Ice Ages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of
 Only a few years later, the Danish-Norwegian geologist Jens Esmark (1762–1839) argued for a sequence of worldwide ice ages. In a paper published in 1824, Esmark proposed changes in climate as the cause of those glaciations. He attempted to show that they originated from changes in Earth's orbit. Esmark discovered the similarity between moraines near Haukalivatnet lake near sea level in
Only a few years later, the Danish-Norwegian geologist Jens Esmark (1762–1839) argued for a sequence of worldwide ice ages. In a paper published in 1824, Esmark proposed changes in climate as the cause of those glaciations. He attempted to show that they originated from changes in Earth's orbit. Esmark discovered the similarity between moraines near Haukalivatnet lake near sea level in
 There have been at least five major ice ages in Earth's history (the Huronian,
There have been at least five major ice ages in Earth's history (the Huronian,  Rocks from the earliest well-established ice age, called the Huronian, have been dated to around 2.4 to 2.1 billion years ago during the early Proterozoic Eon. Several hundreds of kilometers of the Huronian Supergroup are exposed north of the north shore of Lake Huron, extending from near Sault Ste. Marie to Sudbury, northeast of Lake Huron, with giant layers of now-lithified till beds, dropstones, varves, outwash, and scoured basement rocks. Correlative Huronian deposits have been found near
Rocks from the earliest well-established ice age, called the Huronian, have been dated to around 2.4 to 2.1 billion years ago during the early Proterozoic Eon. Several hundreds of kilometers of the Huronian Supergroup are exposed north of the north shore of Lake Huron, extending from near Sault Ste. Marie to Sudbury, northeast of Lake Huron, with giant layers of now-lithified till beds, dropstones, varves, outwash, and scoured basement rocks. Correlative Huronian deposits have been found near  The evolution of land plants at the onset of the
The evolution of land plants at the onset of the
 Within the current glaciation, more temperate and more severe periods have occurred. The colder periods are called ''glacial periods'', the warmer periods ''interglacials'', such as the Eemian Stage. There is evidence that similar glacial cycles occurred in previous glaciations, including the Andean-Saharan and the late Paleozoic ice house. The glacial cycles of the late Paleozoic ice house are likely responsible for the deposition of cyclothems.
Glacials are characterized by cooler and drier climates over most of Earth and large land and sea ice masses extending outward from the poles. Mountain glaciers in otherwise unglaciated areas extend to lower elevations due to a lower
Within the current glaciation, more temperate and more severe periods have occurred. The colder periods are called ''glacial periods'', the warmer periods ''interglacials'', such as the Eemian Stage. There is evidence that similar glacial cycles occurred in previous glaciations, including the Andean-Saharan and the late Paleozoic ice house. The glacial cycles of the late Paleozoic ice house are likely responsible for the deposition of cyclothems.
Glacials are characterized by cooler and drier climates over most of Earth and large land and sea ice masses extending outward from the poles. Mountain glaciers in otherwise unglaciated areas extend to lower elevations due to a lower

 The Milankovitch cycles are a set of cyclic variations in characteristics of Earth's orbit around the Sun. Each cycle has a different length, so at some times their effects reinforce each other and at other times they (partially) cancel each other.
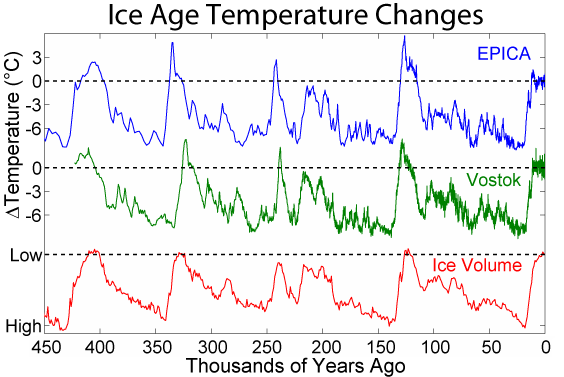
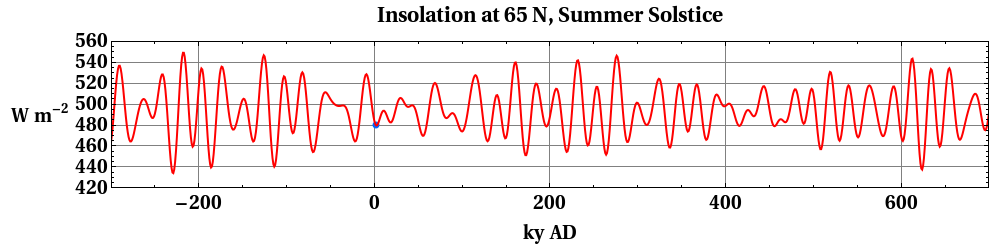
There is strong evidence that the Milankovitch cycles affect the occurrence of glacial and interglacial periods within an ice age. The present ice age is the most studied and best understood, particularly the last 400,000 years, since this is the period covered by ice cores that record atmospheric composition and proxies for temperature and ice volume. Within this period, the match of glacial/interglacial frequencies to the Milanković orbital forcing periods is so close that orbital forcing is generally accepted. The combined effects of the changing distance to the Sun, the precession of Earth's axis, and the changing tilt of Earth's axis redistribute the sunlight received by Earth. Of particular importance are changes in the tilt of Earth's axis, which affect the intensity of seasons. For example, the amount of solar influx in July at 65 degrees north
The Milankovitch cycles are a set of cyclic variations in characteristics of Earth's orbit around the Sun. Each cycle has a different length, so at some times their effects reinforce each other and at other times they (partially) cancel each other.
There is strong evidence that the Milankovitch cycles affect the occurrence of glacial and interglacial periods within an ice age. The present ice age is the most studied and best understood, particularly the last 400,000 years, since this is the period covered by ice cores that record atmospheric composition and proxies for temperature and ice volume. Within this period, the match of glacial/interglacial frequencies to the Milanković orbital forcing periods is so close that orbital forcing is generally accepted. The combined effects of the changing distance to the Sun, the precession of Earth's axis, and the changing tilt of Earth's axis redistribute the sunlight received by Earth. Of particular importance are changes in the tilt of Earth's axis, which affect the intensity of seasons. For example, the amount of solar influx in July at 65 degrees north
 The current geological period, the
The current geological period, the
''Global chronostratigraphical correlation table for the last 2.7 million years v. 2007b.''
, jpg version 844 KB. Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England During the most recent North American glaciation, during the latter part of the This Wisconsin glaciation left widespread impacts on the North American landscape. The
This Wisconsin glaciation left widespread impacts on the North American landscape. The
 Although the last glacial period ended more than 8,000 years ago, its effects can still be felt today. For example, the moving ice carved out the landscape in Canada (See Canadian Arctic Archipelago), Greenland, northern Eurasia and Antarctica. The erratic boulders, till, drumlins, eskers, fjords, kettle lakes,
Although the last glacial period ended more than 8,000 years ago, its effects can still be felt today. For example, the moving ice carved out the landscape in Canada (See Canadian Arctic Archipelago), Greenland, northern Eurasia and Antarctica. The erratic boulders, till, drumlins, eskers, fjords, kettle lakes,
Cracking the Ice Age
from PBS * *
Eduard Y. Osipov, Oleg M. Khlystov. Glaciers and meltwater flux to Lake Baikal during the Last Glacial Maximum.
* {{Authority control Geological history of the Great Lakes Glaciology History of climate variability and change History of science
 An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
s and alpine glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and greenhouse periods during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the ice age called Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial period, glacial and interglacial, interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma (million ...
. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed '' glacial periods'' (''glacials, glaciations, glacial stages, stadials, stades'', or colloquially, ''ice ages''), and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called '' interglacials'' or ''interstadials''.
In glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or, more generally, ice and natural phenomena that involve ice.
Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, clim ...
, the term ''ice age'' is defined by the presence of extensive ice sheets in the northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, the current Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
epoch is an interglacial period of an ice age. The accumulation of anthropogenic greenhouse gases is projected to delay the next glacial period.
History of research
In 1742, Pierre Martel (1706–1767), an engineer and geographer living inGeneva
Geneva ( , ; ) ; ; . is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland and the most populous in French-speaking Romandy. Situated in the southwest of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the ca ...
, visited the valley of Chamonix in the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
of Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
. Two years later he published an account of his journey. He reported that the inhabitants of that valley attributed the dispersal of erratic boulders to the glaciers, saying that they had once extended much farther. Later similar explanations were reported from other regions of the Alps. In 1815 the carpenter and chamois hunter Jean-Pierre Perraudin (1767–1858) explained erratic boulders in the Val de Bagnes in the Swiss canton of Valais as being due to glaciers previously extending further. An unknown woodcutter from Meiringen in the Bernese Oberland advocated a similar idea in a discussion with the Swiss-German geologist Jean de Charpentier (1786–1855) in 1834. Comparable explanations are also known from the Val de Ferret in the Valais and the Seeland in western Switzerland and in Goethe
Johann Wolfgang (von) Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German polymath who is widely regarded as the most influential writer in the German language. His work has had a wide-ranging influence on Western literature, literary, Polit ...
's scientific work. Such explanations could also be found in other parts of the world. When the Bavarian naturalist Ernst von Bibra (1806–1878) visited the Chilean Andes in 1849–1850, the natives attributed fossil moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and Rock (geology), rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a gla ...
s to the former action of glaciers.
Meanwhile, European scholars had begun to wonder what had caused the dispersal of erratic material. From the middle of the 18th century, some discussed ice as a means of transport. The Swedish mining expert Daniel Tilas (1712–1772) was, in 1742, the first person to suggest drifting sea ice was a cause of the presence of erratic boulders in the Scandinavian and Baltic regions. In 1795, the Scottish philosopher and gentleman naturalist, James Hutton (1726–1797), explained erratic boulders in the Alps by the action of glaciers. Two decades later, in 1818, the Swedish botanist Göran Wahlenberg (1780–1851) published his theory of a glaciation of the Scandinavian peninsula. He regarded glaciation as a regional phenomenon.
Rogaland
Rogaland () is a Counties of Norway, county in Western Norway, bordering the North Sea to the west and the counties of Vestland to the north, Telemark to the east and Agder to the east and southeast. As of 1 January 2024, it had a population of 49 ...
and moraines at branches of Jostedalsbreen. Esmark's discovery were later attributed to or appropriated by Theodor Kjerulf
Theodor Kjerulf (30 March 182525 October 1888) was a Norway, Norwegian geologist and professor at the University of Oslo. He also served as director of the Norwegian Geological Survey.
Biography
He was born in Oslo, Christiania (now Oslo), Norway ...
and Louis Agassiz
Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz ( ; ) FRS (For) FRSE (May 28, 1807 – December 14, 1873) was a Swiss-born American biologist and geologist who is recognized as a scholar of Earth's natural history.
Spending his early life in Switzerland, he recei ...
.
During the following years, Esmark's ideas were discussed and taken over in parts by Swedish, Scottish and German scientists. At the University of Edinburgh Robert Jameson (1774–1854) seemed to be relatively open to Esmark's ideas, as reviewed by Norwegian professor of glaciology Bjørn G. Andersen (1992). Jameson's remarks about ancient glaciers in Scotland were most probably prompted by Esmark. In Germany, Albrecht Reinhard Bernhardi (1797–1849), a geologist and professor of forestry at an academy in Dreissigacker (since incorporated in the southern Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
n city of Meiningen), adopted Esmark's theory. In a paper published in 1832, Bernhardi speculated about the polar ice caps once reaching as far as the temperate zones of the globe.
In Val de Bagnes, a valley in the Swiss Alps
The Alps, Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps, represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss Plateau and the Swiss portion of the Jura Mountains, one of its three main Physica ...
, there was a long-held local belief that the valley had once been covered deep in ice, and in 1815 a local chamois hunter called Jean-Pierre Perraudin attempted to convert the geologist Jean de Charpentier to the idea, pointing to deep striations in the rocks and giant erratic boulders as evidence. Charpentier held the general view that these signs were caused by vast floods, and he rejected Perraudin's theory as absurd. In 1818 the engineer Ignatz Venetz joined Perraudin and Charpentier to examine a proglacial lake above the valley created by an ice dam as a result of the 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora, which threatened to cause a catastrophic flood when the dam broke. Perraudin attempted unsuccessfully to convert his companions to his theory, but when the dam finally broke, there were only minor erratics and no striations, and Venetz concluded that Perraudin was right and that only ice could have caused such major results. In 1821 he read a prize-winning paper on the theory to the Swiss Society, but it was not published until Charpentier, who had also become converted, published it with his own more widely read paper in 1834.
In the meantime, the German botanist Karl Friedrich Schimper (1803–1867) was studying mosses which were growing on erratic boulders in the alpine upland of Bavaria. He began to wonder where such masses of stone had come from. During the summer of 1835 he made some excursions to the Bavarian Alps. Schimper came to the conclusion that ice must have been the means of transport for the boulders in the alpine upland. In the winter of 1835–36 he held some lectures in Munich. Schimper then assumed that there must have been global times of obliteration ("Verödungszeiten") with a cold climate and frozen water. Schimper spent the summer months of 1836 at Devens, near Bex, in the Swiss Alps with his former university friend Louis Agassiz
Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz ( ; ) FRS (For) FRSE (May 28, 1807 – December 14, 1873) was a Swiss-born American biologist and geologist who is recognized as a scholar of Earth's natural history.
Spending his early life in Switzerland, he recei ...
(1801–1873) and Jean de Charpentier. Schimper, Charpentier and possibly Venetz convinced Agassiz that there had been a time of glaciation. During the winter of 1836–37, Agassiz and Schimper developed the theory of a sequence of glaciations. They mainly drew upon the preceding works of Venetz, Charpentier and on their own fieldwork. Agassiz appears to have been already familiar with Bernhardi's paper at that time. At the beginning of 1837, Schimper coined the term "ice age" (''"Eiszeit"'') for the period of the glaciers. In July 1837 Agassiz presented their synthesis before the annual meeting of the Swiss Society for Natural Research at Neuchâtel. The audience was very critical, and some were opposed to the new theory because it contradicted the established opinions on climatic history. Most contemporary scientists thought that Earth had been gradually cooling down since its birth as a molten globe.
In order to persuade the skeptics, Agassiz embarked on geological fieldwork. He published his book ''Study on Glaciers'' ("Études sur les glaciers") in 1840. Charpentier was put out by this, as he had also been preparing a book about the glaciation of the Alps. Charpentier felt that Agassiz should have given him precedence as it was he who had introduced Agassiz to in-depth glacial research. As a result of personal quarrels, Agassiz had also omitted any mention of Schimper in his book.
It took several decades before the ice age theory was fully accepted by scientists. This happened on an international scale in the second half of the 1870s, following the work of James Croll, including the publication of ''Climate and Time, in Their Geological Relations'' in 1875, which provided a credible explanation for the causes of ice ages.
Evidence
There are three main types of evidence for ice ages: geological, chemical, and paleontological. ''Geological'' evidence for ice ages comes in various forms, including rock scouring and scratching,glacial moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris ( regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice s ...
s, drumlins, valley cutting, and the deposition of till or tillites and glacial erratics. Successive glaciations tend to distort and erase the geological evidence for earlier glaciations, making it difficult to interpret. Furthermore, this evidence was difficult to date exactly; early theories assumed that the glacials were short compared to the long interglacials. The advent of sediment and ice cores revealed the true situation: glacials are long, interglacials short. It took some time for the current theory to be worked out.
The ''chemical'' evidence mainly consists of variations in the ratios of isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s in fossils present in sediments and sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s and ocean sediment cores. For the most recent glacial periods, ice cores provide climate proxies, both from the ice itself and from atmospheric samples provided by included bubbles of air. Because water containing lighter isotopes has a lower heat of evaporation, its proportion decreases with warmer conditions. This allows a temperature record to be constructed. This evidence can be confounded, however, by other factors recorded by isotope ratios.
The ''paleontological'' evidence consists of changes in the geographical distribution of fossils. During a glacial period, cold-adapted organisms spread into lower latitudes, and organisms that prefer warmer conditions become extinct or retreat into lower latitudes. This evidence is also difficult to interpret because it requires:
#sequences of sediments covering a long period of time, over a wide range of latitudes and which are easily correlated;
#ancient organisms which survive for several million years without change and whose temperature preferences are easily diagnosed; and
#the finding of the relevant fossils.
Despite the difficulties, analysis of ice core and ocean sediment cores has provided a credible record of glacials and interglacials over the past few million years. These also confirm the linkage between ice ages and continental crust phenomena such as glacial moraines, drumlins, and glacial erratics. Hence the continental crust phenomena are accepted as good evidence of earlier ice ages when they are found in layers created much earlier than the time range for which ice cores and ocean sediment cores are available.
Major ice ages
 There have been at least five major ice ages in Earth's history (the Huronian,
There have been at least five major ice ages in Earth's history (the Huronian, Cryogenian
The Cryogenian (from , meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It is the second of the three periods of the Neoproterozoic era, preceded by the Tonian and followed by the Ediacaran.
The Cryoge ...
, Andean-Saharan, late Paleozoic, and the latest Quaternary Ice Age). Outside these ages, Earth was previously thought to have been ice-free even in high latitudes; such periods are known as greenhouse periods. However, other studies dispute this, finding evidence of occasional glaciations at high latitudes even during apparent greenhouse periods.
 Rocks from the earliest well-established ice age, called the Huronian, have been dated to around 2.4 to 2.1 billion years ago during the early Proterozoic Eon. Several hundreds of kilometers of the Huronian Supergroup are exposed north of the north shore of Lake Huron, extending from near Sault Ste. Marie to Sudbury, northeast of Lake Huron, with giant layers of now-lithified till beds, dropstones, varves, outwash, and scoured basement rocks. Correlative Huronian deposits have been found near
Rocks from the earliest well-established ice age, called the Huronian, have been dated to around 2.4 to 2.1 billion years ago during the early Proterozoic Eon. Several hundreds of kilometers of the Huronian Supergroup are exposed north of the north shore of Lake Huron, extending from near Sault Ste. Marie to Sudbury, northeast of Lake Huron, with giant layers of now-lithified till beds, dropstones, varves, outwash, and scoured basement rocks. Correlative Huronian deposits have been found near Marquette, Michigan
Marquette ( ) is the county seat of Marquette County, Michigan, Marquette County and the largest city in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, United States. Located on the shores of Lake Superior, Marquette is a major port known primarily for shippin ...
, and correlation has been made with Paleoproterozoic glacial deposits from Western Australia. The Huronian ice age was caused by the elimination of atmospheric methane, a greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
, during the Great Oxygenation Event.
The next well-documented ice age, and probably the most severe of the last billion years, occurred from 720 to 630 million years ago (the Cryogenian
The Cryogenian (from , meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It is the second of the three periods of the Neoproterozoic era, preceded by the Tonian and followed by the Ediacaran.
The Cryoge ...
period) and may have produced a Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth is a historical geology, geohistorical hypothesis that proposes that during one or more of Earth's greenhouse and icehouse Earth, icehouse climates, the planet's planetary surface, surface became nearly entirely freezing, fr ...
in which glacial ice sheets reached the equator, possibly being ended by the accumulation of greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es such as produced by volcanoes. "The presence of ice on the continents and pack ice on the oceans would inhibit both silicate weathering and photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, which are the two major sinks for at present." It has been suggested that the end of this ice age was responsible for the subsequent Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
and Cambrian explosion, though this model is recent and controversial.
The Andean-Saharan occurred from 460 to 420 million years ago, during the Late Ordovician and the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
period.
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
period caused a long term increase in planetary oxygen levels and reduction of levels, which resulted in the late Paleozoic icehouse. Its former name, the Karoo glaciation, was named after the glacial tills found in the Karoo region of South Africa. There were extensive polar ice caps at intervals from 360 to 260 million years ago in South Africa during the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
and early Permian periods. Correlatives are known from Argentina, also in the center of the ancient supercontinent Gondwanaland.
Although the Mesozoic Era retained a greenhouse climate over its timespan and was previously assumed to have been entirely glaciation-free, more recent studies suggest that brief periods of glaciation occurred in both hemispheres during the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
. Geologic and palaeoclimatological records suggest the existence of glacial periods during the Valanginian
In the geologic timescale, the Valanginian is an age or stage of the Early or Lower Cretaceous. It spans between 137.05 ± 0.2 Ma and 132.6 ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). The Valanginian Stage succeeds the Berriasian Stage of the Lower Cretac ...
, Hauterivian
The Hauterivian is, in the geologic timescale, an age in the Early Cretaceous Epoch or a stage in the Lower Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 132.6 ± 2 Ma and 125.77 (million years ago). The Hauterivian is preceded by the Valangi ...
, and Aptian
The Aptian is an age (geology), age in the geologic timescale or a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early Cretaceous, Early or Lower Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), S ...
stages of the Early Cretaceous. Ice-rafted glacial dropstones indicate that in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, ice sheets may have extended as far south as the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
during the Hauterivian and Aptian. Although ice sheets largely disappeared from Earth for the rest of the period (potential reports from the Turonian
The Turonian is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS' geologic timescale, the second age (geology), age in the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch, or a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the Upper Cretaceous series (stratigraphy), ...
, otherwise the warmest period of the Phanerozoic, are disputed), ice sheets and associated sea ice appear to have briefly returned to Antarctica near the very end of the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (s ...
just prior to the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.
The Quaternary Glaciation / Quaternary Ice Age started about 2.58 million years ago at the beginning of the Quaternary Period when the spread of ice sheets in the Northern Hemisphere began. Since then, the world has seen cycles of glaciation with ice sheets advancing and retreating on 40,000- and 100,000-year time scales called glacial periods, glacials or glacial advances, and interglacial periods, interglacials or glacial retreats. Earth is currently in an interglacial, and the last glacial period ended about 11,700 years ago. All that remains of the continental ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
s are the Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
and Antarctic ice sheets and smaller glaciers such as on Baffin Island.
The definition of the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
as beginning 2.58 Ma is based on the formation of the Arctic ice cap. The Antarctic ice sheet began to form earlier, at about 34 Ma, in the mid- Cenozoic ( Eocene-Oligocene Boundary). The term Late Cenozoic Ice Age is used to include this early phase.University of Houston-Clear Lake - Disasters Class Notes - Chapter 12: Climate Change sce.uhcl.edu/Pitts/disastersclassnotes/chapter_12_Climate_Change.doc
Ice ages can be further divided by location and time; for example, the names ''Riss'' (180,000–130,000 years bp) and '' Würm'' (70,000–10,000 years bp) refer specifically to glaciation in the Alpine region. The maximum extent of the ice is not maintained for the full interval. The scouring action of each glaciation tends to remove most of the evidence of prior ice sheets almost completely, except in regions where the later sheet does not achieve full coverage.
Glacials and interglacials
 Within the current glaciation, more temperate and more severe periods have occurred. The colder periods are called ''glacial periods'', the warmer periods ''interglacials'', such as the Eemian Stage. There is evidence that similar glacial cycles occurred in previous glaciations, including the Andean-Saharan and the late Paleozoic ice house. The glacial cycles of the late Paleozoic ice house are likely responsible for the deposition of cyclothems.
Glacials are characterized by cooler and drier climates over most of Earth and large land and sea ice masses extending outward from the poles. Mountain glaciers in otherwise unglaciated areas extend to lower elevations due to a lower
Within the current glaciation, more temperate and more severe periods have occurred. The colder periods are called ''glacial periods'', the warmer periods ''interglacials'', such as the Eemian Stage. There is evidence that similar glacial cycles occurred in previous glaciations, including the Andean-Saharan and the late Paleozoic ice house. The glacial cycles of the late Paleozoic ice house are likely responsible for the deposition of cyclothems.
Glacials are characterized by cooler and drier climates over most of Earth and large land and sea ice masses extending outward from the poles. Mountain glaciers in otherwise unglaciated areas extend to lower elevations due to a lower snow line
The climatic snow line is the boundary between a snow-covered and snow-free surface. The actual snow line may adjust seasonally, and be either significantly higher in elevation, or lower. The permanent snow line is the level above which snow wil ...
. Sea levels drop due to the removal of large volumes of water above sea level in the icecaps. There is evidence that ocean circulation patterns are disrupted by glaciations. The glacials and interglacials coincide with changes in orbital forcing of climate due to Milankovitch cycles, which are periodic changes in Earth's orbit and the tilt of Earth's rotational axis.
Earth has been in an interglacial period known as the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
for around 11,700 years, and an article in ''Nature'' in 2004 argues that it might be most analogous to a previous interglacial that lasted 28,000 years. Predicted changes in orbital forcing suggest that the next glacial period would begin at least 50,000 years from now. Moreover, anthropogenic forcing from increased greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es is estimated to potentially outweigh the orbital forcing of the Milankovitch cycles for hundreds of thousands of years.
Feedback processes
Each glacial period is subject to positive feedback mechanisms, which makes it more severe, andnegative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
which dampens the overall climate response to different types of forcing. In the case of Quaternary ice ages, Earth's high albedo from ice sheets and atmospheric dust as well as low concentrations of atmospheric contributed to cold glacial climates.

Positive
An important form of feedback is provided by Earth's albedo, which is how much of the sun's energy is reflected rather than absorbed by Earth. Ice and snow increase Earth's albedo, while forests reduce its albedo. When the air temperature decreases, ice and snow fields grow, and they reduce forest cover. This continues until competition with a negative feedback mechanism forces the system to an equilibrium. One theory is that when glaciers form, two things happen: the ice grinds rocks into dust, and the land becomes dry and arid. This allows winds to transport iron rich dust into the open ocean, where it acts as a fertilizer that causes massive algal blooms that pulls large amounts of out of the atmosphere. This in turn makes it even colder and causes the glaciers to grow more. In 1956, Ewing and Donn hypothesized that an ice-free Arctic Ocean leads to increased snowfall at high latitudes. When low-temperature ice covers the Arctic Ocean there is little evaporation or sublimation and the polar regions are quite dry in terms of precipitation, comparable to the amount found in mid-latitudedesert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
s. This low precipitation allows high-latitude snowfalls to melt during the summer. An ice-free Arctic Ocean absorbs solar radiation during the long summer days, and evaporates more water into the Arctic atmosphere. With higher precipitation, portions of this snow may not melt during the summer and so glacial ice can form at lower altitudes ''and'' more southerly latitudes, reducing the temperatures over land by increased albedo as noted above. Furthermore, under this hypothesis the lack of oceanic pack ice allows increased exchange of waters between the Arctic and the North Atlantic Oceans, warming the Arctic and cooling the North Atlantic. (Current projected consequences of global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
include a brief ice-free Arctic Ocean period by 2050.) Additional fresh water flowing into the North Atlantic during a warming cycle may also reduce the global ocean water circulation. Such a reduction (by reducing the effects of the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolin ...
) would have a cooling effect on northern Europe, which in turn would lead to increased low-latitude snow retention during the summer. It has also been suggested that during an extensive glacial, glaciers may move through the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, extending into the North Atlantic Ocean far enough to block the Gulf Stream.
Negative
Ice sheets that form during glaciations erode the land beneath them. This can reduce the land area above sea level and thus diminish the amount of space on which ice sheets can form. This mitigates the albedo feedback, as does the rise in sea level that accompanies the reduced area of ice sheets, since open ocean has a lower albedo than land. Another negative feedback mechanism is the increased aridity occurring with glacial maxima, which reduces the precipitation available to maintain glaciation. The glacial retreat induced by this or any other process can be amplified by similar inverse positive feedbacks as for glacial advances. According to research published in '' Nature Geoscience'', human emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) will defer the next glacial period. Researchers used data on Earth's orbit to find the historical warm interglacial period that looks most like the current one and from this have predicted that the next glacial period would usually begin within 1,500 years. They go on to predict that emissions have been so high that it will not.Causes
The causes of ice ages are not fully understood for either the large-scale ice age periods or the smaller ebb and flow of glacial–interglacial periods within an ice age. The consensus is that several factors are important: atmospheric composition, such as the concentrations ofcarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
(the specific levels of the previously mentioned gases are now able to be seen with the new ice core samples from the European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica (EPICA) Dome C in Antarctica over the past 800,000 years); changes in Earth's orbit around the Sun known as Milankovitch cycles; the motion of tectonic plates resulting in changes in the relative location and amount of continental and oceanic crust on Earth's surface, which affect wind and ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s; variations in solar output; the orbital dynamics of the Earth–Moon system; the impact of relatively large meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
s and volcanism including eruptions of supervolcanoes.
Some of these factors influence each other. For example, changes in Earth's atmospheric composition (especially the concentrations of greenhouse gases) may alter the climate, while climate change itself can change the atmospheric composition (for example by changing the rate at which weathering removes ).
Maureen Raymo, William Ruddiman and others propose that the Tibetan and Colorado Plateaus are immense "scrubbers" with a capacity to remove enough from the global atmosphere to be a significant causal factor of the 40 million year Cenozoic Cooling trend. They further claim that approximately half of their uplift (and "scrubbing" capacity) occurred in the past 10 million years.
Changes in Earth's atmosphere
There is evidence thatgreenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
levels fell at the start of ice ages and rose during the retreat of the ice sheets, but it is difficult to establish cause and effect (see the notes above on the role of weathering). Greenhouse gas levels may also have been affected by other factors which have been proposed as causes of ice ages, such as the movement of continents and volcanism.
The Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth is a historical geology, geohistorical hypothesis that proposes that during one or more of Earth's greenhouse and icehouse Earth, icehouse climates, the planet's planetary surface, surface became nearly entirely freezing, fr ...
hypothesis maintains that the severe freezing in the late Proterozoic was ended by an increase in levels in the atmosphere, mainly from volcanoes, and some supporters of Snowball Earth argue that it was caused in the first place by a reduction in atmospheric . The hypothesis also warns of future Snowball Earths.
In 2009, further evidence was provided that changes in solar insolation provide the initial trigger for Earth to warm after an Ice Age, with secondary factors like increases in greenhouse gases accounting for the magnitude of the change.
Position of the continents
The geological record appears to show that ice ages start when the continents are in positions which block or reduce the flow of warm water from the equator to the poles and thus allow ice sheets to form. The ice sheets increase Earth'sreflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in Reflection (physics), reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the respon ...
and thus reduce the absorption of solar radiation. With less radiation absorbed the atmosphere cools; the cooling allows the ice sheets to grow, which further increases reflectivity in a positive feedback loop. The ice age continues until the reduction in weathering causes an increase in the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
.
There are three main contributors from the layout of the continents that obstruct the movement of warm water to the poles:
* A continent sits on top of a pole, as Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
does today.
* A polar sea is almost land-locked, as the Arctic Ocean is today.
* A supercontinent covers most of the equator, as Rodinia did during the Cryogenian
The Cryogenian (from , meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It is the second of the three periods of the Neoproterozoic era, preceded by the Tonian and followed by the Ediacaran.
The Cryoge ...
period.
Since today's Earth has a continent over the South Pole and an almost land-locked ocean over the North Pole, geologists believe that Earth will continue to experience glacial periods in the geologically near future.
Some scientists believe that the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
are a major factor in the current ice age, because these mountains have increased Earth's total rainfall and therefore the rate at which carbon dioxide is washed out of the atmosphere, decreasing the greenhouse effect. The Himalayas' formation started about 70 million years ago when the Indo-Australian Plate collided with the Eurasian Plate, and the Himalayas are still rising by about 5 mm per year because the Indo-Australian plate is still moving at 67 mm/year. The history of the Himalayas broadly fits the long-term decrease in Earth's average temperature since the mid-Eocene, 40 million years ago.
Fluctuations in ocean currents
Another important contribution to ancient climate regimes is the variation ofocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s, which are modified by continent position, sea levels and salinity, as well as other factors. They have the ability to cool (e.g. aiding the creation of Antarctic ice) and the ability to warm (e.g. giving the British Isles a temperate as opposed to a boreal climate). The closing of the Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama, historically known as the Isthmus of Darien, is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North America, North and South America. The country of Panama is located on the i ...
about 3 million years ago may have ushered in the present period of strong glaciation over North America by ending the exchange of water between the tropical Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Analyses suggest that ocean current fluctuations can adequately account for recent glacial oscillations. During the last glacial period the sea-level fluctuated 20–30 m as water was sequestered, primarily in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
ice sheets. When ice collected and the sea level dropped sufficiently, flow through the Bering Strait (the narrow strait between Siberia and Alaska is about 50 m deep today) was reduced, resulting in increased flow from the North Atlantic. This realigned the thermohaline circulation in the Atlantic, increasing heat transport into the Arctic, which melted the polar ice accumulation and reduced other continental ice sheets. The release of water raised sea levels again, restoring the ingress of colder water from the Pacific with an accompanying shift to northern hemisphere ice accumulation.
According to a study published in ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'' in 2021, all glacial periods of ice ages over the last 1.5 million years were associated with northward shifts of melting Antarctic icebergs which changed ocean circulation patterns, leading to more CO2 being pulled out of the atmosphere. The authors suggest that this process may be disrupted in the future as the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the seco ...
will become too warm for the icebergs to travel far enough to trigger these changes.
Uplift of the Tibetan plateau
Matthias Kuhle's geological theory of Ice Age development was suggested by the existence of an ice sheet covering the Tibetan Plateau during the Ice Ages (Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
?). According to Kuhle, the plate-tectonic uplift of Tibet past the snow-line has led to a surface of c. 2,400,000 square kilometres (930,000 sq mi) changing from bare land to ice with a 70% greater albedo. The reflection of energy into space resulted in a global cooling, triggering the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
Ice Age. Because this highland is at a subtropical latitude, with four to five times the insolation of high-latitude areas, what would be Earth's strongest heating surface has turned into a cooling surface.
Kuhle explains the interglacial periods by the 100,000-year cycle of radiation changes due to variations in Earth's orbit. This comparatively insignificant warming, when combined with the lowering of the Nordic inland ice areas and Tibet due to the weight of the superimposed ice-load, has led to the repeated complete thawing of the inland ice areas.
Variations in Earth's orbit
 The Milankovitch cycles are a set of cyclic variations in characteristics of Earth's orbit around the Sun. Each cycle has a different length, so at some times their effects reinforce each other and at other times they (partially) cancel each other.
There is strong evidence that the Milankovitch cycles affect the occurrence of glacial and interglacial periods within an ice age. The present ice age is the most studied and best understood, particularly the last 400,000 years, since this is the period covered by ice cores that record atmospheric composition and proxies for temperature and ice volume. Within this period, the match of glacial/interglacial frequencies to the Milanković orbital forcing periods is so close that orbital forcing is generally accepted. The combined effects of the changing distance to the Sun, the precession of Earth's axis, and the changing tilt of Earth's axis redistribute the sunlight received by Earth. Of particular importance are changes in the tilt of Earth's axis, which affect the intensity of seasons. For example, the amount of solar influx in July at 65 degrees north
The Milankovitch cycles are a set of cyclic variations in characteristics of Earth's orbit around the Sun. Each cycle has a different length, so at some times their effects reinforce each other and at other times they (partially) cancel each other.
There is strong evidence that the Milankovitch cycles affect the occurrence of glacial and interglacial periods within an ice age. The present ice age is the most studied and best understood, particularly the last 400,000 years, since this is the period covered by ice cores that record atmospheric composition and proxies for temperature and ice volume. Within this period, the match of glacial/interglacial frequencies to the Milanković orbital forcing periods is so close that orbital forcing is generally accepted. The combined effects of the changing distance to the Sun, the precession of Earth's axis, and the changing tilt of Earth's axis redistribute the sunlight received by Earth. Of particular importance are changes in the tilt of Earth's axis, which affect the intensity of seasons. For example, the amount of solar influx in July at 65 degrees north latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
varies by as much as 22% (from 450 W/m2 to 550 W/m2). It is widely believed that ice sheets advance when summers become too cool to melt all of the accumulated snowfall from the previous winter. Some believe that the strength of the orbital forcing is too small to trigger glaciations, but feedback mechanisms like may explain this mismatch.
While Milankovitch forcing predicts that cyclic changes in Earth's orbital elements can be expressed in the glaciation record, additional explanations are necessary to explain which cycles are observed to be most important in the timing of glacial–interglacial periods. In particular, during the last 800,000 years, the dominant period of glacial–interglacial oscillation has been 100,000 years, which corresponds to changes in Earth's orbital eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values be ...
and orbital inclination. Yet this is by far the weakest of the three frequencies predicted by Milankovitch. During the period 3.0–0.8 million years ago, the dominant pattern of glaciation corresponded to the 41,000-year period of changes in Earth's obliquity (tilt of the axis). The reasons for dominance of one frequency versus another are poorly understood and an active area of current research, but the answer probably relates to some form of resonance in Earth's climate system. Recent work suggests that the 100K year cycle dominates due to increased southern-pole sea-ice increasing total solar reflectivity.
The "traditional" Milankovitch explanation struggles to explain the dominance of the 100,000-year cycle over the last 8 cycles. Richard A. Muller, Gordon J. F. MacDonald, and others have pointed out that those calculations are for a two-dimensional orbit of Earth but the three-dimensional orbit also has a 100,000-year cycle of orbital inclination. They proposed that these variations in orbital inclination lead to variations in insolation, as Earth moves in and out of known dust bands in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. Although this is a different mechanism to the traditional view, the "predicted" periods over the last 400,000 years are nearly the same. The Muller and MacDonald theory, in turn, has been challenged by Jose Antonio Rial.
William Ruddiman has suggested a model that explains the 100,000-year cycle by the modulating effect of eccentricity (weak 100,000-year cycle) on precession (26,000-year cycle) combined with greenhouse gas feedbacks in the 41,000- and 26,000-year cycles. Yet another theory has been advanced by Peter Huybers who argued that the 41,000-year cycle has always been dominant, but that Earth has entered a mode of climate behavior where only the second or third cycle triggers an ice age. This would imply that the 100,000-year periodicity is really an illusion created by averaging together cycles lasting 80,000 and 120,000 years. This theory is consistent with a simple empirical multi-state model proposed by Didier Paillard. Paillard suggests that the late Pleistocene glacial cycles can be seen as jumps between three quasi-stable climate states. The jumps are induced by the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
al forcing, while in the early Pleistocene the 41,000-year glacial cycles resulted from jumps between only two climate states. A dynamical
model explaining this behavior was proposed by Peter Ditlevsen. This is in support of the suggestion that the late Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
glacial cycles are not due to the weak 100,000-year eccentricity cycle, but a non-linear response to mainly the 41,000-year obliquity cycle.
Variations in the Sun's energy output
There are at least two types of variation in the Sun's energy output: * In the very long term, astrophysicists believe that the Sun's output increases by about 7% every one billion years. * Shorter-term variations such as sunspot cycles, and longer episodes such as the Maunder Minimum, which occurred during the coldest part of the Little Ice Age. The long-term increase in the Sun's output cannot be a cause of ice ages.Volcanism
Volcanic eruptions may have contributed to the inception and/or the end of ice age periods. At times during the paleoclimate, carbon dioxide levels were two or three times greater than today. Volcanoes and movements in continental plates contributed to high amounts of CO2 in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide from volcanoes probably contributed to periods with highest overall temperatures. One suggested explanation of thePaleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
The Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum (PETM), alternatively ”Eocene thermal maximum 1 (ETM1)“ and formerly known as the "Initial Eocene" or “Late Paleocene thermal maximum", was a geologically brief time interval characterized by a ...
is that undersea volcanoes released methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
from clathrates and thus caused a large and rapid increase in the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
. There appears to be no geological evidence for such eruptions at the right time, but this does not prove they did not happen.
Recent glacial and interglacial phases
 The current geological period, the
The current geological period, the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
, which began about 2.6 million years ago and extends into the present, is marked by warm and cold episodes, cold phases called glacials ( Quaternary ice age) lasting about 100,000 years, and warm phases called interglacials lasting 10,000–15,000 years. The last cold episode of the Last Glacial Period ended about 10,000 years ago. Earth is currently in an interglacial period of the Quaternary, called the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
.
Glacial stages in North America
The major glacial stages of the current ice age in North America are the Illinoian, Eemian, andWisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin glaciation, also called the Wisconsin glacial episode, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated ...
. The use of the Nebraskan, Afton, Kansan, and Yarmouthian stages to subdivide the ice age in North America has been discontinued by Quaternary geologists and geomorphologists. These stages have all been merged into the Pre-Illinoian in the 1980s.Gibbard, P.L., S. Boreham, K.M. Cohen and A. Moscariello, 2007''Global chronostratigraphical correlation table for the last 2.7 million years v. 2007b.''
, jpg version 844 KB. Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England During the most recent North American glaciation, during the latter part of the
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
(26,000 to 13,300 years ago), ice sheets extended to about 45th parallel north. These sheets were thick.
 This Wisconsin glaciation left widespread impacts on the North American landscape. The
This Wisconsin glaciation left widespread impacts on the North American landscape. The Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
and the Finger Lakes were carved by ice deepening old valleys. Most of the lakes in Minnesota and Wisconsin were gouged out by glaciers and later filled with glacial meltwaters. The old Teays River drainage system was radically altered and largely reshaped into the Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
drainage system. Other rivers were dammed and diverted to new channels, such as Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the Canada–United States border, border between the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York (s ...
, which formed a dramatic waterfall and gorge, when the waterflow encountered a limestone escarpment. Another similar waterfall, at the present Clark Reservation State Park near Syracuse, New York
Syracuse ( ) is a City (New York), city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, United States. With a population of 148,620 and a Syracuse metropolitan area, metropolitan area of 662,057, it is the fifth-most populated city and 13 ...
, is now dry.
The area from Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
to Nantucket, Massachusetts was formed from glacial till, and the plethora of lakes on the Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield ( ), also called the Laurentian Shield or the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), th ...
in northern Canada can be almost entirely attributed to the action of the ice. As the ice retreated and the rock dust dried, winds carried the material hundreds of miles, forming beds of loess
A loess (, ; from ) is a clastic rock, clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposition (geology), deposits.
A loess ...
many dozens of feet thick in the Missouri Valley. Post-glacial rebound
Post-glacial rebound (also called isostatic rebound or crustal rebound) is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound an ...
continues to reshape the Great Lakes and other areas formerly under the weight of the ice sheets.
The Driftless Area, a portion of western and southwestern Wisconsin along with parts of adjacent Minnesota
Minnesota ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario to the north and east and by the U.S. states of Wisconsin to the east, Iowa to the so ...
, Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Ill ...
, and Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, was not covered by glaciers.
Last Glacial Period in the semiarid Andes around Aconcagua and Tupungato
A specially interesting climatic change during glacial times has taken place in the semi-arid Andes. Beside the expected cooling down in comparison with the current climate, a significant precipitation change happened here. So, researches in the presently semiarid subtropic Aconcagua-massif (6,962 m) have shown an unexpectedly extensive glacial glaciation of the type "ice stream network". The connected valley glaciers exceeding 100 km in length, flowed down on the East-side of this section of the Andes at 32–34°S and 69–71°W as far as a height of 2,060 m and on the western luff-side still clearly deeper. Where current glaciers scarcely reach 10 km in length, the snowline (ELA) runs at a height of 4,600 m and at that time was lowered to 3,200 m asl, i.e. about 1,400 m. From this follows that—beside of an annual depression of temperature about c. 8.4 °C— here was an increase in precipitation. Accordingly, at glacial times the humid climatic belt that today is situated several latitude degrees further to the S, was shifted much further to the N.Effects of glaciation
 Although the last glacial period ended more than 8,000 years ago, its effects can still be felt today. For example, the moving ice carved out the landscape in Canada (See Canadian Arctic Archipelago), Greenland, northern Eurasia and Antarctica. The erratic boulders, till, drumlins, eskers, fjords, kettle lakes,
Although the last glacial period ended more than 8,000 years ago, its effects can still be felt today. For example, the moving ice carved out the landscape in Canada (See Canadian Arctic Archipelago), Greenland, northern Eurasia and Antarctica. The erratic boulders, till, drumlins, eskers, fjords, kettle lakes, moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and Rock (geology), rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a gla ...
s, cirque
A (; from the Latin word ) is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by Glacier#Erosion, glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie (from , meaning a pot or cauldron) and ; ). A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform a ...
s, horns, etc., are typical features left behind by the glaciers. The weight of the ice sheets was so great that they deformed Earth's crust and mantle. After the ice sheets melted, the ice-covered land rebounded. Due to the high viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
of Earth's mantle, the flow of mantle rocks which controls the rebound process is very slow—at a rate of about 1 cm/year near the center of rebound area today.
During glaciation, water was taken from the oceans to form the ice at high latitudes, thus global sea level dropped by about 110 meters, exposing the continental shelves and forming land-bridges between land-masses for animals to migrate. During deglaciation, the melted ice-water returned to the oceans, causing sea level to rise. This process can cause sudden shifts in coastlines and hydration systems resulting in newly submerged lands, emerging lands, collapsed ice dams resulting in salination of lakes, new ice dams creating vast areas of freshwater, and a general alteration in regional weather patterns on a large but temporary scale. It can even cause temporary reglaciation. This type of chaotic pattern of rapidly changing land, ice, saltwater and freshwater has been proposed as the likely model for the Baltic and Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
n regions, as well as much of central North America at the end of the last glacial maximum, with the present-day coastlines only being achieved in the last few millennia of prehistory. Also, the effect of elevation on Scandinavia submerged a vast continental plain that had existed under much of what is now the North Sea, connecting the British Isles to Continental Europe.
The redistribution of ice-water on the surface of Earth and the flow of mantle rocks causes changes in the gravitational field
In physics, a gravitational field or gravitational acceleration field is a vector field used to explain the influences that a body extends into the space around itself. A gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenomena, such as ...
as well as changes to the distribution of the moment of inertia of Earth. These changes to the moment of inertia result in a change in the angular velocity, axis, and wobble of Earth's rotation.
The weight of the redistributed surface mass loaded the lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
, caused it to flex and also induced stress within Earth. The presence of the glaciers generally suppressed the movement of faults below. During deglaciation, the faults experience accelerated slip triggering earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
s. Earthquakes triggered near the ice margin may in turn accelerate ice calving and may account for the Heinrich events. As more ice is removed near the ice margin, more intraplate earthquake
An intraplate earthquake occurs in the ''interior'' of a Plate tectonics, tectonic plate, in contrast to an interplate earthquake on the ''boundary'' of a tectonic plate. They are relatively rare compared to the more familiar interplate earthqu ...
s are induced and this positive feedback may explain the fast collapse of ice sheets.
In Europe, glacial erosion and isostatic sinking from the weight of ice made the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, which before the Ice Age was all land drained by the Eridanos River.
Future ice ages
Based on past estimates for interglacial durations of about 10,000 years, there was some concern in the 1970s that the next glacial period would be imminent. Human impact is now seen as possibly extending what would already be an unusually long warm period. Ice ages go through cycles of about 100,000 years, but the next one may well be avoided due to human carbon dioxide emissions. According to Stephen Barker ofCardiff University
Cardiff University () is a public research university in Cardiff, Wales. It was established in 1883 as the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire and became a founding college of the University of Wales in 1893. It was renamed Unive ...
, without human interference, the next glaciation of the Earth would "occur within the next 11,000 years, and it would end in 66,000 years’ time."
A 2015 report by the Past Global Changes Project says simulations show that a new glaciation is unlikely to happen within the next approximately 50,000 years, before the next strong drop in Northern Hemisphere summer insolation occurs "if either atmospheric concentration
remains above 300 ppm or cumulative carbon emissions exceed 1000 Pg C" (i.e. 1,000 gigatonnes carbon). "Only for an atmospheric content below the preindustrial level may a glaciation occur within the next 10 ka. ... Given the continued anthropogenic emissions, glacial inception is very unlikely to occur in the next 50 ka, because the timescale for and temperature reduction toward unperturbed values in the absence of active removal is very long PCC, 2013 and only weak precessional forcing occurs in the next two precessional cycles." (A precessional cycle is around 21,000 years, the time it takes for the perihelion to move all the way around the tropical year.)
See also
* * * * * * List of Ice Age species preserved as permafrost mummies * * *References
Works cited
* Historical SimulationExternal links
Cracking the Ice Age
from PBS * *
Eduard Y. Osipov, Oleg M. Khlystov. Glaciers and meltwater flux to Lake Baikal during the Last Glacial Maximum.
* {{Authority control Geological history of the Great Lakes Glaciology History of climate variability and change History of science