Web development is the work involved in developing a
website
A website (also written as a web site) is any web page whose content is identified by a common domain name and is published on at least one web server. Websites are typically dedicated to a particular topic or purpose, such as news, educatio ...
for the
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
(
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
) or an
intranet
An intranet is a computer network for sharing information, easier communication, collaboration tools, operational systems, and other computing services within an organization, usually to the exclusion of access by outsiders. The term is used in ...
(a private network).
Web development can range from developing a simple single
static page of
plain text
In computing, plain text is a loose term for data (e.g. file contents) that represent only characters of readable material but not its graphical representation nor other objects ( floating-point numbers, images, etc.). It may also include a lim ...
to complex
web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
s,
electronic business
Electronic business (also known as online business or e-business) is any kind of business or commercial activity that includes sharing information across the internet. Commerce constitutes the exchange of products and services between businesses, ...
es, and
social network service
A social networking service (SNS), or social networking site, is a type of online social media platform which people use to build social networks or social relationships with other people who share similar personal or career content, interests ...
s. A more comprehensive list of tasks to which Web development commonly refers, may include
Web engineering
The World Wide Web has become a major delivery platform for a variety of complex and sophisticated enterprise applications in several domains. In addition to their inherent multifaceted functionality, these Web applications exhibit complex behavi ...
,
Web design
Web design encompasses many different skills and disciplines in the production and maintenance of websites. The different areas of web design include web graphic design; user interface design (UI design); authoring, including standardised code a ...
,
Web content development
Web content development is the process of researching, writing, gathering, organizing, and editing information for publication on websites. Website content may consist of prose, graphics, pictures, recordings, movies, or other digital assets th ...
, client liaison,
client-side/
server-side scripting
Server-side scripting is a technique used in web development which involves employing scripts on a web server which produces a response customized for each user's (client's) request to the website. Scripts can be written in any of a number of s ...
,
Web server
A web server is computer software and underlying Computer hardware, hardware that accepts requests via Hypertext Transfer Protocol, HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, co ...
and
network security configuration, and
e-commerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) refers to commercial activities including the electronic buying or selling products and services which are conducted on online platforms or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile co ...
development.
Among Web professionals, "Web development" usually refers to the main non-design aspects of building Web sites: writing
markup and
coding. Web development may use
content management system
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content ( content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New ...
s (CMS) to make content changes easier and available with basic technical skills.
For larger organizations and businesses, Web development teams can consist of hundreds of people (
Web developer
A web developer is a programmer who develops World Wide Web applications using a client–server model. The applications typically use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in the client, and any general-purpose programming language in the server. is used ...
s) and follow standard methods like
Agile methodologies while developing Web sites.
Smaller organizations may only require a single permanent or contracting developer, or secondary assignment to related job positions such as a
graphic designer
A graphic designer is a practitioner who follows the discipline of graphic design, either within companies or organizations or independently. They are professionals in design and visual communication, with their primary focus on transforming ...
or
information systems
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems comprise four components: task, people, structu ...
technician. Web development may be a collaborative effort between departments rather than the domain of a designated department. There are three kinds of Web developer specialization:
front-end developer, back-end developer, and full-stack developer. Front-end developers are responsible for behavior and visuals that run in the user browser, while back-end developers deal with the servers. Since the commercialization of the Web, the industry has boomed and has become one of the most used technologies ever.
Evolution of the World Wide Web and web development
Origin/ Web 1.0
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow a ...
created the
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
in 1989 at CERN.
The primary goal in the development of the Web was to fulfill the automated information-sharing needs of academics affiliated with institutions and various global organizations. Consequently,
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
was developed in 1993.
Web 1.0 is described as the first paradigm wherein users could only view material and provide a small amount of information.
Core protocols of web 1.0 were
HTTP
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, wher ...
, HTML and
URI
Uri may refer to:
Places
* Canton of Uri, a canton in Switzerland
* Úri, a village and commune in Hungary
* Uri, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Uri, Jammu and Kashmir, a town in India
* Uri (island), off Malakula Island in V ...
.
Web 2.0
Web 2.0
Web 2.0 (also known as participative (or participatory) web and social web) refers to websites that emphasize user-generated content, ease of use, participatory culture, and interoperability (i.e., compatibility with other products, systems, a ...
, a term popularised by
Dale Dougherty
Dale Dougherty (born 1956) is a co-founder of O'Reilly Media, along with Tim O'Reilly and helped develop O'Reilly's publishing business. He is the author of the O'Reilly book ''sed & awk''.
Biography
Dougherty was the founder, in 1993, and publi ...
, then vice president of O'Reilly, during a 2004 conference with Media Live, marks a shift in internet usage, emphasizing interactivity.
Web 2.0 introduced increased user engagement and communication. It evolved from the static, read-only nature of Web 1.0 and became an integrated network for engagement and communication. It is often referred to as a user-focused, read-write online network.
In the realm of Web 2.0 environments, users now have access to a platform that encourages sharing activities such as creating music, files, images, and movies. The architecture of Web 2.0 is often considered the "backbone of the internet," using standardized
XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
(Extensible Markup Language) tags to authorize information flow from independent platforms and
online database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of Data (computing), data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, Application software, applications, and ...
s.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0, considered the third and current version of the web, was introduced in 2014. The concept envisions a complete redesign of the web. Key features include the integration of
metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive ...
, precise information delivery, and improved
user experience
User experience (UX) is how a user interacts with and experiences a product, system or service. It includes a person's perceptions of utility, ease of use, and efficiency. Improving user experience is important to most companies, designers, a ...
s based on preferences, history, and interests.
Web 3.0 aims to turn the web into a sizable, organized database, providing more functionality than traditional search engines. Users can customize navigation based on their preferences, and the core ideas involve identifying data sources, connecting them for efficiency, and creating user profiles.
This version is sometimes also known as
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
To enable the encoding o ...
.
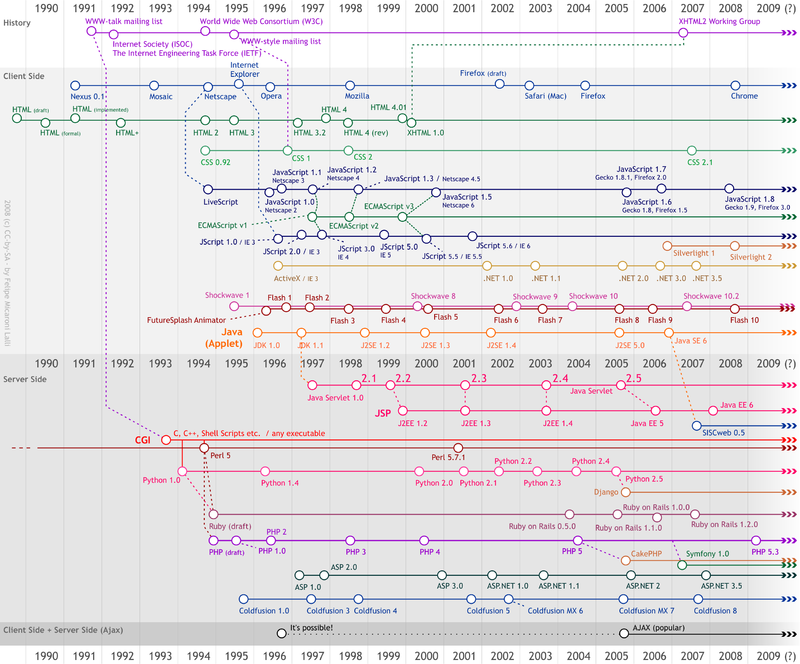
Evolution of web development technologies
The journey of web development technologies began with simple
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
pages in the early days of the internet. Over time, advancements led to the incorporation of
CSS for styling and
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have ...
for interactivity. This evolution transformed static websites into dynamic and responsive platforms, setting the stage for the complex and feature-rich web applications we have today.
* Static HTML Pages (1990s)
* Introduction of
CSS (late 1990s)
*
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have ...
and Dynamic HTML (1990s - early 2000s)
*
AJAX
Ajax may refer to:
Greek mythology and tragedy
* Ajax the Great, a Greek mythological hero, son of King Telamon and Periboea
* Ajax the Lesser, a Greek mythological hero, son of Oileus, the king of Locris
* Ajax (play), ''Ajax'' (play), by the an ...
(1998)
* Rise of
Content management system
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content ( content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New ...
s (CMS) (mid-2000s)
*
Mobile web
The mobile web comprises mobile browser-based World Wide Web services accessed from handheld mobile devices, such as smartphones or feature phones, through a mobile network, mobile or other wireless network.
History and development
Traditiona ...
(late 2000s - 2010s)
*
Single-page application
A single-page application (SPA) is a web application or website that interacts with the user by dynamically rewriting the current web page with new data from the web server, instead of the default method of loading entire new pages. The goal is fas ...
s (SPAs) and front-end frameworks (2010s)
*
Server-side javaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have a ...
(2010s)
*
Microservices
In software engineering, a microservice architecture is an architectural pattern that organizes an application into a collection of loosely coupled, fine-grained services that communicate through lightweight protocols. This pattern is characterize ...
and
API-driven development (2010s - present)
*
Progressive web app
A progressive web application (PWA), or progressive web app, is a type of web app that can be installed on a device as a standalone application software, application. PWAs are installed using the offline cache of the device's web browser.
PWAs w ...
s (PWAs) (2010s - present)
*
JAMstack Architecture (2010s - present)
*
WebAssembly
WebAssembly (Wasm) defines a portable binary-code format and a corresponding text format for executable programs as well as software interfaces for facilitating communication between such programs and their host environment.
The main goal of ...
(Wasm) (2010s - present)
*
Serverless computing
Serverless computing is "a cloud service category in which the customer can use different cloud capability types without the customer having to provision, deploy and manage either hardware or software resources, other than providing customer appli ...
(2010s - present)
*
AI and
machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
integration (2010s - present)
Web development in future will be driven by advances in browser technology, Web internet infrastructure, protocol standards, software engineering methods, and application trends.
Web development life cycle
The web development life cycle is a method that outlines the stages involved in building websites and web applications. It provides a structured approach, ensuring optimal results throughout the development process.
A typical Web Development process can be divided into 7 steps.
Analysis
Debra Howcraft and John Carroll proposed a methodology in which web development process can be divided into sequential steps. They mentioned different aspects of analysis.
Phase one involves crafting a web strategy and analyzing how a website can effectively achieve its goals. Keil et al.'s research identifies the primary reasons for software project failures as a lack of top management commitment and misunderstandings of system requirements. To mitigate these risks, Phase One establishes strategic goals and objectives, designing a system to fulfill them. The decision to establish a web presence should ideally align with the organization's corporate information strategy.
The analysis phase can be divided into 3 steps:
* Development of a web strategy
* Defining objectives
* Objective analysis
During this phase, the previously outlined objectives and available resources undergo analysis to determine their feasibility. This analysis is divided into six tasks, as follows:
* Technology analysis: Identification of all necessary technological components and tools for constructing, hosting, and supporting the site.
* Information analysis: Identification of user-required information, whether static (web page) or dynamic (pulled "live" from a database server).
* Skills analysis: Identification of the diverse skill sets necessary to complete the project.
* User analysis: Identification of all intended users of the site, a more intricate process due to the varied range of users and technologies they may use.
* Cost analysis: Estimation of the development cost for the site or an evaluation of what is achievable within a predefined budget.
* Risk analysis: Examination of any major risks associated with site development.
Following this analysis, a more refined set of objectives is documented. Objectives that cannot be presently fulfilled are recorded in a Wish List, constituting part of the Objectives Document. This documentation becomes integral to the iterative process during the subsequent cycle of the methodology.
Planning: sitemap and wireframe
It is crucial for
web developer
A web developer is a programmer who develops World Wide Web applications using a client–server model. The applications typically use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in the client, and any general-purpose programming language in the server. is used ...
s to be engaged in formulating a plan and determining the optimal architecture and selecting the
frameworks. Additionally, developers/consultants play a role in elucidating the total cost of ownership associated with supporting a website, which may surpass the initial development expenses.
Key aspects in this step are:
*
Sitemap
A sitemap is a list of pages of a web site within a domain.
There are three primary kinds of sitemap:
* Sitemaps used during the planning of a website by its designers
* Human-visible listings, typically hierarchical, of the pages on a site
* ...
creation
*
Wireframe creation
*
Tech stack
In computing, a solution stack or software stack is a set of software subsystems or components needed to create a complete platform such that no additional software is needed to support applications. Applications are said to "run on" or "run on ...
Design and layout
Following the analysis phase, the development process moves on to the
design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
phase, which is guided by the objectives document. Recognizing the incremental growth of websites and the potential lack of good design architecture, the methodology includes iteration to account for changes and additions over the life of the site. The design phase, which is divided into
Information Design
Information design is the practice of presenting information in a way that fosters an efficient and effective understanding of the information. The term has come to be used for a specific area of graphic design related to displaying information ...
and
Graphic Design
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art that involves creating visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of ...
, results in a detailed Design Document that details the structure of the website,
database data structures, and
CGI scripts.*
The following step, design testing, focuses on early, low-cost testing to identify inconsistencies or flaws in the design. This entails comparing the website's design to the goals and objectives outlined in the first three steps. Phases One and Two involve an iterative loop in which objectives in the Objectives Document are revisited to ensure alignment with the design. Any objectives that are removed are added to the Wish List for future consideration.
Key aspects in this step are:
*
Page layout
In graphic design, page layout is the arrangement of visual elements on a page. It generally involves organizational principles of composition to achieve specific communication objectives.
The high-level page layout involves deciding on the ...
s
* Review
* Approval
Content creation
No matter how visually appealing a website is, good communication with clients is critical. The primary purpose of content production is to create a communication channel through the
user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
by delivering relevant information about your firm in an engaging and easily understandable manner. This includes:
* Developing appealing calls to action
* Making creative headlines
* Content formatting for readability
* Carrying out line editing
* Text updating throughout the site development process.
The stage of content production is critical in establishing the branding and marketing of your website or web application. It serves as a platform for defining the purpose and goals of your online presence through compelling and convincing content.
Development
During this critical stage, the website is built while keeping its fundamental goal in mind, paying close attention to all graphic components to assure the establishment of a completely working site.
The procedure begins with the development of the main page, which is followed by the production of interior pages. The site's navigational structure is being refined in particular.
During this development phase, key functionality such as the
Content Management System
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content ( content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New ...
, interactive contact forms, and shopping carts are activated.
The coding process includes creating all of the site's software and installing it on the appropriate
Web servers. This can range from simple things like posting to a Web server to more complex tasks like establishing
database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
connections.
Testing, review and launch
In any web project, the testing phase is incredibly intricate and difficult. Because
web apps
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
are frequently designed for a diverse and often unknown user base running in a range of technological environments, their complexity exceeds that of
traditional Information Systems (IS). To ensure maximum reach and efficacy, the website must be tested in a variety of contexts and technologies. The website moves to the delivery stage after gaining final approval from the designer. To ensure its preparation for launch, the quality assurance team performs rigorous testing for functionality, compatibility, and performance.
Additional testing is carried out, including integration, stress,
scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
, load, resolution, and
cross-browser compatibility. When the approval is given, the website is pushed to the server via
FTP
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and dat ...
, completing the development process.
Key aspects in this step are:
* Test Lost Links
* Use code validators
* Check
browser
Maintenance and updating
The web development process goes beyond deployment to include a variety of post-deployment tasks.
Websites, in example, are frequently under ongoing maintenance, with new items being uploaded on a daily basis. The maintenance costs increases immensely as the site grows in size. The accuracy of content on a website is critical, demanding continuous monitoring to verify that both information and links, particularly external links, are updated. Adjustments are made in response to user feedback, and regular support and maintenance actions are carried out to maintain the website's long-term effectiveness.
Traditional development methodologies
Debra Howcraft and John Carroll discussed a few traditional web development methodologies in their research paper:
* Waterfall: The
waterfall
A waterfall is any point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge
of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf.
Waterfalls can be formed in seve ...
methodology comprises a sequence of cascading steps, addressing the development process with minimal iteration between each stage. However, a significant drawback when applying the waterfall methodology to the development of websites (as well as information systems) lies in its rigid structure, lacking iteration beyond adjacent stages. Any methodology used for the development of Web-sites must be flexible enough to cope with change.
* Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method (SSADM):
Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method
Structured systems analysis and design method (SSADM) is a systems approach to the analysis and design of information systems. SSADM was produced for the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency, a UK government office concerned with the u ...
(SSADM) is a widely used methodology for systems analysis and design in information systems and software engineering. Although it does not cover the entire lifecycle of a development project, it places a strong emphasis on the stages of analysis and design in the hopes of minimizing later-stage, expensive errors and omissions.
* Prototyping:
Prototyping
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to ...
is a software development approach in which a preliminary version of a system or application is built to visualize and test its key functionalities. The prototype serves as a tangible representation of the final product, allowing stakeholders, including users and developers, to interact with it and provide feedback.
* Rapid Application Development:
Rapid Application Development
Rapid application development (RAD), also called rapid application building (RAB), is both a general term for adaptive software development approaches, and the name for James Martin's method of rapid development. In general, RAD approaches to ...
(RAD) is a software development methodology that prioritizes speed and flexibility in the development process. It is designed to produce high-quality systems quickly, primarily through the use of iterative prototyping and the involvement of end-users. RAD aims to reduce the time it takes to develop a system and increase the adaptability to changing requirements.
* Incremental Prototyping: Incremental prototyping is a software development approach that combines the principles of prototyping and
incremental development. In this methodology, the development process is divided into small increments, with each increment building upon the functionality of the previous one. At the same time, prototypes are created and refined in each increment to better meet user requirements and expectations.
Key technologies in web development
Developing a fundamental knowledge of
client-side and
server-side dynamics is crucial.
The goal of
front-end development is to create a website's
user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
and visual components that users may interact with directly. On the other hand,
back-end development works with databases, server-side logic, and application functionality. Building reliable and user-friendly online applications requires a comprehensive approach, which is ensured by collaboration between front-end and back-end engineers.
Front-end development
Front-end development is the process of designing and implementing the user interface (UI) and
user experience
User experience (UX) is how a user interacts with and experiences a product, system or service. It includes a person's perceptions of utility, ease of use, and efficiency. Improving user experience is important to most companies, designers, a ...
(UX) of a
web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
. It involves creating visually appealing and interactive elements that users interact with directly. The primary technologies and concepts associated with front-end development include:
Technologies
The 3 core technologies for front-end development are:
* HTML (Hypertext Markup Language):
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
provides the structure and organization of content on a webpage.
* CSS (Cascading Style Sheet): Responsible for styling and layout,
CSS enhances the presentation of HTML elements, making the application visually appealing.
* JavaScript: It is used to add interactions to the web pages. Advancement in
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have ...
has given rise to many popular front- end frameworks like React, Angular and Vue.js etc.
User interface design
User experience design
User experience design (UX design, UXD, UED, or XD), upon which is the centralized requirements for "User Experience Design Research" (also known as UX Design Research), defines the experience a user would go through when interacting with a compa ...
focuses on creating interfaces that are intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable for users. It involves understanding user behavior, conducting usability studies, and implementing design principles to enhance the overall satisfaction of users interacting with a website or application. This involves
wireframing,
prototyping
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to ...
, and implementing design principles to enhance user interaction. Some of the popular tools used for UI Wireframing are -
* Sketch for detailed,
vector-based design
* Moqups for beginners
*
Figma
Figma is a collaborative web application for interface design, with additional offline features enabled by desktop applications for macOS and Windows. The feature set of Figma focuses on user interface and user experience design, with an empha ...
for a free wireframe app
* UXPin for handing off design documentation to developers
* MockFlow for project organization
*
Justinmind for interactive wireframes
* Uizard for AI-assisted wireframing
Another key aspect to keep in mind while designing is
Web Accessibility
Web accessibility, or eAccessibility,European CommissionCommunication from the Commission to the Council, the European Parliament and the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: eAccessibility, EC(2005)1095 pu ...
- Web accessibility ensures that digital content is available and usable for people of all abilities. This involves adhering to standards like the
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are part of a series published by the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), the main international standards organization for the Internet. They are a set of re ...
(WCAG), implementing features like alternative text for images, and designing with considerations for diverse user needs, including those with disabilities.
Responsive design
It is important to ensure that web applications are accessible and visually appealing across various devices and screen sizes.
Responsive design
Responsive web design (RWD) or responsive design is an approach to web design that aims to make web pages render well on a variety of devices and window or screen sizes from minimum to maximum display size to ensure usability and satisfactio ...
uses CSS media queries and flexible layouts to adapt to different viewing environments.
Front-end frameworks
A
framework is a high-level solution for the reuse of software pieces, a step forward in simple library-based reuse that allows for sharing common functions and generic logic of a domain application.
Frameworks and
libraries
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
are essential tools that expedite the development process. These tools enhance developer productivity and contribute to the maintainability of large-scale applications. Some popular front-end frameworks are:
*
React: A JavaScript library for building user interfaces, maintained by Facebook. It allows developers to create reusable UI components.
*
Angular: A TypeScript-based front-end framework developed and maintained by Google. It provides a comprehensive solution for building dynamic single-page applications.
*
Vue.js: A progressive JavaScript framework that is approachable yet powerful, making it easy to integrate with other libraries or existing projects.
State management
Managing the state of a web application to ensure data consistency and responsiveness. State management libraries like
Redux (for
React) or
Vuex
Vuex is an open-source state management library for Vue.js applications and a JavaScript framework. It was created by Evan You, the developer behind Vue.js, to provide a centralized store for managing state in Vue.js applications, making it easi ...
(for
Vue.js) play a crucial role in complex applications.
Back-end development
Back-end development involves building the server-side logic and
database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
components of a
web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
. It is responsible for processing user requests, managing data, and ensuring the overall functionality of the application. Key aspects of back-end development include:
Server/ cloud instance
An essential component of the architecture of a web application is a
server
Server may refer to:
Computing
*Server (computing), a computer program or a device that provides requested information for other programs or devices, called clients.
Role
* Waiting staff, those who work at a restaurant or a bar attending custome ...
or
cloud instance. A
cloud instance is a virtual server instance that can be accessed via the
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
and is created, delivered, and hosted on a public or private cloud. It functions as a physical server that may seamlessly move between various devices with ease or set up several instances on one server. It is therefore very dynamic, scalable, and economical.
Databases
Database management
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and ana ...
is crucial for
storing,
retrieving, and managing data in web applications. Various database systems, such as
MySQL
MySQL () is an Open-source software, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A rel ...
,
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL ( ) also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source software, free and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance. PostgreSQL features transaction processing, transactions ...
, and
MongoDB
MongoDB is a source-available, cross-platform, document-oriented database program. Classified as a NoSQL database product, MongoDB uses JSON-like documents with optional database schema, schemas. Released in February 2009 by 10gen (now MongoDB ...
, play distinct roles in organizing and structuring data. Effective database management ensures the responsiveness and efficiency of data-driven web applications. There are 3 types of databases:
*
Relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
s: Structured databases that use tables to organize and relate data. Common Examples include -
MySQL
MySQL () is an Open-source software, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A rel ...
,
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL ( ) also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source software, free and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance. PostgreSQL features transaction processing, transactions ...
and many more.
* NoSQL databases:
NoSQL databases are designed to handle
unstructured or
semi-structured data and can be more flexible than
relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
s. They come in various types, such as
document-oriented,
key-value stores, column-family stores, and
graph database
A graph database (GDB) is a database that uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. A key concept of the system is the graph (or edge or relationship). The graph relates the dat ...
s. Examples:
MongoDB
MongoDB is a source-available, cross-platform, document-oriented database program. Classified as a NoSQL database product, MongoDB uses JSON-like documents with optional database schema, schemas. Released in February 2009 by 10gen (now MongoDB ...
,
Cassandra
Cassandra or Kassandra (; , , sometimes referred to as Alexandra; ) in Greek mythology was a Trojan priestess dedicated to the god Apollo and fated by him to utter true prophecy, prophecies but never to be believed. In modern usage her name is e ...
,
ScyllaDB
ScyllaDB is a source-available distributed NoSQL wide-column data store. It was designed to be compatible with Apache Cassandra while achieving significantly higher throughputs and lower latencies. It supports the same protocols as Cassandra ( CQ ...
,
CouchDB
Apache CouchDB is an open-source document-oriented NoSQL database, implemented in Erlang.
CouchDB uses multiple formats and protocols to store, transfer, and process its data. It uses JSON to store data, JavaScript as its query language using ...
,
Redis
Redis (; Remote Dictionary Server) is an in-memory key–value database, used as a distributed cache and message broker, with optional durability. Because it holds all data in memory and because of its design, Redis offers low- latency reads ...
.
* Document stores:
Document stores store data in a
semi-structured format, typically using
JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced or ) is an open standard file format and electronic data interchange, data interchange format that uses Human-readable medium and data, human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consi ...
or
XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
documents. Each document can have a different structure, providing flexibility. Examples:
MongoDB
MongoDB is a source-available, cross-platform, document-oriented database program. Classified as a NoSQL database product, MongoDB uses JSON-like documents with optional database schema, schemas. Released in February 2009 by 10gen (now MongoDB ...
,
CouchDB
Apache CouchDB is an open-source document-oriented NoSQL database, implemented in Erlang.
CouchDB uses multiple formats and protocols to store, transfer, and process its data. It uses JSON to store data, JavaScript as its query language using ...
.
* Key-value stores:
Key-value stores store data as pairs of keys and values. They are simple and efficient for certain types of operations, like
caching. Examples:
Redis
Redis (; Remote Dictionary Server) is an in-memory key–value database, used as a distributed cache and message broker, with optional durability. Because it holds all data in memory and because of its design, Redis offers low- latency reads ...
,
DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is a managed NoSQL database service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It supports key-value and document data structures and is designed to handle a wide range of applications requiring scalability and performance.
History
We ...
.
* Column-family stores:
Column-family stores organize data into columns instead of rows, making them suitable for large-scale
distributed systems
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different computer network, networked computers.
The components of a distribu ...
and analytical workloads. Examples:
Apache Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is a free and open-source software, free and open-source database management system designed to handle large volumes of data across multiple Commodity computing, commodity servers. The system prioritizes availability and scalab ...
,
HBase
HBase is an open-source non-relational distributed database modeled after Google's Bigtable and written in Java. It is developed as part of Apache Software Foundation's Apache Hadoop project and runs on top of HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File Sy ...
.
* Graph databases:
Graph database
A graph database (GDB) is a database that uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. A key concept of the system is the graph (or edge or relationship). The graph relates the dat ...
s are designed to represent and query data in the form of graphs. They are effective for handling relationships and network-type data. Examples:
Neo4j
Neo4j is a graph database management system (GDBMS) developed by Neo4j Inc.
The data elements Neo4j stores are nodes, edges connecting them, and attributes of nodes and edges. Described by its developers as an ACID-compliant transactional d ...
,
Amazon Neptune.
* In-memory databases:
In-memory database
An in-memory database (IMDb, or main memory database system (MMDB) or memory resident database) is a database management system that primarily relies on main memory for computer data storage. It is contrasted with database management systems that e ...
s store data in the system's main memory (
RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM most commonly refers to:
* A male sheep
* Random-access memory, computer memory
* Ram Trucks, US, since 2009
** List of vehicles named Dodge Ram, trucks and vans
** Ram Pickup, produced by Ram Trucks
Ram, ram, or RAM may also ref ...
) rather than on disk. This allows for faster data access and retrieval. Examples:
Redis
Redis (; Remote Dictionary Server) is an in-memory key–value database, used as a distributed cache and message broker, with optional durability. Because it holds all data in memory and because of its design, Redis offers low- latency reads ...
,
Memcached
Memcached (pronounced variously /mɛmkæʃˈdiː/ ''mem-cash-dee'' or /ˈmɛmkæʃt/ ''mem-cashed'') is a general-purpose distributed memory-caching system. It is often used to speed up dynamic database-driven websites by caching data and object ...
.
* Time-series databases:
Time-series databases are optimized for handling time-stamped data, making them suitable for applications that involve tracking changes over time. Examples:
InfluxDB
InfluxDB is a time series database (TSDB) developed by the company InfluxData. It is used for storage and retrieval of time series data in fields such as operations monitoring, application metrics, Internet of Things sensor data, and real-time a ...
, OpenTSDB.
* NewSQL databases:
NewSQL
NewSQL is a class of relational database management system, relational database management systems that seek to provide the scalability of NoSQL systems for online transaction processing (OLTP) workloads while maintaining the ACID guarantees of a t ...
databases aim to provide the scalability of NoSQL databases while maintaining the
ACID
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) of traditional relational databases. Examples:
Google Spanner,
CockroachDB
CockroachDB is a source-available distributed SQL database management system developed by Cockroach Labs.
The relational functionality is built on top of a distributed, transactional, consistent key-value store that can survive a variety of d ...
.
* Object-oriented databases:
Object-oriented databases
An object database or object-oriented database is a database management system in which information is represented in the form of objects as used in object-oriented programming. Object databases are different from relational databases which are ...
store data in the form of objects, which can include both
data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
and methods. They are designed to work seamlessly with object-oriented programming languages. Examples:
db4o
db4o (database for objects) was an embeddable open-source object database for Java and .NET developers. It was developed, commercially licensed and supported by Actian. In October 2014, Actian declined to continue to actively pursue and promote ...
,
ObjectDB.
The choice of a database depends on various factors such as the nature of the data, scalability requirements, performance considerations, and the specific use case of the application being developed. Each type of database has its strengths and weaknesses, and selecting the right one involves considering the specific needs of the project.
Application programming interface (APIs)
Application Programming Interfaces
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build su ...
are sets of rules and protocols that allow different software applications to communicate with each other. APIs define the methods and data formats that applications can use to request and exchange information.
*
REST
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a software architectural style that was created to describe the design and guide the development of the architecture for the World Wide Web. REST defines a set of constraints for how the architecture of ...
ful APIs and
GraphQL
GraphQL is a data query and manipulation language that allows specifying what data is to be retrieved (" declarative data fetching") or modified. A GraphQL server can process a client query using data from separate sources and present the res ...
are common approaches for defining and interacting with web services.
= Types of APIs
=
*
Web API
A web API is an application programming interface (API) for either a web server or a web browser.
As a web development concept, it can be related to a web application's client side (including any web frameworks being used).
A server-side web AP ...
s: These are APIs that are accessible over the internet using standard web protocols such as HTTP. RESTful APIs are a common type of web API.
* Library APIs: These APIs provide pre-built functions and procedures that developers can use within their code.
* Operating System APIs: These APIs allow applications to interact with the underlying
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
, accessing features like file systems, hardware, and system services.
Server-side languages
Programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
s aimed at server execution, as opposed to client browser execution, are known as
server-side languages. These programming languages are used in web development to perform operations including
data processing
Data processing is the collection and manipulation of digital data to produce meaningful information. Data processing is a form of ''information processing'', which is the modification (processing) of information in any manner detectable by an o ...
, database interaction, and the creation of
dynamic content
A dynamic web page is a web page constructed at runtime (during software execution), as opposed to a ''static web page'', delivered as it is stored.
A server-side dynamic web page is a web page whose construction is controlled by an application ...
that is delivered to the client's browser. A key element of server-side programming is
server-side scripting
Server-side scripting is a technique used in web development which involves employing scripts on a web server which produces a response customized for each user's (client's) request to the website. Scripts can be written in any of a number of s ...
, which allows the server to react to client requests in real time.
Some popular server-side languages are:
# PHP:
PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared towards web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by the PHP Group. ...
is a widely used,
open-source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
server-side scripting language. It is embedded in HTML code and is particularly well-suited for web development.
# Python:
Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (prog ...
is a versatile, high-level programming language used for a variety of purposes, including server-side web development. Frameworks like
Django and
Flask
Flask may refer to:
Container
* Hip flask, a small container used to carry liquid
* Laboratory flask, laboratory glassware for holding larger volumes than simple test tubes
** Erlenmeyer flask, a common laboratory flask with a flat bottom, a c ...
make it easy to build web applications in Python.
# Ruby:
Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapph ...
is an object-oriented programming language, and it is commonly used for web development.
Ruby on Rails
Ruby on Rails (simplified as Rails) is a server-side web application framework written in Ruby under the MIT License. Rails is a model–view–controller (MVC) framework, providing default structures for a database, a web service, and web pa ...
is a popular web framework that simplifies the process of building web applications.
# Java:
Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language. Java-based frameworks like
Spring are commonly used for building enterprise-level web applications.
# Node.js (JavaScript): While JavaScript is traditionally a client-side language,
Node.js enables developers to run JavaScript on the server side. It is known for its event-driven, non-blocking
I/O model, making it suitable for building scalable and high-performance applications.
# C# (C Sharp):
C# is a programming language developed by Microsoft and is commonly used in conjunction with the
.NET
The .NET platform (pronounced as "''dot net"'') is a free and open-source, managed code, managed computer software framework for Microsoft Windows, Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems. The project is mainly developed by Microsoft emplo ...
framework for building web applications on the Microsoft stack.
# ASP.NET:
ASP.NET
ASP.NET is a server-side web-application framework designed for web development to produce dynamic web pages. It was developed by Microsoft to allow programmers to build dynamic web sites, applications and services. The name stands for Ac ...
is a web framework developed by Microsoft, and it supports languages like C# and
VB.NET
Visual Basic (VB), originally called Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET), is a multi-paradigm, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft and implemented on .NET, Mono, and the .NET Framework. Microsoft launched VB.NET in 2002 as the ...
. It simplifies the process of building dynamic web applications.
# Go (Golang):
Go is a statically typed language developed by Google. It is known for its simplicity and efficiency and is increasingly being used for building scalable and high-performance web applications.
# Perl:
Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Though Perl is not officially an acronym, there are various backronyms in use, including "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language".
Perl was developed ...
is a versatile scripting language often used for web development. It is known for its powerful
text-processing capabilities.
# Swift: Developed by Apple,
Swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIF ...
is used for server-side development in addition to iOS and macOS app development.
# Lua:
Lua is used for some embedded web servers, e.g. the configuration pages on a
router, including
OpenWRT
OpenWrt (from ''open wireless router'') is an open-source project for embedded operating systems based on Linux kernel, Linux, primarily used on Embedded system, embedded devices to Router (computing), route network traffic. The main components ...
.
Security measures
Implementing security measures to protect against common vulnerabilities, including
SQL injection
In computing, SQL injection is a code injection technique used to attack data-driven applications, in which malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field for execution (e.g. to dump the database contents to the attacker). SQL injec ...
,
cross-site scripting
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability that can be found in some web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting vulnerability may be ...
(XSS), and
cross-site request forgery
Cross-site request forgery, also known as one-click attack or session riding and abbreviated as CSRF (sometimes pronounced ''sea-surf'') or XSRF, is a type of malicious exploit of a website or web application where unauthorized commands are submit ...
(CSRF).
Authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with iden ...
and
authorization
Authorization or authorisation (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences), in information security, computer security and identity management, IAM (Identity and Access Managemen ...
mechanisms are crucial for securing data and user access.
Testing, debugging and deployment
Thorough
testing and
debugging
In engineering, debugging is the process of finding the Root cause analysis, root cause, workarounds, and possible fixes for bug (engineering), bugs.
For software, debugging tactics can involve interactive debugging, control flow analysis, Logf ...
processes are essential for identifying and resolving issues in a web application. Testing may include
unit testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration ...
,
integration testing
Integration testing is a form of software testing in which multiple software components, modules, or services are tested together to verify they work as expected when combined. The focus is on testing the interactions and data exchange between i ...
, and
user acceptance testing
In engineering and its various subdisciplines, acceptance testing is a test conducted to determine if the requirements of a specification or contract are met. It may involve chemical tests, physical tests, or performance tests.
In systems en ...
. Debugging involves pinpointing and fixing errors in the code, ensuring the reliability and stability of the application.
*
Unit Testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration ...
: Testing individual components or functions to verify that they work as expected.
*
Integration Testing
Integration testing is a form of software testing in which multiple software components, modules, or services are tested together to verify they work as expected when combined. The focus is on testing the interactions and data exchange between i ...
: Testing the interactions between different components or modules to ensure they function correctly together.
* Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD):
CI/CD
In software engineering, CI/CD or CICD is the combined practices of continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) or, less often, continuous deployment. They are sometimes referred to collectively as continuous development or contin ...
pipelines automate testing,
deployment
Deployment may refer to:
* Military deployment, the movement of armed forces and their logistical support
* Software deployment, all of the activities that make a software system available for use
* System deployment
The deployment of a mecha ...
, and delivery processes, allowing for faster and more reliable releases.
Full-stack development
Full-stack development refers to the practice of designing, building, and maintaining the entire
software stack
In computing, a solution stack or software stack is a set of software subsystems or components needed to create a complete platform such that no additional software is needed to support applications. Applications are said to "run on" or "run on ...
of a web application. This includes both the
frontend (client-side) and
backend (server-side) components, as well as the
database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
and any other necessary infrastructure. A full-stack developer is someone who has expertise in working with both the frontend and backend technologies, allowing them to handle all aspects of web application development.
*
MEAN
A mean is a quantity representing the "center" of a collection of numbers and is intermediate to the extreme values of the set of numbers. There are several kinds of means (or "measures of central tendency") in mathematics, especially in statist ...
(MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js) and
MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) are popular full-stack development stacks that streamline the development process by providing a cohesive set of technologies.
Web development tools and environments
Efficient web development relies on a set of tools and environments that streamline the coding and collaboration processes:
#
Integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
s (IDEs): Tools like
Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code, commonly referred to as VS Code, is an integrated development environment developed by Microsoft for Windows, Linux, macOS and web browsers. Features include support for debugging, syntax highlighting, intelligent code comp ...
,
Atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
, and
Sublime Text
Sublime Text is a text and source code editor featuring a minimal interface, syntax highlighting and code folding with native support for numerous programming and markup languages, search and replace with support for regular expressions, an in ...
provide features such as
code highlighting,
autocompletion
Autocomplete, or word completion, is a feature in which an application predicts the rest of a word a user is typing. In Android and iOS smartphones, this is called predictive text. In graphical user interfaces, users can typically press the t ...
, and
version control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code t ...
integration, enhancing the development experience.
#
Version control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code t ...
:
Git
Git () is a distributed version control system that tracks versions of files. It is often used to control source code by programmers who are developing software collaboratively.
Design goals of Git include speed, data integrity, and suppor ...
is a widely used version control system that allows developers to track changes, collaborate seamlessly, and roll back to previous versions if needed.
#
Collaboration tool
A collaboration tool helps people to collaborate. The purpose of a collaboration tool is to support a group of two or more individuals to accomplish a common goal or objective. Collaboration tools can be either of a non-technological nature suc ...
s: Communication platforms like
Slack,
project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
tools such as
Jira, and
collaboration platforms like
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug trackin ...
facilitate effective teamwork and project management.
Security practices in web development
Security
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercion). Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be persons and social groups, objects and institutions, ecosystems, or any other entity or ...
is paramount in web development to protect against
cyber threats and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of user data. Best practices include encryption, secure coding practices, regular
security audits, and staying informed about the latest
security vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are flaws or weaknesses in a system's design, implementation, or management that can be exploited by a malicious actor to compromise its security.
Despite a system administrator's best efforts to achieve complete correctness, vir ...
and patches.
* Common threats: Developers must be aware of common security threats, including
SQL injection
In computing, SQL injection is a code injection technique used to attack data-driven applications, in which malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field for execution (e.g. to dump the database contents to the attacker). SQL injec ...
,
cross-site scripting
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability that can be found in some web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting vulnerability may be ...
(XSS), and
cross-site request forgery
Cross-site request forgery, also known as one-click attack or session riding and abbreviated as CSRF (sometimes pronounced ''sea-surf'') or XSRF, is a type of malicious exploit of a website or web application where unauthorized commands are submit ...
(CSRF).
* Secure coding practices: Adhering to secure coding practices involves input validation, proper data sanitization, and ensuring that sensitive information is stored and transmitted securely.
* Authentication and authorization: Implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as
OAuth
OAuth (short for open authorization) is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords. Th ...
or
JSON Web Token
JSON Web Token (JWT, suggested pronunciation , same as the word "jot") is a Internet Standard#Proposed Standard, proposed Internet standard for creating data with optional Signature (cryptography), signature and/or optional encryption whose Payl ...
s (JWT), ensures that only authorized users can access specific resources within the application.
Agile methodology in web development
Agile manifesto and principles
Agile is a set of principles and values for software development that prioritize flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction. The four key values are:
* Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
* Working software over comprehensive documentation.
* Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
* Responding to change over following a plan.
Agile concepts in web development
# Iterative and incremental development: Building and refining a web application through small, repeatable cycles, enhancing features incrementally with each iteration.
# Scrum and kanban: Employing agile frameworks like
Scrum
Scrum may refer to:
* Autozam Scrum, a microvan and pickup truck sold in Japan by Mazda
* Line of scrimmage, line separating football teams before a play
* Media scrum, an impromptu press conference, often held immediately outside an event such a ...
for structured sprints or
Kanban
Kanban ( meaning signboard) is a scheduling system for lean manufacturing (also called just-in-time manufacturing, abbreviated JIT). Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, developed kanban to improve manufacturing efficiency. The ...
for continuous flow to manage tasks and enhance team efficiency.
# Cross-functional teams: Forming collaborative teams with diverse skill sets, ensuring all necessary expertise is present for comprehensive web development.
# Customer collaboration: Engaging customers throughout the development process to gather feedback, validate requirements, and ensure the delivered product aligns with expectations.
# Adaptability to change: Embracing changes in requirements or priorities even late in the development process to enhance the product's responsiveness to evolving needs.
# User stories and backlog: Capturing functional requirements through user stories and maintaining a backlog of prioritized tasks to guide development efforts.
# Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD): Implementing automated processes to continuously integrate code changes and deliver updated versions, ensuring a streamlined and efficient development pipeline.
See also
*
Outline of web design and web development
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to web design and web development, two very related fields:
Web design – field that encompasses many different skills and disciplines in the production and maintenance o ...
*
Web design
Web design encompasses many different skills and disciplines in the production and maintenance of websites. The different areas of web design include web graphic design; user interface design (UI design); authoring, including standardised code a ...
*
Web development tools
Web development tools (often abbreviated to dev tools) allow web developers to test, modify and debug their websites. They are different from website builders and integrated development environments (IDEs) in that they do not assist in the direct ...
*
Web application development
*
Web developer
A web developer is a programmer who develops World Wide Web applications using a client–server model. The applications typically use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in the client, and any general-purpose programming language in the server. is used ...
References
{{Authority control
