Isleworth map on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Isleworth ( ) is a suburban town in the
Isleworth ( ) is a suburban town in the

This infirmary functioned until 1920, when it became 'West Middlesex Hospital'. In 1931 it was upgraded to a county hospital, but in 1948 (under the NHS) 'County' was dropped from its title. It later became a
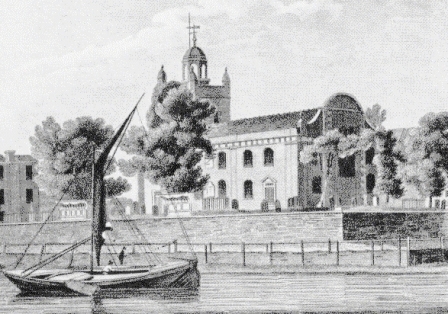
 All Saints' Church, Isleworth is the ancient parish church for the area. Others include:
* St Francis of Assisi Church
* St Bridget's RC Church
* St John's Church
* St Mary's Church
* St Mary the Virgin Church
* Isleworth
All Saints' Church, Isleworth is the ancient parish church for the area. Others include:
* St Francis of Assisi Church
* St Bridget's RC Church
* St John's Church
* St Mary's Church
* St Mary the Virgin Church
* Isleworth
Joseph banks.jpg, Sir Joseph Banks
Banks' house.jpg, Banks' house, known as Spring Grove House
Spring Grove House 18th Century.jpg, Spring Grove House in the 18th century
Pears House full west front 1902.jpg, Spring Grove House in 1902
VanGogh 1887 Selbstbildnis.jpg, Vincent van Gogh, painted by himself ten years after residing in Isleworth
Turner selfportrait.jpg, J. M. W. Turner
*Peter Oliver (painter), Peter Oliver (1594–1648), watercolour copyist and miniature portrait artist, lived in his native Isleworth. He painted many figures at the courts of Kings King James I of England, James I and King Charles I of England, Charles I.
*Marina Dellap was a resident of Isleworth in 1765. She was enslaved and lived in the home of Mrs Dellap near All Saints’ Church in Isleworth. She ran away on 26 May 1765. Marina was in her 20s, had arrived from Jamaica about a year before, spoke English and had a child. She was a skilled seamstress. It is likely that Marina arrived in England with Elizabeth Bouffan after the death of her husband Alexander Dellap, with whom they lived in Saint Catherine Parish, St Catherine, Jamaica.
*Prince was a resident of Isleworth in 1765. He was enslaved by a merchant called Mr Shea. Prince was aged 24, from Guinea and a musician who played the French horn. Prince ran away from Mr Shea on 13 August 1765 and is likely to have known Marina Dellap. She was seen with someone matching Prince’s description (wearing an old brown livery coat turned up with red).
*In 1779, Joseph Banks, Sir Joseph Banks, botanist, took a lease on, and eventually bought, a house with along the northern side of what is now London Road. It became known as "Spring Grove House". Although he also had a home in central London, he spent much time and effort on his Isleworth property. He steadily created a renowned botanical masterpiece on the estate, achieved primarily with many of the great variety of foreign plants he had collected on his great travels around the world, particularly with Captain Cook to Australia and the South Seas. Banks died in 1820, and over the next thirty years the house was considerably modified and enlarged by a new owner, Henry Pownall, who then sold the estate in 1850 for partial redevelopment.
*In 1804, J. M. W. Turner lived for a short time in Sion Ferry House in Isleworth, where he drew inspiration from the picturesque banks of the River Thames. His paintings thereafter include the Palace of Westminster, Houses of Parliament and
 A period of intense mansion-building occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries. There was a triple attraction to the area in those times. Its rural, waterside beauty had become well recognised over two hundred years or so, and a few palaces, monasteries and mansions already existed. Then the royal court began to appear at Kew, so the adjacent districts on both sides of the Thames became very fashionable places for the rich and famous to build their grand homes. Some of the cachet dropped away when the court eventually left Kew; most high-quality here survived well The Blitz and social turmoil to enable many to reach grade II* (the mid category) of architectural listed building.
* Syon House Duke of Somerset Duke of Northumberland. (standing, listed Grade 1) Although this grand house has had a close connection with Isleworth for 450 years, it has very grand architecture as the only non-royal ducal main home ('family seat, seat') in
A period of intense mansion-building occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries. There was a triple attraction to the area in those times. Its rural, waterside beauty had become well recognised over two hundred years or so, and a few palaces, monasteries and mansions already existed. Then the royal court began to appear at Kew, so the adjacent districts on both sides of the Thames became very fashionable places for the rich and famous to build their grand homes. Some of the cachet dropped away when the court eventually left Kew; most high-quality here survived well The Blitz and social turmoil to enable many to reach grade II* (the mid category) of architectural listed building.
* Syon House Duke of Somerset Duke of Northumberland. (standing, listed Grade 1) Although this grand house has had a close connection with Isleworth for 450 years, it has very grand architecture as the only non-royal ducal main home ('family seat, seat') in  *Silver Hall No. 1 ''(South of North Street, with four acres)'' [1.6 hectares] Sir John Smith Bt, Privy to William & Mary Lady Harcourt, widow of Sir W Harcourt, Chancellor (Demolished 1801)'And So Make a City Here' by G E Bate F.R.Hist.S. p121 published: Thomasons Hounslow 1948
*Silver Hall No. 2 ''(North of North Street)'' Joseph Dixon. (Demolished 1950)
* Kendal House. ''(Twickenham Road, near Mill Plat)'' Duchess of Kendal (mistress to George I).
*Somerset House
*Gunnersbury House. ''(At the junction of Bridge Road and London Road)'' (Demolished c. 1972).
*Silver Hall No. 1 ''(South of North Street, with four acres)'' [1.6 hectares] Sir John Smith Bt, Privy to William & Mary Lady Harcourt, widow of Sir W Harcourt, Chancellor (Demolished 1801)'And So Make a City Here' by G E Bate F.R.Hist.S. p121 published: Thomasons Hounslow 1948
*Silver Hall No. 2 ''(North of North Street)'' Joseph Dixon. (Demolished 1950)
* Kendal House. ''(Twickenham Road, near Mill Plat)'' Duchess of Kendal (mistress to George I).
*Somerset House
*Gunnersbury House. ''(At the junction of Bridge Road and London Road)'' (Demolished c. 1972).
*Isleworth House Sir William Cooper, chaplain to George III. Renamed Nazareth House in 1892 when it was established as the present residential nursing home and convent. (standing) *Countess of Charleville's Villa Harriet Charlotte Beaujolais (Campbell), Countess of Charleville. *Wyke House *Little Syon (formerly Cromwell House) Sir Richard Wynn Bt. (Demolished 1818). *Gumley House John Gumley (Commissary-General to the Army) William Pulteney, 1st Earl of Bath, The Earl of Bath (Gumley's son-in-law) General Lord Lake.
*Shrewsbury House George Talbot, 14th Earl of Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury House lay to the east of Upper Square, in the area known as Lion Wharf, once Beck's Wharf, also Shrewsbury Wharf. The 14th Earl inherited the lease in 1719 and later by Act of Parliament gained full rights to the property (in exchange for certain fee-farm rents) from an almshouse charity established by a former landlord, Sir Thomas Ingram, from whom the 1st Duke of Shrewsbury had originally leased the site. Around 1778 the 14th Earl started the process by which the house converted to a school for boys of Roman Catholic parents.
*Gumley House John Gumley (Commissary-General to the Army) William Pulteney, 1st Earl of Bath, The Earl of Bath (Gumley's son-in-law) General Lord Lake.
*Shrewsbury House George Talbot, 14th Earl of Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury House lay to the east of Upper Square, in the area known as Lion Wharf, once Beck's Wharf, also Shrewsbury Wharf. The 14th Earl inherited the lease in 1719 and later by Act of Parliament gained full rights to the property (in exchange for certain fee-farm rents) from an almshouse charity established by a former landlord, Sir Thomas Ingram, from whom the 1st Duke of Shrewsbury had originally leased the site. Around 1778 the 14th Earl started the process by which the house converted to a school for boys of Roman Catholic parents.
 *Gordon House, by the River Thames at Railshead Rd. (standing, listed Grade II*). General Humphrey Bland Lord James Hay Lord John Kennedy-Erskine. Lord and Lady Frederick Gordon Earl of Kilmorey Judge T C Haliburton MP. In Lord Hay's time this was named 'Seaton House', after his ancestral home in Aberdeenshire. It was next bought by King William IV at 8,000 guineas for his (illegitimate) daughter Lady Augusta, who married Lord John Kennedy-Erskine of Dun, the son of the First Marquis of Ailsa who lived next door in St Margaret's House. Gordon House is being renovated.
*Spring Grove House Sir Joseph Banks Andrew Pears. (standing, Grade II)
: In 1862 Francis Pears decided to expand his Pears soap, soap making business and bought land alongside the London Road for a factory. Another, larger, factory was opened along the opposite side of the road in the 1880s and soap was made on the site until 1962. His son Andrew bought the Spring Grove House estate in 1886 and greatly extended the house in 1894. ''Pictures are shown under 'Notable residents'.''
*Keppel House Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel, First Lord of the Admiralty Augustus Keppel.
*Lacy House A 17th-century house rebuilt in 1750 for James Lacy (actor), James Lacy, of Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, Drury Lane Theatre.
*Gordon House, by the River Thames at Railshead Rd. (standing, listed Grade II*). General Humphrey Bland Lord James Hay Lord John Kennedy-Erskine. Lord and Lady Frederick Gordon Earl of Kilmorey Judge T C Haliburton MP. In Lord Hay's time this was named 'Seaton House', after his ancestral home in Aberdeenshire. It was next bought by King William IV at 8,000 guineas for his (illegitimate) daughter Lady Augusta, who married Lord John Kennedy-Erskine of Dun, the son of the First Marquis of Ailsa who lived next door in St Margaret's House. Gordon House is being renovated.
*Spring Grove House Sir Joseph Banks Andrew Pears. (standing, Grade II)
: In 1862 Francis Pears decided to expand his Pears soap, soap making business and bought land alongside the London Road for a factory. Another, larger, factory was opened along the opposite side of the road in the 1880s and soap was made on the site until 1962. His son Andrew bought the Spring Grove House estate in 1886 and greatly extended the house in 1894. ''Pictures are shown under 'Notable residents'.''
*Keppel House Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel, First Lord of the Admiralty Augustus Keppel.
*Lacy House A 17th-century house rebuilt in 1750 for James Lacy (actor), James Lacy, of Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, Drury Lane Theatre.
Lacy's son inherited the property but his extravagance compelled him to sell the house, to the Hon. Sir Edward Walpole K.B. He bequeathed it to his daughter, widow of Bishop of Exeter, and after that it was acquired by the Earl of Warwick. After him came the famous playwright Richard Sheridan, who by then had already produced his two masterpieces ''School for Scandal'' and ''The Rivals''. Lacy House was demolished in the 1830s. *St Margaret's House (Lacy House rebuilt and renamed) First Marquis of Ailsa. *Kilmorey House (replaced St Margarets House in 1853). Built for 2nd Earl of Kilmorey but never lived in. Became the Royal Naval School for Girls (1856–1940). (Demolished 1950).
File:The Duke of Northumberland's River - geograph.org.uk - 21939.jpg, Parkland section of the Duke of Northumberland's River
File:St Mary, Osterley Road, Isleworth, TW7 - geograph.org.uk - 1570544.jpg, St Mary's Church, Osterley Road
File:Great West Road, London TW7 - geograph.org.uk - 1058158.jpg, Great West Road near the Gillette Tower, Gillette Corner
File:Syon mono small 1783.jpg, Syon House, Isleworth and partly in Brentford, in 1783
File:Little Syon.jpg, Little Syon in 1802 ''(Built 1592)''
File:Somerset House Isleworth.jpg, Somerset House in 1800
File:Shrewsbury House.jpg, Shrewsbury House
File:Lacy House.jpg, Lacy House, late 18th century
Hounslow Council
{{Authority control Isleworth, Areas of London Districts of the London Borough of Hounslow Districts of London on the River Thames Places formerly in Middlesex
 Isleworth ( ) is a suburban town in the
Isleworth ( ) is a suburban town in the London Borough of Hounslow
The London Borough of Hounslow ( ) is a London borough in west London, England, forming part of Outer London. It is governed by Hounslow London Borough Council.
The borough stretches from near Central London in the east (Chiswick) to the b ...
, West London, England.
It lies immediately east of Hounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
and west of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
and its tributary the River Crane. Isleworth's original area of settlement, alongside the Thames, is known as Old Isleworth. The northwest corner of the town, bordering on Osterley
Osterley ( ) is an affluent district of Isleworth in west London, England, from Charing Cross in the London Borough of Hounslow. Most of its land use is mixed agricultural and aesthetic parkland at Osterley House (National Trust), charity-r ...
to the north and Lampton to the west, is known as Spring Grove.
Isleworth's former Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after th ...
frontage of approximately one mile, excluding that of the Syon Park estate, was reduced to little over half a mile in 1994 when a borough boundary realignment was effected in order to unite the district of St Margaret's wholly within London Borough of Richmond upon Thames
The London Borough of Richmond upon Thames () in south-west Greater London, London, England, forms part of Outer London and is the only London boroughs, London borough on both sides of the River Thames. It was created in 1965 when three smaller ...
. As a result, most of Isleworth's riverside is that part overlooking the islet of Isleworth Ait: the short-length River Crane flows into the Thames south of the Isleworth Ait, and its artificial distributary the Duke of Northumberland's River
The Duke of Northumberland's River or D. O. N. River consists of separate upper and lower Canal, artificial watercourses in west London, United Kingdom. The older name Isleworth Mill Stream/River more accurately describes the economic motivati ...
west of the Isleworth Ait, one of two Colne
Colne () is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Borough of Pendle in Lancashire, England. The town is northeast of Nelson, Lancashire, Nelson, northeast of Burnley and east of Preston, Lancashire, Preston.
The ...
distributaries constructed for aesthetic reasons between 1600 and 1750.
Etymology
History
Roman and Anglo Saxon
Excavations around the eastern end of the Syon Park estate have unearthed evidence of a Romano-British settlement. 'Gislheresuuyrth', meaning inOld English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
''Enclosure belonging to man calledGīslhere'', is first referred to as a permanent settlement in an Anglo-Saxon charter in the year 695. The Domesday Book says that during the reign (1042–1066) of Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was King of England from 1042 until his death in 1066. He was the last reigning monarch of the House of Wessex.
Edward was the son of Æthelred the Unready and Emma of Normandy. He succeede ...
the manor belonged to "Earl Algar" (probably Ælfgar of Mercia), and a modern road off South St today carries his name.'And So Make a City Here' by G E Bate F.R.Hist.S. p68 published: Thomasons Hounslow 1948
Granted to St Valeri Barons
Isleworth was a well-cultivated farming and trading settlement, more valuable than many of its neighbours, stretching from theMiddlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, former county in South East England, now mainly within Greater London. Its boundaries largely followed three rivers: the River Thames, Thames in the south, the River Lea, Le ...
bank of the River Thames west to the centre of Hounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
(including the land of later Hounslow Priory) and as far as the borders of Southall (in Hayes parish at the time) at the time of the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
in 1066. The Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
(1086) as ''Gistelesworde'' records its 55 ploughlands, 118 households and amount rendered, £72 per year, to its feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring socie ...
overlords. After the Conquest, successive Norman barons of the St Valeri family held the manor of Isleworth but there is no evidence that they ever lived there – it being held as a source of revenue and power. One of the later barons gave several manorial rents and privileges to London's Hospital of St Giles. He also gave the church and advowson to the Abbey of St Valeri, which stood at the mouth of the Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
* Somme, Queensland, Australia
* Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), ...
in Picardy
Picardy (; Picard language, Picard and , , ) is a historical and cultural territory and a former regions of France, administrative region located in northern France. The first mentions of this province date back to the Middle Ages: it gained it ...
.
Transfer to Earldom of Cornwall
In 1227, when he took control of England from his childhood regents, Henry III seized Isleworth and other property of the St Valeri family and gave the manor to his brother,Richard, 1st Earl of Cornwall
Richard (5 January 1209 – 2 April 1272) was an English prince who was King of the Romans from 1257 until his death in 1272. He was the second son of John, King of England, and Isabella, Countess of Angoulême. Richard was nominal Count of P ...
. He built a new moated manor house, which is described in the Black Book of the Exchequer – having a tiled roof, chimney, two bedchambers and an inner courtyard. Beyond the moat was an outer courtyard with a number of buildings for servants and supplies, and a short distance away was a watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as mill (grinding), milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in ...
.
The exact location of this house is not recorded, but a report of an area long ago known as 'Moated Place' puts the likely place between the Northumberland Arms and Twickenham Road, with the watermill being near Railshead, on the River Crane (not where the traditional Isleworth mill 'Kidd's Mill', because the stream there is artificial and did not exist at that time). The seemingly classic medieval manor house was burned down during the Second Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in Kingdom of England, England between the forces of barons led by Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of Henry III of England, King Hen ...
in 1264.
Advowson, right to appoint the vicar
The Abbey of St Valeri in Picardy held the livings (benefice
A benefice () or living is a reward received in exchange for services rendered and as a retainer for future services. The Roman Empire used the Latin term as a benefit to an individual from the Empire for services rendered. Its use was adopted by ...
s) and revenues of several English parish church lands and, responding to growing disquiet over these foreign holdings, in 1391 it transferred those of Isleworth (for a fee) to William of Wykeham, who endowed them to Winchester College
Winchester College is an English Public school (United Kingdom), public school (a long-established fee-charging boarding school for pupils aged 13–18) with some provision for day school, day attendees, in Winchester, Hampshire, England. It wa ...
, which he founded. The Wardens and Scholars of Winchester College therefore became proprietors of productive rectory (which had glebe
A glebe (, also known as church furlong, rectory manor or parson's close(s)) is an area of land within an ecclesiastical parish used to support a parish priest. The land may be owned by the church, or its profits may be reserved to the church. ...
lands). This lasted for 150 years, then in 1543 King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement w ...
exchanged with Winchester certain manors elsewhere for five churches in Middlesex, including All Saints.
Four years later he gave the Isleworth rectory and advowson to the Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset
Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset, 1st Earl of Hertford, 1st Viscount Beauchamp (150022 January 1552) was an English nobleman and politician who served as Lord Protector of England from 1547 to 1549 during the minority of his nephew King E ...
, but they returned to the crown when the Duke was executed in 1552. Soon after, they were given to the Dean and Canons of St George's Chapel, Windsor
St George's Chapel, formally titled The King's Free Chapel of the College of St George, Windsor Castle, at Windsor Castle in England is a castle chapel built in the late-medieval Perpendicular Gothic style. It is a Royal Peculiar (a church und ...
, with whom they remain today. The castle-like stone church tower by the river remains from this period, see below.
Transfer of Manor to Syon Monastery
In 1415Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (1216–1281 ...
granted nuns from the Swedish Bridgettine order land on the bank of the Thames, in Twickenham parish opposite his new Sheen Palace, where they built their first house Syon Monastery
Syon Abbey , also called simply Syon, was a dual monastery of men and women of the Bridgettines, Bridgettine Order, although it only ever had abbesses during its existence. It was founded in 1415 and stood, until its demolition in the 16th cent ...
. In 1422 Henry V transferred ownership of Isleworth Manor from the Duchy of Cornwall
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between "sovereign ...
to Syon Monastery, which in 1431 selected a new location within their manor to rebuild their monastery. This is the site of the present Syon House.
Granted to Duke of Somerset
Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
demolished most of Syon Monastery after 1539 and the site and manor was granted to Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset
Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset, 1st Earl of Hertford, 1st Viscount Beauchamp (150022 January 1552) was an English nobleman and politician who served as Lord Protector of England from 1547 to 1549 during the minority of his nephew King E ...
. It was Seymour who built Syon House in 1548. Lady Jane Grey was taken from here to the Tower by Royal barge in anticipation of her being crowned Queen of England.
Acquired by Earl of Northumberland
Forty-six years later, in 1594 Queen Elizabeth I granted a lease of the manor of Syon toHenry Percy, 9th Earl of Northumberland
Henry Percy, 9th Earl of Northumberland, Order of the Garter, KG (27 April 1564 – 5 November 1632) was an English people, English nobleman. He was a grandee and one of the wealthiest peers of the court of Elizabeth I. Under James VI and I, Ja ...
on his marriage to Dorothy Devereux the younger daughter of Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex
Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex (16 September 1539 – 22 September 1576), was an English nobleman and general. From 1573 until his death he fought in Ireland in connection with the Plantations of Ireland, most notably the Rathlin Island ...
, who later received a grant of the freehold from King James I in 1604. It has remained in the possession of the Percy family, now the Dukedom of Northumberland, for over four hundred years. The Royalist army occupied the house during the Battle of Brentford in November 1642. Syon Park was rebuilt and landscaped by the Adam brothers and "Capability" Brown between 1766 and 1773. It became the new home of the Dukes of Northumberland
Duke of Northumberland is a noble title that has been created three times in English and British history, twice in the Peerage of England and once in the Peerage of Great Britain. The current holder of this title is Ralph Percy, 12th Duke of N ...
when Northumberland House
Northumberland House (also known as Suffolk House when owned by the Earls of Suffolk) was a large Jacobean architecture, Jacobean Townhouse (Great Britain), townhouse in London, so-called because it was, for most of its history, the London re ...
in the Strand was demolished in 1874.Georgian and Victorian times
Much of Isleworth became orchards in the 18th century (including part of Hugh Ronalds' renowned nursery), and then market gardens in the 19th century, supplying the London markets. Lower Square and Church Street still have buildings dating from the 18th and early 19th centuries. A striking element of this period was the establishment in Isleworth of many mansions and large houses, principally for aristocrats and high achievers. This phenomenon arose owing mainly to the collection of royal and noble residences and ecclesiastical establishments that already existed nearby. The subject is examined in depth in the "Notable houses" section. There is evidence of a Black community in Isleworth in the 18th century. This community was primarily made up of enslaved people of colour, from Africa, Asia or the Caribbean. Some of these people had fled from bondage and chose to seek their freedom in the streets of London. With very few exceptions, little is known about people of colour in 18th century London. However, as a result of contemporary sources like advertisements seeking the capture and return of runaway slaves, an insight can be gained into the lives of two people, Marina Dellap and Prince, who resided in the area in 1765.20th century
The first half of the 20th century for Isleworth generally was characterised by a very substantial amount of artisan and white-collar residential development throughout the town, at the expense of numerous market gardens. The former western area was ceded to the town and parish ofHounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
, which was invested as a civil parish in 1927. This period also included the building of several new factories and offices, mostly towards the north-east, up to the town's eastern boundary with New Brentford. This rapid spread of building transformed the nature of Isleworth's layout in the space of just fifty years, from an agrarian pattern to an urban one.
Isleworth's former Thames frontage of approximately one mile, excluding that of the Syon estate, which is shared with Brentford, was reduced to in 1994 when a borough boundary realignment was ordered by the UK's Local Government Minister to add land to the district of St Margarets, Twickenham.
Geography
Elevations range from in the northwest to by the Thames at the opposite extreme OD. The boundaries are longstanding, subject to twentieth-century western and southern circonscriptions: Isleworth is east of the town ofHounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
which has more retail and offices, in the borough of that name; west of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
; north of its tributary and the northern confluence of the Crane (before 1998 its southern channel); and south of the crest by the M4 motorway
The M4, originally the London-South Wales Motorway, is the third longest motorway in the United Kingdom, running from west London to southwest Wales. The English section to the Severn Bridge was constructed between 1961 and 1971; the Welsh ele ...
separating the Brent and Crane catchments. Half of the River Crane flows into the Thames south of the Ait, and its distributary
A distributary, or a distributary channel is a stream channel that branches off and flows a main stream channel. It is the opposite of a ''tributary'', a stream that flows another stream or river. Distributaries are a result of river bifurc ...
the Duke of Northumberland's River
The Duke of Northumberland's River or D. O. N. River consists of separate upper and lower Canal, artificial watercourses in west London, United Kingdom. The older name Isleworth Mill Stream/River more accurately describes the economic motivati ...
flows toward its midpoint from the west.
Amenities
Isleworth is home to Isleworth Crown Court whose original remit has been expanded to include judicial work formerly conducted at the Middlesex Crown Court; an extension to create six new courtrooms was completed in 2009. The town's municipal facilities include a public library, a public leisure centre with swimming pool, a gymnasium, four recreation grounds, and a town hall. There used to be a film studio in Worton Road, Isleworth. Known variously as Worton Hall Studios and Isleworth Studios, its most notable film was ''The African Queen'' (1951) starringHumphrey Bogart
Humphrey DeForest Bogart ( ; December 25, 1899 – January 14, 1957), nicknamed Bogie, was an American actor. His performances in classic Hollywood cinema made him an American cultural icon. In 1999, the American Film Institute selected Bogart ...
and Katharine Hepburn
Katharine Houghton Hepburn (May 12, 1907 – June 29, 2003) was an American actress whose Katharine Hepburn on screen and stage, career as a Golden Age of Hollywood, Hollywood leading lady spanned six decades. She was known for her headstrong ...
. After the Studio closed, the premises became a Mining Research Establishment for the National Coal Board
The National Coal Board (NCB) was the statutory corporation created to run the nationalised coal mining industry in the United Kingdom. Set up under the Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946, it took over the United Kingdom's collieries on "ve ...
. It is now an industrial estate.
Isleworth has been home to satellite television broadcaster Sky
The sky is an unobstructed view upward from the planetary surface, surface of the Earth. It includes the atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere and outer space. It may also be considered a place between the ground and outer space, thus distinct from ...
since its launch in 1989 by Rupert Murdoch
Keith Rupert Murdoch ( ; born 11 March 1931) is an Australian - American retired business magnate, investor, and media mogul. Through his company News Corp, he is the owner of hundreds of List of assets owned by News Corp, local, national, a ...
. Originally centred on Grant Way, the sprawling campus around Gillette Corner once took in New Horizons Court and is now the sole occupier of the Centaurs Business Park, with offices, studios, production space, research and development facilities, plus a dedicated energy centre including a wind turbine by Arup Associates
Arup Group Limited, trading as Arup, is a British multinational professional services firm headquartered in London that provides design, engineering, architecture, planning, and advisory services across every aspect of the built environment. ...
.
The Boat Cathja is moored in Old Isleworth. This is unique 38 metre barge which has been the home of a mental health charity since 1996. It helps mentally disabled people a chance to hone into their artistic skills. Situated on the boat is the Sculpture "The Heron" by Martin Cotts.
Isleworth was home to opera group ''Isleworth Baroque'' (now Richmond Opera) from 2002 to 2015.
Hospitals
Brentford Workhouse Infirmary and West Middlesex Hospital (historic) The Brentford Poor Law Union had a workhouse built in 1838 covering much land to the east of Twickenham Road in Isleworth. At the turn of the 20th century, this was totally rebuilt as an infirmary, with a much larger workhouse newly erected in the grounds.The Workhouse – www.workhouses.org.ukThis infirmary functioned until 1920, when it became 'West Middlesex Hospital'. In 1931 it was upgraded to a county hospital, but in 1948 (under the NHS) 'County' was dropped from its title. It later became a
teaching hospital
A teaching hospital or university hospital is a hospital or medical center that provides medical education and training to future and current health professionals. Teaching hospitals are almost always affiliated with one or more universities a ...
, and added 'University' to its title in 1980. The Victorian buildings were closed in 2003, and redeveloped as housing, called Union Lane, after the original workhouse. The hospital was rebuilt on the adjacent site.
West Middlesex University Hospital (NHS Trust)
This is a major acute hospital on the Twickenham Road, Isleworth, with 394 beds, providing the full range of services expected of a general hospital. It serves residents of both the London boroughs of Hounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
and Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, California, a city in the United States
* Richmond, London, a town in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, England
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town ...
. As a university hospital it is affiliated with Imperial College London
Imperial College London, also known as Imperial, is a Public university, public research university in London, England. Its history began with Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Prince Albert, husband of Queen Victoria, who envisioned a Al ...
. A programme of building, renovation and modernisation in recent years has resulted in the hospital offering modern facilities.
Percy House Auxiliary Military Hospital (historic)
Within the old union workhouse complex stood a school, facing Twickenham Road, called Percy House – Percy being the surname of the dukes of Northumberland. Owing to its gradual disuse as a school it was adapted to function as a military hospital during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
of 1914–18. From 1915 onwards it treated some 5,000 war-wounded soldiers, and ceased operation at the end of 1918. Among the VAD nurses was Sophia Duleep Singh. The building was demolished in 1978.
Mogden Isolation Hospital (historic)
For nearly a hundred years an isolation hospital existed on the south side of Mogden Lane, which runs west from Twickenham Road. Opened in 1897, Mogden Isolation Hospital was renamed 'South Middlesex Fever Hospital' in 1938 but continued under local authority control. When the National Health Service was formed it became, in 1948, simply South Middlesex Hospital. It closed in 1991.
Education
West Thames College
West Thames College is a medium-sized college of further education, further and higher education in West London, England. It was formed in 1976, originally named Hounslow Borough College, having gained its current name in 1993. The college has tw ...
, a further education college
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is additional education to that received at secondary school that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. It ...
, is located in Isleworth.
Secondary schools
* The Green School for Girls * Gumley House Convent School (girls) * Isleworth and Syon School (boys) * The Green School for Boys *Oaklands School (Special Educational Needs
Special educational needs (SEN), also known as special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) in the United Kingdom refers to the education of children who require different education provision to the mainstream system.
Meaning
The meaning of S ...
)
Primary schools
*Ashton House School *The Blue School (Church of England) *Isleworth Town *Ivybridge *Marlborough *Smallberry Green *Spring Grove Primary *St Mary's (Roman Catholic) *WorpleChurches
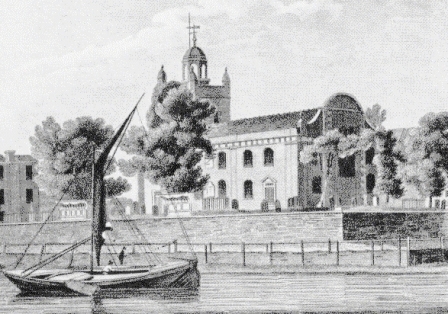
 All Saints' Church, Isleworth is the ancient parish church for the area. Others include:
* St Francis of Assisi Church
* St Bridget's RC Church
* St John's Church
* St Mary's Church
* St Mary the Virgin Church
* Isleworth
All Saints' Church, Isleworth is the ancient parish church for the area. Others include:
* St Francis of Assisi Church
* St Bridget's RC Church
* St John's Church
* St Mary's Church
* St Mary the Virgin Church
* Isleworth Congregational Church
Congregationalism (also Congregational Churches or Congregationalist Churches) is a Reformed Christian (Calvinist) tradition of Protestant Christianity in which churches practice congregational government. Each congregation independently a ...
Transport
Routes
The principal road in Isleworth is the London Road (A 315), which broadly follows the route of one of the early roads the Romans constructed in Britannia, namely Tamesis Street, built across the wide heathlands ''en route'' to Silchester, from where other roads led to Bath, Winchester and Salisbury. As this road from the centre of London passes through Westminster it is called 'Piccadilly' and then 'Knightsbridge'. In Kensington it is 'High Street', in Hammersmith 'King Street', in Chiswick it's the 'High Road', in Brentford it's the 'High Street', and as Isleworth's 'London Road' passes into Hounslow it again becomes 'High Street'. In former times it was part of the 'King's Highway' to Windsor. A bigger road was completed in 1925, named the Great West Road (A 4), moving in much the same direction and forming the notional northern boundary of Isleworth. A six-lane dual carriageway for most of its length, with attendant cycle paths, it fulfilled the purpose of bypassing the bottlenecks of Brentford and Hounslow high streets to relieve the old road from London of traffic heading to and from Windsor and beyond. A later branch extension off this new road, named the Great South West Road, carried traffic south-westwards and this had the additional effect of relieving the London Road of traffic heading to and from Staines-upon-Thames and beyond. The other throughway in this category is the Twickenham Road (A 310), which branches off London Road west of the Syon estate and takes traffic to Twickenham, Teddington and beyond. This was the King's Highway to Hampton Court, so in years past those houses fronting on Twickenham Road, such as Somerset House, Kendal House and the two Silver Halls would have been favoured with a royal gaze from time to time.Bus and tram
Horse bus operation came to Isleworth in the mid-1800s. The predominant London bus operator from 1856 to 1933 was theLondon General Omnibus Company
The London General Omnibus Company or LGOC, was the principal bus operator in London between 1855 and 1933. It was also, for a short period between 1909 and 1912, a motor bus manufacturer.
Overview
The London General Omnibus Company was f ...
, after which the London Passenger Transport Board
The London Passenger Transport Board was the organisation responsible for local public transport in London and its environs from 1933 to 1948. In common with all London transport authorities from 1933 to 2000, the public name and brand was Londo ...
was formed. On 19 October 1856 the LGOC took over an existing horse bus operation between Isleworth and St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Paul the Apostle, is an Anglican cathedral in London, England, the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London in the Church of Engl ...
with the buses painted red.
Electric trams started running in Isleworth in 1901, from a depot situated on the north side of London Road, near the border with Hounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
. The original operating company was London United Tramways
London United Tramways Company Limited was an operator of trams and trolleybuses in the western and southern suburbs of London, UK, from 1894 to 1933, when it passed to the London Passenger Transport Board.
Origins
The company was formed in 189 ...
, which was subsumed into the new London Passenger Transport Board
The London Passenger Transport Board was the organisation responsible for local public transport in London and its environs from 1933 to 1948. In common with all London transport authorities from 1933 to 2000, the public name and brand was Londo ...
in 1933. In 1935 the depot was converted to trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or troll ...
operation. It was designed in a horseshoe shape with a travelator at the far end, which had a turntable added for the trolleybuses. Originally known as Hounslow Depot, it was renamed Isleworth and given the code "IH" in 1950. It had a capacity for 37 vehicles and only ever operated one service: the 57 tram route which, on conversion, became the 657 trolleybus route. Both the 57 and 657 operated between Hounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
and Shepherd's Bush
Shepherd's Bush is a suburb of West London, England, within the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham west of Charing Cross, and identified as a major metropolitan centre in the London Plan.
Although primarily residential in character, its ...
Green via Isleworth, Brentford
Brentford is a suburban town in West (London sub region), West London, England and part of the London Borough of Hounslow. It lies at the confluence of the River Brent and the River Thames, Thames, west of Charing Cross.
Its economy has dive ...
, Chiswick
Chiswick ( ) is a district in West London, split between the London Borough of Hounslow, London Boroughs of Hounslow and London Borough of Ealing, Ealing. It contains Hogarth's House, the former residence of the 18th-century English artist Wi ...
, and Goldhawk Road. From 1902 the Hounslow terminus of the 57 tram was the "Hussar" in Staines Road, Hounslow Heath. In July 1922 the service was cut back to terminate at the "Bell" at the western end of Hounslow High Street. A special turning place half a mile along Staines Road, at its junction with Wellington Road, was built for the 657 trolleybus. At different times there were ambitious plans to extend the tram lines westward to Staines-upon-Thames
Staines-upon-Thames, also known simply as Staines, is a market town in northwest Surrey, England, around west of central London. It is in the Borough of Spelthorne, at the confluence of the River Thames and River Colne, Hertfordshire, Colne. ...
and even to Maidenhead
Maidenhead is a market town in the Royal Borough of Windsor and Maidenhead in the county of Berkshire, England. It lies on the southwestern bank of the River Thames, which at this point forms the border with Buckinghamshire. In the 2021 Census, ...
, but these never came about and the modern replacement motor bus route 237 traverses exactly the same roads between Hounslow Heath and Shepherd's Bush as the trams did over 110 years ago (with a short extension to White City).
When the 657 figured in the final London trolleybus conversion of all, on 8 May 1962, Isleworth Depot was closed and its staff were transferred to nearby Hounslow
Hounslow ( ) is a large suburban district of West London, England, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 14 metropolitan cen ...
Bus Garage (coded "AV"). The replacement motor bus service was provided by an extension of route 117, which up to then had run between Egham and Hounslow. In 1978 the 117 between Hounslow and Shepherd's Bush was superseded by an eastward extension to route 237. Until this time the 237 had operated between Chertsey
Chertsey is a town in the Borough of Runnymede, Surrey, England, southwest of central London. It grew up around Chertsey Abbey, founded in AD 666 by Earconwald, St Erkenwald, and gained a municipal charter, market charter from Henry I of Engla ...
and Hounslow with single deck buses – a truly suburban route. As part of the privatisation of London bus services
The privatisation of London bus services was the process of the transfer of operation of buses in London from public bodies to private companies.
For half a century, operation of London bus services for public transport was under the direct con ...
, Hounslow Garage passed to London United that later was purchased by Transdev
Transdev, formerly Veolia Transdev, is a France-based international private-sector company which operates public transport. It has operations in 17 countries and territories as of November 2020.
Transdev was formed on 3 April 2011 via the merg ...
and later over by the RATP Group
The RATP Group () is a French state-owned enterprise (Établissement public à caractère industriel et commercial, EPIC) that operates public transport systems primarily in Paris, France. Headquartered in Paris, it originally operated under th ...
.
Another trolleybus service serving Isleworth was the 667, formerly the 67 tram, which passed through en route from Hampton Court
Hampton Court Palace is a Listed building, Grade I listed royal palace in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, southwest and upstream of central London on the River Thames. Opened to the public, the palace is managed by Historic Royal ...
to Hammersmith
Hammersmith is a district of West London, England, southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, and identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
It ...
via Hampton Hill, Fulwell, Twickenham
Twickenham ( ) is a suburban district of London, England, on the River Thames southwest of Charing Cross. Historic counties of England, Historically in Middlesex, since 1965 it has formed part of the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, who ...
, Busch Corner, Brentford and Chiswick. Upon its transfer to motor bus operation, as part of the final London trolleybus conversions, the route had its number changed from 667 to 267
__NOTOC__
Year 267 ( CCLXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Paternus and Arcesilaus (or, less frequently, year 1020 ''Ab urbe condita''). The d ...
. Tram 67, trolleybus 667 and motor bus 267 were all operated from Fulwell bus garage. The history of the ownership of Fulwell (coded "FW") is exactly as for Hounslow Garage above.
On Summer Bank Holidays a special service was operated between Shepherd's Bush and Hampton Court. In tram days this was route 65, but trolleybuses showed number 667 towards Hampton Court and 657 on the return journey. This service did not survive the trolleybuses' withdrawal.
A long-established motor bus route serving Isleworth (and Hounslow) was the number 37. This was one of the earliest motor bus routes introduced by the London General Omnibus Company
The London General Omnibus Company or LGOC, was the principal bus operator in London between 1855 and 1933. It was also, for a short period between 1909 and 1912, a motor bus manufacturer.
Overview
The London General Omnibus Company was f ...
and it originally ran from Isleworth to Peckham
Peckham ( ) is a district in south-east London, within the London Borough of Southwark. It is south-east of Charing Cross. At the 2001 Census the Peckham ward had a population of 14,720.
History
"Peckham" is a Saxon place name meaning the vi ...
via St Margarets, Richmond, London, Richmond, Barnes, London, Barnes, Putney, Wandsworth, Clapham Junction (area), Clapham Junction, Clapham Common, Brixton, Herne Hill and East Dulwich. It was later extended westward to Hounslow (going round the back streets to avoid the low railway bridge in St John's Road and to serve Isleworth railway station) and for a brief time in the 1920s offered a summer Sunday service extension as far as Maidenhead. Even without that short-lived extension the 37 was one of London's longest routes. Between 1922 and 1938 its western terminus was the "Hussar" at Hounslow Heath but was then cut back to turn at Hounslow Bus Garage (later Bus Station). At the beginning the terminus in Isleworth was the forecourt of the Northumberland Arms public house and the destination boards displayed "ISLEWORTH Market Place". Later, for "short" journeys, this was changed to stands in Magdala Road and then in South Street, outside the Public Hall. In 1991 this historic route was curtailed to run between Peckham and Putney, and the section between Richmond and Hounslow via Isleworth became a new, more localised service numbered H37.
Rail
Isleworth has only one rail service. It consists of a loop branch line running off the minor main line service operated by South Western Railway (train operating company), South Western Railway between central London and Reading. On the down-service the loop begins at the Barnes junction, then travels through Chiswick and Brentford before entering Isleworth by crossing the River Brent just south of the A4 trunk road. Thereafter it serves the two stations of Syon Lane and Isleworth before leaving the town just north of the Woodlands estate and passing under Bridge Road. The service usually runs at fifteen-minute intervals. Following its next stop at Hounslow the loop re-enters the main line on the up-service shortly before the Whitton station. Nearest National Rail stations * Isleworth railway station, Isleworth * Syon Lane railway station, Syon Lane Nearest London Underground stations * Osterley station, Osterley ''Piccadilly Line'' * Hounslow East station, Hounslow East ''Piccadilly Line'' * Richmond station (London), Richmond ''District Line''River passenger services (history)
1840 ''George J Aungier:'' "There is a ferry, called Church Ferry, for foot passengers, from the church over the river to West Sheen, Kew, &c. and another at the southern extremity of the village, called Rails-head Ferry." 1947 Rails-head Ferry still existed, more than fifty years after the nearby footbridge had been built. 1952 Typical pleasure boat of the mid-20th century seen here from Isleworth Promenade.Notable residents
Hampton Court
Hampton Court Palace is a Listed building, Grade I listed royal palace in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, southwest and upstream of central London on the River Thames. Opened to the public, the palace is managed by Historic Royal ...
from the Thames.
*Ian Gilmour, who became 3rd Baronet of Craigmillar, was Secretary of State for Defence and Lord Privy Seal during the 1970s. He lived at the current Ferry House, on the same site as above, for fifty-three years until his death in 2007.
*Post-impressionist artist Vincent van Gogh moved to Isleworth in 1876 to become a teacher and assistant preacher at a local school. A blue plaque exists on the house he lived in alongside Twickenham Road.
*Andrew Pears was the third generation head of the Pears (soap), Pears soap business located in Isleworth, and in 1886 he bought Spring Grove House. He rebuilt it in 1892/94 on a grander scale, retaining the structure, facing the building with new red brickwork, and adding large rear extensions. This created a sizeable mansion, most of which still stands. The house is now part of West Thames College
West Thames College is a medium-sized college of further education, further and higher education in West London, England. It was formed in 1976, originally named Hounslow Borough College, having gained its current name in 1993. The college has tw ...
. There is a memorial to the Pears family in Isleworth cemetery, including Thomas Pears (1882–1912) who died on the RMS Titanic, RMS ''Titanic''.
*George Manville Fenn (1831-1909) was a prolific English novelist, journalist, editor and educationalist who lived in Isleworth and is buried there. Many of his novels were written for young adults.
*Walter R. Booth (1869–1938), creator of the first British animated cartoon film, ''The Hand of the Artist'', constructed his own outdoor studio in the back garden of Neville Lodge, Woodlands Road, Isleworth in 1906 with Harold Bastick as his cameraman. At least fifteen films a year were made up to 1915, after which he entered the publicity film market, making advertising shorts for Cadbury.
*Arthur Penty (1875–1937), an architect and writer on guild socialism and distributism lived in Church Street, Old Isleworth (1926–1937). He is commemorated by a blue plaque.
*Eileen Sheridan (cyclist), Eileen Sheridan (1923–2023), a champion English cyclist of the 1940s and 1950s, lived in Church Street, Old Isleworth for many years.
* Jack Simmons (historian), Jack Simmons (1915–2000), historian, was born in Isleworth. In 1947 he became the first professor of history at University College, Leicester, which became the University of Leicester in 1957. He was the university's acting vice-chancellor from 1962 until 1975.
* Ronald Chetwynd-Hayes (1919–2001) was born in Isleworth. For over 30 years, Chetwynd-Hayes published more than 200 short stories, 8 novels, and over 20 collections, as well as editing 24 anthologies including many of the Fontana Ghost Stories series of anthologies.
* Sir David Attenborough (1926–) Born in Isleworth. His career as the face and voice of natural history programmes has endured for more than 60 years. He is best known for writing and presenting the nine ''Life (2009 TV series), Life'' Television program, series, in conjunction with the BBC Natural History Unit.
* William Hartnell, actor, best known as the First Doctor in ''Doctor Who'' from 1963 to 1966, lived opposite the London Apprentice, Isleworth, London Apprentice pub from the 1920s, next door to his guardian, the art collector Hugh Blaker.
* Vince Taylor (1939–1991), British rock and roll singer and main inspiration for David Bowie's Ziggy Stardust persona, spent his early life in Isleworth.
* Ellen Edith Hannah Redknap (1906–1991), author lived at Worton Way and wrote under the name of Erroll Collins. She was active during the 1940s, specialising in adventure and science fiction for boys.
* Presenter Fiona Phillips lives in Isleworth.
* Patsy Morris, victim of unsolved murder in 1980 and reportedly the childhood girlfriend of serial killer Levi Bellfield, also from Isleworth.
*Joan Bicknell was born here, professor of psychiatry and human rights advocate for people with intellectual disabilities.
* Edd Gould (1988–2012) creator of ''Eddsworld'', a popular YouTube channel.
* Earl Rhodes, former actor, lives in Isleworth.
* Dave Brock, founder of space rock group Hawkwind, was born in Isleworth.
* Ruel (singer), Ruel, Australian singer-songwriter, was born in Isleworth.
* Ben Turnbull, artist, was born in Isleworth.
* Ellie Beaven, Actress was born and grew up in Isleworth
* Thomas Allistone (1823–1896), a soldier in the 11th Hussars who took part in the Charge of the Light Brigade.
Fictional residents
*In the 2001 feature film ''Gosford Park'', Sir William McCordle had one of his factories in Isleworth and Robert Parks was raised in orphanage in Isleworth. *In the ITV (TV network), ITV television series, ''Agatha Christie's Poirot'', Isleworth is often mentioned as the home town of Chief Inspector Japp.Landmarks
Notable houses
 A period of intense mansion-building occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries. There was a triple attraction to the area in those times. Its rural, waterside beauty had become well recognised over two hundred years or so, and a few palaces, monasteries and mansions already existed. Then the royal court began to appear at Kew, so the adjacent districts on both sides of the Thames became very fashionable places for the rich and famous to build their grand homes. Some of the cachet dropped away when the court eventually left Kew; most high-quality here survived well The Blitz and social turmoil to enable many to reach grade II* (the mid category) of architectural listed building.
* Syon House Duke of Somerset Duke of Northumberland. (standing, listed Grade 1) Although this grand house has had a close connection with Isleworth for 450 years, it has very grand architecture as the only non-royal ducal main home ('family seat, seat') in
A period of intense mansion-building occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries. There was a triple attraction to the area in those times. Its rural, waterside beauty had become well recognised over two hundred years or so, and a few palaces, monasteries and mansions already existed. Then the royal court began to appear at Kew, so the adjacent districts on both sides of the Thames became very fashionable places for the rich and famous to build their grand homes. Some of the cachet dropped away when the court eventually left Kew; most high-quality here survived well The Blitz and social turmoil to enable many to reach grade II* (the mid category) of architectural listed building.
* Syon House Duke of Somerset Duke of Northumberland. (standing, listed Grade 1) Although this grand house has had a close connection with Isleworth for 450 years, it has very grand architecture as the only non-royal ducal main home ('family seat, seat') in Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, former county in South East England, now mainly within Greater London. Its boundaries largely followed three rivers: the River Thames, Thames in the south, the River Lea, Le ...
. It is chronicled in an exhaustive history.
 *Silver Hall No. 1 ''(South of North Street, with four acres)'' [1.6 hectares] Sir John Smith Bt, Privy to William & Mary Lady Harcourt, widow of Sir W Harcourt, Chancellor (Demolished 1801)'And So Make a City Here' by G E Bate F.R.Hist.S. p121 published: Thomasons Hounslow 1948
*Silver Hall No. 2 ''(North of North Street)'' Joseph Dixon. (Demolished 1950)
* Kendal House. ''(Twickenham Road, near Mill Plat)'' Duchess of Kendal (mistress to George I).
*Somerset House
*Gunnersbury House. ''(At the junction of Bridge Road and London Road)'' (Demolished c. 1972).
*Silver Hall No. 1 ''(South of North Street, with four acres)'' [1.6 hectares] Sir John Smith Bt, Privy to William & Mary Lady Harcourt, widow of Sir W Harcourt, Chancellor (Demolished 1801)'And So Make a City Here' by G E Bate F.R.Hist.S. p121 published: Thomasons Hounslow 1948
*Silver Hall No. 2 ''(North of North Street)'' Joseph Dixon. (Demolished 1950)
* Kendal House. ''(Twickenham Road, near Mill Plat)'' Duchess of Kendal (mistress to George I).
*Somerset House
*Gunnersbury House. ''(At the junction of Bridge Road and London Road)'' (Demolished c. 1972).*Isleworth House Sir William Cooper, chaplain to George III. Renamed Nazareth House in 1892 when it was established as the present residential nursing home and convent. (standing) *Countess of Charleville's Villa Harriet Charlotte Beaujolais (Campbell), Countess of Charleville. *Wyke House *Little Syon (formerly Cromwell House) Sir Richard Wynn Bt. (Demolished 1818).
 *Gumley House John Gumley (Commissary-General to the Army) William Pulteney, 1st Earl of Bath, The Earl of Bath (Gumley's son-in-law) General Lord Lake.
*Shrewsbury House George Talbot, 14th Earl of Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury House lay to the east of Upper Square, in the area known as Lion Wharf, once Beck's Wharf, also Shrewsbury Wharf. The 14th Earl inherited the lease in 1719 and later by Act of Parliament gained full rights to the property (in exchange for certain fee-farm rents) from an almshouse charity established by a former landlord, Sir Thomas Ingram, from whom the 1st Duke of Shrewsbury had originally leased the site. Around 1778 the 14th Earl started the process by which the house converted to a school for boys of Roman Catholic parents.
*Gumley House John Gumley (Commissary-General to the Army) William Pulteney, 1st Earl of Bath, The Earl of Bath (Gumley's son-in-law) General Lord Lake.
*Shrewsbury House George Talbot, 14th Earl of Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury House lay to the east of Upper Square, in the area known as Lion Wharf, once Beck's Wharf, also Shrewsbury Wharf. The 14th Earl inherited the lease in 1719 and later by Act of Parliament gained full rights to the property (in exchange for certain fee-farm rents) from an almshouse charity established by a former landlord, Sir Thomas Ingram, from whom the 1st Duke of Shrewsbury had originally leased the site. Around 1778 the 14th Earl started the process by which the house converted to a school for boys of Roman Catholic parents.
 *Gordon House, by the River Thames at Railshead Rd. (standing, listed Grade II*). General Humphrey Bland Lord James Hay Lord John Kennedy-Erskine. Lord and Lady Frederick Gordon Earl of Kilmorey Judge T C Haliburton MP. In Lord Hay's time this was named 'Seaton House', after his ancestral home in Aberdeenshire. It was next bought by King William IV at 8,000 guineas for his (illegitimate) daughter Lady Augusta, who married Lord John Kennedy-Erskine of Dun, the son of the First Marquis of Ailsa who lived next door in St Margaret's House. Gordon House is being renovated.
*Spring Grove House Sir Joseph Banks Andrew Pears. (standing, Grade II)
: In 1862 Francis Pears decided to expand his Pears soap, soap making business and bought land alongside the London Road for a factory. Another, larger, factory was opened along the opposite side of the road in the 1880s and soap was made on the site until 1962. His son Andrew bought the Spring Grove House estate in 1886 and greatly extended the house in 1894. ''Pictures are shown under 'Notable residents'.''
*Keppel House Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel, First Lord of the Admiralty Augustus Keppel.
*Lacy House A 17th-century house rebuilt in 1750 for James Lacy (actor), James Lacy, of Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, Drury Lane Theatre.
*Gordon House, by the River Thames at Railshead Rd. (standing, listed Grade II*). General Humphrey Bland Lord James Hay Lord John Kennedy-Erskine. Lord and Lady Frederick Gordon Earl of Kilmorey Judge T C Haliburton MP. In Lord Hay's time this was named 'Seaton House', after his ancestral home in Aberdeenshire. It was next bought by King William IV at 8,000 guineas for his (illegitimate) daughter Lady Augusta, who married Lord John Kennedy-Erskine of Dun, the son of the First Marquis of Ailsa who lived next door in St Margaret's House. Gordon House is being renovated.
*Spring Grove House Sir Joseph Banks Andrew Pears. (standing, Grade II)
: In 1862 Francis Pears decided to expand his Pears soap, soap making business and bought land alongside the London Road for a factory. Another, larger, factory was opened along the opposite side of the road in the 1880s and soap was made on the site until 1962. His son Andrew bought the Spring Grove House estate in 1886 and greatly extended the house in 1894. ''Pictures are shown under 'Notable residents'.''
*Keppel House Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel, First Lord of the Admiralty Augustus Keppel.
*Lacy House A 17th-century house rebuilt in 1750 for James Lacy (actor), James Lacy, of Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, Drury Lane Theatre.Lacy's son inherited the property but his extravagance compelled him to sell the house, to the Hon. Sir Edward Walpole K.B. He bequeathed it to his daughter, widow of Bishop of Exeter, and after that it was acquired by the Earl of Warwick. After him came the famous playwright Richard Sheridan, who by then had already produced his two masterpieces ''School for Scandal'' and ''The Rivals''. Lacy House was demolished in the 1830s. *St Margaret's House (Lacy House rebuilt and renamed) First Marquis of Ailsa. *Kilmorey House (replaced St Margarets House in 1853). Built for 2nd Earl of Kilmorey but never lived in. Became the Royal Naval School for Girls (1856–1940). (Demolished 1950).
Demography and housing
In the 2011 United Kingdom census, 2011 Census, the Isleworth ward of Hounslow was recorded as being 51% White British. Other significant ethnic groups were Other Whites (11.7%), Black Africans (7%), Indian people, Indians (6.4%), and Other Asians (5.6%). The proportion who ethnically identify as Classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom, BAME (Black, Asian and minority Ethnic) was 34.8% of the population. 63.3% of people living in Isleworth were born in England. The other most common countries of birth were India (3.1%), Somalia (2.1%), Ireland (1.7%) and Pakistan (1.4%). The largest religious affiliations in Isleworth are Christians (49.5%), those with no religion (20.7%), Muslims (13.9%), Hindus (3.7%) and Sikhs (2.4%).Adjacent towns or districts
References
Further reading
"A History of the Urban Districts of Heston and Isleworth" (Gill and Sons, London).Gallery
External links
Hounslow Council
{{Authority control Isleworth, Areas of London Districts of the London Borough of Hounslow Districts of London on the River Thames Places formerly in Middlesex