IMAX on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
IMAX is a proprietary system of high-resolution cameras, film formats, film projectors, and

by Mark Wilson (Gizmodo.com, published May 29, 2009) The previous mechanism was inadequate to handle this intermittent mechanical movement that was three times longer, and so Jones's invention was necessary for the novel IMAX projector method with its horizontal film feed. As it became clear that a single, large-screen image had more impact than multiple smaller ones and was a more viable product direction, Multiscreen changed its name to IMAX. Co-founder Graeme Ferguson explained how the name IMAX originated:
 '' Tiger Child'', the first IMAX film, was demonstrated at
'' Tiger Child'', the first IMAX film, was demonstrated at

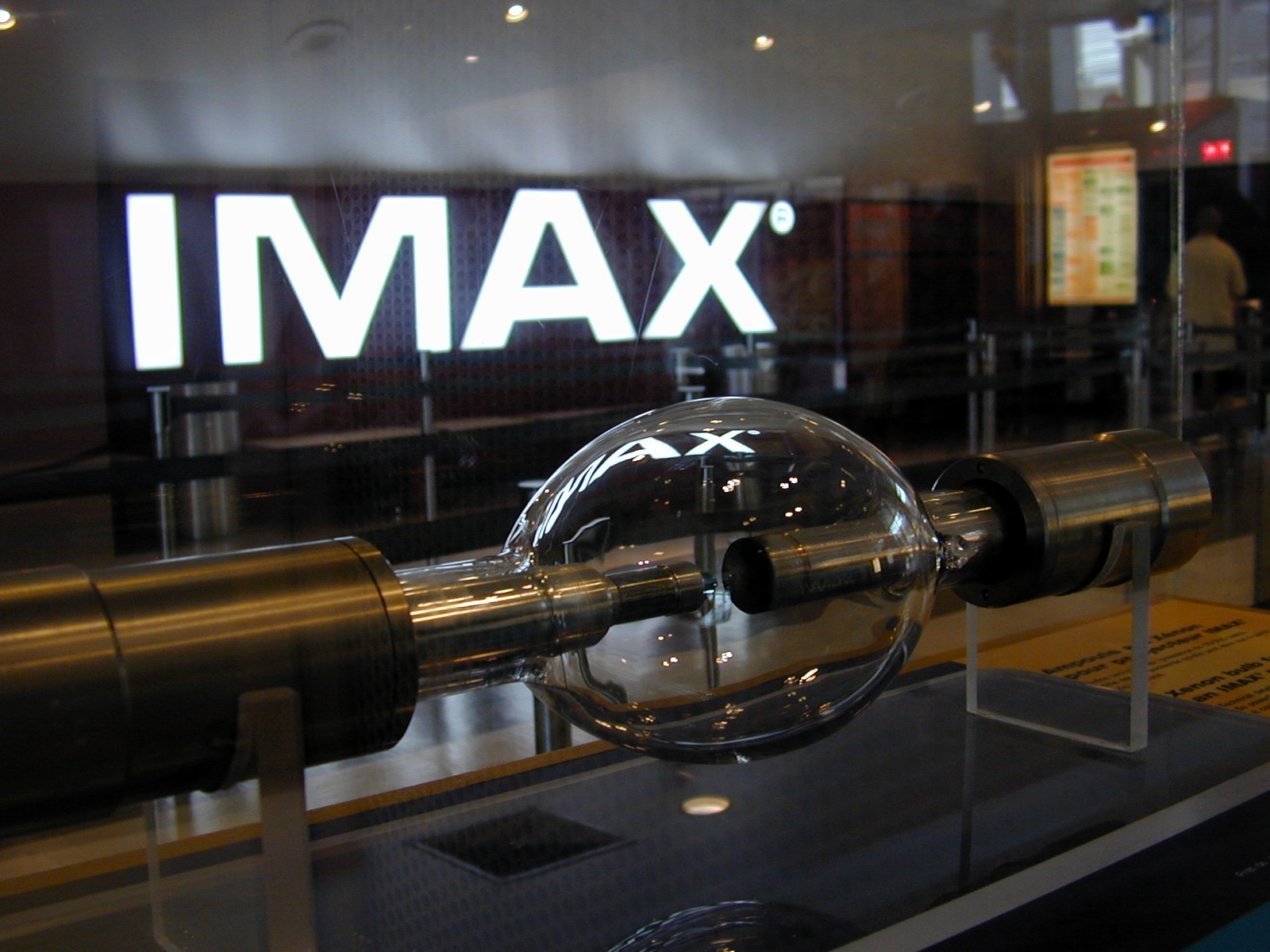 Transporting the large film stock through the optical system presented challenges for both the camera and the projector. Conventional 70 mm systems were not steady enough for the 586× magnification. On the projector side, William Shaw adapted an Australian patent (no. 291,375) for film transport called the "rolling loop" by adding a
Transporting the large film stock through the optical system presented challenges for both the camera and the projector. Conventional 70 mm systems were not steady enough for the 586× magnification. On the projector side, William Shaw adapted an Australian patent (no. 291,375) for film transport called the "rolling loop" by adding a
 The
The


 In the late-1960s, the San Diego Hall of Science (later known as the San Diego Space and Science Foundation) began searching North America for a large-format film system to project on the dome of their planned tilted
In the late-1960s, the San Diego Hall of Science (later known as the San Diego Space and Science Foundation) began searching North America for a large-format film system to project on the dome of their planned tilted
LFexaminer.com.
Some have criticized the company's marketing approach, with the format being dubbed "Lie-MAX". The company has defended the format by saying it has a bigger screen, brighter picture and better sound than standard theatres. Despite the differences with digital IMAX, the cost-effective format has aided in the company's worldwide growth, especially in Russia and China.
 In the US, IMAX has mostly been used for specialty applications. The expense and logistical challenges of producing and presenting IMAX films have led to approximately 40 minutes shorter running times than conventional films. Most are documentaries suited for institutional venues such as museums and science centers. IMAX cameras have been used while orbiting the Earth, climbing
In the US, IMAX has mostly been used for specialty applications. The expense and logistical challenges of producing and presenting IMAX films have led to approximately 40 minutes shorter running times than conventional films. Most are documentaries suited for institutional venues such as museums and science centers. IMAX cameras have been used while orbiting the Earth, climbing
 IMAX cameras have flown in space on 17 occasions, NASA astronauts have used handheld IMAX cameras to document missions, and an IMAX camera has also been mounted in the payload bay of the Shuttle. Space shuttle mission STS-41-C filmed the deployment of the Long Duration Exposure Facility, LDEF (Long duration exposure facility) and the repair of the Solar Maximum Mission, Solar Max satellite. This footage was included in the 1985 IMAX movie ''The Dream Is Alive''. Kennedy Space Center in Florida has two IMAX 3D theaters. These show space movies, including footage shot on missions and narrated by celebrities. Two of the IMAX cameras used by NASA are now on display at the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., Washington DC.
IMAX cameras have flown in space on 17 occasions, NASA astronauts have used handheld IMAX cameras to document missions, and an IMAX camera has also been mounted in the payload bay of the Shuttle. Space shuttle mission STS-41-C filmed the deployment of the Long Duration Exposure Facility, LDEF (Long duration exposure facility) and the repair of the Solar Maximum Mission, Solar Max satellite. This footage was included in the 1985 IMAX movie ''The Dream Is Alive''. Kennedy Space Center in Florida has two IMAX 3D theaters. These show space movies, including footage shot on missions and narrated by celebrities. Two of the IMAX cameras used by NASA are now on display at the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., Washington DC.
 Many IMAX films have been remastered into High-definition television, HDTV format (cropped to fit into HDTV's 16:9 aspect ratio) for the MOJO HD, HDNet and HD Theatre networks and release on DVD and Blu-ray Disc. In July 2005, the London IMAX, BFI IMAX Cinema in London became the first to host live music concerts, using a digital non-IMAX projector. The Science Museum London and BFI IMAX Cinema have also hosted Electronic sports, computer game tournaments using digital projectors. Several amusement park attractions have integrated IMAX film segments, including Back to the Future: The Ride formerly at Universal Destinations & Experiences, Universal Studios in Florida and California, Horizons (Epcot attraction), Horizons formerly at Epcot and Soarin’ Over California at Disney California Adventure and Epcot.
Many IMAX films have been remastered into High-definition television, HDTV format (cropped to fit into HDTV's 16:9 aspect ratio) for the MOJO HD, HDNet and HD Theatre networks and release on DVD and Blu-ray Disc. In July 2005, the London IMAX, BFI IMAX Cinema in London became the first to host live music concerts, using a digital non-IMAX projector. The Science Museum London and BFI IMAX Cinema have also hosted Electronic sports, computer game tournaments using digital projectors. Several amusement park attractions have integrated IMAX film segments, including Back to the Future: The Ride formerly at Universal Destinations & Experiences, Universal Studios in Florida and California, Horizons (Epcot attraction), Horizons formerly at Epcot and Soarin’ Over California at Disney California Adventure and Epcot.
Large Formats
Describes the differences between the three different "large-format" or "giant-screen" formats, the IMAX Digital format, and the conventional formats.
IMAX Soundtracks Database
* YouTube videos explaining the theater operation and maintenance processes o
threading & playing
a 70mm IMAX film
building a filmalt
by splicing together 40 reels shipped in 7 boxes making one feature-length film 9 miles long weighing 1,200 pounds, an
replacing the projector's xenon lamp
($5600 bulb cost). {{DEFAULTSORT:Imax IMAX, 3D imaging Canadian inventions Film and video technology Film formats Motion picture film formats Special-venue films Theatres Premium large format movie formats
theater
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors to present experiences of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communi ...
s known for having very large screens with a tall aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a geometry, geometric shape is the ratio of its sizes in different dimensions. For example, the aspect ratio of a rectangle is the ratio of its longer side to its shorter side—the ratio of width to height, when the rectangl ...
(approximately either 1.43:1 or 1.90:1) and steep stadium seating, with the 1.43:1 ratio format being available only in few selected locations.
Graeme Ferguson, Roman Kroitor, Robert Kerr, and William C. Shaw were the co-founders of what would be named the IMAX Corporation
IMAX Corporation is a Canadian production theater company which designs and manufactures IMAX cameras and Projection screen, projection systems as well as performing film development, production, post-production and distribution to IMAX-affiliat ...
(founded in September 1967 as Multiscreen Corporation, Ltd.), and they developed the first IMAX cinema projection standards in the late 1960s and early 1970s in Canada.
IMAX GT is the premium large format. The digital format uses dual laser projectors, which can show 1.43 digital content when combined with a 1.43 screen. The film format uses very large screens of and, unlike most conventional film projectors, the film runs horizontally so that the image width can be greater than the width of the film stock
Film stock is an analog medium that is used for recording motion pictures or animation. It is recorded on by a movie camera, developed,
edited, and projected onto a screen using a movie projector. It is a strip or sheet of transparent pl ...
. It is called the 15/70 format. They can be purpose-built theaters and dome theaters, and many installations of this type limit themselves to a projection of high quality, short documentaries.
The dedicated buildings and projectors required high construction and maintenance costs, necessitating several compromises in the following years. To reduce costs, the IMAX SR and MPX systems were introduced in 1998 and 2004, respectively, to make IMAX available to multiplex
Multiplex may refer to:
Science and technology
* Multiplex communication, combining many signals into one transmission circuit or channel
** Multiplex (television), a group of digital television or radio channels that are combined for broadcast
* ...
and existing theaters. The SR system featured slightly smaller screens than GT theatres, though still in purpose-built auditoriums with a 1.43:1 aspect ratio. The MPX projectors were solely used to retrofit existing multiplex auditoriums, losing much of the quality of the GT experience.
Later came the introduction of the IMAX Digital 2K and IMAX with Laser 4K in 2008 and 2014 respectively, still limited in respect to the 70 megapixels of equivalent resolution of the original 15/70 film. Both technologies are purely digital and suitable to retrofit existing theaters. Since 2018, the Laser system has been employed to retrofit full dome installations, with limited results due to the large area of a dome screen.
History
Multiscreen Corporation
The single-projector/single-camera system they eventually settled upon was designed and built by Shaw based upon a novel "Rolling Loop" film-transport technology purchased from Peter Ronald Wright Jones, a machine shop worker from Brisbane, Australia. Film projectors do not continuously flow the film in front of the bulb, but instead "stutter" the film travel so that each frame can be illuminated in a momentarily-paused still image. This requires a mechanical apparatus to buffer the jerky travel of the film strip. The older technology of running 70 mm film vertically through the projector used only five sprocket perforations on the sides of each frame; however, the IMAX method used fifteen perforations per frame.How Regular Movies Become "IMAX" Filmsby Mark Wilson (Gizmodo.com, published May 29, 2009) The previous mechanism was inadequate to handle this intermittent mechanical movement that was three times longer, and so Jones's invention was necessary for the novel IMAX projector method with its horizontal film feed. As it became clear that a single, large-screen image had more impact than multiple smaller ones and was a more viable product direction, Multiscreen changed its name to IMAX. Co-founder Graeme Ferguson explained how the name IMAX originated:
... the incorporation date f the company wasSeptember 1967. ... he name changecame a year or two later. We first called the company Multiscreen Corporation because that, in fact, was what people knew us as. ... After about a year, our attorney informed us that we could never copyright or trademark Multivision. It was too generic. It was a descriptive word. The words that you can copyright are words like Kleenex or Xerox or Coca-Cola. If the name is descriptive, you can't trademark it so you have to make up a word. So we were sitting at lunch one day in a Hungarian restaurant in Montreal and we worked out a name on a placemat on which we wrote all the possible names we could think of. We kept working with the idea of maximum image. We turned it around and came up with IMAX.The name change actually happened more than two years later, because a key patent filed on January 16, 1970, was assigned under the original name Multiscreen Corporation, Limited. IMAX Chief Administration Officer Mary Ruby was quoted as saying, "Although many people may think 'IMAX' is an
acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each wor ...
, it is, in fact, a made-up word."
IMAX Corporation
 '' Tiger Child'', the first IMAX film, was demonstrated at
'' Tiger Child'', the first IMAX film, was demonstrated at Expo '70
The or Expo '70 was a world's fair held in Suita, Osaka Prefecture, Japan, between 15 March and 13 September 1970. Its theme was "Progress and Harmony for Mankind." In Japanese, Expo '70 is often referred to as . It was the first world's fair ...
in Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
, Japan. The first permanent IMAX installation was built at the Cinesphere
Cinesphere is the world's first permanent IMAX movie theatre, located on the grounds of Ontario Place in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Constructed in 1971, it is the largest IMAX theatre in Ontario. The theatre has both IMAX 70mm and IMAX with Laser ...
theatre at Ontario Place
Ontario Place was an entertainment venue, event venue, and park in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The venue is located on three artificial landscaped islands just off-shore in Lake Ontario, south of Exhibition Place, and southwest of Downtown Toron ...
in Toronto. It debuted in May 1971, showing the film '' North of Superior''. The installation remained in place during Ontario Place's hiatus for redevelopment. The Cinesphere was renovated while Ontario Place was closed and re-opened on November 3, 2017, with IMAX 70 mm and IMAX with laser illumination.
During Expo '74 in Spokane, Washington
Spokane ( ) is the most populous city in eastern Washington and the county seat of Spokane County, Washington, United States. It lies along the Spokane River, adjacent to the Selkirk Mountains, and west of the Rocky Mountain foothills, south o ...
, an IMAX screen that measured was featured in the 'Environmental Theater' of the US Pavilion, the largest structure in the expo; at the time, it was the largest movie screen in the world. It became the first IMAX Theatre to not be partnered with any other brand of movie theatres. About five million visitors viewed the short film ''Man Belongs to the Earth
A man is an adult male human. Before adulthood, a male child or adolescent is referred to as a boy.
Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the fathe ...
''. Because the screen covered the viewer's total visual field when looking directly forward, most felt a sensation of motion and some experienced motion sickness
Motion sickness occurs due to a difference between actual and expected motion. Symptoms commonly include nausea, vomiting, cold sweat, headache, dizziness, tiredness, loss of appetite, and increased salivation. Complications may rarely include ...
.
The large pavilion screen was torn down after the exposition closed and was replaced by a nearby permanent IMAX theater which opened in 1978 and was demolished in 2018; however, its screen size is less than half. Due to protests, the City of Spokane officials decided to work with the IMAX Corporation to demolish the 1978 theatre, under the condition they renovate the former US Pavilion itself into IMAX's first permanent ''outdoor'' giant-screen theatre. The plan was to use material on the inside of the structure similar to that used when first constructed. However, it was expected to last only five years, due to weather conditions destroying previous materials. Concept art has been released in videos featured on Spokane's renovation site, and its budget revealed that seating is planned for more than 2,000.
The first permanent IMAX Dome installation, the Eugene Heikoff and Marilyn Jacobs Heikoff Dome Theatre at the Reuben H. Fleet Science Center
The Fleet Science Center is a science museum and planetarium in Balboa Park (San Diego), Balboa Park in San Diego, California. Established in 1973, it was the first science museum to combine interactive science exhibits with a planetarium and an ...
, opened in San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
's Balboa Park in 1973. It doubles as a planetarium theater. The first permanent IMAX 3D theatre was built in Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, British Columbia, for '' Transitions'' at Expo '86, and was in use until September 30, 2009. It was located at the tip of Canada Place, a Vancouver landmark.
Digital projection
In 2008, IMAX extended its brand into traditional theaters with the introduction of Digital IMAX, a lower-cost system that uses two 2K digital projectors to project on a 1.90:1 aspect ratio screen. This lower-cost option, which allowed for the conversion of existing multiplex theater auditoriums, helped IMAX to grow from 299 screens worldwide at the end of 2007 to over 1,000 screens by the end of 2015. , there were 1,302 IMAX theatres located in 75 countries, of which 1,203 were in commercial multiplexes. The switch to digital projection came at a steep cost in image quality, with 2K projectors having roughly an order of magnitude less resolution than traditional IMAX film projectors. Maintaining the same 7-story screen size would only make this loss more noticeable, so many new theaters were instead built with significantly smaller screens. These newer theaters with much lower resolution and much smaller screens soon began to be referred to by the derogatory name "LieMAX", particularly because the company still marketed the new screens similarly to the old ones, without making the major differences clear to the public, going so far as to market the smallest "IMAX" screen, having 10 times less area, similarly to the largest while persisting with the same brand name. Since 2002, some feature films have been converted into IMAX format for displaying in IMAX theatres, and some have also been (partially) shot in IMAX. By late 2017, 1,302 IMAX theatre systems were installed in 1,203 commercial multiplexes, 13 commercial destinations, and 86 institutional settings in 75 countries, with less than a quarter of those having the capability to show 70mm film at the resolution of the large format as originally conceived.Technical aspects
Camera

Film cameras
The IMAX cinema process increases theimage resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies ...
by using a larger film frame; in relative terms, a frame of IMAX format film has three times the theoretical horizontal resolution of a frame of 35 mm film. To achieve such increased image resolution, which IMAX estimates at approximately 12,000 lines (6,000 line pair modulations) of horizontal resolution (18K), 65 mm film stock passes horizontally through the IMAX movie camera, 15 perforations at a time. At 24 frames per second, this means that the film moves through the camera at per minute (just over 6 km/h). In a conventional 65 mm camera, the film passes vertically through the camera, five perforations at a time, or per minute. In comparison, in a conventional 35 mm camera, 35 mm film passes vertically through the camera, at four (smaller) perforations at a time, which translates to per minute.
In the Todd-AO
Todd-AO is an American post-production company founded in 1953 by Mike Todd and Robert Naify, providing sound-related services to the motion picture and television industries. The company retains one facility, in the Los Angeles area.
Todd-AO ...
70 mm-format of widescreen cinema, the image area of a 65 mm film-frame is ; in the IMAX-format of widescreen cinema, the film-frame dimensions are . To match the standard image resolution of the moving image produced with the film-speed of 24 frames per second
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (co ...
, an IMAX film requires three times the length of (negative) film stock required for a 65 mm film of comparable scope and cinematic technique
This article contains a list of cinematic techniques that are divided into categories and briefly described.
Basic definitions of terms
;180-degree rule
:A continuity editorial technique in which sequential shots of two or more actors within ...
.
In March 2022, IMAX announced a new initiative in cooperation with Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company, referred to simply as Kodak (), is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in film photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated i ...
, Panavision
Panavision Inc. is an American motion picture equipment company (law), company founded in 1954 specializing in cameras and photographic lens, lenses, based in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk a ...
, and FotoKem to develop "a new fleet of next generation IMAX film cameras", with a goal to deploy the first four units in the next two years. Christopher Nolan
Sir Christopher Edward Nolan (born 30 July 1970) is a British and American filmmaker. Known for his Cinema of the United States, Hollywood Blockbuster (entertainment), blockbusters with complex storytelling, he is considered a leading filmma ...
and Jordan Peele
Jordan Haworth Peele (born February 21, 1979) is an American actor, comedian and filmmaker. He is known for his film and television work in the Comedy film, comedy and Horror film, horror genres. He has received List of awards and nominations r ...
are among a group of advisors, made up of filmmakers and cinematographers, assisting in identifying new specs and features for the prototype development phase.
In a May 2024 interview with Collider, IMAX CEO Richard Gelfond revealed that there will be four new identical cameras that will be 30% quieter than the existing cameras. ''The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' (''WSJ''), also referred to simply as the ''Journal,'' is an American newspaper based in New York City. The newspaper provides extensive coverage of news, especially business and finance. It operates on a subscriptio ...
'' revealed that the new cameras will be made out of carbon fiber and titanium, and they will feature a five inch color display along with wireless capability.
Phantom 65 IMAX 3D digital camera
In 2011, IMAX announced a 4K 3D digital camera. The camera was developed alongsideVision Research
''Vision Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal specializing in the neuroscience and psychology of the visual system
The visual system is the physiological basis of visual perception (the ability to perception, detect and process ...
and AbelCine, integrating two Phantom 65 engines. A prototype camera was used for the documentary '' Born to be Wild'', in which approximately 10% of the finished film was shot with the system. The company has said they have no intention of replacing the higher resolution film cameras with the new digital camera, but the latter can be used in scenes that require a lightweight or relatively small 3D camera. While IMAX has completed the production camera and has placed it in service on several films, they have no plans to produce an IMAX film solely with the new digital system. '' Transformers: Age of Extinction'' is the first feature film partially filmed with the Phantom 65 IMAX 3D camera.
Arri Alexa IMAX digital camera
In 2015, IMAX announced a 2D digital camera that was developed alongsideArri
Arri Group () (stylized as "ARRI") is a German manufacturer of motion picture film equipment. Based in Munich, the company was founded in 1917. It produces professional motion picture cameras, lenses, lighting and post-production equipment. It ...
, the camera being based on the latter company's Arri Alexa 65 technology. The first production to use the camera was '' Captain America: Civil War''. The Russo brothers
Anthony Russo (born February 3, 1970) and Joseph Russo (born July 18, 1971), collectively known as the Russo brothers ( ), are American filmmakers. They direct most of their work together, and their work has grossed more than $6.8 billion worl ...
have stated that they solely used the Arri Alexa IMAX on '' Avengers: Infinity War'' (2018) and '' Avengers: Endgame'' (2019).
For '' Transformers: The Last Knight'', two Arri Alexa IMAX cameras were combined in a rig to provide native 3D, with the film containing 98% of IMAX footage.
IMAX certified cameras
In September 2020, IMAX launched the "Filmed for IMAX" program, which certifies high-quality digital cameras that can be used to create IMAX-format films. As the scope of certified cameras expands, it will be easier for filmmakers to create films to meet the projection needs of the IMAX giant screen theater. '' Top Gun: Maverick'' (shot with the Sony CineAlta Venice) and ''Dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat ...
'' (shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF) were among the first films that used IMAX-certified cameras. Other films between 2021 and 2023 that captured with this program are '' The Suicide Squad'' (shot with the Red Ranger Monstro and Komodo), ''Shang-Chi and the Legend of the Ten Rings
''Shang-Chi and the Legend of the Ten Rings'' is a 2021 American superhero film based on Marvel Comics featuring the character Shang-Chi. Produced by Marvel Studios and distributed by Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures, it is List of Marvel ...
'' (shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF), '' The Battle at Lake Changjin'' and ''The Battle at Lake Changjin II
''The Battle at Lake Changjin II'' (released in the United Kingdom as ''The Battle at Water Gate Bridge''), is a 2022 war film, war drama film co-produced and co-directed by Chen Kaige, Tsui Hark and Dante Lam, written by Lan Xiaolong and Huang J ...
'' (shot with the Red Ranger Monstro), '' Eternals'' (shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF), '' Doctor Strange in the Multiverse of Madness'' (shot with Panavision Millennium DXL2), '' Thor: Love and Thunder'' (shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF), '' Black Panther: Wakanda Forever'' (shot with the Sony CineAlta Venice), '' Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 3'' (shot with the Red V-Raptor), '' The Marvels'' (shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF) and '' Dune: Part Two'' (shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF).
Film stock
The IMAX format is generically called "15/70" film, the name referring to the 15 sprocket holes or perforations per frame. The film's bulk and weight require horizontal platters, rather than conventional vertically mounted film reels. IMAX film is fed through the projector horizontally, and the film is drawn from the inner circumference of the platter, not from the outer circumference like in conventional film reels. A system is in place to keep the film in the outer circumference from flying outwards due to centrifugal force while the platter is spinning. IMAX film is shipped to theaters in several small reels that are spliced into one continuous length that is then wound into a platter, a process that may take hours to complete. Films may be several kilometers in length: ''Avatar'', which was 2:45 hours in duration, was close to long. Platters are handled using special forklifts. IMAX platters range from diameter to accommodate 1 to 2.75 hours of film. Platters with a 2.5 hour feature film weigh . IMAX uses ESTAR-based print film in their 15/70 rolling-loop film projection systems. ESTAR-based print film provides greater precision. The chemical development process does not change the size or shape of ESTAR print film, and IMAX's pin registration system (''especially that of the camera mechanism'') does not tolerate eithersprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the whe ...
-hole or film-thickness variations, but the film can still swell or shrink under varying temperature and humidity. This requires projection booths to be kept at a temperature of between 20 and 23.8 °C and a humidity of 50%. The film is too large to be moved using its sprockets, so they are instead used for registration, to aid in aligning the film. A feature film platter can cost to print. The camera negative is actually 65 mm film stock, but it runs horizontally and with 15 perforations per frame. The camera, like the projector, has a vacuum system; this makes the camera noisy, forbidding the sync-sound recording of quiet scenes. The camera has enough film for three minutes of shooting. The large frame of the film also imposes optical limitations such as an extremely shallow depth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus (optics), focus in an image captured with a camera. See also the closely related depth of focus.
Factors affecting depth ...
when shooting with an open aperture.
Soundtrack – double-system
To use more of the image area, IMAX film does not include an embedded soundtrack. Instead, the IMAX system specifies a separate six-channel magnetic film, recorded and played back on a film follower locked to picture, just asVitaphone
Vitaphone was a sound film system used for feature films and nearly 1,000 short subjects made by Warner Bros. and its sister studio First National Pictures, First National from 1926 to 1931. Vitaphone is the last major analog sound-on-disc sys ...
had been (utilizing 16-inch 33 1/3 RPM electrical transcription discs) in the early 20th century, and was the same technology used to provide the 7-channel soundtrack accompanying films photographed and exhibited in the Cinerama process in the mid-1950s. By the early 1990s, a separate DTS-based 6-track digital sound system was used, similarly locked to the projector by a SMPTE time code
SMPTE timecode ( or ) is a set of cooperating standards to label individual frames of video or film with a timecode. The system is defined by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers in the SMPTE 12M specification. SMPTE revised ...
synchronization apparatus, the audio played off a series of proprietarily encoded CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold b ...
discs. In the late 1990s, IMAX upgraded this system to use a hard drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
that carries a single uncompressed audio
Audio most commonly refers to sound, as it is transmitted in signal form. It may also refer to:
Sound
*Audio signal, an electrical representation of sound
*Audio frequency, a frequency in the audio spectrum
*Digital audio, representation of sound ...
file. These are converted directly to analogue rather than processed through a decoding method such as DTS. IMAX film and IMAX digital cinemas utilise a 6-channel surround sound system - with Left, Centre, Right speakers behind the screen similar to conventional cinemas, plus an additional "top center" speaker to create the effect of height in the screen. There are also 2 rear left and rear right surround sound speaker, arranged as clusters of speakers rather than a spaced array of speakers such as used in a Dolby surround sound system. IMAX with Laser adds another 6 channels of sound: 4 channels of overhead speakers plus 2 extra side surround speakers.
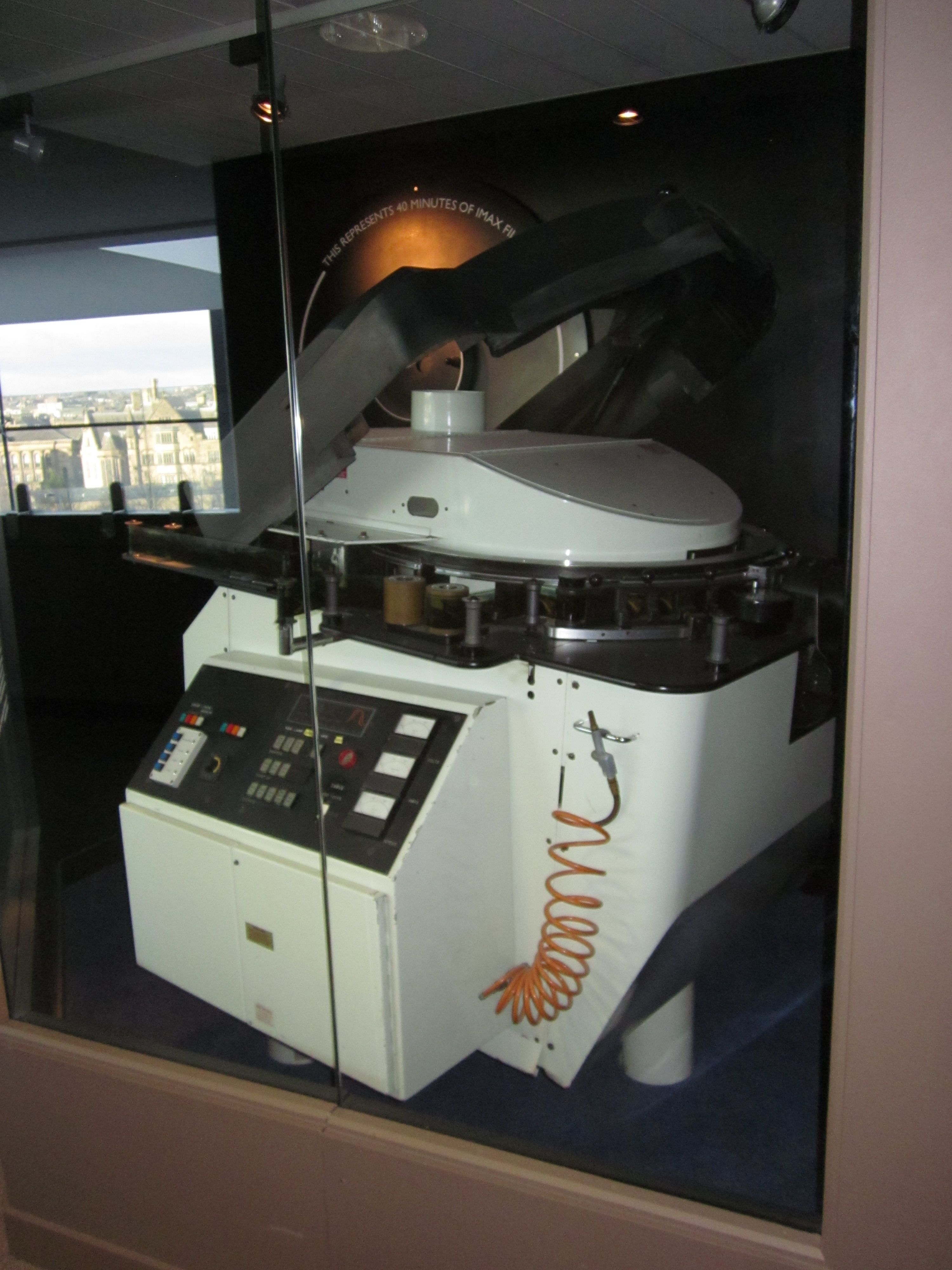
Projectors
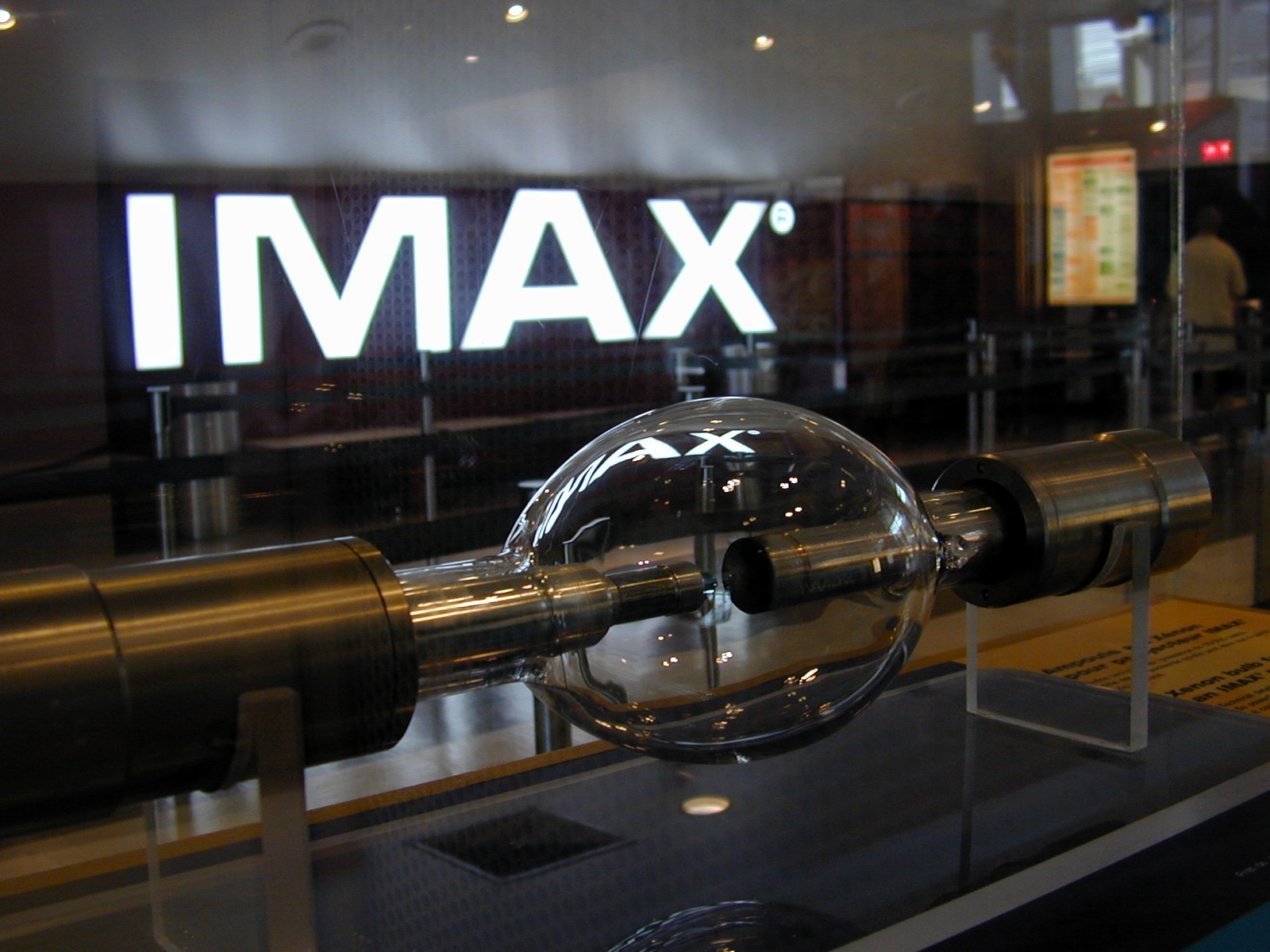 Transporting the large film stock through the optical system presented challenges for both the camera and the projector. Conventional 70 mm systems were not steady enough for the 586× magnification. On the projector side, William Shaw adapted an Australian patent (no. 291,375) for film transport called the "rolling loop" by adding a
Transporting the large film stock through the optical system presented challenges for both the camera and the projector. Conventional 70 mm systems were not steady enough for the 586× magnification. On the projector side, William Shaw adapted an Australian patent (no. 291,375) for film transport called the "rolling loop" by adding a compressed air
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air in vehicle tires and shock absorbers are commonly used for improved traction and reduced vibration. Compressed air is an important medium for t ...
"puffer" to accelerate the film, and put a cylindrical lens in the projector's "aperture block". The rolling loop mechanism is used to move the film in projectors and cameras; the sprockets in the film are only used for registration as the film is too large to be moved with sprockets at the necessary speeds for projection and filming without damage.
The projector uses a vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressur ...
to pull the film into contact with this lens. Thus the " field flattener" flattens the image field. The lens is twice the height of the film and connects to a pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek 'wind, breath') is the use of gas or pressurized air in mechanical systems.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located a ...
piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder a ...
so it can be moved up or down while the projector is running. This way, if a piece of dust comes off the film and sticks to the lens, the projectionist can switch to a clean portion of the lens at the push of a button. The lens also has "wiper bars" made of a felt
Felt is a textile that is produced by matting, condensing, and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic fiber, acrylic or acrylonitrile or ...
or brush-like material that wipes dust off the lens as it moves up or down. The projector uses a vacuum to keep the film flat and oriented correctly for projection. The shutter of an IMAX projector is also kept open for longer than a 35 mm projector shutter to increase image brightness.
IMAX projectors are pin-stabilized; this means that four registration pins engage the perforations at the corners of the projected frame to ensure perfect alignment. Shaw added cam
Cam or CAM may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cam (mechanism), a mechanical linkage which translates motion
* Camshaft, a shaft with a cam
* Camera or webcam, a device that records images or video
In computing
* Computer-aided manufacturin ...
-controlled arms to decelerate each frame to eliminate the microscopic shaking as the frame "settled" onto the registration pins. The projector's shutter is open around 20% longer than in conventional equipment, and the light source is brighter. The xenon short-arc lamps are made with a thin envelope of fused quartz
Fused quartz, fused silica or quartz glass is a glass consisting of almost pure silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) in amorphous (non-crystalline) form. This differs from all other commercial glasses, such as soda-lime glass, lead glass, or borosi ...
and contain xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
gas at a pressure of about 25 atmospheres (). Because of this, projectionists are required to wear protective body armor
Body armour, personal armour (also spelled ''armor''), armoured suit (''armored'') or coat of armour, among others, is armour for human body, a person's body: protective clothing or close-fitting hands-free shields designed to absorb or deflect ...
when changing or handling the lamp in case it breaks (e.g., due to a drop to the floor) because of the danger from flying quartz shards propelled by the high pressure of the xenon gas within; this applies to all projection xenon lamps. An IMAX xenon lamp runs on DC power, lasts for 1,000 hours and requires its own pump and water cooler. The projector's optics also require compressed air cooling. An IMAX projector weighs up to 1.8 tonnes (2 short tons) and is over tall and long. The projector is raised and locked into position before each screening.
IMAX Corporation has released four projector types that use its 15-perforation, 70 mm film format: GT (Grand Theatre), GT 3D (dual rotor), SR (Small Rotor), and MPX, which was designed for retrofitted theatres. In July 2008, the company introduced a digital projection system, which it has not given a distinct name or brand, designed for multiplex theatres with screens no wider than . All IMAX projectors, except the standard GT system, can project 3D images. GT 3D projectors require two separate lamps and polarized projection optics.
Digital projection
 The
The digital cinema
Digital cinema is the digital technology used within the film industry to distribute or project motion pictures as opposed to the historical use of reels of motion picture film, such as 35 mm film. Whereas film reels have to be shipped to mo ...
IMAX projection system, debuted in 2008, is designed for use with shorter 1.90:1 aspect ratio screens. The system uses two 2K projectors that can present either 2D or 3D content in DCI or IMAX Digital Format (IDF; which in itself is a superset of DCI). IDF initially used 2K-resolution Christie xenon projectors, with a Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
Digital Light Processing (DLP) engine, but in 2012 IMAX announced that they would be switching to Barco as their primary supplier. The two 2K images are projected superimposed on each other with a half-pixel offset, using super-resolution imaging
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that improve the resolution of an imaging system. In optical SR the diffraction limit of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital imaging sensors is enhanced ...
to increase the perceived resolution to approximately 2.9K.
For 3D presentations, one projector is used to display the image for each eye, while 2D presentations use the superimposed images to allow for a brighter 75 cd/m2 image. The Digital IMAX projection system includes a proprietary IMAX Image Enhancer that modifies the output of the digital media server based on feedback from cameras and microphones in the auditorium, and maintains alignment with sub-pixel accuracy.
Mainly because the system facilitates inexpensive distribution of IMAX features, the company announced in February 2012 that they were renovating specially selected locations around the world to present both 70 mm analog as well as digital presentations. To do so, IMAX developed a rail system that moves the projectors in and out to accommodate either a full-frame film print or a digital-only release. These theaters were prepared in time for the release of ''The Dark Knight Rises
''The Dark Knight Rises'' is a 2012 superhero film directed by Christopher Nolan, who co-wrote the screenplay with his brother Jonathan Nolan, and the story with David S. Goyer. Based on the DC Comics character Batman, it is the final instal ...
'' in July 2012.
Laser projection
In April 2012, IMAX began testing a new 4K laser projection system, based on patents licensed fromEastman Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company, referred to simply as Kodak (), is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in film photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated i ...
. Like the 3D film and digital systems, it used two projectors, but it improved over the smaller digital screens by retaining the traditional IMAX aspect ratio and let films be shown on screens wide or more. In December 2014, IMAX began rolling out its new dual 4K laser projector system, dubbed "IMAX with Laser" and known as IMAX GT, with the first installation occurring at the Cineplex Scotiabank Theatre in Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
. The system allows digital projection of the 1.43:1 aspect ratio surface of a traditional IMAX screen, but can also be used on other screens, e.g. with an 1.90:1 aspect ratio.
The system replaces the xenon arc lamp
A xenon arc lamp is a highly specialized type of gas discharge lamp, an electric light that produces light by passing electricity through ionized xenon gas at high pressure. It produces a bright white light to simulate sunlight, with applications ...
of a traditional digital projector with a laser light source, and is capable of 60 fps with "50 percent greater" brightness than the Digital Cinema Initiatives
Digital Cinema Initiatives, LLC (DCI) is a consortium of major motion picture studios, formed to establish specifications for a common systems architecture for digital cinema systems.
The organization was formed in March 2002 by Metro-Goldwyn- ...
spec, a contrast ratio "double" that of IMAX 15/70 mm film projection and "higher" than the 2,500:1 contrast ratio of IMAX's xenon lamp-based projection systems, and displaying the full Rec. 2020 color gamut. The system also features a new 12-channel surround sound system, which adds an additional speaker on either side of the theater as well as four new overhead speakers.
While still not matching the theoretical resolution of traditional IMAX film, which is estimated at up to 12,000 lines of horizontal resolution on the 65 mm camera negative (12K) and approximately 6,000 on a 35 mm release print (6K), the new laser system features dual-4K resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) with a 16:9 asp ...
projectors, each capable of displaying four times the detail of one Digital IMAX projector. Like Digital IMAX, images from the two projectors are projected superimposed on each other with a half-pixel offset, using super-resolution imaging
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that improve the resolution of an imaging system. In optical SR the diffraction limit of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital imaging sensors is enhanced ...
, which makes the perceived resolution greater than 4K. In-theater cameras and microphones are used to automatically calibrate the projectors and sound system between showings. For 3D presentations, one projector is used to display the image for each eye, while 2D presentations use the superimposed images to allow for a brighter image. For 3D presentations, IMAX with Laser systems use dichroic filter
In optics, a dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths (colours) (not to be confused with dispersion), or one in which light rays having different polarizations are ab ...
glasses, similar to those used by Dolby 3D, as opposed to the linear polarization glasses used in Digital IMAX theaters.
On April 24, 2018, IMAX announced that they would begin rolling out a new single-unit version of their laser projector system later that year, with this iteration designed to replace the IMAX Xenon digital projection system for 1.90:1 screens.
Theatres
IMAX theatres are described as either "Classic Design" (purpose-built structures), or "Multiplex Design" (retrofitted auditoriums). Classic IMAX theatre construction differs significantly from conventional theatres. The increased resolution lets the audience be much closer to the screen. Typically all rows are within one screen height – conventional theatre seating runs 8 to 12-screen heights. Also, the rows of seats are set at a steep angle (up to 30° in some domed theatres) so that the audience is facing the screen directly. The world's largest IMAX screen currently stands inLeonberg
Leonberg (; ) is a town in the German federal state of Baden-Württemberg about to the west of Stuttgart, the state capital. About 45,000 people live in Leonberg, making it the third-largest borough in the rural district () of Böblingen (afte ...
near Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; ; Swabian German, Swabian: ; Alemannic German, Alemannic: ; Italian language, Italian: ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city of the States of Germany, German state of ...
, Germany and measures . Until the Leonberg IMAX opened in 2021, the largest operating IMAX screen was in IMAX Melbourne, located within the Melbourne Museum
The Melbourne Museum is a natural and cultural history museum located in the Carlton Gardens in Melbourne, Australia.
Located adjacent to the Royal Exhibition Building, the museum was opened in 2000 as a project of the Government of Victoria, ...
in Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
, Australia, measuring . Until its demolition in 2016, the world's largest IMAX screen had been in IMAX Sydney in Darling Harbour
Darling Harbour is a harbour and neighborhood adjacent to the city centre of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, that is made up of a large recreational and pedestrian precinct that is situated on western outskirts of the Sydney central busines ...
, Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
, Australia, measuring . It reopened on 12 October 2023, with a screen measuring 693 square meters within The Ribbon building, after years of extensive redevelopment, making it the world's third-largest screen.
Variations
Dome and Omnimax


 In the late-1960s, the San Diego Hall of Science (later known as the San Diego Space and Science Foundation) began searching North America for a large-format film system to project on the dome of their planned tilted
In the late-1960s, the San Diego Hall of Science (later known as the San Diego Space and Science Foundation) began searching North America for a large-format film system to project on the dome of their planned tilted dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
planetarium. The standard IMAX projector was unsuitable for use inside a dome because it had a tall lamp house on top. IMAX Corporation redesigned its system, adding an elevator
An elevator (American English) or lift (Commonwealth English) is a machine that vertically transports people or freight between levels. They are typically powered by electric motors that drive traction cables and counterweight systems suc ...
to lift the projector to the center of the dome from the projection booth below. Spectra Physics designed a suitable lamphouse that took smaller, lamps and placed the bulb behind the lens instead of above the projector. In 1970, Ernst Leitz Canada, Ltd. (now ELCAN Optical Technologies) won a contract to develop and manufacture a fisheye lens
A fisheye lens is an ultra wide angle lens, ultra wide-angle lens that produces strong Distortion (optics), visual distortion intended to create a wide panorama, panoramic or Sphere#Hemisphere, hemispherical image. Fisheye lenses achieve extremel ...
projection system optimized to project an image onto a dome instead of a flat screen.
The dome system, which the San Diego Hall of Science called "Omnimax", uses films shot with a camera equipped with a fisheye lens
A fisheye lens is an ultra wide angle lens, ultra wide-angle lens that produces strong Distortion (optics), visual distortion intended to create a wide panorama, panoramic or Sphere#Hemisphere, hemispherical image. Fisheye lenses achieve extremel ...
that squeezes a highly distorted anamorphic
Anamorphic format is a cinematography technique that captures widescreen images using recording media with narrower native Aspect ratio (image), aspect ratios. Originally developed for 35 mm movie film, 35 mm film to create widescreen pres ...
180° field of view onto the 65 mm IMAX film. The lens is aligned below the center of the frame, and most of the bottom half of the circular field falls beyond the edge of the film. The part of the field that would fall below the edge of the dome is masked. When filming, the camera is aimed upward at an angle that matches the tilt of the dome. When projected through a matching fisheye lens onto a dome, the original panoramic view is recreated. Omnimax wraps 180° horizontally, 100° above the horizon and 22° below the horizon for a viewer at the center of the dome. Omnimax premiered in 1973, showing '' Voyage to the Outer Planets'' (produced by Graphic Films) and '' Garden Isle'' (by Roger Tilton Films) on a double bill. Later in the 70s a successful Omnimax center was built at Caesars Palace, Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
, and ran strongly through the 80s and 90s, eventually being closed and rebuilt.
IMAX has since renamed its Omnimax system "IMAX Dome", but some theaters (primarily those opened before the 2000s) continue to call it "Omnimax".
IMAX Dome theatres are used in theme parks and many North American museums, particularly those with a scientific focus, where the technical aspects of the system may be highlighted as part of the attraction. The projection room is often windowed to allow public viewing of the equipment in operation, and it is often accompanied by informational placards like other exhibits. For some theaters, before the show begins, the screen can be backlit to show the speakers and girders behind it.
The screen may be a permanent fixture, such as at the Museum of Science and Industry ( Henry Crown Space Center) in Chicago, Illinois; the Fort Worth Museum of Science and History; the Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and a center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and wikt:statesman, statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin ...
in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; the St. Louis Science Center; Boston's Museum of Science; Richmond's Science Museum of Virginia; the Charlotte Observer IMAX Dome Theatre at Discovery Place, Charlotte, North Carolina; Birmingham, Alabama's McWane Science Center; US Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the Cincinnati Museum Center at Union Terminal; the Great Lakes Science Center in Cleveland, Ohio; the Ontario Science Centre in Toronto, Ontario; and Science World in Vancouver, British Columbia.
Alternatively, the dome may be lowered and raised as needed, such as at the Science Museum of Minnesota, and the former installation at the Canadian Museum of History
The Canadian Museum of History () is a national museum on anthropology, Canadian history, cultural studies, and ethnology in Gatineau, Quebec, Canada. The purpose of the museum is to promote the heritage of Canada, as well as support related res ...
(where it shared an auditorium with a standard IMAX screen, all replaced with a Barco CINE+ digital theatre system in 2016). The entire dome could be raised to show flat-screen features, and repositioned for immersive features.
While the majority of museum installations focus on educational and documentary films, on special occasions entertainment films are also shown, such as '' Charlie and the Chocolate Factory'' at the Oregon Museum of Science and Industry. The largest screen in North America is at the Science World in Vancouver, British Columbia, which has a dome screen in size.
Due to the age of the IMAX Dome format as well as its entirely analogue nature, some theatres may opt to replace their existing IMAX Dome systems with newer, more versatile digital systems. Examples of former IMAX Dome theatres that have had their IMAX equipment replaced with newer equipment include Tietomaa Science Centre in Oulu, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
(which replaced its IMAX 8/70 equipment from 1988 with a Barco DP4K-32B 4K projection system in 2013), the Omni-Theatre at Science Centre Singapore, the National Museum of Natural Science in Taichung
Taichung (, Wade–Giles: '), officially Taichung City, is a special municipality (Taiwan), special municipality in central Taiwan. Taichung is Taiwan's second-largest city, with more than 2.85 million residents, making it the largest city in Ce ...
, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
(which both had their original IMAX Dome 1570 projection systems installed respectively in 1987 and 1985 replaced with Evans & Sutherland Digistar 5 8K digital systems in 2015), and the Jennifer Chalsty Planetarium at Liberty Science Center in Jersey City
Jersey City is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, second-most populous
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, which replaced its IMAX Dome 1570 projection system from 1993 (when built was the largest IMAX Dome/OMNIMAX theatre in the world) with an Evans & Sutherland Digistar 6 "True8K" digital system in 2017.
In November 2018, the Hackworth IMAX dome in The Tech Museum (now The Tech Interactive) replaced its 70 mm IMAX projector with a 4K IMAX Laser projector. It became the first digital IMAX Laser dome theater in the world.
3D
To create the illusion of depth, the IMAX 3D process uses two separate camera lenses that represent the left and right eyes. The lenses are separated by a distance of , the average distance between a human's eyes. Two separate rolls of film are used to capture the images they produce. The IMAX 3D camera weighs over . By projecting the two films superimposed on the screen and using one of several available methods to direct only the correct image to each eye, viewers see a 3D image on a 2D screen. One method is to use polarizing filters to oppositely polarize the light used in projecting each image. The viewer wears glasses with polarizing filters oriented to match the projector filters, so that the filter over each eye blocks the light used to project the images intended for the other eye. In another method, the two projections rapidly alternate. While one image is being shown, the projection of its mate is blocked. Each frame is shown more than once to increase the rate and suppress flicker. The viewer wears shutter glasses withliquid crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as i ...
shutters that block or transmit light in sync with the projectors, so each eye sees only the images meant for it.
Several of the early films that had been produced in digital 3D for release in conventional theaters were also presented in IMAX 3D, including ''Avatar
Avatar (, ; ) is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means . It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appearance" is sometimes u ...
'', ''Gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
'' and ''The Amazing Spider-Man
''The Amazing Spider-Man'' is an ongoing American superhero American comic book, comic book series featuring the Marvel Comics superhero Spider-Man as its title character and main protagonist. Being in the Earth 616, mainstream continuity of t ...
''. The first full-color IMAX 3D film was the 1986 short documentary '' Transitions'', produced for Expo 86
The 1986 World Exposition on Transportation and Communication, or simply Expo 86, was a world's fair held in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada from May 2 until October 13, 1986. The fair, the theme of which was "Transportation and Communicatio ...
in Vancouver.
HD
Variations on IMAX included the 48 frames per second IMAX HD process, which sought to produce smoother, more lifelike motion, while also reducing the blurring of moving objects, by doubling the normal film rate. The IMAX HD system was tested in 1992 at the Canada Pavilion of theSeville Expo '92
The Universal Exhibition of Seville 1992 – Expo '92 (officially: ) was a universal exhibition held from Monday 20 April to Monday 12 October 1992, at the , in Seville, Spain. The theme for the expo was "The Age of Discoveries", celebrating the ...
with the film ''Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. ...
''. Higher production costs, and the high "wear-and-tear" on the prints and projectors, doomed the IMAX HD system, but, not before many theatres had been retrofitted to project at 48 frames, especially in Canada, in order to play ''Momentum''. In the 1990s theme parks in Thailand, Germany, and Las Vegas used IMAX HD for their Motion Simulator rides. The Disney parks attraction Soarin' Over California
''Soarin, also known as ''Soarin' Over California'', ''Soarin' Around the World'', ''Soaring Over the Horizon'' and ''Soaring: Fantastic Flight'', is a flight motion simulator attraction at Disney California Adventure, Epcot, Shanghai Disneyla ...
features a modification of both IMAX HD and IMAX Dome, projecting in 48 frames per second.
Digital
Because 70 mm film and projectors are costly, difficult to produce en masse, and the size of auditoriums that house full-size IMAX screens make them expensive to construct, IMAX debuted a digital projection system in 2008 to use with shorter 1.89:1 aspect ratio screens. It uses two 2K-resolution projectors that can present either 2D or 3D content in DCI or IMAX Digital Format (IDF; which in itself is a superset of DCI). The digital installations have caused some controversy, as many theaters have branded their screens as IMAX after merely retrofitting standard auditoriums with IMAX digital projectors. The screen sizes in these auditoriums are much smaller than those in the purpose-built auditoriums of the original 15/70 IMAX format, and are limited to the 1.89:1 aspect ratio. Another disadvantage is the much lower resolution of digital IMAX. The technology has a maximum perceived resolution of 2.9K, compared to traditional IMAX 70 mm projection, which has an estimated resolution of 12K. Some reviewers have also noted that many non-IMAX theaters are projecting films at4K resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) with a 16:9 asp ...
through competing brands such as Dolby Cinema and UltraAVX.
IMAX has held to a uniform branding of "The IMAX Experience" across various underlying technologies and screen sizes.Hyder, James (October 16, 2008). ''Is IMAX the next "New Coke"?'' LF Examiner, October 16, 2008. Retrieved froLFexaminer.com.
Some have criticized the company's marketing approach, with the format being dubbed "Lie-MAX". The company has defended the format by saying it has a bigger screen, brighter picture and better sound than standard theatres. Despite the differences with digital IMAX, the cost-effective format has aided in the company's worldwide growth, especially in Russia and China.
IMAXShift
In May 2016, IMAX announced the test launch of IMAXShift, a multimedia indoor cycling concept, but decided to discontinue it June 4, 2017.Virtual reality
On September 2, 2016, IMAX announced plans to includevirtual reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a Simulation, simulated experience that employs 3D near-eye displays and pose tracking to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video gam ...
(VR) into the IMAX theater experience with the opening of a new VR center in Los Angeles that would use a new StarVR headset created by Acer. The VR experience was intended for short but interactive videos. IMAX opened a total of seven IMAX VR centers and established a fund for the creation of VR content, as well as partnering with Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
for the production of IMAX VR cameras. However, , all seven IMAX VR centers have closed.
Films
Entertainment
 In the US, IMAX has mostly been used for specialty applications. The expense and logistical challenges of producing and presenting IMAX films have led to approximately 40 minutes shorter running times than conventional films. Most are documentaries suited for institutional venues such as museums and science centers. IMAX cameras have been used while orbiting the Earth, climbing
In the US, IMAX has mostly been used for specialty applications. The expense and logistical challenges of producing and presenting IMAX films have led to approximately 40 minutes shorter running times than conventional films. Most are documentaries suited for institutional venues such as museums and science centers. IMAX cameras have been used while orbiting the Earth, climbing Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
, exploring the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean, and visiting the Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
. A film about the Mars Exploration Rovers, titled '' Roving Mars'' (2006), used exclusive data from the rovers.
An early attempt at presenting mainstream entertainment in IMAX format was '' The Rolling Stones: Live at the Max'' (1991), an 85-minute compilation of concert footage filmed in IMAX during the rock band's 1990 Steel Wheels tour, edited to give the impression of a single concert. In the 1990s, more entertainment short films were created, notably '' T-Rex: Back to the Cretaceous'' in 1998, and '' Haunted Castle'' in 2001 (both in 3D). In 1995, French director Jean-Jacques Annaud
Jean-Jacques Annaud (; born 1 October 1943) is a French film director, screenwriter and producer. He directed ''Quest for Fire (film), Quest for Fire'' (1981), ''The Name of the Rose (film), The Name of the Rose'' (1986), ''The Bear (1988 film), ...
directed '' Wings of Courage'', the first dramatic picture shot for IMAX. In 1998 and 1999, '' More'' and '' The Old Man and the Sea'' became the first short films produced using the IMAX format; both earned Academy Award nominations, with ''Old Man and the Sea'' becoming the only IMAX film to win an Oscar. In 2000, Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly referred to as simply Disney, is an American multinational mass media and entertainment industry, entertainment conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios (Burbank), Walt Di ...
produced ''Fantasia 2000
''Fantasia 2000'' is a 1999 American animated musical anthology film produced by Walt Disney Feature Animation. Produced by Roy E. Disney and Donald W. Ernst, it is the sequel to Disney's 1940 animated feature film '' Fantasia''. Like its p ...
'', the first full-length animated feature initially released exclusively in the IMAX format.
Use in Hollywood productions
Before the end of the 1990s, theatrical features were deemed impossible to run in IMAX venues at the time, as there was a technical limitation on the size of the film reel where films had to run around two hours. Originally, IMAX andPixar
Pixar (), doing business as Pixar Animation Studios, is an American animation studio based in Emeryville, California, known for its critically and commercially successful computer-animated feature films. Pixar is a subsidiary of Walt Disney ...
considered releasing ''Toy Story
''Toy Story'' is a 1995 American animated adventure comedy film produced by Pixar Animation Studios for Walt Disney Pictures. It is the first installment in the Toy Story (franchise), ''Toy Story'' franchise and the Firsts in animation, firs ...
'' in IMAX 3D, but test results showed that the render resolution could not match the size of the IMAX image. DreamWorks in the early 2000s wanted to re-release ''Shrek
''Shrek'' is a 2001 American animated fantasy comedy film directed by Andrew Adamson and Vicky Jenson, and written by Ted Elliott, Terry Rossio, Joe Stillman, and Roger S. H. Schulman, loosely based on the 1990 children's picture boo ...
'' in IMAX 3D, but this too was canceled as a result of creative changes in the studio. These failed attempts at re-releases did inspire IMAX to experiment and improve their ability in presenting computer animation in their theaters. Their compilation '' CyberWorld'' was the result, which contained new original animation and IMAX-presented versions of computer-animated tests and music videos. ''Cyberworld'' even presented open-matte 3D versions of the bar sequence from '' Antz'' and the " Homer3" segment from ''The Simpsons
''The Simpsons'' is an American animated sitcom created by Matt Groening and developed by Groening, James L. Brooks and Sam Simon for the Fox Broadcasting Company. It is a Satire (film and television), satirical depiction of American life ...
''; both coincidentally were animated at Pacific Data Images.
Walt Disney Pictures
Walt Disney Pictures is an American film Film production company, production company and subsidiary of Walt Disney Studios (division), the Walt Disney Studios, a division of Disney Entertainment, which is owned by the Walt Disney Company. The st ...
became the first studio to release theatrical films in the IMAX process. Released on New Year's Day in 2000, ''Fantasia 2000
''Fantasia 2000'' is a 1999 American animated musical anthology film produced by Walt Disney Feature Animation. Produced by Roy E. Disney and Donald W. Ernst, it is the sequel to Disney's 1940 animated feature film '' Fantasia''. Like its p ...
'' was the studio's first IMAX release and the first theatrical feature presented in IMAX theaters. It was originally planned as a standard theatrical release, but in agreeing with the company to release the film, the IMAX sound system incorporated a multi-channel and multi-layer stereo system for the orchestrated soundtrack, similar to the Fantasound system Walt Disney had envisioned for the original film in 1940. The company agreed to Disney's terms and conditions to gain the exclusive first showings of the film. These included a limited engagement of four months (from January 1 to April 30) and 50% of the box office receipts. Not all IMAX cinemas were prepared to accept Disney's terms to present the film; however, following the IMAX release, a standard 35 mm run followed in June at regular theaters.
Although ''Fantasia 2000'' had a lukewarm financial run, the critical praise for its use of the IMAX format convinced Disney to put more releases in the giant-screen format in the pipeline. In 2002, IMAX re-issues of ''Beauty and the Beast
"Beauty and the Beast" is a fairy tale written by the French novelist Gabrielle-Suzanne Barbot de Villeneuve and published in 1740 in (''The Young American and Marine Tales'').
Villeneuve's lengthy version was abridged, rewritten, and publish ...
'' and ''The Lion King
''The Lion King'' is a 1994 American animated musical coming-of-age drama film directed by Roger Allers and Rob Minkoff, produced by Don Hahn, and written by Irene Mecchi, Jonathan Roberts, and Linda Woolverton. Produced by Walt Disney ...
'' were released in select theaters over the winter and Christmas seasons of that year. New digital masters were created from the original CAPS production files and select scenes of animation were cleaned up to make use of the high resolution IMAX film negatives. ''Treasure Planet
''Treasure Planet'' is a 2002 American animated science fiction film, science fiction adventure film directed by John Musker and Ron Clements and written by Musker, Clements and Rob Edwards (screenwriter), Rob Edwards. Produced by Walt Disney ...
'' was also released in select IMAX theaters and was the first theatrical film released in regular and IMAX theaters simultaneously. But all of these releases had underwhelming box office returns and Disney canceled later big-screen re-releases, including ''Aladdin (1992 Disney film), Aladdin''.
With the unveiling of the DMR process (see below), Warner Bros. Pictures especially embraced the format beginning in 2003 with the two ''The Matrix, Matrix'' sequels, ''The Matrix Reloaded, Reloaded'' and ''The Matrix Revolutions, Revolutions''. Since ''Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban (film), The Prisoner of Azkaban'' in 2004, Warner Bros. began releasing Harry Potter (film series), the ''Harry Potter'' film franchise in IMAX to strong financial success. Also in 2004 the studio released Robert Zemeckis' motion-capture film ''The Polar Express (film), The Polar Express'' in IMAX 3D. ''Polar Express'' became the most successful film released in IMAX theaters, producing at least a quarter of the film's gross of $302 million from fewer than 100 IMAX screens. Success for Warner Bros. and IMAX followed in later years with ''I Am Legend (film), I Am Legend'', ''Happy Feet'', ''Batman Begins'' and ''The Dark Knight''. Progressively other studios became further interested in releasing films in IMAX through the DMR process and have earned success through it. In May 2009, J. J. Abrams's ''Star Trek (2009 film), Star Trek'' was released in IMAX venues for the initial two weeks of its theatrical run and opened to $8.3 million. The IMAX opening weekends of ''The Avengers (2012 film), The Avengers'' and ''Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 2'' have since grossed $15 million.
Though they were not filmed with IMAX cameras, ''Skyfall'' and ''The Amazing Spider-Man
''The Amazing Spider-Man'' is an ongoing American superhero American comic book, comic book series featuring the Marvel Comics superhero Spider-Man as its title character and main protagonist. Being in the Earth 616, mainstream continuity of t ...
'' were optimized for IMAX digital screens when they were released. Both movies were filmed in high-resolution cameras and the digital negative ratio was equal to that of the IMAX Digital frame. ''Skyfall'' increased the visual information of the entire film while ''Amazing Spider-Man'' optimized the finale battle with the Lizard. When James Cameron's ''Titanic (1997 film), Titanic'' was restored and re-released in theaters there was also specially made an open-matte version for IMAX. In 2010 after years of successful IMAX DMR releases, Warner Bros. signed a deal to release up to 20 feature films in IMAX up to 2013, including educational documentaries that were in production.
In May 2015, Marvel Studios announced that its next two ''Avengers'' films – '' Avengers: Infinity War'' (2018) and '' Avengers: Endgame'' (2019) – would be filmed entirely in IMAX, the first Hollywood feature films to do so, using a modified version of Arri
Arri Group () (stylized as "ARRI") is a German manufacturer of motion picture film equipment. Based in Munich, the company was founded in 1917. It produces professional motion picture cameras, lenses, lighting and post-production equipment. It ...
's Alexa 65 digital camera. The camera was used first to film select sequences in another Marvel production, 2016's '' Captain America: Civil War''.
DMR (Digital Media Remastering)
IMAX's proprietary DMR (Digital Media Remastering) process Video scaler, up-converts conventional films to IMAX format. This special digital intermediate technology let IMAX venues show films shot on 35mm for conventional theaters. In 2002, ''Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones'' and an IMAX-format re-release of the 1995 film ''Apollo 13 (film), Apollo 13'', were the first official applications of the DMR process. Because of projection limitations at the time, the studios had to edit ''Apollo 13'' and ''Attack of the Clones'' to have a shorter playing time. As IMAX updated the system and expanded the size of the platters, the later DMR releases did not have this limitation; current platters provide a run time of up to 175 minutes. Reviewers have generally praised the results of the DMR blowup process, which are visually and audibly superior to the same films projected in 35mm. But some filmmakers, such as producer Frank Marshall (film producer), Frank Marshall, point out that DMR blowups are not comparable to films created directly in the 70 mm 15 perf IMAX format, and that directors Ron Howard and George Lucas expected better. They note that the decline of Cinerama coincided roughly with its replacement by a simpler, cheaper, technically inferior version, and view DMR with alarm. IMAX originally reserved the phrase "the IMAX experience" for true 70 mm productions, but now allows its use on DMR productions as well. After ''The Lion King'' in 2003, no Hollywood studio engaged in re-releasing and restoring classic films through the IMAX DMR process until 2012 although ongoing conversion of new releases continued and continued to grow in number. James Cameron's ''Titanic'' underwent both 3D conversion and DMR conversion to 3D in 2012 as did ''Men in Black 3''. In August 2012 IMAX and Paramount Pictures announced a one-week exclusive re-release of ''Raiders of the Lost Ark'' on September 7, 2012, to promote the release of the Blu-Ray collection. The film, before it underwent DMR, was already restored in a 4K digital intermediate with 7.1 surround sound from the original negative. The process for IMAX theaters, like with the complete restoration, was supervised by Steven Spielberg and sound designer Ben Burtt. "I didn't know if the 1981 print would stand up to a full IMAX transfer, so I came expecting a sort of grainy, muddy, and overly enlarged representation of the movie I had made years ago", Spielberg said. "I was blown away by the fact that it looked better than the movie I had made years ago."Feature films
Many recent features have employed IMAX cameras for select scenes; however, before 2018 no full-length feature film was shot entirely using IMAX cameras due to the numerous difficulties presented with the format – the cameras were much larger and heavier than standard cameras and the noise they produced made dialogue recording difficult. The 15/70 cameras have short film loads ranging from 30 seconds to two minutes and the cost of the film stock was much greater than standard 35mm film. However, these issues have been minimized thanks to the digital Arri Alexa IMAX camera, with two films having been shot entirely with the camera. ''The Dark Knight'' features six sequences (a total of 28 minutes) shot using IMAX. According to the film's press notes, this was the "first time ever that a major feature film has been even partially shot using IMAX cameras". Even before ''Dark Knight'', Nolan had wanted to shoot a film in the IMAX format, and he also used it for quiet scenes that it would make pictorially interesting. Nolan said that he wished that it were possible to shoot the entire film in IMAX: "if you could take an IMAX camera to Mount Everest or outer space, you could use it in a feature movie." Nolan chose to edit some of the IMAX sequences using the original camera negative to eliminate generation loss, while scenes that were digitally mastered were scanned and printed out at 8 thousand lines of horizontal resolution (8K). When the film opened in 94 IMAX venues in 2008, all of them were sold out for the opening weekend. A year later, director Michael Bay was inspired by IMAX's use in ''The Dark Knight'' to feature big-screen sequences in ''Transformers: Revenge of the Fallen''. The film's co-writer Roberto Orci suggested that the IMAX footage would be 3D, but Bay later said that considering himself an "old school" filmmaker, he found 3D gimmicky and added that shooting in IMAX was easier than using stereoscopic cameras. The IMAX version of the film, in the end, contained almost ten minutes of IMAX-filmed footage out of the two and a half-hour film. Bay later partially filmed the third ''Transformers (film series), Transformers'' film, ''Transformers: Dark of the Moon, Dark of the Moon'' in 3D but without IMAX. Bay returned to IMAX for the fourth film, ''Transformers: Age of Extinction, Age of Extinction'', in 2014. It was the first feature film shot using digital IMAX 3D cameras. He again used IMAX 3D cameras while shooting the fifth film, '' Transformers: The Last Knight'', filming 98% of the film with 2 Alexa/IMAX cameras attached together to a special mount. Two years later, Terrence Malick's ''The Tree of Life (film), The Tree of Life'' filmed select sequences using IMAX cameras, and often used natural light. The film used a mix of 35mm film and regular 65mm and the IMAX 15/70 mm format. The set of guidelines they fine-tuned for this film included an edict to achieve maximum resolution whenever possible. "We would have preferred to shoot the entire movie in IMAX," says cinematographer of the film Emmanuel Lubezki. "When the 65mm and IMAX scenes do appear in the movie, they give you a jolt. It's a feeling of enhancement and majesty. It's almost as if someone cleaned off the window you were looking through". However the film wasn't screened on any IMAX screen. After ''The Tree of Life'', Brad Bird's ''Mission: Impossible – Ghost Protocol'' included 25 minutes of footage shot using IMAX cameras. Bird believed that using IMAX format would bring back "a level of showmanship" to the presentation of Hollywood films, which he believes the industry has lost due to its emphasis on screening films in Multiplex (movie theater), multiplexes as opposed to grand theaters, and vetoing "first runs" in favor of wider initial releases. He also added that the IMAX format offered the viewer more immersion than digital 3D due to its brighter, higher quality image, which is projected on a larger screen, without the need for specialised glasses. ''Ghost Protocol'' opened on December 16, 2011, in almost 500 IMAX venues worldwide a week before its wide release where it earned third place in the box office and $12 million. As with ''The Dark Knight'',Christopher Nolan
Sir Christopher Edward Nolan (born 30 July 1970) is a British and American filmmaker. Known for his Cinema of the United States, Hollywood Blockbuster (entertainment), blockbusters with complex storytelling, he is considered a leading filmma ...
decided to film sequences of the sequel, ''The Dark Knight Rises
''The Dark Knight Rises'' is a 2012 superhero film directed by Christopher Nolan, who co-wrote the screenplay with his brother Jonathan Nolan, and the story with David S. Goyer. Based on the DC Comics character Batman, it is the final instal ...
'', in 15/70mm IMAX. Nolan elected not to film in 3D and stated that he intends to focus on improving image quality and scale using the IMAX format. In a then-Hollywood record, ''The Dark Knight Rises'' featured 72 minutes of footage shot in 70mm IMAX (roughly 2.5 times that of ''The Dark Knight's'' 28 minutes, however, this record was later overtaken by another Nolan film, ''Dunkirk'', which featured 79 minutes of IMAX) Because of the considerable noise IMAX cameras make, they used standard 35mm cameras to shoot dialogue scenes, and dubbed dialogue in scenes shot with IMAX cameras. Chairman and president of the IMAX Corporation Greg Foster stated that IMAX plans to run the film in its theaters for two months, despite only being contractually committed to run the film for two weeks in some theaters.
J. J. Abrams's ''Star Trek Into Darkness'', Francis Lawrence's ''The Hunger Games: Catching Fire'', Luc Besson's ''Lucy (2014 film), Lucy'', and Christopher Nolan's ''Interstellar (film), Interstellar'' are films that were released between 2013 and 2014 that had sequences filmed with 15/70 IMAX cameras.
On July 9, 2014, Bad Robot (J. J. Abrams's production company) confirmed via a picture uploaded to Twitter that one sequence in Disney and Lucasfilm's ''Star Wars: The Force Awakens'' would be captured with the IMAX 15/70 perf film camera, in addition to the standard 35 mm film cameras that Abrams and his cinematographer Dan Mindel have employed for shooting the movie. The next installment in the franchise Rian Johnson's ''Star Wars: The Last Jedi'', released in December 2017, also included sequences shot with 15/70mm IMAX cameras.
Adele's music video "Hello (Adele song)#Music video, Hello", released in 2015, became the first music video that was partially filmed with IMAX cameras.
In April 2015, Marvel Studios announced that Russo brothers
Anthony Russo (born February 3, 1970) and Joseph Russo (born July 18, 1971), collectively known as the Russo brothers ( ), are American filmmakers. They direct most of their work together, and their work has grossed more than $6.8 billion worl ...
' '' Captain America: Civil War'' would be the first film to use the new Arri Alexa IMAX 2D digital camera, which was used to shoot approximately 15 minutes of the film. In May 2015, the Russo brothers announced that their films '' Avengers: Infinity War'' and '' Avengers: Endgame'', released in 2018 and 2019, the first Hollywood feature films shot entirely in IMAX, albeit using Arri Alexa IMAX cameras instead of 15/70 perf film.
Rihanna's music video "Sledgehammer (Rihanna song), Sledgehammer", released in 2016, was the second music video to use the new Arri Alexa IMAX camera.
Other films between 2016 and 2021 that captured with IMAX cameras were Zack Snyder's ''Batman v Superman: Dawn of Justice'', Clint Eastwood's ''Sully (film), Sully'', Damien Chazelle's ''First Man (film), First Man'', Jon Favreau's ''The Lion King (2019 film), The Lion King, ''Patty Jenkins' ''Wonder Woman 1984'' and Cary Joji Fukunaga's ''No Time to Die''. ''Sully'' was filmed with Arri Alexa IMAX cameras for almost the entire film and ''The Lion King'' for select sequences. The rest had sequences that were filmed with 15/70 mm IMAX cameras.
Five Chinese titles have been captured with IMAX digital cameras (including two with IMAX-certified cameras); selected scenes in Jiang Wen's ''Gone with the Bullets'' in 2014, the entirety of Guan Hu's ''The Eight Hundred'' in 2020, almost all of Chen Sicheng's ''Detective Chinatown 3'' in 2021 and the entirety of Chen Kaige, Tsui Hark and Dante Lam's '' The Battle at Lake Changjin'' and ''The Battle at Lake Changjin II
''The Battle at Lake Changjin II'' (released in the United Kingdom as ''The Battle at Water Gate Bridge''), is a 2022 war film, war drama film co-produced and co-directed by Chen Kaige, Tsui Hark and Dante Lam, written by Lan Xiaolong and Huang J ...
'' with IMAX-certified List of Red Digital Cinema cameras, Red Ranger Monstro cameras in 2020 and 2022.
Christopher Nolan used 15/70 IMAX cameras again on his next film, ''Dunkirk (2017 film), Dunkirk''. However, unlike the previous films, where he used the cameras for select sequences, Nolan used IMAX as the primary shooting format, with 75% (about 79 minutes) of the 106-minute film featuring footage shot in 70 mm IMAX (breaking the aforementioned record that a previous Nolan film, ''The Dark Knight Rises
''The Dark Knight Rises'' is a 2012 superhero film directed by Christopher Nolan, who co-wrote the screenplay with his brother Jonathan Nolan, and the story with David S. Goyer. Based on the DC Comics character Batman, it is the final instal ...
'', held). This was possible due to the sparsity of dialogue in the film, as 15/70 mm IMAX cameras are notoriously noisy (a few dialogue-heavy scenes were shot with regular 70 mm film cameras from Panavision
Panavision Inc. is an American motion picture equipment company (law), company founded in 1954 specializing in cameras and photographic lens, lenses, based in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk a ...
). IMAX cameras were also used hand-held for the first time, as Nolan was advised by both Steven Spielberg and Ron Howard that it was the best way to shoot on vessels. ''Dunkirk'' received the widest release on 70mm IMAX since his last film, ''Interstellar (film), Interstellar'', with the film being released on the format in 37 theaters around the world. The director's 2020 film, ''Tenet (film), Tenet'' filmed 76 minutes with 15/70 mm IMAX cameras, the rest of the film was shot with regular 70 mm film cameras from Panavision
Panavision Inc. is an American motion picture equipment company (law), company founded in 1954 specializing in cameras and photographic lens, lenses, based in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk a ...
. The film's six-minute opening sequence was shown before IMAX screenings of ''Star Wars: The Rise of Skywalker''. Tenet was shown over 13 theaters globally in 70mm IMAX.
In September 2020, IMAX announced a new program called 'Filmed in IMAX', a new partnership with camera manufacturers to meet filmmaker demand for the format. Through the program, IMAX will certify digital cameras with brands including Arri Alexa, Panavision
Panavision Inc. is an American motion picture equipment company (law), company founded in 1954 specializing in cameras and photographic lens, lenses, based in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk a ...
, Red Digital Cinema and CineAlta, Sony to work in the IMAX format when paired with its post-production process. The new program certifies the Arri Alexa LF and Arri Alexa#Alexa_Mini_LF, Mini LF, Panavision cameras#Digital video, Panavision Millennium DXL2, List of Red Digital Cinema cameras, Red Ranger Monstro and Komodo and CineAlta#List of CineAlta cameras, Sony's CineAlta Venice cameras along with the Arri Alexa IMAX camera previously announced with Arri Rental. As part of the program, IMAX will also certify independent camera rental houses that can supply certified cameras worldwide, starting with Panavision, Arri and Keslow Camera. IMAX will select only a limited number of films to participate in the program each year. James Gunn's '' The Suicide Squad'' (shot with the Red Ranger Monstro and Komodo), Colin Tilley's ''If I Can't Have Love, I Want Power (film), If I Can't Have Love, I Want Power'' (shot with the Arri Alexa IMAX), Destin Daniel Cretton's ''Shang-Chi and the Legend of the Ten Rings
''Shang-Chi and the Legend of the Ten Rings'' is a 2021 American superhero film based on Marvel Comics featuring the character Shang-Chi. Produced by Marvel Studios and distributed by Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures, it is List of Marvel ...
'', Denis Villeneuve's ''Dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat ...
'', Chloé Zhao's '' Eternals'' (all three titles shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF) and Joseph Kosinski's '' Top Gun: Maverick'' (shot with the Sony CineAlta Venice) are among the first releases certified as 'Filmed in IMAX' through the new program.
Other films between 2022 and 2024 that are captured with IMAX-certified cameras are Sam Raimi's '' Doctor Strange in the Multiverse of Madness'' (Shot with the Panavision Millennium DXL2), Taika Waititi's '' Thor: Love and Thunder'' (shot with Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF), Ryan Coogler's '' Black Panther: Wakanda Forever'' (shot with the Sony CineAlta Venice), Peyton Reed's ''Ant-Man and the Wasp: Quantumania'' (Shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF), Michael B. Jordan's ''Creed III'' (shot with the Sony CineAlta Venice), James Wan's ''Aquaman and the Lost Kingdom'' (Shot with the Panavision Millennium DXL2), James Gunn's '' Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 3'' (Shot with the Red V-Raptor), Christopher McQuarrie's ''Mission: Impossible – Dead Reckoning Part One'' (Shot with Arri Alexa LF, Mini LF and Sony CineAlta Venice), Nia DaCosta's '' The Marvels'' (Shot with the Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF), Ángel Manuel Soto's ''Blue Beetle (film), Blue Beetle'', Denis Villeneuve's '' Dune: Part Two'' (shot with Arri Alexa LF and Mini LF).
In March 2022, IMAX plans to develop new 15/70 cameras that would be created with input from filmmakers such as Jordan Peele
Jordan Haworth Peele (born February 21, 1979) is an American actor, comedian and filmmaker. He is known for his film and television work in the Comedy film, comedy and Horror film, horror genres. He has received List of awards and nominations r ...
and Christopher Nolan. The work will be done in collaboration with Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company, referred to simply as Kodak (), is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in film photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated i ...
, camera maker Panavision
Panavision Inc. is an American motion picture equipment company (law), company founded in 1954 specializing in cameras and photographic lens, lenses, based in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk a ...
, and post-production company and film lab FotoKem. The large format company is also consulting with leading cinematographers including Linus Sandgren (''No Time to Die''), Rachel Morrison (''Black Panther (film), Black Panther''), Bradford Young (''Arrival (film), Arrival''), Dan Mindel (''Star Trek (2009 film), Star Trek'') and Nolan's go-to DP, Hoyte van Hoytema. Peele's 2022 film ''Nope (film), Nope'' was filmed with the current generation of 15/70 IMAX cameras and Kodak 65mm film. IMAX intends to add at least four new 15/70mm cameras to its offing over the next two years, with the first new camera expected to be put into use by late 2023.
In April 2022, it was announced that the 2022 Pixar
Pixar (), doing business as Pixar Animation Studios, is an American animation studio based in Emeryville, California, known for its critically and commercially successful computer-animated feature films. Pixar is a subsidiary of Walt Disney ...
animated film ''Lightyear (film), Lightyear'' to have created a virtual IMAX camera in its production and the first 'animated' film to captured it. "We created a virtual IMAX camera with 1.43:1 aspect ratio and developed a pipeline to allow us to simultaneously shoot the film for IMAX, and then crop down for our standard 2.39:1 format," Jane Yen, Lightyear visual effects supervisor, revealed during a press conference. One of the two director's of photography Jeremy Lasky later said "I think this is the first that has been made for IMAX in this way. There's about a third of the film that was shot for IMAX. And the easy answer is that we have a set of lenses. And when I say lenses, I mean CG made". A set of lenses that recreate the look of an anamorphic lens, which is your typical wide screen. You'll notice things out of focus in the background instead of being round are like stretched a little bit. There's like that blue lens flare that you see. It's anamorphic lenses where the way to shoot wide screen in the sixties, seventies, and then later got phased out a little bit, but they're still used today. But those effects call to a period of sci-fi that we were looking at, which is why those same lenses or versions of those lenses were used on ''WALL-E''". Later he recommend "So for the 30 or so minutes of the movie in IMAX, we shot with those lenses opened up to the 1.43 aspect ratio and composed for that while keeping the composition as clear and as solid for a 2.39 crop from the center. So the wide screen image is pulled out of the IMAX image. Which all sounds really technical, but all it really means is, when you're watching it an IMAX screen, we were thinking about those scenes as IMAX. And it wasn't just some after the film was done, blow up of the movie".
In December 2022, it was announced that IMAX have certified the Red V-Raptor as a new certified camera and that James Gunn's '' Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 3'' will be the first film to shoot with the cameras instead of the Red Ranger Monstro.
Nolan's ''Oppenheimer (film), Oppenheimer'' was also filmed with the current generation of 15/70mm IMAX cameras and Kodak 65 mm film. It is also the first film to shoot sections in IMAX black and white analog photography.
In space exploration
 IMAX cameras have flown in space on 17 occasions, NASA astronauts have used handheld IMAX cameras to document missions, and an IMAX camera has also been mounted in the payload bay of the Shuttle. Space shuttle mission STS-41-C filmed the deployment of the Long Duration Exposure Facility, LDEF (Long duration exposure facility) and the repair of the Solar Maximum Mission, Solar Max satellite. This footage was included in the 1985 IMAX movie ''The Dream Is Alive''. Kennedy Space Center in Florida has two IMAX 3D theaters. These show space movies, including footage shot on missions and narrated by celebrities. Two of the IMAX cameras used by NASA are now on display at the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., Washington DC.
IMAX cameras have flown in space on 17 occasions, NASA astronauts have used handheld IMAX cameras to document missions, and an IMAX camera has also been mounted in the payload bay of the Shuttle. Space shuttle mission STS-41-C filmed the deployment of the Long Duration Exposure Facility, LDEF (Long duration exposure facility) and the repair of the Solar Maximum Mission, Solar Max satellite. This footage was included in the 1985 IMAX movie ''The Dream Is Alive''. Kennedy Space Center in Florida has two IMAX 3D theaters. These show space movies, including footage shot on missions and narrated by celebrities. Two of the IMAX cameras used by NASA are now on display at the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., Washington DC.
Awards
In 1996, IMAX was awarded the Oscar for Scientific and Technical Achievement by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences. The award cited IMAX's innovations in creating and developing a method of filming and exhibiting large-format, wide-angle motion pictures. To date, ten native-format IMAX format films have received Academy Awards nomination, with one winner. While on technical aspects and the usage of the IMAX system, only Hoyte van Hoytema's cinematography on ''Oppenheimer (film), Oppenheimer'' has won, while Wally Pfister's cinematography on ''The Dark Knight'' and Hoytema’s cinematography on ''Dunkirk (2017 film), Dunkirk'' have also earned nominations. * ''The Eruption of Mount St. Helens!'', 1980 Documentary Short Subject * ''Fires of Kuwait'', 1992 Documentary Feature * ''The Living Sea'', 1995 Documentary Short Subject * ''Special Effects: Anything Can Happen'', 1996 Documentary Short Subject * ''Cosmic Voyage (1996 film), Cosmic Voyage'', 1996 Documentary Short Subject * ''Amazon (1997 film), Amazon'', 1997 Documentary Short Subject * ''Alaska: Spirit of the Wild'', 1997 Documentary Short Subject * '' More'', 1998 Animated Short Film * '' The Old Man and the Sea'', 1999 Animated Short Film (Winner) * ''Dolphins (2000 film), Dolphins'', 2000 Documentary Short SubjectOther uses
 Many IMAX films have been remastered into High-definition television, HDTV format (cropped to fit into HDTV's 16:9 aspect ratio) for the MOJO HD, HDNet and HD Theatre networks and release on DVD and Blu-ray Disc. In July 2005, the London IMAX, BFI IMAX Cinema in London became the first to host live music concerts, using a digital non-IMAX projector. The Science Museum London and BFI IMAX Cinema have also hosted Electronic sports, computer game tournaments using digital projectors. Several amusement park attractions have integrated IMAX film segments, including Back to the Future: The Ride formerly at Universal Destinations & Experiences, Universal Studios in Florida and California, Horizons (Epcot attraction), Horizons formerly at Epcot and Soarin’ Over California at Disney California Adventure and Epcot.
Many IMAX films have been remastered into High-definition television, HDTV format (cropped to fit into HDTV's 16:9 aspect ratio) for the MOJO HD, HDNet and HD Theatre networks and release on DVD and Blu-ray Disc. In July 2005, the London IMAX, BFI IMAX Cinema in London became the first to host live music concerts, using a digital non-IMAX projector. The Science Museum London and BFI IMAX Cinema have also hosted Electronic sports, computer game tournaments using digital projectors. Several amusement park attractions have integrated IMAX film segments, including Back to the Future: The Ride formerly at Universal Destinations & Experiences, Universal Studios in Florida and California, Horizons (Epcot attraction), Horizons formerly at Epcot and Soarin’ Over California at Disney California Adventure and Epcot.
Technical specifications
IMAX (15/70) * spherical lenses * 70 mm film, 15 perforations per frame * horizontal rolling loop movement, from right to left (viewed from emulsion side) * 24 frames per second * ''camera aperture'': * ''projection aperture'': at least less than camera aperture on the vertical axis and at least less on the horizontal axis * ''aspect ratio'': 1.43:1 * ''DMR aspect ratio: 1.90:1, 2.39:1'' IMAX Dome/Omnimax ''Same as IMAX with the addition of'': *fisheye lens
A fisheye lens is an ultra wide angle lens, ultra wide-angle lens that produces strong Distortion (optics), visual distortion intended to create a wide panorama, panoramic or Sphere#Hemisphere, hemispherical image. Fisheye lenses achieve extremel ...
es
* lens optically centered below film horizontal center line
* projected elliptically on a dome screen, 20° below and 110° above perfectly centered viewers
Competitors
In late 2014, Dolby announced Dolby Cinema as an IMAX competitor with super-vivid image mainly in High Dynamic Range with shadow. In Australia and New Zealand, Event Cinemas sells a premium cinema experience with a bigger screen, improved imagery and better seats marketed as Vmax. In the United States Cinemark has its Cinemark XD: Extreme Digital Cinema.See also
* List of films released in IMAX * List of IMAX films * List of IMAX-based rides * China Film Giant Screen, a similar format developed to break IMAX's large-screen monopoly in ChinaReferences
External links
* *Large Formats
Describes the differences between the three different "large-format" or "giant-screen" formats, the IMAX Digital format, and the conventional formats.
IMAX Soundtracks Database
* YouTube videos explaining the theater operation and maintenance processes o
threading & playing
a 70mm IMAX film
building a film
by splicing together 40 reels shipped in 7 boxes making one feature-length film 9 miles long weighing 1,200 pounds, an
replacing the projector's xenon lamp
($5600 bulb cost). {{DEFAULTSORT:Imax IMAX, 3D imaging Canadian inventions Film and video technology Film formats Motion picture film formats Special-venue films Theatres Premium large format movie formats