Madeira on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an
 The Madeira archipelago is located from the African coast, from the closest point in the European coast (the Portuguese town of Sagres, in
The Madeira archipelago is located from the African coast, from the closest point in the European coast (the Portuguese town of Sagres, in
File:Madeira2024OSM.png, Comprehensive map of Madeira's main island.
File:PortoSanto2024OSM.png, Comprehensive map of Madeira's outlying island of Porto Santo.
File:IlhasDesertas2024OSM.png, Map of the ''Ilhas Desertas''.
File:IlhasSelvagens2024OMC.png, Map of the ''Ilhas Selvagens''.
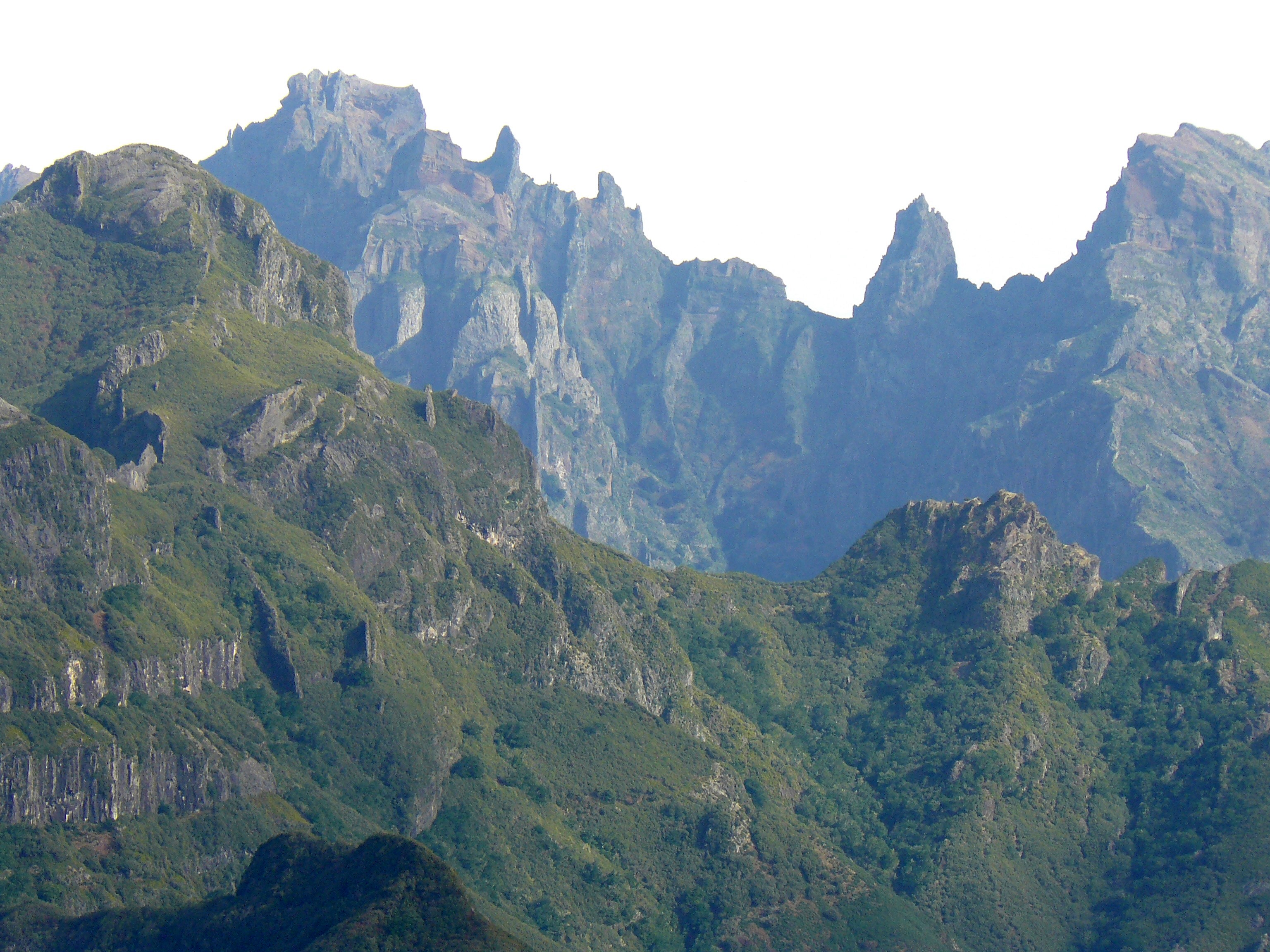 The ten tallest peaks in Madeira exemplify the island's diverse topography.
The ten tallest peaks in Madeira exemplify the island's diverse topography.
 Madeira island is at the top of a massive
Madeira island is at the top of a massive
 Madeira is an
Madeira is an
of the
 Administratively, Madeira is divided into fifty four
Administratively, Madeira is divided into fifty four 
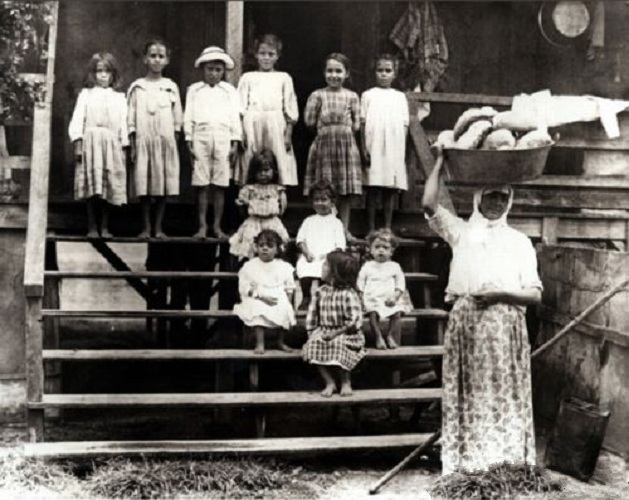 In the 1846 famine, over 6,000 inhabitants migrated to
In the 1846 famine, over 6,000 inhabitants migrated to

 The Madeira International Business Center (MIBC)
The Madeira International Business Center (MIBC)

 Because of the geographic situation of Madeira in the Atlantic Ocean, the island has an abundance of fish of various kinds. The species that are consumed the most are espada ( black scabbardfish), blue fin tuna,
Because of the geographic situation of Madeira in the Atlantic Ocean, the island has an abundance of fish of various kinds. The species that are consumed the most are espada ( black scabbardfish), blue fin tuna,

 Madeira wine is a
Madeira wine is a
''World History Encyclopedia'' – The Portuguese Colonization of Madeira
. *
Madeira's Government Website
. * {{Authority control 1420s establishments in the Portuguese Empire 1976 disestablishments in the Portuguese Empire 1976 establishments in Portugal Autonomous Regions of Portugal Integral overseas territories Islands of Macaronesia Outermost regions of the European Union Populated places established in the 1420s States and territories established in 1976 Volcanoes of Portugal Wine regions of Portugal Islands of Africa NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union
autonomous region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, zone, entity, unit, region, subdivision, province, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or territory, internal territory of a sovereign state that has ...
of Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
. It is an archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
situated in the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
, in the region of Macaronesia
Macaronesia (; ) is a collection of four volcanic archipelagos in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of North Africa and Europe. Each archipelago is made up of a number of list of islands in the Atlantic Oc ...
, just under north of the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, west of the Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and southwest of mainland Portugal. Madeira sits on the African Tectonic Plate, but is culturally, politically and ethnically associated with Europe, with its population predominantly descended from Portuguese settlers. Its population was 251,060 in 2021. The capital of Madeira is Funchal
Funchal () officially Funchal City (), is the capital, largest city and a Municipality (Portugal), municipality in Portugal's Madeira, Autonomous Region of Madeira, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean. The city has a population of 105,795, making it ...
, on the main island's south coast.
The archipelago includes the islands of Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ...
, Porto Santo, and the Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands
The Savage Islands or Selvagens Islands ( ; also known as the Salvage Islands) are a small Portugal, Portuguese archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean, south of Madeira and north of the Canary Islands.30,000), white-faced storm-petrel (>80,0 ...
. Roughly half of the population lives in Funchal. The region has political and administrative autonomy through the Administrative Political Statute of the Autonomous Region of Madeira provided for in the Portuguese Constitution. The region is an integral part of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
as an outermost region
The special territories of members of the European Economic Area (EEA) are the 32 special territories of Member state of the European Union, EU member states and European Free Trade Association, EFTA member states which, for historical, geograph ...
. Madeira generally has a mild/moderate subtropical climate with mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
summer droughts and winter rain. Many microclimates are found at different elevations.
Madeira, uninhabited at the time, was claimed by Portuguese sailors in the service of Prince Henry the Navigator
Princy Henry of Portugal, Duke of Viseu ( Portuguese: ''Infante Dom Henrique''; 4 March 1394 – 13 November 1460), better known as Prince Henry the Navigator (), was a Portuguese prince and a central figure in the early days of the Portuguese ...
in 1419 and settled after 1420. The archipelago is the first territorial discovery of the exploratory period of the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
.
Madeira is a year-round resort, particularly for Portuguese, but also British (148,000 visits in 2021), and Germans (113,000). It is by far the most populous and densely populated Portuguese island. The region is noted for its Madeira wine, flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
, and fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
, with its pre-historic laurel forest
Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and el ...
, classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. The destination is certified by EarthCheck. The main harbour in Funchal has long been the leading Portuguese port in cruise ship dockings, an important stopover for Atlantic passenger cruises between Europe, the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
and North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
. In addition, the International Business Centre of Madeira, also known as the Madeira Free Trade Zone, was established in the 1980s. It includes (mainly tax-related) incentives.
History
Ancient
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
in his ''Parallel Lives
*
Culture of ancient Greece
Culture of ancient Rome
Ancient Greek biographical works
Ethics literature
History books about ancient Rome
Cultural depictions of Gaius Marius
Cultural depictions of Mark Antony
Cultural depictions of Cicero
...
'' (''Sertorius'', 75 AD) referring to the military commander Quintus Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius ( – 73 or 72 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian Peninsula. Defying the regime of Sulla, Sertorius became the independent ruler of Hispania for m ...
(d. 72 BC), relates that after his return to Cádiz
Cádiz ( , , ) is a city in Spain and the capital of the Province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is located in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula off the Atlantic Ocean separated fr ...
, he met sailors who spoke of idyllic Atlantic islands: "The islands are said to be two in number separated by a very narrow strait and lie from Africa. They are called the Isles of the Blessed."
Archaeological evidence suggests that the islands may have been visited by the Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
s sometime between 900 and 1030.
Accounts by Muhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abdullah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani as-Sabti, or simply al-Idrisi (; ; 1100–1165), was an Arab Muslim geographer and cartographer who served in the court of King Roger II at Palermo, Sicily. Muhammad al-Idrisi was born in C ...
state that the Mugharrarin ("the adventurers" – seafarers from Lisbon) came across an island where they found "a huge quantity of sheep, the meat of which was bitter and inedible" before going to the more inhabited Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
. This island, possibly Madeira or Hierro, must have been inhabited or previously visited by people for livestock to be present.
Legend
During the reign of KingEdward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
, lovers Robert Machim and Anna d'Arfet were said to have fled from England to France in 1346. Driven off course by a violent storm, their ship ran aground along the coast of an island that may have been Madeira. Later, this legend was the basis of the naming of the city of Machico on the island, in memory of the young lovers.
European exploration
Madeira appears in several medieval manuscripts, including the '' Book of Knowledge of All Kingdoms'' from the early 14th century, the Medici-Laurentian Atlas from 1351, the ''Soleri Portolani'' from 1380 and 1385 and Corbitis Atlas from the late 14th century. These texts refer to Madeira as ''Lecmane'', ''Lolegname,'' ''Legnami'' (the isle of wood), ''Puerto'' or Porto Santo, ''deserte'' or deserta, and ''desierta''. It is widely accepted that knowledge of these Atlantic islands existed before their better-documented discovery and successful settlement by theKingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal was a Portuguese monarchy, monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also known as the Kingdom of Portugal a ...
.
In 1418, two captains, João Gonçalves Zarco
João Gonçalves Zarco ( 1390 – 21 November 1471) was a Portuguese explorer who established settlements and recognition of the Madeira, Madeira Islands, and was appointed first captain of Funchal by Henry the Navigator.
Life
Zarco was born in ...
and Tristão Vaz Teixeira, while exploring the African coast in the service of Prince Henry the Navigator
Princy Henry of Portugal, Duke of Viseu ( Portuguese: ''Infante Dom Henrique''; 4 March 1394 – 13 November 1460), better known as Prince Henry the Navigator (), was a Portuguese prince and a central figure in the early days of the Portuguese ...
, were driven off course by a storm to an island which they named (English: "holy harbour") in gratitude for divine deliverance from a shipwreck.
The following year, Zarco and Vaz organised an expedition with Bartolomeu Perestrello. The trio travelled to the island of Porto Santo, claimed it on behalf of the Portuguese Crown, and established a settlement. The new settlers observed "a heavy black cloud suspended to the southwest" and upon investigation discovered the larger island they called ().
Settlement
The first Portuguese settlers began colonizing the islands around 1420 or 1425. The three governors, knights of the Order of Christ and navigators: João Gonçalves Zarco, Tristão Vaz Teixeira and Bartolomeu Perestrelo, along with their respective families, became the first settlers of the archipelago divided by three captaincies (respectively and Funchal, Machico and Porto Santo). This colonization process began in 1425, by order of King João I, with people of modest means, some former prisoners of the Kingdom and a group of people from the lower nobility, including fishermen and peasant farmers who willingly left Portugal for a new life on the islands, a better one, they hoped, than was possible in a Portugal which had been ravaged by theBlack Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
, and where the best farmlands were strictly controlled by the nobility.
Initially, the settlers produced wheat for their own sustenance but later began to export wheat to mainland Portugal. In earlier times, fish and vegetables were the settlers' main means of subsistence.
Grain production began to fall and the ensuing crisis forced Henry the Navigator
Princy Henry of Portugal, Duke of Viseu ( Portuguese: ''Infante Dom Henrique''; 4 March 1394 – 13 November 1460), better known as Prince Henry the Navigator (), was a Portuguese prince and a central figure in the early days of the Portuguese ...
to order other commercial crops to be planted so that the islands could be profitable. These specialised plants, and their associated industrial technology, created one of the major revolutions on the islands and fuelled Portuguese industry. Following the introduction of the first water-driven sugar mill on Madeira, sugar production increased to over 6,000 ''arrobas'' (an ''arroba'' was equal to ) by 1455, using advisers from Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
and financed by Genoese capital (Genoa acted as an integral part of the island economy until the 17th century). The accessibility of Madeira attracted Genoese and Flemish traders, who were keen to bypass Venetian monopolies.
Sugarcane production was the primary engine of the island's economy, which quickly afforded the Funchal metropolis economic prosperity. The production of sugar cane attracted adventurers and merchants from all parts of Europe, especially Italians
Italians (, ) are a European peoples, European ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common Italian culture, culture, History of Italy, history, Cultural heritage, ancestry and Italian language, language. ...
, Basques
The Basques ( or ; ; ; ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a Basque culture, common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous peoples, ...
, Catalans
Catalans ( Catalan, French and Occitan: ''catalans''; ; ; or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to Catalonia, who speak Catalan. The current official category of "Catalans" is that of the citizens of Catalonia, a nationality and autono ...
, and Flemish. This meant that, in the second half of the fifteenth century, the city of Funchal became a mandatory port of call for European trade routes.
Slaves were used during the island's period of sugar trade to cultivate sugar cane alongside paid workers, though slave owners were only a small minority of the Madeiran population, and those who did own slaves owned only a few. Slaves consisted of Guanches
The Guanche were the Indigenous peoples, indigenous inhabitants of the Spain, Spanish Canary Islands, located in the Atlantic Ocean some to the west of modern Morocco and the North African coast. The islanders spoke the Guanche language, which i ...
from the nearby Canary Islands. Barbary corsairs
The Barbary corsairs, Barbary pirates, Ottoman corsairs, or naval mujahideen (in Muslim sources) were mainly Muslim corsairs and privateers who operated from the largely independent Barbary states. This area was known in Europe as the Barba ...
from North Africa, who enslaved Europeans from ships and coastal communities throughout the Mediterranean region, captured 1,200 people in Porto Santo in 1617.
Until the first half of the sixteenth century, Madeira was one of the major sugar markets of the Atlantic. Apparently, it is in Madeira that, in the context of sugar production, slave labour was applied for the first time. The colonial system of sugar production was put into practice on the island of Madeira, on a much smaller scale, and later transferred, on a large scale, to other overseas production areas.
Sugar mills were gradually abandoned, with few remaining, which gave way to other markets in Madeira.
In the 17th century, as Portuguese sugar production was shifted to Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe and elsewhere, Madeira's most important commodity product became its wine. Sugar plantations were replaced by vineyards, originating in the so-called ‘Wine Culture’, which acquired international fame and provided the rise of a new social class, the Bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) are a class of business owners, merchants and wealthy people, in general, which emerged in the Late Middle Ages, originally as a "middle class" between the peasantry and aristocracy. They are traditionally contrasted wi ...
.
With the increase of commercial treaties with England, important English merchants settled on the Island and, ultimately, controlled the increasingly important island wine trade. The English traders settled in the Funchal as of the seventeenth century, consolidating the markets from North America, the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
and England itself. The Madeira wine became very popular in the markets and it is also said to have been used in a toast during the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another state or failed state, or are breaka ...
by the Founding Fathers of the United States
The Founding Fathers of the United States, often simply referred to as the Founding Fathers or the Founders, were a group of late-18th-century American Revolution, American revolutionary leaders who United Colonies, united the Thirteen Colon ...
.
As a result of a high demand for the season, there was a need to prepare guides for visitors. The first tourist guide of Madeira appeared in 1850 and focused on elements of history, geology, flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
, fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
and customs of the island. Regarding hotel infrastructures, the British and the Germans were the first to launch the Madeiran hotel chain. The historic Belmond Reid's Palace opened in 1891 as the "Reid's New Hotel" and is still open to this day.
The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
first amicably occupied the island in 1801 whereafter Colonel William Henry Clinton became governor. A detachment of the 85th Regiment of Foot under Lieutenant-colonel James Willoughby Gordon garrisoned the island.
After the Peace of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France, the Spanish Empire, and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it set t ...
, British troops withdrew in 1802, only to reoccupy Madeira in 1807 until the end of the Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1808–1814) was fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French ...
in 1814. In 1846 James Julius Wood wrote a series of seven sketches of the island. In 1856, British troops recovering from cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
, and widows and orphans of soldiers fallen in the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
, were stationed in Funchal, Madeira.
World War I
During theGreat War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
on 3 December 1916, a German U-boat, , captained by Max Valentiner, entered Funchal
Funchal () officially Funchal City (), is the capital, largest city and a Municipality (Portugal), municipality in Portugal's Madeira, Autonomous Region of Madeira, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean. The city has a population of 105,795, making it ...
harbour on Madeira. ''U-38'' torpedoed and sank three ships, bringing the war to Portugal by extension. The ships sunk were:
* CS ''Dacia'' (), a British cable-laying vessel. ''Dacia'' had previously undertaken war work off the coast of Casablanca
Casablanca (, ) is the largest city in Morocco and the country's economic and business centre. Located on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Chaouia (Morocco), Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a populatio ...
and Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 mill ...
. It was in the process of diverting the German South American cable into Brest, France.
* SS ''Kanguroo'' (), a French specialized "heavy-lift" transport.
* ''Surprise'' (), a French gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.
History Pre-steam ...
. Her commander and 34 crewmen (including 7 Portuguese) were killed.
After attacking the ships, ''U-38'' bombarded Funchal for two hours from a range of about . Batteries on Madeira returned fire and eventually forced ''U-38'' to withdraw.
On 12 December 1917, two German U-boats, ''SM U-156
SM ''U-156'' was a German Empire, German Type U 151 submarine, Type U 151 U-boat commissioned in 1917 for the Imperial German Navy. From 1917 until her disappearance in September 1918 she was part of the U-Kreuzer Flotilla, and was responsible f ...
'' and '' SM U-157'' (captained by Max Valentiner), again bombarded Funchal. This time the attack lasted around 30 minutes. The U-boats fired 40 shells. There were three fatalities and 17 wounded; a number of houses and Santa Clara church were hit.
The last Austrian Emperor, Charles I, was exiled to Madeira after the war. Determined to prevent an attempt to restore Charles to the throne, the Council of Allied Powers agreed he could go into exile on Madeira because it was isolated in the Atlantic and easily guarded. He died there on 1 April 1922 and his coffin lies in a chapel of the Church of Our Lady of Monte.
Geography
 The Madeira archipelago is located from the African coast, from the closest point in the European coast (the Portuguese town of Sagres, in
The Madeira archipelago is located from the African coast, from the closest point in the European coast (the Portuguese town of Sagres, in Algarve
The Algarve (, , ) is the southernmost NUTS statistical regions of Portugal, NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities (concelho, ''concelhos'' or ''município ...
) and from the capital of Portugal, Lisbon
Lisbon ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 567,131, as of 2023, within its administrative limits and 3,028,000 within the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, metropolis, as of 2025. Lisbon is mainlan ...
(approximately a one-and-a-half-hour flight). Madeira inhabits the extreme south of the Tore-Madeira Ridge, a bathymetric structure oriented along a north-northeast to south-southwest axis that extends for . This structure consists of long geomorphological relief that extends from the abyssal plain to ; its highest submersed point reaches a depth of about (around latitude 36°N). The origins of the Tore-Madeira Ridge are not clearly established, but may have resulted from a buckling of the lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
.
Islands and islets
*Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ...
(), including Ilhéu de Agostinho, Ilhéu de São Lourenço, Ilhéu Mole (northwest); Total population: 262,456 (2011 Census).
* Porto Santo (), including Ilhéu de Baixo ou da Cal, Ilhéu de Ferro, Ilhéu das Cenouras, Ilhéu de Fora, Ilhéu de Cima; Total population: 5,483 (2011 Census).
* Desertas Islands (), including the three uninhabited islands: Deserta Grande Island, Bugio Island
Bugio Island () — is one of the three islands of the Portuguese Desertas Islands archipelago, a small chain of islands in the Madeira, Madeira Islands Archipelago of Macaronesia.
It is located in the Atlantic Ocean off the western coast of Nor ...
and Ilhéu de Chão.
* Savage Islands
The Savage Islands or Selvagens Islands ( ; also known as the Salvage Islands) are a small Portugal, Portuguese archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean, south of Madeira and north of the Canary Islands.30,000), white-faced storm-petrel (>80,0 ...
(), archipelago 280 km south-southeast of Madeira Island including three main uninhabited islands and 16 islets in two groups: the Northeast Group ( Selvagem Grande Island, Ilhéu de Palheiro da Terra, Ilhéu de Palheiro do Mar) and the Southwest Group (Selvagem Pequena Island
Selvagem Pequena Island () is an island in the southeast group of the Savage Islands, Madeira, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the ...
, Ilhéu Grande, Ilhéu Sul, Ilhéu Pequeno, Ilhéu Fora, Ilhéu Alto, Ilhéu Comprido, Ilhéu Redondo, Ilhéu Norte).
Peaks
 The ten tallest peaks in Madeira exemplify the island's diverse topography.
The ten tallest peaks in Madeira exemplify the island's diverse topography. Pico Ruivo
Pico Ruivo () is the highest peak on Madeira Island and the third highest in Portugal, standing at in the Santana municipality. Accessible only by foot, it can be reached from either Pico do Areeiro or via a shorter, easier trail from Achada ...
is the highest at 1,862 metres. Madeira's mountaintops offer panoramic vistas of rugged terrain and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, attracting hikers and nature enthusiasts seeking stunning views and challenging trails.
Madeira Island
shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more viscous lava ...
that rises about from the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, on the Tore underwater mountain range. The volcano formed atop an east–west rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben ...
in the oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramaf ...
along the African Plate, beginning during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
epoch (5 million years ago), continuing into the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
(700,000 years ago). This was followed by extensive erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
, producing two large amphitheatres opening southward in the central part of the island. Volcanic activity later resumed, producing scoria cone
A cinder cone or scoria cone is a steep, conical landform of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic ash, clinkers, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or l ...
s and lava flow
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
s atop the eroded shield. The most recent volcanic eruptions were on the west-central part of the island 6,500 years ago, creating more cinder cone
A cinder cone or scoria cone is a steep, volcanic cone, conical landform of loose pyroclastic rock, pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic ash, clinkers, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are forme ...
s and lava flows.
It is the largest island of the group with an area of , a length of (from Ponte de São Lourenço to Ponta do Pargo). It is approximately at its widest point (from Ponta da Cruz to Ponta de São Jorge), with a coastline of . It has a mountain ridge that extends along the centre of the island, reaching at its highest point (Pico Ruivo
Pico Ruivo () is the highest peak on Madeira Island and the third highest in Portugal, standing at in the Santana municipality. Accessible only by foot, it can be reached from either Pico do Areeiro or via a shorter, easier trail from Achada ...
), staying below 200 metres along its eastern extent. The primitive volcanic foci responsible for the central mountainous area, consisted of the peaks: Ruivo (1,862 m), Torres (1,851 m), Arieiro (1,818 m), Cidrão (1,802 m), Cedro (1,759 m), Casado (1,725 m), Grande (1,657 m), Ferreiro (1,582 m). At the end of this eruptive phase, reefs encircled the island, its marine vestiges evident in a calcareous layer in the area of Lameiros, in São Vicente. Sea cliffs, such as Cabo Girão
Cabo Girão () is a lofty sea cliff located along the southern coast of the island of Madeira, in the Portuguese archipelago of Madeira, geographically part of Africa. Cabo Girão is a tourist lookout point, with up to 1800 visitors a day. The lo ...
, valleys and ravines extend from this central spine, leaving the interior generally inaccessible. Daily life is concentrated in the many villages at the mouths of the ravines, through which the heavy autumn and winter rains travel to the sea.
Climate
Madeira has many different bioclimates. Based on differences in sun exposure, humidity, and annual mean temperature, clear variations distinguish north- and south-facing regions, as well as some islands. The islands are strongly influenced by theGulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolin ...
and Canary Current
The Canary Current is a wind-driven surface current that is part of the North Atlantic Gyre. This eastern boundary current branches south from the North Atlantic Current and flows southwest about as far as Senegal where it turns west and later jo ...
, giving it mild to warm year-round temperatures. According to the Instituto de Meteorologia (IPMA), the average annual temperature at Funchal weather station is for the 1981–2010 period. Relief
Relief is a sculpture, sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''wikt:relief, relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give ...
is a determinant factor on precipitation levels; areas such as the Madeira Natural Park can get as much as of precipitation a year. Madeira hosts lush laurel forests, while Porto Santo, a much flatter island, has a semiarid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of se ...
(''BSh''). In most winters snowfall occurs in the mountains.
Biodiversity
Endemic plant and animal species
In the south, little is left of the indigenous subtropical rainforest that once covered the island (the original settlers set fires to clear the land for farming) and named it (''madeira'' means "wood" in Portuguese). However, in the north, the valleys harbor native trees. These '' laurissilva''forests
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological functio ...
, notably those on the northern slopes, are designated as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. Madeira's paleobotanical record reveals that ''laurissilva'' forest has existed for at least 1.8 million years. Critically endangered species such as the vine '' Jasminum azoricum'' and the rowan '' Sorbus maderensis'' are endemic. The Madeiran large white butterfly
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossi ...
was an endemic subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
of the large white that inhabited the ''laurissilva'' forests but has not been seen since 1977.
Madeiran wall lizard
Madeiran wolf spider
'' Hogna ingens'', the Deserta Grande wolf spider, is endemic to the Madeira archipelago, specifically Deserta Grande Island. It is critically endangered. It is considered the largest member of itsfamily
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
. Restoration efforts are underway.
Birds
Three species of birds are endemic to Madeira: the Trocaz pigeon, the Madeira Chaffinch and the Madeira firecrest. In addition extinct species include the Madeiran scops owl, two rail species, ''Rallus adolfocaesaris'' and ''R. lowei'', and twoquail
Quail is a collective name for several genera of mid-sized birds generally placed in the order Galliformes. The collective noun for a group of quail is a flock, covey, or bevy.
Old World quail are placed in the family Phasianidae, and New ...
species, ''Coturnix lignorum'' and ''C. alabrevis'', and the Madeiran wood pigeon, a subspecies of the common wood pigeon and which was last seen in the early 20th century.
A Great Auk
The great auk (''Pinguinus impennis''), also known as the penguin or garefowl, is an Extinction, extinct species of flightless bird, flightless auk, alcid that first appeared around 400,000 years ago and Bird extinction, became extinct in the ...
bone is known from the Selvagens, suggesting this seabird visited at least sporadically.
Mice
Madeira is home to six species of brown mice, believed to be descendants of common European brown mice brought to the island byVikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
in the 9th century (or conceivably by 15th century Portuguese settlers), but diversified to the point where they cannot interbreed with their ancestral species or with one another. They have essentially the same genes, but rearranged to give different chromosome numbers: the ancestral species has 40 chromosomes, whereas the Madeira species have from 22 to 30. The deep valleys of Madeira are separated by high ground, and the different species of mice do not encounter each other.
''Levadas''
Politics
Political autonomy
Due to its distinct geography, economy, social and cultural situation, as well as the historical autonomic aspirations of the population, the Autonomous Regions of Madeira was established in 1976. Although it is a politico-administrative autonomous region, the Portuguese constitution specifies both a regional and national connection, obliging their administrations to maintain democratic principles and promote regional interests, while reinforcing national unity. As defined by the Portuguese constitution and other laws, Madeira possesses its own political and administrativestatute
A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wil ...
and has its own government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
. The branches of Government are the Regional Government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such a ...
and the Legislative Assembly, the latter elected by universal suffrage
Universal suffrage or universal franchise ensures the right to vote for as many people bound by a government's laws as possible, as supported by the " one person, one vote" principle. For many, the term universal suffrage assumes the exclusion ...
, using the D'Hondt method
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is an apportionment method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in proportional representation among political parties. It belongs to ...
of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions (Political party, political parties) amon ...
.
The president of the Regional Government is appointed by the Representative of the Republic according to the results of the election to the legislative assemblies.
The sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
of the Portuguese Republic is represented in Madeira by the Representative of the Republic, appointed by the President of the Republic on the advice of the Government of the Republic. The tasks of the Representative of the Republic are to sign and order the publication of regional legislative decrees and regional regulatory decrees or to exercise the right of veto over regional laws, should these laws be unconstitutional. Before the sixth amendment to the Portuguese Constitution passed in 2006, this responsibility was held by a more-powerful Minister of the Republic, who was proposed by the Government and appointed by the President.
Status within the European Union
 Madeira is an
Madeira is an Outermost Region
The special territories of members of the European Economic Area (EEA) are the 32 special territories of Member state of the European Union, EU member states and European Free Trade Association, EFTA member states which, for historical, geograph ...
(OMR) of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, meaning that due to its geographical situation, it is entitled to derogation
Derogation is a legal term of art, which allows for part or all of a provision in a legal measure to be applied differently, or not at all, in certain cases. European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working ConditionsDerogation publi ...
from some EU policies.
According to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union
The Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU) is one of two treaties forming the constitutional basis of the European Union (EU), the other being the Treaty on European Union (TEU). It was previously known as the Treaty Establish ...
, both primary and secondary European Union law
European Union law is a system of Supranational union, supranational Law, laws operating within the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). It has grown over time since the 1952 founding of the European Coal and Steel Community, to promote ...
applies to Madeira, with possible derogations to take account of its "structural social and economic situation (...) which is compounded by their remoteness, insularity, small size, difficult topography and climate, economic dependence on a few products, the permanence and combination of which severely restrain their development".Article 349of the
Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union
The Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU) is one of two treaties forming the constitutional basis of the European Union (EU), the other being the Treaty on European Union (TEU). It was previously known as the Treaty Establish ...
. An example of such derogation is seen in the approval of the International Business Centre of Madeira and other state aid policies to help the rum industry.
It forms part of the European Union customs area, the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
and the European Union Value Added Tax Area.
Foreign relations and defence
Foreign affairs and defence are the responsibility of the national government. The Madeira Military Zone is thePortuguese Army
The Portuguese Army () is the land component of the Portuguese Armed Forces, Armed Forces of Portugal and is also its largest branch. It is charged with the defence of Portugal, in co-operation with other branches of the Armed Forces. With its ...
's command for ground forces stationed in the islands, centering on the 3rd Garrison Regiment based at Funchal. The Navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
tasks the patrol vessels ''Tejo'' and ''Mondego'' specifically to Madeira, as well as other vessels as required, in order to patrol Portugal's large economic zone. To support search and rescue, the Portuguese Air Force
The Portuguese Air Force () is the air force, aerial warfare force of Portugal. Locally it is referred to by the acronym FAP but internationally is often referred to by the acronym PRTAF. It is the youngest of the three branches of the Portuguese ...
maintains a staging base on Porto Santo Island
Porto Santo Island () is a Portuguese island and municipality northeast of Madeira Island in the North Atlantic Ocean; it is the northernmost and easternmost island of the archipelago of Madeira, located in the Atlantic Ocean west of Europe a ...
incorporating detachments of C-295 aircraft and Merlin
The Multi-Element Radio Linked Interferometer Network (MERLIN) is an interferometer array of radio telescopes spread across England. The array is run from Jodrell Bank Observatory in Cheshire by the University of Manchester on behalf of UK Re ...
helicopters.
Administrative divisions
 Administratively, Madeira is divided into fifty four
Administratively, Madeira is divided into fifty four parishes
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or ...
and eleven municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
:

Funchal
Sister Jurisdictions
Madeira Island has the following sister jurisdictions: :Aosta Valley
The Aosta Valley ( ; ; ; or ), officially the Autonomous Region of Aosta Valley, is a mountainous Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region in northwestern Italy. It is bordered by Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, Fr ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
(1987)
: Jersey
Jersey ( ; ), officially the Bailiwick of Jersey, is an autonomous and self-governing island territory of the British Islands. Although as a British Crown Dependency it is not a sovereign state, it has its own distinguishing civil and gov ...
(1998)
: Eastern Cape
The Eastern Cape ( ; ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa. Its capital is Bhisho, and its largest city is Gqeberha (Port Elizabeth). Due to its climate and nineteenth-century towns, it is a common location for tourists. It is also kno ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
: Jeju Province
Jeju Province (; ), officially Jeju Special Self-Governing Province (Jeju language, Jeju: ; ), is the southernmost Provinces of South Korea, province of South Korea, consisting of eight inhabited and 55 uninhabited islands, including Marado, Udo ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
(2007)
: Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
(2009)
Demographics
Diaspora
Madeirans migrated to the United States,Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
, Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, sometimes known simply as Saint Vincent or SVG, is an island country in the eastern Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies, at the south ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
and Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
. Madeiran immigrants in North America mostly clustered in New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
and mid-Atlantic states
The Mid-Atlantic is a region of the United States located in the overlap between the nation's Northeastern and Southeastern states. Traditional definitions include seven U.S. states: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virg ...
, Toronto, Northern California, and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
. The city of New Bedford
New Bedford is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. It is located on the Acushnet River in what is known as the South Coast (Massachusetts), South Coast region. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, New Bedford had a ...
is especially rich in Madeirans, hosting the Museum of Madeira Heritage. The annual Madeiran and Luso-American celebration, the Feast of the Blessed Sacrament, the world's largest celebration of Madeiran heritage, regularly draws crowds of tens of thousands to the city's Madeira Field.
 In the 1846 famine, over 6,000 inhabitants migrated to
In the 1846 famine, over 6,000 inhabitants migrated to British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies. It was located on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first known Europeans to encounter Guia ...
. In 1891 they numbered 4.3% of the population. In 1902 5,000 Portuguese people, mostly Madeirans, lived in Honolulu
Honolulu ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the county seat of the Consolidated city-county, consolidated City and County of Honol ...
, Hawaii. By 1910 this grew to 21,000.
1849 saw an emigration of Protestant religious exiles from Madeira to the United States, by way of Trinidad and elsewhere in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
. Most of them settled in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
with financial and physical aid of the American Protestant Society, headquartered in New York City. In the late 1830s physician and Presbyterian minister Reverend Robert Reid Kalley, from Scotland made a stop at Funchal, Madeira on his way to a mission in China, with his wife, so that she could recover from an illness. Kalley and his wife stayed on Madeira where he began preaching the Protestant gospel and converting islanders from Catholicism. Eventually, he was arrested and imprisoned for his religious conversion activities. Another Scottish missionary, William Hepburn Hewitson, took on Protestant ministerial activities in Madeira. By 1846, about 1,000 Protestant Madeirenses, who were discriminated against and the subjects of mob violence because of their religious conversions, chose to immigrate to Trinidad and elsewhere in the West Indies in answer a call for sugar plantation workers. The exiles did not fare well there. The tropical climate was unfamiliar and they found themselves in serious economic difficulties. By 1848, the American Protestant Society raised money and sent Rev. Manuel J. Gonsalves, a Baptist minister and a naturalized U.S. citizen from Madeira, to work with Rev. Arsénio da Silva, who had emigrated with the exiles from Madeira, to arrange to resettle those who wanted to come to the United States. Rev. da Silva died in early 1849. Later in 1849, Rev. Gonsalves was then charged with escorting the exiles from Trinidad to settle in Sangamon and Morgan counties in Illinois on land purchased with funds raised by the American Protestant Society. Accounts state that anywhere from 700 to 1,000 exiles came to the United States at this time.
Several large Madeiran communities continue around the world, including in the UK and Jersey
Jersey ( ; ), officially the Bailiwick of Jersey, is an autonomous and self-governing island territory of the British Islands. Although as a British Crown Dependency it is not a sovereign state, it has its own distinguishing civil and gov ...
. The Portuguese British community, made up mostly of Madeirans, celebrate Madeira Day.
In Venezuela the Madeiran Portuguese settled in cities such as Caracas
Caracas ( , ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas (CCS), is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern p ...
and rural areas of the interior. According to figures from the 1990s, around 70% of the Portuguese diaspora in that country was made up of Madeirans and their descendants, initially dedicated to activities such as agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, but later, due to the lack of government support, the emigrants concentrated on commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
in the large Venezuelan cities. Among the companies founded by Madeirans are the supermarkets Central Madeirense, Excelsior Gama, Supermercados Unicasa and Automercados Plaza, and many renowned bakeries. A state in Venezuela called Portuguesa was named after its large Portuguese population.
Immigration
Madeira is part of theSchengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
.
Due to its growing popularity, Madeira's population has grown, reaching 253,259 in 2022, of whom the majority are locals. But Madeira has, for many years, witnessed a rising foreign population. As of 31 December 2022, immigrants in the region totaled 11,793 people, representing an increase of 13.3% compared to 2021. “Nationals from Venezuela (19.7%), the United Kingdom (11.8%), Germany (9.4%) and Brazil (9.2%) continue to represent the main foreign communities in the region”, according to the DREM (Madeira Statistics Department).
Economy
Thegross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
(GDP) reached nearly 7 billion euros in 2023, accounting for 2.6% of Portugal's economic output. GDP per capita was of 27,370 euros or 73% of the EU27 average. The GDP per employee was 71% of the EU average.
Madeira embraced Bitcoin
Bitcoin (abbreviation: BTC; Currency symbol, sign: ₿) is the first Decentralized application, decentralized cryptocurrency. Based on a free-market ideology, bitcoin was invented in 2008 when an unknown entity published a white paper under ...
by implementing policies that exempt Bitcoin investors from paying personal income taxes in the region. Madeira Regional Government President Miguel Albuquerque confirmed the inauguration of a business hub focused solely on Bitcoin and related innovations. Speaking in a dialogue with Prince Filip Karađorđević of Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
at Bitcoin Amsterdam 2023, he framed the move as a significant step toward technological advancements and international partnerships.
Madeira International Business Center

 The Madeira International Business Center (MIBC)
The Madeira International Business Center (MIBC) free trade zone
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re- exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject t ...
has led to additional infrastructure, production shops and essential services for small and medium-sized industrial enterprises. MIBC comprises three sectors of investment: the Industrial Free Trade Zone, the International Shipping Register – MAR and International Services. Madeira's tax regime has been approved by the European Commission as legal State Aid and its deadline was extended through 2027. MIBC was created formally in the 1980s as a tool of regional economic policy. It consists of (mainly tax) incentives, granted with the objective of attracting investment into Madeira.
Favorable operational and fiscal conditions were approved by the European Commission under Article 299 of the Treaty on European Union
The Treaty on the European Union (2007) is one of the primary Treaties of the European Union, alongside the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU). The TEU forms the basis of EU law, by setting out general principles of the EU's ...
. The MIBC is integrated in the Portuguese and EU legal systems and is regulated and supervised by Portuguese and EU authorities in a transparent and stable business environment, clearly distinguished from so-called "tax havens" and "offshore jurisdictions". In 2015, the EC authorized a state aid regime for companies incorporated between 2015 and 2020 and extended the regime of tax reductions through 2027. The tax regime is outlined in Article 36°-A of the Portuguese Tax Incentives Statute. Available data demonstrates that this programme aided the local labor market, through the creation of qualified jobs and for professionals who have returned to Madeira; increased productivity; expanded business tourism from the visits of investors and their clients and suppliers, and other sectors such as real estate. Telecommunications and other services benefit from a larger client base. Companies attracted by MIBC represent over 40% of revenue in terms of corporate income tax for the Government of Madeira and nearly 3.000 jobs. Salaries there are above average in comparison with the wages paid in other sectors.
Regional government
Madeira has been a significant recipient ofEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
funding, totaling €2 billion. In 2012, it was reported that despite a population of just 250,000, the local administration owed some €6 billion. The Portuguese treasury (IGCP) assumed Madeira's debt management between 2012 and 2015. The region works with the central government on a long-term plan to reduce debt levels and commercial debt stock. Moody's
Moody's Ratings, previously and still legally known as Moody's Investors Service and often referred to as Moody's, is the bond credit rating business of Moody's Corporation, representing the company's traditional line of business and its histo ...
noted that the region made significant fiscal consolidation efforts and that its tax revenue collection has improved. Tax revenues increased by 41% between 2012 and 2016, helping the region to reduce its deficit to operating revenue ratio to 10% in 2016 from 77% in 2013.
Tourism
Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
is an important sector in the region's economy, contributing 20% to the region's GDP, providing support throughout the year for commercial, transport and other activities and constituting a significant market for local products. The share in Gross Value Added of hotels and restaurants (9%) also highlights this phenomenon. The island of Porto Santo, with its beach and its climate, is entirely devoted to tourism.
Visitors are mainly from Europe, with Portuguese, British, German and French tourists providing the main contingents (2021). The average annual occupancy rate was 60.3% in 2008, reaching its maximum in March and April, when it exceeds 70%.
The best time to visit Madeira is during spring and autumn for mild weather and fewer crowds, making it ideal for outdoor activities. Summer is perfect for beach lovers but can be crowded, while winter offers mild temperatures and fewer tourists, making it ideal for experiencing the island's waterfalls.
Whale watching
Whale watching
Whale watching is the practice of observing whales and dolphins (cetaceans) in their natural habitat. Whale watching is mostly a recreational activity (cf. birdwatching), but it can also serve scientific and/or educational purposes.Hoyt, E. ...
has become very popular in recent years. Many species of dolphins, such as common dolphin
The common dolphin (''Delphinus delphis'') is the most abundant cetacean in the world, with a global population of about six million. Despite this fact and its vernacular name, the common dolphin is not thought of as the archetypal dolphin, wit ...
, spotted dolphin, striped dolphin, bottlenose dolphin
The bottlenose dolphin is a toothed whale in the genus ''Tursiops''. They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus contains three species: the common bot ...
, short-finned pilot whale
The short-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala macrorhynchus'') is one of the two species of cetaceans in the genus ''Pilot whale, Globicephala'', which it shares with the long-finned pilot whale (''G. melas''). It is part of the oceanic dolphin ...
, and whales such as Bryde's whale
Bryde's whale ( ), or the Bryde's whale complex, putatively comprises three species of rorqual and possibly four. The "complex" means the number and classification remain unclear because of a lack of definitive information and research. The c ...
, Sei whale
The sei whale ( , ; ''Balaenoptera borealis'') is a baleen whale. It is one of ten rorqual species, and the third-largest member after the blue and fin whales. It can grow to in length and weigh as much as . Two subspecies are recognized: ...
, fin whale
The fin whale (''Balaenoptera physalus''), also known as the finback whale or common rorqual, is a species of baleen whale and the second-longest cetacean after the blue whale. The biggest individual reportedly measured in length, wi ...
, sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the Genus (biology), genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the s ...
, beaked whale
Beaked whales (systematic name Ziphiidae) are a Family (biology), family of cetaceans noted as being one of the least-known groups of mammals because of their deep-sea habitat, reclusive behavior and apparent low abundance. Only three or four of ...
s can be spotted near the coast or offshore.
Sustainable development
Electricity on Madeira is provided solely through EEM (Empresa de Electricidade da Madeira, SA, which holds a monopoly for the provision of electrical supply on the autonomous region) and consists largely of fossil fuels, but with a significant supply of seasonal hydroelectricity from the levada system, wind power and a small amount of solar. Energy production comes from conventional thermal and hydropower, as well as wind and solar energy. The Ribeira dos Soccoridoshydropower
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, ...
plant, rated at 15MW, utilises a pumped hydropower
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing.
A PSH system stores energy in the form of gravitational potent ...
reservoir to recycle mountain water during the dry summer.
Battery technologies are being tested to minimise Madeira's reliance on fossil fuel imports. Renault SA and EEM piloted the Sustainable Porto Santo—Smart Fossil Free Island project on Porto Santo to demonstrate how fossil fuels can be entirely replaced with renewable energy, using a 3.3 MWh battery. Madeira operates a 15 MW 1-hour lithium iron phosphate
Lithium iron phosphate or lithium ferro-phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosp ...
battery with black start capability.
In the first half of 2022, 33% of the electricity consumed on the Portuguese archipelago of Madeira was sourced from renewable energy, a milestone achieved through a collaborative initiative co-funded by the European Union (EU).
Central to this accomplishment are the centuries-old stone pipes known as levadas, spanning thousands of kilometers and dating back to the fifteenth century. These levadas efficiently transport rainwater from northern regions to the south, serving various purposes such as human consumption, agriculture, and electricity production.
The Socorridos hydroelectric power station, fueled by water conveyed through the levadas, stands as the island's principal hydraulic system, providing power consistently throughout the year. A significant aspect of the EU-funded multi-million euro project involved enhancing water storage capacity, including the construction of a 5.4-kilometer tunnel and additional mountain tunnels, presenting formidable engineering challenges.
Wind power complements the system, facilitating the movement of stored water uphill during peak demand periods. The treated water serves dual purposes—human consumption and agriculture—while also functioning as a renewable energy source. Nuno Jorge Pereira, Water Production Director for Wood, Water, and Waste (ARM), elucidates the strategic use of water volumes to adapt to energy production levels.
This €34.7 million project, with €17.3 million co-financed by the European Cohesion Policy, not only mitigates concerns about drought but also earned acclaim as one of the best EU co-funded projects in the EGIOSTAR Awards.
The optimized Socorridos plant has notably alleviated water-related challenges for local farmers.
Transport
The islands have two airports, Cristiano Ronaldo International Airport and Porto Santo Airport, on the islands of Madeira and Porto Santo respectively. From Cristiano Ronaldo International Airport the most frequent flights are toLisbon
Lisbon ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 567,131, as of 2023, within its administrative limits and 3,028,000 within the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, metropolis, as of 2025. Lisbon is mainlan ...
. There are also direct flights to over 30 other airports in Europe and nearby islands.
Transport between the two main islands is by plane, or ferries from the Porto Santo Line, the latter also carrying vehicles. Visiting the interior of the islands is now easy thanks to construction of the ''Vias Rápidas'', major roads that cross the island. Modern roads reach all points of interest on the islands.
Funchal has an extensive public transportation system. Bus companies, including Horários do Funchal, which has been operating for over a hundred years, have regularly scheduled routes to all points of interest on the island.
Culture
Music

Folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
music in Madeira is widespread and mainly uses local musical instruments such as the machete
A machete (; ) is a broad blade used either as an agricultural implement similar to an axe, or in combat like a long-bladed knife. The blade is typically long and usually under thick. In the Spanish language, the word is possibly a dimin ...
, rajão
The rajão () is a 5-stringed instrument from Madeira, Portugal. The instrument traces back to the country's Music of Portugal, regional folk music, where it is used in folklore dances of Portugal in addition to other stringed instruments from ...
, brinquinho and cavaquinho, which are used in traditional folkloric dances like the .
Emigrants from Madeira also influenced the creation of new musical instruments. In the 1880s, the ukulele
The ukulele ( ; ); also called a uke (informally), is a member of the lute (ancient guitar) family of instruments. The ukulele is of Portuguese origin and was popularized in Hawaii. The tone and volume of the instrument vary with size and con ...
was created, based on two small guitar-like instruments of Madeiran origin, the cavaquinho and the rajão
The rajão () is a 5-stringed instrument from Madeira, Portugal. The instrument traces back to the country's Music of Portugal, regional folk music, where it is used in folklore dances of Portugal in addition to other stringed instruments from ...
. The ukulele was introduced to the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands () are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the Hawaii (island), island of Hawaii in the south to nort ...
by Portuguese immigrants from Madeira and Cape Verde. Three immigrants in particular, Madeiran cabinet makers Manuel Nunes, José do Espírito Santo, and Augusto Dias, are generally credited as the first ukulele makers. Two weeks after they disembarked from the '' SS Ravenscrag'' in late August 1879, the ''Hawaiian Gazette'' reported that "Madeira Islanders recently arrived here, have been delighting the people with nightly street concerts." The Madeiran band NAPA represented Portugal in the 2025 Eurovision Song Contest with the song Deslocado.
Cuisine
 Because of the geographic situation of Madeira in the Atlantic Ocean, the island has an abundance of fish of various kinds. The species that are consumed the most are espada ( black scabbardfish), blue fin tuna,
Because of the geographic situation of Madeira in the Atlantic Ocean, the island has an abundance of fish of various kinds. The species that are consumed the most are espada ( black scabbardfish), blue fin tuna, swordfish
The swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as the broadbill in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are the sole member of the Family (biology), family Xiphiidae. They ...
, white marlin
The white marlin (''Tetrapterus albida/Kajikia albida''), also known as Atlantic white marlin, marlin, skilligalee, is a species of billfish that lives in the epipelagic zone of the tropical and subtropical Atlantic Ocean. They are found between t ...
, blue marlin, albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Scombriformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct ...
, bigeye tuna
The bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus'') is a species of true tuna of the genus ''Thunnus'', belonging to the wider mackerel family (biology), family Scombridae. In Hawaiian language, Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ahi, the other being t ...
, wahoo
The wahoo (''Acanthocybium solandri'') is a scombrid fish found worldwide in tropical and subtropical seas. In Hawaii, the wahoo is known as ono. The species is sometimes called hoo in the United States. It is best known to sports fishermen, a ...
, spearfish
Spearfish may refer to:
Places
* Spearfish, South Dakota, United States
* North Spearfish, South Dakota, United States
* Spearfish Formation, a geologic formation in the United States
Biology
* ''Tetrapturus'', a genus of marlin with shorter ...
, skipjack tuna
The skipjack tuna (''Katsuwonus pelamis'') is a perciform fish in the tuna family, Scombridae, and is the only member of the genus ''Katsuwonus''. It is also known as katsuo, arctic bonito, mushmouth, oceanic bonito, striped tuna or victor fish. ...
and many others are found in the local dishes as they are found along the coast of Madeira. Espada is usually fried in a batter and accompanied by fried banana ( Espada com banana) and sometimes a passionfruit sauce. Bacalhau
() is the Portuguese word for cod and—in a culinary context— dried and salted cod. Fresh (unsalted) cod is referred to as ' (fresh cod).
Portuguese and other cuisines
dishes are common in Portugal, and also in former Portuguese colonie ...
is also popular, as it is in Mainland Portugal.
There are many different meat dishes on Madeira, one of the most popular being espetada. Espetada is traditionally made of large chunks of beef rubbed in garlic, salt and bay leaf and marinated for 4 to 6 hours in Madeira wine, red wine vinegar and olive oil then skewered onto a bay laurel
''Laurus nobilis'' is an aromatic evergreen tree or large shrub with green, glabrous (smooth) leaves. It is in the flowering plant family Lauraceae. According to Flora Cretica (Kleinsteuber Books, 2024, ISBN 978-3-9818110-5-6) the stem can be 1 ...
stick and left to grill over smouldering wood chips. These are so integral a part of traditional eating habits that a special iron stand is available with a T-shaped end, each branch of the "T" having a slot in the middle to hold a brochette (espeto in Portuguese); a small plate is then placed underneath to collect the juices. The brochettes are very long and have a V-shaped blade in order to pierce the meat more easily. It is usually accompanied with the local bread called bolo do caco. A traditional holiday dish is "Carne de Vinho e Alhos", which is most closely associated with the pig slaughter that was held a few weeks before Christmas. A big event, traditionally it was attended by everyone in the village. The dish is made of pork which marinates for three days in white wine, vinegar, salt, and pepper and is then cooked with small potatoes, sliced carrots, and turnip. Another common meat dish is “Picado" – cubed beef cooked in a mushroom sauce and accompanied by fries.
Other popular dishes in Madeira include açorda, feijoada and carne de vinha d'alhos.
Traditional pastries in Madeira usually contain local ingredients, one of the most common being ''mel de cana'', literally "sugarcane honey" (molasses
Molasses () is a viscous byproduct, principally obtained from the refining of sugarcane or sugar beet juice into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, the method of extraction, and the age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is usuall ...
). The traditional cake of Madeira is called '' Bolo de Mel'', which translates as (Sugarcane) "Honey Cake" and according to custom, is never cut with a knife, but broken into pieces by hand. It is a rich and heavy cake. The cake commonly known as " Madeira cake" in England is named after Madeira wine.
Malasadas are a local confection which are mainly consumed during the Carnival of Madeira. Pastéis de nata, as in the rest of Portugal, are also very popular.
Milho frito is a popular dish in Madeira that is similar to the Italian dish polenta
Polenta (, ) is an Italian cuisine, Italian dish of boiled cornmeal that was historically made from other grains. It may be allowed to cool and solidify into a loaf that can be baked, fried or Grilling, grilled.
The variety of cereal used is ...
fritta. Açorda Madeirense is another popular local dish.
Madeira is known for the high quality of its cherimoya
The cherimoya (''Annona cherimola''), also spelled chirimoya and called chirimuya by the Quechua people, is a species of edible fruit-bearing plant in the genus ''Annona'', from the family Annonaceae, which includes the closely related sweetsop ...
fruits. The Annona Festival is traditional and held annually in the parish of Faial. This event encourages the consumption of this fruit and its derivatives, such as liqueurs, puddings, ice cream and smoothies.
Beverages
 Madeira wine is a
Madeira wine is a fortified wine
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Command ...
produced in the Madeira Islands; varieties may be sweet or dry. It has a history dating back to the Age of Exploration
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
when Madeira was a standard port of call for ships heading to the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
or East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies) is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The ''Indies'' broadly referred to various lands in Eastern world, the East or the Eastern Hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainl ...
. To prevent the wine from spoiling, neutral grape spirit
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
s were added. However, wine producers of Madeira discovered, when an unsold shipment of wine returned to the islands after a round trip, that the flavour of the wine had been transformed by exposure to heat and movement. Today, Madeira is noted for its unique winemaking process that involves heating the wine and deliberately exposing the wine to some levels of oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
.T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' pg 340–341 Dorling Kindersley 2005 Most countries limit the use of the term ''Madeira'' to those wines that come from the Madeira Islands, to which the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
grants Protected designation of origin
The protected designation of origin (PDO) is a type of geographical indication of the European Union aimed at preserving the designations of origin of food-related products. The designation was created in 1992 and its main purpose is to designat ...
(PDO) status.
A local beer called Coral is produced by the Madeira Brewery, which dates from 1872. It has achieved 2 Monde Selection
Monde Selection is an annual non-competitive award open to food, drinks, and cosmetics products, created in 1961. It is run by the commercial company, International Institute for Quality Selections, Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brusse ...
Grand Gold Medals, 24 Monde Selection Gold Medals and 2 Monde Selection Silver Medals. Other alcoholic drinks are also popular in Madeira, such as the locally created Poncha
Poncha is a traditional alcoholic drink from the island of Madeira, made with aguardente de cana (distilled alcohol made from sugar cane juice), honey, sugar, and either orange juice or lemon juice. Some varieties include other fruit juices.
I ...
, Niquita, Pé de Cabra, and Aniz, as well as Portuguese drinks such as Macieira Brandy, Licor Beirão.
Laranjada is a type of carbonated soft drink with an orange flavour, its name being derived from the Portuguese word ''laranja'' ("orange"). Launched in 1872 it was the first soft drink to be produced in Portugal, and remains very popular to the present day. Brisa drinks, a brand name, are also very popular and come in a range of flavours.
Sport
Football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
is the most popular sport in Madeira and the island was indeed the first place in Portugal to host a match, organised by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
residents in 1875. The island is the birthplace of international star Cristiano Ronaldo
Cristiano Ronaldo dos Santos Aveiro (; born 5 February 1985) is a Portuguese professional Association football, footballer who plays as a Forward (association football), forward for and Captain (association football), captains both Saudi Pr ...
and is home to two prominent teams, C.S. Marítimo and C.D. Nacional, the latter of which he played youth football for before leaving to join Sporting CP
Sporting Clube de Portugal (), otherwise referred to as Sporting CP or simply Sporting (particularly within Portugal), or as Sporting Lisbon in other countries,
.
As well as football, the island is also home to professional sports teams in basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
( CAB Madeira) and handball
Handball (also known as team handball, European handball, Olympic handball or indoor handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of thr ...
( Madeira Andebol SAD, who were runners up in the 2019 European Challenge Cup). Madeira was also the host of the 2003 World Handball Championship.
The Rally Vinho da Madeira is a rally race held annually since 1959, considered one of the biggest sporting events on the island It was part of the European Rally Championship
The European Rally Championship (officially FIA European Rally Championship) is an rallying, automobile rally competition held annually on the European continent and organized by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA).
The champion ...
from 1979 to 2012 and the Intercontinental Rally Challenge
The Intercontinental Rally Challenge was an Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile, FIA-sanctioned rallying series organised by SRW Events and Eurosport, Eurosport Events, and aimed to "give new opportunities to young or amateur rally drivers ...
from 2006 to 2010.
Other popular sporting activities include golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various Golf club, clubs to hit a Golf ball, ball into a series of holes on a golf course, course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standa ...
at one of the island's two courses (plus one on Porto Santo), surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suita ...
, scuba diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub ...
, and hiking
A hike is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century. Long hikes as part of a religious pilgrimage have existed for a much longer time.
"Hi ...
.
Postage stamps
Portugal has issued postage stamps for Madeira during several periods, beginning in 1868.See also
* " Have Some Madeira M'Dear" * Geology of Madeira * List of birds of Madeira * Madeira Islands Open, an annual European Tour golf tournament * Surfing in Madeira *Islands ofMacaronesia
Macaronesia (; ) is a collection of four volcanic archipelagos in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of North Africa and Europe. Each archipelago is made up of a number of list of islands in the Atlantic Oc ...
**Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
** Cabo Verde
**Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
References
Bibliography
* * * *External links
''World History Encyclopedia'' – The Portuguese Colonization of Madeira
. *
Madeira's Government Website
. * {{Authority control 1420s establishments in the Portuguese Empire 1976 disestablishments in the Portuguese Empire 1976 establishments in Portugal Autonomous Regions of Portugal Integral overseas territories Islands of Macaronesia Outermost regions of the European Union Populated places established in the 1420s States and territories established in 1976 Volcanoes of Portugal Wine regions of Portugal Islands of Africa NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union