history of paper on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
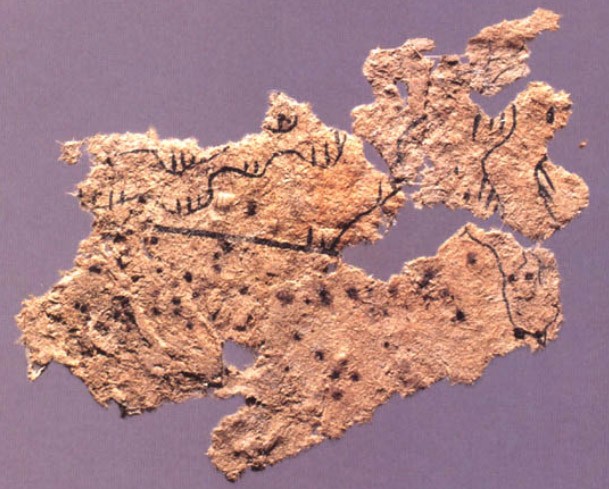


 Archaeological evidence of papermaking predates the traditional attribution given to
Archaeological evidence of papermaking predates the traditional attribution given to
 A manuscript from the 13th century has also elaborated the process of papermaking. This text shows how papermakers were undertaking multiple steps to produce high-quality paper. This papermaking instruction or recipe is a chapter under the title of ''al-kâghad al-baladî'' (local paper) from the manuscript of ''al-Mukhtara'fî funûn min al-ṣunan'' attributed to ''al-Malik al-Muẓaffar'', a Yemeni ruler of Rasulids. The bark of fig trees, as the main source of papermaking in this recipe, went through frequent cycles of soaking, beating and drying. The process took 12 days to produce 100 sheets of high-quality paper. During the pulping stage, the beaten fibres were transformed into different sizes of ''Kubba'' (cubes) which they were used as standard scales to manufacture a certain number of sheets. The dimensions were determined based on three citrus fruit: limun (lemon), utrunja (orange) and narenja (Tangerine). A summarized version of this detailed process is as below. Each individual phase was repeated several times.
* Soaking paper in a pool
* Dewatering paper through squeezing and pressing
* Making balls from the pulp
* Pressing the balls
* Drying the paper by sticking them to the wall and exposing the final product into the sun
A manuscript from the 13th century has also elaborated the process of papermaking. This text shows how papermakers were undertaking multiple steps to produce high-quality paper. This papermaking instruction or recipe is a chapter under the title of ''al-kâghad al-baladî'' (local paper) from the manuscript of ''al-Mukhtara'fî funûn min al-ṣunan'' attributed to ''al-Malik al-Muẓaffar'', a Yemeni ruler of Rasulids. The bark of fig trees, as the main source of papermaking in this recipe, went through frequent cycles of soaking, beating and drying. The process took 12 days to produce 100 sheets of high-quality paper. During the pulping stage, the beaten fibres were transformed into different sizes of ''Kubba'' (cubes) which they were used as standard scales to manufacture a certain number of sheets. The dimensions were determined based on three citrus fruit: limun (lemon), utrunja (orange) and narenja (Tangerine). A summarized version of this detailed process is as below. Each individual phase was repeated several times.
* Soaking paper in a pool
* Dewatering paper through squeezing and pressing
* Making balls from the pulp
* Pressing the balls
* Drying the paper by sticking them to the wall and exposing the final product into the sun
 The use of human and animal powered mills was known to Chinese and Muslim papermakers. However, the evidence for water-powered paper mills is elusive among both prior to the 11th century.: : Scholars have identified paper mills, likely human or animal powered, in
The use of human and animal powered mills was known to Chinese and Muslim papermakers. However, the evidence for water-powered paper mills is elusive among both prior to the 11th century.: : Scholars have identified paper mills, likely human or animal powered, in

Paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
is a thin nonwoven material traditionally made from a combination of milled plant and textile fibres. The first paper-like plant-based writing sheet was papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
in Egypt, but the first true papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is Pulp and paper industry, made using industrial machinery, while handmade pape ...
process was documented in China during the Eastern Han
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
period (25–220 AD), traditionally attributed to the court official Cai Lun
Cai Lun ( zh, s=蔡伦; courtesy name: Jingzhong ( zh, labels=no, t=敬仲, s=敬仲); – 121 CE), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Ts'ai Lun, was a Eunuchs in China, Chinese eunuch court official of the Eastern Han dynasty. H ...
. This plant-puree conglomerate produced by pulp mill
A pulp mill is a manufacturing facility that converts wood chips or other plant fiber sources into a thick fiber board which can be shipped to a paper mill for further processing. Pulp can be manufactured using mechanical, semi-chemical, or ...
s and paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt ...
s was used for writing, drawing, and money. During the 8th century, Chinese paper making spread to the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, replacing papyrus. By the 11th century, papermaking was brought to Europe, where it replaced animal-skin-based parchment and wood panels. By the 13th century, papermaking was refined with paper mills using waterwheels in Spain. Later improvements to the papermaking process came in 19th century Europe with the invention of wood-based papers.
Although there were precursors such as papyrus in the Mediterranean world and amate in the pre-Columbian Americas, these are not considered true paper. Nor is true parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared Tanning (leather), untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves and goats. It has been used as a writing medium in West Asia and Europe for more than two millennia. By AD 400 ...
considered paper: used principally for writing, parchment is heavily prepared animal skin that predates paper and possibly papyrus. In the 20th century with the advent of plastic manufacture, some plastic "paper" was introduced, as well as paper-plastic laminates, paper-metal laminates, and papers infused or coated with different substances to produce special properties.
Precursors

Papyrus
The word "paper" is etymologically derived from ''papyrus'',Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
for the ''Cyperus papyrus
''Cyperus papyrus'', better known by the common names papyrus, papyrus sedge, paper reed, Indian matting plant, or Nile grass, is a species of aquatic plant, aquatic flowering plant belonging to the sedge family Cyperaceae. It is a Hardiness (pla ...
'' plant. Papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
is a thick, paper-like material produced from the pith of the ''Cyperus papyrus'' plant which was used in ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
and other Mediterranean societies for writing
Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language ...
long before paper was used in China.
Papyrus is prepared by cutting off thin ribbon-like strips of the pith (interior) of the ''Cyperus papyrus'' plant and then laying out the strips side-by-side to make a sheet. A second layer is then placed on top, with the strips running perpendicular to the first. The two layers are then pounded together using a mallet to make a sheet. The result is very strong, but has an uneven surface, especially at the edges of the strips. When used in scrolls, repeated rolling and unrolling causes the strips to come apart again, typically along vertical lines. This effect can be seen in many ancient papyrus documents.
Paper contrasts with papyrus in that the plant material is broken down through maceration or disintegration before the paper is pressed. This produces a much more even surface and no natural weak direction in the material which falls apart over time. Unlike paper, papyrus is created by pressing, matting, and pounding the ''Cyperus papyrus'' plant, which only grew in Egypt and Sicily, and drying it to create the end product. The words 'papyrus' and its derivative, 'paper', have often been used interchangeably despite referring to different products created through different methods. Although it was used to great effect in Greece and Rome, papyrus has several downsides compared to paper. It was geographically limited by the ''Cyperus papyrus'' plant, which was primarily grown in Egypt. The Arabs tried to grow the plant north of Baghdad in the 830s but failed. While not especially expensive, it was more laborious to create papyrus with an even surface, and paper was more abundant and affordable than papyrus. It was also fragile, sensitive to moisture, and restricted to a scroll format of no more than 30–35 feet.
By the end of the 9th century, paper had become more popular than papyrus in the Muslim World. In Asia and Africa, paper displaced papyrus as the primary writing material by the mid-10th century. In Europe, papyrus co-existed with parchment for several hundred years until it largely disappeared by the 11th century.
Paper in China

 Archaeological evidence of papermaking predates the traditional attribution given to
Archaeological evidence of papermaking predates the traditional attribution given to Cai Lun
Cai Lun ( zh, s=蔡伦; courtesy name: Jingzhong ( zh, labels=no, t=敬仲, s=敬仲); – 121 CE), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Ts'ai Lun, was a Eunuchs in China, Chinese eunuch court official of the Eastern Han dynasty. H ...
, an imperial eunuch official of the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
(202 BCE – 220 CE), thus the exact date or inventor of paper cannot be deduced. The earliest extant paper fragment was unearthed at Fangmatan
Fangmatan () is an archeological site located near Tianshui in China's Gansu province. The site was located within the Qin state, and includes several burials dating from the Warring States period through to the early Western Han.
Tomb 1
The ...
in Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
province, and was likely part of a map, dated to 179–141 BCE.
Fragments of paper have also been found at Dunhuang dated to 65 BCE and at Yumen pass, dated to 8 BCE.
The invention traditionally attributed to Cai Lun, recorded hundreds of years after it took place, is dated to 105 CE. The innovation is a type of paper made of mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of 19 species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinat ...
and other bast fibre
Bast fibre (also called phloem fibre or skin fibre) is plant fibre collected from the phloem (the "inner bark", sometimes called "skin") or bast surrounding the stem of certain dicotyledonous plants. Some of the economically important bast fibre ...
s along with fishing nets, old rags, and hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest ...
waste which reduced the cost of paper production, which prior to this, and later, in the West, depended solely on rags.
Techniques
During the Shang (1600–1050 BCE) and Zhou (1050–256 BCE) dynasties ofancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, documents were ordinarily written on bone or bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of mostly evergreen perennial plant, perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily (biology), subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family, in th ...
(on tablets or on bamboo strips sewn and rolled together into scrolls), making them very heavy, awkward to use, and hard to transport. The light material of silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
was sometimes used as a recording medium, but was normally too expensive to consider. The Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
Chinese court official Cai Lun
Cai Lun ( zh, s=蔡伦; courtesy name: Jingzhong ( zh, labels=no, t=敬仲, s=敬仲); – 121 CE), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Ts'ai Lun, was a Eunuchs in China, Chinese eunuch court official of the Eastern Han dynasty. H ...
(c. 50–121 CE) is credited as the inventor of a method of papermaking (inspired by wasps and bees) using rags and other plant fibers in 105 CE. However, the discovery of specimens bearing written Chinese character
Chinese characters are logographs used to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represent the only on ...
s in 2006 at Fangmatan
Fangmatan () is an archeological site located near Tianshui in China's Gansu province. The site was located within the Qin state, and includes several burials dating from the Warring States period through to the early Western Han.
Tomb 1
The ...
in north-east China's Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
Province suggests that paper was in use by the ancient Chinese military more than 100 years before Cai, in 8 BCE, and possibly much earlier as the map fragment found at the Fangmatan tomb site dates from the early 2nd century BCE. It therefore would appear that "Cai Lun's contribution was to improve this skill systematically and scientifically, fix a recipe for papermaking".
Cai Lun's biography in the '' Twenty-Four Histories'' says:
uses Wade-Giles transcription
:In ancient times writings and inscriptions were generally made on tablets of bamboo or on pieces of silk called chih. But silk being costly and bamboos heavy they were not convenient to use. Tshai Lun then initiated the idea of making paper from the bark of trees, remnants of hemp, rags of cloth and fishing nets. He submitted the process to the emperor in the first year of Yuan-Hsing (105 CE) and received praise for his ability. From this time, paper has been in use everywhere and is universally called the paper of Marquis Tshai.
The production process may have originated from the practice of pounding and stirring rags in water, after which the matted fibres were collected on a mat. The bark of paper mulberry was particularly valued and high quality paper was developed in the late Han period using the bark of ''tán'' (檀; sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus ''Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods. Sanda ...
). Although bark paper emerged during the Han dynasty, the predominant material used for paper was hemp until the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
when rattan and mulberry bark paper gradually prevailed. After the Tang dynasty, rattan paper declined because it required specific growing areas, was slow in growth, and had a long regeneration cycle. The most prestigious kind of bark paper was known as Chengxintang Paper, which emerged during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, and was only used for imperial purposes. Ouyang Xiu described it as shiny, elaborate, smooth, and elastic. In the Eastern Jin period a fine bamboo screen-mould treated with insecticidal dye for permanence was used in papermaking. After printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
was popularized during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
the demand for paper grew substantially. The supply of bark could not keep up with the demand for paper, resulting in the invention of new kinds of paper using bamboo during the Song dynasty. In the year 1101, 1.5 million sheets of paper were sent to the capital.
Uses
Among the earliest known uses of paper was padding and wrapping delicate bronze mirrors according to archaeological evidence dating to the reign ofEmperor Wu of Han
Emperor Wu of Han (156 – 29 March 87BC), born Liu Che and courtesy name Tong, was the seventh Emperor of China, emperor of the Han dynasty from 141 to 87 BC. His reign lasted 54 years – a record not broken until the reign of the Kangxi ...
from the 2nd century BCE. Padding doubled as both protection for the object as well as the user in cases where poisonous "medicine" were involved, as mentioned in the official history of the period. Although paper was used for writing by the 3rd century CE, paper continued to be used for wrapping (and other) purposes. Toilet paper
Toilet paper (sometimes called toilet/bath/bathroom tissue, or toilet roll) is a tissue paper product primarily used to clean the human anus, anus and surrounding region of Human feces, feces (after defecation), and to clean the external gen ...
was used in China from around the late 6th century. In 589, the Chinese scholar-official Yan Zhitui (531–591) wrote: "Paper on which there are quotations or commentaries from Five Classics or the names of sages, I dare not use for toilet purposes". An Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
traveler who visited China wrote of the curious Chinese tradition of toilet paper in 851, writing: "... he Chinesedo not wash themselves with water when they have done their necessities; but they only wipe themselves with paper".
During the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
(618–907) paper was folded and sewn into square bags to preserve the flavor of tea. In the same period, it was written that tea was served from baskets with multi-colored paper cups and paper napkins of different size and shape. During the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
(960–1279) the government produced the world's first known paper-printed money, or banknote
A banknote or bank notealso called a bill (North American English) or simply a noteis a type of paper money that is made and distributed ("issued") by a bank of issue, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commerc ...
(''see Jiaozi and Huizi''). Paper money was bestowed as gifts to government officials in special paper envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
s. During the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
(1271–1368), the first well-documented European in Medieval China, the Venetian merchant Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
remarked how the Chinese burned paper effigies shaped as male and female servants, camels, horses, suits of clothing and armor while cremating the dead during funerary rites
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect t ...
.
Impact of paper
According to Timothy Hugh Barrett, paper played a pivotal role in early Chinese written culture, and a "strong reading culture seems to have developed quickly after its introduction, despite political fragmentation." Indeed, the introduction of paper had immense consequences for the book world. It meant books would no longer have to be circulated in small sections or bundles, but in their entirety. Books could now be carried by hand rather than transported by cart. As a result, individual collections of literary works increased in the following centuries. Textual culture seems to have been more developed in the south by the early 5th century, with individuals owning collections of several thousand scrolls. In the north an entire palace collection might have been only a few thousand scrolls in total. By the early 6th century, scholars in both the north and south were capable of citing upwards of 400 sources in commentaries on older works. A small compilation text from the 7th century included citations to over 1,400 works. The personal nature of texts was remarked upon by a late 6th century imperial librarian. According to him, the possession of and familiarity with a few hundred scrolls was what it took to be socially accepted as an educated man. According to Endymion Wilkinson, one consequence of the rise of paper in China was that "it rapidly began to surpass the Mediterranean empires in book production." During the Tang dynasty, China became the world leader in book production. In addition the gradual spread of woodblock printing from the late Tang and Song further boosted their lead ahead of the rest of the world. However, despite the initial advantage afforded to China by the paper medium, by the 9th century its spread and development in the Middle East had closed the gap between the two regions. Between the 9th to early 12th centuries, libraries in Cairo, Baghdad, and Cordoba held collections larger than even the ones in China, and dwarfed those in Europe. From about 1500 the maturation of paper making and printing in Southern Europe also had an effect in closing the gap with the Chinese. The Venetian Domenico Grimani's collection numbered 15,000 volumes by the time of his death in 1523. After 1600, European collections completely overtook those in China. The Bibliotheca Augusta numbered 60,000 volumes in 1649 and surged to 120,000 in 1666. In the 1720s the Bibliothèque du Roi numbered 80,000 books and the Cambridge University 40,000 in 1715. After 1700, libraries in North America also began to overtake those of China, and toward the end of the century,Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
's private collection numbered 4,889 titles in 6,487 volumes. The European advantage only increased further into the 19th century as national collections in Europe and America exceeded a million volumes while a few private collections, such as that of Lord Acton, reached 70,000.
Paper became central to the three arts of China – poetry, painting, and calligraphy. In later times paper constituted one of the 'Four Treasures of the Scholar's Studio,' alongside the brush, the ink, and the inkstone.
Paper in Asia
After its origin in centralChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, the production and use of paper spread steadily. It is clear that paper was used at Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Sachu (Dunhuang) was ...
by 150 CE, in Loulan in the modern-day province of Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
by 200, and in Turpan
Turpan () or Turfan ( zh, s=吐鲁番) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 693,988 (2020). The historical center of the ...
by 399. Paper was concurrently introduced in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
sometime between the years 280 and 610.
Eastern Asia
Paper spread to Vietnam in the 3rd century, to Korea in the 4th century, and to Japan in the 5th century. The paper of Korea was famed for being glossy white and was especially prized for painting and calligraphy. It was among the items commonly sent to China as tribute. The Koreans spread paper to Japan possibly as early as the 5th century but the Buddhist monk Damjing's trip to Japan in 610 is often cited as the official beginning of papermaking there.Islamic world
Origin
Paper was used inCentral Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
by the 8th century but its origin is not clear. According to the 11th century Persian historian, Al-Thaʽālibī, Chinese prisoners captured at the Battle of Talas in 751 introduced paper manufacturing to Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
.Meggs, Philip B. ''A History of Graphic Design.'' John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1998. (pp 58) However, there are no contemporary Arab sources for this battle. A Chinese prisoner, Du Huan, who later returned to China reported weavers, painters, goldsmiths, and silversmiths among the prisoners taken, but no papermakers. According to Al-Nadim, a writer in Baghdad during the 10th century, Chinese craftsmen made paper in Khorasan:
According to Jonathan Bloom – a scholar of Islamic and Asian Art with a focus on paper and printing, the connection between Chinese prisoners and the introduction of paper in Central Asia is "unlikely to be factual". Archaeological evidence shows that paper was already known and used in Samarkand decades before 751 CE. Seventy-six texts in Sogdian, Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, and Chinese have also been found near Panjakent, likely predating the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana
The Muslim conquest of Transoxiana, also called the Arab conquest of Transoxiana, was part of the early Muslim conquests. It began shortly after the Muslim conquest of Persia enabled the Arabs to enter Central Asia. Relatively small-scale incur ...
. Bloom argues that based on differences in Chinese and Central Asian papermaking techniques and materials, the story of Chinese papermakers directly introducing paper to Central Asia is probably metaphorical. Chinese paper was mostly made of bast fibers while Islamic paper was primarily made of waste material like rags. The paper-making innovations in Central Asia may be pre-Islamic, probably aided by the Buddhist merchants and monks of China and Central Asia. The Islamic civilization helped spread paper and paper-making into the Middle East after the 8th-century. By 981, paper had spread to Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
and Georgian monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which m ...
in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
. It arrived into Europe centuries later, and then to many other parts of the world. A historical remnant of this legacy is the continued use of the word "ream" to count bundles of paper, a word derived from Arabic ''rizma'' (bundle, bale).
Shift from parchment to paper
During the 8th century, paper started to replace parchment as the primary writing material for administrative uses in Baghdad, the capital of Abbasids. According toIbn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732–808 Hijri year, AH) was an Arabs, Arab Islamic scholar, historian, philosopher and sociologist. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest social scientists of the Middle Ages, and cons ...
, a renowned Muslim historiographer, parchment was rare, and a great increase in the number of correspondents throughout Islamic territories, resulted in an order issued by Al-Fadl ibn Yahya, the Abbasid's Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
, for the manufacture of paper to replace parchment.
There are records of paper being made at Gilgit
Gilgit (; Shina language, Shina: ; ) is a city in Pakistani-administered Gilgit-Baltistan, Gilgit–Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region.The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kas ...
in Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
by the sixth century, in Samarkand by 751, in Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
by 793, in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
by 900, and in Fes, Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
around 1100, in Syria e.g. Damascus, and Aleppo, in Andalusia around 12th century, in Persia e.g. Maragheh by 13th century, Isfahan by 14th century, Ghazvin and Kerman, in India e.g. Dowlat Abad by the 16th century.Harrison, Frederick. ''A Book about Books''. London: John Murray, 1943. p. 79.
Mandl, George. "Paper Chase: A Millennium in the Production and Use of Paper". Myers, Robin & Michael Harris (eds). ''A Millennium of the Book: Production, Design & Illustration in Manuscript & Print, 900–1900''. Winchester: St. Paul’s Bibliographies, 1994. p. 182.
Mann, George. ''Print: A Manual for Librarians and Students Describing in Detail the History, Methods, and Applications of Printing and Paper Making''. London: Grafton & Co., 1952. p. 79.
McMurtrie, Douglas C. ''The Book: The Story of Printing & Bookmaking''. London: Oxford University Press, 1943. p. 63. A Persian geography book written by an unknown author in the 10th century, '' Hodud al-Alam'', is the oldest known manuscripts mentioning papermaking industry in Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
. The writer stated that the city was famous for paper manufacturing and the product was exported to many other cities as a high-quality item. Samarkand kept its reputation for papermaking over few centuries even once the industry spread across other Islamic areas. For instance, it is said that some ministers in Egypt preferred ordering their required paper to Samarkand from which the paper was transported all the way to Egypt.
In Baghdad, particular neighborhoods were allocated to paper manufacturing and in Bazaar paper merchants and sellers owned distinct sectors being called Paper Market or ''Suq al-Warraqin'', a street which was lined with more than 100 paper and booksellers' shops. In 1035 a Persian traveler, Nasir Khusraw
Nasir Khusraw (; 1004 – between 1072–1088) was an Isma'ili poet, philosopher, traveler, and missionary () for the Isma'ili Fatimid Caliphate.
Despite being one of the most prominent Isma'ili philosophers and theologians of the Fatimids and ...
, visiting markets in Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
noted that vegetables, spices and hardware were wrapped in paper for the customers. In the 12th century one street named "Kutubiyyin" or book sellers Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
as it contained more than 100 bookshops.
The expansion of public and private libraries and illustrated books within Islamic lands was one of the notable outcomes of the drastic increase in the availability of paper. However, paper was still an upmarket good given the remarkable required inputs, e.g. primary materials and labours, to produce the item in the absence of advanced mechanical machinery. In one account Ibn al-Bawwab, a Persian calligrapher and illuminator, had been promised by the Sultan to be given precious garments in response to his services. When the Sultan deferred delivering the promised clothes, he instead proposed taking the papers stored in the Sultan's library as his present.
In another account, the hospitality of a minister in Baghdad, Ibn Al-Forat, had been described by his generosity in freely giving away papers to his guests or visitors.
Types of paper
A wide range of papers with distinctive properties and varying places of origin were manufactured and utilised across Islamic domains. Papers were typically named based on several criteria: * Origins (e.g.Isfahani, Baghdadi, Halabi, Mesri, Samarkandi, Dowlat Abadi, Shami, Charta Damascena), * Sizes (Solsan, Nesfi,...), * People who have supported the paper development (e.g. Nuhi, Talhi, Jafari, Mamuni, Mansouri).Paper primary materials
Bast (hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest ...
and flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
), cotton, and old rags and ropes were the major input materials for producing the pulp. Sometimes a mixture of materials was also used for pulp making, such as cotton and hemp, or flax and hemp. Other uncommon primary materials such as fig tree bark are also reported in some manuscripts.
Papermaking process
Very few sources have mentioned the methods, phases and applied tools in the papermaking process though. A painting from an illustrated book in Persian has depicted different stages and required tools of the traditional workflow. The painting has distinguished two major phases of the papermaking process: * Pulp making and pulp dewatering: water power mill mixes linen wastes (Karbas) and rags, as the primary materials of papermaking, with water. They are well beaten in stone pits. In the next step, the watery pulp is poured into a piece of fabric, tied around two workers’ waists, to get initially dewatered and probably homogenised and purified. Once the pulp is dewatered into a considerable extent it passes through the next treatment phase. * Paper final treatments: this phase consists of several consequent steps e.g. moulding the pulp with a square laid with wire-like lines (dipping the mould in the vat containing pulp), pressing,sizing
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption ...
, drying and polishing. Each step in this phase is undertaken by a particular device. For instance, in the drying process, the paper was stuck to the wall with the use of horsehair.
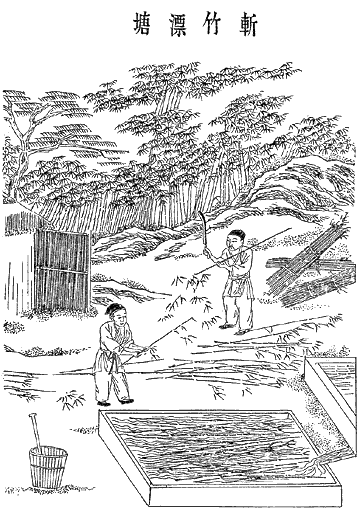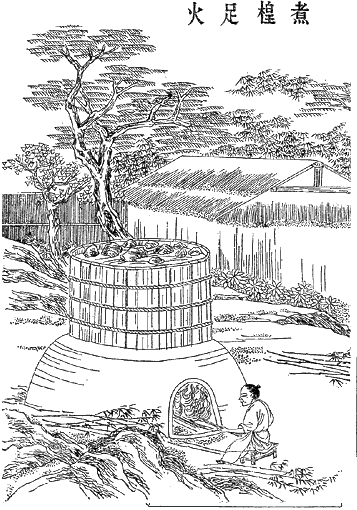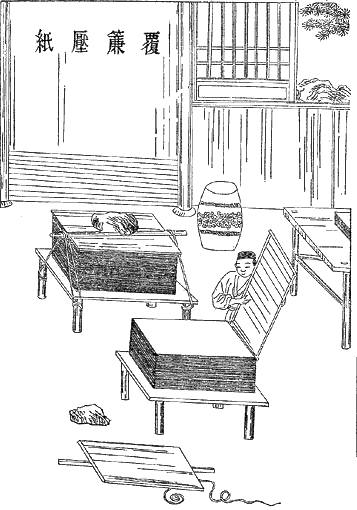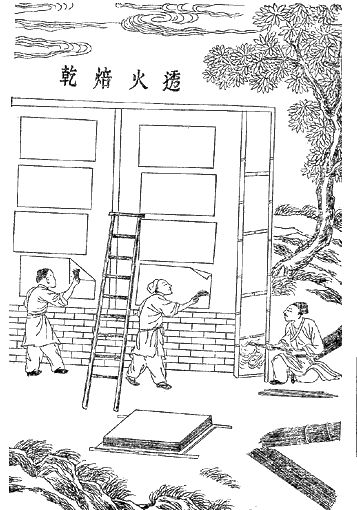
 A manuscript from the 13th century has also elaborated the process of papermaking. This text shows how papermakers were undertaking multiple steps to produce high-quality paper. This papermaking instruction or recipe is a chapter under the title of ''al-kâghad al-baladî'' (local paper) from the manuscript of ''al-Mukhtara'fî funûn min al-ṣunan'' attributed to ''al-Malik al-Muẓaffar'', a Yemeni ruler of Rasulids. The bark of fig trees, as the main source of papermaking in this recipe, went through frequent cycles of soaking, beating and drying. The process took 12 days to produce 100 sheets of high-quality paper. During the pulping stage, the beaten fibres were transformed into different sizes of ''Kubba'' (cubes) which they were used as standard scales to manufacture a certain number of sheets. The dimensions were determined based on three citrus fruit: limun (lemon), utrunja (orange) and narenja (Tangerine). A summarized version of this detailed process is as below. Each individual phase was repeated several times.
* Soaking paper in a pool
* Dewatering paper through squeezing and pressing
* Making balls from the pulp
* Pressing the balls
* Drying the paper by sticking them to the wall and exposing the final product into the sun
A manuscript from the 13th century has also elaborated the process of papermaking. This text shows how papermakers were undertaking multiple steps to produce high-quality paper. This papermaking instruction or recipe is a chapter under the title of ''al-kâghad al-baladî'' (local paper) from the manuscript of ''al-Mukhtara'fî funûn min al-ṣunan'' attributed to ''al-Malik al-Muẓaffar'', a Yemeni ruler of Rasulids. The bark of fig trees, as the main source of papermaking in this recipe, went through frequent cycles of soaking, beating and drying. The process took 12 days to produce 100 sheets of high-quality paper. During the pulping stage, the beaten fibres were transformed into different sizes of ''Kubba'' (cubes) which they were used as standard scales to manufacture a certain number of sheets. The dimensions were determined based on three citrus fruit: limun (lemon), utrunja (orange) and narenja (Tangerine). A summarized version of this detailed process is as below. Each individual phase was repeated several times.
* Soaking paper in a pool
* Dewatering paper through squeezing and pressing
* Making balls from the pulp
* Pressing the balls
* Drying the paper by sticking them to the wall and exposing the final product into the sun
Paper properties
Near Eastern paper is mainly characterized by sizing with a variety of starches such as rice, katira (gumtragacanth
Tragacanth is a natural gum obtained from the dried sap of several species of Middle Eastern Fabaceae, legumes of the genus ''Astragalus (plant), Astragalus'', including ''Astragalus adscendens, A. adscendens'', ''Astragalus gummifer, A. gummifer ...
), wheat, and white sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
. Rice and white sorghum were more widely used. Paper usually was placed on a hard surface and a smooth device called ''mohreh'' was used to rub the starch against the paper until it became perfectly shiny.
The laborious process of papermaking was refined and machinery was designed for bulk manufacturing of paper. Production began in Baghdad, where a method was invented to make a thicker sheet of paper, which helped transform papermaking from an art into a major industry. The use of water-powered pulp mill
A pulp mill is a manufacturing facility that converts wood chips or other plant fiber sources into a thick fiber board which can be shipped to a paper mill for further processing. Pulp can be manufactured using mechanical, semi-chemical, or ...
s for preparing the pulp material used in papermaking dates back to Samarkand in the 8th century. The use of human/animal-powered paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt ...
s has also been identified in Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 C ...
-era Baghdad during 794–795, though this should not be confused with later water-powered paper mills (see '' Paper mills'' section below). The Muslims also introduced the use of trip hammer
Trip may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
Fictional characters
* Trip (Pokémon), Trip (''Pokémon''), a ''Pokémon'' character
* Trip (Power Rangers), in the American television series ''Time Force Power Rangers''
* Trip, in the 2013 film ...
s (human- or animal-powered) in the production of paper, replacing the traditional Chinese mortar and pestle
A mortar and pestle is a set of two simple tools used to prepare ingredients or substances by compression (physics), crushing and shear force, grinding them into a fine Paste (rheology), paste or powder in the kitchen, laboratory, and pharmacy. ...
method. In turn, the trip hammer method was later employed by the Chinese. Historically, trip hammers were often powered by a water wheel, and are known to have been used in China as long ago as 40 BCE or maybe even as far back as the Zhou dynasty (1050 BCE–221 BCE), though the trip hammer is not known to have been used in Chinese papermaking until after its use in Muslim papermaking.
By the 9th century, Muslims were using paper regularly, although for important works like copies of the revered Qur'an
The Quran, also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation directly from God ('' Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides ...
, vellum
Vellum is prepared animal skin or membrane, typically used as writing material. It is often distinguished from parchment, either by being made from calfskin (rather than the skin of other animals), or simply by being of a higher quality. Vellu ...
was still preferred. Advances in book
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, ...
production and bookbinding
Bookbinding is the process of building a book, usually in codex format, from an ordered stack of paper sheets with one's hands and tools, or in modern publishing, by a series of automated processes. Firstly, one binds the sheets of papers alon ...
were introduced.
In Muslim countries they made books lighter—sewn with silk and bound with leather-covered paste boards; they had a flap that wrapped the book up when not in use. As paper was less reactive to humidity, the heavy boards were not needed.
Since the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest ...
in 1096, paper manufacturing in Damascus had been interrupted by wars, but its production continued in two other centres. Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
continued with the thicker paper, while Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
became the center of the thinner papers. Papermaking was diffused across the Islamic world, from where it travelled further toward west into Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. Paper manufacture was introduced to India in the 13th century by Arab merchants, where it almost wholly replaced traditional writing materials.
Indian subcontinent
The evidence of paper use on theIndian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
appears first in the second half of the 7th century. Its use is mentioned by 7th– and 8th-century Chinese Buddhist pilgrim memoirs as well as some Indian Buddhists, as ''Kakali'' and ''Śaya'' – likely Indian transliteration of Chinese ''Zhǐ'' (tsie). Yijing
The ''I Ching'' or ''Yijing'' ( ), usually translated ''Book of Changes'' or ''Classic of Changes'', is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. The ''I Ching'' was originally a divination manual in ...
wrote about the practice of priests and laypeople in India printing Buddha image on silk or paper, and worshipping these images. Elsewhere in his memoir, I-Ching wrote that Indians use paper to make hats, to reinforce their umbrellas and for sanitation. Xuangzang mentions carrying 520 manuscripts from India back to China in 644 CE, but it is unclear if any of these were on paper.
Thin sheets of birch bark and specially treated palm-leaves remained the preferred writing surface for literary works through late medieval period in most of India. The earliest Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
paper manuscript found is a paper copy of the '' Shatapatha Brahmana'' in Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
, dated to 1089, while the earliest Sanskrit paper manuscripts in Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
are dated between 1180 and 1224. Some of oldest surviving paper manuscripts have been found in Jain temples of Gujarat and Rajasthan, and paper use by Jain scribes is traceable to around 12th-century. According to the historical trade-related archives such as Cairo Geniza
The Cairo Geniza, alternatively spelled the Cairo Genizah, is a collection of some 400,000 Judaism, Jewish manuscript fragments and Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid administrative documents that were kept in the ''genizah'' or storeroom of the Ben Ezra ...
found in the synagogues of the Middle East, Jewish merchants – such as Ben Yiju originally from Tunisia who moved to India – imported large quantities of paper into ports of Gujarat, Malabar coast and other parts of India by the 11th-century to partly offset the goods they exported from India.
According to Irfan Habib, it is reasonable to presume that paper manufacturing reached Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
(now part of south Pakistan) before 11th-century with the start of Arab rule in Sindh. Fragments of Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
manuscripts found in the Sindhi city ruins of Mansura, which was destroyed ''circa'' 1030, confirm the use of paper in Sindh. Amir Khusrau of Delhi Sultanate mentions paper-making operations in 1289.
In the 15th century, Chinese traveler Ma Huan praised the quality of paper in Bengal, describing it as white paper that is made from "bark of a tree" and is as "glossy and smooth as deer's skin". The use of tree bark as a raw material for paper suggests that the paper manufacturing in the eastern states of India may have come directly from China, rather than Sultanates formed by West Asian or Central Asian conquests. Paper technology likely arrived in India from China through Tibet and Nepal around mid-7th century, while Nepal, Bengal, and Assam were part of the Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (,) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. It expanded further under the 38th king, Trisong De ...
; Buddhist monks being able to freely travel, exchange ideas and goods across the empire. This exchange is evidenced by the Indian talapatra binding methods that were adopted by Chinese monasteries such as at Tunhuang for preparing sutra books from paper. Most of the earliest surviving sutra books in Tibetan monasteries are on Chinese paper strips held together with Indian manuscript binding methods. Further, the analysis of the woodblock book covers of these historic manuscripts has confirmed that it was made of tropical wood indigenous to India, not Tibet.
Kaghaz
The Persian word for paper, kaghaz is a borrowing from Sogdian kʾɣδʾ, itself in turn possibly borrowed from Chinese (紙). Kaghaz was loaned into numerous other languages, includingArabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
()—an early development which shaped the spelling of the Persian word itself— Bengali (কাগজ), Georgian (ქაღალდი), Kurdish, Marathi (कागद), Nepali, Telugu, and the various Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic langua ...
. Through the Ottoman conquest of the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
the Persian kaghaz entered the languages of the region through Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish (, ; ) was the standardized register of the Turkish language in the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extensively, in all aspects, from Arabic and Persian. It was written in the Ottoman Turkish alphabet. ...
(), including Serbian, where it generated the word for "documentation" (ćage).
Historian Nile Green explains that the increased access to paper had a role in the expansion of Persian into bureaucratic and in turn literary activities, that is, the domain of written Persian ("Persographia") in large parts of Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
.
Paper in Europe
The oldest known paper document in Europe is the Mozarab Missal of Silos from the 11th century, probably using paper made in the Islamic part of the Iberian Peninsula. They used hemp andlinen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong and absorbent, and it dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. Lin ...
rags as a source of fiber. The first recorded paper mill in the Iberian Peninsula was in Xàtiva
Xàtiva (; ) is a town in eastern Spain, in the province of Valencia, on the right (western) bank of the river Albaida and at the junction of the Valencia, Spain, Valencia–Murcia and Valencia Albacete railways. It is located 25 km ...
in 1056.
Papermaking reached Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
as early as 1085 in Toledo and was firmly established in Xàtiva
Xàtiva (; ) is a town in eastern Spain, in the province of Valencia, on the right (western) bank of the river Albaida and at the junction of the Valencia, Spain, Valencia–Murcia and Valencia Albacete railways. It is located 25 km ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
by 1150. During the 13th century mills were established in Amalfi, Fabriano, and Treviso
Treviso ( ; ; ) is a city and (municipality) in the Veneto region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 87.322 inhabitants (as of December 2024). Some 3,000 live within the Venetian wall ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, and other Italian towns by 1340. Papermaking then spread further northwards, with evidence of paper being made in Troyes
Troyes () is a Communes of France, commune and the capital of the Departments of France, department of Aube in the Grand Est region of north-central France. It is located on the Seine river about south-east of Paris. Troyes is situated within ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
by 1348, in Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
sometime around 1340–1350, and in Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
by 1390 in a mill set up by Ulman Stromer. This was just about the time when the woodcut printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating work of art, artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand proces ...
technique was transferred from fabric to paper in the old master print
An old master print (also spaced masterprint) is a work of art produced by a printing process within the Western tradition (mostly by Old Masters). The term remains current in the art trade, and there is no easy alternative in English to distingu ...
and popular prints. There was a paper mill in Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
by 1432 and the first mill in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
was set up by John Tate around 1490 near Hertford
Hertford ( ) is the county town of Hertfordshire, England, and is also a civil parish in the East Hertfordshire district of the county. The parish had a population of 26,783 at the 2011 census.
The town grew around a Ford (crossing), ford on ...
, but the first commercially successful paper mill in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
did not occur before 1588 when John Spilman set up a mill near Dartford
Dartford is the principal town in the Borough of Dartford, Kent, England. It is located south-east of Central London and
is situated adjacent to the London Borough of Bexley to its west. To its north, across the Thames Estuary, is Thurrock in ...
in Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
. During this time, paper making spread to Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
by 1469, to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
by 1491, to Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
by 1576, to the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
by 1586, to Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
by 1596, and to Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
by 1612.
Arab prisoners who settled in a town called Borgo Saraceno in the Italian Province of Ferrara
The province of Ferrara (; ) is a Provinces of Italy, province in the Italy, Italian region of Emilia-Romagna. Its capital is the city of Ferrara. As of May 2023, it has a population of 338,143 inhabitants over an area of . The province contains ...
introduced Fabriano artisans in the Province of Ancona the technique of making paper by hand. At the time they were renowned for their wool-weaving and manufacture of cloth. Fabriano papermakers considered the process of making paper by hand an art form and were able to refine the process to successfully compete with parchment which was the primary medium for writing at the time. They developed the application of stamping hammers to reduce rags to pulp for making paper, sizing
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption ...
paper by means of animal glue
Animal glue is an adhesive that is created by prolonged boiling of animal connective tissue in a process called Rendering (animal products), rendering. In addition to being used as an adhesive, it is used for coating and sizing, in decorative co ...
, and creating watermarks in the paper during its forming process. The Fabriano used glue obtained by boiling scrolls or scraps of animal skin to size the paper; it is suggested that this technique was recommended by the local tanneries. The introduction of the first European watermarks in Fabriano was linked to applying metal wires on a cover laid against the mould which was used for forming the paper.
They adapted the waterwheels from the fuller's mills to drive a series of three wooden hammers per trough. The hammers were raised by their heads by cams fixed to a waterwheel's axle made from a large tree trunk.
Americas

Amate
In the Americas, archaeological evidence indicates that a similar bark-paper writing material was used by theMaya
Maya may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Mayan languages, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (East Africa), a p ...
no later than the 5th century CE. Called '' amatl'' or '' amate'', it was in widespread use among Mesoamerican cultures until the Spanish conquest. The earliest sample of amate was found at Huitzilapa near the Magdalena Municipality, Jalisco, Mexico, belonging to the shaft tomb culture. It is dated to 75 BCE.
There is some uncertainty as to whether or not the Mesoamerican paper can be considered true paper owing to the thorough destruction of their civilization by the Spanish. The Mayans used a writing material called ''huun'' starting from the 5th century. It was made from the inner bark of the wild fig tree. It was cut and stretched thin rather than made of randomly woven fibers, which according to one source, disqualified it as true paper. The Mayans made codices out of ''huun''. The Toltecs and Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the ...
also had their own form of paper. The Aztec ''amatl'' ( amate) was used for writing, decorations, rituals, and as material for masks. Aztec paper, like Mayan paper, is not considered true paper by some. Like its predecessors, it was made from the inner bark of the wild fig tree, beaten, stretched, and dried. There are also records of paper made from agave
''Agave'' (; ; ) is a genus of monocots native to the arid regions of the Americas. The genus is primarily known for its succulent and xerophytic species that typically form large Rosette (botany), rosettes of strong, fleshy leaves.
Many plan ...
, which was course and bumpy, and was probably used for purposes other than writing. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was a pivotal event in the history of the Americas, marked by the collision of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the Spanish Empire. Taking place between 1519 and 1521, this event saw the Spanish conquistad ...
, the Aztecs began using paper imported by the Spanish for works such as the ''Codex Mendoza
The Codex Mendoza is an Aztec codices, Aztec codex, believed to have been created around the year 1541. It contains a history of both the Aztec rulers and their conquests as well as a description of the daily life of pre-conquest Aztec society. ...
''. There were 42 amate producing Aztec villages prior to the Spanish Conquest, all of which have ceased their operations by the modern day. The Otomi people in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
still make amate today but have trouble meeting demand due to a dwindling supply of fig and mulberry trees, which are in danger of extinction.
United States
European papermaking spread to the Americas first inMexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
by 1575 and then in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
by 1690.
The American paper industry began with the establishment of the first paper mill in British America
British America collectively refers to various British colonization of the Americas, colonies of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and its predecessors states in the Americas prior to the conclusion of the American Revolutionary War in 1 ...
in 1690 by William Rittenhouse of Philadelphia with the help of Pennsylvania's first printer, William Bradford. For two decades it would remain the only mill in the colonies, and for the next two centuries the city would remain the preeminent center of paper manufacturing and publishing. The first paper mills relied solely on rag paper production, with cotton rags generally imported from Europe. However, by the mid-19th century the sulfite process had begun to proliferate in other regions with better access to wood pulp, and by 1880, America had become the largest producer of paper goods in the world. While the Delaware Valley
The Philadelphia metropolitan area, also known as Greater Philadelphia and informally called the Delaware Valley, the Philadelphia tri-state area, and locally and colloquially Philly–Jersey–Delaware, is a major metropolitan area in the Nor ...
remained an important region in paper production and publishing through the late nineteenth century, Philadelphia was overtaken by regions using these new processes which had greater access to water power and wood pulp.
The earliest of these mills were centered in New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
and Upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region of New York (state), New York that lies north and northwest of the New York metropolitan area, New York City metropolitan area of downstate New York. Upstate includes the middle and upper Hudson Valley, ...
, the latter of which became home to International Paper, the largest pulp and paper company in the world, which held a 20% market share in 2017, and at its peak produced more than 60% of the continent's newsprint in 1898, before an industry shift to Canada. Chief among papermaking cities in New England and the world was Holyoke, Massachusetts
Holyoke is a city in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States, that lies between the western bank of the Connecticut River and the Mount Tom Range. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a population of 38,247. Loca ...
, at one time making 80% of the writing paper of the United States and home to the ill-fated American Writing Paper Company, the world's largest producer of fine papers by 1920. By 1885 the Paper City, as it is still called, produced 190 tons per day, more than twice Philadelphia's capacity. Quickly it became a hub of paper machinery and turbine technology, host to the largest paper mills in the world in the 1890s, and D. H. & A. B. Tower, the largest paper mill engineering firm in the United States in the 19th century. The Tower Brothers and their associates would be responsible for designing mills on five continents. In the United States the firm supported the Berkshires' paper industry, building the first mills used to make U.S. currency by the Crane Company, as well as the first sulfite process mills of Kimberly Clark in Wisconsin, allowing the company to be the first west of the Appalachians to adopt the process, with access to vast forest resources.
The pulp and paper industry continued to develop in other regions, including California, Ohio's Miami Valley, with centers in Dayton
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
, Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
, and Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
, as well as regions of the South, like Texas and Georgia, the latter being home to Georgia Pacific and WestRock, the 2nd and 3rd respective largest paper producers in the United States today. Wisconsin's industry nevertheless endured and as of 2019 it had far and away the most paper manufacturers in the country, with 34 such enterprises. While only smaller specialty manufacturers remained in Pennsylvania and New England, New York retained 28 mills, followed by Georgia with 20, Michigan with 17, and Alabama with 16 respectively.
Paper mills
 The use of human and animal powered mills was known to Chinese and Muslim papermakers. However, the evidence for water-powered paper mills is elusive among both prior to the 11th century.: : Scholars have identified paper mills, likely human or animal powered, in
The use of human and animal powered mills was known to Chinese and Muslim papermakers. However, the evidence for water-powered paper mills is elusive among both prior to the 11th century.: : Scholars have identified paper mills, likely human or animal powered, in Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 C ...
-era Baghdad during 794–795.
It is evident that throughout the Islamic lands e.g. Iran, Syria (Hama and Damascus), and North Africa (Egypt and Tripoli) water power mills were extensively used to beat the flax and rag wastes to prepare the paper pulp
Donald Hill has identified a possible reference to a water-powered paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt ...
in Samarkand, in the 11th-century work of the Persian scholar Abu Rayhan Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (; ; 973after 1050), known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian peoples, Iranian scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously "Father of Comparative religion, Co ...
, but concludes that the passage is "too brief to enable us to say with certainty" that it refers to a water-powered paper mill. This is seen by Halevi as evidence of Samarkand first harnessing waterpower in the production of paper, but notes that it is not known if waterpower was applied to papermaking elsewhere across the Islamic world at the time. Burns remains sceptical, given the isolated occurrence of the reference and the prevalence of manual labour in Islamic papermaking elsewhere prior to the 13th century.
Clear evidence of a water-powered paper mill dates to 1282 in the Iberian Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
. A decree by the Christian king Peter III addresses the establishment of a royal " molendinum", a proper hydraulic mill, in the paper manufacturing centre of Xàtiva
Xàtiva (; ) is a town in eastern Spain, in the province of Valencia, on the right (western) bank of the river Albaida and at the junction of the Valencia, Spain, Valencia–Murcia and Valencia Albacete railways. It is located 25 km ...
. The crown innovation was operated by the Muslim Mudéjar
Mudéjar were Muslims who remained in Iberia in the late medieval period following the Christian reconquest. It is also a term for Mudéjar art, which was greatly influenced by Islamic art, but produced typically by Christian craftsmen for C ...
community in the Moorish quarter of Xàtiva, though it appears to have been resented by sections of the local Muslim papermakering community; the document guarantees them the right to continue the way of traditional papermaking by beating the pulp manually and grants them the right to be exempted from work in the new mill. Paper making centers began to multiply in the late 13th century in Italy, reducing the price of paper to one sixth of parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared Tanning (leather), untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves and goats. It has been used as a writing medium in West Asia and Europe for more than two millennia. By AD 400 ...
and then falling further; paper making centers reached Germany a century later.
The first paper mill north of the Alps was established in Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
by Ulman Stromer in 1390; it is later depicted in the lavishly illustrated ''Nuremberg Chronicle
The ''Nuremberg Chronicle'' is an illustrated encyclopedia consisting of world historical accounts, as well as accounts told through biblical paraphrase. Subjects include human history in relation to the Bible, illustrated mythological creatures, ...
''. From the mid-14th century onwards, European paper milling underwent a rapid improvement of many work processes.
Fiber sources
Before the industrialisation of the paper production the most common fibre source was recycled fibres from used textiles, called rags. The rags were from hemp,linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong and absorbent, and it dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. Lin ...
and cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
. It was not until the introduction of wood pulp
Pulp is a fibrous Lignocellulosic biomass, lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically, or mechanically isolating the cellulose fiber, cellulosic fibers of wood, fiber crops, Paper recycling, waste paper, or cotton paper, rag ...
in 1843 that paper production was not dependent on recycled materials from ragpickers. It was not realized at the time how unstable wood pulp paper is.
A means of removing printing inks from paper, allowing it to be re-used, was invented by German jurist Justus Claproth in 1774. Today this process is called deinking.
19th-century advances in papermaking
Although cheaper than vellum, paper remained expensive, at least in book-sized quantities, through the centuries, until the advent of steam-driven paper making machines in the 19th century, which could make paper with fibres fromwood pulp
Pulp is a fibrous Lignocellulosic biomass, lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically, or mechanically isolating the cellulose fiber, cellulosic fibers of wood, fiber crops, Paper recycling, waste paper, or cotton paper, rag ...
. Although older machines pre-dated it, the Fourdrinier papermaking machine became the basis for most modern papermaking. Nicholas Louis Robert of Essonnes, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, was granted a patent for a continuous paper making machine in 1799. At the time he was working for Leger Didot with whom he quarrelled over the ownership of the invention. Didot sent his brother-in-law, John Gamble, to meet Sealy and Henry Fourdrinier
Henry Fourdrinier (11 February 1766 – 3 September 1854) was a British people, British paper-making entrepreneur.
He was born in 1766, the son of paper maker and stationer Henry Fourdrinier, and grandson of the engraver Paul Fourdrinier, 1698� ...
, stationers of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, who agreed to finance the project. Gamble was granted British patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
2487 on 20 October 1801. With the help particularly of Bryan Donkin
Bryan Donkin FRS FRAS (22 March 1768 – 27 February 1855) developed the first paper making machine and created the world's first commercial canning factory. These were the basis for large industries that continue to flourish today. Bryan D ...
, a skilled and ingenious mechanic, an improved version of the Robert original was installed at Frogmore Paper Mill, Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and one of the home counties. It borders Bedfordshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Essex to the east, Greater London to the ...
, in 1803, followed by another in 1804. A third machine was installed at the Fourdriniers' own mill at Two Waters. The Fourdriniers also bought a mill at St Neots intending to install two machines there and the process and machines continued to develop.
However, experiments with wood showed no real results in the late 18th century and at the start of the 19th century. By 1800, Matthias Koops (in London, England) further investigated the idea of using wood to make paper, and in 1801 he wrote and published a book titled ''Historical account of the substances which have been used to describe events, and to convey ideas, from the earliest date, to the invention of paper.'' His book was printed on paper made from wood shavings (and adhered together). No pages were fabricated using the pulping method (from either rags or wood). He received financial support from the royal family to make his printing machines and acquire the materials and infrastructure needed to start his printing business. But his enterprise was short lived. Only a few years following his first and only printed book (the one he wrote and printed), he went bankrupt. The book was very well done (strong and had a fine appearance), but it was very costly.
Then in the 1830s and 1840s, two men on two different continents took up the challenge, but from a totally new perspective. Both Friedrich Gottlob Keller
Friedrich Gottlob Keller (27 June 1816 – 8 September 1895) was a German machinist and inventor, who (at the same time as Charles Fenerty) invented the wood pulp process for use in papermaking. He is widely known for his wood-cut machine (used fo ...
and Charles Fenerty
Charles Fenerty ( January 1821 – 10 June 1892) was a Canadian inventor who invented the wood pulp process for papermaking, which was first adapted into the production of newsprint. Fenerty was also a poet, writing over 32 known poems.
Early li ...
began experiments with wood but using the same technique used in paper making; instead of pulping rags, they thought about pulping wood. And at about the same time, by mid-1844, they announced their findings. They invented a machine which extracted the fibres from wood (exactly as with rags) and made paper from it. Charles Fenerty also bleached the pulp so that the paper was white. This started a new era for paper making. By the end of the 19th-century almost all printers in the western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
were using wood instead of rags to make paper.
Together with the invention of the practical fountain pen and the mass-produced pencil
A pencil () is a writing or drawing implement with a solid pigment core in a protective casing that reduces the risk of core breakage and keeps it from marking the user's hand.
Pencils create marks by physical abrasion, leaving a trail of ...
of the same period, and in conjunction with the advent of the steam driven rotary printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
, wood based paper caused a major transformation of the 19th-century economy and society in industrialized countries. With the introduction of cheaper paper, schoolbooks, fiction, non-fiction, and newspapers became gradually available by 1900. Cheap wood based paper also meant that keeping personal diaries or writing letters became possible and so, by 1850, the clerk
A clerk is a white-collar worker who conducts record keeping as well as general office tasks, or a worker who performs similar sales-related tasks in a retail environment. The responsibilities of clerical workers commonly include Records managem ...
, or writer, ceased to be a high-status job.
Early wood-based paper deteriorated as time passed, meaning that much of the output of newspapers and books from this period either has disintegrated or is in poor condition; some has been photographed or digitized (scanned). The acid nature of the paper, caused by the use of alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , such that is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium ...
, produced what has been called a slow fire, slowly converting the paper to ash. Documents needed to be written on more expensive rag paper. In the 2nd half of the 20th century cheaper acid-free paper based on wood was developed, and it was used for hardback and trade paperback books. However, paper that has not been de-acidified was still cheaper, and remains in use (2020) for mass-market paperback books, newspapers, and in underdeveloped countries.
Determining provenance
Determining the provenance of paper is a complex process that can be done in a variety of ways. The easiest way is using a known sheet of paper as an exemplar. Using known sheets can produce an exact identification. Next, comparing watermarks with those contained in catalogs or trade listings can yield useful results. Inspecting the surface can also determine age and location by looking for distinct marks from the production process. Chemical and fiber analysis can be used to establish date of creation and perhaps location.See also
* Kaghaz * Barkcloth * History of origami *Paperless office
A paperless office (or paper-free office) is a Workplace, work environment in which the use of paper is eliminated or greatly reduced. This is done by converting documents and other papers into digital form, a process known as digitization. Propone ...
*Papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * (alk. paper) * Bloom, Jonathan (2001). Paper before print: the history and impact of paper in the Islamic world. Yale University Press. * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Paper PaperPaper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
Paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
Forest history
History by topic