from South Arabia, they migrated to the Levant in the 3rd century and established what would eventually become a Christian kingdom under the aegis of the Byzantine Empi ...
s; the Persian clients were the
Lakhmid
The Lakhmid kingdom ( ), also referred to as al-Manādhirah () or as Banū Lakhm (), was an Arab kingdom that was founded and ruled by the Lakhmid dynasty from to 602. Spanning Eastern Arabia and Sawad, Southern Mesopotamia, it existed as a d ...
s. The Ghassanids and Lakhmids feuded constantly, which kept them occupied, but that did not greatly affect the Byzantines or the Persians. In the 6th and 7th centuries, various factors destroyed the balance of power that had held for so many centuries.
The conflict with the Byzantines greatly contributed to its weakness, by draining Sassanid resources, leaving it a prime target for the Muslims.
Social problems
Sasanian society was divided into four classes: priests, warriors, secretaries, and commoners. The latter formed the bulk of the population, served as its sole tax base, and remained its poorest class.
At the climax of
Khosrow II's ambitious Byzantine territory conquests in the
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and much of
Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, taxes rose dramatically, and most people could not pay. Years of Sassanid-Byzantine wars had ruined trade routes and industry, the population's main income sources. The existing Sassanid administrative structure proved inadequate when faced with the combined demands of a suddenly expanded empire, economy, and population. Rapid turnover of rulers and increasing provincial landholder (
dehqan
The ''dehqân'' (; , ''dihqân'' in Classical Persian) or ''dehgân'' (; ) were a class of land-owning magnates during the Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that w ...
) power further diminished the Sasanians. Over a period of fourteen years and twelve successive kings, the Sassanid Empire weakened considerably, and the power of the central authority passed into the hands of its generals. Even when a strong king emerged following a series of coups, the
Sassanids never completely recovered.
Events
Revolt of the Arab client states (602)
The Byzantine clients, the Arab
Ghassanids
The Ghassanids, also known as the Jafnids, were an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe. Originally from South Arabia, they migrated to the Levant in the 3rd century and established what would eventually become a Christian state, Christian kingdom unde ...
, converted to the
Monophysite
Monophysitism ( ) or monophysism ( ; from Greek , "solitary" and , "nature") is a Christological doctrine that states that there was only one nature—the divine—in the person of Jesus Christ, who was the incarnated Word. It is rejected as ...
form of
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, which was regarded as
heretical by the established Byzantine
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
. The Byzantines attempted to suppress the heresy, alienating the Ghassanids and sparking rebellions on their desert frontiers. The
Lakhmids
The Lakhmid kingdom ( ), also referred to as al-Manādhirah () or as Banū Lakhm (), was an Arab kingdom that was founded and ruled by the Lakhmid dynasty from to 602. Spanning Eastern Arabia and Sawad, Southern Mesopotamia, it existed as a d ...
also revolted against the Persian king Khusrau II.
Nu'man III (son of Al-Monder IV), the first Christian Lakhmid king, was deposed and killed by
Khusrau II in 602, because of his attempt to throw off Persian suzerainty. After Khusrau's assassination in 628, the Persian Empire fractured and the
Lakhmids
The Lakhmid kingdom ( ), also referred to as al-Manādhirah () or as Banū Lakhm (), was an Arab kingdom that was founded and ruled by the Lakhmid dynasty from to 602. Spanning Eastern Arabia and Sawad, Southern Mesopotamia, it existed as a d ...
were effectively semi-independent. It is now widely believed that the annexation of the Lakhmid kingdom was one of the main factors behind the fall of the Sasanian Empire and the subsequent Islamic conquest of Persia, as the
Lakhmid
The Lakhmid kingdom ( ), also referred to as al-Manādhirah () or as Banū Lakhm (), was an Arab kingdom that was founded and ruled by the Lakhmid dynasty from to 602. Spanning Eastern Arabia and Sawad, Southern Mesopotamia, it existed as a d ...
s agreed to act as spies for the
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
after being defeated in the
Battle of Hira by
Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arabs, Arab military commander. He initially led campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career ...
.
Byzantine–Sassanid War (602–628)
The Persian ruler
Khosrau II (Parviz) defeated a dangerous rebellion within his own empire,
Bahram Chobin
Bahrām Chōbīn () or Wahrām Chōbēn (Middle Persian: ; died 591), also known by his epithet Mehrbandak ("servant of Mithra"), was a nobleman, general, and political leader of the late Sasanian Empire and briefly its ruler as Bahram VI ().
So ...
's rebellion. He then turned his focus to his traditional Byzantine enemies, leading to the
Byzantine-Sassanid War of 602–628. For a few years, he succeeded. From 612 to 622, he extended the Persian borders almost to the same extent that they were under the
Achaemenid dynasty
The Achaemenid dynasty ( ; ; ; ) was a royal house that ruled the Achaemenid Empire, which eventually stretched from Egypt and Thrace in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east.
Origins
The history of the Achaemenid dy ...
(550–330 BC), capturing Western states as far as
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
,
Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
(the conquest of the latter being assisted by a Jewish army), and more.
The Byzantines regrouped and pushed back in 622 under
Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
. Khosrau was defeated at the
Battle of Nineveh in 627, and the Byzantines recaptured all of
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and penetrated far into the Persian provinces of
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. In 629, Khosrau's general
Shahrbaraz
Shahrbaraz (also spelled Shahrvaraz or Shahrwaraz; New Persian: ) was shah (king) of the Sasanian Empire from 27 April 630 to 9 June 630. He usurped the throne from Ardashir III, and was killed by Iranian nobles after forty days. Before usurp ...
agreed to peace, and the border between the two empires was once again the same as it had been in 602.
Plague of Sheroe
The Plague of Sheroe (627–628) was one of several epidemics that occurred in or close to Iran within two centuries after the first epidemic was brought by the Sasanian armies from its campaigns in
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
,
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, and
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
. It caused the death of many Aryan and therefore contributed to the fall of the Sasanian Empire.
Execution of Khosrau II
Khosrau II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 ...
was executed in 628 and, as a result, there were numerous claimants to the throne; from 628 to 632 there were ten kings and queens of Persia. The last,
Yazdegerd III
Yazdegerd III (also Romanized as ''Yazdgerd'', ''Yazdgird'') was the last Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar (son of Khosrow II), Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.
Ascending the throne a ...
, was a grandson of Khosrau II and was said to be a mere child aged 8 years.
Muhammad's Letter
After the
Treaty of Hudaybiyyah
The Treaty of al-Hudaybiya () was an event that took place during the lifetime of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was a pivotal treaty between Muhammad, representing the state of Medina, and the tribe of the Quraysh in Mecca in March 628 (corres ...
in 628, Islamic tradition holds that
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
sent many letters to the princes, kings, and chiefs of the various tribes and kingdoms of the time, exhorting them to convert to Islam and bow to the order of God. These letters were carried by ambassadors to
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
,
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
,
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
,
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
,
Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
, and the city of
Al-Hirah
Al-Hira ( Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient Lakhmid Arabic city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq.
The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian government established the Lakhmid state (Al-Hirah) on the edge of the ...
in Iraq on the same day.
This assertion has been brought under scrutiny by some modern historians of Islam—notably Grimme and Caetani. Particularly in dispute is the assertion that Khosrau II received a letter from Muhammad, as the Sassanid court ceremony was notoriously intricate, and it is unlikely that a letter from what at the time was a minor regional power would have reached the hands of the Shahanshah.
With regards to Persia, Muslim histories further recount that at the beginning of the seventh year of migration, Muhammad appointed one of his officers, Abdullah Huzafah Sahmi Qarashi, to carry his letter to
Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 ...
inviting him to convert:
There are differing accounts of the reaction of
Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 ...
.
Military
Years of warfare between the Sasanians and the Byzantines, as well as the strain of the
Khazar invasion of Transcaucasia, had exhausted the army. No effective ruler followed
Khosrau II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 ...
, causing chaos in society and problems in the provincial administration, until
Yazdegerd III
Yazdegerd III (also Romanized as ''Yazdgerd'', ''Yazdgird'') was the last Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar (son of Khosrow II), Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.
Ascending the throne a ...
rose to power. All these factors undermined the strength of the Persian army. Yazdegerd III was merely 8 years old when he came to the throne and, lacking experience, did not try to rebuild the army. The Sasanian Empire was highly decentralized, and was in fact a "confederation" with the
Parthians, who themselves retained a high level of independence.
After the last Sasanian-Byzantine war, the Parthians wanted to withdraw from the confederation, and the Sasanians were thus ill-prepared and ill-equipped to mount an effective and cohesive defense against the
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
armies.
Moreover, the powerful northern and eastern Parthian families, the Kust-i Khwarasan and Kust-i Adurbadagan, withdrew to their respective strongholds and made peace with the Arabs, refusing to fight alongside the
Sasanians
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign ...
.
Pourshariati argues that the
Arab conquest of Mesopotamia
The Arab conquest of Mesopotamia was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 638 AD. The Arab Muslim forces of Caliph Umar first attacked Sasanian territory in 633, when Khalid ibn al-Walid invaded Mesopotamia (then known as the Sasa ...
"took place, not, as has been conventionally believed, in the years 632–634, after the accession of the last Sasanian king
Yazdgerd III (632–651) to power, but in the period from 628 to 632."
An important consequence of this change in timeline means that the
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
conquest started precisely when the Sasanians and Parthians were engaged in internecine warfare over who was to succeed the Sasanian throne.
When Arab squadrons made their first raids into Sasanian territory, Yazdegerd III did not consider them a threat, and he refused to send an army to encounter the invaders. When the main Arab army reached the Persian borders, Yazdegerd III procrastinated in dispatching an army against the Arabs. Even
Rostam-e Farokhzad, who was both
Eran Spahbod and
Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory.
The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the Anglo-Norman ''roy'' (Old Frenc ...
, did not see the Arabs as a threat. Without opposition, the Arabs had time to consolidate and fortify their positions.
When hostilities between the Sasanians and the Arabs finally began, the Persian army faced fundamental problems. While their
heavy cavalry
Heavy cavalry was a class of cavalry intended to deliver a battlefield charge and also to act as a Military reserve, tactical reserve; they are also often termed ''shock cavalry''. Although their equipment differed greatly depending on the re ...
had proved effective against the Roman forces, it was too slow and regimented to act with full force against the agile and unpredictable lightly armed Arab cavalry and foot archers.
The Persian army had a few initial successes. War elephants temporarily halted the Arab army, but when Arab veterans returned from the Syrian fronts, where they had been fighting against Byzantine forces, they provided crucial instruction on how to effectively counter the war elephants.
These factors contributed to the decisive Sassanid defeat at the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. The Persians, who had only one generation before conquered Egypt and Asia Minor, lost decisive battles when nimble, lightly armed Arabs accustomed to skirmishes and desert warfare attacked them. The Arab squadrons defeated the Persian army in several more battles culminating in the
Battle of Nahāvand, the last major battle of the Sassanids. The Sassanid dynasty came to an end with the death of Yazdegerd III in 651.
Rise of the Caliphate
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
died in June 632, and
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
took the title of
Caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
and political successor at
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
. Soon after
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
's succession, several Arab tribes revolted, in the
Ridda Wars
The Ridda Wars were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes, some of which were led by rival prophet claimants. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in ...
(
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
for the Wars of Apostasy). The Ridda Wars preoccupied the
Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
until March 633, and ended with the entirety of the Arab Peninsula under the authority of the Caliph at Medina.
Abu Bakr set in motion a historical trajectory (continued later by Umar and Uthman) that in a few decades led to one of the
largest empires in history,
[Fred M. Donner, "Muhammad and the Believers: At the Origins of Islam", Harvard University Press, 2010, ]
'' beginning with a confrontation with the Sassanid Empire under the general
Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arabs, Arab military commander. He initially led campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career ...
.
Conquest of Mesopotamia (633–638)
First invasion (633)
After the
Ridda wars
The Ridda Wars were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes, some of which were led by rival prophet claimants. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in ...
, a tribal chief of northeastern Arabia,
Al-Muthanna ibn Haritha
Al-Muthanna ibn Haritha al-Shaybani () was a Muslim Arabs, Arab General officer, general in the Rashidun army, army of the Rashidun Caliphate.
Career
Al-Muthanna was a commander of the Muslim Arabs in al-Hira, from which they were conducting raid ...
, raided the Sasanian towns in
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, actions that generated a considerable amount of booty was collected.
[Akbar Shah Najeebabadi, The history of Islam. B0006RTNB4.] Al-Muthanna ibn Haritha went to Medina to inform Abu Bakr about his success and was appointed commander of his people, after which he began to raid deeper into Mesopotamia. Using the mobility of his
light cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and body armor, armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was p ...
, he could easily raid any town near the desert and disappear again into the desert, beyond the reach of the
Sasanian army. Al-Muthanna's acts made Abu Bakr think about the expansion of the
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
.
[Tabari: Vol. 2, p. 554.]
To ensure victory, Abu Bakr used a volunteer army and put his best general,
Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arabs, Arab military commander. He initially led campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career ...
, in command. After defeating the self-proclaimed prophet
Musaylimah
Musaylima (), d.632, was a claimant of prophethood from the Banu Hanifa tribe. Based from Diriyah in present day Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, he claimed to be a prophet and was an enemy of Islam in 7th-century Arabia. He was a leader of the enemies of ...
in the
Battle of Yamama
The Battle of Yamama was fought in December 632 as part of the Ridda Wars against a rebellion within the Rashidun Caliphate in the region of al-Yamama (in present-day Saudi Arabia, South of Riyadh City) between the forces of Abu Bakr and Musay ...
, Khalid was still at
Al-Yamama
Al-Yamama () is a historical region in south-eastern Najd in modern-day Saudi Arabia.
Only a handful of centralized states ever arose in the Yamama, but it figured prominently in early Islamic history, becoming a central theater in the Ridd ...
when Abu Bakr ordered him to invade the Sasanian Empire. Making
Al-Hirah
Al-Hira ( Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient Lakhmid Arabic city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq.
The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian government established the Lakhmid state (Al-Hirah) on the edge of the ...
the objective of Khalid, Abu Bakr sent reinforcements and ordered the tribal chiefs of northeastern Arabia, Al-Muthanna ibn Haritha, Mazhur bin Adi, Harmala and Sulma to operate under Khalid's command. Around the third week of March 633 (first week of
Muharram
Al-Muharram () is the first month of the Islamic calendar. It is one of the four sacred months of the year when warfare is banned. It precedes the month of Safar. The tenth of Muharram is known as Ashura, an important day of commemoration in ...
12th Hijrah) Khalid set out from Al-Yamama with an army of 10,000.
The tribal chiefs, with 2,000 warriors each, joined him, swelling his ranks to 18,000. After entering Mesopotamia, he dispatched messages to every governor and deputy who ruled the provinces calling on them to either embrace Islam or pay tribute. Khalid did not receive any responses and continued with his tactical plans.
Khalid went on to win decisive victories in four consecutive battles: the
Battle of Chains
The Battle of Sallasil ( ''Dhat al-Salasil''), often referred to as the Battle of Chains, was the first battle fought between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian Persian Empire in April 633. The battle was fought in Kazima ( ...
, fought in April; the
Battle of River
The Battle of the River, also known as Battle of Al Madhar, took place in Mesopotamia ( Asoristan Province) between the forces of the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Empire. Muslims, under Khalid ibn al-Walid's command, defeated the numeric ...
, fought in the third week of April; the
Battle of Walaja
The Battle of Walaja () was fought in Mesopotamia in May 633 between the Rashidun Caliphate army under Khalid ibn al-Walid and Al-Muthanna ibn Haritha against the Sassanid Empire and its Arab allies.
Khalid defeated the Sasanian forces by us ...
the following month (where he successfully used a
double envelopment manoeuvre), and the
Battle of Ullais, fought in mid-May. The Persian court, already disturbed by internal problems, was thrown into chaos. In the last week of May, the important city of
Al-Hirah
Al-Hira ( Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient Lakhmid Arabic city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq.
The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian government established the Lakhmid state (Al-Hirah) on the edge of the ...
fell to the Muslims. After resting his armies, in June, Khalid
laid siege to the city of
al-Anbar, which surrendered in July. Khalid then moved south, and
conquered the city of Ayn al-Tamr in the last week of July. At this point, most of what is now Iraq was under Islamic control.
Khalid received a call for aid from northern Arabia at Dawmat al-Jandal, where another Muslim Arab general,
Iyad ibn Ghanm
Iyad ibn Ghanm ibn Zuhayr al-Fihri (; died 641) was an Arab commander who played a leading role in the Muslim conquests of al-Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia) and northern Syria. He was among the handful of Qurayshi tribesmen to embrace Islam before ...
, was trapped among the rebel tribes. Khalid went there and defeated the rebels in the
Battle of Dawmat al-Jandal in the last week of August. Upon his return, he received news of the assembling of a large Persian army. He decided to defeat them all separately to avoid the risk of being defeated by a large unified Persian army. Four divisions of Persian and Christian Arab auxiliaries were present at Hanafiz, Zumiel, Sanni and Muzieh. Khalid divided his army into three units, and employed them in well-coordinated attacks against the Persians from three different sides at night, in the
Battle of Muzayyah, then the
Battle of Saniyy, and finally the
Battle of Zumail, all during the month of November. These devastating defeats ended Persian control over Mesopotamia, and left the Persian capital
Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
vulnerable. Before attacking Ctesiphon, Khalid decided to eliminate all Persian forces in the south and west. He accordingly
marched against the border city of Firaz, where he allegedly defeated the
combined forces of the Sasanian Persians, the
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
s and
Christian Arabs in December. However this has been disputed, as there is doubt to any large-scale Persian forces, and the suspect elements of the battle including casualty numbers and a lack of names of allied commanders point to an Islamic cover-up, which may have in fact been a defeat of Khalid.
This battle was the last in his conquest of Mesopotamia. While Khalid was on his way to attack Qadissiyah (a key fort en route to Ctesiphon), Abu Bakr ordered him to the Roman front in Syria to assume command there.
Second invasion (634–636)
Battle of the Bridge
According to the will of Abu Bakr, Umar was to continue the conquest of Syria and Mesopotamia. On the northeastern borders of the Empire, in Mesopotamia, the situation was rapidly deteriorating. During
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
's era,
Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arabs, Arab military commander. He initially led campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career ...
had left Mesopotamia with half his army of 9000 soldiers to assume command in Syria, whereupon the Persians decided to take back their lost territory. The Muslim army was forced to leave the conquered areas and concentrate on the border. Umar immediately sent reinforcements to aid Muthanna ibn Haritha in Mesopotamia under the command of
Abu Ubaid al-Thaqafi.
At that time, a series of battles between the Persians and Arabs occurred in the region of
Sawad, such as
Namaraq,
Kaskar and Baqusiatha, in which the Arabs managed to maintain their presence in the area. Later on, the Persians defeated Abu Ubaid in the
Battle of the Bridge. Muthanna bin Haritha was later victorious in the
Battle of Buwayb. In 635
Yazdgerd III sought an alliance with Emperor
Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
of the
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
, marrying the latter's daughter (or, by some traditions, his granddaughter) in order to seal the arrangement. While Heraclius prepared for a major offence in the Levant, Yazdegerd ordered the concentration of massive armies to push the Muslims out of Mesopotamia for good through a series of well-coordinated attacks on two fronts.


Battle of Qadisiyyah
Umar ordered his army to retreat to the Arabian border and began raising armies at
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
for another campaign into Mesopotamia. Owing to the critical situation, Umar wished to command the army personally, but the members of
Majlis ash-Shura demurred, claiming that the two-front war required Umar's presence in Medina. Accordingly, Umar appointed
Saad ibn Abi Waqqas, a respected senior officer, even though Saad was suffering from sciatica. Saad left Medina with his army in May 636 and arrived at
Qadisiyyah in June.
While Heraclius launched his offensive in May 636, Yazdegerd was unable to muster his armies in time to provide the Byzantines with Persian support. Umar, allegedly aware of this alliance and not wanting to risk a battle with two great powers simultaneously, quickly reinforced the Muslim army at
Yarmouk to engage and defeat the Byzantines. Meanwhile, he ordered Saad to enter into peace negotiations with Yazdegerd III and invite him to convert to
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
to prevent Persian forces from taking the field. Heraclius instructed his general
Vahan not to engage in battle with the Muslims before receiving explicit orders. Fearing more Arab reinforcements, Vahan attacked the Muslim army in the
Battle of Yarmouk
The Battle of the Yarmuk (also spelled Yarmouk; ) was a major battle between the army of the Byzantine Empire and the Arab Muslim forces of the Rashidun Caliphate. The battle consisted of a series of engagements that lasted for six days in Aug ...
in August 636, and was routed.
With the Byzantine threat ended, the Sasanian Empire was still a formidable power with vast manpower reserves, and the Arabs soon found themselves confronting a huge Persian army with troops drawn from every corner of the empire, including war elephants, and commanded by its foremost generals. Within three months, Saad defeated the Persian army in the
Battle of al-Qādisiyyah, effectively ending Sasanian rule west of Persia proper. This victory is largely regarded as a decisive turning point in Islam's growth: with the bulk of Persian forces defeated, Saad with his companions later conquered
Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
(
Battle of Babylon (636)),
Kūthā, Sābāṭ (
Valashabad) and Bahurasīr (
Veh-Ardashir).
Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
, the capital of the Sassanid Empire,
fell in March 637 after a siege of three months.
Final campaign and conquest (636–638)
In December 636, Umar ordered
Utbah ibn Ghazwan to head south to capture
al-Ubulla (known as "port of Apologos" in the
Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and Roman commerce, trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports lik ...
) and
Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
, in order to cut ties between the Persian garrison there and
Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
. Utbah ibn Ghazwan arrived in April 637, and captured the region. The Persians withdrew to the
Maysan
Maysan Governorate () is a governorate in southeastern Iraq, bordering Iran. Its administrative centre is the city of Amarah, and it is composed of six districts. Before 1976, it was named Amara Province.
Etymology
This region was called ''Messè ...
region, which the Muslims seized later as well.
After the conquest of Ctesiphon, several detachments were immediately sent west to capture
Circesium
Circesium ( ', ), known in Arabic as al-Qarqisiya, was a Roman fortress city near the junction of the Euphrates and Khabur rivers, located at the empire's eastern frontier with the Sasanian Empire. Procopius calls it the "farthest fortress" (φ ...
and
Heet, both forts at the Byzantine border. Several fortified Persian armies were still active north-east of Ctesiphon at
Jalawla and north of the
Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
at
Tikrit
Tikrit ( ) is a city in Iraq, located northwest of Baghdad and southeast of Mosul on the Tigris River. It is the administrative center of the Saladin Governorate. In 2012, it had a population of approximately 160,000.
Originally created as a f ...
and
Mosul
Mosul ( ; , , ; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. It is the second largest city in Iraq overall after the capital Baghdad. Situated on the banks of Tigris, the city encloses the ruins of the ...
.
After withdrawal from Ctesiphon, the Persian armies gathered at Jalawla, a place of strategic importance due to routes leading from here to Mesopotamia,
Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
and
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
. The Persian forces at Jalawla were commanded by Mihran. His deputy was Farrukhzad, a brother of Rustam, who had commanded the Persian forces at the
Battle of al-Qadisiyyah
The Battle of al-Qadisiyyah ( ; ) took place between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Empire in November 636. It resulted in a decisive victory for the Rashidun army and is considered to be one of the most significant engagements of the ...
. Umar decided to deal with Jalawla first, thereby clearing the way to the north, before taking any decisive action against Tikrit and Mosul. Umar appointed
Hashim ibn Utbah to take Jalawla and Abdullah ibn Muta'am to conquer
Tikrit
Tikrit ( ) is a city in Iraq, located northwest of Baghdad and southeast of Mosul on the Tigris River. It is the administrative center of the Saladin Governorate. In 2012, it had a population of approximately 160,000.
Originally created as a f ...
and
Mosul
Mosul ( ; , , ; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. It is the second largest city in Iraq overall after the capital Baghdad. Situated on the banks of Tigris, the city encloses the ruins of the ...
. In April 637, Hashim led 12,000 troops from Ctesiphon to win a victory over the Persians at the
Battle of Jalawla. He then laid siege to Jalawla for seven months, ending in the city's capture. Then, Abdullah ibn Muta'am marched against Tikrit and captured the city with the help of
Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, after fierce resistance. He next sent an army to
Mosul
Mosul ( ; , , ; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. It is the second largest city in Iraq overall after the capital Baghdad. Situated on the banks of Tigris, the city encloses the ruins of the ...
which surrendered on the condition of paying
Jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
. With victory at Jalawla and occupation of the Tikrit-Mosul region, the whole of Mesopotamia was under Muslim control.
Thereafter, a Muslim force under Qa'qa marched in pursuit of the escaping Persians at Khaniqeen, 25 kilometres (15 mi) from Jalawla on the road to Iran, still under the command of Mihran. Qa'qa defeated the Persian forces in the Battle of Khaniqeen and captured the city. The Persians then withdrew to
Hulwan. Qa'qa followed and laid siege to the city, which was captured in January 638. Qa'qa sought permission to operate deeper in Persia, but Umar rejected the proposal, writing in response:
Persian raids in Mesopotamia (638–641)
By February 638 there was a lull in the fighting on the Persian front. The Suwad, the
Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
valley, and the
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
valley were now under complete Muslim control. The Persians had withdrawn to
Persia proper, east of the
Zagros mountains
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
. The Persians continued raiding Mesopotamia, which remained politically unstable. It seemed the Zagros range was the dividing line between the
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
and the Sassanids. In the latter part of 638,
Hormuzan, who was one of the seven great chiefs of Persia, and had commanded a corps at the
Battle of Qadisiyyah, intensified his raids in Mesopotamia. Saad, on Umar's instructions, attacked Hormuzan, while Utbah ibn Ghazwan, aided by Nouman ibn Muqarin, attacked
Ahvaz
Ahvaz (; ) is a city in the Central District of Ahvaz County, Khuzestan province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is home to Persians, Arabs and other groups such as Qashqai and Kurds. Languages spok ...
and forced Hormuzan into a peace treaty, under which Ahvaz would remain in Hormuzan's possession as a Muslim vassal state and would pay tribute. Hormuzan broke the treaty, leading Umar to send
Abu Musa Ashaari
Abu Musa Abd Allah ibn Qays al-Ash'ari (), better known as Abu Musa al-Ash'ari () (died c. 662 or 672) was a companion of Muhammad and an important figure in early Islamic history. He was at various times governor of Basra and Kufa and was involv ...
, governor of
Busra, to deal with him. After another defeat, Hormuzan signed another treaty on similar terms to the last. This peace also proved short-lived once Hormuzan was reinforced by fresh Persian troops sent by Emperor
Yazdgerd III in late 640. The troops concentrated at Tuster, north of Ahvaz. Umar sent the Governor of
Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
,
Ammar ibn Yasir
Ammar ibn Yasir (; July 657 C.E.) was a ''Sahabi'' (Companion) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a commander in the early Muslim conquests. His parents, Sumayya and Yasir ibn Amir, were the first martyrs of the Ummah. Ammar converted to I ...
, the governor of
Busra, Abu Musa, and Nouman ibn Muqarin there, where Hormuzan was defeated, captured and sent to Umar in Medina. Hormuzan apparently converted to Islam and remained a useful adviser to Umar throughout the remainder of the Persian campaign. He is also believed to be the mastermind behind Umar's assassination in 644.
After the victory at
Tustar,
Abu Musa
Abu Musa ( , , ) is an Iranian island in the eastern Persian Gulf, found near the entrance of Strait of Hormuz. Due to the depth of sea, oil tankers and big ships have to pass between Abu Musa and Greater and Lesser Tunbs, making these is ...
marched against the strategically important
Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital o ...
in January 641, capturing it after a siege of a couple of months. Next, Abu Musa marched against Junde Sabur, the only place left of military importance in the Persian province of
Khuzistan
Khuzestan province () is one of the 31 Provinces of Iran. Located in the southwest of the country, the province borders Iraq and the Persian Gulf, covering an area of . Its capital is the city of Ahvaz. Since 2014, it has been part of Iran's ...
, which surrendered to the Muslims after a siege of a few weeks.
Battle of Nahavand (642)
After the conquest of
Khuzistan
Khuzestan province () is one of the 31 Provinces of Iran. Located in the southwest of the country, the province borders Iraq and the Persian Gulf, covering an area of . Its capital is the city of Ahvaz. Since 2014, it has been part of Iran's ...
, Umar wanted peace. Though considerably weakened, the image of the Persian Empire as a fearsome superpower still resonated in the minds of the newly-ascendant Arabs, and Umar was wary of unnecessary military engagement with it, preferring to leave the rump of the Persian Empire alone, commenting, "I wish there was a mountain of fire between us and the Persians, so that neither they could get to us, nor we to them."
Persian pride was hurt by the Arab conquest, making the ''status quo'' intolerable.

After the defeat of the Persian forces at the
Battle of Jalula in 637, Yazdgerd III went to
Rey and from there moved to
Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium& ...
, where he set up his capital and directed his chiefs to conduct continuous raids in Mesopotamia. Within four years, Yazdgerd III felt powerful enough to challenge the Muslims again for control of Mesopotamia. Accordingly, he recruited 100,000 hardened veterans and young volunteers from all parts of Persia, under the command of Mardan Shah, which marched to
Nahavand
Nahavand () is a city in the Central District of Nahavand County, Hamadan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. It is south of the city of Hamadan, west of Malayer and northwest of Borujerd.
Inhabited ...
for the last titanic struggle with the Caliphate.
The Governor of
Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
,
Ammar ibn Yasir
Ammar ibn Yasir (; July 657 C.E.) was a ''Sahabi'' (Companion) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a commander in the early Muslim conquests. His parents, Sumayya and Yasir ibn Amir, were the first martyrs of the Ummah. Ammar converted to I ...
, received intelligence of the Persian movements and concentration at Nahavand and reported them to Umar. Although Umar had expressed a desire for Mesopotamia to be his easternmost frontier, the concentration of the Persian army at Nahavand forced him to act. He now believed that as long as Persia proper remained under Sasanian rule, the raids into Mesopotamia would continue. Hudheifa ibn Al Yaman was appointed commander of the forces of Kufa, and was ordered to march to Nahavand. Abu Musa was to march to Nahavand from
Busra, while
Nouman ibn Muqarrin marched from Ctesiphon. Umar decided to personally take the army concentrated at Medina to Nahavand to assume overall command. The members of the Majlis al-
Shura
Shura () is the term for collective decision-making in Islam. It can, for example, take the form of a council or a referendum. The Quran encourages Muslims to decide their affairs in consultation with each other.
Shura is mentioned as a praise ...
suggested that Umar should command the campaign from Medina, appointing an astute field commander for Nahavand. Umar acquiesced, appointing
Mugheera ibn Shuba as commander of the forces concentrated at Medina, and Nouman ibn Muqarrin as commander-in-chief at Nahavand. The Muslim army first concentrated at Tazar, and then defeated the Persians at the
Battle of Nahavand
The Battle of Nahavand ( ', '), also spelled Nihavand or Nahawand, was fought in 642 between the Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun Muslims, Muslim Rashidun army, forces under Caliphate, caliph Umar and Sasanian Empire, Sasanian Persian armies under ...
in December 642. Nouman died in the action, and, as per Umar's instructions, Hudheifa ibn Al Yaman became the new commander-in-chief. Thereafter, the Muslims captured the whole district of
Hamadan
Hamadan ( ; , ) is a mountainous city in western Iran. It is located in the Central District of Hamadan County in Hamadan province, serving as the capital of the province, county, and district. As of the 2016 Iranian census, it had a po ...
, encountering only feeble resistance.
Conquest of Persia (642–651)
After several years, Caliph Umar adopted a new offensive policy, preparing to launch a full-scale invasion of what remained of the Sasanian Empire. The Battle of Nahavand was one of the most decisive battles in Islamic history
and proved to be the key to Persia. After the devastating defeat at Nahavand, the last Sassanid emperor, Yazdegerd III, fled to different parts of Persia to raise a new army, with limited success, while Umar attempted to capture him.
Strategic planning for the conquest of Persia
Umar decided to strike the Persians immediately after their defeat at Nahavand, while he still possessed a psychological advantage. Umar had to decide which of three provinces to conquer first:
Fars in the south,
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
in the north or
Isfahan
Isfahan or Esfahan ( ) is a city in the Central District (Isfahan County), Central District of Isfahan County, Isfahan province, Iran. It is the capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is located south of Tehran. The city ...
in the center. Umar chose Isfahan, as it was the heart of the Persian Empire and a conduit for supply and communications among the Sasanian garrisons, and its capture would isolate Fars and Azerbaijan from
Khorasan, Yazdegerd's stronghold. After he had taken Fars and Isfahan, the next attacks would be simultaneously launched against Azerbaijan, the northwestern province, and
Sistan
Sistān (), also known as Sakastān (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly correspond ...
, the easternmost province of the Persian Empire.
The conquest of those provinces would leave Khorasan isolated and vulnerable, the last stage of the conquest of Sassanid Persia.
Preparations were complete by January 642. The success of the plan depended upon how effectively Umar could coordinate these attacks from Medina, about 1500 kilometers from Persia, and upon the skill of his field commanders. Umar adopted a different approach to the command structure. Instead of appointing a single field commander to press the campaign, Umar appointed several commanders, each assigned a different mission. Once a commander's mission ended, he would become an ordinary soldier under the new field commander for the latter's mission. The purpose of this strategy was to allow commanders to mix with their soldiers and to remind them that they are like everyone else: command is only given to the most competent, and, once the battle is over, the commander returns to his previous position.
On the eve of the campaign, Umar, in order to boost morale, decided to reinstall Khalid as field commander, four years after his dismissal.
Khalid's reputation as the conqueror of the Eastern Roman provinces demoralized the Persian commanders, most of whom had already been defeated by him during his conquest of Mesopotamia in 633. Before Umar could issue the reappointment order, Khalid died in
Emesa.
Throughout the Persian campaign, Umar even appointed the commanders of the wings, the center and the
cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
of the army. Umar strictly instructed his commanders to consult him before making any decisive move in Persia. All the commanders, before starting their assigned campaigns, were instructed to send a detailed report of the geography and terrain of the region and the positions of the Persian
garrison
A garrison is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a military base or fortified military headquarters.
A garrison is usually in a city ...
s,
fort
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
s, cities and troops. Umar then would send them a detailed plan of how he wanted the region to be captured. Only the tactical issues were left to the field commanders to tackle in accordance with the situation they faced at their fronts. Umar appointed the best available and well-reputed commanders for the campaign.
Conquest of Central Iran

In the wake of Khalid's demise, Umar appointed Abdullah ibn Uthman as commander of the Muslim forces for the invasion of
Isfahan
Isfahan or Esfahan ( ) is a city in the Central District (Isfahan County), Central District of Isfahan County, Isfahan province, Iran. It is the capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is located south of Tehran. The city ...
. From Nahavand, Nu'man ibn Muqaarin marched to
Hamadan
Hamadan ( ; , ) is a mountainous city in western Iran. It is located in the Central District of Hamadan County in Hamadan province, serving as the capital of the province, county, and district. As of the 2016 Iranian census, it had a po ...
, and then proceeded 370 kilometres (230 mi) southeast to the city of
Isfahan
Isfahan or Esfahan ( ) is a city in the Central District (Isfahan County), Central District of Isfahan County, Isfahan province, Iran. It is the capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is located south of Tehran. The city ...
, defeating a Sasanian army there. The Sassanian commander,
Shahrvaraz Jadhuyih, along with another Sasanian general, was killed during the battle. Nu'man, reinforced by fresh troops from Busra and Kufa under the command of
Abu Musa Ashaari
Abu Musa Abd Allah ibn Qays al-Ash'ari (), better known as Abu Musa al-Ash'ari () (died c. 662 or 672) was a companion of Muhammad and an important figure in early Islamic history. He was at various times governor of Basra and Kufa and was involv ...
and
Ahnaf ibn Qais, then besieged the city.
[The Muslim Conquest of Persia By A.I. Akram. Ch:11 ,] The siege continued for a few months before the city surrendered.
In 651, Nu'aym ibn Muqaarin, Nu'man's brother, marched northeast to
Rey, Iran
Shahre Ray, Shahr-e Ray, Shahre Rey, or Shahr-e Rey (, ) or simply Ray or Rey (), is the capital of Rey County in Tehran Province, Iran. Formerly a distinct city, it has now been absorbed into the metropolitan area of Greater Tehran as the 20 ...
, about 320 kilometres (200 mi) from Hamadan, and laid siege to the city, which surrendered after fierce resistance. Nu'aym then marched 240 kilometres (150 mi) northeast toward
Qom
Qom (; ) is a city in the Central District of Qom County, Qom province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is the seventh largest metropolis and also the seventh largest city in Iran. The city is ...
, which was captured without much resistance. This represented the boundary of the Isfahan region. Further northeast was
Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
, and southeast lay
Sistan
Sistān (), also known as Sakastān (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly correspond ...
. Meanwhile, Hamadan and Rey had rebelled. Umar sent Nu'aym, whose brother Nu'man had recently died, to Hamadan to crush the rebellion and clear Isfahan's western frontier. Nu'aym recaptured Hamadan after a bloody battle, and then proceeded to Rey. There too the Persians resisted but were defeated outside the fort, and the Muslims recaptured the city.
[The History of Al-Tabari: The Challenge to the Empires, Translated by Khalid Yahya Blankinship, Published by SUNY Press, 1993, ] The Persian citizens sued for peace, agreeing to pay the
Jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
. From Rey, Nu'aym moved north to
Tabaristan
Tabaristan or Tabarestan (; ; from , ), was a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. It corresponded to the present-day province of Mazandaran, which became the predominant name of the area from the 11th-century onward ...
, south of the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
.
The ruler of
Tabaristan
Tabaristan or Tabarestan (; ; from , ), was a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. It corresponded to the present-day province of Mazandaran, which became the predominant name of the area from the 11th-century onward ...
then signed a peace treaty with the
Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
.
Conquest of Fars
First Muslim invasion and the successful Sasanian counter-attack
The Muslim invasion of
Fars began in 638/9, when the Rashidun governor of
Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
,
al-'Ala' ibn al-Hadrami, having defeated some rebellious Arab tribes, seized an island in the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
. Although al-'Ala' and the rest of the Arabs had been ordered to not invade Fars or its surrounding islands, he and his men continued their raids into the province. Al-'Ala quickly prepared an army which he divided into three groups, one under al-Jarud ibn Mu'alla, the second under al-Sawwar ibn Hammam, and the third under Khulayd ibn al-Mundhir ibn Sawa.
When the first group entered Fars, it was quickly defeated and al-Jarud was killed. The same thing soon happened to the second group. Khulayd and the third group kept the defenders at bay, but were blocked from withdrawing to Bahrain by the Sasanians. Umar, having found out about al-'Ala's invasion of Fars, had him replaced with
Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas
Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas ibn Wuhayb al-Zuhri () was an Arabs, Arab Muslims, Muslim commander. He was the founder of Kufa and served as its governor under Umar, Umar ibn al-Khattab. He played a leading role in the Muslim conquest of Persia and was a cl ...
as governor. Umar then ordered
Utbah ibn Ghazwan to send reinforcements to Khulayd. Once the reinforcements arrived, Khulayd and some of his men managed to withdraw to Bahrain, while the rest withdrew to
Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
.
Second and last Muslim invasion
In ,
Uthman ibn Abi al-As seized
Bishapur
Bishapur (Middle Persian: ''Bay-Šāpūr''; , ''Bishâpûr'') was an ancient city in Sasanid Persia (Iran) on the ancient road between Persis and Elam. The road linked the Sassanid capitals Estakhr (very close to Persepolis) and Ctesiphon. It ...
, which signed a peace treaty. In 644, al-'Ala' once again attacked Fars from Bahrain, reaching as far as
Estakhr, until he was repulsed by the Persian governor (''
marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian: 𐭬𐭫𐭱𐭰𐭠𐭭𐭯 transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from Middle Persian: 𐭬𐭫𐭱 ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the Middle Persian suffix: 𐭡𐭭𐭯 ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ...
'') of Fars,
Shahrag. Some time later, Uthman ibn Abi al-As managed to establish a military base at
Tawwaj, and soon defeated and killed Shahrag near
Rew-shahr. Persian convert to
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, Hormoz ibn Hayyan al-'Abdi, was then sent by Uthman ibn Abi al-As to attack a fortress known as Senez on the coast of Fars. After the accession of
Uthman ibn Affan
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until Assassination of Uthman, his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable Companions of the Prophet, companion of ...
as the new
Rashidun Caliph
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the Muslim community and po ...
on 11 November, the inhabitants of Bishapur, under the leadership of Shahrag's brother, declared independence, but were defeated. The Persian historian
al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al ...
said this occurred in 646.
In 648, 'Abd-Allah ibn al-'Ash'ari forced the governor of Estakhr, Mahak, to surrender the city. Its citizens rebelled in 649/650 while its newly appointed governor,
'Abd-Allah ibn 'Amir, was trying to capture
Gor. The military governor of Estakhr, 'Ubayd Allah ibn Ma'mar, was defeated and killed. In 650/651, Yazdegerd went there to plan an organized resistance against the Arabs, and, after some time, went to Gor. Estakhr put up a weak resistance and was soon sacked by the Arabs, who killed over 40,000 defenders. The Arabs then quickly seized Gor,
Kazerun and
Siraf, while Yazdegerd fled to
Kerman
Kerman (; ) is a city in the Central District (Kerman County), Central District of Kerman County, Kerman province, Kerman province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district.
History
Kerman was founded as a def ...
. Muslim control of Fars remained shaky for a time, with several local rebellions following the conquest.
Conquest of Southeastern Persia (Kerman and Makran)

The expedition to
Kerman
Kerman (; ) is a city in the Central District (Kerman County), Central District of Kerman County, Kerman province, Kerman province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district.
History
Kerman was founded as a def ...
, under Suhail ibn Adi, was sent at roughly the same time as the expeditions to
Sistan
Sistān (), also known as Sakastān (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly correspond ...
and
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
. Suhail marched from Busra in 643; passing through
Shiraz
Shiraz (; ) is the List of largest cities of Iran, fifth-most-populous city of Iran and the capital of Fars province, which has been historically known as Pars (Sasanian province), Pars () and Persis. As of the 2016 national census, the popu ...
and
Persepolis
Persepolis (; ; ) was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and ...
, he joined with other armies and then marched against Kerman, which was subdued after a pitched battle with the local garrisons.
Conquest of Sakastan

The Arabs were raiding Sakastan as early as Umar's caliphate. The first real invasion took place in 650, when
Abd-Allah ibn Amir, having secured his position in Kerman, sent an army under Mujashi ibn Mas'ud there. After crossing the
Dasht-i Lut desert, Mujashi ibn Mas'ud reached Sakastan, but suffered a heavy defeat and was forced to retreat.
One year later, Abd-Allah ibn Amir sent an army under
Rabi ibn Ziyad Harithi to Sakastan. After some time, Rabi reached Zaliq, a Sakastani border town, where he forced the
dehqan
The ''dehqân'' (; , ''dihqân'' in Classical Persian) or ''dehgân'' (; ) were a class of land-owning magnates during the Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that w ...
of the town to acknowledge Rashidun authority. He then did the same at the fortress of Karkuya, which had a famous
fire temple mentioned in the
Tarikh-i Sistan. He then seized more land in the province. Next, he besieged the provincial capital,
Zrang, and, after a heavy battle outside the city, its governor,
Aparviz, surrendered. When Aparviz went to Rabi ibn Ziyad to negotiate a treaty, he saw that Rabi was using the bodies of two dead soldiers as a chair. This horrified Aparviz, who, in order to spare the inhabitants of Sakastan from the Arabs, made peace with them in return for a heavy tribute of 1 million
dirham
The dirham, dirhem or drahm is a unit of currency and of mass. It is the name of the currencies of Moroccan dirham, Morocco, the United Arab Emirates dirham, United Arab Emirates and Armenian dram, Armenia, and is the name of a currency subdivisi ...
s, including 1,000 slave boys (or girls) bearing 1,000 golden vessels. Rabi ibn Ziyad was then appointed governor of the province.
Eighteen months later, Rabi was summoned to
Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
, and was replaced by 'Abd al-Rahman ibn Samura. The inhabitants of Sakastan used this opportunity to rebel, defeating the Muslim garrison at Zrang. When 'Abd al-Rahman ibn Samura reached Sakastan, he suppressed the rebellion and defeated the
Zunbils of
Zabulistan, seizing
Bust and a few cities in
Zabulistan.
Conquest of
Iranian Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan or Azarbaijan (, , ), also known as Iranian Azerbaijan, is a historical region in northwestern Iran that borders Iraq and Turkey to the west and Armenia, Azerbaijan, and the Azerbaijani exclave of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republ ...

The conquest of
Iranian Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan or Azarbaijan (, , ), also known as Iranian Azerbaijan, is a historical region in northwestern Iran that borders Iraq and Turkey to the west and Armenia, Azerbaijan, and the Azerbaijani exclave of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republ ...
started in 651, part of a simultaneous attack launched against Kerman and Makran in the southeast (described above), against Sistan in the northeast and against Azerbaijan in the northwest. Hudheifa ibn Al Yaman was assigned Azerbaijan. Hudheifa marched from Rey in central Persia to
Zanjan, a well-fortified Persian stronghold in the north. The Persians came out of the city and gave battle, but Hudheifa defeated them, captured the city, and those who sought peace were granted it on the usual ''
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
'' conditions.
From Zanjan, Hudheifa marched to
Ardabil
Ardabil (, ) is a city in northwestern Iran. It is in the Central District (Ardabil County), Central District of Ardabil County, Ardabil province, Ardabil province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district.
The ...
which surrendered peacefully. Hudheifa then continued his march north along the western coast of the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
and captured
Bab al-Abwab by force.
At this point Hudheifa was recalled by
Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable companion of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, played a major role ...
, to be replaced by
Bukair ibn Abdullah and Utba ibn Farqad. They were sent to carry out a two-pronged attack against Azerbaijan: Bukair along the western coast of the Caspian Sea, and Uthba into the heart of Azerbaijan. On his way north Bukair was halted by a large Persian force under
Isfandiyar, the son of
Farrukhzad. A pitched battle was fought, after which Isfandiyar was defeated and captured. In return for his life, he agreed to surrender his estates in Azerbaijan and persuade others to submit to Muslim rule.
Uthba ibn Farqad then defeated Bahram, brother of Isfandiyar. He too sued for peace. Azerbaijan then surrendered to Caliph Umar, agreeing to pay the annual ''jizya''.
Conquest of Armenia
The Muslims had conquered
Byzantine Armenia in 638–639.
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
, remained in Persian hands, along with
Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
. Umar refused to take any chances; he did not consider the Persians weak, which facilitated the speedy conquest of the Persian Empire. Again Umar sent simultaneous expeditions to the far north-east and north-west of the Persian Empire, one to
Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
in late 643 and the other to
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
.
Bukair ibn Abdullah was ordered to capture
Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი, ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), ( ka, ტფილისი, tr ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia ( ...
. From Bab, on the western coast of the Caspian Sea, Bukair continued his march north. Umar employed his traditional successful strategy of multi-pronged attacks. While Bukair was still kilometres away from
Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი, ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), ( ka, ტფილისი, tr ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia ( ...
, Umar instructed him to divide his army into three corps. Umar appointed Habib ibn Muslaima to capture Tiflis, Abdulrehman to march north against the mountains and Hudheifa to march against the southern mountains. With the success of all three missions, the advance into Armenia came to an end with the death of Umar in November 644. By then almost the whole of the South
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
was captured.
Conquest of Khorasan
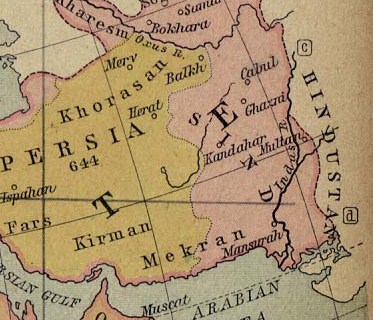
Khorasan was the second-largest province of the Sasanian Empire. It stretched from what is now northeastern Iran, northwestern Afghanistan and southern Turkmenistan. In 651 the conquest of Khurasan was assigned to
Ahnaf ibn Qais.
Ahnaf marched from
Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
and took a short and less frequented route via
Rey and
Nishapur
Nishapur or Neyshabur (, also ) is a city in the Central District (Nishapur County), Central District of Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Ni ...
. Rey was already in Muslim hands and Nishapur surrendered without resistance. From Nishapur, Ahnaf marched to
Herat
Herāt (; Dari/Pashto: هرات) is an oasis city and the third-largest city in Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Se ...
in western Afghanistan. Herat was a fortified town, and the
resulting siege lasted for a few months before it surrendered, bringing the whole of southern Khorasan under Muslim control. Ahnaf then marched north directly to
Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium& ...
, in present-day
Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
. Merv was the capital of Khurasan and here Yazdegred III held his court. On hearing of the Muslim advance, Yazdegerd III left for
Balkh
Balkh is a town in the Balkh Province of Afghanistan. It is located approximately to the northwest of the provincial capital city Mazar-i-Sharif and approximately to the south of the Amu Darya and the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border. In 2021 ...
. No resistance was offered at Merv, and the Muslims occupied the capital of Khurasan without a fight. Ahnaf stayed at Merv and waited for reinforcement from Kufa. Meanwhile, Yazdegerd had also gathered considerable power at Balkh and allied with the Turkic Khan of
Farghana, who personally led the relief contingent. Umar ordered Ahnaf to break up the alliance. The Khan of Farghana, realizing that fighting against the Muslims might endanger his own kingdom, withdrew from the alliance and pulled back to Farghana. The remainder of Yazdegerd's army was defeated at the
Battle of Oxus River and retreated across the
Oxus
The Amu Darya ( ),() also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus ( ), is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Ku ...
to
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
. Yazdegerd himself narrowly escaped to
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.The Muslims had now reached the outermost frontiers of Persia. Beyond that lay the lands of the
Turks and still further lay China. Ahnaf returned to Merv and sent a detailed report of his success to the anxiously waiting Umar, and sought permission to cross the Oxus river and invade Transoxiana. Umar ordered Ahnaf to stand down and instead consolidate his power south of the Oxus.
Persian rebellion and reconquest
Umar was assassinated in November 644 by a Persian slave named
Abu Lu'lu'a Firuz
(, from Middle Persian: ''Pērōz''), also known in modern Persian-language sources as () or (), was a Sasanian Persian slave who assassinated Umar ibn al-Khattab (), the second Islamic caliph, in November 644.
After having been capture ...
, after having refused to lift a tax imposed upon the latter. Soon after, Abu Lu'lu'a's was either executed or committed suicide. In retaliation,
Ubayd Allah ibn Umar
Ubayd Allah ibn Umar ibn al-Khattab (; died summer 657) was a son of Caliph Umar (). His killing of Hormuzan, whom he suspected of involvement in his father's assassination in 644, and his pardon by Caliph Uthman () was opposed by Ali, the cou ...
(one of Umar's sons) killed Abu Lu'lu'a's daughter, and declared his intention to kill all non-Arabs residing in Medina. Acting upon a claim that they had been seen conspiring with Abu Lu'lu'a while he was holding the murder weapon, Ubayd Allah killed
Hurmuzān, an ex-
Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign ...
military officer who had been working for Umar as an adviser after his capture by the Muslims, and Jufayna, a Christian man from the city of
Al-Hira
Al-Hira ( Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient Lakhmid Arabic city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq.
The Sasanian government established the Lakhmid state (Al-Hirah) on the edge of the Arabian Desert ...
in Iraq who had been taken to Medina to serve as a tutor. Just like Abu Lu'lu'a's assassination of Umar over something as trivial as a tax burden, Ubayd Allah's retaliatory killing of apparently random non-Arabs bears witness to the strong tensions that existed between Arabs and non-Arabs in the early Islamic caliphate.
Uthman ibn Affan
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until Assassination of Uthman, his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable Companions of the Prophet, companion of ...
(644–656) succeeded Umar as caliph. During his reign, almost the whole of the former Sassanid empire's territory rebelled from time to time, requiring him to send several military expeditions to crush the rebellions and recapture Persia and its vassal states. The main rebellions were in the Persian provinces of
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
,
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
,
Fars,
Sistan
Sistān (), also known as Sakastān (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly correspond ...
(in 649),
Khorasan (651), and
Makran
Makran (), also mentioned in some sources as ''Mecran'' and ''Mokrān'', is the southern coastal region of Balochistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in the Balochistan province in Pakistan and in Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. I ...
(650). Finally, in 651,
Yazdegerd III
Yazdegerd III (also Romanized as ''Yazdgerd'', ''Yazdgird'') was the last Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar (son of Khosrow II), Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.
Ascending the throne a ...
, the last Sassanid emperor, was killed near
Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium& ...
by a local miller for his purse, thus putting an end to both his dynasty and to organized Persian resistance. Meanwhile, Uthman's empire expanded beyond the borders of the Sasanian Empire, to
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
,
Baluchistan
Balochistan ( ; , ), also spelled as Baluchistan or Baluchestan, is a historical region in West and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. This arid region of de ...
, and the
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
. For many decades to come, this was the easternmost limit of Muslim rule.
Persia under Muslim rule
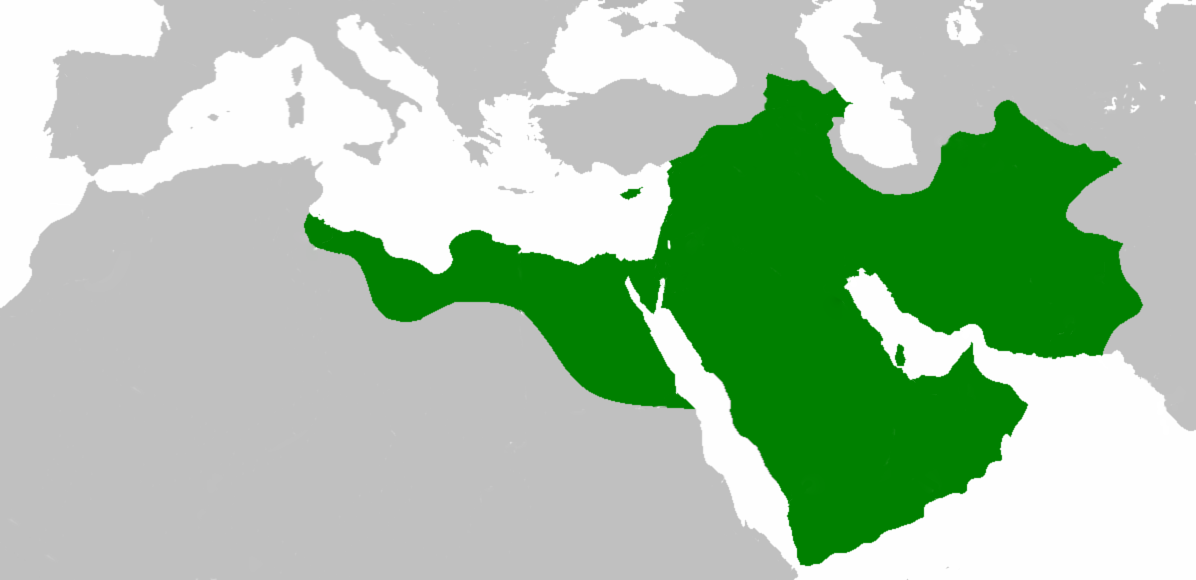
According to
Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis, (31 May 1916 – 19 May 2018) was a British-American historian specialized in Oriental studies. He was also known as a public intellectual and political commentator. Lewis was the Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near ...
:
Arab Muslims conquests have been variously seen in Iran: by some as a blessing, the advent of the true faith, the end of the age of ignorance and heathenism; by others as a humiliating national defeat, the conquest and subjugation of the country by foreign invaders. Both perceptions are of course valid, depending on one's angle of vision. Iran was Islamized, but it was not Arabized. Persians remained Persians. And after an interval of silence, Iran reemerged as a separate, different and distinctive element within Islam, eventually adding a new element even to Islam itself. Culturally, politically, and most remarkable of all even religiously, the Iranian contribution to this new Islamic civilization is of immense importance. The work of Iranians can be seen in every field of cultural endeavor, including Arabic poetry, to which poets of Iranian origin composing their poems in Arabic made a very significant contribution. In a sense, Iranian Islam is a second advent of Islam itself, a new Islam sometimes referred to as Islam-i Ajam. It was this Persian Islam, rather than the original Arab Islam, that was brought to new areas and new peoples: to the Turks, first in Central Asia and then in the Middle East in the country which came to be called Turkey, and of course to India. The Ottoman Turks brought a form of Iranian civilization to the walls of Vienna.
Administration
Under Umar and his immediate successors, the Arab conquerors attempted to maintain their political and cultural cohesion despite the attractions of the civilizations they had conquered. The Arabs initially settled in the garrison towns rather than on scattered estates.
The new non-Muslim subjects were tolerated by the state and known as ''
dhimmi
' ( ', , collectively ''/'' "the people of the covenant") or () is a historical term for non-Muslims living in an Islamic state with legal protection. The word literally means "protected person", referring to the state's obligation under ''s ...
'' (''protected''), and were to pay a special tax, the
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
(''tribute''), which was calculated at varying individual rates, usually two
dirham
The dirham, dirhem or drahm is a unit of currency and of mass. It is the name of the currencies of Moroccan dirham, Morocco, the United Arab Emirates dirham, United Arab Emirates and Armenian dram, Armenia, and is the name of a currency subdivisi ...
s for able-bodied men of military age, in return for exemption from military service. Women and children were exempted from the jizya.
Mass conversions were neither desired nor allowed, at least in the first few centuries of Arab rule.
[Boyce, Mary (1979), Zoroastrians: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices, London: Routledge, pg.150]
Umar is reported to have issued the following instructions about the unconverted people: "Make it easy for him, who can not pay tribute; help him who is weak, let them keep their titles, but do not give them our
kuniyat 'Arabic traditional nicknames or titles''"
[''The Caliphs and Their Non-Muslim Subjects''. By A. S. Tritton, pg.138.]
Umar's liberal policies were continued by at least his immediate successors. In his dying charge to Uthman, he is reported to have said, "I charge the caliph after me to be kind to the dhimmis, to keep their covenant, to protect them and not to burden them over their strength."
As a matter of practicality, the jizya replaced the Sasanian poll taxes, which tended to be much higher than the jizya. In addition to the jizya, the old Sasanian ''land tax'' (known in Arabic as ''Kharaj'') was also adopted. Umar is said to have occasionally set up commissions to survey tax burdens in order to ensure that they wouldn't be more than the land could bear. It is reported that Zoroastrians were subjected to humiliation and ridicule when paying the
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
in order to make them feel inferior.
At least under the Rashiduns and early Umayyads, the administrative system of the late Sasanian period was largely retained: a pyramidal system where each quarter of the state was divided into provinces, the provinces into districts, and the districts into sub-districts. Provinces were called ''ustan'' (Middle Persian ''ostan''), and the districts ''shahrs'', centered upon a district capital known as a ''shahristan''. The subdistricts were called ''tasok'' in Middle Persian, which was adopted into Arabic as ''tassuj'' (plural ''tasasij'').
Religion
Zoroastrians were made to pay an extra tax called
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
, or be killed,
enslaved or imprisoned. Those paying jizya were subjected to insults and humiliation by the tax collectors.
Zoroastrians who were captured as slaves in wars were given their freedom if they converted to Islam.
While giving freedom of choice, the Arab conquerors designated privileges for those who converted to Islam. The conversion process was slow and uncompleted, stretching over many centuries, with a majority of Persians still following Zoroastrianism at the turn of the millennium.
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
leaders in their effort to win converts encouraged attendance at Muslim prayer with promises of money and allowed the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
to be recited in
Persian instead of Arabic so that it would be intelligible to all.
Islam was readily accepted by
Zoroastrians who were employed in industrial and artisan positions because, according to Zoroastrian dogma, such occupations that involved defiling fire made them impure.
[The preaching of Islam: a history of the propagation of the Muslim faith By Sir Thomas Walker Arnold, pg.170–180] Moreover, Muslim missionaries did not encounter difficulty in explaining Islamic tenets to Zoroastrians, as there were many similarities between the faiths. According to
Thomas Walker Arnold, the Persian would meet
Ahura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ; or , ),The former is the New Persian rendering of the Avestan form, while the latter derives from Middle Persian. also known as Horomazes (),, is the only creator deity and Sky deity, god of the sky in the ancient Iranian ...
and
Ahriman
Angra Mainyu (; ) is the Avestan name of Zoroastrianism's hypostasis of the "destructive/evil spirit" and the main adversary in Zoroastrianism either of the Spenta Mainyu, the "holy/creative spirits/mentality", or directly of Ahura Mazda, th ...
under the names of
Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...
and
Iblis
Iblis (), alternatively known as Eblīs, also known as Shaitan, is the leader of the Shayatin, devils () in Islam. According to the Quran, Iblis was thrown out of Jannah#Jinn, angels, and devils, heaven after refusing to prostrate himself bef ...
.
In
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, Islam was spread due to
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a membe ...
missionary efforts particularly under the reigns of
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan (; 6 February 743) was the tenth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 724 until his death in 743.
Early life
Hisham was born in Damascus, the administrative capital of the Umayyad Caliphate, in AH 72 (691–692 CE). Hi ...
and
Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz
Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz ibn Marwan (; February 720) was the eighth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 717 until his death in 720. He is credited to have instituted significant reforms to the Umayyad central government, by making it much more efficient and ...
.
There were also large and thriving
Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
and
Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
communities, along with smaller numbers of
Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
s and other groups. The population moved slowly and steadily toward
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. The nobility and citizens converted first. Islam spread more slowly among the peasantry and the ''
dihqans'', or landed gentry. By the late 10th century, the majority of the Persians had become Muslim.
Until the 15th century, most Persian Muslims were
Sunni Muslims
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Musli ...
of the
Shafi'i
The Shafi'i school or Shafi'i Madhhab () or Shafi'i is one of the four major schools of fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence), belonging to the Ahl al-Hadith tradition within Sunni Islam. It was founded by the Muslim scholar, jurist, and traditionis ...
and
Hanafi
The Hanafi school or Hanafism is the oldest and largest Madhhab, school of Islamic jurisprudence out of the four schools within Sunni Islam. It developed from the teachings of the Faqīh, jurist and theologian Abu Hanifa (), who systemised the ...
legal schools, with the rise of the
Safavid
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
s in the early 16th century and their
forced conversion of Sunnis, Shi'a Islam came to dominate the land.
Language of Persia
During the
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
, the official language of Persia (including Mesopotamia) remained
Middle Persian (Pahlavi), just as the official languages of
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
remained
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, both languages came to the region through the conquering Greek Macedonian and Persian Achaemenid empires. During the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member o ...
, the Umayyads made
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
the primary language of their subjected people throughout their empire. Particularly,
Al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf
Abu Muhammad al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi Aqil al-Thaqafi (; ), known simply as al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf (), was the most notable governor who served the Umayyad Caliphate. He began his service under Caliph Abd al-Malik (), who successiv ...
(661–714) officially changed the administrative language of Iraq from Middle Persian (Pahlavi) to Arabic, this was the first since the
Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
that a Semitic language was reinstated as an official language in Mesopotamia (
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
). Arabic mainly supplanted other
Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of th ...
sister language
In historical linguistics, sister languages are languages that are descended from a common ancestral language. Every language in a language family that descends from the same language as the others is a sister to them.
A commonly given example is ...
s, like
Coptic in Egypt and
Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
and
Punic
The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians (and sometimes as Western Phoenicians), were a Semitic people who migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' ...
in the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
region (Berber is still spoken and official in Algeria and Morocco), but the more distant
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
languages like Middle Persian and Kurdish proved to be more enduring. Most of Middle Persian structure and vocabulary survived, evolving into
New Persian
New Persian (), also known as Modern Persian () is the current stage of the Persian language spoken since the 8th to 9th centuries until now in Greater Iran and surroundings. It is conventionally divided into three stages: Early New Persian (8th ...
. Persian incorporated a certain amount of Arabic vocabulary, especially words pertaining to religion (and later to science and arts), and it switched from the
Pahlavi scripts
Pahlavi may refer to:
Iranian royalty
* Seven Parthian clans, ruling Parthian families during the Sasanian Empire
* Pahlavi dynasty, the ruling house of Imperial State of Persia/Iran from 1925 until 1979
** Reza Shah Pahlavi (1878–1944), Shah ...
to a
modified version of the Arabic alphabet. Today Persian is spoken officially in
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
,
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, and
Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
.
Urbanisation
The Arab conquest of Persia led to a period of extreme
urbanisation
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also ...
in Iran, starting with the ascension of the
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 C ...
dynasty and ending in the 11th century CE.
This was particularly true for the eastern parts of the country, for regions like
Khorasan and
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
. During this period, Iran saw the development of massive metropolises, some reaching population numbers of up to 200,000 people.
This period of extreme urbanisation was followed in the late 11th and early 12th century by a collapse of the Iranian economy, which led to large scale emigrations of Iranians into Central Asia, India, the rest of the Middle East, and Anatolia. This catastrophe has been cited by some as reason for the Persian language becoming widespread throughout Central Asia and large parts of the Middle East.
See also
References
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
History of Iran: Islamic Conquestfrom the Iran Chamber Society.
The Arab conquestsat History World.
at Mecca Books.
{{Iran topics
Invasions of Iran
7th century in Iran
Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign ...
Book burnings
Destroyed libraries

 After the defeat of the Persian forces at the Battle of Jalula in 637, Yazdgerd III went to Rey and from there moved to
After the defeat of the Persian forces at the Battle of Jalula in 637, Yazdgerd III went to Rey and from there moved to  In the wake of Khalid's demise, Umar appointed Abdullah ibn Uthman as commander of the Muslim forces for the invasion of
In the wake of Khalid's demise, Umar appointed Abdullah ibn Uthman as commander of the Muslim forces for the invasion of  The expedition to
The expedition to  The Arabs were raiding Sakastan as early as Umar's caliphate. The first real invasion took place in 650, when Abd-Allah ibn Amir, having secured his position in Kerman, sent an army under Mujashi ibn Mas'ud there. After crossing the Dasht-i Lut desert, Mujashi ibn Mas'ud reached Sakastan, but suffered a heavy defeat and was forced to retreat.
One year later, Abd-Allah ibn Amir sent an army under Rabi ibn Ziyad Harithi to Sakastan. After some time, Rabi reached Zaliq, a Sakastani border town, where he forced the
The Arabs were raiding Sakastan as early as Umar's caliphate. The first real invasion took place in 650, when Abd-Allah ibn Amir, having secured his position in Kerman, sent an army under Mujashi ibn Mas'ud there. After crossing the Dasht-i Lut desert, Mujashi ibn Mas'ud reached Sakastan, but suffered a heavy defeat and was forced to retreat.
One year later, Abd-Allah ibn Amir sent an army under Rabi ibn Ziyad Harithi to Sakastan. After some time, Rabi reached Zaliq, a Sakastani border town, where he forced the  The conquest of
The conquest of  Khorasan was the second-largest province of the Sasanian Empire. It stretched from what is now northeastern Iran, northwestern Afghanistan and southern Turkmenistan. In 651 the conquest of Khurasan was assigned to Ahnaf ibn Qais. Ahnaf marched from
Khorasan was the second-largest province of the Sasanian Empire. It stretched from what is now northeastern Iran, northwestern Afghanistan and southern Turkmenistan. In 651 the conquest of Khurasan was assigned to Ahnaf ibn Qais. Ahnaf marched from