|
Ĺšcinawa
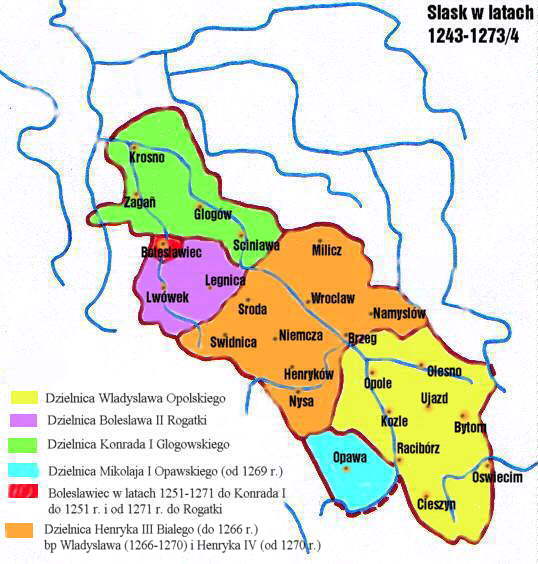
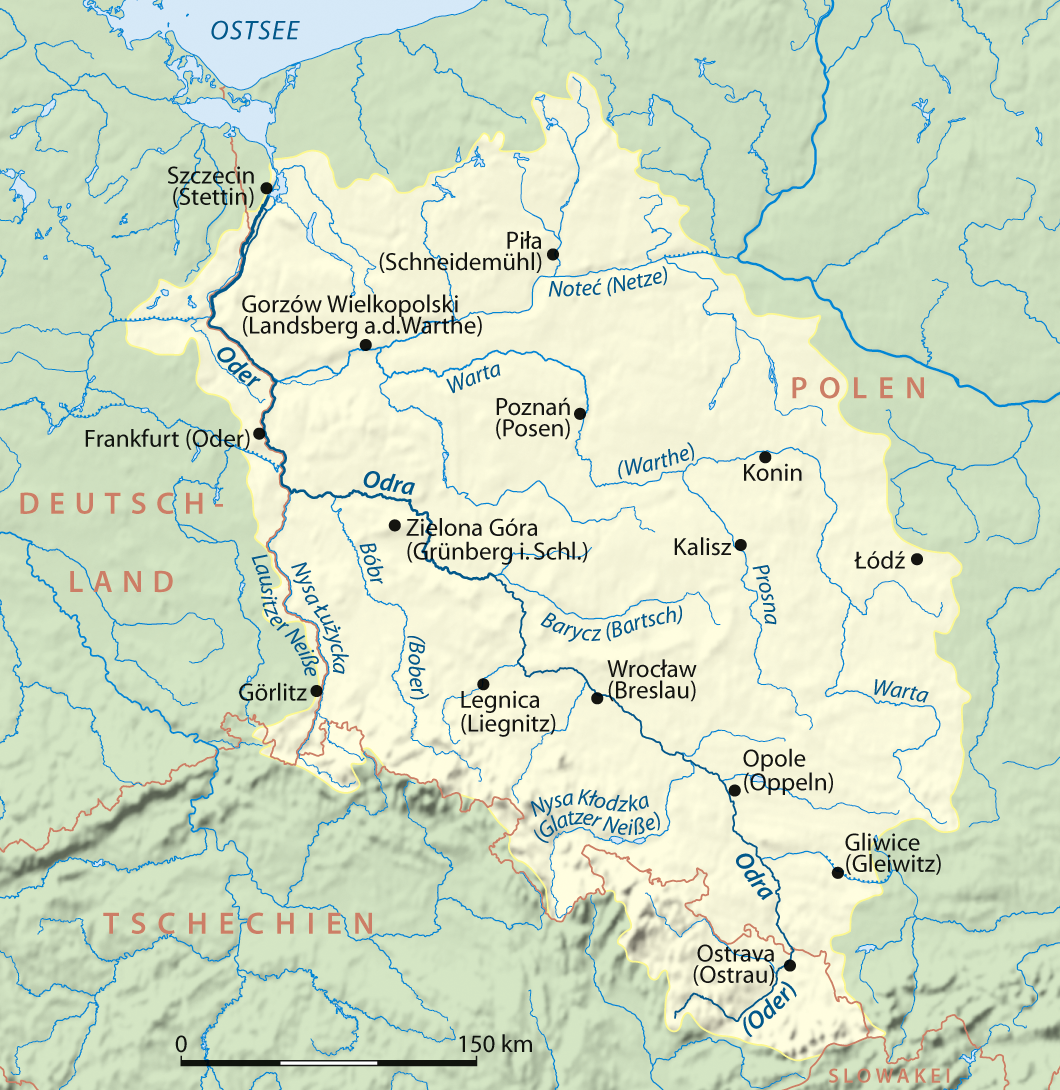
Ścinawa () is a town and municipality on the Oder river in the Lower Silesian region of Poland. The Ścinawa train station is a key gateway for travel throughout the region, connecting major destinations such as Wrocław and Głogów. As of 2019, the town's population is 5,582. It is part of Lubin County in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, and is the seat of the municipality called Gmina Ścinawa. History Ścinawa was first documented as a possession of the newly established Sanctuary of St. Jadwiga, Trzebnica, Trzebnica Abbey in a deed issued by Pope Innocent III, which dates back to 1202, when it was part of fragmented Kingdom of Poland, Poland. Town privileges were first granted between 1248 and 1259 by Konrad I, Duke of Głogów. The town church of St John's was first constructed in 1209. After the partition of the Duchy of Głogów by Konrad's sons in 1273, Ścinawa became the capital of a duchy in its own right under the rule of Konrad II the Hunchback. It was again united wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gmina Ĺšcinawa
Gmina Ścinawa is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Lubin County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. Its seat is the town of Ścinawa, which lies approximately east of Lubin, and north-west of the regional capital Wrocław. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2019 its total population is 9,938. Neighbouring gminas Gmina Ścinawa is bordered by the gminas of Gmina Lubin, Lubin, Gmina Prochowice, Prochowice, Gmina Rudna, Rudna, Gmina Wińsko, Wińsko and Gmina Wołów, Wołów. Villages Apart from the town of Ścinawa, the gmina contains the villages of Buszkowice, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Buszkowice, Chełmek Wołowski, Dąbrowa Środkowa, Dębiec, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Dębiec, Dłużyce, Dziesław, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Dziesław, Dziewin, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Dziewin, Grzybów, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Grzybów, Jurcz, Krzyżowa, Lubin County, Krzyżowa, Lasowice, Lubin County, Lasowice, Parszowice, Przychowa, Prz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Henry III, Duke Of GĹ‚ogĂłw
Henry III of Głogów (; 1251/60 – 11 December 1310) was a duke of Duchy of Głogów, Głogów from 1274 to his death and also duke of parts of Greater Poland during 1306–1310. He was one of the sons (probably the second) of Konrad I, Duke of Głogów, Konrad I, Duke of Głogów, by his first wife Salome of Greater Poland, Salome, daughter of Duke Wladislaw Odonicz, Władysław of Greater Poland. Life Early years Little is known about his first years of life. In 1267 Henry III participated in the canonization of his great-grandmother Hedwig of Andechs. At the time of his father's death in 1274 he and his brothers are still minors; for this, his step-mother Sophie of Landsberg (widow of his father) and the Chancellor Mikołaj took their guardianship. Shortly after, they sold the towns of Bolesławiec and Nowogrodziec to the Archbishop of Magdeburg. Beginning of cooperation with Henry II Probus The first participation of Henry III in the political arena was in 1277, when toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Konrad II The Hunchback
Konrad II the Hunchback () (1252/65 – 11 October 1304) was Duke of Ścinawa from 1278 to 1284, patriarch of Aquileia in 1299, and Duke of Żagań from 1284 until his death. Biography He was the second son of Konrad I, Duke of Głogów by his first wife Salome, daughter of Duke Władysław of Greater Poland. His nickname "Hunchback" (''Garbaty'') appears in contemporary chronicles probably due to his religious career. Konrad II first appeared on the chronicles at the ceremony of the canonization of his paternal great-grandmother Hedwig of Andechs in 1267. Ten years later he joined his elder brother Henry III in the Battle of Stolec (24 April 1277) which culminated in a disastrous defeat. Shortly after these events, Konrad was sent to Bologna, Italy to study in order to take important ecclesiastical posts in the future. During his absence, Henry IV Probus ruled Ścinawa on his behalf. When Konrad II returned to his Duchy in 1280, the Duke of Wrocław refused to return control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
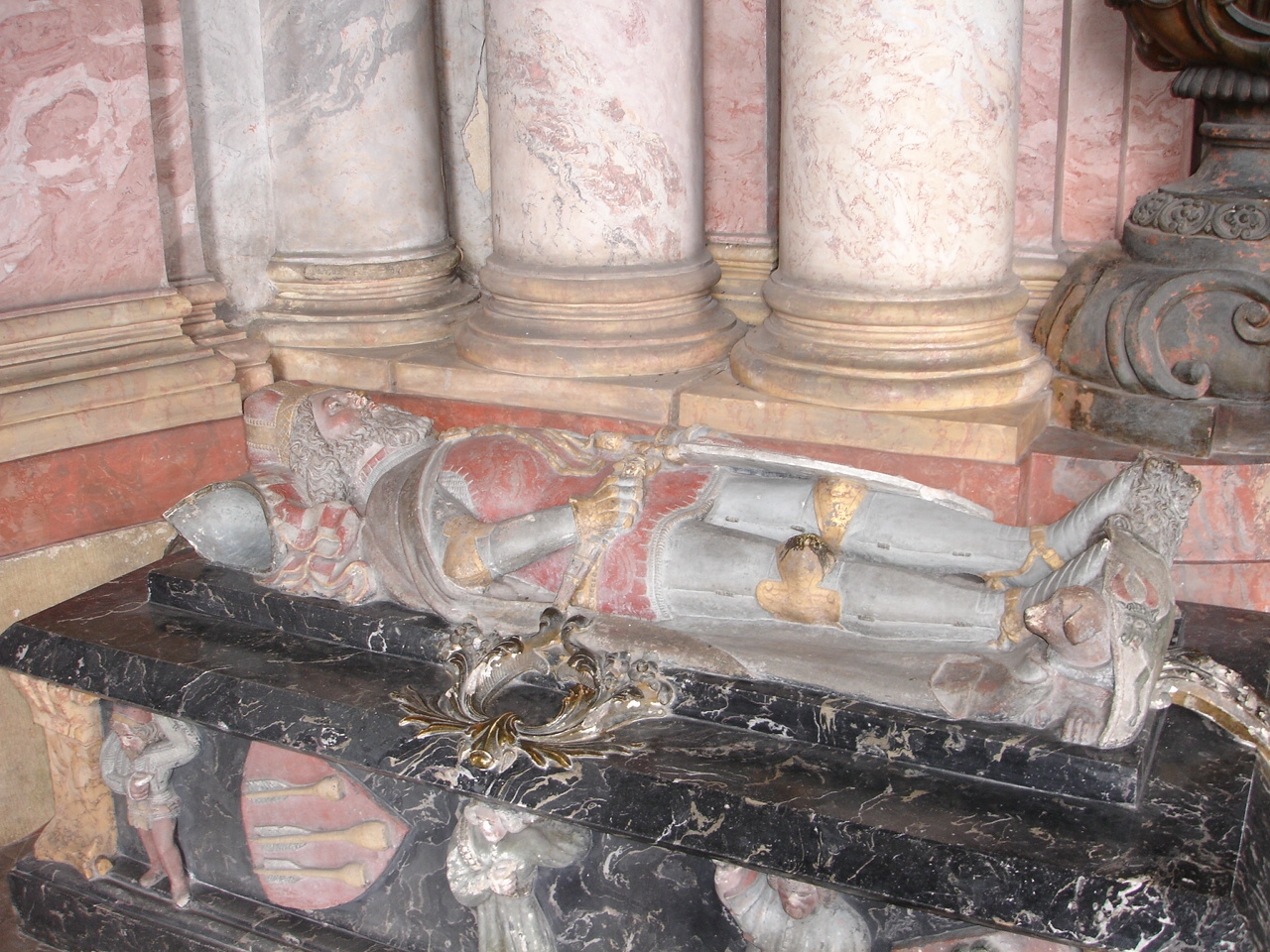
Bolko II The Small
Bolko II the Small ( – 28 July 1368), was the last independent Duke of the Piast dynasty in Silesia. He was Duke of Świdnica from 1326, Duke of Jawor and Lwówek from 1346, Duke of Lusatia from 1364, Duke over half of Brzeg and Oława from 1358, Duke of Siewierz from 1359, and Duke over half of Głogów and Ścinawa from 1361. He was the oldest son of Bernard, Duke of Świdnica, by his wife Kunigunde, daughter of Władysław I the Elbow-high, Duke of Kuyavia and, from 1320, King of Poland. Like his grandfather, King Elbow-high, Bolko II was of small stature; his nickname, "the Small" (''Mały''), reflects this and was used in contemporary sources. Early years After the death of his father in 1326, Bolko II, with his younger brother Henry II as co-ruler, succeeded him in all his domains. Because both princes were still in their teenage years, they were at first aided by their two paternal uncles, Dukes Bolko II of Ziębice and Henry I of Jawor, as well as their mother Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lubin County
__NOTOC__ Lubin County () ( German:Lüben Kreis) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of . Its administrative seat and largest town is Lubin, and its only other town is Ścinawa. As of 2019 the total population of the county is 106,211, out of which the population of Lubin is 72,428, the population of Ścinawa is 5,582, and the rural population is 28,201. Neighbouring counties Lubin County is bordered by Głogów County to the north, Góra County to the north-east, Wołów County to the east, Legnica County to the south and Polkowice County to the north-west. Administrative division The county is subdivided into four gmina The gmina (Polish: , plural ''gminy'' ) is the basic unit of the administrative division of Poland, similar to a municipality. , there were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Duchy Of GĹ‚ogĂłw
The Duchy of Głogów (, ) or Duchy of Glogau () was one of the Duchies of Silesia, formed in course of the medieval fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies. Its capital was Głogów in Lower Silesia. It existed in 1177–1185 and 1251–1506 and was ruled by the Silesian Piasts, followed by John Corvinus and the Jagiellonian dynasty. History In 1177, under the rule of Konrad Spindleshanks, the youngest son of High Duke Władysław II the Exile of Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Poland, the town of Głogów had already become the capital of a duchy in its own right. However, when Konrad died between 1180 and 1190, his duchy was again inherited by his elder brother Bolesław I the Tall, and re-incorporated to the Duchy of Silesia/Wrocław. After the death of Bolesław's grandson Duke Henry II the Pious at the 1241 Battle of Legnica his sons in 1248 divided the Lower Silesian Duchy of Wrocław among themselves. Konrad I, Duke of Głogów, Konrad I, a child when his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Konrad I, Duke Of GĹ‚ogĂłw
Konrad I of GĹ‚ogĂłw (; – 6 August 1273/74), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Silesian duke of GĹ‚ogĂłw from 1249/50 until his death. Life Konrad was the fourth son of Henry II the Pious, Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland from 1238, by his wife Anna, daughter of the PĹ™emyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia. At the time of his father's death in the 1241 Battle of Legnica against the Golden Horde, he and his younger brother WĹ‚adysĹ‚aw were placed under the guardianship of their eldest brother Duke BolesĹ‚aw II Rogatka. After Henry's sudden death, the Silesian Piasts were not able to maintain their dominant position: BolesĹ‚aw II tried to succeed his father on the Polish throne at KrakĂłw, but eventually could not prevail against his Piast cousin Konrad I of Masovia. In order to avoid further fragmentation of the paternal lands, the elder duke, with the approval of their mother, sent Konrad to study in Paris, where he was to be educated with the intention of becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship (, ) in southwestern Poland, is one of the 16 Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeships (provinces) into which Poland is divided. It covers an area of and has a total population of 2,899,986. It is one of the wealthiest provinces in Poland, as natural resources such as copper, Lignite, brown coal and rock materials are widely present. Its capital and largest city is Wrocław, situated on the Oder, Oder River. The voivodeship is host to several spa towns, many castles and palaces, and the Giant Mountains, with several ski resorts. For this reason, tourism is a large part of this region's economy. History In the past 1,200 years, the region has been part of Great Moravia, the Medieval Kingdom of Poland, the Crown of Bohemia, Kingdom of Hungary, Habsburg monarchy (Austria), Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire, and modern Poland after 1945. Silesian tribes settled the lands at the end of the first millennium after the Migration Period. In the 9th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocław. The first state to have a stable hold over the territory of what will be considered Lower Silesia was the short-lived Great Moravia in the 9th century. Afterwards, in the Middle Ages, Lower Silesia was part of Piast-ruled Poland. It was one of the leading regions of Poland, and its capital Wrocław was one of the main cities of the Polish Kingdom. Lower Silesia emerged as a distinctive region during the fragmentation of Poland in 1172, when the Duchies of Opole and Racibórz, considered Upper Silesia since, were formed of the eastern part of the Duchy of Silesia, and the remaining, western part was since considered Lower Silesia. During the , German settlers were invited to settle in the region, which until then had a Polish majority. As a result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany as part of the Oder–Neisse line. The river ultimately flows into the Szczecin Lagoon north of Szczecin and then into three branches (the Dziwna, Świna and Peene) that empty into the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea. Names The Oder is known by several names in different languages, but the modern ones are very similar: English and ; Czech, Polish, and , ; (); ; Medieval Latin: ''Od(d)era''; Renaissance Latin: ''Viadrus'' (invented in 1534). The origin of this name is said by onomastician Jürgen Udolph to come from the Illyrian word ''*Adra'' (“water vein”). Ptolemy knew the modern Oder as the Συήβος (''Suebos''; Latin ''Suevus''), a name apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Treaty Of Trencin
The Treaty of Trentschin was concluded on 24 August 1335 between King Casimir III the Great, Casimir III of Poland and King John of Bohemia together with his son Margrave Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV. The agreement was reached by the agency of Casimir's brother-in-law King Charles I of Hungary and signed at TrenÄŤĂn Castle, Trentschin Castle in the Kingdom of Hungary (present-day TrenÄŤĂn, Slovakia). It initiated the transfer of suzerainty over the former Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Polish province of Duchy of Silesia, Silesia to the Kingdom of Bohemia, whereafter the Duchies of Silesia were incorporated into the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, Bohemian Crown and thus became part of the Holy Roman Empire. Following the integration of this treaty, the three kingdoms of Bohemia, Hungary, and Poland met at the Congress of Visegrád (1335), First Congress of Visegrad later in 1335 to further discuss the division of land. This congress also made the treaty official. Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Casimir III The Great
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king from the Piast dynasty. Casimir inherited a kingdom weakened by war and under his rule it became relatively prosperous and wealthy. He reformed the Polish army and doubled the size of the kingdom. He reformed the judicial system and introduced several undying codified statutes, gaining the title "the Polish Justinian I, Justinian". Casimir built extensively and founded the Jagiellonian University (back then simply called the University of Krakow),Saxton, 1851, p. 535 the oldest List of universities in Poland, Polish university and List of oldest universities in continuous operation, one of the oldest in the world. He also confirmed privileges and protections previously granted to Jews and encouraged them to settle in Poland in great numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |