The history of the United States from 1917 to 1945 was marked by
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the
interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, the
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, and
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
The United States tried and failed to broker a peace settlement for
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, then entered the war after Germany launched a submarine campaign against U.S. merchant ships that were supplying Germany's enemy countries. The publicly stated goals were to uphold American honor, crush German militarism, and reshape the postwar world. After a slow mobilization, the United States of America helped bring about a decisive victory by supplying badly needed financing, food, and millions of fresh and eager soldiers. After the war, the United States of America rejected the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
and did not join the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
.
In 1920, the manufacture, sale, import and export of alcohol was prohibited by the
Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Eighteenth Amendment (Amendment XVIII) to the United States Constitution established the prohibition of alcohol in the United States. The amendment was proposed by Congress on December 18, 1917, and ratified by the requisite number of sta ...
. Possession of liquor, and drinking it, was never illegal before. The overall level of alcohol consumption did go down, however, state and local governments avoided aggressive enforcement. The federal government was overwhelmed with cases, so that
bootlegging and
speakeasies
A speakeasy, also called a beer flat or blind pig or blind tiger, was an illicit establishment that sold alcoholic beverages. The term may also refer to a retro style bar that replicates aspects of historical speakeasies.
In the United State ...
flourished in every city. Well-organized criminal gangs exploded in numbers, finances, power, and influence on city politics.
A few local domestic-terrorist attacks from radicals, like the
1920 Wall Street Bombing and the
1919 United States anarchist bombings
From April through June 1919, a series of bombings were carried out or attempted across the United States by Galleanists (followers of Italian insurrectionary anarchist Luigi Galleani). The targets included anti-immigration politicians, anti ...
sparked the first
Red Scare
A Red Scare is a form of moral panic provoked by fear of the rise of left-wing ideologies in a society, especially communism and socialism. Historically, red scares have led to mass political persecution, scapegoating, and the ousting of thos ...
.
Culture wars
A culture war is a form of cultural conflict (metaphorical "war") between different social groups who struggle to politically impose their own ideology (moral beliefs, humane virtues, and religious practices) upon mainstream society, or upon t ...
between fundamentalist Christians and modernists became more intense, as demonstrated by prohibition, the Ku Klux Klan (
KKK), and the highly publicized
Scopes Trial.
The nation enjoyed a period of sustained prosperity in the 1920s. Agriculture went through a bubble in soaring land prices that collapsed in 1921, and that sector remained depressed. Coal mining was shrinking as oil became the main energy source. Otherwise most sectors prospered. Construction flourished as office buildings, factories, paved roads, and new housing was evident everywhere. Automobile production soared, suburban housing expanded and the nation's homes, towns and cities were electrified, along with some farms. Prices were stable, and the
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
(GDP) grew steadily until 1929, when the financial speculation bubble burst as Wall Street crashed.
In foreign policy President Wilson helped found the League of Nations but the U.S. never joined it, as the Congress refused to give up its constitutional role in declaring war. The nation instead took the initiative to disarm the world, most notably at the
Washington Conference in 1921–22. Washington also helped stabilize the European economy through the
Dawes Plan
The Dawes Plan temporarily resolved the issue of the reparations that Germany owed to the Allies of World War I. Enacted in 1924, it ended the crisis in European diplomacy that occurred after French and Belgian troops occupied the Ruhr in re ...
and the
Young Plan
The Young Plan was a 1929 attempt to settle issues surrounding the World War I reparations obligations that Germany owed under the terms of Treaty of Versailles. Developed to replace the 1924 Dawes Plan, the Young Plan was negotiated in Paris f ...
. The
Immigration Act of 1924
The Immigration Act of 1924, or Johnson–Reed Act, including the Asian Exclusion Act and National Origins Act (), was a United States federal law that prevented immigration from Asia and set quotas on the number of immigrants from every count ...
was aimed at stabilizing the traditional ethnic balance and strictly limiting the total inflow. The act completely blocked Asian immigrants, providing no means for them to get in.
The
Wall Street Crash of 1929 and the ensuing Great Depression led to government efforts to restart the economy and help its victims. The recovery, however, was very slow. The nadir of the Great Depression was 1933, and recovery was rapid until the recession of 1938 proved a setback. There were no major new industries in the 1930s that were big enough to drive growth the way autos, electricity and construction had been so powerful in the 1920s. GDP surpassed 1929 levels in 1940.
By 1939,
isolationist
Isolationism is a term used to refer to a political philosophy advocating a foreign policy that opposes involvement in the political affairs, and especially the wars, of other countries. Thus, isolationism fundamentally advocates neutrality an ...
sentiment in America had ebbed, and after the stunning fall of France in 1940 to
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, the United States began rearming itself and sent a large stream of money and military supplies to Britain and the Soviet Union. Following the
attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of ...
, the United States entered World War II to fight against Nazi Germany,
Fascist Italy
Fascist Italy () is a term which is used in historiography to describe the Kingdom of Italy between 1922 and 1943, when Benito Mussolini and the National Fascist Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. Th ...
, and
Imperial Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
, known as the "
Axis Powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
". Italy surrendered in 1943, and Germany and Japan in 1945, after massive devastation and loss of life, while the US emerged far richer and with few casualties.
World War I
Entry
Firmly maintaining neutrality when
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
began in Europe in 1914, the United States helped supply the
Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
, but could not ship anything to the
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
because of the
British blockade of Germany. Sympathies among many politically and culturally influential Americans had favored the British cause from the start of the war, as typified by industrialist
Samuel Insull
Samuel Insull (November 11, 1859 – July 16, 1938) was a British American business magnate. He was an innovator and investor based in Chicago who helped create an integrated electrical infrastructure in the United States. Insull created hold ...
, born in London, who helped young Americans enlist in British or Canadian forces. On the other hand, especially in the Midwest, many
Irish Americans
Irish Americans () are Irish ethnics who live within in the United States, whether immigrants from Ireland or Americans with full or partial Irish ancestry.
Irish immigration to the United States
From the 17th century to the mid-19th c ...
and
German Americans
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
opposed any American involvement, the Irish because they hated the British, and the Germans because they feared they would come under personal attack. The suffragist movement included many pacifists, and most churches opposed the war.
German efforts to use their submarines ("
U-boats
U-boats are naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the First and Second World Wars. The term is an anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the German term refers to any submarine. Austro-Hungarian Na ...
") to blockade Britain resulted in the deaths of American travelers and sailors, and attacks on passenger liners caused public outrage. Most notable was
torpedoing without warning the passenger liner ''Lusitania'' in 1915. Germany promised not to repeat; however it reversed position in early 1917, believing that
unrestricted U-boat warfare against all ships headed to Britain would win the war, albeit at the cost of American entry. When Americans read the text of the German offer to Mexico, known as the
Zimmermann Telegram, they saw an offer for Mexico to go to war with Germany against the United States, with German funding, with the promise of the return of the lost territories of Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. On April 1, 1917, Wilson called for war, emphasizing that the U.S. had to fight to maintain its honor and to have a decisive voice in shaping the new postwar world. Congress voted on April 6, 1917, to declare war, but it was far from unanimous.
Germania
German Americans were sometimes accused of being too sympathetic to the
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
. Former president
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
denounced "
hyphenated American
In the United States, the term hyphenated American refers to the use of a hyphen (in some styles of writing) between the name of an ethnicity and the word in compound nouns, e.g., as in . Calling a person a "hyphenated American" was used as ...
ism", insisting that
dual loyalties were impossible in wartime. A small minority came out for Germany, or ridiculed the British. About 1% of the 480,000 enemy aliens of German birth were imprisoned in 1917–18. The allegations included spying for Germany, or endorsing the German war effort. Thousands were forced to buy war bonds to show their loyalty. One person was killed by a mob; in
Collinsville, Illinois
Collinsville is a city located mainly in Madison County and partially in St. Clair County, Illinois, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 24,366. Collinsville is approximately east of St. Louis, Missouri, and is ...
, German-born
Robert Prager
Robert Paul Prager (February 28, 1888 – April 5, 1918) was a German immigrant who was lynched in the United States during World War I due to growing anti-German sentiment. Prager initially worked as a baker in southern Illinois before taking ...
was dragged from jail as a suspected spy and lynched.
The war saw a
phobia of anything German engulf the nation;
sauerkraut
Sauerkraut (; , ) is finely cut raw cabbage that has been fermented by various lactic acid bacteria. It has a long shelf life and a distinctive sour flavor, both of which result from the lactic acid formed when the bacteria ferment the sugar ...
was rechristened "liberty cabbage".
Patriotism
The Wilson Administration created the
Committee on Public Information
The Committee on Public Information (1917–1919), also known as the CPI or the Creel Committee, was an independent agency of the government of the United States under the Wilson administration created to influence public opinion to support the ...
(CPI) to control war information and provide pro-war propaganda. The private
American Protective League
The American Protective League (1917–1919) was an organization of private citizens sponsored by the United States Department of Justice that worked with federal law enforcement agencies during the World War I era. Its mission was to identify sus ...
, working with the
Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
, was one of many private right-wing "patriotic associations" that sprang up to support the war and at the same time fight labor unions and various left-wing and anti-war organizations. The U.S. Congress passed, and Wilson signed, the
Espionage Act of 1917
The Espionage Act of 1917 is a United States federal law enacted on June 15, 1917, shortly after the United States entered World War I. It has been amended numerous times over the years. It was originally found in Title 50 of the U.S. Code ( ...
and the
Sedition Act of 1918
Sedition is overt conduct, such as speech or organization, that tends toward rebellion against the established order. Sedition often includes subversion of a constitution and incitement of discontent toward, or insurrection against, establ ...
. The Sedition Act criminalized any expression of opinion that used "disloyal, profane, scurrilous or abusive language" about the U.S. government, flag or armed forces. Government police action, private vigilante groups and public war hysteria compromised the civil liberties of many Americans who disagreed with Wilson's policies.
Draft
The United States was remarkably unprepared for war in 1917, since it had not fought a major conflict since 1865. The military was small by modern standards and used out-dated weapons. A hasty expansion and modernization of the armed forces was thus launched. The draft began in spring 1917 but volunteers were also accepted. Four million men and thousands of women joined the services for the duration.
Economic confusion in 1917
In terms of munitions production, the 15 months after April 1917 involved an amazing parade of mistakes, misguided enthusiasm, and confusion. Americans were willing enough, but they did not know their proper role. Washington was unable to figure out what to do when, or even to decide who was in charge. Typical of the confusion was the coal shortage that hit in December 1917. Because coal was by far the major source of energy and heat a grave crisis ensued. There was in fact plenty of coal being mined, but 44,000 loaded freight and coal cars were tied up in horrendous traffic jams in the rail yards of the
East Coast. Two hundred ships were waiting in
New York Harbor
New York Harbor is a bay that covers all of the Upper Bay. It is at the mouth of the Hudson River near the East River tidal estuary on the East Coast of the United States.
New York Harbor is generally synonymous with Upper New York Bay, ...
for cargo that was delayed by the mess. The solution included nationalizing the coal mines and the railroads for the duration, shutting down factories one day a week to save fuel, and enforcing a strict system of priorities. Only in March 1918 did Washington finally take control of the crisis
Women
The war saw many women taking what were traditionally men's jobs for the first time. Many worked on the
assembly line
An assembly line, often called ''progressive assembly'', is a manufacturing process where the unfinished product moves in a direct line from workstation to workstation, with parts added in sequence until the final product is completed. By mechan ...
s of factories, producing tanks, trucks and munitions. For the first time, department stores employed African American women as elevator operators and cafeteria waitresses. The
Food Administration helped housewives prepare nutritious meals with less waste and with optimum use of the foods available. Most important, the morale of the women remained high, as millions joined the Red Cross as volunteers to help soldiers and their families. With rare exceptions, the women did not protest the draft.
Labor
Samuel Gompers
Samuel Gompers (; January 27, 1850December 11, 1924) was a British-born American cigar maker, labor union leader and a key figure in American labor history. Gompers founded the American Federation of Labor (AFL) and served as the organization's ...
, head of the
American Federation of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutual ...
, and nearly all labor unions were strong supporters of the war effort. They minimized strikes as wages soared and full employment was reached. The AFL unions strongly encouraged their young men to enlist in the military, and fiercely opposed efforts to reduce recruiting and slow war production by the anti-war labor union called the
Industrial Workers of the World
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), whose members are nicknamed "Wobblies", is an international labor union founded in Chicago, United States in 1905. The nickname's origin is uncertain. Its ideology combines general unionism with indu ...
(IWW) and also left-wing
Socialists
Socialism is an economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes the economic, political, and socia ...
. President Wilson appointed Gompers to the powerful
Council of National Defense
The Council of National Defense was a United States organization formed during World War I to coordinate resources and industry in support of the war effort, including the coordination of transportation, industrial and farm production, financial s ...
, where he set up the War Committee on Labor. The AFL membership soared to 2.4 million in 1917. In 1919, the Union tried to make their gains permanent and called a series of major strikes in meat, steel and other industries. The strikes, all of which failed, forced unions back to their position around 1910. Anti-war socialists controlled the IWW, which fought against the war effort and was in turn shut down by legal action by the federal government.
American Expeditionary Forces
On the battlefields of the
Western Front, the fresh
American Expeditionary Forces
The American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) was a formation of the United States Armed Forces on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front during World War I, composed mostly of units from the United States Army, U.S. Army. The AEF was establis ...
troops were enthusiastically welcomed by the war-weary
Allied armies in the summer of 1918. They arrived at the rate of 10,000 a day, at a time that the
Imperial German Army
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the leadership of Kingdom o ...
was unable to replace its losses. After the Allies turned back the powerful final German offensive (
Spring Offensive), the Americans played a central role in the Allied final offensive (
Hundred Days Offensive
The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allied offensives that ended the First World War. Beginning with the Battle of Amiens (8–12 August) on the Western Front, the Allies pushed the Imperial Germa ...
). Victory over Germany was achieved on
November 11, 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed in a railroad car, in the Compiègne Forest near the town of Compiègne, that ended fighting on land, at sea, and in the air in World War I between the Entente and their las ...
.
Using questionnaires filled out by doughboys as they left the Army, Gutièrrez reported they were not cynical or disillusioned. They fought "for honor, manhood, comrades, and adventure, but especially for duty."
Aftermath


A popular
Tin Pan Alley
Tin Pan Alley was a collection of History of music publishing, music publishers and songwriters in New York City that dominated the American popular music, popular music of the United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Originally ...
song of 1919 asked, concerning the United States troops returning from World War I, "
". In fact, many did not remain "down on the farm"; there was a great migration of youth from farms to nearby towns and smaller cities. The average distance moved was only 10 miles (16 km). Few went to the cities with over 100,000 people. However, agriculture became increasingly mechanized with widespread use of the
tractor
A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a Trailer (vehicle), trailer or machinery such as that used in agriculture, mining or constructio ...
, other heavy equipment, and superior techniques disseminated through
County Agents, who were employed by state agricultural colleges and funded by the Federal government.
In 1919,
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
campaigned for congress to ratify the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
and allow the U.S. to join the new
League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
, which he had been instrumental in creating. Wilson rejected the Republican compromise on the issue, and it failed for lack of a 2/3 majority. During his grueling cross-country tour to promote the League, Wilson suffered a series of strokes. He never recovered physically and lost his leadership skills and was unable to negotiate or compromise. The Senate rejected entry into the League and the U.S. never joined.
Defeat in the Great War left Germany in a state of revolutionary turmoil and heavily in debt for
war reparations
War reparations are compensation payments made after a war by one side to the other. They are intended to cover damage or injury inflicted during a war. War reparations can take the form of hard currency, precious metals, natural resources, in ...
, payments to the victorious
Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
. The Allies in turn owed large sums to the US Treasury for war loans. Under the multi-national
Dawes Plan
The Dawes Plan temporarily resolved the issue of the reparations that Germany owed to the Allies of World War I. Enacted in 1924, it ended the crisis in European diplomacy that occurred after French and Belgian troops occupied the Ruhr in re ...
, American and British banks loaned money to Germany to stabilize its currency and expand production, which then allowed it to pay reparations to countries like Britain and France.
In the 1920s, European and American economies reached new levels of industrial production and prosperity.
1919: strikes, riots and scares
Urban America was in turmoil throughout 1919. The huge number of returning veterans could not find work, something the Wilson administration had given little thought to. After the war, fear of subversion resumed in the context of the Red Scare, massive strikes in major industries (steel, meatpacking) and violent race riots. Radicals bombed Wall Street, and
workers went on strike in Seattle in February. During 1919, a series of more than 20 riotous and violent black-white race-related incidents occurred. These included the
Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
,
Omaha
Omaha ( ) is the List of cities in Nebraska, most populous city in the U.S. state of Nebraska. It is located in the Midwestern United States along the Missouri River, about north of the mouth of the Platte River. The nation's List of United S ...
, and
Elaine Race Riot
The Elaine massacre occurred on September 30October 2, 1919, at Hoop Spur in the vicinity of Elaine in rural Phillips County, Arkansas, where African Americans were organizing against peonage and abuses in tenant farming. As many as several h ...
s.
A phenomenon known as the ''
Red Scare
A Red Scare is a form of moral panic provoked by fear of the rise of left-wing ideologies in a society, especially communism and socialism. Historically, red scares have led to mass political persecution, scapegoating, and the ousting of thos ...
'' took place 1918–1919. With the rise of violent Communist revolutions in Europe, leftist radicals were emboldened by the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia and were eager to respond to Lenin's call for world revolution. On May 1, 1919, a parade in
Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–United States border, Canada–U.S. maritime border ...
, protesting the imprisonment of the
Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of th ...
leader,
Eugene Debs
Eugene Victor Debs (November 5, 1855 – October 20, 1926) was an American socialist, political activist, trade unionist, one of the founding members of the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), and five-time candidate of the Socialist Party o ...
, erupted into the violent
May Day Riots. A series of bombings by the far left in 1919 and assassination attempts further inflamed the situation. Attorney General
A. Mitchell Palmer conducted the
Palmer Raids
The Palmer Raids were a series of raids conducted in November 1919 and January 1920 by the United States Department of Justice under the administration of President Woodrow Wilson to capture and arrest suspected socialists, especially anarchist ...
, a series of raids and arrests of non-citizen
socialists
Socialism is an economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes the economic, political, and socia ...
,
anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state w ...
, radical unionists, and immigrants. They were charged with planning to overthrow the government. By 1920, over 10,000 arrests were made, and the immigrants caught up in these raids were deported back to Europe, most notably the anarchist
Emma Goldman
Emma Goldman (June 27, 1869 – May 14, 1940) was a Russian-born Anarchism, anarchist revolutionary, political activist, and writer. She played a pivotal role in the development of anarchist political philosophy in North America and Europ ...
, who years before had attempted to assassinate industrialist
Henry Clay Frick
Henry Clay Frick (December 19, 1849 – December 2, 1919) was an American industrialist, financier, and art patron. He founded the H. C. Frick & Company coke manufacturing company, was chairman of the Carnegie Steel Company and played a major ...
.
Women's suffrage
After a
long period of agitation, U.S. women were able in 1920 to obtain the necessary votes from a majority of men to obtain the right to vote in all state and federal elections. Women participated in the 1920 presidential and congressional elections.
Politicians responded to the new electorate by emphasizing issues of special interest to women, especially prohibition, child health, public schools, and world peace. Women did respond to these issues, but in terms of general voting they shared the same outlook and the same voting behavior as men.
The suffrage organization
NAWSA became the
League of Women Voters
The League of Women Voters (LWV) is a nonpartisan American nonprofit political organization. Founded in 1920, its ongoing major activities include Voter registration, registering voters, providing voter information, boosting voter turnout and adv ...
. Alice Paul's National Woman's Party began lobbying for full equality and the
Equal Rights Amendment
The Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) was a proposed amendment to the Constitution of the United States, United States Constitution that would explicitly prohibit sex discrimination. It is not currently a part of the Constitution, though its Ratifi ...
, which would pass Congress during the second wave of the women's movement in 1972, but was not ratified and never took effect. The main surge of women voting came in 1928, when the
big-city machines realized they needed the support of women to elect
Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith (December 30, 1873 – October 4, 1944) was the 42nd governor of New York, serving from 1919 to 1920 and again from 1923 to 1928. He was the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party's presidential nominee in the 1 ...
, while rural
dry counties
In the United States, a dry county is a county whose local government forbids the sale of any kind of alcoholic beverages. Some prohibit off-premises sale, some prohibit on-premises sale, and some prohibit both. The vast majority of counties no ...
mobilized women to support
Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
and vote for Republican
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was the 31st president of the United States, serving from 1929 to 1933. A wealthy mining engineer before his presidency, Hoover led the wartime Commission for Relief in Belgium and ...
. Catholic women were reluctant to vote in the early 1920s, but they registered in very large numbers for the 1928 election—the first in which Catholicism was a major issue. A few women were elected to office, but none became especially prominent during this time period. Overall, the women's rights movement was dormant in the 1920s, since Susan B. Anthony and the other prominent activists had died, and apart from
Alice Paul
Alice Stokes Paul (January 11, 1885 – July 9, 1977) was an American Quaker, suffragette, suffragist, feminist, and women's rights activist, and one of the foremost leaders and strategists of the campaign for the Nineteenth Amendment to the Unit ...
few younger women came along to replace them.
Roaring Twenties
In the
U.S. presidential election of 1920, the
Republican Party returned to the White House with the landslide victory of
Warren G. Harding
Warren Gamaliel Harding (November 2, 1865 – August 2, 1923) was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he was one of the most ...
, who promised a "return to normalcy" after the years of war, ethnic hatreds, race riots and exhausting reforms. Harding used new advertising techniques to lead the GOP to a massive landslide, carrying the major cities as many Irish Catholics and Germans, feeling betrayed, temporarily deserted the Democrats.
Prosperity
Except for a recession in 1920–21, the economy enjoyed a long period of prosperity. Good times were widespread for all sectors (except agriculture and coal mining). New industries flourished especially electric power, movies, automobiles, gasoline, tourist travel, highway construction, and housing.
"The business of America is business," proclaimed President Coolidge. Entrepreneurship flourished and was widely hailed. Business interests had captured control of the regulatory agencies established before 1915 and used progressive rhetoric, emphasizing technological efficiency and prosperity as the keys to social improvement.
William Allen White
William Allen White (February 10, 1868 – January 29, 1944) was an American newspaper editor, politician, author, and leader of the Progressive movement. Between 1896 and his death, White became a spokesman for Middle America (United States), ...
, a leading progressive spokesman, supported GOP candidate
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was the 31st president of the United States, serving from 1929 to 1933. A wealthy mining engineer before his presidency, Hoover led the wartime Commission for Relief in Belgium and ...
in 1928 as one who could "spiritualize" business prosperity and make it serve progressive ends.
The energy was a key to the economy, especially electricity, and oil. As electrification reached all the cities and towns, consumers demanded new products such as light bulbs, refrigerators, and toasters. Factories installed electric motors and saw productivity surge. With the
oil booms in Texas, Oklahoma, and California, the United States dominated world petroleum production, now even more important in an age of automobiles and trucks.
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was the 31st president of the United States, serving from 1929 to 1933. A wealthy mining engineer before his presidency, Hoover led the wartime Commission for Relief in Belgium and ...
became world famous by leading the
Commission for Relief in Belgium
The Commission for Relief in Belgium (CRB, or simply Belgian Relief) was an international, predominantly American, organization that arranged for the supply of food to German-occupied Belgium and northern France during the First World War.
It ...
in World War I. He directed the
U.S. Food Administration when the U.S. entered the war and served as Secretary of Commerce in the 1920s. An energetic exponent of
progressivism
Progressivism is a Left-right political spectrum, left-leaning political philosophy and Reformism, reform political movement, movement that seeks to advance the human condition through social reform. Adherents hold that progressivism has unive ...
he promoted engineering-style efficiency in business and public service, and promoted standardization, elimination of waste, and international trade. He easily won the
Republican presidential nomination in 1928 and defeated Democrat
Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith (December 30, 1873 – October 4, 1944) was the 42nd governor of New York, serving from 1919 to 1920 and again from 1923 to 1928. He was the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party's presidential nominee in the 1 ...
in a landslide.
The promise of prosperity made Hoover president, but the reality of economic decline ruined him, as Democrats tarred him with blame for the
Great Depression in the United States
In the United States, the Great Depression began with the Wall Street Crash of October 1929 and then spread worldwide. The nadir came in 1931–1933, and recovery came in 1940. The stock market crash marked the beginning of a decade of high u ...
. He was falsely accused of ignoring the crisis. Starting in late 1929 he tried multiple new ways to reverse the economic collapse as the world-wide Great Depression engulfed the United States. He called in all the experts for advice and looked for voluntary solutions that did not require government compulsion. No matter what he did the economy spiraled downward, hitting bottom just as he left office in early 1933. He lacked the political skills to rally support and was defeated in a landslide
in 1932 by
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
. After this loss, Hoover became staunchly
conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
, and spoke widely against liberal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
policies.
Unions
Labor unions grew very rapidly during the war, emerging with a large membership, full treasuries, and a temporary government guarantee of the right of collective bargaining. Inflation was high during the war, but wages went up even faster. However, unions were weak in heavy industry, such as automobiles and steel. Their main strength was in construction, printing, railroads, and other crafts where the
AFL
AFL may refer to:
Education
* Angel Foundation for Learning, a Canadian Roman Catholic charity
* Ankara Science High School, a high school in Ankara, Turkey, natively referred to as ''Ankara Fen Liesi''
* Assessment for learning
Military
* ...
had a strong system in place. Total union membership had soared from 2.7 million in 1914 to 5 million at its peak in 1919. An aggressive spirit appeared in 1919, as demonstrated by the general strike in Seattle and the police strike in Boston. The larger unions made a dramatic move for expansion in 1919 by calling major strikes in clothing, meatpacking, steel, coal, and railroads. The corporations fought back, and the strikes failed. The unions held on to their gains among machinists, textile workers, and seamen, and in such industries as food and clothing, but overall membership fell back to 3.5 million, where it stagnated until the New Deal passed the
Wagner Act
The National Labor Relations Act of 1935, also known as the Wagner Act, is a foundational statute of United States labor law that guarantees the right of private sector employees to organize into trade unions, engage in collective bargaining, an ...
in 1935.
Real earnings (after taking inflation, unemployment, and short hours into account) of all employees doubled over 1918–45. Setting 1918 as 100, the index went to 112 in 1923, 122 in 1929, 81 in 1933 (the low point of the depression), 116 in 1940, and 198 in 1945.
The bubble of the late 1920s was reflected by the extension of credit to a dangerous degree, including in the
stock market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange a ...
, which rose to record high levels. Government size had been at low levels, causing major freedom of the economy and more prosperity. It became apparent in retrospect after the
stock market crash of 1929 that credit levels had become dangerously inflated.
Immigration restriction
The United States became more
anti-immigration
Opposition to immigration, also known as anti-immigration, is a political position that seeks to restrict immigration. In the modern sense, immigration refers to the entry of people from one state or territory into another state or territory in ...
in outlook during this period. The American
Immigration Act of 1924
The Immigration Act of 1924, or Johnson–Reed Act, including the Asian Exclusion Act and National Origins Act (), was a United States federal law that prevented immigration from Asia and set quotas on the number of immigrants from every count ...
limited immigration from countries where 2% of the total
U.S. population
The United States is the third most populous country in the world, and the most populous in the Americas and the Western Hemisphere, with an estimated population of 340,110,988 on July 1, 2024, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. This was a ...
, per the 1890 census (not counting African Americans), were immigrants from that country. Thus, the massive influx of Europeans that had come to America during the first two decades of the century slowed to a trickle. Asians and citizens of India were prohibited from immigrating altogether.
Jazz

The "
Jazz Age
The Jazz Age was a period from 1920 to the early 1930s in which jazz music and dance styles gained worldwide popularity. The Jazz Age's cultural repercussions were primarily felt in the United States, the birthplace of jazz. Originating in New O ...
" symbolized the popularity of new musics and dance forms, which attracted younger people in all the large cities as the older generation worried about the threat of looser sexual standards as suggested by the uninhibited "
flapper
Flappers were a subculture of young Western women prominent after the First World War and through the 1920s who wore short skirts (knee length was considered short during that period), bobbed their hair, listened to jazz, and flaunted their ...
." In every locality, Hollywood discovered an audience for its silent films. It was an age of celebrities and heroes, with movie stars, boxers, home run hitters, tennis aces, and football standouts grabbing widespread attention.
Black culture, especially in music and literature, flourished in many cities such as New Orleans, Memphis, and Chicago but nowhere more than in New York City, site of the
Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African-American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics, and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the ti ...
. The
Cotton Club
The Cotton Club was a 20th-century nightclub in New York City. It was located on 142nd Street and Lenox Avenue from 1923 to 1936, then briefly in the midtown Theater District until 1940. The club operated during the United States' era of P ...
nightclub and the
Apollo Theater
The Apollo Theater (formerly the Hurtig & Seamon's New Theatre; also Apollo Theatre or 125th Street Apollo Theatre) is a multi-use Theater (structure), theater at 253 125th Street (Manhattan), West 125th Street in the Harlem neighborhood of U ...
became famous venues for artists and writers.
Radio was a new industry that grew explosively from homemade
crystal sets, picking up faraway stations to stations in every large city by the mid-decade. By 1927 two national networks had been formed, the
NBC Red Network
The National Broadcasting Company's NBC Radio Network (also known as the NBC Red Network from 1927 to 1942) was an American commercial radio network which was in continuous operation from 1926 through 1999. Along with the NBC Blue Network, it wa ...
and the
Blue Network
The Blue Network (previously known as the NBC Blue Network) was the on-air name of a now defunct American Commercial broadcasting, radio network, which broadcast from 1927 through 1945.
Beginning as one of the two radio networks owned by the ...
(ABC). The broadcast fare was mostly music, especially by
big band
A big band or jazz orchestra is a type of musical ensemble of jazz music that usually consists of ten or more musicians with four sections: saxophones, trumpets, trombones, and a rhythm section. Big bands originated during the early 1910s and ...
s.
Prohibition
In 1920, the manufacture, sale, import and export of alcohol was prohibited by the
Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Eighteenth Amendment (Amendment XVIII) to the United States Constitution established the prohibition of alcohol in the United States. The amendment was proposed by Congress on December 18, 1917, and ratified by the requisite number of sta ...
in an attempt to alleviate high rates of alcoholism and, especially, political corruption led by saloon-based politicians. It was enforced at the federal level by the
Volstead Act
The National Prohibition Act, known informally as the Volstead Act, was an act of the 66th United States Congress designed to execute the 18th Amendment (ratified January 1919) which established the prohibition of alcoholic drinks. The Anti- ...
. Most states let the federals do the enforcing. Drinking or owning liquor was not illegal, only the manufacture or sale. National Prohibition ended in 1933, although it continued for a while in some states. Prohibition is considered by most (but not all) historians to have been a failure because
organized crime
Organized crime is a category of transnational organized crime, transnational, national, or local group of centralized enterprises run to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally thought of as a f ...
was strengthened.
[Daniel Okrent, ''Last Call: The Rise and Fall of Prohibition'' (2010)]
Ku Klux Klan
Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
(KKK) is the name of three entirely different organizations (1860s, 1920s, post 1960) that used the same nomenclature and costumes but had no direct connection. The KKK of the 1920s was a purification movement that rallied against crime, especially violation of prohibition, and decried the growing "influence" of "big-city" Catholics and
Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, many of them immigrants and their descendants from Ireland as well as Southern and Eastern Europe. Its membership was often exaggerated but possibly reached as many as 4 million men, but no prominent national figure claimed membership; no daily newspaper endorsed it, and indeed most actively opposed the Klan. Membership was verily evenly spread across the nation's white Protestants,
North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
,
West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
, and
South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
, urban and rural. Historians in recent years have explored the Klan in depth. The KKK of the 1860s and the current KKK were indeed violent. However, historians discount lurid tales of a murderous group in the 1920s. Some crimes were probably committed in
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
states but were quite uncommon elsewhere. The local Klans seem to have been poorly organized and were exploited as money-making devices by organizers more than anything else. (Organizers charged a $10 application fee and up to $50 for costumes.) Nonetheless, the KKK had become prominent enough that it staged a huge rally in Washington DC in 1925. Soon afterward, the national headlines reported rape and murder by the KKK leader in
Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
, and the group quickly lost its mystique and nearly all its members.
Scopes "Monkey" Trial
The
Scopes Trial of 1925 was a
Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
court case that tested a state law which forbade the teaching of "any theory that denies the story of the
Divine Creation of man as taught in the Bible, and to teach instead that man has descended from a lower order of animals." The law was the result of a systematic drive by religious
Fundamentalists
Fundamentalism is a tendency among certain groups and individuals that are characterized by the application of a strict literal interpretation to scriptures, dogmas, or ideologies, along with a strong belief in the importance of distinguishin ...
to throw back the onslaught of modern ideas in theology and science. In a spectacular trial that drew national attention thanks to the roles of three-time Democratic presidential candidate
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator, and politician. He was a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running three times as the party' ...
for the prosecution and famed lawyer
Clarence Darrow
Clarence Seward Darrow (; April 18, 1857 – March 13, 1938) was an American lawyer who became famous in the 19th century for high-profile representations of trade union causes, and in the 20th century for several criminal matters, including the ...
for the defense,
John T. Scopes
John Thomas Scopes (August 3, 1900 – October 21, 1970) was a teacher in Dayton, Tennessee, who was charged on May 5, 1925, with violating Tennessee's Butler Act, which prohibited the teaching of human evolution in Tennessee schools. He was trie ...
was convicted of teaching evolution, but the verdict was overturned on a technicality. The Fundamentalists were widely ridiculed, with writers like
H. L. Mencken
Henry Louis Mencken (September 12, 1880 – January 29, 1956) was an American journalist, essayist, satirist, cultural critic, and scholar of American English. He commented widely on the social scene, literature, music, prominent politicians, ...
poking merciless ridicule at them; their efforts to pass state laws proved a failure.
Federal government

Led by Commerce Secretary Herbert Hoover, the federal government in the 1920s took on an increasing role in business and economic affairs. In addition to Prohibition, the government obtained new powers and duties such as funding and overseeing the new
U.S. Highway system
The United States Numbered Highway System (often called U.S. Routes or U.S. Highways) is an integrated network of roads and highways numbered within a nationwide grid in the contiguous United States. As the designation and numbering of these h ...
, controlling agriculture, and regulating radio and commercial aviation. The result was a rapid spread of standardized roads and broadcasts that were welcomed by most Americans.
The
Harding Administration was rocked by the
Teapot Dome scandal
The Teapot Dome scandal was a political corruption scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Warren G. Harding. It centered on Interior Secretary Albert B. Fall, who had leased Navy petroleum reserves at Teapot Do ...
, the most famous of a number of episodes involving Harding's cabinet members. The president, exhausted and dismayed from the news of the scandals, died of a heart attack in August 1923. His vice-president, Calvin Coolidge, succeeded him. Coolidge could not have been a more different personality than his predecessor. Dour, puritanical, and spotlessly honest, his White House stood in sharp contrast to the drinking, gambling, and womanizing that went on under Harding. In 1924, he was easily elected in his own right with the slogan "Keep Cool With Coolidge". Overall, the Harding and Coolidge administrations marked a return to the hands-off style of 19th-century presidents in contrast to the activism of Roosevelt and Wilson. Coolidge, who spent the entire summer on vacation during his years in office, famously said "The business of the American people is business."
When Coolidge declined to run again in the
1928 election, the Republican Party nominated engineer and
Secretary of Commerce
The United States secretary of commerce (SecCom) is the head of the United States Department of Commerce. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to commerce. The secretary rep ...
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was the 31st president of the United States, serving from 1929 to 1933. A wealthy mining engineer before his presidency, Hoover led the wartime Commission for Relief in Belgium and ...
, who was elected by a wide margin over
Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith (December 30, 1873 – October 4, 1944) was the 42nd governor of New York, serving from 1919 to 1920 and again from 1923 to 1928. He was the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party's presidential nominee in the 1 ...
, the first Catholic nominee. Hoover was a technocrat who had low regard for politicians. Instead he was a believer in the efficacy of individualism and business enterprise, with a little coordination by the government, to cure all problems. He envisioned a future of unbounded plenty and the imminent end of poverty in America. A year after his election, the stock market crashed, and the nation's economy slipped downward into the
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
.
After the crash, Hoover attempted to put in place many efforts to restore the economy, especially the fast-sinking agricultural sector. None worked. Hoover believed in stimulus spending and encouraged state and local governments, as well as the federal government, to spend heavily on public buildings, roads, bridges—and, most famously, the
Hoover Dam
The Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado, Black Canyon of the Colorado River (U.S.), Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. Constructed between 1931 and 1936, d ...
on the Colorado River. But with tax revenues falling fast, the states and localities plunged into their own fiscal crises. Republicans, following their traditional mass drums, along with pressure from the farm bloc, passed the
Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act
The Tariff Act of 1930, also known as the Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act, was a protectionist trade measure signed into law in the United States by President Herbert Hoover on June 17, 1930. Named after its chief congressional sponsors, Senator Reed ...
, which raised tariffs. Canada and other nations retaliated by raising their tariffs on American goods and moving their trade in other directions. American imports and exports plunged by more than two thirds, but since international trade was less than 5% of the American economy, the damage done was limited. The entire world economy, led by the United States, had fallen into a downward spiral that got worse and worse, and in 1931–32 began plunging downward even faster. Hoover had Congress set up a new relief agency, the
Reconstruction Finance Corporation
The Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC) was an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the United States federal government that served as a lender of last resort to US banks and businesses. Established in ...
, in 1932, but it proved too little too late.
Great Depression

Historians and economists still have not agreed on the
causes of the Great Depression
The causes of the Great Depression in the early 20th century in the United States have been extensively discussed by economists and remain a matter of active debate. They are part of the larger debate about economic crises and recessions. Alth ...
, but there is general agreement that it began in the United States in late 1929 and was either started or worsened by "
Black Thursday
Black Thursday is a term used to refer to typically negative, notable events that have occurred on a Thursday. It has been used in the following cases:
*6 February 1851 – devastating day of bushfires in Victoria, Australia
*21 June 1877 execut ...
," the
stock market crash
A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often fol ...
of Thursday, October 29, 1929. Sectors of the US economy had been showing some signs of distress for months before October 1929. Business inventories of all types were three times as large as they had been a year before (an indication that the public was not buying products as rapidly as in the past), and other signposts of economic health—freight carloads, industrial production, and wholesale prices—were slipping downward.
The events in the United States triggered a worldwide
depression, which led to
deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases i ...
and a great increase in
unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
. In the United States between 1929 and 1933, unemployment soared from 3% of the workforce to 25%, while manufacturing output collapsed by one-third. Local relief was overwhelmed. Unable to support their families, many unemployed men deserted (often going to "
Hooverville
Hoovervilles were shanty towns built during the Great Depression by the homeless in the United States. They were named after Herbert Hoover, who was President of the United States during the onset of the Depression and was widely blamed for it. T ...
s") so the meager relief supplies their families received would stretch further. For many, their next meal was found at a
soup kitchen
A soup kitchen, food kitchen, or meal center is a place where food is offered to Hunger, hungry and homeless people, usually for no price, cost, or sometimes at a below-market price (such as coin Donation, donations). Frequently located in Low i ...
, if at all.
Adding to the misery of the times,
drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
arrived in the
Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include th ...
. Decades of bad farming practices caused the topsoil to erode, and combined with the weather conditions (the 1930s was the overall warmest decade of the 20th century in North America) caused an ecological disaster. The dry soil was lifted by wind and blown into huge dust storms that blanketed entire towns, a phenomenon that continued for several years. Those who had lost their homes and livelihoods in the
Dust Bowl
The Dust Bowl was a period of severe dust storms that greatly damaged the ecology and agriculture of the American and Canadian prairies during the 1930s. The phenomenon was caused by a combination of natural factors (severe drought) and hum ...
were lured westward by advertisements for work put out by
agribusiness
Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy,
in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise.
The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit ...
in western states, such as California. The migrants came to be called
Okies
An Okie is a person identified with the state of Oklahoma, or their descendants. This connection may be residential, historical or cultural. For most Okies, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their bei ...
,
Arkies, and other derogatory names as they flooded the labor supply of the agricultural fields, driving down wages, pitting desperate workers against each other. They came into competition with Mexican laborers, who were deported en masse back to their home country.
In the South, the fragile economy collapsed further. To escape, rural workers and
sharecropper
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement in which a landowner allows a tenant (sharecropper) to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land. Sharecropping is not to be conflated with tenant farming, providing the tenant a ...
s migrated north by train, both black and white. By 1940 they were attracted by booming munitions factories in plants in the
Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of Northern America is a binational Canadian– American region centered on the Great Lakes that includes the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin and the Ca ...
Nationwide, farmers had been experiencing depressed market conditions for their crops and goods since the end of World War I. Many family farms that had been mortgaged during the 1920s to provide money to "get through until better times" were
foreclosed
Foreclosure is a legal process in which a lender attempts to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has stopped making payments to the lender by forcing the sale of the asset used as the collateral for the loan.
Formally, a mort ...
when farmers were unable to make payments.
The New Deal
In the United States, upon accepting
Democratic nomination for president in 1932,
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
promised "a new deal for the American people," a phrase that has endured as a label for his administration and its many domestic achievements.
The Republicans, blamed for the Depression, or at least for lack of an adequate response to it, were easily defeated by Roosevelt in
1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident (1932), Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort ...
.
Roosevelt entered office with no single ideology or plan for dealing with the depression. The "new deal" was often contradictory, pragmatic, and experimental. What some considered incoherence of the New Deal's ideology, however, was the presence of several competing ones, based on programs and ideas not without precedents in the American political tradition. The New Deal consisted of many different efforts to end the Great Depression and reform the American economy. Many of them failed, but there were enough successes to establish it as the most important episode of the 20th century in the creation of the modern American state.
The desperate economic situation, combined with the substantial Democratic victories in the 1932 Congressional elections, gave Roosevelt unusual influence over Congress in the "First Hundred Days" of his administration. He used his leverage to win rapid passage of a series of measures to create welfare programs and regulate the banking system, stock market, industry and agriculture.
"Bank holiday" and Emergency Banking Act

On March 6, two days after taking office, Roosevelt issued a proclamation closing all American banks for four days until Congress could meet in a special session. Ordinarily, such an action would cause widespread panic. But the action created a general sense of relief. First, many states had already closed down the banks before March 6. Second, Roosevelt astutely and euphemistically described it as a "bank holiday." And third, the action demonstrated that the federal government was stepping in to stop the alarming pattern of bank failures.
Three days later, President Roosevelt sent to Congress the
Emergency Banking Act
__NOTOC__
The Emergency Banking Relief Act (E.B.R.A.), (), was an act passed by the United States Congress in March 1933 in an attempt to stabilize the banking system.
Bank holiday
Beginning on February 14, 1933, Michigan, an industrial sta ...
, a generally conservative bill, drafted in large part by holdovers from the Hoover administration, designed primarily to protect large banks from being dragged down by the failing smaller ones. The bill provided for
United States Treasury Department
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States. It is one of 15 current U.S. government departments.
The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and ...
inspection of all banks before they would be allowed to reopen, for federal assistance to tottering large institutions, and for a thorough reorganization of those in greatest difficulty. A confused and frightened Congress passed the bill within four hours of its introduction. Three-quarters of the banks in the
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of ...
reopened within the next three days, and $1 billion in hoarded currency and gold flowed back into them within a month. The immediate banking crisis was over. The
Glass–Steagall Act established various provisions designed to prevent another Great Depression from happening again. These included separating investment from savings and loan banks and forbidding the purchase of stock with no money down. Roosevelt also removed the currency of the United States from the gold standard, which was widely blamed for limiting the money supply and causing deflation, although the silver standard remained until 1971. Private ownership of gold bullion and certificates was banned and would remain so until 1975.
Economy Act
On the morning after passage of the Emergency Banking Act, Roosevelt sent to Congress the
Economy Act
The Economy Act of 1933, officially titled the Act of March 20, 1933 (ch. 3, , is an Act of Congress that cut the salaries of federal workers and reduced benefit payments to veterans, moves intended to reduce the federal deficit in the United St ...
, which was designed to convince the public, and moreover the business community, that the federal government was in the hands of no radical. The act proposed to balance the federal budget by cutting the salaries of government employees and reducing pensions to veterans by as much as 15%.
Otherwise, Roosevelt warned, the nation faced a $1 billion deficit. The bill revealed clearly what Roosevelt had always maintained: that he was as much of a fiscal conservative at heart as his predecessor was. And like the banking bill, it passed through Congress almost instantly—despite heated protests by some congressional progressives.
Farm programs
The celebrated First Hundred Days of the new administration also produced a federal program to protect American farmers from the uncertainties of the market through subsidies and production controls, the
Agricultural Adjustment Act
The Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) was a United States federal law of the New Deal era designed to boost agricultural prices by reducing surpluses. The government bought livestock for slaughter and paid farmers Subsidy, subsidies not to plant ...
(AAA), which Congress passed in May 1933. The AAA reflected the desires of leaders of various farm organizations and Roosevelt's
Secretary of Agriculture
The United States secretary of agriculture is the head of the United States Department of Agriculture. The position carries similar responsibilities to those of agriculture ministers in other governments
The department includes several organiz ...
,
Henry A. Wallace
Henry Agard Wallace (October 7, 1888 – November 18, 1965) was the 33rd vice president of the United States, serving from 1941 to 1945, under President Franklin D. Roosevelt. He served as the 11th U.S. secretary of agriculture and the 10th U.S ...
.
Relative farm incomes had been falling for decades. The AAA included reworkings of many long-touted programs for agrarian relief, which had been demanded for decades. The most important provision of the AAA was the provision for crop reductions—the "domestic allotment" system, which was intended to raise prices for farm commodities by preventing surpluses from flooding the market and depressing prices further. The most controversial component of the system was the destruction in summer 1933 of growing crops and newborn livestock that exceeded the allotments. They had to be destroyed to get the plan working. However, gross farm incomes increased by half in the first three years of the New Deal and the relative position of farmers improved significantly for the first time in twenty years. Urban
food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices affect producers and consumers of food. Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing and food di ...
went up slightly, because the cost of the grains was only a small fraction of what the consumer paid. Conditions improved for the great majority of commercial farmers by 1936. The income of the farm sector almost doubled from $4.5 billion in 1932 to $8.9 billion in 1941 just before the war. Meanwhile, food prices rose 22% in nine years from an index of 31.5 in 1932, to 38.4 in 1941.

However, rural America contained many isolated farmers scratching out a subsistence income. The new deal set up programs such as the
Resettlement Administration
The Resettlement Administration (RA) was a New Deal U.S. federal agency created May 1, 1935. It relocated struggling urban and rural families to communities planned by the federal government. On September 1, 1937, it was succeeded by the Farm S ...
and the
Farm Security Administration
The Farm Security Administration (FSA) was a New Deal agency created in 1937 to combat rural poverty during the Great Depression in the United States. It succeeded the Resettlement Administration (1935–1937).
The FSA is famous for its small but ...
to help them, but was very reluctant to help them buy farms.
'Alphabet soup'
Roosevelt also created an ''
alphabet soup'' of new federal regulatory agencies such as the
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street crash of 1929. Its primary purpose is to enforce laws against market m ...
(SEC) to oversee the stock market and a reform of the banking system that included the
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is a State-owned enterprises of the United States, United States government corporation supplying deposit insurance to depositors in American commercial banks and savings banks. The FDIC was cr ...
(FDIC) to establish a system of insurance for deposits.
The most successful initiatives in alleviating the miseries of the Great Depression were a series of relief measures to aid some of the 15 million unemployed Americans, among them the
Civilian Conservation Corps
The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) was a voluntary government unemployment, work relief program that ran from 1933 to 1942 in the United States for unemployed, unmarried men ages 18–25 and eventually expanded to ages 17–28. The CCC was ...
, the
Civil Works Administration
The Civil Works Administration (CWA) was a short-lived job creation program established by the New Deal during the Great Depression in the United States in order to rapidly create mostly manual-labor jobs for millions of unemployed workers. The j ...
, and the
Federal Emergency Relief Administration
The Federal Emergency Relief Administration (FERA) was a program established by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1933, building on the Hoover administration's Emergency Relief and Construction Act. It was replaced in 1935 by the Works Progre ...
.
The early New Deal also began the
Tennessee Valley Authority
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) is a federally owned electric utility corporation in the United States. TVA's service area covers all of Tennessee, portions of Alabama, Mississippi, and Kentucky, and small areas of Georgia, North Carolin ...
, an unprecedented experiment in flood control, public power, and regional planning.
Second New Deal
The
Second New Deal
The Second New Deal is a term used by historians to characterize the second stage, 1935–36, of the New Deal programs of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The most famous laws included the Emergency Relief Appropriation Act, the Banking Act, the ...
(1935–36) was the second stage of the
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
programs. President
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
announced his main goals in January 1935: improved use of national resources, security against old age, unemployment and illness, and
slum clearance
Slum clearance, slum eviction or slum removal is an urban renewal strategy used to transform low-income settlements with poor reputation into another type of development or housing. This has long been a strategy for redeveloping urban communities; ...
, as well as a national welfare program (the WPA) to replace state relief efforts. The most important programs included
Social Security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
, the
National Labor Relations Act
The National Labor Relations Act of 1935, also known as the Wagner Act, is a foundational statute of United States labor law that guarantees the right of private sector employees to organize into trade unions, engage in collective bargaining, an ...
("Wagner Act"), the Banking Act,
rural electrification
Rural electrification is the process of bringing electrical power to rural and remote areas. Rural communities are suffering from colossal market failures as the national grids fall short of their demand for electricity. As of 2019, 770 million ...
, and
breaking up utility holding companies. Programs that were later ended by the Supreme Court or the
Conservative coalition
The conservative coalition, founded in 1937, was an unofficial alliance of members of the United States Congress which brought together the conservative wings of the Republican and Democratic parties to oppose President Franklin Delano Rooseve ...
included the
Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration (WPA; from 1935 to 1939, then known as the Work Projects Administration from 1939 to 1943) was an American New Deal agency that employed millions of jobseekers (mostly men who were not formally educated) to car ...
(WPA), the
National Youth Administration
The National Youth Administration (NYA) was a New Deal agency sponsored by Presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt, Franklin D. Roosevelt during his presidency. It focused on providing work and education for Americans between the ages of 16 and 25. ...
(NYA), the
Resettlement Administration
The Resettlement Administration (RA) was a New Deal U.S. federal agency created May 1, 1935. It relocated struggling urban and rural families to communities planned by the federal government. On September 1, 1937, it was succeeded by the Farm S ...
, and programs for retail price control,
farm rescues, coal stabilization, and
taxes on the rich and the
Undistributed profits tax The undistributed profits tax was enacted in 1936 by the United States administration of President Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR), during the Great Depression. The UP tax was a revenue program for FDR's New Deal. The act was controversial even within ...
. Liberals in Congress passed the
Bonus Bill for World War veterans over FDR's veto.
The Second New Deal proved especially controversial as it attempted to redistribute wealth, income and power in favor of the poor, the old, farmers and labor unions. Liberals strongly supported the new direction, and formed the
New Deal coalition
The New Deal coalition was an American political coalition that supported the Democratic Party beginning in 1932. The coalition is named after President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal programs, and the follow-up Democratic presidents. It was ...
of union members, big city machines, the white South, and ethnic minorities to support it. Conservatives, typified by the
American Liberty League
The American Liberty League was an American political organization formed in 1934. Its membership consisted primarily of wealthy business elites and prominent political figures, who were for the most part conservatives opposed to the New Deal of P ...
, were strongly opposed.
Labor agitation

Roosevelt's first term saw a massive amount of labor upheaval. In 1934 alone, there was the
1934 West Coast waterfront strike that brought all of San Francisco into a four-day general strike, the
Minneapolis Teamsters Strike of 1934
The Minneapolis general strike of 1934 grew out of a strike by Teamsters against most of the trucking companies operating in Minneapolis, the major distribution center for the Upper Midwest. The strike began on May 16, 1934 in the Market Distri ...
that brought the Teamsters and other unions out for a strike causing the governor to declare martial law, the
1934 textile workers strike that brought hundreds of thousands of textile workers on the East Coast out on strike, as well as other strikes.
The
Industrial Workers of the World
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), whose members are nicknamed "Wobblies", is an international labor union founded in Chicago, United States in 1905. The nickname's origin is uncertain. Its ideology combines general unionism with indu ...
(IWW) and the communists no longer being a force in the labor movement, the conservative
American Federation of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutual ...
, which organized along
craft union
Craft unionism refers to a model of trade unionism in which workers are organised based on the particular craft or trade in which they work. It contrasts with industrial unionism, in which all workers in the same industry are organized into the sa ...
lines and which preached labor/capital cooperation, dominated the U.S. labor movement until the 1930s. In 1935, eight unions within the AFL organized the
Congress of Industrial Organizations
The Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) was a federation of Labor unions in the United States, unions that organized workers in industrial unionism, industrial unions in the United States and Canada from 1935 to 1955. Originally created in ...
(CIO) to promote
industrial unionism
Industrial unionism is a trade union organising method through which all workers in the same industry are organized into the same union, regardless of skill or trade, thus giving workers in one industry, or in all industries, more leverage in b ...
. The CIO unions were expelled by the AFL in 1936, and in 1938 they formed a rival federation to the AFL. The CIO had much success in organizing, with the
Steel Workers Organizing Committee The Steel Workers Organizing Committee (SWOC) was one of two precursor labor organizations to the United Steelworkers. It was formed by the CIO ( Committee for Industrial Organization) on June 7, 1936. It disbanded in 1942 to become the United Ste ...
getting a contract with
U.S. Steel
The United States Steel Corporation is an American steel company based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It maintains production facilities at several additional locations in the U.S. and Central Europe.
The company produces and sells steel products, ...
in 1937, and winning the
Flint Sit-Down Strike
The 1936–1937 Flint sit-down strike, also known as the General Motors sit-down strike, or the great GM sit-down strike, was a sitdown strike at the General Motors plant in Flint, Michigan, United States. It changed the United Automobile Worke ...
and getting
General Motors
General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing f ...
to recognize the
United Auto Workers
The United Auto Workers (UAW), fully named International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America, is an American labor union that represents workers in the United States (including Puerto Rico) and sou ...
(UAW) as the collective bargainer for GM workers. Having succeeded with GM, the UAW next turned its attention to Chrysler, which quickly came to terms. The last of the Big Three would prove to be a harder nut to crack, as Henry Ford remained absolutely opposed to unions. His security forces beat several UAW organizers outside the company's River Rouge plant in May 1937. Despite pressure on all fronts, Ford would not budge until a wildcat strike in 1941 convinced him to give in and unionize.
Recession of 1937 and recovery
The economy eventually recovered from the low point of the winter of 1932–33, with sustained improvement until 1937, when the
Recession of 1937
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a period of broad decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be tr ...
brought back 1934 levels of unemployment. There is a broad consensus among scholars that the New Deal policies did not lengthen and deepen the depression; only 5% of professional historians and 27% of professional economists believe it served to lengthen and deepen the Great Depression. Apart from the WPA and CCC, most New Deal spending programs, such as the PWA and AAA, operated through private firms.
The
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
and Roosevelt's leadership were under assault during Roosevelt's second term, which suffered new economic setbacks in the Recession of 1937. A sharp economic downturn began in the fall of 1937 and continued through most of 1938. Conservatives said it was caused by the labor unions' assault on industry through massive strikes and the way the New Deal discourages further investment. Keynesian economists argued it was a result of a premature effort by FDR to balance the budget by reducing federal spending. The administration reacted by launching a rhetorical campaign against business monopoly power, which was cast as the villain. The Supreme Court began busily dismantling the New Deal by ruling many of its programs unconstitutional and Roosevelt sought to replace the judges with more sympathetic ones in his infamous "Court Packing". Despite that, the New Deal gradually wound down and by 1939 the president had turned his attention towards foreign policy.
But the administration's other response to the 1937 downturn had more tangible results. Ignoring his own Treasury Department, Roosevelt embarked on an antidote to the depression, reluctantly abandoning his efforts to balance the budget and launching a $5 billion spending program in the spring of 1938, an effort to increase mass purchasing power and attack deflation. Roosevelt explained his program in a
fireside chat
The fireside chats were a series of evening radio addresses given by Franklin D. Roosevelt, the 32nd President of the United States, between 1933 and 1944. Roosevelt spoke with familiarity to millions of Americans about recovery from the Great D ...
in which he finally acknowledged that it was up to the government to "create an economic upturn" by making "additions to the purchasing power of the nation."
World War II and the end of the Great Depression
It was not until the administration expanded Federal spending to support
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, that the nation's economy fully recovered.
Between 1939 and 1944 (the peak of wartime production), the nation's output almost doubled. Consequently, unemployment plummeted—from 14% in 1940 to less than 2% in 1943, as the labor force grew by ten million.
The war economy was not so much a triumph of free enterprise as the result of government bankrolling business. While unemployment remained high throughout the New Deal years, consumption, investment, and net exports—the pillars of economic growth—remained low. It was World War II, not the New Deal, which finally ended the crisis. Nor did the New Deal substantially alter the distribution of power within American society and economy; and it had only a small impact on the distribution of wealth among the population.
Legacies of the New Deal
A 2017 review of the published scholarship summarized the findings of researchers as follows:
The studies find that public works and relief spending had state income multipliers of around one, increased consumption activity, attracted internal migration, reduced crime rates, and lowered several types of mortality. The farm programs typically aided large farm owners but eliminated opportunities for share croppers, tenants, and farm workers. The Home Owners' Loan Corporation's purchases and refinancing of troubled mortgages staved off drops in housing prices and home ownership rates at relatively low ex post cost to taxpayers. The Reconstruction Finance Corporation's loans to banks and railroads appear to have had little positive impact, although the banks were aided when the RFC took ownership stakes.
Although the New Deal did not end the depression, it increased the regulatory functions of the federal government in the stock market, the banking system, and others. It also produced a new political coalition that sustained the
Democratic Party as the majority party in national politics for more than a generation after its own end.
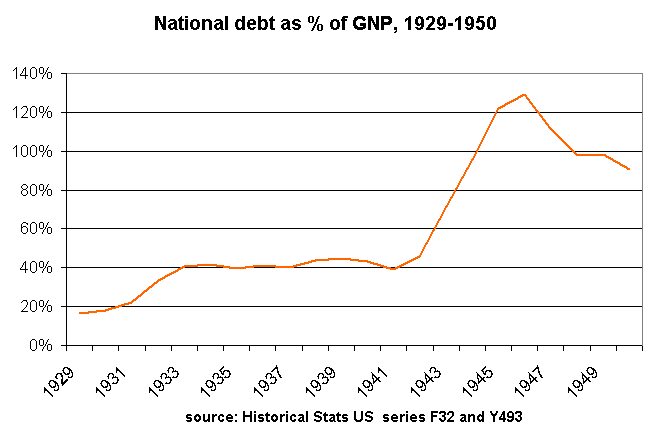
Laying the foundations for the postwar era, Roosevelt and the New Deal helped enhance the power of the federal government as a whole. Roosevelt also established the presidency as the preeminent center of authority within the federal government. By creating a large array of protections for various groups of citizens—workers, farmers, and others—who suffered from the crisis, enabling them to challenge the powers of the corporations, the Roosevelt administration generated a set of political ideas—known to later generations as New Deal liberalism—that remained a source of inspiration for decades and that helped shape the next experiment in liberal reform, the
Great Society
The Great Society was a series of domestic programs enacted by President Lyndon B. Johnson in the United States between 1964 and 1968, aimed at eliminating poverty, reducing racial injustice, and expanding social welfare in the country. Johnso ...
of the 1960s.
On the other hand, the Roosevelt administration and its liberalism became the source of a vigorous conservative reaction. Led in Congress by Senator
Robert A. Taft
Robert Alphonso Taft Sr. (September 8, 1889 – July 31, 1953) was an American politician, lawyer, and scion of the Republican Party's Taft family. Taft represented Ohio in the United States Senate, briefly served as Senate majority le ...
and the
Conservative coalition
The conservative coalition, founded in 1937, was an unofficial alliance of members of the United States Congress which brought together the conservative wings of the Republican and Democratic parties to oppose President Franklin Delano Rooseve ...
, they blocked almost all New Deal proposals after 1936, and shut down the WPA, CCC and many other programs by 1943. Eventually in the 1970s and 1980s, a bipartisan coalition ended most New Deal regulations and programs. The most important remaining ones in the 21st century are
Social Security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
and the
Securities and Exchange Commission
The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street crash of 1929. Its primary purpose is to enforce laws against market m ...
.
Foreign policy, 1919–1941
In the 1920s, American policy was an active participant in the international community, while it systematically ignoring the League of Nations. Instead Washington set up numerous diplomatic ventures, and used the enormous financial power of the United States to dictate major diplomatic questions in Europe.
Presidents Harding, Coolidge, and Hoover avoided any political commitments or alliances with anyone else. Franklin Roosevelt followed suit before World War II broke out in 1939. They minimized contact with the League of Nations. However, as historian Jerald Combs reports their administrations in no way returned to 19th-century isolationism. The key Republican leaders:
: including
Elihu Root
Elihu Root (; February 15, 1845February 7, 1937) was an American lawyer, Republican Party (United States), Republican politician, and statesman who served as the 41st United States Secretary of War under presidents William McKinley and Theodor ...
,
Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes (April 11, 1862 – August 27, 1948) was an American politician, academic, and jurist who served as the 11th chief justice of the United States from 1930 to 1941. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
, and Hoover himself, were Progressives who accepted much of Wilson's internationalism. ... They did seek to use American political influence and economic power to goad European governments to moderate the Versailles peace terms, induce the Europeans to settle their quarrels peacefully, secure disarmament agreements, and strengthen the European capitalist economies to provide prosperity for them and their American trading partners.
The
Washington Naval Conference
The Washington Naval Conference (or the Washington Conference on the Limitation of Armament) was a disarmament conference called by the United States and held in Washington, D.C., from November 12, 1921, to February 6, 1922.
It was conducted out ...
was the most successful diplomatic venture in the 1920s. It was held in Washington, under the Chairmanship of Secretary of State
Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes (April 11, 1862 – August 27, 1948) was an American politician, academic, and jurist who served as the 11th chief justice of the United States from 1930 to 1941. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
from 12 November 1921 to 6 February 1922. Conducted outside the auspice of the League of Nations, it was attended by nine nations—the United States, Japan, China, France, Great Britain, Italy, Belgium, Netherlands, and Portugal Russia and Germany were pariahs and were not invited. It focused on resolving misunderstandings or conflicts regarding interests in the Pacific Ocean and East Asia. The main achievement was a series of naval disarmament agreements agreed to by all the participants, that lasted for a decade. It resulted in three major treaties:
Four-Power Treaty
The Four-Power Treaty (四カ国条約, ''Shi-ka-koku Jōyaku'') was a treaty signed by the United States, the United Kingdom, France and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast ...
,
Five-Power Treaty
The Washington Naval Treaty, also known as the Five-Power Treaty, was signed during 1922 among the major Allies of World War I, which agreed to prevent an arms race by limiting naval construction. It was negotiated at the Washington Naval Confer ...
(the ''Washington Naval Treaty''), the
Nine-Power Treaty
The Nine-Power Treaty () or Nine-Power Agreement () was a 1922 treaty affirming the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Republic of China as per the Open Door Policy. The Nine-Power Treaty was signed on 6 February 1922 by all of the att ...
, and a number of smaller agreements. These treaties preserved peace during the 1920s but were not renewed, as the world scene turned increasingly negative after 1930.
The
Dawes Plan
The Dawes Plan temporarily resolved the issue of the reparations that Germany owed to the Allies of World War I. Enacted in 1924, it ended the crisis in European diplomacy that occurred after French and Belgian troops occupied the Ruhr in re ...
was a multi-national attempt to solve to the crisis of reparations that arose when Germany failed to meet the war reparations required of it under the Treaty of Versailles. When Germany was declared in default, French and Belgian troops
occupied the key industrial Ruhr district of Germany. The crisis was solved by a compromise in the form of the Dawes Plan in 1924. Under the plan, developed by a committee headed by American
Charles G. Dawes, New York and London banks loaned Germany hundreds of millions of dollars to stabilize its currency and expand production, which then allowed it to pay reparations.
Problems with the Dawes Plan, notably its lack of a total reparations amount, led to the 1928
Young Plan
The Young Plan was a 1929 attempt to settle issues surrounding the World War I reparations obligations that Germany owed under the terms of Treaty of Versailles. Developed to replace the 1924 Dawes Plan, the Young Plan was negotiated in Paris f ...
, developed under the leadership of the American
Owen D. Young
Owen D. Young (October 27, 1874July 11, 1962) was an American industrialist, businessman, lawyer and diplomat at the Second Reparations Conference (SRC) in 1929, as a member of the German Reparations International Commission.
He is known for th ...
. It established German reparation requirements at 112 billion marks () and created a schedule of payments that would see Germany complete payments by 1988. As a result of the severe impact of the Great Depression on the German economy, reparations were
suspended for a year in 1931. A treaty to further reduce reparations was agreed on at the 1932
Lausanne Conference, but it failed to be ratified by the countries involved. Reparations were not restarted until after 1953, when West Germany
paid the entire remaining balance.
Mexico
Since the turmoil of the Mexican revolution had died down, the Harding administration was prepared to normalize relations with Mexico. Between 1911 and 1920 American imports from Mexico increased from $57,000,000 to $179,000,000 and exports from $61,000,000 to $208,000,000. Commerce Secretary
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was the 31st president of the United States, serving from 1929 to 1933. A wealthy mining engineer before his presidency, Hoover led the wartime Commission for Relief in Belgium and ...
took the lead in order to promote trade and investments other than in oil and land, which had long dominated bilateral economic ties. President
Álvaro Obregón
Álvaro Obregón Salido (; 19 February 1880 – 17 July 1928) was a Mexican general, inventor and politician who served as the 46th President of Mexico from 1920 to 1924. Obregón was re-elected to the presidency in 1928 but was assassinated b ...
assured Americans that they would be protected in Mexico, and Mexico was granted recognition in 1923. A major crisis erupted in the mid-1930s when the Mexican government expropriated millions of acres of land from hundreds of American property owners as part of President
Lázaro Cárdenas
Lázaro Cárdenas del Río (; 21 May 1895 – 19 October 1970) was a Mexican army officer and politician who served as president of Mexico from 1934 to 1940. Previously, he served as a general in the Constitutional Army during the Mexican Revo ...
's land redistribution program. No compensation was provided to the American owners. The emerging threat of the Second World War forced the United States to agree to a compromise solution. The US negotiated an agreement with President
Manuel Avila Camacho
Manuel may refer to:
People
* Manuel (name), a given name and surname
* Manuel (''Fawlty Towers''), a fictional character from the sitcom ''Fawlty Towers''
* Manuel I Komnenos, emperor of the Byzantine Empire
* Manuel I of Portugal, king of Po ...
that amounted to a military alliance.
Intervention ends in Latin America
Small-scale military interventions continued after 1921 as the
Banana Wars
The Banana Wars were a series of conflicts that consisted of military occupation, police action, and Interventionism (politics), intervention by the United States in Central America and the Caribbean between the end of the Spanish–American W ...
tapered off. The Hoover administration began a goodwill policy and withdrew all military forces. President Roosevelt announced the "
Good Neighbor Policy" by which the United States would no longer intervene to promote good government, but would accept whatever governments were locally chosen. His Secretary of State
Cordell Hull
Cordell Hull (October 2, 1871July 23, 1955) was an American politician from Tennessee and the longest-serving U.S. Secretary of State, holding the position for 11 years (1933–1944) in the administration of President Franklin Delano Roosevel ...
endorsed article 8 of the 1933 Montevideo Convention on Rights and Duties of States; it provides that "no state has the right to intervene in the internal or external affairs of another".
Isolationism in 1930s
In the 1930s, the United States entered the period of deep isolationism, rejecting international conferences, and focusing moment mostly on reciprocal tariff agreements with smaller countries of Latin America.
Coming of war: 1937–1941
President Roosevelt tried to avoid repeating what he saw as Woodrow Wilson's mistakes in World War I. He often made exactly the opposite decision. Wilson called for neutrality in thought and deed, while Roosevelt made it clear his administration strongly favored Britain and China. Unlike the loans in World War I, the United States made large-scale grants of military and economic aid to the Allies through
Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (),3,000 Hurricanes and >4,000 other aircraft)
* 28 naval vessels:
** 1 Battleship. (HMS Royal Sovereign (05), HMS Royal Sovereign)
* ...
, with little expectation of repayment. Wilson did not greatly expand war production before the declaration of war; Roosevelt did. Wilson waited for the declaration to begin a draft; Roosevelt started one in 1940. Wilson never made the United States an official ally but Roosevelt did. Wilson never met with the top Allied leaders but Roosevelt did. Wilson proclaimed independent policy, as seen in the 14 Points, while Roosevelt always had a collaborative policy with the Allies. In 1917, United States declared war on Germany; in 1941, Roosevelt waited until the enemy attacked at Pearl Harbor. Wilson refused to collaborate with the Republicans; Roosevelt named leading Republicans to head the War Department and the Navy Department. Wilson let General John J. Pershing make the major military decisions; Roosevelt made the major decisions in his war including the "
Europe first
Europe first, also known as Germany first, was the key element of the grand strategy agreed upon by the United States and the United Kingdom during World War II after the United States joined the war in December 1941. According to this policy, the ...
" strategy. He rejected the idea of an armistice and demanded unconditional surrender. Roosevelt often mentioned his role in the Wilson administration, but added that he had profited more from Wilson's errors than from his successes.
World War II
Foreign and military policy
Isolationist
Isolationism is a term used to refer to a political philosophy advocating a foreign policy that opposes involvement in the political affairs, and especially the wars, of other countries. Thus, isolationism fundamentally advocates neutrality an ...
sentiment with regard to foreign wars in America had ebbed, but the United States at first declined to enter the war, limiting itself to giving supplies and weapons via
Lend Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (), to Britain,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, and the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. American feeling changed drastically with the sudden Japanese
attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of ...
. The U.S. enthusiastically went to war against
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, Italy, and Nazi Germany. Italy surrendered in 1943, followed by Germany and Japan in 1945. The United States was one of the "
Allied Big Four", alongside the United Kingdom,
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. The U.S. emerged relatively unscathed from the war, with even greater economic and military influence. The economy doubled and tripled in size as a massive industrial mobilization was accompanied by artificial wage and price controls. 16 million men entered the military (most were drafted), in addition to 300,000 women volunteers. After a series of defeats inflicted by Japan, the U.S. Navy turned the tide at Midway (June 1942), then inexorably moved toward total destruction of the Japanese military. After small-scale invasions of North Africa (1942) and Italy (1943), the main American effort was a strategic bombing campaign that destroyed the German Luftwaffe, followed by a massive invasion of France in 1944. American forces met up with Soviet forces marching into Germany from the east in May 1945. Overall, the entire nation was turned into a vast war machine, affecting society more than any other conflict fought by the United States, except perhaps the Civil War.
After winning re-election to unprecedented
third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', i.e., the third in a series of fractional parts in a sexagesimal number system
Places
* 3rd Street (di ...
and
fourth terms, Roosevelt's health was rapidly deteriorating; he died on April 12, 1945.
Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
had not been kept informed of major foreign policy and military decisions, but he continued most of Roosevelt's wartime policies. Truman moved sharply to the right in replacing FDR's liberal cabinet.
With its merchant fleet sunk by American submarines, Japan ran short of aviation gasoline and fuel oil. The U.S. Navy in June 1944 captured islands within bombing range of Tokyo. Strategic bombing using the
B-29
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is a retired American four-engined Propeller (aeronautics), propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to ...
destroyed all the major cities in 1945, as the U.S. captured Iwo Jima and Okinawa after heavy losses. With conventional and
atomic bombs falling, an Allied invasion imminent, and an unexpected Soviet attack sweeping through Manchuria, the Emperor of Japan
surrendered. Japan was
occupied by the Americans under
Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American general who served as a top commander during World War II and the Korean War, achieving the rank of General of the Army (United States), General of the Army. He served with dis ...
; MacArthur's five year rule transformed Japan's government, society and economy along American lines into a peaceful democracy and a close ally of the U.S.
Homefront
Economics
The main contributions of the U.S. to the Allied war effort comprised money, industrial output, food, petroleum, technological innovation, and (especially 1944–45), soldiers. Much of the focus in Washington was maximizing the economic output of the nation. The overall result was a dramatic increase in GDP, the export of vast quantities of supplies to the Allies and to American forces overseas, the end of unemployment, and a rise in civilian consumption even as 40% of the GDP went to the war effort. This was achieved by tens of millions of workers moving from low-productivity occupations to high efficiency jobs, improvements in productivity through better technology and management, and the move into the active labor force of students, retired people, housewives, and the unemployed, and an increase in hours worked. It was exhausting; leisure activities declined sharply. People tolerated the extra work because of patriotism, the pay, and the confidence it was only "for the duration" and life would return to normal as soon as the war was won. Most durable goods became unavailable, and meat, clothing, and gasoline was tightly rationed. In industrial areas housing was in short supply as people doubled up and lived in cramped quarters. Prices and wages were controlled, and Americans saved a high portion of their incomes, which led to renewed growth after the war instead of a return to depression.
Taxes and controls
Federal tax policy was highly contentious during the war, with President
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
battling a
conservative Congress. Everyone agreed on the need for high taxes to pay for the war. Roosevelt tried unsuccessfully to impose a 100% tax on incomes over $25,000 (equal to $ today), while Congress enlarged the base downward. By 1944 nearly every employed person was paying federal income taxes (compared to 10% in 1940).
Many controls were put on the economy. The most important were price controls, imposed on most products and monitored by the
Office of Price Administration
The Office of Price Administration (OPA) was established within the Office for Emergency Management of the United States government by Executive Order 8875 on August 28, 1941. The functions of the OPA were originally to control money ( price con ...
. Wages were also controlled. Corporations dealt with numerous agencies, especially the War production Board (WPB), and the War and Navy departments, which had the purchasing power and priorities that largely reshaped and expanded industrial production.
Rationing
In 1942 a rationing system was begun to guarantee minimum amounts of necessities to everyone (especially poor people) and prevent inflation. Tires were the first item to be rationed in January 1942 because supplies of natural rubber were interrupted. Gasoline rationing proved an even better way to allocate scarce rubber. By 1943 one needed government issued ration coupons to purchase typewriters, sugar, gasoline, bicycles, footwear, fuel oil, silk, nylon, coffee, stoves, shoes, meat, cheese, butter, margarine, canned foods, dried fruits, jam, and many other items. Some items—like new automobiles and appliances—were no longer made. The rationing system did not apply to used goods (like clothes or cars). The ration system was complex and confusing, but high levels of patriotism made it acceptable as people helped each other through the maze of rules.
To get a classification and a book of rationing stamps, one had to appear before a local rationing board. Each person in a household received a ration book, including babies and children. When purchasing gasoline, a driver had to present a gas card along with a ration book and cash. Ration stamps were valid only for a set period to forestall hoarding. All forms of automobile racing were banned, including the
Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly shortened to Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indian ...
. Sightseeing driving was banned, too.
People had more money than they could spend, so they saved it, especially in government savings bonds. Bond rallies in many cities featured Hollywood film stars, who drew in the crowds needed to make the program a success. The buyer paid 3/4 of the face value of a war bond, and received the full face value back after a set number of years. Workers were challenged to put "at least 10% of every paycheck into Bonds". Compliance was very high, with entire factories of workers earning a special "Minuteman" flag to fly over their plant if all workers belonged to the "Ten Percent Club". There were seven major War Loan drives, all of which exceeded their goals. An added advantage was that citizens who were putting their money into War Bonds were not putting it into the home front wartime economy.
Work force
The unemployment problem ended in the United States with the beginning of World War II, when stepped up wartime production created millions of new jobs and the draft pulled young men out of the labor pool.
Women also joined the workforce to replace men who had joined the forces, though in fewer numbers. Roosevelt stated that the efforts of civilians at home to support the war through personal sacrifice was as critical to winning the war as the efforts of the soldiers themselves. "
Rosie the Riveter
Rosie the Riveter is an allegorical
cultural icon in the United States who represents the women who worked in factories and shipyards during World War II, many of whom produced munitions and war supplies. These women sometimes took entirely n ...
" became the symbol of women laboring in manufacturing. The war effort brought about significant changes in the role of women in society as a whole. At the end of the war, many of the munitions factories closed. Other women were replaced by returning veterans. However most women who wanted to continue working did so.
Labor shortages were felt in agriculture, even though most farmers were given an occupational exemption and few were drafted. Large numbers volunteered or moved to cities for factory jobs. At the same time many agricultural commodities were in greater demand by the military and for the civilian populations of Allies. In some areas schools were temporarily closed at harvest time to enable students to work. About 400,000 German
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
were used as
farm laborers both during and immediately after the war.
With the war's ever increasing need for able bodied men consuming America's labor force in the early 1940s, industry turned to teen-aged boys and girls to fill in as replacements.
[Hinshaw (1943)] Consequently, many states had to change their child-labor laws to allow these teenagers to work. By 1943, there were almost three million American teenage boys and girls working in American fields and factories.
In the process of bringing great numbers of children into the workforce, the War altered the lives of many adolescents. Lured by high wartime wages, they took jobs and forgot about their education. Between 1940 and 1944, the number of teenage workers in America increased by 1.9 million; the number attending school declined by 1.25 million.
Labor unions

The war mobilization changed the relationship of the
Congress of Industrial Organizations
The Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) was a federation of Labor unions in the United States, unions that organized workers in industrial unionism, industrial unions in the United States and Canada from 1935 to 1955. Originally created in ...
(CIO) with both employers and the national government. Both the CIO and the larger
American Federation of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutual ...
(AFL) grew rapidly in the war years.
Nearly all the unions that belonged to the CIO were fully supportive of both the war effort and of the Roosevelt administration. However the United Mine Workers, who had taken an isolationist stand in the years leading up to the war and had opposed Roosevelt's reelection in 1940, left the CIO in 1942. The major unions supported a wartime no-strike pledge that aimed to eliminate not only major strikes for new contracts, but also the innumerable small strikes called by
shop steward
A union representative, union steward, or shop steward is an employee of an organization or company who represents and defends the interests of their fellow employees as a trades/labour union member and official. Rank-and-file members of the un ...
s and local union leadership to protest particular grievances. In return for labor's no-strike pledge, the government offered arbitration to determine the wages and other terms of new contracts. Those procedures produced modest wage increases during the first few years of the war but not enough to keep up with inflation, particularly when combined with the slowness of the arbitration machinery.
Even though the complaints from union members about the no-strike pledge became louder and more bitter, the CIO did not abandon it. The Mine Workers, by contrast, who did not belong to either the AFL or the CIO for much of the war, threatened numerous strikes including a successful twelve-day strike in 1943. The strikes and threats made mine leader
John L. Lewis
John Llewellyn Lewis (February 12, 1880 – June 11, 1969) was an American leader of Labor unions in the United States, organized labor who served as president of the United Mine Workers, United Mine Workers of America (UMW) from 1920 to 1960. ...
a much hated man and led to legislation hostile to unions.
All the major unions grew stronger during the war. The government put pressure on employers to recognize unions to avoid the sort of turbulent struggles over union recognition of the 1930s, while unions were generally able to obtain maintenance of membership clauses, a form of
union security, through arbitration and negotiation. Workers also won benefits, such as vacation pay, that had been available only to a few in the past while wage gaps between higher skilled and less skilled workers narrowed. Most union leaders saw women as temporary wartime replacements for the men in the armed forces. It was important that the wages of these women be kept high so that the veterans would get high wages.
Racial tensions and Japanese American internment
The cities were relatively peaceful; much-feared large-scale race riots did not happen, but there were small-scale confrontations, notably the
1943 race riot in Detroit and the anti-Mexican
Zoot Suit Riots
The Zoot Suit Riots were a series of riots that took place June 3–8, 1943, in Los Angeles, California, United States, involving United States Armed Forces, American servicemen stationed in Southern California and young Latino and Mexican ...
in Los Angeles in 1943. Some German and Italian individuals were rounded up and interned as enemy aliens who lacked U.S. citizenship and were known by the FBI as supporters of the enemy. On February 19, 1942, President Roosevelt signed
Executive Order 9066
Executive Order 9066 was a President of the United States, United States presidential executive order signed and issued during World War II by United States president Franklin D. Roosevelt on February 19, 1942. "This order authorized the fo ...
, following claims by California Attorney General
Earl Warren
Earl Warren (March 19, 1891 – July 9, 1974) was an American attorney and politician who served as the 30th governor of California from 1943 to 1953 and as the 14th Chief Justice of the United States from 1953 to 1969. The Warren Court presid ...
and General
John L. DeWitt
John Lesesne DeWitt (9 January 1880 – 20 June 1962) was a four-star general in the United States Army. He was best known for overseeing the internment of Japanese Americans during World War II.
After the attack on Pearl Harbor by the Japanes ...
that Japanese-Americans had engaged in pro-Japanese espionage against the U.S. Government. As a result, around 100,000 persons of Japanese ancestry on the
West Coast and their children were
interned
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without Criminal charge, charges or Indictment, intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects ...
by the U.S. government and sent to inland camps. The 100,000 or more Japanese Americans in Hawaii were not interned. The American camps were closed in February 1945.
End of an era
1945 marked the end of an era. In foreign policy the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
was established on October 24, 1945, to serve as a world body to help prevent future world wars. By a vote of 65 to 7, the
United States Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and ...
, on December 4, 1945, approved the treaty that set full American participation in the UN, with a veto in the all-important Security Council. This marked a turn away from the traditional interest in strategic local concerns of the U.S. and toward more international involvement.
Fears of a postwar depression did not materialize, thanks in part to the large stock of savings that paid for the pent-up demands for housing, cars, new clothes—and babies. The
Baby Boom
A baby boom is a period marked by a significant increase of births. This demography, demographic phenomenon is usually an ascribed characteristic within the population of a specific nationality, nation or culture. Baby booms are caused by various ...
began as the veterans returned, many moving to the rapidly expanding suburbs. Optimism was the hallmark of the new age—an age of grand expectations.
See also
*
History of the United States (1945–1964)
The history of the United States from 1945 to 1964 was a time of high economic growth and general prosperity. It was also a time of confrontation as the capitalist United States and its allies politically opposed the Soviet Union and other commu ...
*
Attacks on the United States (1900–1945)
*
Liberalism in the United States
Liberalism in the United States is based on concepts of unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of consent of the governed, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, the separation of church and st ...
*
Timeline of the history of the United States (1900–1929)
This section of the timeline of United States history concern events from 1900 to 1929.
1900s
Presidency of William McKinley
*1900 – President William McKinley reelected; Theodore Roosevelt elected vice president.
Presidency of Theodore ...
*
Timeline of the history of the United States (1930–1949)
This section of the timeline of United States history concerns events from 1930 to 1949.See Richard B. Morris, ''Encyclopedia of American History'' (Harper and Brothers, 1953 and later editions)online/ref>
1930s
Presidency of Herbert C. Hoover ...
*
Great Depression in the United States
In the United States, the Great Depression began with the Wall Street Crash of October 1929 and then spread worldwide. The nadir came in 1931–1933, and recovery came in 1940. The stock market crash marked the beginning of a decade of high u ...
**
Timeline of the Great Depression
**
Causes of the Great Depression
The causes of the Great Depression in the early 20th century in the United States have been extensively discussed by economists and remain a matter of active debate. They are part of the larger debate about economic crises and recessions. Alth ...
**
Wall Street Crash of 1929
*
Presidency of Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson served as the 28th president of the United States from March 4, 1913, to March 4, 1921. A Democrat and former governor of New Jersey, Wilson took office after winning the 1912 presidential election, where he defeated the Repu ...
*
Presidency of Warren G. Harding
Warren G. Harding's tenure as the 29th president of the United States lasted from March 4, 1921, until his death on August 2, 1923. Harding presided over the country in the aftermath of World War I. A Republican from Ohio, Harding held office d ...
*
Presidency of Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge's tenure as the 30th president of the United States began on August 2, 1923, when Coolidge became president upon Warren G. Harding, Warren G. Harding's death, and ended on March 4, 1929. A Republican Party (United States), Republi ...
*
Presidency of Herbert Hoover
Herbert Hoover's tenure as the 31st president of the United States began on his inauguration on March 4, 1929, and ended on March 4, 1933. Hoover, a Republican, took office after a landslide victory in the 1928 presidential election over Dem ...
*
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
, under Franklin Roosevelt
*
Presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt, first and second terms
*
Presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt, third and fourth terms
*
Timeline of the Franklin D. Roosevelt presidency
References
Further reading
*
Allen, Frederick Lewis. ''Only Yesterday: An Informal History of the 1920s'' (1931) bestselling, well-written histor
full text online free
* Bagby, Wesley M. ''America's international relations since World War I'
online(Oxford University Press, 1999)
*
Black, Conrad. ''Franklin Delano Roosevelt: Champion of Freedom'' (2012)
excerpt
* Campbell, D'Ann. ''Women at War with America: Private Lives in a Patriotic Era'' (1984), wives, workers and WACs in World War II
online
* Dooley, Roger Burke. ''From Scarface to Scarlett: American films in the 1930s'' (1981)
* Field, Alexander J. ''Great Leap Forward: 1930s Depression and US Economic Growth'' (Yale UP, 2011) 387pp
* Fraser, Steve. ''Labor Will Rule: Sidney Hillman and the rise of American labor'' (1993). on the CIO
*
Hamby, Alonzo L. ''For the Survival of Democracy: Franklin Roosevelt and the World Crisis of the 1930s'' (2004
excerpt and text search
* Hoehling, A. A. ''Home Front, U. S. A. The Story of World War II Over Here'' (1966)
*
Kagan, Robert. ''The Ghost at the Feast: America and the Collapse of World Order, 1900-1941'' (Knopf, 2023
excerpt*
Kennedy, David M. "What the New Deal Did," ''Political Science Quarterly,'' (Summer 2009) 124#2 pp 251–268
*
Kennedy, David M. ''Freedom from Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929–1945'' (Oxford History of the United States) (2001), 990pp; Pulitzer Prize
*
Kyvig, David E. ''Daily Life in the United States, 1920–1940: How Americans Lived During the Roaring Twenties and the Great Depression'
online(2004)
*
Leuchtenburg, William E. ''The Perils of Prosperity, 1914–1932'
online(1993) 332pp.
*
Leuchtenburg, William E. ''Franklin D. Roosevelt and the New Deal 1932 – 1940'' (1963
online*
Malin, James C. ''The United States after the World War''
onlinedetailed analysis of foreign and economic policies
*
*
Marty, Martin E. ''Modern American Religion, Volume 2: The Noise of Conflict, 1919–1941'' (1997)
excerpt
* Miller, Nathan. ''New World Coming: The 1920s and the Making of Modern America'' (2003).
*
Morris, Charles R. ''A Rabble of Dead Money: The Great Crash and the Global Depression: 1929–1939'' (PublicAffairs, 2017), 389 pp
online review
* Morris, Richard B. ''Encyclopedia of American History'' (1953 and later editions
online*
Murray Robert K. ''The Harding Era 1921–1923: Warren G. Harding and his Administration.'' University of Minnesota Press, 1969, a standard academic study
*
Nevins, Allan and
Louis M. Hacker. ''The United States and Its Place in World Affairs, 1918-1943'' (1943
online* Olszowka, John, et al. ''America in the Thirties'' (Syracuse University Press, 2014) 296 pp
excerpt
* Plotke, David. ''Building a Democratic Political Order: Reshaping American Liberalism in the 1930s and 1940s'' (Cambridge UP, 2006)
*
Shindler, Colin. ''Hollywood goes to war: films and American society, 1939–1952'' (Routledge, 2014)
*
Smith, Gaddis. ''American Diplomacy During the Second World War, 1941-1945'' (1965
online*
Tindall, George Brown. ''The Emergence of the New South, 1913–1945'
online(LSU Press, 1967)
*
Ware, Susan. ''Holding Their Own: American Women in the 1930s'
online(Twayne, 1982)
*
Wright, Esmond. "The Foreign Policy of Woodrow Wilson: A Re-Assessment. Part 1: Woodrow Wilson and the First World War" ''History Today''. (Mar 1960) 10#3 pp 149–157
**
Wright, Esmond. "The Foreign Policy of Woodrow Wilson: A Re-Assessment. Part 2: Wilson and the Dream of Reason" ''History Today'' (Apr 1960) 19#4 pp 223–231
*
Zieger, Robert H. ''The CIO 1935–1955'' (1995).
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:History of the United States (1917-1945)
History of the United States by period

 A popular
A popular  The "
The " Led by Commerce Secretary Herbert Hoover, the federal government in the 1920s took on an increasing role in business and economic affairs. In addition to Prohibition, the government obtained new powers and duties such as funding and overseeing the new
Led by Commerce Secretary Herbert Hoover, the federal government in the 1920s took on an increasing role in business and economic affairs. In addition to Prohibition, the government obtained new powers and duties such as funding and overseeing the new  Historians and economists still have not agreed on the
Historians and economists still have not agreed on the  However, rural America contained many isolated farmers scratching out a subsistence income. The new deal set up programs such as the
However, rural America contained many isolated farmers scratching out a subsistence income. The new deal set up programs such as the  Roosevelt's first term saw a massive amount of labor upheaval. In 1934 alone, there was the 1934 West Coast waterfront strike that brought all of San Francisco into a four-day general strike, the
Roosevelt's first term saw a massive amount of labor upheaval. In 1934 alone, there was the 1934 West Coast waterfront strike that brought all of San Francisco into a four-day general strike, the  Laying the foundations for the postwar era, Roosevelt and the New Deal helped enhance the power of the federal government as a whole. Roosevelt also established the presidency as the preeminent center of authority within the federal government. By creating a large array of protections for various groups of citizens—workers, farmers, and others—who suffered from the crisis, enabling them to challenge the powers of the corporations, the Roosevelt administration generated a set of political ideas—known to later generations as New Deal liberalism—that remained a source of inspiration for decades and that helped shape the next experiment in liberal reform, the
Laying the foundations for the postwar era, Roosevelt and the New Deal helped enhance the power of the federal government as a whole. Roosevelt also established the presidency as the preeminent center of authority within the federal government. By creating a large array of protections for various groups of citizens—workers, farmers, and others—who suffered from the crisis, enabling them to challenge the powers of the corporations, the Roosevelt administration generated a set of political ideas—known to later generations as New Deal liberalism—that remained a source of inspiration for decades and that helped shape the next experiment in liberal reform, the  The war mobilization changed the relationship of the
The war mobilization changed the relationship of the