King Tomaš on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Stephen Thomas ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Stefan Tomaš, Стефан Томаш, sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, label=none, Stjepan Tomaš, Стјепан Томаш; 1411 – 10 July 1461), a member of the
 Tvrtko II died in November 1443. The ''
Tvrtko II died in November 1443. The ''
 Thomas' intention to marry Kosača's daughter Catherine was made known in April, their lands and borders reverting to ''
Thomas' intention to marry Kosača's daughter Catherine was made known in April, their lands and borders reverting to ''
 The Holy See put King Thomas under its protection in 1455, and promised that he would be given back the lands taken by Turks and his treacherous magnates if the Christians defeated the Ottomans. In 1456, Thomas sent a letter to
The Holy See put King Thomas under its protection in 1455, and promised that he would be given back the lands taken by Turks and his treacherous magnates if the Christians defeated the Ottomans. In 1456, Thomas sent a letter to  The situation in Hungary took a sharp turn for the worse immediately after the celebrated victory over the Turks. The victorious commanders, including János Hunyadi, died of plague, Ulrich of Celje was murdered, and even the young King Ladislaus died suddenly the following year. The aged
The situation in Hungary took a sharp turn for the worse immediately after the celebrated victory over the Turks. The victorious commanders, including János Hunyadi, died of plague, Ulrich of Celje was murdered, and even the young King Ladislaus died suddenly the following year. The aged
 A large Turkish raid in February 1458 forced Thomas to sign a truce, despite his earlier crusading vows, but Mehmed no longer insisted on the cession of the four towns; he intended to conquer Serbia instead. At that time, King Thomas dropped the plan of having his son marry an illegitimate daughter of Francesco Sforza; the match with a bastard daughter of a duke was far beneath the King's expectations for Stephen. Instead, he successfully negotiated with Lazar's widow, the Byzantine princess
A large Turkish raid in February 1458 forced Thomas to sign a truce, despite his earlier crusading vows, but Mehmed no longer insisted on the cession of the four towns; he intended to conquer Serbia instead. At that time, King Thomas dropped the plan of having his son marry an illegitimate daughter of Francesco Sforza; the match with a bastard daughter of a duke was far beneath the King's expectations for Stephen. Instead, he successfully negotiated with Lazar's widow, the Byzantine princess
 The fall of Serbia meant that the eastern border of Thomas' realm was now the bulwark of Christendom. However, Bosnia was not Mehmed's priority. Thomas was forced to surrender northeastern Bosnia, namely Usora, Srebrenica, Zvornik and Teočak, in early 1460, allowing the Turks to cross the
The fall of Serbia meant that the eastern border of Thomas' realm was now the bulwark of Christendom. However, Bosnia was not Mehmed's priority. Thomas was forced to surrender northeastern Bosnia, namely Usora, Srebrenica, Zvornik and Teočak, in early 1460, allowing the Turks to cross the
 Thomas was a man of many contradictions. His good looks and noble comportment greatly impressed his contemporaries. The Italian
Thomas was a man of many contradictions. His good looks and noble comportment greatly impressed his contemporaries. The Italian
House of Kotromanić
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air cond ...
, reigned from 1443 until his death as the penultimate king of Bosnia
This is a list of monarchs of Bosnia, containing Ban (title), bans and kings of Medieval Bosnia; Bosnia (early medieval), Banate of Bosnia, Kingdom of Bosnia.
Duke (1084–1095)
Bans (1154–1377)
Kings and queen (1377–1463)
All Bosnian ki ...
.
An illegitimate son of King Ostoja, Thomas succeeded King Tvrtko II, but his accession was not recognized by the leading magnate
The term magnate, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
of the Kingdom of Bosnia
The Kingdom of Bosnia ( / Краљевина Босна), or Bosnian Kingdom (''Bosansko kraljevstvo'' / Босанско краљевство), was a medieval kingdom that lasted for nearly a century, from 1377 to 1463, and evolved out of the ...
, Stjepan Vukčić Kosača
Stjepan Vukčić Kosača (1404–1466) was a powerful Bosnian Nobility, nobleman who was politically active from 1435 to 1466; the last three decades of Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Middle Ages, Bosnian medieval history. During this period, ...
. The two engaged in a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
which ended when the King repudiated his wife, Vojača, and married the insubordinate nobleman's daughter, Catherine
Katherine (), also spelled Catherine and Catherina, other variations, is a feminine given name. The name and its variants are popular in countries where large Christian populations exist, because of its associations with one of the earliest Ch ...
. Thomas and his second wife, both raised in the Bosnian Church
The Bosnian Church ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Crkva bosanska, Црква босанска) was an autonomous Christian church in medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Historians traditionally connected the church with the Bogomils, although this ...
tradition, converted to Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and sponsored construction of churches and monasteries throughout the kingdom.
Throughout his reign, Thomas waged a war with the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate () was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is mistakenly considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and Moravi ...
over the lucrative mining town of Srebrenica
Srebrenica ( sr-cyrl, Сребреница, ) is a town and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is a small mountain town, with its main industry being salt mining and a nearby spa.
During the Bosnian War in 1995, Srebr ...
and its surroundings, in addition to (or in conjunction with) multiple conflicts with his father-in-law. Moreover, he had a tense relationship with the menacing Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. After years of skirmishes and raids, Thomas appeared willing to lead the Christian coalition against the Turks, but received no assistance from fellow Christian rulers. Having failed to expand into Croatia proper
In contemporary geography, the terms Central Croatia () and Mountainous Croatia () are used to describe most of the area sometimes historically known as Croatia or Croatia proper (), one of the four historical regions of the Republic of Croa ...
, Thomas turned again to the east in 1458, arranging a match between his son Stephen
Stephen or Steven is an English given name, first name. It is particularly significant to Christianity, Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is w ...
and the Serbian heiress Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a female given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religion
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blesse ...
. Bosnian control over the remnants of the Serbian Despotate lasted merely a month before the Ottoman conquest of the state. King Thomas' failure to defend Serbia permanently damaged his reputation in Europe. Wishing to improve his image among Europe's Catholics, Thomas turned against the Bosnian Church, thus becoming the first ruler of Bosnia to engage in religious persecution
Religious persecution is the systematic oppression of an individual or a group of individuals as a response to their religion, religious beliefs or affiliations or their irreligion, lack thereof. The tendency of societies or groups within socie ...
.
Thomas' sometime contradictory traits earned him both admiration and scorn from his contemporaries. His son Stephen succeeded him, and immediately proved more apt at dealing with the challenges of the time.
Background
Thomas was the son of King Ostoja, who died in 1418, and his mistress, whose name is not recorded. He was a doublyadulterine
Adultery is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and legal consequences, the concept e ...
child, as both his father and mother were married at the time of his birth. Thomas was raised as a member of the Bosnian Church
The Bosnian Church ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Crkva bosanska, Црква босанска) was an autonomous Christian church in medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Historians traditionally connected the church with the Bogomils, although this ...
, to which his parents adhered. Tvrtko II
Stephen Tvrtko II ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Stjepan/Stefan Tvrtko, Стјепан/Стефан Твртко; died in November 1443), also known as Tvrtko Tvrtković (), was a member of the House of Kotromanić who reigned as King of Bosnia from 1404 to 1409 ...
deposed Stephen Ostojić
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the fir ...
, Ostoja's only known legitimate child and successor, in 1421. Thomas' illegitimate older brother, Radivoj, unsuccessfully contested Tvrtko's rule with the help of the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks () were a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group in Anatolia. Originally from Central Asia, they migrated to Anatolia in the 13th century and founded the Ottoman Empire, in which they remained socio-politically dominant for the e ...
and the Kosača family, the leading magnate
The term magnate, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s of the Kingdom of Bosnia
The Kingdom of Bosnia ( / Краљевина Босна), or Bosnian Kingdom (''Bosansko kraljevstvo'' / Босанско краљевство), was a medieval kingdom that lasted for nearly a century, from 1377 to 1463, and evolved out of the ...
.
The narrative sources refer to Thomas (as well as his father and brother) as a Kristić, which is thought to be the name of a cadet branch
A cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets (realm, titles, fiefs, property and incom ...
of the Kotromanić dynasty
The House of Kotromanić ( sr-cyrl, Котроманић, Kotromanići / Котроманићи) was a late medieval Bosnian noble and later royal dynasty. Rising to power in the middle of the 13th century as bans of Bosnia, with control ove ...
. Thomas was thus closely related to Tvrtko II, likely his first cousin.
Avoiding the limelight during the reign of Tvrtko II, Thomas lived with a commoner named Vojača and their children. He was loyal to King Tvrtko, and together the two took part in a skirmish in Usora, where Thomas was wounded. His loyalty likely influenced the childless and ailing King to ensure his succession; Thomas was certainly preferable to his brother Radivoj, whom Tvrtko detested. Count Hermann II of Celje
Hermann II (; early 1360s – 13 October 1435), Count of Celje, was a Styrian prince and magnate, most notable as the faithful supporter and father-in-law of the Hungarian king and Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund of Luxembourg. Hermann's loyalty t ...
, a descendant of the Kotromanić family once designated as heir presumptive
An heir presumptive is the person entitled to inherit a throne, peerage, or other hereditary honour, but whose position can be displaced by the birth of a person with a better claim to the position in question. This is in contrast to an heir app ...
, had died in 1435.
Accession to coronation
 Tvrtko II died in November 1443. The ''
Tvrtko II died in November 1443. The ''Stanak
''Stanak'' is the most common name used to refer to the assembly of nobility in medieval Bosnia. The assembly, in the original Bosančica: (), was also known as the ''Rusag'' (from the Hungarian word ''orszag'', meaning "state" or "nation"), ' ...
'' approved his choice of heir, and Thomas was duly elected king by 5 December. Like his predecessors, he added the royal name Stephen to his own. However, the kingdom's most powerful magnate, Grand Duke
Grand duke (feminine: grand duchess) is a European hereditary title, used either by certain monarchs or by members of certain monarchs' families. The title is used in some current and former independent monarchies in Europe, particularly:
* in ...
Stjepan Vukčić Kosača
Stjepan Vukčić Kosača (1404–1466) was a powerful Bosnian Nobility, nobleman who was politically active from 1435 to 1466; the last three decades of Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Middle Ages, Bosnian medieval history. During this period, ...
, refused to accept Thomas as king, and announced his support for Radivoj. The authorities of the neighbouring Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
immediately expressed concern about the situation. Kosača and Radivoj appealed to Ragusa not to recognize Thomas as king, but to no avail. Simultaneously, Hermann's grandson Ulrich II pressed his claim to the Bosnian throne and tried to gather support among Thomas's opponents. Because of this, Thomas hastened to send word of his accession to foreign rulers, including the German king Frederick IV, Ulrich's rival, and Ragusan and Venetian authorities, hoping to receive recognition. Ulrich was occupied with the feud
A feud , also known in more extreme cases as a blood feud, vendetta, faida, clan war, gang war, private war, or mob war, is a long-running argument or fight, often between social groups of people, especially family, families or clans. Feuds begin ...
waged against him by Frederick, as well as with the succession struggle in Hungary, where he had taken side with his cousin, queen dowager Elizabeth of Luxembourg
Elizabeth of Luxembourg (; 7 October 1409 – 19 December 1442) was queen consort of Hungary, queen consort of Germany and Bohemia.
The only child of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, King of Hungary and Bohemia, Elizabeth was expected to asce ...
and her infant son Ladislaus against the reigning monarch Vladislav I, leaving Thomas ample space of maneuver.Vjekoslav Klaić, ''Povijest Hrvata, od najstarijih vremena do svršetka XIX. stoljeća'', Vol. 3 (Zagreb: 1974), pp 206-207.
Succession war
King Thomas acted resolutely to strengthen his position. In January 1444, he penetrated the Bosnian-held region ofZachlumia
Zachlumia or Zachumlia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Zahumlje, Захумље, ), also Hum, was a medieval principality located in the modern-day regions of Herzegovina and southern Dalmatia (today parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia, r ...
, ruled by the Kosačas. Kosača's nephew Ivaniš Pavlović
Ivaniš Pavlović ( sr-cyr, Иваниш Павловић; June 1423 – November 1450) was a ''Knyaz, knez'' and later a Grand Duke of Bosnia from the noble family of Pavlović noble family, Pavlović, who had their estates in the eastern parts o ...
accompanied him, and the Radivojević family, the discontented vassals of the Kosačas, joined them upon their arrival. The party soon took Drijeva, thus restoring the important customs town to the royal domain
Crown land, also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. Today, in Commonwealth realm ...
for the first time in three decades. Pressed by his simultaneous war with Venice, and receiving no help from the Ottoman Turks, Kosača agreed to a truce in March. Both sides hoped to buy time to regain strength for future clashes. King Thomas tried to exact the promise of help from Venice in the event of a Hungarian offensive against him, even offering 25-year-long control over some of his towns and mines to the Republic in return. However, throughout May successful negotiations with Hungary rendered this cession
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdicti ...
unnecessary. János Hunyadi
John Hunyadi (; ; ; ; ; – 11 August 1456) was a leading Hungarian military and political figure during the 15th century, who served as regent of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1446 to 1453, under the minor Ladislaus V.
According to most con ...
's intercession with King Vladislaus I led to Hungarian recognition of Thomas in June, for which the grateful King of Bosnia promised Hunyadi free passage, shelter, an annual income and assistance in any matter. Thus, by summer, Thomas had secured his grip on the throne.
In July 1444, the Hungarian king informed Thomas of his intention to break the truce with the Ottomans. King Thomas decided to make the best of his membership in the Christian coalition. In May he had already conquered the lucrative silver mining
Silver mining is the extraction of silver by mining. Silver is a precious metal and holds high economic value. Because silver is often found in intimate combination with other metals, its extraction requires the use of complex technologies. In ...
town of Srebrenica
Srebrenica ( sr-cyrl, Сребреница, ) is a town and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is a small mountain town, with its main industry being salt mining and a nearby spa.
During the Bosnian War in 1995, Srebr ...
, taken by the Ottomans from the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate () was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is mistakenly considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and Moravi ...
, which in turn had taken it from Bosnia. He now decided to resume his war against the rebellious Kosača, an Ottoman tributary. The Turks were now ready to assist the Duke and broke into Bosnia, forcing the King to flee from Kozograd to Bobovac
Bobovac ( sh-Cyrl, Бобовац) a historic site, was a fortified royal capital city of medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina, and as such a seat of Bosnian rulers during 14th and 15th century. It is located near today's Vareš and the village of Bo ...
, and enabling Kosača to reverse all his losses. In August, the Ottomans restored Serbia to Đurađ Branković
Đurađ Vuković Branković ( sr-Cyrl, Ђурађ Вуковић Бранковић, ; 1377 – 24 December 1456) served as the Serbian Despot from 1427 to 1456, making him one of the final rulers of medieval Serbia.
In 1429, Branković was form ...
, who allied with Kosača against King Thomas. The destruction of the Hungarian army in November 1444 at the Battle of Varna
The Battle of Varna took place on 10 November 1444 near Varna in what is today eastern Bulgaria. The Ottoman army under Sultan Murad II (who did not actually rule the sultanate at the time) defeated the Crusaders commanded by King Władysła ...
, where King Vladislaus himself perished, left Thomas vulnerable. Forced again to rely solely on Venice, Thomas repeated his earlier offer, but the Republic declined and made peace with Kosača. In April 1445, Thomas lost Srebrenica and the entire Drina Valley to Branković. Ivaniš Pavlović came to his aid again, and the two advanced towards Pomorje
Pomorje ( sr-Cyrl, Поморје), also known (in plural) as the Lands of Pomorje (), is a medieval term, used in Byzantine title, and at end of the 12th century, during the reign of Stefan Nemanja (1166–1196), inherited by Serbian monarchs, ...
. Thomas retook Drijeva, but his advance was suddenly halted, perhaps by another Turkish incursion or a truce. Hostilities finally ended in September.
Conversion and marriage
Having failed to strengthen royal authority by force, King Thomas decided to seek another way to pacify the kingdom. A rapprochement with Kosača via marriage with his daughterCatherine
Katherine (), also spelled Catherine and Catherina, other variations, is a feminine given name. The name and its variants are popular in countries where large Christian populations exist, because of its associations with one of the earliest Ch ...
was probably already envisaged in 1445, when Thomas improved relations with the Holy See
The Holy See (, ; ), also called the See of Rome, the Petrine See or the Apostolic See, is the central governing body of the Catholic Church and Vatican City. It encompasses the office of the pope as the Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop ...
in order to be cleared of the "stain of illegitimacy
Legitimacy, in traditional Western common law, is the status of a child born to parents who are legally married to each other, and of a child conceived before the parents obtain a legal divorce.
Conversely, ''illegitimacy'', also known as ''b ...
" as well as to receive an annulment
Annulment is a legal procedure within secular and religious legal systems for declaring a marriage null and void. Unlike divorce, it is usually retroactive, meaning that an annulled marriage is considered to be invalid from the beginning alm ...
of his union with Vojača. Pope Eugene IV
Pope Eugene IV (; ; 1383 – 23 February 1447), born Gabriele Condulmer, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 11 March 1431 to his death, in February 1447. Condulmer was a Republic of Venice, Venetian, and a nephew ...
responded affirmatively on 29 May. By that time, Thomas appears to have decided to join the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
. Negotiations with Kosača intensified in the beginning of 1446. King Thomas was then finally converted from Bosnian Christianity to Roman Catholicism by Tommaso Tommasini, Bishop of Lesina; however, Cardinal Juan Carvajal only performed the baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water eit ...
in 1457.
 Thomas' intention to marry Kosača's daughter Catherine was made known in April, their lands and borders reverting to ''
Thomas' intention to marry Kosača's daughter Catherine was made known in April, their lands and borders reverting to ''status quo ante bellum
The term is a Latin phrase meaning 'the situation as it existed before the war'.
The term was originally used in treaties to refer to the withdrawal of enemy troops and the restoration of prewar leadership. When used as such, it means that no ...
''. The prospective bride, a Bosnian Christian, also had to convert to Catholicism for the marriage to proceed. These developments angered Ivaniš Pavlović and Petar Vojsalić, another vassal, but in the end no conflict with them took place. Elaborate festivities marked the royal wedding in mid-May in Milodraž
Milodraž was a settlement in the Kingdom of Bosnia, situated on an important road connecting the towns of Visoko during the Middle Ages, Visoko and Fojnica. No remains of it have been found, but royal charters and Republic of Ragusa, Ragusan doc ...
, conducted by Catholic rite, followed by the couple's coronation
A coronation ceremony marks the formal investiture of a monarch with regal power using a crown. In addition to the crowning, this ceremony may include the presentation of other items of regalia, and other rituals such as the taking of special v ...
in Mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a imperial unit, British imperial unit and United States customary unit of length; both are based on the older English unit of Unit of length, le ...
. For the first time, a crown was sent from Rome to be placed on the head of a Bosnian king. The Bishop of Feltre and papal legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the Pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title '' legatus'') is a personal representative of the Pope to foreign nations, to some other part of the Catho ...
to Bosnia, another Tommaso Tommasini, fetched the crown from the Cathedral of Saint Domnius
The Cathedral of Saint Domnius (), known locally as the ''Sveti Dujam'' or colloquially ''Sveti Duje'', is the Catholic cathedral in Split, Croatia. The cathedral is the seat of the Archdiocese of Split-Makarska, currently headed by Archbishop ...
in Spalato
Split (, ), historically known as Spalato (; ; see other names), is the second-largest city of Croatia after the capital Zagreb, the largest city in Dalmatia and the largest city on the Croatian coast. The Split metropolitan area is home to a ...
in July, but it never reached Thomas.
As it facilitated alliances with Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
rulers and came along with Western cultural influences (in art
Art is a diverse range of cultural activity centered around ''works'' utilizing creative or imaginative talents, which are expected to evoke a worthwhile experience, generally through an expression of emotional power, conceptual ideas, tec ...
, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
and fashion
Fashion is a term used interchangeably to describe the creation of clothing, footwear, Fashion accessory, accessories, cosmetics, and jewellery of different cultural aesthetics and their mix and match into Clothing, outfits that depict distinct ...
) that penetrated Bosnia, Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
became the preferable faith early in Thomas' reign. Many Bosnian noblemen followed the King's example in converting to Catholicism, but some soon returned to the Bosnian Church; Kosača wrote that he considered conversion, but never went through with it. Churches and Franciscan monasteries sprang up throughout Bosnia during Thomas' reign, some erected by the King himself. Despite his efforts to project an image of a good Catholic king, Thomas' religious policy was not initially so resolute. He continued honoring Bosnian Christians and their clergy as his predecessors had done, which led to disputes with local Franciscans. Pope Eugene agreed that, for political reasons, King Thomas had to tolerate heretics.
Peak
Peace brought unusual stability to Bosnia as well as security to Thomas. He retook Srebrenica once again in the autumn of 1446, and eventually struck a short-lived compromise with Branković by which the two would share the town and its mining revenues. It was not to last, however. Unfounded rumour had it that Hungarian noblemen considered offering theHoly Crown of Hungary
The Holy Crown of Hungary ( , ), also known as the Crown of Saint Stephen, named in honour of Saint Stephen I of Hungary, was the coronation crown used by the Kingdom of Hungary for most of its existence; kings were crowned with it since the tw ...
to him, which testified to his growing reputation. The Ottomans, who wanted to weaken Bosnia by encouraging internal division, were very displeased by the kingdom's stability. At the request of Đurađ Branković, the Turks broke into both King Thomas' personal lands, and those of his father-in-law, in March 1448, plundering and burning towns. Kosača, who now called himself "''Herzog
(; feminine ; masculine plural ; feminine plural ) is a German hereditary title held by one who rules a territorial duchy, exercises feudal authority over an estate called a duchy, or possesses a right by law or tradition to be referred to ...
'' of Saint Sava
Saint Sava (, ; Old Church Slavonic: ; Glagolitic: ; ; 1169 or 1174 – 14 January 1235/6), known as the Enlightener or the Illuminator, was a Serbs, Serbian prince and Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox monk, abbot of Studenica Monastery, Studeni ...
", was thus forced to side with Branković against his son-in-law and king. In mid-September, Branković's brother-in-law Thomas Kantakouzenos, leading an army that included Kosača himself, soundly defeated King Thomas.
King Thomas reconquered Srebrenica again in February 1449, but hostilities continued until 1451, when the King made peace again with his insubordinate father-in-law. The dispute was even taken before the Diet of Hungary
The Diet of Hungary or originally: Parlamentum Publicum / Parlamentum Generale () was the most important political assembly in Hungary since the 12th century, which emerged to the position of the supreme legislative institution in the Kingdom ...
. To finance this incessant warfare, as well as to sustain the royal court, King Thomas engaged in vigorous commerce and made business deals with Dalmatian traders. He relied heavily on his silver mining, but profited most from his salt trade
A salt road (also known as a salt route, salt way, saltway, or salt trading route) refers to any of the prehistoric and historical trade routes by which essential salt was transported to regions that lacked it.
From the Bronze Age (in the 2nd m ...
monopolies.
In-laws' conflict
In 1451 when Kosača sought to improve his own economy through a war with the Republic of Ragusa, Thomas refused to join either side, but still interceded withPope Nicholas V
Pope Nicholas V (; ; 15 November 1397 – 24 March 1455), born Tommaso Parentucelli, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 6 March 1447 until his death in March 1455. Pope Eugene IV made him a Cardinal (Catholic Chu ...
to prevent his father-in-law's excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in Koinonia, communion with other members o ...
. However, Ragusa persisted and promised to return the favor by helping Thomas take Drijeva from Kosača, and Hodidjed from the Turks. In the summer, Thomas was even approached by Kosača's family, namely the King's brother-in-law Vladislav
Vladislav ( (', '); , ; Russian language, Russian, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, Bulgarian language, Bulgarian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, sh-Cyrl, Владислав, ) is a male given names, given name of Slavs, Slavic origin. Variatio ...
and mother-in-law Jelena, who were gravely offended when the Duke took his son's charming Sienese bride as his concubine. In mid-December, Thomas finally agreed with Ragusa on a pact against his infamous father-in-law, but the war ended abruptly when Hungary and the Ottomans signed a truce which specifically forbade the latter's tributary to attack Ragusa.
Open rebellion against Stjepan Kosača broke out in March 1452. Vladislav, along with his mother and grandmother, raised an army and took control over most of his father's territory. Thomas, Vladislav's king and brother-in-law, answered his call for help and arrived with his army the following month. Ragusa also joined them. However, King Thomas proved reluctant to attack and soon went back north to ward off a Turkish incursion. Kosača seized the opportunity to enlist help from Venice, which took Drijeva from Vladislav, and to entice uprisings against the rebels themselves. Thomas returned, as he had promised, chasing the Venetians from Drijeva and easily defeating his brother-in-law's enemies. The coalition then suddenly fell apart when it became clear that Vladislav would not hand over parts of his patrimony that Thomas claimed as his due, namely Drijeva and Blagaj, which was the Kosača seat and the key to Zachlumia.
New conflict emerged in 1453 upon the death of Petar Talovac, who had governed Croatia proper
In contemporary geography, the terms Central Croatia () and Mountainous Croatia () are used to describe most of the area sometimes historically known as Croatia or Croatia proper (), one of the four historical regions of the Republic of Croa ...
as ban on behalf of the Hungarian king. Both Thomas and his recently widowed father-in-law wished to gain control of Talovac's allodial land by offering marriage to his widow, Hedwig Garai; Kosača proposed himself, while Thomas suggested his son Stephen
Stephen or Steven is an English given name, first name. It is particularly significant to Christianity, Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is w ...
. Kosača invited Turks to Bosnia in autumn, but neither prevailed as Venice moved in to protect Talovac's heirs. They then made peace, realizing that the Ottomans, who had just stunned Europe by conquering Constantinople, would soon be at their gates as well. Another concern was the end of regency
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
for the hitherto underage Hungarian king Ladislaus the Posthumous
Ladislaus V, more commonly known as Ladislaus the Posthumous (; ; ; ; 22 February 144023 November 1457), was Duke of Austria and King of Hungary, King of Croatia, Croatia and King of Bohemia, Bohemia. He was the posthumous birth, posthumous son ...
, which decreased the influence of Thomas' friend János Hunyadi, and led to the rise of Ulrich of Celje, who was supported by Kosača. After Ladislaus made Ulrich the new Ban of Croatia, the latter started seizing control of Croatian towns, which met strong opposition from Thomas. The Bosnian king feared that Ulrich would take Talovac's land and have his territory border Kosača's. Not wishing to break peace with his father-in-law yet again, the King turned to Venice for help.
Christian coalition
 The Holy See put King Thomas under its protection in 1455, and promised that he would be given back the lands taken by Turks and his treacherous magnates if the Christians defeated the Ottomans. In 1456, Thomas sent a letter to
The Holy See put King Thomas under its protection in 1455, and promised that he would be given back the lands taken by Turks and his treacherous magnates if the Christians defeated the Ottomans. In 1456, Thomas sent a letter to Pope Callixtus III
Pope Callixtus III (, , ; 31 December 1378 – 6 August 1458), born Alonso de Borja (), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 April 1455 to his death, in August 1458.
Borgia spent his early career as a professor ...
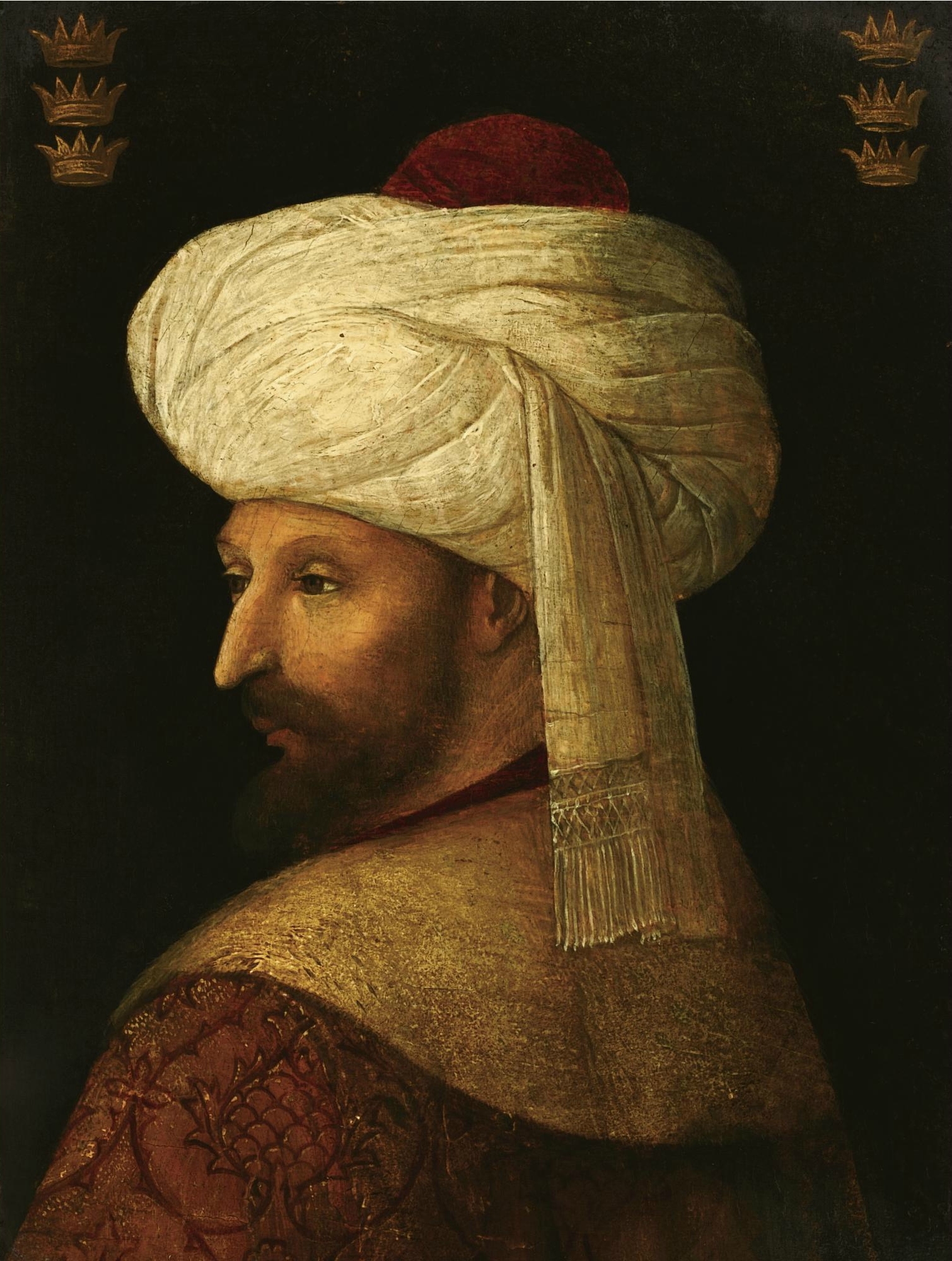
asking him to find a bride for his son Stephen, hoping that the Holy See would provide him with a daughter-in-law of royal blood. Preparations were under way for another Ottoman attack on Hungary in the beginning of that year. Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II (; , ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror (; ), was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from August 1444 to September 1446 and then later from February 1451 to May 1481.
In Mehmed II's first reign, ...
, the Ottoman sultan, issued unusual demands to the King of Bosnia and his nobles, the Kosačas and the Pavlović family. He asked Thomas to send 10,000 loads of food, his father-in-law 8,000 and Petar Pavlović 4,000. Mehmed also demanded that they commit their troops and personally take part in the war on the Ottoman side. He also requested from Thomas the cession of four towns: two in the middle of Bosnia and two bordering Hungary and Venetian Dalmatia
Venetian Dalmatia () refers to the territories of Dalmatia under the rule of the Republic of Venice, mainly from the 15th to the 18th centuries. Dalmatia was first sold to Venice in 1409 but Venetian Dalmatia was not fully consolidated until 1420, ...
. This was all refused.
By now Thomas suspected that Mehmed also intended to conquer his kingdom. Therefore, he started taking more interest in a Christian coalition against the Turks, and cooperating more closely with his father-in-law. The lack of a firmer action against the Ottomans was blamed on Bosnian Christians, whom he described as being more inclined towards the Muslims than towards other Christians. The heavy Ottoman defeat by Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
and Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
at the Battle of Belgrade in July 1456 did nothing to alleviate Thomas' situation, as Mehmed started exerting an even greater pressure on Bosnia. In addition to financial extortion, Thomas was now forbidden to export silver, which Mehmed claimed for himself. This severe crippling of the Bosnian economy suffocated the kingdom.
Đurađ Branković
Đurađ Vuković Branković ( sr-Cyrl, Ђурађ Вуковић Бранковић, ; 1377 – 24 December 1456) served as the Serbian Despot from 1427 to 1456, making him one of the final rulers of medieval Serbia.
In 1429, Branković was form ...
also died, his despotate
Despot or ''despotes'' () was a senior Byzantine court title that was bestowed on the sons or sons-in-law of reigning emperors, and initially denoted the heir-apparent of the Byzantine emperor.
From Byzantium it spread throughout the late medi ...
passing to his son Lazar Branković
Lazar Branković ( sr-cyr, Лазар Бранковић; – 20 February 1458) was Despot of Serbia from 1456 to 1458. He was the third son of Despot Đurađ Branković and his wife, Eirene Kantakouzene. He died without sons, and was succeed ...
. Realizing that Hungary was drastically weakened, and that he had crossed the point of no return by refusing the Sultan's demands, Thomas decided to step forward to head the Christian coalition. In August 1456, Ragusa received an information from the King in the utmost secrecy: he was intent on declaring war on the Turks. He was far from capable of succeeding, and even suffered a Turkish raid in the beginning of 1457.
Pope Callixtus III took King Thomas very seriously: he ordered that the King of Bosnia be handed the Crusaders' cross, the papal flag and the crusading fund, marking him as the leader of the coalition in July 1457. However, Thomas relied not on his own dubious strength, but on the assistance of Western rulers. His emissaries to King Alfonso V of Aragon
Alfonso the Magnanimous (Alfons el Magnànim in Catalan language, Catalan) (139627 June 1458) was King of Aragon and King of Sicily (as Alfons V) and the ruler of the Crown of Aragon from 1416 and King of Naples (as Alfons I) from 1442 until his ...
, Doge Francesco Foscari
Francesco Foscari (19 June 1373 – 1 November 1457) was the 65th Doge of the Republic of Venice from 1423 to 1457. His reign, the longest of all Doges in Venetian history, lasted 34 years, 6 months and 8 days, and coincided with the inception ...
of Venice, Duke Francesco I Sforza
Francesco I Sforza (; 23 July 1401 – 8 March 1466) was an Italian condottiero who founded the Sforza dynasty in the duchy of Milan, ruling as its (fourth) Duke of Milan, duke from 1450 until his death.
In the 1420s, he participated in the ...
of Milan, and Duke Philip the Good
Philip III the Good (; ; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) ruled as Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death in 1467. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonged. During his reign, ...
of Burgundy all reported refusals of help. Cardinal Carvajal was sent to Bosnia to meet with King Thomas. Cardinal Giovanni Castiglione sceptically wrote that Carvajal would have been better off if he had stayed in Buda
Buda (, ) is the part of Budapest, the capital city of Hungary, that lies on the western bank of the Danube. Historically, “Buda” referred only to the royal walled city on Castle Hill (), which was constructed by Béla IV between 1247 and ...
. Indeed, Carvajal found Thomas ill-equipped to deal with the enemy. The Pope became disillusioned with him, and transferred the leadership of the Christian coalition to the Albanian lord Skanderbeg
Gjergj Kastrioti (17 January 1468), commonly known as Skanderbeg, was an Albanians, Albanian Albanian nobility, feudal lord and military commander who led Skanderbeg's rebellion, a rebellion against the Ottoman Empire in what is today Albania, ...
.
Fall into disrepute
Expansion efforts
The ultimately failed crusading efforts did not preclude Thomas from seeking expansion. The death of the heirless Ulrich of Celje reopened the possibility of seizing Talovac lands, but his father-in-law moved more quickly, leading to a new brief cooling in their relations. However, in January 1458 a new opportunity arose on Bosnia's eastern border. The turmoil that followed the death of Lazar Branković enabled Thomas to retake the formerly Bosnian part of theDrina
The Drina ( sr-Cyrl, Дрина, ) is a long river in the Balkans, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Al ...
River valley, conquered by Lazar's father in the preceding decade, as well as to expand into its right bank. Thomas captured a total of eleven towns, keeping Srebrenica, Zvornik
Zvornik ( sr-cyrl, Зворник, ) is a city in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. In 2013, it had a population of 58,856 inhabitants. Zvornik is located on the Drina River, on the eastern slopes of Majevica mountain, at the altitude of ...
and Teočak
Teočak ( sr-cyrl, Теочак) is a municipality located in Tuzla Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The center of the municipality is the village of Teočak-Krstac.
Geography
The municipali ...
for himself, and distributing the rest among the local nobility who swore fealty to him. He then turned his attention back to Croatia. He suggested to Venice that since the Hungarians had not yet appointed a new ban of Croatia
Ban of Croatia () was the title of local rulers or office holders and after 1102, viceroys of Croatia. From the earliest periods of the Croatian state, some provinces were ruled by Ban (title), bans as a ruler's representative (viceroy) and sup ...
, he and the Republic should split the banate among themselves. In June, he warned Venice that the new Hungarian king Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus (; ; ; ; ; ) was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia from 1458 to 1490, as Matthias I. He is often given the epithet "the Just". After conducting several military campaigns, he was elected King of Bohemia in 1469 and ...
, Hunyadi's son, would not be a good neighbour to either Bosnia or Venice if he took hold of Croatia.
 A large Turkish raid in February 1458 forced Thomas to sign a truce, despite his earlier crusading vows, but Mehmed no longer insisted on the cession of the four towns; he intended to conquer Serbia instead. At that time, King Thomas dropped the plan of having his son marry an illegitimate daughter of Francesco Sforza; the match with a bastard daughter of a duke was far beneath the King's expectations for Stephen. Instead, he successfully negotiated with Lazar's widow, the Byzantine princess
A large Turkish raid in February 1458 forced Thomas to sign a truce, despite his earlier crusading vows, but Mehmed no longer insisted on the cession of the four towns; he intended to conquer Serbia instead. At that time, King Thomas dropped the plan of having his son marry an illegitimate daughter of Francesco Sforza; the match with a bastard daughter of a duke was far beneath the King's expectations for Stephen. Instead, he successfully negotiated with Lazar's widow, the Byzantine princess Helena Palaiologina
Helena Palaiologina (; 3 February 1428 – 11 April 1458) was a Byzantine princess of the Palaiologos family, who became Queen of Cyprus and Armenia, titular Queen consort of Jerusalem, and Princess of Antioch through her marriage to King John ...
, about a marriage between Stephen and her oldest daughter, Helena
Helena may refer to:
People
*Helena (given name), a given name (including a list of people and characters with the name)
*Katri Helena (born 1945), Finnish singer
* Saint Helena (disambiguation), this includes places
Places
Greece
* Helena ...
. That way Thomas procured not only a daughter-in-law of imperial blood, but also found a way to extend the Kotromanić rule to the Despotate of Serbia, now reduced to the Smederevo Fortress
The Smederevo Fortress () is a medieval fortified city in Smederevo, Serbia, which was the temporary capital of Serbia in the Middle Ages. It was built between 1427 and 1430 on the order of Despot Đurađ Branković, the ruler of the Serbian De ...
and its surroundings, as Lazar had left no sons.
Thomas sent word of the plans to King Matthias, his feudal overlord, in October. In early December, Thomas himself went to meet Matthias at a diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
in Szeged
Szeged ( , ; see also #Etymology, other alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat ...
. Matthias was thrilled and urged Thomas to send his son as soon as possible. During Thomas' long absence, Turks broke into Bosnia and besieged Bobovac and Vranduk, but his son Stephen and brother Radivoj escaped. Thomas returned to Bosnia in mid-January 1459 and took up the fight against the attackers, even trying to eject them from Hodidjed. In mid-April, he raided the outskirts of Hodidjed and besieged the fort.
Meanwhile, Thomas' son had married Lazar's daughter and taken possession of Smederevo. Thomas boasted about his son being made despot, but the arrangement was cut short by the arrival of Mehmed at the head of a vast force before the walls of Smederevo. Terrified, Thomas' son and brother agreed to surrender the town and fortress on 20 June in exchange for safe conduct
Safe conduct, safe passage, or letters of transit, is the situation in time of international conflict or war where one state, a party to such conflict, issues to a person (usually, an enemy state's subject) a pass or document to allow the enemy ...
. Thomas and Radivoj were bitterly reproached by the Hungarian king. Matthias told all Europe that Thomas had sold the fortress of paramount importance to the enemy. Thomas took great pains to clear his name, explaining to Pope Pius II
Pope Pius II (, ), born Enea Silvio Bartolomeo Piccolomini (; 18 October 1405 – 14 August 1464), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 August 1458 to his death in 1464.
Aeneas Silvius was an author, diplomat, ...
that Smederevo could not have been defended. The King sent a delegation to the Council of Mantua in July, promising to do his best to hold the Turks back and begging for help. The only ruler to provide assistance to Thomas was Bianca Maria Visconti
Bianca Maria Visconti (31 March 1425 – 28 October 1468) also known as Bianca Maria Sforza or Blanca Maria was Duchess of Milan from 1450 to 1468 by marriage to Francesco I Sforza. She was regent of Marche during the absence of her spouse in 14 ...
, Duchess of Milan, who sent 300 men via Ancona
Ancona (, also ; ) is a city and a seaport in the Marche region of central Italy, with a population of around 101,997 . Ancona is the capital of the province of Ancona, homonymous province and of the region. The city is located northeast of Ro ...
.
Religious persecution
Unlike in other Balkan states of the time, the politics of Bosnia were not dominated by religion, and its rulers as well as the common people were entirely indifferent to the religious beliefs of others. However, this changed in 1459 when the Ottoman threat became greater. Pope Pius II informed Thomas that he would not come to his aid as long as the Bosnian Church was tolerated. Thomas was anxious to appear as a good Catholic in the wake of Hungarian accusations of betraying theChristendom
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which Christianity is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christen ...
.
The decision Thomas took in 1459 made him the first Bosnian ruler to persecute people for their religious beliefs, a policy popes had long demanded by the Holy See. The Bosnian Church had been decimated by Catholic, and then even Orthodox, proselytization and its own low morale. Thomas' order that its clergy either convert or leave his domain was followed by confiscation of their considerable property, which probably helped him make the otherwise difficult decision. The persecution lasted almost two years. 12,000 people were forcefully converted, while forty members of the clergy fled to his father-in-law's domain. In 1461, he sent three men accused of heresy to be questioned by Cardinal Juan de Torquemada in Rome. The Bosnian Church was thus all but annihilated by King Thomas.
The persecution did little to restore Thomas' reputation in Catholic Europe. When possession of the formerly Talovac-held Čačvina Castle
Čačvina is a settlement (Croatia), settlement in the Cities of Croatia, City of Trilj in Croatia. In 2021, its population was 59.
Geography
Čačvina is located on the edge of a small karst field at an altitude of 683 meters along the Trilj� ...
caused another feud with his father-in-law in 1459, Kosača accused him of having invited the Turks who plundered his land. The accusation reached Pope Pius, who ordered that the King be excommunicated if such a grave offense against Christian interests were proven. Though Thomas probably did invite the Turkish raiders, the excommunication never took place.
Last years
 The fall of Serbia meant that the eastern border of Thomas' realm was now the bulwark of Christendom. However, Bosnia was not Mehmed's priority. Thomas was forced to surrender northeastern Bosnia, namely Usora, Srebrenica, Zvornik and Teočak, in early 1460, allowing the Turks to cross the
The fall of Serbia meant that the eastern border of Thomas' realm was now the bulwark of Christendom. However, Bosnia was not Mehmed's priority. Thomas was forced to surrender northeastern Bosnia, namely Usora, Srebrenica, Zvornik and Teočak, in early 1460, allowing the Turks to cross the Sava
The Sava, is a river in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. From its source in Slovenia it flows through Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally reac ...
to the Hungarian regions of Slavonia
Slavonia (; ) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria County, Istria, one of the four Regions of Croatia, historical regions of Croatia. Located in the Pannonian Plain and taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with f ...
and Syrmia
Syrmia (Ekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srem, Срем, separator=" / " or Ijekavian sh-Latn-Cyrl, Srijem, Сријем, label=none, separator=" / ") is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is div ...
. Both Thomas and his father-in-law were aware that the Ottoman conquest of Bosnia
The Ottoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina was a process that started roughly in 1386, when the first Ottoman attacks on the Kingdom of Bosnia took place. In 1451, more than 65 years after its initial attacks, the Ottoman Empire officially es ...
was inevitable. They continued to seek foreign assistance, but were also preparing for a life in exile. However, this prospect did not help them settle their differences and put up a more effective defence.
Thomas, still estranged from his in-laws, fell ill in June 1461 and requested a physician from Ragusa. He died in July, aged around 50. He was buried in the royal mausoleum in Bobovac.
The circumstances of his death are unclear. Rumours circulated, first recorded by a gunsmith from Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
, that the King's death was not natural. Specifically, it was said that his brother Radivoj and son Stephen had conspired against him. Later narratives also involved Mehmed and Matthias in the plot, with the Hungarian king as the mastermind. These rumours are generally dismissed by historians. Stephen succeeded him, to the benefit of the doomed kingdom, as the ruptures between the monarch and his nobles were finally healed.
Personality and legacy
 Thomas was a man of many contradictions. His good looks and noble comportment greatly impressed his contemporaries. The Italian
Thomas was a man of many contradictions. His good looks and noble comportment greatly impressed his contemporaries. The Italian condottiero
Condottieri (; singular: ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian military leaders active during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The term originally referred specifically to commanders of mercenary companies, derived from the ...
Gaspare Broglio da Lavello (son of Angelo Tartaglia), whom he met in 1452, wrote that he had never met a prince more refined and dignified, surpassing even the intellectual humanist Federico da Montefeltro
Federico da Montefeltro, also known as Federico III da Montefeltro Order of the Garter, KG (7 June 1422 – 10 September 1482), was one of the most successful mercenary captains (''condottiero, condottieri'') of the Italian Renaissance, and Duk ...
, Broglio's idol. At the same time, Thomas' inconstancy and lack of courage inspired disdain. He was capable of both great generosity and pettiness. Fickleness damaged his reputation abroad, while religious persecution and forced conversions caused disapproval at home; he was cursed in the early years of the Ottoman rule for robbing the indigenous Bosnian Church of its property.
Thomas' union with Vojača produced at least four children: Stephen (who succeeded him), a son who died as a child during a pilgrimage to Meleda, a daughter who married a Hungarian nobleman in 1451, and another daughter who married in 1451. With Catherine, who outlived both him and his kingdom, Thomas had a son named Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it ''Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
in 1449 and a daughter named Catherine
Katherine (), also spelled Catherine and Catherina, other variations, is a feminine given name. The name and its variants are popular in countries where large Christian populations exist, because of its associations with one of the earliest Ch ...
in 1453.
Family tree
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * {{Authority control Bosnian monarchs 15th-century births 1461 deaths Kotromanić dynasty Converts to Roman Catholicism from the Bosnian Church Bosnia and Herzegovina Roman Catholics Roman Catholic monarchs 15th-century Bosnian people Year of birth unknown Year of birth uncertain Kings of Bosnia