Henryk IV Probus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Henry Probus (
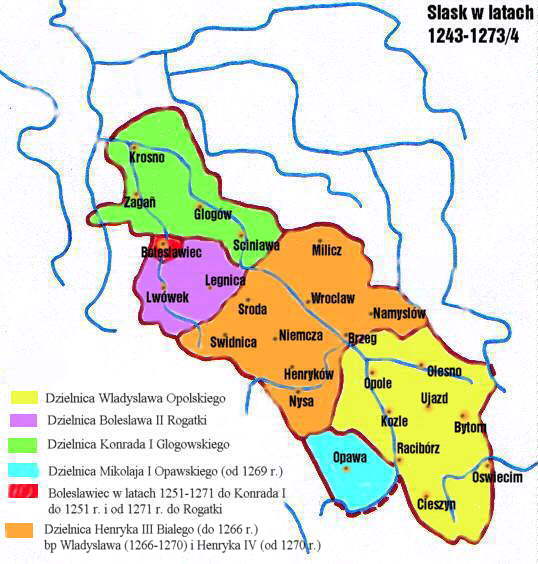 In 1273 Henry IV was formally proclaimed an adult and by himself assumed the government of his Silesian Duchy of Wrocław, which, however, after the split between
In 1273 Henry IV was formally proclaimed an adult and by himself assumed the government of his Silesian Duchy of Wrocław, which, however, after the split between


Herzog Heinrich von Breslau
in the
Genealogical database by Herbert Stoyan
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Henry 04 Probus 1250s births 1290 deaths 13th-century Polish monarchs Polish Roman Catholics Dukes of Wrocław People excommunicated by the Catholic Church Place of birth missing Minnesingers
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for the Righteous; or ''Prawy''; ; – 23 June 1290) was a member of the Silesian branch of the royal Polish Piast dynasty. He was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
from 1266 as well as the ruler of the Seniorate Province of Kraków and High Duke of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ...
from 1288 until his death in 1290.
Life
Henry IV was the only son of Duke Henry III the White of Silesia-Wrocław by his first wife Judith, daughter of DukeKonrad I of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia (ca. 1187/88 – 31 August 1247), from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243.
Life
Konrad w ...
.
Early life and tutelage
A minor upon the early death of his father in 1266, Henry IV was placed under the guardianship of his paternal uncle, ArchbishopWładysław of Salzburg
Władysław of Salzburg, also known as Władysław of Wrocław () or Władysław of Silesia (, ; – 27 April 1270), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was co-ruler in the Duchy of Silesia, Duchy of Wrocław since 1248. He served as chancellor of ...
. The Archbishop decided that the constant travels between Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
and Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
were inappropriate for a child, and, in 1267, sent Henry to Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
to be raised at the court of King Ottokar II of Bohemia
Ottokar II (; , in Městec Králové, Bohemia – 26 August 1278, in Dürnkrut, Austria, Dürnkrut, Lower Austria), the Iron and Golden King, was a member of the Přemyslid dynasty who reigned as King of Bohemia from 1253 until his death in 1278 ...
. Ottokar after Władysław's death in 1270 also took over Wrocław.
Shortly after the death of his uncle (who left him as his universal heir), Henry IV returned to Wrocław, where he found himself under the direct care of one of the closest advisers of his late father, Simon Gallicusa. Henry IV received a careful education, which may explain his subsequent interest in culture and poetry (there are reasonable suspicions that the Duke had asperger syndrome
Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome or Asperger's, is a diagnostic label that has historically been used to describe a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and no ...
). The cooperation between Henry IV and King Ottokar II was exemplary. In 1271 Henry IV participated in an armed expedition against Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, which brought an attack on Wrocław by the Árpád princes and their allies, the Dukes of Greater and Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
.
 In 1273 Henry IV was formally proclaimed an adult and by himself assumed the government of his Silesian Duchy of Wrocław, which, however, after the split between
In 1273 Henry IV was formally proclaimed an adult and by himself assumed the government of his Silesian Duchy of Wrocław, which, however, after the split between Opole
Opole (; ; ; ) is a city located in southern Poland on the Oder River and the historical capital of Upper Silesia. With a population of approximately 127,387 as of the 2021 census, it is the capital of Opole Voivodeship (province) and the seat of ...
, Legnica
Legnica (; , ; ; ) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. As well as being the seat of the county, since 1992 the city has been the seat of the Diocese of Legnica. Le ...
and Głogów only comprised the eastern part of the Lower Silesian lands. He began to follow a policy which was more independent from Bohemia, including in respect to friendly relations with his Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
n cousin Duke Władysław of Opole and also with duke Przemysł II
Przemysł II ( also given in English and Latin language, Latin as ''Premyslas'' or ''Premislaus'' or in Polish as '; 14 October 1257 – 8 February 1296) was the Duke of Poznań from 1257–1279, of Greater Poland from 1279 to 1296, of Kraków fr ...
of Greater Poland.
Kidnapping of Henry IV by Bolesław II the Bald
Henry supported King Ottokar II in his fierce conflict with King Rudolph I of Germany in 1276, giving food and refuge to the Bohemian troops. When Ottokar was placed under theImperial ban
The imperial ban () was a form of outlawry in the Holy Roman Empire. At different times, it could be declared by the Holy Roman Emperor, by the Imperial Diet, or by courts like the League of the Holy Court (''Vehmgericht'') or the '' Reichskammerg ...
, Duke Bolesław II the Bald of Legnica took the occasion, had his nephew Henry seized at Jelcz and imprisoned him in 1277.
Fortunately for Henry IV, the reaction to his imprisonment was indignation. Ottokar's Polish allies, Duke Henry III of Głogów and Duke Przemysł II of Greater Poland attempted to enforce Henry IV's liberation. The Bohemian king however only sent febrile appeals and request for release. Henry IV's allies were defeated by Duke Bolesław II 's son Henry V the Fat in the bloody Battle of Stolec (24 April 1277), where both Dukes Przemysł II and Henry III were captured.
Henry IV could obtain his freedom only at the end of the year, when he finally decided to capitulate after hearing the defeat of his main ally King Ottokar II against the Imperial and Hungarian troops at the 1278 Battle on the Marchfeld
The Battle on the Marchfeld (''i.e. Morava (river), Morava Field''; ; ; ); at Dürnkrut, Austria, Dürnkrut and Jedenspeigen took place on 26 August 1278 and was a decisive event for the history of Central Europe for the following centuries. T ...
. Henry IV was forced to give Bolesław II one-third of his duchy including the towns of Środa Śląska and Strzegom
Strzegom () is a town in Świdnica County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the Gmina Strzegom administrative district (gmina). It lies approximately north-west of Świdnica, and west of the regional capit ...
and forced to pledge Krosno Odrzańskie
Krosno Odrzańskie () is a town in Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland, on the east bank of Oder River, at the confluence with the Bóbr. With 11,319 inhabitants (2019) it is the capital of Krosno County, Lubusz Voivodeship, Krosno County.
His ...
, which he had obtained from the Dukes of Głogów in 1273–1274, in order to obtain the money for his ransom.
Ottokar II's death and Regency of Bohemia
While Henry himself did not take part in the Battle on the Marchfeld, he had sent reinforcements to King Ottokar II, whose death was a serious blow to the Wrocław duke. After hearing the news of Ottokar's death, Henry IV went toPrague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
and attempted to gain the guardianship of the king's son Wenceslaus II, as one of his closest relatives (Henry IV's paternal grandmother was Anna of Bohemia, a daughter of late King Ottokar I) and ally.
He was however not successful due to the actions of King Rudolph I of Germany, who in his capacity as King of the Romans
King of the Romans (; ) was the title used by the king of East Francia following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German king between his election and coronatio ...
had given the regency over Bohemia to the Ascanian margrave Otto V, Margrave of Brandenburg-Salzwedel. As compensation, the German king gave Henry IV the Bohemian County of Kladsko as a fief.
Homage to King Rudolph I in 1280
Upon the death of his Bohemian ally, Henry IV reconciled with King Rudolph I and in 1280 went to his Austrian court inVienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, where Henry tried to obtain for himself the Polish royal crown.
Some historians believed that the Duke of Wrocław took the opportunity from his homage to King Rudolph I to expose him the possibility of becoming King of Poland. At that time, he also made an alliance with Duke Władysław of Opole, who promised to help Henry IV with the condition that his daughter (perhaps called Constance), who had recently married Henry IV, was crowned with him as Polish queen if he would obtain the royal investiture.
Attempts at authority over Silesia and Poland
The relation of Henry IV with his Silesian relatives, in general, was not good. In 1280 he again suffered the invasion of the Duke Henry V the Fat of Legnica, who was supported by the Margrave of Brandenburg, who could resist with unusual difficulty. In order to normalize the situation in February of the next year Henry IV organized a meeting in Sądowel, a village located in the Duchy of Wrocław, for the purpose to find ways of mutual cooperation between the Silesian dukes. Henry IV, however, had other plans: immediately he captured his long-time enemy, Duke Henry V the Fat of Legnica, as well as his own allies, Dukes Henry III of Głogów and Przemysł II of Greater Poland, in order to obtain political concessions from them. Przemysł II was forced to give the strategic Lesser Polish land of Wieluń (also known as Ruda) and to acknowledge Henry IV's overlordship, paying homage to him. In subsequent years, the good politics of Henry IV were reflected in the voluntary submission of the Silesian dukes Przemko of Ścinawa andBolko I of Opole
Bolko I of Opole (; before 21 October 1258 – 14 May 1313), was a Duke of Opole from 1282 (until 1284 with his brother as co-ruler), Niemodlin and Strzelce Opolskie until his death.
He was the third son of Władysław, Duke of Opole- Racibórz, ...
; the re-unification of Silesia seemed within reach.
However, not all the Silesian dukes accepted his authority: Dukes Bolko I the Strict
Bolko (Bolesław) I the Strict, also known as Bolko (Bolesław) of Jawor ( or ''Srogi'' or ''Jaworski''; 1252/56 – 9 November 1301), was a Duke of Lwówek Śląski, Lwówek 1278–81 (with his brother as co-ruler) and Duchy of Jawor, Jawor after ...
, Konrad II the Hunchback and three of the four sons of Władysław of Opole: Casimir of Bytom, Mieszko I of Cieszyn and Przemysław of Racibórz were completely against Henry's politics. With the Opole Dukes, the situation was more delicate: in 1287, Henry IV obtained the annulment of his marriage with their sister, who was sent back to her homeland. The fourth of Władysław's sons, Bolko I, remained faithful to Henry IV's politics.
The first attempt of Henry IV to take the Seniorate Province
Seniorate Province, also known as the Senioral Province, was a district principality in the Duchy of Poland that was formed in 1138, following the fragmentation of the state.Kwiatkowski, Richard. The Country That Refused to Die: The Story of t ...
at Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
was during 1280–1281, as a response to the invasion which the Polish High Duke Leszek II the Black had made against Wrocław before. However, this trip ended unsuccessfully.
Conflict with Bishop Thomas II of Wrocław
In the years 1282–1287 Henry IV was involved in a long-lasting dispute with the Bishop of Wrocław Tomas II Zaremba. The first phase of the conflict was already noted in the years 1274–1276, concluded with arbitration which was not satisfied any of the parts. The disputes erupted again in 1282; this time, the conflict was for the lands and properties seized by the church in a difficult period that followed after theBattle of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica (), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz () or Battle of Wahlstatt (), was fought between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces at the village of Legnickie Pole (''Wahlstatt''), approximately southeast of the ci ...
, and for the violation of the immunity of the Church hierarchy in trials.
At the beginning of 1282, the Bishop sent their complaint to the Papal Legate Philip of Ferno, which was to address the settlement of the dispute. His ruling was favorable to the Church hierarchy, and Henry IV appealed. In 1283 Henry IV organized a big Episcopal convention in Nysa, whose main attraction was a knight's tournament. However, the tensions continued and Thomas II, using the support of the Papal Legate, and wanting to break the rebelliousness of Henry IV he excommunicated him and the whole Duchy in March 1284. However, the Duke of Wrocław refused to subject to the Bishop's will and in the same year appealed to Pope Martin IV
Pope Martin IV (; born Simon de Brion; 1210/1220 – 28 March 1285), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 February 1281 until his death in 1285. He was the last French pope to hold his court in Rome before ...
. It soon became clear, of course, that he could not expect a positive message from Rome. Despite Thomas II's efforts to subordinate the local clergy under his rule, several religious Orders remained faithful to Henry IV, among others, the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
s. The conflict continued, even after the unsuccessful attempts for mediation by the Archbishop of Gniezno
This is a list of archbishops of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Gniezno, Archdiocese of Gniezno, who are simultaneously primate (bishop), primates of Poland since 1418.Jakub Świnka
Jakub Świnka (died 4 March 1314) was a Polish Catholic priest, the Archbishop of Gniezno and a notable politician and statesman, supporter of the idea of unification of all Polish lands under the rule of Władysław I the Elbow-high ("the Short") ...
.
In 1285 Henry IV took advantage of his power over the clergy and confiscated some lands which belonged to the bishopric Duchy of Nysa– Otmuchów. The humiliated Bishop Thomas II was forced to emigrate to the Duchy of Racibórz
Duchy of Racibórz (, , ) was one of the duchies of Silesia, formed during the medieval fragmentation of Poland into provincial duchies. Its capital was Racibórz in Upper Silesia.
States and territories disestablished in the 1200s
States and ...
. The last act of the dispute took place in 1287 when Henry IV entered Racibórz. Thomas II was no longer able to escape and finally decided to subordinate to the Duke of Wrocław. But Henry IV was generous in his triumph: he restored the rich lands obtained earlier from the Bishopric and also founded a Kolegiata consecrated to the Holy Cross.
Meanwhile, in foreign politics, Henry IV continued to try to obtain the subordination of the other Silesian Dukes, which indirectly could bring him the Royal Crown. In 1284 he used the betrayal of the Greater Poland noble family of Zaremba (Thomas II's family) as a pretext to capture the town of Kalisz
Kalisz () is a city in central Poland, and the second-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship, with 97,905 residents (December 2021). It is the capital city of the Kalisz Region. Situated on the Prosna river in the southeastern part of Gr ...
. It soon became clear that the Dukes of Greater Poland never accepted this loss, so after some discussions, Kalisz was exchanged with the town of Ołobok by Duke Przemysł II.
Henry IV, High Duke of Poland
On 30 September 1288, Leszek II the Black, Duke of Sieradz and High Duke of Poland, died without issue. This event opened an opportunity for Henry IV to realize his ambitious plans to gain Kraków and the title of High Duke. With this purpose, he began to find suitable allies from 1287, when he reconciled with Przemysł II, returning him Wieluń. According to the Professor and HistorianOswald Balzer
Oswald Marian Balzer (23 January 1858 in Chodorów – 11 January 1933 in Lwów) was a Polish historian of law and statehood who was one of the most renowned Polish historians of his time.
In 1887 he became a professor at the University of L ...
, shortly before began the preparations to the First Coalition of Piast Dukes formed by Leszek II the Black, Henry IV, Przemysł II and Henry III of Głogow, which had the intention to make the unification of Poland. Notwithstanding the veracity of this theory, after hearing the news of Leszek II's death, Henry IV was ready for action.
Henry IV's major contenders for the Kraków throne were Leszek II's half-brother Władysław I the Elbow-high and Duke Bolesław II of Płock, who counted on the support of the Lesser Poland nobility. However, the Duke of Płock failed to obtain the decisive support of the Castellan Sulk the Bear (''Sułk z Niedźwiedzia''), who was the Governor of the city. On 26 February 1289, the bloody Battle of Siewierz took place between the troops of the Dukes of Płock
Płock (pronounced ), officially the Ducal Capital City of Płock, is a city in central Poland, on the Vistula river, in the Masovian Voivodeship. According to the data provided by Central Statistical Office (Poland), GUS on 31 December 2021, the ...
and Kuyavia
Kuyavia (; ), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western (with th ...
, and Henry IV's troops, supported by King Rudolph I and the Dukes of Opole
Opole (; ; ; ) is a city located in southern Poland on the Oder River and the historical capital of Upper Silesia. With a population of approximately 127,387 as of the 2021 census, it is the capital of Opole Voivodeship (province) and the seat of ...
, Głogów and Ścinawa (Steinau). The battle ended with a victory for the Masovia-Kuyavia coalition; from two of Henry IV's allies, Duke Przemko of Ścinawa was killed in the battle, and Duke Bolko I of Opole was seriously injured and captured by Władysław I the Elbow-high.
Despite this success, Duke Bolesław II of Płock unexpectedly resigned his pretensions, leaving all the Kraków inheritance to Wladyslaw I the Elbow-high. As the war turned favorable to him, Wladyslaw I, with the assistance of the Bishop of Kraków
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role ...
, Paul of Półkozic (who was later imprisoned after rebelled against him), managed to besiege and capture Wawel castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established o ...
and forced the Silesian troops to retreat to Skała.
However, Henry IV regrouped his forces and marched against Kraków in person at the head of his army in August 1289. Thanks to the betrayal of the Kraków townspeople and the help of the Franciscans (who even hid him in their monastery), Henry IV took the city and was recognized as High Duke. Despite his victory, Henry IV decided to remain in Sandomierz
Sandomierz (pronounced: ; , ) is a historic town in south-eastern Poland with 23,863 inhabitants (), situated on the Vistula River near its confluence with the San, in the Sandomierz Basin. It has been part of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy ...
.

Internal politics
During his reign, Henry succeeded in strengthening central power across his duchy, as well as improving its economy. He supported progress of mining and cities, many of which received German city law and various privileges. He was also an educated man, fluently spoke several languages and actively supported Western court culture and chivalric ethos. Henry himself was a talented poet; two of his poems were recorded inCodex Manesse
The Codex Manesse (also or Pariser Handschrift) is a (a German term for a manuscript containing songs) which is the single most comprehensive source of Middle High German ''Minnesang'' poetry. It was written and illustrated manuscript, illustr ...
.
Death
Henry IV died suddenly in 1290, aged no more than thirty-two years. The details of his death, given by the chronicler Ottokar of Styria, are seen by some historians as very reliable and by others as doubtful. The year of his death is widely accepted, and confirmation for this can be found in numerous sources. However, the exact day was variously given by the sources. One, the most supported by far of the largest number of sources, and given by the Church of St. John the Baptist, was 23 June. There are, however, other proposals: 24 June, 22 July, and even in April.Poisoning
About the real cause of Henry IV's death, there are several independent sources: these are the tombs of the Silesian Dukes, the Chronicle ofJan Długosz
Jan Długosz (; 1 December 1415 – 19 May 1480), also known in Latin as Johannes Longinus, was a Polish priest, chronicler, diplomat, soldier, and secretary to Bishop Zbigniew Oleśnicki of Kraków. He is considered Poland's first histo ...
, and later chroniclers, like the Bohemian Chronicle of Pulkawy and the Chronicle of Ottokar of Styria.
According to Ottokar of Styria, who seems to be the most accurate in details, Henry IV aspired to the title of the King of Poland, asking the Pope for permission for a coronation. The negotiations were successful, and he sent to Rome 12,000 '' grzywnas'' as a present to the Pope. But when the envoy reached Italy it was noted that 400 ''grzywnas'' were stolen during the trip, and the Pope, infuriated, cancelled all negotiations with Henry IV. Although the embezzler was able to escape from the papal fury and the justice of the Doge of Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
, it is known that Henry IV wanted to punish him. In order to prevent the imminent revenge of the Duke it was decided to get rid of him: a false lawyer (brother of one of the Duke's doctors) was employed at the court of Wrocław, and slowly poisoned Henry IV. While another doctor, called Guncelin, recognizing the symptoms of poisoning, was able to rescue the Duke from an imminent death, causing severe vomiting and cleansing the body; but the assassin was not discovered, and this time put the poison in the knife used by Henry IV to cut his bread. The poison was finally detected, but it was too late to save the Duke. Henry IV died in the Catholic faith, deciding not to prosecute or punish his killers.
This is a very long story of the Duke's death and only some elements are confirmed by other sources. Ottokar of Styria told the story in many details in agreement with that provided by the ''Kronika Zbrasławska''. Other sources related that a chaplain named Aleksy, as a deputy of King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia
Wenceslaus II Přemyslid (; ; 27 SeptemberK. Charvátová, ''Václav II. Král český a polský'', Prague 2007, p. 18. 1271 – 21 June 1305) was King of Bohemia (1278–1305), Duke of Cracow (1291–1305), and King of Poland (1296–130 ...
had betrayed Henry IV's interests and tried to give the crown to the "King of Kalisz" Przemysł II. In this story the theft of the envoy to Rome was also mentioned, only the epilogue was a little different: here, the thief was killed by his own servants in the streets of Rome.
Killers
Following the version of Ottokar of Styria, should be sought among the Wrocław townspeople (just like Henry IV's father) two brothers, one of them was lawyer and the other doctor. The only two persons who could be identified as the brothers were John (who was an adviser of the Duchy and a lawyer) and Jakob (known as ''Magister'', so probably a doctor), sons of one Goćwina, who was a doctor in the court of Henry III the White. They still in their posts at the time of Henry IV's death. It's assumed that they acted on behalf of Henry V the Fat, who wanted to obtain Kraków and with this the title of High Duke, but was not any evidence to support this. There is no other person who will take advantage of the Duke's death, and could be linked to the circumstances of the death of Henry IV.Henry IV's testament
According to the chroniclers, the dying Henry IV made two documents. One to the Wrocław church (which give the desired permissions to the Bishop to obtain the full sovereignty over the Duchy of Nysa– Otmuchów) and other politic (who regulated the issue of his inheritance). Under this will, he bequeathed the Duchy of Wrocław to Duke Henry III of Głogów, andKraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
-with the title of High Duke- to Przemysł II
Przemysł II ( also given in English and Latin language, Latin as ''Premyslas'' or ''Premislaus'' or in Polish as '; 14 October 1257 – 8 February 1296) was the Duke of Poznań from 1257–1279, of Greater Poland from 1279 to 1296, of Kraków fr ...
. In case of the death of one of the princes, the other could take possession over his districts, which further arrangements according to custom. Many historians, however, believed the existence of a third document. If it was true, this would be a step towards the reunification of Poland, and Henry IV, who was denigrated particularly in the earlier literature, was really a conscious promoter of Poland interests and a true patriot (apart from the merits of raising the awareness of the problems of ethnic and linguistic diversity in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
). Only the testament to the Church (who was not count with the return of Kłodzko
Kłodzko (; ; ; ) is a historic town in south-western Poland, in the region of Lower Silesia. It is situated in the centre of the Kłodzko Valley, on the Eastern Neisse (Nysa Kłodzka) river.
Kłodzko is the seat of Kłodzko County (and of the ru ...
to King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia
Wenceslaus II Přemyslid (; ; 27 SeptemberK. Charvátová, ''Václav II. Král český a polský'', Prague 2007, p. 18. 1271 – 21 June 1305) was King of Bohemia (1278–1305), Duke of Cracow (1291–1305), and King of Poland (1296–130 ...
as an excuse for mixing in the Silesian affairs) was fully implemented. Henry IV was buried in the Kolegiata of the Holy Cross and St. Bartholomeus in Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
, which he founded.
Henry V the Fat could take Wrocław with support of King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia, after the local nobility refused to accept the rule of Henry III of Głogów. Wenceslaus II himself gained the Seniorate Province
Seniorate Province, also known as the Senioral Province, was a district principality in the Duchy of Poland that was formed in 1138, following the fragmentation of the state.Kwiatkowski, Richard. The Country That Refused to Die: The Story of t ...
, but Duke Przemysł II could retain the title of High Duke.
During World War II German anthropologists wanted to prove the "''Germanic look''" of Henry IV. To this end, his remains were removed and were to be tested. Unfortunately, they were lost during the war. The sarcophagus is now in the National Museum in Wrocław.
Marriages
Around March 1280, Henry IV married firstly with the daughter of Duke Władysław of Opole (b. ca. 1256/65? – d. 1287/88?), perhaps called Constance. After almost seven years of childless union, the Duke of Wrocław obtain the annulment of his marriage under the grounds of sterility, although this fact is disputed by modern historians. By 1288, Henry IV married secondly with Matilda (b. ca. 1270 – d. bef. 1 June 1298), daughter of Margrave Otto V "the Tall" ofBrandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
– Salzwedel. The Professor and historian Ewa Maleczyńska alleged that the real reason of the divorce of Henry IV was that he maintain an affair with Matilda and wanted to marry her. They had no children.
See also
* History of Poland (966–1385) * History of Silesia *Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Pol ...
*Dukes of Silesia
The Duke of Silesia was the title of sons and descendants of the Polish people, Polish Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth. In accordance with the Testament of Bolesław III Krzywousty, last will and testament of Bolesław, upon his death his lands were d ...
References
"Piastowie. Leksykon biograficzny", Cracow, 1999.External links
Herzog Heinrich von Breslau
in the
Codex Manesse
The Codex Manesse (also or Pariser Handschrift) is a (a German term for a manuscript containing songs) which is the single most comprehensive source of Middle High German ''Minnesang'' poetry. It was written and illustrated manuscript, illustr ...
(1304/40).Genealogical database by Herbert Stoyan
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Henry 04 Probus 1250s births 1290 deaths 13th-century Polish monarchs Polish Roman Catholics Dukes of Wrocław People excommunicated by the Catholic Church Place of birth missing Minnesingers