Labrador Sea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the 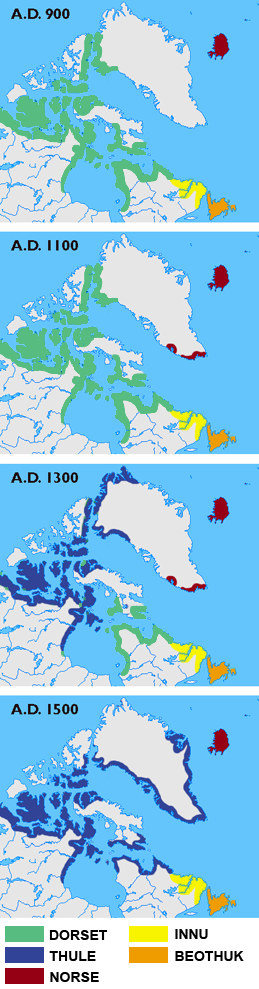
 The Labrador Sea is about deep and wide where it joins the Atlantic Ocean. It becomes shallower, to less than towards Baffin Bay (see depth map) and passes into the wide Davis Strait. A deep
The Labrador Sea is about deep and wide where it joins the Atlantic Ocean. It becomes shallower, to less than towards Baffin Bay (see depth map) and passes into the wide Davis Strait. A deep
 The Labrador duck was a common bird on the Canadian coast until the 19th century, but is now extinct. Other coastal animals include the Labrador wolf (''Canis lupus labradorius''), caribou (''Rangifer'' spp.),
The Labrador duck was a common bird on the Canadian coast until the 19th century, but is now extinct. Other coastal animals include the Labrador wolf (''Canis lupus labradorius''), caribou (''Rangifer'' spp.),
Ledum groenlandicum Oeder – Labrador Tea
(PDF) . Retrieved on 2013-03-20.
North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe a ...
between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
. The sea is flanked by continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, and northeast. It connects to the north with Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay (Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Ar ...
through the Davis Strait. It is a marginal sea
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Terminology
* Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Oce ...
of the Atlantic.
The sea formed upon separation of the North American Plate and Greenland Plate that started about 60 million years ago and stopped about 40 million years ago. It contains one of the world's largest turbidity current
A turbidity current is most typically an underwater current of usually rapidly moving, sediment-laden water moving down a slope; although current research (2018) indicates that water-saturated sediment may be the primary actor in the process. T ...
channel systems, the Northwest Atlantic Mid-Ocean Channel
The Northwest Atlantic Mid-Ocean Channel (NAMOC) is the main body of a turbidity current system of channels and canyons running on the sea bottom from the Hudson Strait, through the Labrador Sea and ending at the Sohm Abyssal Plain in the Atlant ...
(NAMOC), that runs for thousands of kilometers along the sea bottom toward the Atlantic Ocean.
The Labrador Sea is a major source of the North Atlantic Deep Water, a cold water mass that flows at great depth along the western edge of the North Atlantic, spreading out to form the largest identifiable water mass in the World Ocean.

History
The Labrador Sea formed upon separation of the North American Plate and Greenland Plate that started about 60 million years ago (Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
) and stopped about 40 million years ago. A sedimentary basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsidence ...
, which is now buried under the continental shelves, formed during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
. Onset of magmatic sea-floor spreading was accompanied by volcanic eruptions of picrites and basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
s in the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
at the Davis Strait and Baffin Bay.
Between about 500 BC and 1300 AD, the southern coast of the sea contained Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of ...
, Beothuk and Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, ...
settlements; Dorset tribes were later replaced by Thule people
The Thule (, , ) or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by the year 1000 and expanded eastward across northern Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people o ...
.
Extent
TheInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organisation representing hydrography. , the IHO comprised 98 Member States.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ensure that the world's seas, oceans and navigable waters ...
defines the limits of the Labrador Sea as follows:
On the North: the South limit of Davis Strait 60° North betweenGreenland Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...and Labrador]. On the East: a line from Cape St. Francis (Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland) to Cape Farewell, Greenland, Cape Farewell (Greenland). On the West: the East Coast of Labrador and Newfoundland and the Northeast limit of theGulf of St. Lawrence The Gulf of St. Lawrence () is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the St. Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semi-enclosed sea, covering an area of about and containing about of water, at an average depth of . ...– a line running from Cape Bauld (North point of Kirpon Island, ) to the East extreme of Belle Isle and on to the Northeast Ledge (). Thence a line joining this ledge with the East extreme of Cape St. Charles (52°13'N) in Labrador.
Natural Resources Canada
Natural Resources Canada (NRCan; french: Ressources naturelles Canada; french: RNCan, label=none)Natural Resources Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Natural Resources (). is the Struc ...
uses a slightly different definition, putting the northern boundary of the Labrador Sea on a straight line from a headland on Killiniq Island abutting Lady Job Harbour to Cape Farewell.
Oceanography
 The Labrador Sea is about deep and wide where it joins the Atlantic Ocean. It becomes shallower, to less than towards Baffin Bay (see depth map) and passes into the wide Davis Strait. A deep
The Labrador Sea is about deep and wide where it joins the Atlantic Ocean. It becomes shallower, to less than towards Baffin Bay (see depth map) and passes into the wide Davis Strait. A deep turbidity current
A turbidity current is most typically an underwater current of usually rapidly moving, sediment-laden water moving down a slope; although current research (2018) indicates that water-saturated sediment may be the primary actor in the process. T ...
channel system, which is about wide and long, runs on the bottom of the sea, near its center from the Hudson Strait into the Atlantic. It is called the Northwest Atlantic Mid-Ocean Channel
The Northwest Atlantic Mid-Ocean Channel (NAMOC) is the main body of a turbidity current system of channels and canyons running on the sea bottom from the Hudson Strait, through the Labrador Sea and ending at the Sohm Abyssal Plain in the Atlant ...
(NAMOC) and is one of the world's longest drainage systems of Pleistocene age. It appears as a submarine river bed with numerous tributaries and is maintained by high-density turbidity currents flowing within the levee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastl ...
s.
The water temperature varies between in winter and in summer. The salinity is relatively low, at 31–34.9 parts per thousand. Two-thirds of the sea is covered in ice in winter. Tides are semi-diurnal (i.e. occur twice a day), reaching .
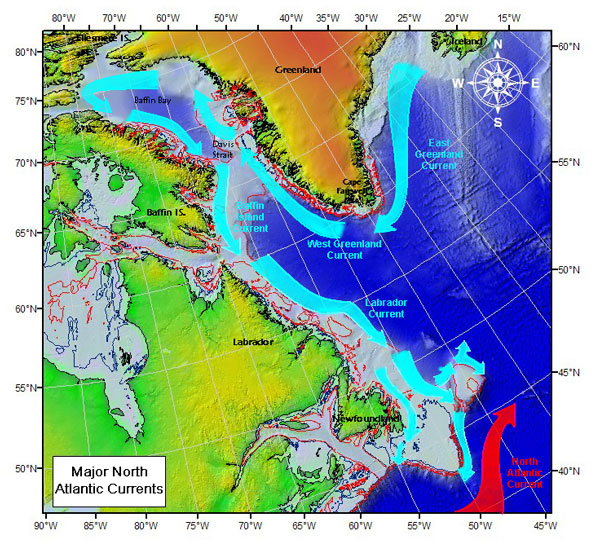
There is an anticlockwise water circulation in the sea. It is initiated by the East Greenland Current and continued by the West Greenland Current, which brings warmer, more saline waters northwards, along the Greenland coasts up to the Baffin Bay. Then, the Baffin Island Current and Labrador Current transport cold and less saline water southward along the Canadian coast. These currents carry numerous icebergs and therefore hinder navigation and exploration of the gas fields beneath the sea bed. The speed of the Labrador current is typically , but can reach in some areas, whereas the Baffin Current is somewhat slower at about . The Labrador Current maintains the water temperature at and salinity between 30 and 34 parts per thousand.
The sea provides a significant part of the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) – a cold water mass that flows at great depth along the western edge of the North Atlantic, spreading out to form the largest identifiable water mass in the World Ocean. The NADW consists of three parts of different origin and salinity, and the top one, the Labrador Sea Water (LSW), is formed in the Labrador Sea. This part occurs at a medium depth and has a relatively low salinity (34.84–34.89 parts per thousand), low temperature () and high oxygen content compared to the layers above and below it. LSW also has a relatively low vorticity, i.e. the tendency to form vortices, than any other water in North Atlantic that reflects its high homogeneity. It has a potential density of 27.76–27.78 mg/cm3 relatively to the surface layers, meaning it is denser, and thus sinks under the surface and remains homogeneous and unaffected by the surface fluctuations.
Fauna
The northern and western parts of the Labrador Sea are covered in ice between December and June. Thedrift ice
Drift ice, also called brash ice, is sea ice that is not attached to the shoreline or any other fixed object (shoals, grounded icebergs, etc.).Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Unlike fast ice, which is "fasten ...
serves as a breeding ground for seals in early spring. The sea is also a feeding ground for Atlantic salmon and several marine mammal species. Shrimp fisheries began in 1978 and intensified toward 2000, as well as cod fishing. However, the cod fishing rapidly depleted the fish population in the 1990s near the Labrador and West Greenland banks and was therefore halted in 1992. Other fishery targets include haddock
The haddock (''Melanogrammus aeglefinus'') is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Melanogrammus''. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean and associated seas w ...
, Atlantic herring, lobster
Lobsters are a family (Nephropidae, synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs have claws, including the first pair, ...
and several species of flatfish and pelagic fish such as sand lance and capelin. They are most abundant in the southern parts of the sea.
Beluga whales, while abundant to the north, in the Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay (Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Ar ...
, where their population reaches 20,000, are rare in the Labrador Sea, especially since the 1950s. The sea contains one of the two major stocks of Sei whales, the other one being the Scotian Shelf. Also common are minke
The minke whale (), or lesser rorqual, is a species complex of baleen whale. The two species of minke whale are the common (or northern) minke whale and the Antarctic (or southern) minke whale. The minke whale was first described by the Danish na ...
and bottlenose whales.
 The Labrador duck was a common bird on the Canadian coast until the 19th century, but is now extinct. Other coastal animals include the Labrador wolf (''Canis lupus labradorius''), caribou (''Rangifer'' spp.),
The Labrador duck was a common bird on the Canadian coast until the 19th century, but is now extinct. Other coastal animals include the Labrador wolf (''Canis lupus labradorius''), caribou (''Rangifer'' spp.), moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
(''Alces alces''), black bear (''Ursus americanus''), red fox (''Vulpes vulpes''), Arctic fox (''Alopex lagopus''), wolverine
The wolverine (), (''Gulo gulo''; ''Gulo'' is Latin for " glutton"), also referred to as the glutton, carcajou, or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species of the family Mustelidae. It is a musc ...
, snowshoe hare (''Lepus americanus''), grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order (biology), order Galliformes, in the family (biology), family Phasianidae. Grouse are presently assigned to the Tribe (biology), tribe Tetraonini (formerly the subfamily Tetraoninae and the family Tetr ...
(''Dendragapus'' spp.), osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown o ...
(''Pandion haliaetus''), raven (''Corvus corax''), ducks, geese, partridge and American wild pheasant.
Flora
Coastal vegetation includes black spruce (''Picea mariana''), tamarack, white spruce (''P. glauca''), dwarf birch (''Betula'' spp.),aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species; some, but not all, are classified by botanists in the section ''Populus'', of the ''Populus'' genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
*'' Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (Chin ...
, willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist ...
(''Salix'' spp.), ericaceous shrubs ('' Ericaceae''), cottongrass (''Eriophorum'' spp.), sedge
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus '' Carex'' ...
(''Carex'' spp.), lichens and moss. Evergreen bushes of Labrador tea, which is used to make herbal teas, are common in the area, both on the Greenland and Canadian coasts.(PDF) . Retrieved on 2013-03-20.
References
{{Authority control Oceanography Seas of Greenland Seas of the Atlantic Ocean Bodies of water of Newfoundland and Labrador Seas of Canada Geography of North America Cenozoic rifts and grabens