|
Tamarack
''Larix laricina'', commonly known as the tamarack, hackmatack, eastern larch, black larch, red larch, or American larch, is a species of larch native to Canada, from eastern Yukon and Inuvik, Northwest Territories east to Newfoundland, and also south into the upper northeastern United States from Minnesota to Cranesville Swamp, West Virginia; there is also an isolated population in central Alaska. Description ''Larix laricina'' is a small to medium-size boreal deciduous conifer tree reaching tall, with a trunk up to diameter. The bark of mature trees is reddish, the young trees are gray with smooth bark. The leaves are needle-like, long, light blue-green, turning bright yellow before they fall in the autumn, leaving the shoots bare until the next spring. The needles are produced in clusters on long woody spur shoots. The cones are the smallest of any larch, only long, with 12-25 seed scales; they are bright red, turning brown and opening to release the seeds when matu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Boreal Forest
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by pinophyta, coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. In North America, it covers most of inland Canada, Alaska, and parts of the northern contiguous United States. In Eurasia, it covers most of Sweden, Finland, much of Russia from Karelia in the west to the Pacific Ocean (including much of Siberia), much of Norway and Estonia, some of the Scottish Highlands, some lowland/coastal areas of Iceland, and areas of northern Kazakhstan, northern Mongolia, and northern Japan (on the island of Hokkaido). The principal tree species, depending on the length of the growing season and summer temperatures, vary across the world. The taiga of North America is mostly spruce; Scandinavian and Finland, Finnish taiga consists of a mix of Norway spruce, spruce, pines and Betula, birch; Russian taiga has spruces, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Larch
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to the cooler regions of the northern hemisphere, where they are found in lowland forests in the high latitudes, and high in mountains further south. Larches are among the dominant plants in the boreal forests of Siberia and Canada. Although they are conifers, larches are deciduous trees that lose their needles in the autumn. Description and distribution The tallest species, '' Larix occidentalis'', can reach . Larch tree crowns are sparse, with the major branches horizontal; the second and third order branchlets are also ± horizontal in some species (e.g. '' L. gmelinii'', '' L. kaempferi''), or characteristically pendulous in some other species (e.g. '' L. decidua'', '' L. griffithii''). Larch shoots are dimorphic, with leaves borne singly on long shoots typically long and bearing several buds, and in dense clusters of 20–50 need ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are around three trillion mature trees in the world currently. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Larix Laricina Foliagecones
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to the cooler regions of the northern hemisphere, where they are found in lowland forests in the high latitudes, and high in mountains further south. Larches are among the dominant plants in the boreal forests of Siberia and Canada. Although they are conifers, larches are deciduous trees that lose their needles in the autumn. Description and distribution The tallest species, ''Larix occidentalis'', can reach . Larch tree crowns are sparse, with the major branches horizontal; the second and third order branchlets are also ± horizontal in some species (e.g. '' L. gmelinii'', '' L. kaempferi''), or characteristically pendulous in some other species (e.g. '' L. decidua'', '' L. griffithii''). Larch shoots are dimorphic, with leaves borne singly on long shoots typically long and bearing several buds, and in dense clusters of 20–50 needles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic, Antarctic. Tundra vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, Cyperaceae, sedges, Poaceae, grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra regions. The ecotone (or ecological boundary region) between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline. The tundra soil is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus. The soil also contains large amounts of biomass and decomposed biomass that has been stored as methane and carbon dioxide in the permafrost, making the tundra soil a carbon sink. As global warming heats the ecosystem and causes soil thawing, the permafrost carbon cycle accelerates and releases much of these soil-contained greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, creating Climate change feedback, a feedback cycle t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Michigan Press
The University of Michigan Press is a university press that is a part of Michigan Publishing at the University of Michigan Library. It publishes 170 new titles each year in the humanities and social sciences. Titles from the press have earned numerous awards, including Lambda Literary Awards, the PEN/Faulkner Award, the Joe A. Callaway Award, and the Nautilus Book Award. The press has published works by authors who have been awarded the Pulitzer Prize, the National Humanities Medal and the Nobel Prize in Economics. History From 1858 to 1930, the University of Michigan had no organized entity for its scholarly publications, which were generally conference proceedings or department-specific research. The University Press was established in 1930 under the university's Graduate School, and in 1935, Frank E. Robbins, assistant to university president Alexander G. Ruthven, was appointed as the managing editor of the University Press. He would hold this position until 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway (Nordland, Troms, Finnmark, Svalbard and Jan Mayen), northernmost Sweden (Västerbotten, Norrbotten and Lapland (Sweden), Lappland), northern Finland (North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu and Lapland (Finland), Lappi), Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), and northern Iceland (Grímsey and Kolbeinsey), along with the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying cryosphere, snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost under the tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tree Line
The tree line is the edge of a habitat at which trees are capable of growing and beyond which they are not. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually low temperatures, extreme snowpack, or associated lack of available moisture). The tree line is sometimes distinguished from a lower timberline, which is the line below which trees form a forest with a closed Canopy (biology), canopy. At the tree line, tree growth is often sparse, stunted, and deformed by wind and cold. This is sometimes known as (German for "crooked wood"). The tree line often appears well-defined, but it can be a more gradual transition. Trees grow shorter and often at lower densities as they approach the tree line, above which they are unable to grow at all. Given a certain latitude, the tree line is approximately 300 to 1000 meters below the permanent snow line and roughly parallel to it. Causes Due to their vertical s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Red Spruce
''Picea rubens'', commonly known as red spruce, is a species of spruce native to eastern North America, ranging from eastern Quebec and Nova Scotia, west to the Adirondack Mountains and south through New England along the Appalachians to western North Carolina and eastern Tennessee.Farjon, A. (1990). ''Pinaceae. Drawings and Descriptions of the Genera''. Koeltz Scientific Books . This species is also known as yellow spruce, West Virginia spruce, eastern spruce, and he-balsam. Red spruce is the provincial tree of Nova Scotia. Description Red spruce is a perennial, shade-tolerant, late successional coniferous tree that under optimal conditions grows to tall with a trunk diameter of about , though exceptional specimens can reach tall and in diameter. It has a narrow conical crown. The leaves are needle-like, yellow-green, long, four-sided, curved, with a sharp point, and extend from all sides of the twig. The bark is gray-brown on the surface and red-brown on the inside, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or butterflies; birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves. Pollinating animals travel from plant to plant carrying pollen on their bodies in a vital interaction that allows the transfer of genetic material critical to the reproductive system of most flowering plants. Self-pollination occurs within a closed flower. Pollination often occurs within a species. When pollination occurs between species, it can produce hybrid (biology), hybrid offspring in nature and in plant breeding work. In angiosperms, after the pollen grain (gametophyte) has landed on the stigma (botany), stigma, it germinates and develops a pollen tube which grows down the style (botany), style until it reaches an ovary (botany), ovary. Its two gametes travel down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
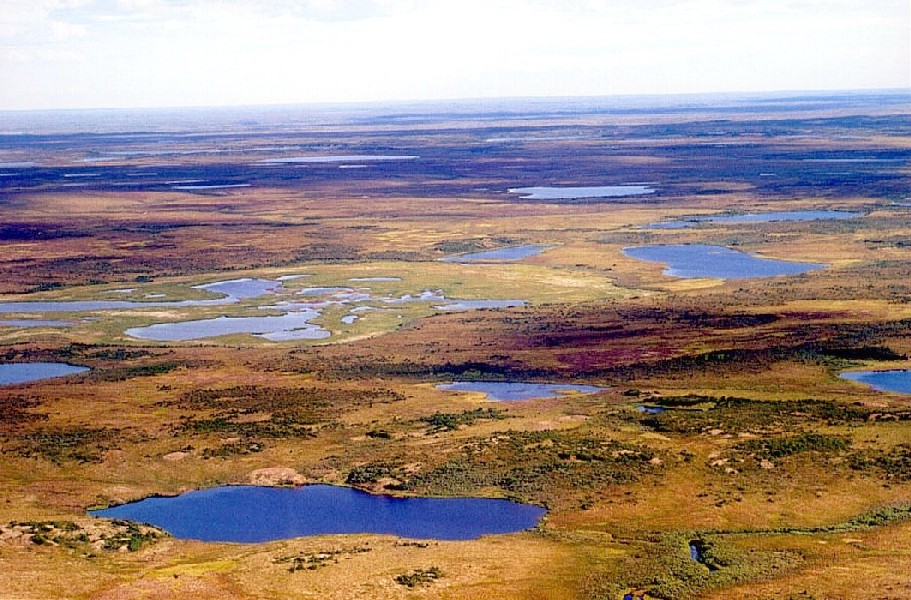
Muskeg
Muskeg (; ; , lit. ''moss bog'') is a peat-forming ecosystem found in several northern climates, most commonly in Arctic and boreal ecosystem, boreal areas. Muskeg is approximately synonymous with bogland, bog or peatland, and is a standard term in Canada and Alaska. The term became common in these areas because it is of Cree language, Cree origin, () meaning "low-lying marsh". Muskeg consists of non-living organic material in various states of decomposition (as peat), ranging from fairly intact sphagnum moss, to sedge peat, to highly decomposed humus. Pieces of wood can make up five to fifteen percent of the peat soil. The water table tends to be near the surface. The sphagnum moss forming it can hold fifteen to thirty times its own weight in water, which allows the spongy wet muskeg to also form on sloping ground. Muskeg patches are ideal habitats for beavers, pitcher plants, agaricales, agaric mushrooms and a variety of other organisms. Composition Muskeg forms because pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225–229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As ''Sphagnum'' moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, ''Sphagnum'' can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing ''Sphagnum'' as 'habitat manipulators' or 'autogenic ecosystem engineers'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and Calcifuge, ericaceous shrubs, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |