Magna Græcia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of

 The original Greek expression ''Megálē Hellás'' (), later translated into Latin as , is attested for the first time in a passage from the 2nd century BC by the Greek historian
The original Greek expression ''Megálē Hellás'' (), later translated into Latin as , is attested for the first time in a passage from the 2nd century BC by the Greek historian
 Another reason was the strong economic growth with the consequent overpopulation of the motherland. The terrain that some of these Greek city-states were in could not support a large city. Politics was also the reason as refugees from Greek city-states tended to settle away from these cities in the colonies.
Greeks settled outside of Greece in two distinct ways. The first was in permanent settlements founded by the Greeks, which formed as independent poleis. The second form was in what historians refer to as '' emporia''; trading posts which were occupied by both Greeks and non-Greeks and which were primarily concerned with the manufacture and sale of goods. Examples of this latter type of settlement are found at Al Mina in the east and Pithekoussai in the west.
From about 750 BC the Greeks began 250 years of expansion, settling colonies in all directions.
Another reason was the strong economic growth with the consequent overpopulation of the motherland. The terrain that some of these Greek city-states were in could not support a large city. Politics was also the reason as refugees from Greek city-states tended to settle away from these cities in the colonies.
Greeks settled outside of Greece in two distinct ways. The first was in permanent settlements founded by the Greeks, which formed as independent poleis. The second form was in what historians refer to as '' emporia''; trading posts which were occupied by both Greeks and non-Greeks and which were primarily concerned with the manufacture and sale of goods. Examples of this latter type of settlement are found at Al Mina in the east and Pithekoussai in the west.
From about 750 BC the Greeks began 250 years of expansion, settling colonies in all directions.

 The first Greek city to be absorbed into the
The first Greek city to be absorbed into the
 During the
During the
File:Paestum BW 2013-05-17 15-01-57.jpg,
 The administrative organisation of Magna Graecia was inherited from the Hellenic poleis, taking up the concept of " city-states" administered by the
The administrative organisation of Magna Graecia was inherited from the Hellenic poleis, taking up the concept of " city-states" administered by the
 Greek coinage of Italy and Sicily originated from local Italiotes and Siceliotes who formed numerous city-states. These
Greek coinage of Italy and Sicily originated from local Italiotes and Siceliotes who formed numerous city-states. These

 Magna Graecia, in some fields such as architecture and urban planning, sometimes surpassed the mother country and the other Greek colonies. In Magna Graecia, as well as in the other Greek colonies, the Doric style enriched with showy decorations was adopted as the dominant architectural style. In Magna Graecia, in particular, a Doric style influenced by the Ionic one was also used, especially in Sicily in the Achaean colonies. In Magna Graecia, limestone was used as a building material due to the difficulty in finding other materials. The Doric style in Magna Graecia reached its apogee, surpassing that of the motherland and the other Greek colonies.
Regarding urban planning, the cities of Magna Graecia, as well as many cities of Greek colonies in other regions, were more orderly and rational in the distribution of spaces than those of the mother country, making the urban fabric more practical. The first examples of urbanistically more rational Greek cities belonged to Magna Graecia, in this case Taranto, Metapontum and Megara Hyblaea. Characteristic of this new urban concept, which later spread also in the motherland to
Magna Graecia, in some fields such as architecture and urban planning, sometimes surpassed the mother country and the other Greek colonies. In Magna Graecia, as well as in the other Greek colonies, the Doric style enriched with showy decorations was adopted as the dominant architectural style. In Magna Graecia, in particular, a Doric style influenced by the Ionic one was also used, especially in Sicily in the Achaean colonies. In Magna Graecia, limestone was used as a building material due to the difficulty in finding other materials. The Doric style in Magna Graecia reached its apogee, surpassing that of the motherland and the other Greek colonies.
Regarding urban planning, the cities of Magna Graecia, as well as many cities of Greek colonies in other regions, were more orderly and rational in the distribution of spaces than those of the mother country, making the urban fabric more practical. The first examples of urbanistically more rational Greek cities belonged to Magna Graecia, in this case Taranto, Metapontum and Megara Hyblaea. Characteristic of this new urban concept, which later spread also in the motherland to
 The Sicilian Greek colonists in Magna Graecia, but also from
The Sicilian Greek colonists in Magna Graecia, but also from
 The colonies sent athletes of all disciplines to the
The colonies sent athletes of all disciplines to the

 * 8th century BC: the first historical colony of Magna Graecia was that of Pithekoussai (current island of Ischia) founded in the 8th century BC by settlers from
* 8th century BC: the first historical colony of Magna Graecia was that of Pithekoussai (current island of Ischia) founded in the 8th century BC by settlers from
 Greek nobles started taking refuge in Italy following the
Greek nobles started taking refuge in Italy following the
 Remains of one atlas in the ''Temple of Olympian Zeus, Agrigento, Olympeion'' field, Valle dei Templi, Agrigento,
Remains of one atlas in the ''Temple of Olympian Zeus, Agrigento, Olympeion'' field, Valle dei Templi, Agrigento,
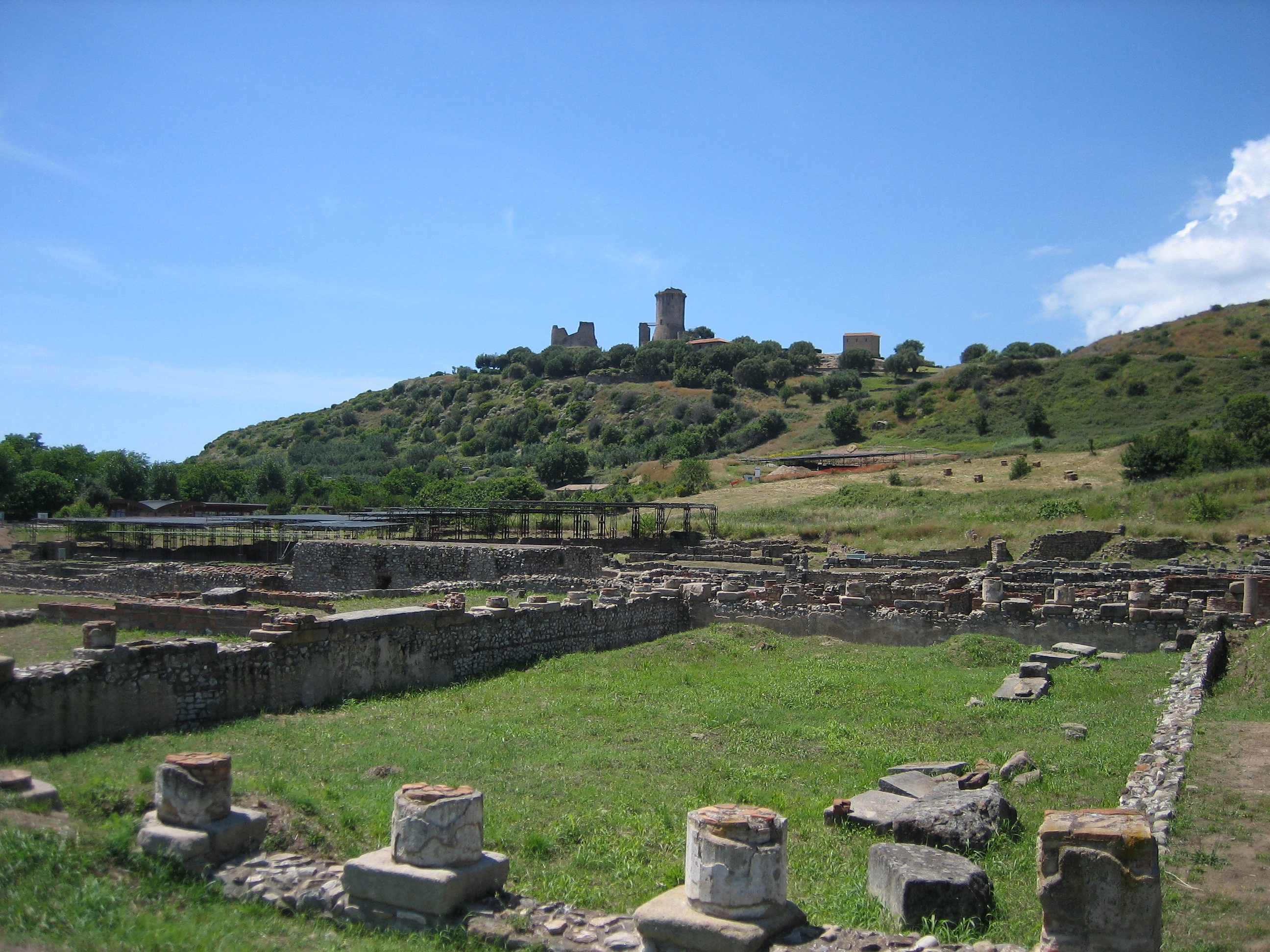 Cilento, Vallo di Diano and Alburni National Park ( Italian ''Parco Nazionale del Cilento, Vallo di Diano e Alburni'') is an Italian national park in the
Cilento, Vallo di Diano and Alburni National Park ( Italian ''Parco Nazionale del Cilento, Vallo di Diano e Alburni'') is an Italian national park in the


"Magna Graecia."
In ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography'', 1854. *A. G. Woodhead, ''The Greeks in the West'', 1962. * Günther Zuntz, ''Persephone: Three Essays on Religion and Thought in Magna Graecia,'' Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1971.
Map
'' Ancient Coins. * David Willey.
Italy rediscovers Greek heritage
'' BBC News. 21 June 2005, 17:19 GMT 18:19 UK. *
Gaze On The Sea
'' Salentine Peninsula, Greece and Greater Greece. (in Italian, Greek and English) *
Oriamu pisulina
'' Traditional Griko song performed by Ghetonia. *
Kalinifta
'' Traditional Griko song performed by amateur local group. *
Second Interdisciplinary Symposium on the Hellenic Heritage of Southern Italy
'' Archaeological Institute of America (AIA). 11 June 2015. (Dates: Monday, 30 May 2016 to Thursday, 2 June 2016.) * Sergio Tofanelli et al.
'' European Journal of Human Genetics, (15 July 2015). {{Authority control
southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
, encompassing the modern Italian regions of Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
, Apulia
Apulia ( ), also known by its Italian language, Italian name Puglia (), is a Regions of Italy, region of Italy, located in the Southern Italy, southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Strait of Ot ...
, Basilicata, Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
, and Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
. These regions were extensively settled by Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
beginning in the 8th century BC.
Initially founded by their ''metropoleis'' (mother cities), the settlements evolved into independent and powerful Greek city-states ('' poleis''). The settlers brought with them Hellenic civilization
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically rel ...
, which over time developed distinct local forms due to both their distance from Greece and the influence of the indigenous peoples of southern Italy. This interaction left a lasting imprint on Italy, including on Roman culture. The Greek settlers also influenced native groups such as the Sicels
The Sicels ( ; or ''Siculī'') were an Indo-European tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily, their namesake, during the Iron Age. They spoke the Siculian language. After the defeat of the Sicels at the Battle of Nomae in 450 BC and the death of ...
and the Oenotrians, many of whom adopted Greek culture and became Hellenized. In areas like architecture and urban planning, the colonies sometimes surpassed the achievements of the motherland. The ancient inhabitants of Magna Graecia are referred to as Italiotes and Siceliotes.
Ruins of several cities from Magna Graecia remain visible today, including Neapolis ("New City", now Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
), Syrakousai ( Syracuse), Akragas ( Agrigento), Taras ( Taranto), Rhegion (Reggio Calabria
Reggio di Calabria (; ), commonly and officially referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the List of cities in Italy, largest city in Calabria as well as the seat of the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria. As ...
), and Kroton ( Crotone). The most populous city was Sybaris (now Sibari), with an estimated population of between 300,000 and 500,000, from 600 to 510 BC.
Governments in these city-states were typically aristocratic, and the cities often engaged in warfare with one another. Their independence came to an end during the Second Punic War, when they were annexed by the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
in 205 BC.
Despite the political changes, cultural life in Magna Graecia flourished. Greek art, literature, and philosophy had a decisive influence on the region, especially in cities like Taras. South Italian Greek pottery, particularly from the 4th century BC, is a notable cultural contribution. Settlers from Magna Graecia also achieved great success in the Ancient Olympic Games
The ancient Olympic Games (, ''ta Olympia''.), or the ancient Olympics, were a series of Athletics (sport), athletic competitions among representatives of polis, city-states and one of the Panhellenic Games of ancient Greece. They were held at ...
—athletes from Crotone alone won 18 titles over 25 Olympiads.
Although most Greek inhabitants of Magna Graecia were fully Latinized during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, traces of Greek language and culture persisted. The Griko people of Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
( Bovesia) and Salento
Salento (; Salentino dialect, Salentino: ''Salentu''; Griko language, Salento Griko: ) is a Cultural area, cultural, List of historical states of Italy, historical, and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apuli ...
(Grecìa Salentina
Grecìa Salentina (Griko for "Salento, Salentine Greece") is an area in the peninsula of Salento in southern Italy, near the town of Lecce which is inhabited by the Griko people, an ethnic Greek people, Greek minority in southern Italy who spea ...
) still maintain aspects of their Greek heritage, including the Griko language. This language is the last living trace of the once-vibrant Greek presence in Magna Graecia.
Terminology

Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
(written around 150 BC), where he ascribed the term to Pythagoras and his philosophical school.
Ancient authors use "Magna Graecia" to mean different parts of southern Italy, including or excluding Sicily, Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
and Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
being the most prominent advocates of the wider definitions. Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
used the term to refer to the territory that had been conquered by the Greeks.
There are various hypotheses on the origin of the name ''Megálē Hellás''. The term could be explained by the prosperity and cultural and economic splendour of the region (6th–5th century BC); notably by the Achaeans of the city of Kroton, to refer to the network of colonies they founded or controlled between the end of the 6th and mid-5th centuries at the time of the Pythagoreans
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek co ...
.
Context
There were several reasons for the Greeks to establish overseas colonies; demographic crises (famine, overcrowding, etc.), '' stasis'', a developing need for new commercial outlets and ports, and expulsion from their homeland after wars. During the Archaic period, the Greekpopulation
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
grew beyond the capacity of the limited arable land of Greece proper, resulting in the large-scale establishment of colonies elsewhere: according to one estimate, the population of the widening area of Greek settlement increased roughly tenfold from 800 BC to 400 BC, from 800,000 to as many as -10 million. This was not simply for trade, but also to found settlements. These Greek colonies were not, as Roman colonies were, dependent on their mother-city, but were independent city-states in their own right.
History

Greek colonisation
According toStrabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
's ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (, ''Geōgraphiká''; or , "Strabo's 17 Books on Geographical Topics") or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Greek in the late 1st century BC, or early 1st cen ...
'', the colonisation of Magna Graecia had already begun by the time of the Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mytho ...
and lasted for several centuries.
Greeks began to settle in southern Italy in the 8th century BC. Their first great migratory wave was by the Euboeans aimed at the Gulf of Naples ( Pithecusae, Cumae) and the Strait of Messina ( Zancle, Rhegium). Pithecusae on the island of Ischia is considered the oldest Greek settlement in Italy, and Cumae their first colony on the mainland of Italy.
The second wave was of the Achaea
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek language, Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaḯa'', ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwest ...
ns who concentrated initially on the Ionian coast ( Metapontion, Poseidonia, Sybaris, Kroton), shortly before 720BC. At an unknown date between the 8th and 6th centuries BC the Athenians, of Ionian lineage, founded Scylletium (near today's Catanzaro).
With colonisation, Greek culture was exported to Italy with its dialects of the Ancient Greek language
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
, its religious rites, and its traditions of the independent ''polis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
''. An original Hellenic civilization
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically rel ...
soon developed, and later interacted with the native Italic civilisations. The most important cultural transplant was the Chalcidean/ Cumaean variety of the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
, which was adopted by the Etruscans; the Old Italic alphabet
The Old Italic scripts are a family of ancient writing systems used in the Italian Peninsula between about 700 and 100 BC, for various languages spoken in that time and place. The most notable member is the Etruscan alphabet, which was the i ...
subsequently evolved into the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered except several letters splitting—i.e. from , and from � ...
, which became the most widely used alphabet in the world.
Secondary colonisation
Over time, due to overpopulation and other political and commercial reasons, the new cities expanded their presence in Italy by founding other Greek cities; effectively expanding the Greek civilisation to the whole territory known today as Magna Graecia. Remains of some of these Greek colonies can be seen today such as those of Neapolis ('new city', nowNaples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
), Syracusae ( Syracuse), Akragas ( Agrigento), Taras ( Taranto) and Rhegion (Reggio Calabria
Reggio di Calabria (; ), commonly and officially referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the List of cities in Italy, largest city in Calabria as well as the seat of the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria. As ...
).
An intense colonisation program was undertaken by Syracuse, at the time of the tyranny of Dionysius I of Syracuse, around 387–385 BC. This phenomenon affected the entire Adriatic coast, and in particular led to the foundation in Italy of Ancon (now Ancona
Ancona (, also ; ) is a city and a seaport in the Marche region of central Italy, with a population of around 101,997 . Ancona is the capital of the province of Ancona, homonymous province and of the region. The city is located northeast of Ro ...
) and Adria
Adria is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Rovigo in the Veneto region of northern Italy, situated between the mouths of the rivers Adige and Po River, Po. The remains of the Etruria, Etruscan city of Atria or Hatria are to be found below ...
; in the Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
n coast he saw the foundation of Issa (current Vis), Pharus ( Stari Grad), Dimus ( Hvar); Lissus (now Lezhë) was founded on the Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
n coast. Issa in turn then founded Tragurium (now Trogir), Corcyra Melaina (now Korčula) and Epetium (now Stobreč, a suburb of Split).
Rhegium (now Reggio Calabria
Reggio di Calabria (; ), commonly and officially referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the List of cities in Italy, largest city in Calabria as well as the seat of the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria. As ...
) founded Pyxus ( Policastro Bussentino) in Lucania; Locri founded Medma ( Rosarno), Polyxena and Hipponium ( Vibo Valentia) in present-day Calabria; Sybaris (now Sibari) revitalised the indigenous centres of Laüs and Scydrus in Calabria and founded Poseidonia (Paestum
Paestum ( , , ) was a major Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea, in Magna Graecia. The ruins of Paestum are famous for their three ancient Greek temples in the Doric order dating from about 550 to 450 BCE that ...
), in Campania; Kroton (now Crotone) founded Terina and participated in the foundation of Caulonia (near Monasterace marina) in Calabria; Messana (now Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
), in collaboration with Rhegium, founded Metaurus ( Gioia Tauro); Taras together with Thurii founded Heracleia ( Policoro) in Lucania in 434 BC, and also Callipolis ('beautiful city').
Expansion and conflict
At the beginning of the 6th century BC, all the main cities of Magna Graecia on the Ionian Sea had achieved a high economic and cultural development, which shifted their interests towards expansion of their territory by waging war on neighbouring cities. The 6th century was therefore characterised by great clashes between the colonies. Some of the clashes that established the new balance and the new relationships of force were the Battle of the Sagra river (the clash between Locri Epizefiri and Kroton), the destruction of Siris (by Sybaris and Metapontum), and the clash between Kroton and Sybaris (which ended with the destruction of the latter). As with all the events of this period precise dates are unknown, but the destruction of Sybaris may have occurred around 510 BC, while the two other clashes are placed around 580-560 BC, with the destruction of Siris before the Battle of the Sagra.Roman Era
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
was Neàpolis in 327BC.
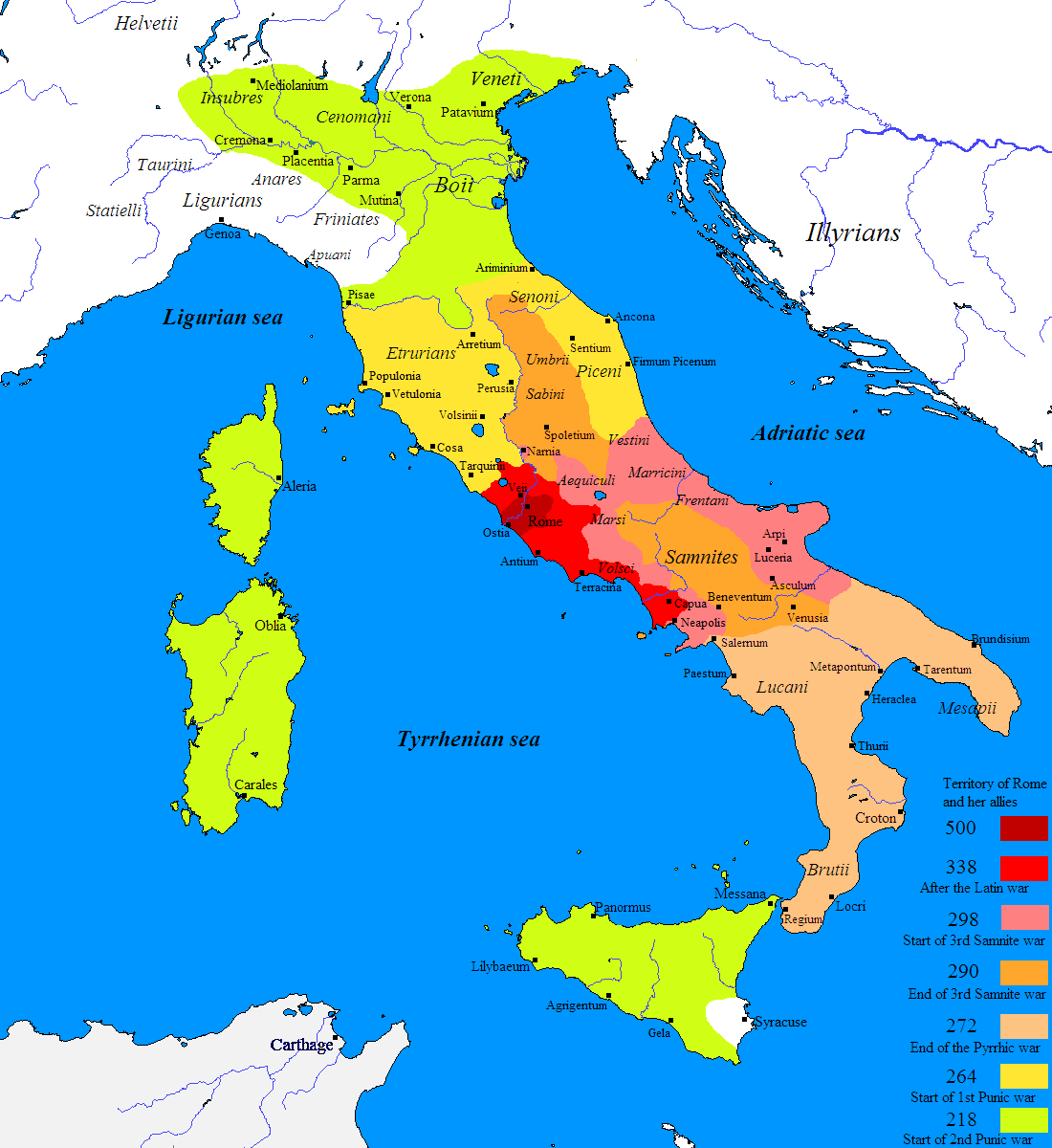
At the beginning of the 3rd century, Rome was a great power but had not yet entered into conflict with most of Magna Graecia, which had been allies of the Samnites. However, the needs of the Roman populace determined their need for territorial expansion towards the south. As the Greek cities of southern Italy came under threat from the Bruttii and Lucanians from the end of the 4th century BC, they asked for help from Rome, which exploited this opportunity by sending military garrisons in the 280s BC.
Following Rome's victory over Taras after the Pyrrhic War in 272BC, most of the cities of southern Italy were linked to Rome with pacts and treaties (''foedera'') which sanctioned a sort of indirect control.
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
was conquered by Rome during the First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
. Only Syracuse remained independent until 212 because its king Hiero II was a devoted ally of the Romans. His grandson Hieronymus however allied with Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
, which prompted the Romans to besiege the city, which fell in 212BC.
After the second Punic War, Rome pursued an unprecedented program of reorganisation in the rest of Magna Graecia, where many of the cities were annexed to the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
in 205BC, as a consequence of their defection to Hannibal. Roman colonies (''civium romanorum'') were the main element of the new territorial control plan starting from the '' lex Atinia'' of 197BC. In 194BC, garrisons of 300 Roman veterans were implanted in Volturnum, Liternum, Puteoli, Salernum and Buxentum, and to Sipontum on the Adriatic. This model was replicated in the territory of the Brettii; 194BC saw the foundation of the Roman colonies of Kroton and Tempsa, followed by the Latin colonies of Copia (193BC) and Valentia (192BC).
The social, linguistic and administrative changes arising from the Roman conquest only took root in this region by the 1st century AD, while Greek culture remained strong and was actively cultivated as shown by epigraphic evidence.
Middle Ages
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, following the disastrous Gothic War, new waves of Byzantine Christian Greeks fleeing the Slavic invasion of Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
settled in Calabria, further strengthened the Hellenic element in the region. The iconoclast emperor Leo III appropriated lands that had been granted to the Papacy in southern Italy and the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire continued to govern the area in the form of the Catapanate of Italy (965 -1071) through the Middle Ages, well after northern Italy fell to the Lombards.
At the time of the Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
' late medieval conquest of southern Italy and Sicily (in the late 12th century), the Salento
Salento (; Salentino dialect, Salentino: ''Salentu''; Griko language, Salento Griko: ) is a Cultural area, cultural, List of historical states of Italy, historical, and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apuli ...
peninsula (the "heel" of Italy), up to one-third of Sicily (concentrated in the Val Demone), and much of Calabria and Lucania were still largely Greek-speaking. Some regions of southern Italy experienced demographic shifts as Greeks began to migrate northwards in significant numbers from regions further south; one such region was Cilento
Cilento () is an Italian mountain range (part of the Lucan Apennines), which gives its name to a geographical region of Campania in the central and southern part of the province of Salerno. Is an important tourist area of southern Italy.
...
, which came to have a Greek-speaking majority. At this time the language had evolved into medieval Greek, also known as Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic; Greek: ) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the F ...
, and its speakers were known as Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Medieval Greek, Greek-speaking Eastern Romans throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia ...
. The resultant fusion of local Byzantine Greek culture with Norman and Arab culture (from the Arab occupation of Sicily) gave rise to Norman-Arab-Byzantine culture in Sicily.
Greek temples
Greek temples (, semantically distinct from Latin language, Latin , "temple") were structures built to house deity statues within Greek sanctuaries in ancient Greek religion. The temple interiors did not serve as meeting places, since the Ancien ...
of Paestum
Paestum ( , , ) was a major Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea, in Magna Graecia. The ruins of Paestum are famous for their three ancient Greek temples in the Doric order dating from about 550 to 450 BCE that ...
, Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
File:Reggio calabria museo nazionale mosaico da kaulon.jpg, Mosaic from Caulonia, Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
, National Museum of Magna Graecia
File:Tavole-palatine - Hera temple.jpg, Temple of Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; ; in Ionic Greek, Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Oly ...
in Metaponto, Basilicata
File:Agrigent BW 2012-10-07 12-24-45.JPG, The Temple "D", Valle dei Templi, Agrigento, Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
File:Milo of Croton Dumont Louvre MR1839.jpg, Milo of Croton
Milo or Milon of Croton () was a famous Ancient Greece, ancient Greek athlete from Crotone, Croton, which is today in the Magna Graecia region of southern Italy.
Milo was a six-time winner at the Ancient Olympic Games, Olympics, once for boys' w ...
File:Archytas of Taras.jpg, Archytas of Taras
File:Tarentum.jpg, 5th-century BC Greek coins of Taras (now Taranto) with the eponym Taras hero riding a dolphin
File:2547 - Milano - Museo archeologico - Piatto apulo - Foto di Giovanni Dall'Orto - 1 feb 2014.jpg, The goddess Nike riding on a two-horse chariot, Apulia
Apulia ( ), also known by its Italian language, Italian name Puglia (), is a Regions of Italy, region of Italy, located in the Southern Italy, southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Strait of Ot ...
n patera
In the material culture of classical antiquity, a ''patera'' () or ''phiale'' ( ) is a shallow ceramic or metal libation bowl. It often has a bulbous indentation ('' omphalos'', "belly button") in the center underside to facilitate holding it, ...
(tray), 4th century BC, Archaeological Museum of Milan
File:Head-Kantharos of a Female Faun or Io (?) LACMA 50.8.25.jpg, Head- Kantharos of a female faun or Io, red-figure pottery, 375–350 BC, Los Angeles County Museum of Art
List of Greek ''poleis''
Mainland Italy
This is a list of the 22 ''poleis'' (" city-states") in Italy, according to Mogens Herman Hansen. It does not list all the Hellenic settlements, only those organised around a ''polis'' structure.Sicily
This is a list of the 46 ''poleis'' (" city-states") in Sicily, according to Mogens Herman Hansen. It does not list all the Hellenic settlements, only those organised around a ''polis'' structure.Not part of Magna Graecia
Administration
 The administrative organisation of Magna Graecia was inherited from the Hellenic poleis, taking up the concept of " city-states" administered by the
The administrative organisation of Magna Graecia was inherited from the Hellenic poleis, taking up the concept of " city-states" administered by the aristocracy
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense Economy, economic, Politics, political, and soc ...
. The cities of Magna Graecia were independent like the Greek '' poleis'' of the motherland, and had an army and a military fleet. There were also cases of tyranny as in Syracuse, governed by the tyrant Dionysius, who fought the Carthaginians until his death.
Economy
In the cities of Magna Graecia, trade, agriculture and crafts developed. Initially oriented to the indigenous Italic populations, the trade was immediately an excellent channel of exchange with the Greeks of the motherland, even if today it is difficult to establish precisely the type of goods traded and the volume of these exchanges.Coinage
 Greek coinage of Italy and Sicily originated from local Italiotes and Siceliotes who formed numerous city-states. These
Greek coinage of Italy and Sicily originated from local Italiotes and Siceliotes who formed numerous city-states. These Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
communities descended from Greek migrants. Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
was so thoroughly Hellenized that it was known as the Magna Graecia. Each of the polities struck their own coinage.
Taras (or Tarentum) was among the most prominent city-states.
By the second century BC, some of these Greek coinages evolved under Roman rule, and can be classified as the first Roman provincial currencies.
Culture
The Greek colonists of Magna Graecia elaborated a civilization, which had peculiar characteristics, due to the distance from the motherland and the influence of the indigenous peoples of southern Italy. From the motherland Greece, art, literature and philosophy decisively influenced the life of the colonies. In Magna Graecia much impetus was given to culture, especially in some cities, such as Taras (now Taranto). Pythagoras moved to Crotone where he founded his school in 530 BC. Among others,Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; ; /524 – /455 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek Greek tragedy, tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is large ...
, Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
, Xenophanes and Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
visited Magna Graecia.
Among the illustrious characters born in Magna Graecia are the philosophers Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; ; fl. late sixth or early fifth century BC) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic ancient Greece, Greek philosopher from Velia, Elea in Magna Graecia (Southern Italy).
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Veli ...
of Elea, Zeno
Zeno may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the given name
* Zeno (surname)
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 B ...
of Elea, Gorgias of Lentini and Empedocles of Agrigento; the Pythagoreans Philolaus of Crotone, Archytas of Taranto, Lysis of Taranto, Echecrates and Timaeus of Locri; the mathematician Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenis ...
of Syracuse; the poets Theocritus
Theocritus (; , ''Theokritos''; ; born 300 BC, died after 260 BC) was a Greek poet from Sicily, Magna Graecia, and the creator of Ancient Greek pastoral poetry.
Life
Little is known of Theocritus beyond what can be inferred from his writings ...
of Syracuse, Stesichorus
Stesichorus (; , ''Stēsichoros''; c. 630 – 555 BC) was a Greek Greek lyric, lyric poet native of Metauros (Gioia Tauro today). He is best known for telling epic stories in lyric metres, and for some ancient traditions about his life, such as hi ...
, Ibycus
Ibycus (; ; ) was an Greek lyric, Ancient Greek lyric poet, a citizen of Rhegium in Magna Graecia, probably active at Samos during the reign of the tyrant Polycrates and numbered by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria in the canon (fiction), ca ...
of Reggio Calabria, Nossis of Locri, Alexis of Thuri and Leonidas of Taranto; the doctors Alcmeon of Crotone and Democedes of Crotone; the sculptor from Reggio Clearchus; the painter Zeuxis, the musicologist Aristoxenus of Taranto and the legislator Zaleucus
Zaleucus (; fl. 7th century BC) was the Ancient Greece, Greek lawgiver of Epizephyrian Locris, in Magna Graecia. According to the Suda, he was previously a slave and a shepherd, and after having been educated he gave laws to his fellow-citizens. ...
of Locri.
Language
A remnant of Greek influence can be found in the survival of the Greek language in some villages of the above-mentioned Salento peninsula (the "heel" of Italy). This living dialect of Greek, known locally as Griko, is found in the Italian regions ofCalabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
and Apulia
Apulia ( ), also known by its Italian language, Italian name Puglia (), is a Regions of Italy, region of Italy, located in the Southern Italy, southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Strait of Ot ...
. ''Griko'' is considered by linguists to be a descendant of Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic; Greek: ) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the F ...
, which had been the majority language of Salento through the Middle Ages, combining also some ancient Doric and local romance elements. There is a rich oral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (19 ...
and Griko folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
, limited now but once numerous, to around 30,000 people, most of them having abandoned their language in favour of Italian. Some scholars, such as Gerhard Rohlfs, argue that the origins of Griko may ultimately be traced to the colonies of Magna Graecia.
Art and architecture

Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
and Miletus
Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and ex ...
, was a checkerboard road network.
In Magna Graecia painting and sculpture also reached a notable level of quality. In Magna Graecia there were examples of excellence in sculpture, coroplastics and bronzes. As for vase painting, many famous Athenian potters moved to Magna Graecia creating works influenced by the culture of the place, making their paintings peculiar and different from those of the motherland, giving rise to the South Italian ancient Greek pottery. Also noteworthy are the mosaics, the goldsmith's art and wall painting.
Noteworthy sculptures from Magna Graecia are the Apollo of Gaza, the Apollo of Piombino, the Dancing Satyr of Mazara del Vallo, the Head of a Philosopher and the '' Riace bronzes'', while notable vases from Magna Graecia are the Darius Vase and the Nestor's Cup. Noteworthy temples of Magna Graecia are the Temple of Concordia, Agrigento, the Temple of Hera Lacinia, the Temple of Heracles, Agrigento, The Temple of Juno in Agrigento, the Temple of Olympian Zeus, Agrigento, the Temple of Apollo (Syracuse), the Temple of Athena (Syracuse), the Temple of Athena (Paestum), the Temple C (Selinus), the Temple E (Selinus), the Temple F (Selinus), the Temple of Juno Lacinia (Crotone), the Second Temple of Hera (Paestum), the Heraion at Foce del Sele, the Temple of Poseidon (Taranto), the Tavole Palatine and the Temple of Victory (Himera).
Theatre
Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
and Apulia
Apulia ( ), also known by its Italian language, Italian name Puglia (), is a Regions of Italy, region of Italy, located in the Southern Italy, southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Strait of Ot ...
, also brought theatrical art from their motherland. The Greek Theatre of Syracuse, the , the , the , the , the , the and the most famous Greek Theater of Taormina, amply demonstrate this.
Only fragments of original dramaturgical works are left, but the tragedies of the three great giants Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; ; /524 – /455 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek Greek tragedy, tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is large ...
, Sophocles
Sophocles ( 497/496 – winter 406/405 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. was an ancient Greek tragedian known as one of three from whom at least two plays have survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or contemporary with, those ...
and Euripides
Euripides () was a Greek tragedy, tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to ...
and the comedies of Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Ancient Greek comedy, comic playwright from Classical Athens, Athens. He wrote in total forty plays, of which eleven survive virtually complete today. The majority of his surviving play ...
are known.
Some famous playwrights in the Greek language came directly from Magna Graecia. Others, such as Aeschylus and Epicharmus, worked for a long time in Sicily. Epicharmus can be considered Syracusan in all respects, having worked all his life with the tyrants of Syracuse. His comedy preceded that of the more famous Aristophanes by staging the gods for the first time in comedy. While Aeschylus, after a long stay in the Sicilian colonies, died in Sicily in the colony of Gela in 456 BC. Epicarmus and Phormis, both of 6th century BC, are the basis, for Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, of the invention of the Greek comedy, as he says in his book on '' Poetics'':
Other native dramatic authors of Magna Graecia, in addition to the Syracusan Phormis mentioned, are Achaeus of Syracuse, Apollodorus of Gela, Philemon of Syracuse and his son Philemon the younger. From Calabria, precisely from the colony of Thurii, came the playwright Alexis. While Rhinthon, although Sicilian from Syracuse, worked almost exclusively for the colony of Taranto.
Sport
 The colonies sent athletes of all disciplines to the
The colonies sent athletes of all disciplines to the Ancient Olympic Games
The ancient Olympic Games (, ''ta Olympia''.), or the ancient Olympics, were a series of Athletics (sport), athletic competitions among representatives of polis, city-states and one of the Panhellenic Games of ancient Greece. They were held at ...
which were periodically held at Olympia and Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
in Greece.
The colonists of Magna Graecia were very fond of the Hellenic games where they could prove to the Greeks that they belonged to the same place of origin, their physical strength and skills in the games were also played by their ancestors dozens of generations earlier. And for this reason the greatest sovereigns demanded that teams be trained to be sent to Greece.
Sport was therefore a channel of communication with the Hellenic peninsula, a means by which the colonies of Magna Graecia showed themselves to the rest of the Hellenic world. The settlers of Magna Graecia had great success in sporting competitions in their homeland. Crotone's athletes won 18 titles in 25 Olympics.
Essential timeline

 * 8th century BC: the first historical colony of Magna Graecia was that of Pithekoussai (current island of Ischia) founded in the 8th century BC by settlers from
* 8th century BC: the first historical colony of Magna Graecia was that of Pithekoussai (current island of Ischia) founded in the 8th century BC by settlers from Chalcis
Chalcis (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: , ), also called Chalkida or Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief city of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from ...
and Eretria in Euboea. Probably, the island settlement of Pithekoussai was only a commercial establishment where the Greeks dealt with other peoples, especially with the Phoenician merchants, even if the issue is controversial.
* 720 BC: the first Greek colony in mainland Italy, Kyme, is founded.
* 7th–6th century BC: maximum splendor of Sibari.
* 6th century BC: maximum splendor of Crotone.
* 6th–3rd century BC: minting of coins by the cities of Magna Graecia.
* 6th–5th century BC: maximum splendour of Magna Graecia due to the Pythagorean reforms and institutions.
* 510 BC: Sibari was defeated by Crotone whose troops were commanded by the famous athlete Milo of Croton
Milo or Milon of Croton () was a famous Ancient Greece, ancient Greek athlete from Crotone, Croton, which is today in the Magna Graecia region of southern Italy.
Milo was a six-time winner at the Ancient Olympic Games, Olympics, once for boys' w ...
. The city of Sibari was destroyed and its population was condemned to exile.
* 5th century BC: maximum splendor of Syracuse.
* 480 BC: Gelon, tyrant of Syracuse, defeated the troops of Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
at Himera
Himera (Greek language, Greek: ), was a large and important ancient Greece, ancient Greek city situated on the north coast of Sicily at the mouth of the river of the same name (the modern Imera Settentrionale), between Panormus (modern Palermo) ...
, in the north of Sicily.
* 474 BC: The fleet led by Hiero I, tyrant of Syracuse, assisted Kyme threatened by the Etruscans. This victory marked the end of the Etruscan extension in Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
.
* 459–454 BC: after an internal civil war in Crotone, the cities of Magna Graecia once linked to it, dissolve the bond of subjection.
* 444–443 BC: foundation of Thourioi. An Athenian expedition, officially Panhellenic because it was made up of Greeks from the islands of the Aegean Sea, founded the city of Thourioi. In reality, the cities of the Aegean Sea were part of the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
, a military league under the rule of Athens. The city of Thourioi hosted important people such as Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
, Protagoras, Hippodamus of Miletus and Lysias
Lysias (; ; c. 445 – c. 380 BC) was a Logographer (legal), logographer (speech writer) in ancient Greece. He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian Canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrac ...
.
* 415–413 BC: The Sicilian Expedition
The Sicilian Expedition was an Classical Athens, Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Classical Athens, Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse and Co ...
occurred. It was an Athenian
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
military expedition to Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, which took place from 415 to 413 BC, during the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, between Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
on one side and Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
, Syracuse and Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
on the other. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat for the Athenian forces, severely impacting Athens. After the first Athenian victories, which put the Syracusan army in serious difficulty, the tide of the war was turned upside-down due to the Spartan reinforcements under the command of Gylippus. The defeat of the Athenian army led to the imprisonment of its soldiers in the Syracusan latomies, where they were forced to live in hardship and suffering until their death; few were the survivors who managed to return to their homeland. The failure of the expedition marked the beginning of the military and political decline of Athens, followed by the aristocratic coup d'état of 411 BC; it also marked Athens' definitive defeat in the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
(404 BC). Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
, an Athenian historian, dedicates two books of his work ''History of the Peloponnesian War
The ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' () is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), which was fought between the Peloponnesian League (led by Sparta) and the Delian League (led by Classical Athens, Athens). The account, ...
'' to the Athenian expedition, to underline the magnitude and exceptionality of the event. Thus he began "a new work, a work on Sicily" which became the background of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC). The ''Parallel Lives
*
Culture of ancient Greece
Culture of ancient Rome
Ancient Greek biographical works
Ethics literature
History books about ancient Rome
Cultural depictions of Gaius Marius
Cultural depictions of Mark Antony
Cultural depictions of Cicero
...
'' of Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
(in particular the ''Life of Nicias'') and the ''Bibliotheca historica
''Bibliotheca historica'' (, ) is a work of Universal history (genre), universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, and describe the h ...
'' of Diodorus Siculus are other important sources on the expedition to Sicily.
* 400 BC: the cities of Magna Graecia overlooking the Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (, ; or ) , , , , is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenians, Tyrrhenian people identified with the Etruscans of Italy.
Geography
The sea is bounded by the islands of C ...
begin to fall into the hands of the Italic peoples
The concept of Italic peoples is widely used in linguistics and historiography of ancient Italy. In a strict sense, commonly used in linguistics, it refers to the Osco-Umbrian languages, Osco-Umbrians and Latino-Faliscan languages, Latino-Falisca ...
.
* 4th century BC: the cultural decline of the cities of Magna Graecia begins.
* 387 BC: Reggio is destroyed by Syracuse.
* 303 BC: peace between Taranto and Lucanians, who had attempted to conquer the city.
* 285 BC: Roman garrisons settle in Thourioi.
* 282–272 BC: Taranto was conquered by the Romans despite the intervention of Pyrrhus ( Pyrrhic War in Italy).
* 264–241 BC: First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
, Rome takes control of Sicily, with the exception of Syracuse, which becomes Rome's ally.
* 215–205 BC: during the Second Punic War Syracuse and then Taranto sided with Carthage. The two cities were conquered by the Romans in 211 after a three-year siege. These events put an end to the independence of all the cities of Magna Graecia, which were annexed to the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
in 205 BC.
Modern and contemporary Italy
 Greek nobles started taking refuge in Italy following the
Greek nobles started taking refuge in Italy following the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
in 1453. Greeks immigrated once again to the region in the 16th and 17th centuries in reaction to the conquest of the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. Especially after the end of the Siege of Coron (1534), large numbers of Greeks took refuge in the areas of Calabria, Salento and Sicily. Greeks from Coroni, the so-called Coronians, were nobles, who brought with them substantial movable property.
Other Greeks who moved to Italy came from the Mani Peninsula of the Peloponnese. The Maniots (their name originating from the Greek word ''mania'') were known for their proud military traditions and for their bloody vendettas, many of which continue today. Another group of Maniot Greeks moved to Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
in the 17th century under the protection of the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
.
Although many of the Greek inhabitants of Magna Graecia were entirely Latinized during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, pockets of Greek culture and language remained and have survived to the present day. One example is the Griko people in Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
( Bovesia) and Salento
Salento (; Salentino dialect, Salentino: ''Salentu''; Griko language, Salento Griko: ) is a Cultural area, cultural, List of historical states of Italy, historical, and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apuli ...
(Grecìa Salentina
Grecìa Salentina (Griko for "Salento, Salentine Greece") is an area in the peninsula of Salento in southern Italy, near the town of Lecce which is inhabited by the Griko people, an ethnic Greek people, Greek minority in southern Italy who spea ...
), some of whom still maintain their Greek language ( Griko language) and customs. The Griko language is the last living trace of the Greek elements that once formed Magna Graecia. Their working practices have been passed down through generations through storytelling and allowing the observation of work. The Italian parliament
The Italian Parliament () is the national parliament of the Italy, Italian Republic. It is the representative body of Italian citizens and is the successor to the Parliament of the Kingdom of Sardinia (1848–1861), the Parliament of the Kingd ...
recognizes the Griko people as an ethnolinguistic minority under the official name of ''Minoranze linguistiche Grike dell'Etnia Griko-Calabrese e Salentina''.
Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
in Sicily is home to a small Greek-speaking minority, which arrived from the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
between 1533 and 1534 when fleeing the expansion of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. They were officially recognised in 2012.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites related to Magna Graecia
Valle dei Templi
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
The Valle dei Templi, or Valley of the Temples, is an archaeological site in Agrigento (ancient Greek ''Akragas''), Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
. It is one of the most outstanding examples of ancient Greek art and architecture of Magna Graecia. The term "valley" is a misnomer, the site is located on a ridge outside the town of Agrigento.
Since 1997, the entire area has been included in the UNESCO World Heritage List. The archaeological and landscape park of the Valle dei Templi, with its 1,300 hectares, is the largest archaeological park in Europe and the Mediterranean basin.
The Valley includes remains of seven temples, all in Doric style. The ascription of the names, apart from that of the '' Olympeion'', is a mere tradition established in Renaissance times. The temples are:
* Temple of Concordia, whose name comes from a Latin inscription found nearby, and which was built in the 5th century BC. Turned into a church in the 6th century AD, it is now one of the best preserved in the Valley.
* Temple of Juno, also built in the 5th century BC. It was burnt in 406 BC by the Carthaginians
The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians (and sometimes as Western Phoenicians), were a Semitic people, Semitic people who Phoenician settlement of North Africa, migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Iron ...
.
* Temple of Heracles, who was one of the most venerated deities in the ancient ''Akragas''. It is the most ancient in the Valley: destroyed by an earthquake, it consists today of only eight columns.
* Temple of Olympian Zeus, built in 480 BC to celebrate the city-state's victory over Carthage. It is characterized by the use of large-scale atlases.
*Temple of Castor and Pollux. Despite its remains including only four columns, it is now the symbol of modern Agrigento.
*Temple of Hephaestus
Hephaestus ( , ; wikt:Hephaestus#Alternative forms, eight spellings; ) is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes.Walter Burkert, ''Greek Religion'' 1985: III.2. ...
( Vulcan), also dating from the 5th century BC. It is thought to have been one of the most imposing constructions in the valley; it is now however one of the most eroded.
*Temple of Asclepius
Asclepius (; ''Asklēpiós'' ; ) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of Apollo), Coronis, or Arsinoe (Greek myth), Ars ...
, located far from the ancient town's walls; it was the goal of pilgrims seeking cures for illness.
The Valley is also home to the so-called Tomb of Theron, a large tuff monument of pyramidal shape; scholars suppose it was built to commemorate the Romans killed in the Second Punic War.
Poseidonia and Elea
 Cilento, Vallo di Diano and Alburni National Park ( Italian ''Parco Nazionale del Cilento, Vallo di Diano e Alburni'') is an Italian national park in the
Cilento, Vallo di Diano and Alburni National Park ( Italian ''Parco Nazionale del Cilento, Vallo di Diano e Alburni'') is an Italian national park in the Province of Salerno
The province of Salerno () is a province in the Campania region of Italy. It has 1,054,766 inhabitants as of 2025.
Geography
The largest towns in the province are: Salerno, the capital, which has a population of 131,950; Cava de' Tirreni, Bat ...
, in Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
in southern Italy. It includes much of the Cilento
Cilento () is an Italian mountain range (part of the Lucan Apennines), which gives its name to a geographical region of Campania in the central and southern part of the province of Salerno. Is an important tourist area of southern Italy.
...
, the Vallo di Diano and the Monti Alburni. It was founded in 1991, and was formerly known as the Parco Nazionale del Cilento e Vallo di Diano. In 1998 it became a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
of UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
, along with the ancient Greek towns of Poseidonia, Elea and the Padula Charterhouse.
Much of the most celebrated features of the Poseidonia site today are the three large temples in the Archaic version of the Greek Doric order
The Doric order is one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of t ...
, dating from about 550 to 450 BC. All are typical of the period, with massive colonnades having a very pronounced entasis (widening as they go down), and very wide capitals resembling upturned mushrooms. Above the columns, only the second Temple of Hera retains most of its entablature, the other two having only the architrave in place. These were dedicated to Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; ; in Ionic Greek, Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Oly ...
and Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretism, syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarde ...
( Juno and Minerva
Minerva (; ; ) is the Roman goddess of wisdom, justice, law, victory, and the sponsor of arts, trade, and strategy. She is also a goddess of warfare, though with a focus on strategic warfare, rather than the violence of gods such as Mars. Be ...
to the Romans), although previously they often have been identified otherwise, following eighteenth-century arguments. The two temples of Hera are right next to each other, while the Temple of Athena is on the other side of the town centre. There were other temples, both Greek and Roman, which are far less well preserved.
Remains of Elea walls, with traces of one gate and several towers, of a total length of over three miles, still exist, and belong to three different periods, in all of which the crystalline limestone of the locality is used. Bricks were also employed in later times; their form is peculiar to this place, each having two rectangular channels on one side, and being about 1.5 inches square, with a thickness of nearly 4 inches They all bear Greek brick-stamps. There are some remains of cisterns on the site, and, various other traces of buildings.
Syracuse
Syracuse was founded in 733 BC by Greek settlers fromCorinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
and Tenea, led by the '' oecist'' (colonizer) Archias. There are many attested variants of the name of the city including ''Syrakousai'', ''Syrakosai'' and ''Syrakō''. In the modern day, the city is listed by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
as a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
along with the Necropolis of Pantalica.
The buildings of Syracuse from the Greek period are:
* The city walls
* The Temple of Apollo, at Piazza Emanuele Pancali, adapted to a church in Byzantine times and to a mosque under Arab rule.
* The Fountain of Arethusa, on Ortygia island. According to a legend, the nymph
A nymph (; ; sometimes spelled nymphe) is a minor female nature deity in ancient Greek folklore. Distinct from other Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature; they are typically tied to a specific place, land ...
Arethusa, hunted by Alpheus, was turned into a spring by Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later tim ...
and appeared here.
* The Greek Theatre of Syracuse, whose cavea is one of the largest ever built by the ancient Greeks: it has 67 rows, divided into nine sections with eight aisles. Only traces of the scene and the orchestra remain. The edifice (still used today) was modified by the Romans, who adapted it to their different style of spectacles, including circus games. Near the theatre are the ''latomìe'', stone quarries, also used as prisons in ancient times. The most famous ''latomìa'' is the '' Orecchio di Dionisio'' ("Ear of Dionysius").
* The Tomb of Archimede, in the Grotticelli Necropolis. Decorated with two Doric columns.
* The Temple of Olympian Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, about outside the city, built around the 6th century BC.
Archaeological sites related to Magna Graecia
Apulia
* Rudiae * SipontoBasilicata
* Heraclea Lucania * Metapontum * Tavole PalatineCalabria
* Caulonia * Krimisa * Laüs * Skylletion * Sybaris * Terina * Thurii * Timpone della MottaCampania
* Cumae * Elea * Heraion at Foce del Sele * PoseidoniaSicily
* Abacaenum * Adranon * Aetna * Akrai * Akrillai * Apollonia * Casmenae * Eryx * Halaesa * Helorus * Heraclea Minoa * Herbessos *Himera
Himera (Greek language, Greek: ), was a large and important ancient Greece, ancient Greek city situated on the north coast of Sicily at the mouth of the river of the same name (the modern Imera Settentrionale), between Panormus (modern Palermo) ...
* Hybla Gereatis
* Maktorion
* Megara Hyblaea
* Monte Adranone
* Morgantina
* Motya
* Naxos
Naxos (; , ) is a Greek island belonging to the Cyclades island group. It is the largest island in the group. It was an important centre during the Bronze Age Cycladic Culture and in the Ancient Greek Archaic Period. The island is famous as ...
* Segesta
* Selinunte
* Tindari
* Valle dei Templi
See also
Notes
References
Sources
* Polyxeni Adam-Veleni and Dimitra Tsangari (editors), ''Greek colonisation: New data, current approaches; Proceedings of the scientific meeting held in Thessaloniki (6 February 2015),'' Athens, Alpha Bank, 2015. * *Michael J. Bennett, Aaron J. Paul, Mario Iozzo, & Bruce M. White, ''Magna Graecia: Greek Art From South Italy and Sicily,'' Cleveland, OH, Cleveland Museum of Art, 2002. * John Boardman, N. G. L. Hammond (editors), ''The'' ''Cambridge Ancient History, vol. III, part 3, The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries B.C.'', Cambridge University Press, 1982. * *Giovanni Casadio & Patricia A. Johnston, ''Mystic Cults in Magna Graecia,'' Austin, University of Texas Press, 2009. *Lucia Cerchiai, Lorenna Jannelli, & Fausto Longo (editors), ''The Greek cities of Magna Graecia and Sicily,'' Photography by Mark E. Smith, Los Angeles, J. Paul Getty Museum, 2004. *Giovanna Ceserani, ''Italy's Lost Greece: Magna Graecia and the Making of Modern Archaeology,'' New York, Oxford University Press, 2012. *T. J. Dunbabin, ''The Western Greeks'', 1948. *M. Gualtieri, ''Fourth Century B.C. Magna Graecia: A Case Study,'' Jonsered, Sweden, P. Åströms, 1993. * Mogens Herman Hansen & Thomas Heine Nielsen, ''An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis'', Oxford University Press, 2004. * R. Ross Holloway, ''Art and Coinage in Magna Graecia,'' Bellinzona, Edizioni arte e moneta, 1978. *Margaret Ellen Mayo, ''The Art of South Italy: Vases From Magna Graecia,'' Richmond, Virginia Museum of Fine Arts, 1982. *Giovanni Pugliese Carratelli, ''The Greek World: Art and Civilization in Magna Graecia and Sicily,'' New York: Rizzoli, 1996. *———— (editor), ''The Western Greeks: Catalog of an exhibition held in the Palazzo Grassi, Venice, March–Dec., 1996,'' Milan, Bompiani, 1976. * William Smith"Magna Graecia."
In ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography'', 1854. *A. G. Woodhead, ''The Greeks in the West'', 1962. * Günther Zuntz, ''Persephone: Three Essays on Religion and Thought in Magna Graecia,'' Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1971.
External links
* * *Map
'' Ancient Coins. * David Willey.
Italy rediscovers Greek heritage
'' BBC News. 21 June 2005, 17:19 GMT 18:19 UK. *
Gaze On The Sea
'' Salentine Peninsula, Greece and Greater Greece. (in Italian, Greek and English) *
Oriamu pisulina
'' Traditional Griko song performed by Ghetonia. *
Kalinifta
'' Traditional Griko song performed by amateur local group. *
Second Interdisciplinary Symposium on the Hellenic Heritage of Southern Italy
'' Archaeological Institute of America (AIA). 11 June 2015. (Dates: Monday, 30 May 2016 to Thursday, 2 June 2016.) * Sergio Tofanelli et al.
'' European Journal of Human Genetics, (15 July 2015). {{Authority control