|
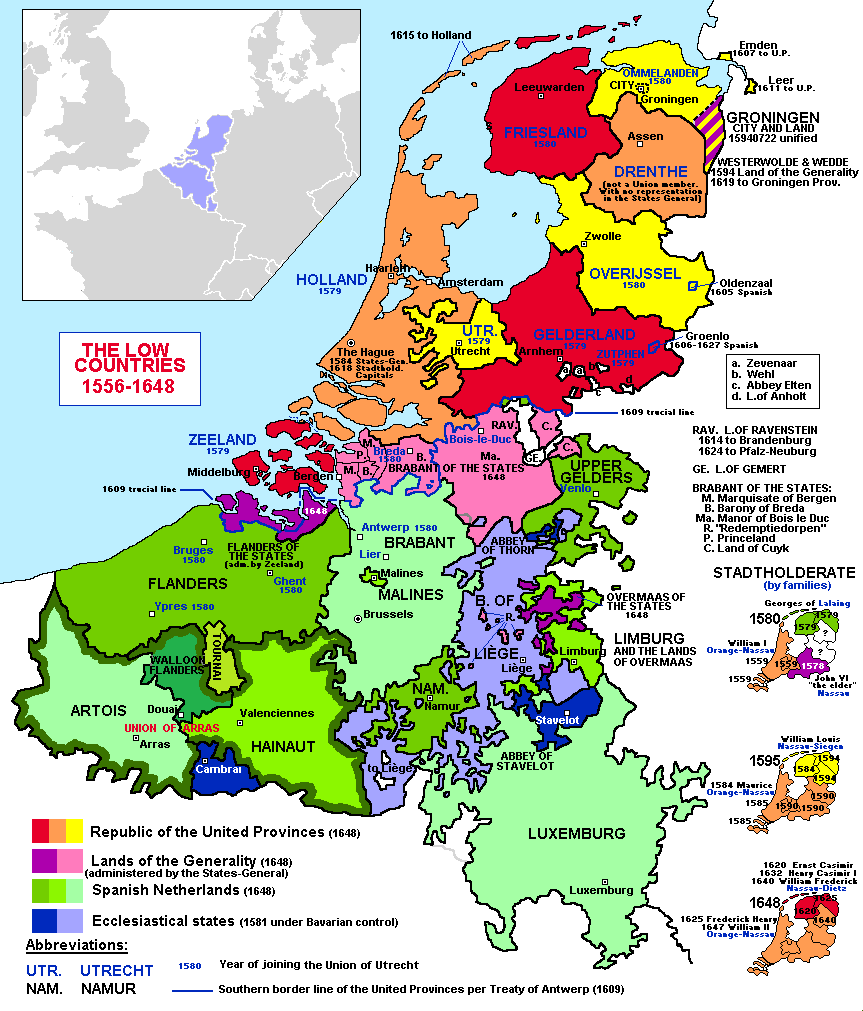
Low Countries
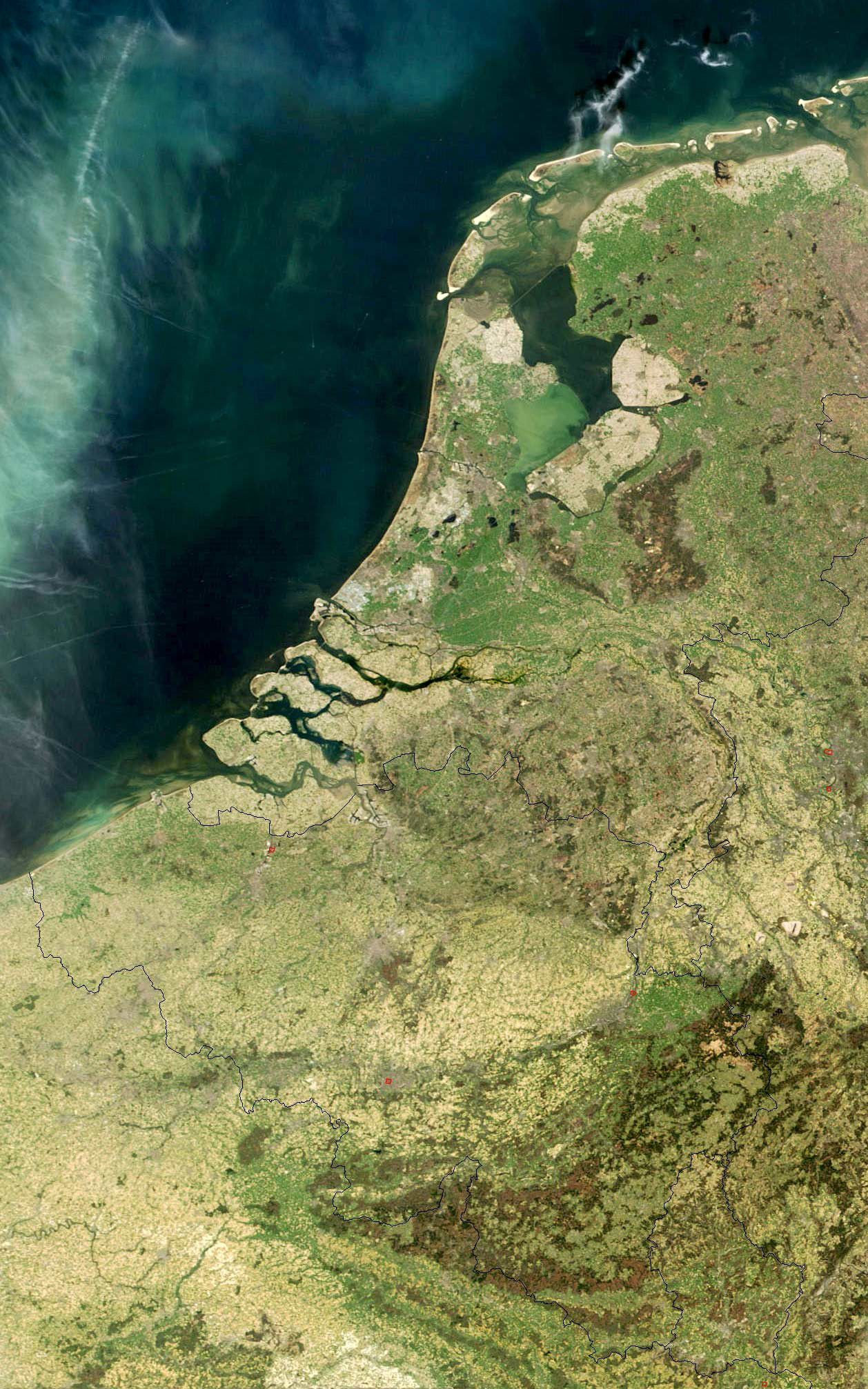
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Benelux" countries: Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands (, which is singular). Geographically and historically, the area can also include parts of France (such as Nord (French department), Nord and Pas-de-Calais) and the Germany, German regions of East Frisia, Geldern, Guelders and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities. Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevated regions are considered part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands consists of Provinces of the Netherlands, twelve provinces; it borders Germany to the east and Belgium to the south, with a North Sea coastline to the north and west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with the United Kingdom, Germany, and Belgium. The official language is Dutch language, Dutch, with West Frisian language, West Frisian as a secondary official language in the province of Friesland. Dutch, English_language, English, and Papiamento are official in the Caribbean Netherlands, Caribbean territories. The people who are from the Netherlands is often referred to as Dutch people, Dutch Ethnicity, Ethnicity group, not to be confused by the language. ''Netherlands'' literally means "lower countries" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchical state or feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often used to describe small monarchies, particularly those in Europe, where the ruler holds the title of prince or an equivalent. Historically, principalities emerged during the Middle Ages as part of the feudal system, where local princes gained significant power within a king's domain. This led to political fragmentation and the creation of mini-states. Over time, many of these principalities consolidated into larger kingdoms and empires, while others retained their independence and prospered. Sovereign principalities which exist today include Liechtenstein, Monaco, and the co-principality of Andorra. Additionally, some royal primogenitures, such as Asturias in Spain, are styled as principalities. The term is also used generically for smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lage Landen (Frankische Tijd)
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Benelux" countries: Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands (, which is singular). Geographically and historically, the area can also include parts of France (such as Nord and Pas-de-Calais) and the German regions of East Frisia, Guelders and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities. Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevated regions are considered part of the Low Countries, including Luxembourg and the south o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the List of languages by total number of speakers, third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders (which includes 60% of the population of Belgium). "1% of the EU population claims to speak Dutch well enough in order to have a conversation." (page 153). Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects. In South America, Dutch is the native l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Figurehead
In politics, a figurehead is a practice of who ''de jure'' (in name or by law) appears to hold an important and often supremely powerful title or office, yet '' de facto'' (in reality) exercises little to no actual power. This usually means that they are head of state, but not head of government. The metaphor derives from the carved figurehead at the prow of a sailing ship. Examples Heads of state in most constitutional monarchies and parliamentary republics are often considered to be figureheads. Commonly cited ones include the monarch of the United Kingdom, who is also head of state of the other Commonwealth realms and head of the Commonwealth, but has no power over the nations in which the sovereign is not head of government and does not exercise power in the realms on their own initiative. Other figureheads include the Emperor of Japan and the Swedish monarch, as well as presidents in a majority of parliamentary republics, such as the presidents of Austria, Bangladesh, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular territory. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradespeople belonging to a professional association. They sometimes depended on grants of letters patent from a monarch or other ruler to enforce the flow of trade to their self-employed members, and to retain ownership of tools and the supply of materials, but most were regulated by the local government. Guild members found guilty of cheating the public would be fined or banned from the guild. A lasting legacy of traditional guilds are the guildhalls constructed and used as guild meeting-places. Typically the key "privilege" was that only guild members were allowed to sell their goods or practice their skill within the city. There might be controls on minimum or maximum prices, hours of trading, numbers of apprentices, and many other things. Critics argued that these rules reduced Free market, fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Northern Italy
Northern Italy (, , ) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. The Italian National Institute of Statistics defines the region as encompassing the four Northwest Italy, northwestern Regions of Italy, regions of Piedmont, Aosta Valley, Liguria and Lombardy in addition to the four Northeast Italy, northeastern Regions of Italy, regions of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Trentino-Alto Adige, Veneto, Friuli-Venezia Giulia and Emilia-Romagna. With a total area of , and a population of 27.4 million as of 2022, the region covers roughly 40% of the Italian Republic and contains 46% of its population. Two of Italy's largest metropolitan areas, Milan and Turin, are located in the region. Northern Italy's GDP was estimated at Euro, €1 trillion in 2021, accounting for 56.5% of the Italian economy. Northern Italy has a rich and distinct culture. Thirty-seven of the fifty-nine List of World Heritage Sites in Italy, World Heritage Sites in Italy are found in the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Renaissance Of The 12th Century
The Renaissance of the 12th century was a period of many changes at the outset of the High Middle Ages. It included social, political and economic transformations, and an intellectual revitalization of Western Europe with strong philosophical and scientific roots. These changes paved the way for later achievements such as the literary and artistic movement of the Italian Renaissance in the 15th century and the Scientific Revolution, scientific developments of the 17th century. Following the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, Western Roman Empire's collapse, Europe experienced a decline in scientific knowledge. However, increased contact with the Islam, Islamic world brought a resurgence of learning. Islamic philosophy, Islamic philosophers and Science in the medieval Islamic world, scientists preserved and expanded upon ancient Greek works, especially those of Aristotle and Euclid, which were translated into Latin, significantly revitalizing European science in the Middle Ages, Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |