AIDS In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
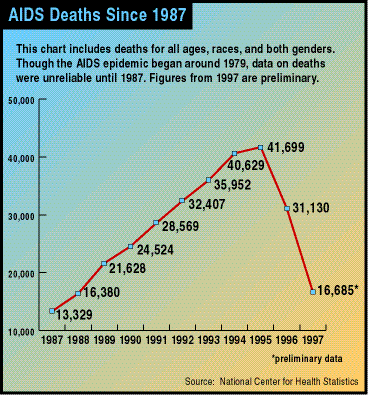
 Great progress was made in the U.S. following the introduction of three-drug anti-HIV treatments ("cocktails") that included antiretroviral drugs.
Great progress was made in the U.S. following the introduction of three-drug anti-HIV treatments ("cocktails") that included antiretroviral drugs.
 Since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic, several U.S. presidents have attempted to implement a national plan to control the issue. In 1987,
Since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic, several U.S. presidents have attempted to implement a national plan to control the issue. In 1987,
 During the HIV/AIDS epidemic of the 1980s, LGBTQ+ communities were further
During the HIV/AIDS epidemic of the 1980s, LGBTQ+ communities were further
 The
The
Document ID 5291
AIDS.gov – The U.S. Federal Domestic HIV/AIDS Resource
AIDSVu.org – Interactive Map Illustrating HIV Prevalence in the United States
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hiv Aids In The United States 1960 establishments in the United States LGBTQ history in the United States
AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
, caused by HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
, found its way to the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
between the 1970s and 1980s, but was first noticed after doctors discovered clusters of Kaposi's sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a type of cancer that can form masses on the skin, in lymph nodes, in the mouth, or in other organs. The skin lesions are usually painless, purple and may be flat or raised. Lesions can occur singly, multiply in a limite ...
and pneumocystis pneumonia
''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia (PCP), also known as ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia (PJP), is a form of pneumonia that is caused by the yeast-like fungus '' Pneumocystis jirovecii''.
''Pneumocystis'' specimens are commonly found in the lungs o ...
in homosexual men
Gay men are male homosexuals. Some bisexual men, bisexual and homoromantic men may dually identify as ''gay'' and a number of gay men also identify as ''queer''. Historic terminology for gay men has included ''Sexual inversion (sexology), in ...
in Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, and San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
in 1981. Treatment of HIV/AIDS is primarily via the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs, and education programs to help people avoid infection.
Initially, infected foreign nationals were turned back at the United States border to help prevent additional infections. The number of United States deaths from AIDS has declined sharply since the early years of the disease's presentation domestically. In the United States in 2016, 1.1 million people aged over 13 lived with an HIV infection, of whom 14% were unaware of their infection. African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, Hispanic/Latino Americans, homosexual
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between people of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" exc ...
and bisexual
Bisexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior toward both males and females. It may also be defined as the attraction to more than one gender, to people of both the same and different gender, or the attraction t ...
men, and intravenous drug users remain the most disproportionately affected populations in the United States.
Mortality and morbidity
, about 700,000 people have died of HIV/AIDS in the United States since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic, and nearly 13,000 people with AIDS in the United States die each year. With improved treatments and betterprophylaxis
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental health a ...
against opportunistic infections, death rates have significantly declined.
The overall death rate among persons diagnosed with HIV/AIDS in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
decreased by sixty-two percent from 2001 to 2012.
Containment
After the HIV/AIDS outbreak in the 1980s, various responses emerged in an effort to alleviate the issue. These included new medical treatments, travel restrictions, and new public health policies in the United States.Medical treatment

 Great progress was made in the U.S. following the introduction of three-drug anti-HIV treatments ("cocktails") that included antiretroviral drugs.
Great progress was made in the U.S. following the introduction of three-drug anti-HIV treatments ("cocktails") that included antiretroviral drugs. David Ho
David Da-i Ho (; pinyin: ''Hé Dà-yī''; born November 3, 1952) is a Taiwanese-American AIDS researcher, physician, and virologist who has made a number of scientific contributions to the understanding and treatment of HIV infection. He w ...
, a pioneer of this approach, was honored as ''Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
'' magazine Man of the Year for 1996. Deaths were rapidly reduced by more than half, with a small but welcome reduction in the yearly rate of new HIV infections. Since this time, AIDS deaths have continued to decline, but much more slowly, and not as completely in African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
as in other population segments.
Travel restrictions
In 1987, theDepartment of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
(HHS) included HIV in its list of "communicable diseases of public health significance," denying immigrants and short term foreign visits from anyone who tested positive for the virus. In 1993, the US Congress passed the National Institutes of Health Revitalization Act of 1993, removing the HHS' authority to dictate HIV as a "public health significance," and explicitly including HIV as a cause for denying immigrants and foreign visitors entry into the US. Anyone seeking US citizenship during the HIV ban was required to undergo a medical exam during the legalization process - testing positive would permanently deny the applicant entry into the country. The law extended to include medication, where foreign travelers could be arrested for having antiretroviral drugs in their carry-on luggage. A famous example was in 1989, when a Dutch traveler to Minnesota was arrested for "several days" because he was carrying AZT
Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), was the first antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use in combination with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent vertica ...
in his luggage.
During the turn of the 21st century, people who were HIV positive and seeking temporary visas or vacationing to the US had to avoid revealing their status on application forms, and either plan for their medication to be sent to the US or stop taking their medication. Eventually the US began offering temporary admission waivers for people who were HIV positive. As stated in an interoffice memorandum in 2004, foreign nationals who were HIV positive could qualify for the waiver for either humanitarian/public interest reasons, or being "attendees of certain designated international events held in the United States".
In early December 2006, President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he i ...
indicated that he would issue an executive order allowing HIV positive people to enter the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
on standard visas. It was unclear whether applicants would still have to declare their HIV status.
In August 2007, Congresswoman Barbara Lee
Barbara Jean Lee (; born July 16, 1946) is an American politician who has served as the 52nd mayor of Oakland since 2025. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Lee previously served as a United States House of Repr ...
of California introduced , the HIV Nondiscrimination in Travel and Immigration Act of 2007. This bill allowed travelers and immigrants entry to the United States without having to disclose their HIV status. The bill died at the end of the 110th Congress.
In July 2008, President George W. Bush signed that lifted the ban in statutory law. However, the United States Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
still held the ban in administrative (written regulation) law. New impetus was added to repeal efforts when Paul Thorn, a UK tuberculosis expert who was invited to speak at the 2009 Pacific Health Summit in Seattle, was denied a visa due to his HIV positive status. A letter written by Mr. Thorn, and read in his place at the Summit, was obtained by Congressman Jim McDermott, who advocated the issue to the Obama administration's Health Secretary.
On October 30, 2009, President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
reauthorized the Ryan White
Ryan Wayne White (December 6, 1971 – April 8, 1990) was an American teenager from Kokomo, Indiana, who became a national poster child for HIV/AIDS in the United States after his school barred him from attending classes following a diagn ...
HIV/AIDS Bill which expanded care and treatment through federal funding to nearly half a million. The Department of Health and Human Services also crafted regulation that would end the HIV Travel and Immigration Ban, effective in January 2010. On January 4, 2010, the United States Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
removed HIV infection from the list of "communicable diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disea ...
of public health significance," due to its not being spread by casual contact, air, food or water, and removed HIV status as a factor to be considered in the granting of travel visas, disallowing HIV status from among the diseases that could prevent people who were not U.S. citizens from entering the country.
Public health policies
 Since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic, several U.S. presidents have attempted to implement a national plan to control the issue. In 1987,
Since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic, several U.S. presidents have attempted to implement a national plan to control the issue. In 1987, Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
created a Presidential Commission on the HIV Epidemic. This commission was recruited to investigate what steps are necessary for responding to the HIV/AIDS outbreak in the country, and the consensus was to establish more HIV testing, focus on prevention and treatment as well as expanding HIV care throughout the United States. However, these changes were not implemented during this time, and the commission recommendations were largely ignored.
Another attempt to respond to the HIV/AIDS outbreak took place in 1996, when Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
established the National AIDS Strategy, which aimed to reduce the number of infections, enhance research on HIV treatment, increase access to resources for people affected by AIDS, and also alleviate the racial disparities in HIV treatment and care. In Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, the 11th International AIDS Conference highlighted the effectiveness highly active antiretroviral therapy
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of mul ...
(HAART), thus creating a new period of optimism. 1996 would mark the first year since the beginning of the epidemic that the number of new HIV/AIDS cases would decline. AIDS was now no longer the leading cause of death in Americans aged 25-44, although it remained the leading cause of death for African Americans in this age group. The AIDS Memorial Quilt would be displayed in its entirety for the last time on the National Mall
The National Mall is a Landscape architecture, landscaped park near the Downtown, Washington, D.C., downtown area of Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States. It contains and borders a number of museums of the Smithsonian Institu ...
in October 1996. 1997 would mark the first time that the number of AIDS-related deaths would substantially decline, with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) reporting a 47% decline in AIDS-related deaths compared to the previous year. The effectiveness of drug therapy such as HAART would be credited for this significant decline in new cases and deaths.
In 2010, Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
created the National HIV/AIDS Strategy for the United States (NHAS), with its three main objectives being to reduce the annual number of HIV infections, reduce health disparities, and increase access to resources and HIV care. However, this new strategy differs in that it includes an Implementation Plan, with a timeline for achieving each of the three goals, as well as a document outlining the specific action plan that will be used.
In 2019, Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
announced a plan in his State of the Union Address to stop new HIV infections in the United States by 2030, though critics pointed to the President's policies reducing access to health insurance, anti-immigrant and anti-transgender policies as undermining this goal. The Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
issued grants to 32 HIV "hotspots" in 2019, and Congress earmarked over $291 million for the president's plan in FY2020.
In February 2019, U.S. District Court Judge Leonie Brinkema issued an temporary order barring the U.S. military for discharging or denying officer commissions to personnel based on HIV status. Judge Brinkema's order became permanent in April 2022.
Localized efforts
Local health educators found it upon themselves to promote modes ofsafe sex
Safe sex is sexual activity using methods or contraceptive devices (such as condoms) to reduce the risk of transmitting or acquiring sexually transmitted infections (STIs), especially HIV. "Safe sex" is also sometimes referred to as safer ...
amongst gay men
Gay men are male homosexuals. Some bisexual men, bisexual and homoromantic men may dually identify as ''gay'' and a number of gay men also identify as ''queer''. Historic terminology for gay men has included ''Sexual inversion (sexology), in ...
, bisexual men
Bisexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior toward both males and females. It may also be defined as the attraction to more than one gender, to people of both the same and different gender, or the attraction t ...
, and other men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM) to combat the HIV/AIDS epidemic. In 1987, Les Pappas, an educator from the San Francisco AIDS Foundation
The San Francisco AIDS Foundation (SFAF) is a nonprofit organization dedicated to providing services for people with HIV/AIDS, with a mission to end the HIV/AIDS in the United States, AIDS epidemic in the United States. They were founded in 1982, ...
(SFAF), spoke at a conference encouraging gay and bisexual men to use condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both external condo ...
s during sexual intercourse. In Pappas' speech, he takes it as the community's responsibility to educate men on using condoms, alluding to the degree of educating gay men as if they had no idea how to use condoms or were even aware of the existence of condoms at all.
Pappas saw opening the eyes of the gay community to condoms would create a successful economic " gay market" that was unprecedented for the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, commonly known as the Bay Area, is a List of regions of California, region of California surrounding and including San Francisco Bay, and anchored by the cities of Oakland, San Francisco, and San Jose, California, S ...
. Where he saw bringing attention to buying and using condoms, Pappas also believed that seeing condom paraphernalia would make gay men embrace their sexuality more, thus practicing safer sex.
Public perception
stigmatized
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
as they became the focus of mass hysteria
Mass psychogenic illness (MPI), also called mass sociogenic illness, mass psychogenic disorder, epidemic hysteria or mass hysteria, involves the spread of illness symptoms through a population where there is no infectious agent responsible for c ...
, suffered isolation and marginalization
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. In the EU context, the Euro ...
, and were targeted with extreme acts of violence in the United States. One of the best known works on the history of HIV/AIDS is the 1987 book '' And the Band Played On'' by Randy Shilts, which contends that Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
's administration dragged its feet in dealing with the crisis due to homophobia
Homophobia encompasses a range of negative attitudes and feelings toward homosexuality or people who identify or are perceived as being lesbian, Gay men, gay or bisexual. It has been defined as contempt, prejudice, aversion, hatred, or ant ...
, while the gay community viewed early reports and public health measures with corresponding distrust, thus allowing the disease to spread further and infect hundreds of thousands more. This resulted in the formation of the AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power
AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power (ACT UP) is an international, grassroots political group working to end the AIDS pandemic. The group works to improve the lives of people with AIDS through direct action, medical research, treatment and advocacy, ...
(ACT UP) by Larry Kramer. Galvanized by the U.S. federal government's inactivity, the movement led by AIDS activists to gain funding for HIV/AIDS research
HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
Transmission
A body of sc ...
, which on a per-patient basis out-paced funding for more prevalent diseases such as cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
and heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
, was used as a model for future lobbying for health research funding.
An early theory asserted that a series of inoculation
Inoculation is the act of implanting a pathogen or other microbe or virus into a person or other organism. It is a method of artificially inducing immunity against various infectious diseases. The term "inoculation" is also used more generally ...
s against hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
that were performed in the gay community of San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
were tainted with HIV. Although there was a high correlation between recipients of that vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
and initial cases of AIDS, this theory has long been discredited. However, the theory has never been officially proven or disproven. HIV, hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
, and hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include ...
are bloodborne diseases with very similar modes of transmission, and those at risk for one are at risk for the others.
Publicity campaigns were started in attempts to counter the incorrect and often vitriolic perception of AIDS as a "gay plague". These included the Ryan White
Ryan Wayne White (December 6, 1971 – April 8, 1990) was an American teenager from Kokomo, Indiana, who became a national poster child for HIV/AIDS in the United States after his school barred him from attending classes following a diagn ...
case, red ribbon campaigns, celebrity dinners, the 1993 film version of ''And the Band Played On'', sex education programs in schools, and television advertisements
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
. Announcements by various celebrities that they had contracted HIV (including actor Rock Hudson
Rock Hudson (born Roy Harold Scherer Jr.; November 17, 1925 – October 2, 1985) was an American actor. One of the most popular film stars of his time, he had a screen career spanning more than three decades, and was a prominent figure in the G ...
, basketball star Magic Johnson
Earvin "Magic" Johnson Jr. (born August 14, 1959) is an American businessman and former professional basketball player. Often regarded as the greatest point guard of all time, Johnson List of NBA players who have spent their entire career w ...
, tennis player Arthur Ashe
Arthur Robert Ashe Jr. (July 10, 1943 – February 6, 1993) was an American professional tennis player. He won three Grand Slam (tennis)#Tournaments, Grand Slam titles in singles and two in doubles. Ashe was the first Black player selected ...
and singer Freddie Mercury
Freddie Mercury (born Farrokh Bulsara; 5 September 1946 – 24 November 1991) was a British singer and songwriter who achieved global fame as the lead vocalist and pianist of the rock band Queen (band), Queen. Regarded as one of the gre ...
) were significant in arousing media attention and making the general public aware of the dangers of the disease to people of all sexual orientations.
Perspective of doctors
The global spread of HIV/AIDS was met with great fear and concern by the American population in the 1980s, much like any other epidemic, and those who were primarily affected wereAfrican Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, Hispanic/Latino Americans, homosexual
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between people of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" exc ...
and bisexual
Bisexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior toward both males and females. It may also be defined as the attraction to more than one gender, to people of both the same and different gender, or the attraction t ...
men, and intravenous drug users. During the early years of the epidemic, doctors began to not treat patients affected with HIV/AIDS, not only to create distance from these groups of people, but also because they were afraid to contract the disease themselves. At the time, a surgeon in Milwaukee stated: "I've got to be selfish. It's an incurable disease that's uniformly fatal, and I'm constantly at risk for getting it. I've got to think about myself. I've got to think about my family. That responsibility is greater than to the patient."
Some doctors thought it was their duty to stay away from the risk of contracting HIV because they had other patients to think of. In a survey of doctors in the mid to late 1980s, a substantial number of physicians indicated that they did not have an ethical obligation to treat and care for those patients affected with HIV/AIDS. A study of primary care
Primary care is a model of health care that supports first-contact, accessible, continuous, comprehensive, and coordinated person-focused care. It aims to optimise population health and reduce disparities across the groups by ensuring equitable ...
providers showed that half would not care for patients if they were given a choice. In 1990, a national survey of doctors showed that "only 24% believed that office-based practitioners should be legally required to provide care to individuals with HIV infection." Nonetheless, there were many doctors who chose to care for patients affected with HIV/AIDS for different reasons: they shared the same sexual orientation as the infected; a commitment to providing care to the diseased; an interest in the mysteries of infectious disease; and/or a desire to tame the awful threat.
By race and ethnicity
African Americans
African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
are the ethnic group most disproportionately affected by HIV/AIDS, compared with other races and ethnicities in the United States. They represented approximately 12% of the U.S. population in 2018, but accounted for an estimated 43% of new HIV infections in 2017. Furthermore, they make up nearly 52% of AIDS-related deaths in the United States. A 2006 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) estimated that about half of the 1 million U.S. citizens living with HIV/AIDS were African–American. A 2010 study published on the ''American Journal of Public Health
The ''American Journal of Public Health'' is a monthly peer-reviewed public health journal published by the American Public Health Association that covers health policy and public health. The journal was established in 1911 and its stated mission ...
'' reported that 64% of women infected with HIV/AIDS in the United States were African–American. In 2019, African–American and multiracial
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races (human categorization), races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicity, ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used ...
populations experienced the highest reported homelessness rates of any other ethnic or racial group diagnosed with HIV/AIDS in the United States. In the year 2021, approximately 60% of new HIV diagnoses among women in the United States were represented by Black women
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
.
Risk factors contributing to the Black HIV/AIDS rate
The United States have a mixed private/public health system, with more privatization than most other developed countries. Access to healthcare services is very important in preventing and treating HIV/AIDS among the U.S. population. It can be affected by health insurance which is available to people through private insurers, Medicare andMedicaid
Medicaid is a government program in the United States that provides health insurance for adults and children with limited income and resources. The program is partially funded and primarily managed by U.S. state, state governments, which also h ...
, which leaves many U.S. citizens still vulnerable and untreated. Historically, African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
have faced discrimination when it comes to receiving healthcare.
Homosexuality is viewed negatively within the African-American community: "In a qualitative study of 745 racially and ethnic diverse undergraduates attending a large Midwestern university, Calzo and Ward (2009) determined that parents of African-American participants discussed homosexuality more frequently than the parents of other respondents. In analyses of the values communicated, Calzo and Ward (2009) reported that Black parents offered greater indication that homosexuality is perverse and unnatural".
Homosexuality
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or Human sexual activity, sexual behavior between people of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexu ...
is also seen as a threat to the African-American empowerment. Masculinity
Masculinity (also called manhood or manliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with men and boys. Masculinity can be theoretically understood as Social construction of gender, socially constructed, and there i ...
is seen as important for the African-American community because it shows that the community is in control of their own destiny. Since the social stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
circling homosexuality is that it is considered "effeminate
Effeminacy or male femininity is the embodiment of feminine traits in boys or men, particularly those considered untypical of men or masculinity. These traits include roles, stereotypes, behaviors, and appearances that are socially associated wi ...
", then homosexuality is seen as a threat to masculinity
Masculinity (also called manhood or manliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with men and boys. Masculinity can be theoretically understood as Social construction of gender, socially constructed, and there i ...
in the African-American community: "Black manhood, then, depends on men's ability to be provider, progenitor, and protector. But, as the Black male performance of parts of this script is thwarted by economic and cultural factors, the performance of Black masculinity becomes predicated on a particular performance of Black sexuality and avoidance of weakness and femininity. If sexuality remains one of the few ways that Black men can recapture a masculinity withheld from them in the marketplace, endorsing Black homosexuality subverts the cultural project of reinscribing masculinity within the Black community." This critical view is influenced by internalized homophobia: "Internalized homophobia is defined as the lesbian, gay, or bisexual individual's inward direction of society's homophobic attitudes (Meyer 1995)."
A homophobic culture and discrimination towards LGBTQ+ people is sustained in the African-American community further through the involvement of Black churches and congregations, because religion is a vital part of the African-American community: "As reported by Peterson and Jones (2009), AA MSM tended to be more involved with religious communities than NHW MSM." Because Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
reiterates homosexuality as a sin
In religious context, sin is a transgression against divine law or a law of the deities. Each culture has its own interpretation of what it means to commit a sin. While sins are generally considered actions, any thought, word, or act considered ...
and social stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
, the African-American community has higher rates of internalized homophobia. This internalized homophobia causes a lower chance of HIV/AIDS education on prevention and care within the African-American community.
"Down-low" subculture among Black MSM
'' Down-low'' is an African-American slang term specifically used within the African-American community that typically refers to asexual subculture
Sexuality and gender identity-based cultures are subcultures and communities composed of people who have shared experiences, backgrounds, or interests due to common sexual or gender identities. Among the first to argue that members of sexual m ...
of Black men who usually identify as heterosexual
Heterosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between people of the opposite sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, heterosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions ...
but actively seek sexual encounters and relations with other men, practice gay cruising, and frequently adopt a specific hip-hop attire during these activities. They generally avoid disclosing their same-sex sexual activities
Same sex may refer to:
* A phrase used in the discussion of sex or gender
* Gonochorism, the state of having just one of at least two distinct sexes in any one individual organism
* Homosexuality, the romantic attraction, sexual attraction or sex ...
, and often have female sexual partner(s), and may be married or single.
In medical research
Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as health research, refers to the process of using scientific methods with the aim to produce knowledge about human diseases, the prevention and treatment of illness, and the promotion of ...
, the term ''down-low'' is used to identify sexual identity-behaviour discordance among men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM). According to a study published in the '' Journal of Bisexuality'', " e Down Low is a lifestyle predominately practiced by young, urban Black men who have sex with other men and women, yet do not identify as gay or bisexual".
In this context, "being on the ''down-low''" is more than just men having sex with men in secret, or a variant of closeted
''Closeted'' and ''in the closet'' are metaphors for LGBTQ people who have not disclosed their sexual orientation or gender identity and aspects thereof, including sexual identity and sexual behavior. This metaphor is associated and sometime ...
homosexuality
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or Human sexual activity, sexual behavior between people of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexu ...
or bisexuality
Bisexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or Human sexual activity, sexual behavior toward both males and females. It may also be defined as the attraction to more than one gender, to people of both the same and different gender, ...
—it is a sexual identity that is, at least partly, defined by its "cult of masculinity
Masculinity (also called manhood or manliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with men and boys. Masculinity can be theoretically understood as Social construction of gender, socially constructed, and there i ...
" and its rejection of what is perceived as White American culture (including what is perceived as White American LGBT culture
LGBTQ culture is a culture shared by lesbian, Gay men, gay, bisexuality, bisexual, transgender, and queer individuals (LGBTQ people). It is sometimes referred to as queer culture (indicating people who are queer), LGBT culture, and LGBTQIA cult ...
) and terms. A 2003 cover story in ''The New York Times Magazine
''The New York Times Magazine'' is an American Sunday magazine included with the Sunday edition of ''The New York Times''. It features articles longer than those typically in the newspaper and has attracted many notable contributors. The magazi ...
'' on the ''down-low'' phenomenon explains that the American Black community sees "homosexuality as a white man's perversion." It then goes on to describe the ''down-low'' subculture as follows:
The CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
cited three findings that relate to African-American men who operate on the ''down-low'' (engage in MSM activity but don't disclose to others):
* African American men who have sex with men (MSM), but who do not disclose their sexual orientation (nondisclosers), have a high prevalence of HIV infection (14%); nearly three times higher than nondisclosing MSMs of other races/ethnicities (5%).
* Confirming previous research, the study of 5,589 MSM, aged 15–29 years, in six U.S. cities found that African American MSM were more likely not to disclose their sexual orientation compared with white MSM (18% vs. 8%).
* HIV-infected nondisclosers were less likely to know their HIV status (98% were unaware of their infection compared with 75% of HIV-positive disclosers), and more likely to have had recent female sex partners.
Hispanic and Latino Americans
Hispanic and Latino Americans
Hispanic and Latino Americans are Americans who have a Spaniards, Spanish or Latin Americans, Latin American background, culture, or family origin. This demographic group includes all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino (demonym), ...
are the second ethnic group most disproportionately affected by HIV/AIDS. The annual number of Hispanics/Latinos newly diagnosed with HIV infection has increased by 7% between 2012 and 2016. Specific Hispanic/Latino populations most heavily affected by HIV/AIDS are men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM), accounting for approximately 80% of estimated HIV incidence among Hispanics/Latinos, followed by transgender Hispanic/Latina women and recent Hispanic/Latino immigrants. Hispanics/Latinos represented 16% of the U.S. population but accounted for 21% of new HIV infections in 2010. This disparity is even more apparent among Hispanic/Latina women, which represent 13% of the population but account for 20% of reported HIV/AIDS cases among women in the United States. Hispanic and Latino Americans accounted for 20% of people living with HIV infection in 2011. Disparities persist in the estimated rate of new HIV infections in Hispanic and Latino Americans In 2010, the rate of new HIV infections for Hispanic/Latino men was 2.9 times that for White American
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person having ...
men, and the rate of new infections for Hispanic/Latina women was 4.2 times that for White American women. Since the epidemic began, more than 100,888 Hispanic and Latino Americans with an AIDS diagnosis have died, including 2,863 in 2016.
Native Americans
Native American communities in the United States see a higher rate of HIV/AIDS in comparison toWhite Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
, Asian Americans
Asian Americans are Americans with Asian diaspora, ancestry from the continent of Asia (including naturalized Americans who are Immigration to the United States, immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of those immigrants).
A ...
, Native Hawaiians
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians; , , , and ) are the Indigenous Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawaiʻi was settled at least 800 years ago by Polynesian ...
and other Pacific Islander Americans
Pacific Islander Americans (also colloquially referred to as Islander Americans) are Americans who are of Pacific Islander ancestry (or are descendants of the Indigenous peoples of Oceania). For its purposes, the United States census also coun ...
. Although Native Americans with HIV/AIDS only represent roughly 1% of positive cases in the U.S. population, the number of diagnoses among Native American gay and bisexual men rose by 54% between 2011 and 2015. Additionally, the survival rate of diagnosed Native Americans was the lowest of all races in the United States between 1998 and 2005.
In recent years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) have put in place a "high impact prevention approach" in partnership with the Indian Health Service and the CDC Tribal Advisory Committee to tackle the growing rates in a culturally appropriate way.
The higher rate of HIV/AIDS cases among Native Americans have been attributed to a number of factors, including socioeconomic disadvantages faced by Native American communities, which may result in difficulty accessing healthcare and high-quality housing. It may be more difficult for Native American gay and bisexual men to access healthcare due to living in rural communities, or due to stigma attached to their sexualities. Native Americans have been reported to have higher rates of other STIs, including chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may occur only several w ...
and gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual c ...
, which also increases likeliness of contracting or transmitting HIV.
As there are over 570 federally recognized Native American tribes, there is some difficulty in creating outreach programs which effectively appeal to all tribes whilst remaining culturally appropriate. As well as fear of social stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
from within Native American communities, there may also be a fear among LGBTQ+ Native Americans of a lack of understanding from health professionals in the United States, particularly among Two-Spirit
''Two-spirit'' (also known as ''two spirit'' or occasionally ''twospirited'', or abbreviated as ''2S'' or ''2E'', especially in Canada) is a umbrella term used by some Indigenous North Americans to describe Native people who fulfill a trad ...
Native Americans. A 2013 NASTAD report calls for the inclusion of LGBTQ+ and Two-Spirit Native American peoples in HIV/AIDS program planning and asserts that "health departments should utilize local experts to better understand regional definitions of "Two Spirit" and incorporate modules on Native gay men and Two Spirit people into cultural sensitivity courses for public health service providers".
Racial disparities related to HIV/AIDS treatment
While there is no cure for HIV/AIDS as of yet, prevention methods and access to medical care are major ways to know one's HIV status, become virally undetectable, and prevent transmission of HIV/AIDS. There are prevention methods to help reduce HIV rates in the United States but these methods are not equally available or accessed. A 2020 study published on the ''American Journal of Public Health
The ''American Journal of Public Health'' is a monthly peer-reviewed public health journal published by the American Public Health Association that covers health policy and public health. The journal was established in 1911 and its stated mission ...
'' reported that the social stigma
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
associated with HIV diagnosis is a "major barrier" that prevents many at-risk and HIV-positive patients from accessing services of HIV prevention and treatment. One prevention method is PrEP
PowerPC Reference Platform (PReP) was a standard system architecture for PowerPC-based computer systems (as well as a reference implementation) developed at the same time as the PowerPC processor architecture. Published by IBM in 1994, it allow ...
, which is a medication taken orally or an injection that prevents HIV transmission. According to the CDC, Pre-exposure prophlyaxis or PrEP usage rates varied significantly by reported race and ethnicity in 2019. For example, out of all the total number of individuals on PrEP, 63% of them identified as White Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
, 8% identified as African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, 14% identified as Hispanic and Latino Americans
Hispanic and Latino Americans are Americans who have a Spaniards, Spanish or Latin Americans, Latin American background, culture, or family origin. This demographic group includes all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino (demonym), ...
, and 9% identified as other.
Healthcare access varies greatly by race and ethnicity in the United States. Out of those living with HIV/AIDS who received medical care only 63% of Native Americans, 61% of African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, 65% of Hispanic and Latino Americans
Hispanic and Latino Americans are Americans who have a Spaniards, Spanish or Latin Americans, Latin American background, culture, or family origin. This demographic group includes all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino (demonym), ...
, and 85% of Native Hawaiians
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians; , , , and ) are the Indigenous Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawaiʻi was settled at least 800 years ago by Polynesian ...
and other Pacific Islander Americans
Pacific Islander Americans (also colloquially referred to as Islander Americans) are Americans who are of Pacific Islander ancestry (or are descendants of the Indigenous peoples of Oceania). For its purposes, the United States census also coun ...
were virally suppressed in 2019. This is in comparison to 71% of White Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
who were virally suppressed in 2019 according to the CDC. African–American, Hispanic/Latino, and multiracial
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races (human categorization), races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicity, ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used ...
populations were significantly more likely to miss at least one medical appointment in the past year compared with White American populations. African–American, Hispanic/Latino, and multiracial populations that were diagnosed with HIV/AIDS in the United States in 2019 all experienced higher need of dental care, SNAP or WIC benefits, shelter or housing services, and/or mental health services than White American populations according to the CDC.
National HIV/AIDS strategy
The 2022–2025 National HIV/AIDS strategy "recognizes racism as a serious public health threat that drives and affects both HIV outcomes and disparities", and while every part of the U.S. is threatened with the HIV/AIDS epidemic, "certain populations bear most of the burden signaling where our HIV prevention, care, and treatment efforts must be focused." The 2022–2025 National HIV/AIDS strategy focuses on five priority populations including:gay men
Gay men are male homosexuals. Some bisexual men, bisexual and homoromantic men may dually identify as ''gay'' and a number of gay men also identify as ''queer''. Historic terminology for gay men has included ''Sexual inversion (sexology), in ...
, bisexual men
Bisexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior toward both males and females. It may also be defined as the attraction to more than one gender, to people of both the same and different gender, or the attraction t ...
, and other men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM), in particular African–American, Hispanic/Latino, and Native American men; African–American women; transgender women
A trans woman or transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity and may experience gender dysphoria (distress brought upon by the discrepancy between a person's gender identity and their ...
; youth aged 13–24 years; and people who inject drugs.
Sex education varies throughout the United States and in some areas could use more informative measures. Sex education on HIV prevention
HIV prevention refers to practices that aim to prevent the spread of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV prevention practices may be undertaken by individuals to protect their own health and the health of those in their community, or may ...
has decreased from 64% (2000) to 41% (2014). Out of the 50 states, 26 put a larger emphasis on abstinence sex education. Abstinence-only sex education
Abstinence-only sex education (also known as sexual risk avoidance education) is a form of sex education that teaches not having sex outside of marriage. It often excludes other types of sexual and reproductive health education, such as birth co ...
is correlated to increasing rates of HIV/AIDS infections, especially among teenagers and young adults.
Activism and response
Starting in the early 1980s, HIV/AIDS activist groups and organizations began to emerge and advocate for people infected with HIV in the United States. Though it was an important aspect of the movement, activism went beyond the pursuit of funding forHIV/AIDS research
HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
Transmission
A body of sc ...
. These groups acted to educate and raise awareness of the disease and its effects on different populations, even those thought to be at low-risk of contracting HIV/AIDS. This was done through publications and "alternative media" created by those living with or close to the disease.
In contrast to this "alternative media" created by activist groups, mass media reports on HIV/AIDS were not as prevalent, most likely due to the stigma surrounding the topic. The general public was therefore not exposed to information regarding the disease. In addition, the federal government and laws in place essentially prevented individuals affected by HIV/AIDS from getting sufficient information about the disease. Risk reduction education was not easily accessible, so activist groups took action in releasing information to the public through these publications.
AIDS activist groups worked to prevent spread of HIV by distributing information about safe sex
Safe sex is sexual activity using methods or contraceptive devices (such as condoms) to reduce the risk of transmitting or acquiring sexually transmitted infections (STIs), especially HIV. "Safe sex" is also sometimes referred to as safer ...
. They also existed to support people living with HIV/AIDS, offering therapy, support groups, and hospice care. Organizations like Gay Men's Health Crisis, People With AIDS, Proyecto ContraSIDA por Vida, the Lesbian AIDS Project, and SisterLove were created to address the needs of certain populations living with HIV/AIDS. Other groups, like the NAMES Project, emerged as a way of memorializing those who had passed, refusing to let them be forgotten by the historical narrative. One group, the Association for Drug Abuse Prevention and Treatment (ADAPT), headed by Yolanda Serrano, coordinated with their local prison, Riker's Island Correctional Facility, to advocate for those imprisoned and HIV positive to be released early, so that they could die in the comfort of their own homes.
Both men and women, heterosexual and LGBTQ+ populations were active in establishing and maintaining these parts of the movement. Because HIV/AIDS was initially thought only to impact gay men
Gay men are male homosexuals. Some bisexual men, bisexual and homoromantic men may dually identify as ''gay'' and a number of gay men also identify as ''queer''. Historic terminology for gay men has included ''Sexual inversion (sexology), in ...
, most narratives of activism focus on their contributions to the movement. However, women also played a significant role in raising awareness, rallying for change, and caring for those impacted by the disease. Lesbian women helped organize and spread information about transmission between women, as well as supporting gay men in their work. Narratives of activism also tend to focus on organizing done in coastal cities, but AIDS activism was present and widespread across both urban and more rural areas of the United States. Organizers sought to address needs specific to their communities, whether that was working to establish needle exchange programs, fighting against housing or employment discrimination, or issues faced primarily by people identified as members of specific groups (such as sex worker
A sex worker is a person who provides sex work, either on a regular or occasional basis. The term is used in reference to those who work in all areas of the sex industry.Oxford English Dictionary, "sex worker" According to one view, sex work is ...
s, mothers and children, or incarcerated people).
During the HIV/AIDS epidemic of the 1980s, LGBTQ+ communities were further stigmatized
Stigma, originally referring to the visible marking of people considered inferior, has evolved to mean a negative perception or sense of disapproval that a society places on a group or individual based on certain characteristics such as their ...
as they became the focus of mass hysteria
Mass psychogenic illness (MPI), also called mass sociogenic illness, mass psychogenic disorder, epidemic hysteria or mass hysteria, involves the spread of illness symptoms through a population where there is no infectious agent responsible for c ...
, suffered isolation and marginalization
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. In the EU context, the Euro ...
, and were targeted with extreme acts of violence in the United States. Initially when the HIV/AIDS epidemic surfaced in the United States, a large proportion of patients were members of the LGBTQ+ community, leading to further stigmatization of the disease. Because of this, the AIDS activist groups took initiative in testing and experimenting with new possible medications for treating HIV, after researchers outside of the community refused. This research originally done by early AIDS activist groups contributed to treatments still being used today.
Among the landmark legal cases in the history of LGBT rights in the United States
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in the United States are at risk of erosion under the Second presidency of Donald Trump, with transgender rights being most at risk. While lesbian, gay and bisexual rights remain a ...
on the topic of HIV/AIDS is '' Braschi vs. Stahl''. Litigant Miguel Braschi sued his landlord for the right to continue living in their rent controlled apartment after his gay partner Leslie Blanchard died of AIDS. The NY Court of Appeals became the first American appellate court to conclude that same-sex relationships are entitled to legal recognition. The case was litigated at the height of the AIDS crisis and the plaintiff himself died only a year after his groundbreaking court victory. The case focused on emotional and economic interdependency rather than on the existence of legal formalities; the verdict made it more difficult for government officials to reject the notion that same-sex couples
A same-sex relationship is a romantic or sexual relationship between people of the same sex. ''Same-sex marriage'' refers to the institutionalized recognition of such relationships in the form of a marriage; civil unions may exist in countries ...
could constitute families and that they were entitled to at least some of the protections afforded by law.
Response from the Catholic Church
 The
The United States Conference of Catholic Bishops
The United States Conference of Catholic Bishops (USCCB) is the episcopal conference of the Catholic Church in the United States. Founded in 2001 after the merger of the National Conference of Catholic Bishops (NCCB) and United States Catholic C ...
was the first church body to address the HIV/AIDS pandemic in 1987 with a document entitled " The Many Faces of AIDS: A Gospel Response." In the document they stated that the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
must provide pastoral care
''The Book of Pastoral Rule'' (Latin: ''Liber Regulae Pastoralis'', ''Regula Pastoralis'' or ''Cura Pastoralis'' — sometimes translated into English ''Pastoral Care'') is a treatise on the responsibilities of the clergy written by Pope Greg ...
to those infected with HIV/AIDS as well as medical care. It called discrimination against people with AIDS "unjust and immoral". The document also rejected extra-marital sex and the use of condoms, and reiterated the Church's teaching that human sexuality was a gift and was to be used in monogamous marriages.
The Catholic Church, with over 117,000 health centers, is the largest private provider of HIV/AIDS care. Individual dioceses around the United States began hiring staff in the 1980s to coordinate AIDS ministry. By 2008, Catholic Charities USA had 1,600 agencies providing services to patients with AIDS, including housing and mental health services. The Archdiocese of New York
The Archdiocese of New York () is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church located in the New York (state), State of New York. It encompasses the boroughs of Manhattan, the Bronx and Staten Island in New York ...
opened a shelter for AIDS patients in 1985. In the same year, they opened a hotline for people to call for resources and information. The Missionaries of Charity
The Missionaries of Charity () is a Catholic centralised religious institute of consecrated life of Pontifical Right for women
established in 1950 by Mother Teresa, now known in the Catholic Church as Saint Teresa of Calcutta. , it consisted o ...
, led by Mother Teresa
Mary Teresa Bojaxhiu (born Anjezë Gonxhe Bojaxhiu, ; 26 August 1910 – 5 September 1997), better known as Mother Teresa or Saint Mother Teresa, was an Albanian-Indian Catholic Church, Roman Catholic nun, founder of the Missionaries of ...
, opened hospices in the Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village, or simply the Village, is a neighborhood on the west side of Lower Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 14th Street (Manhattan), 14th Street to the north, Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the s ...
neighborhood of New York, Washington D.C., and San Francisco in the 1980s. Individual parishes began opening hospices for AIDS patients, with the first being in New Orleans in 1985.
The bishops of the United States issued a pastoral letter in the 1980s, titled ''A Call to Compassion'', saying those with AIDS "deserve to remain within our communal consciousness and to be embraced with unconditional love." In Always Our Children, their 1997 pastoral letter on homosexuality, the American bishops noted "an importance and urgency" to minister to those with AIDS, especially considering the impact it had on the gay community. They encouraged church ministers to include prayers at Mass for those with AIDS and those who care for them, those who have died from AIDS, and all of their friends, families, and companions. They recommended special masses be said for healing with anointing of the sick or other events to take place around the time of World AIDS Day.
In 1987, the bishops of California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
issued a document saying that just as Jesus loved and healed lepers, the blind, the lame, and others, so too should Catholics care for those with AIDS. The year before, they publicly denounced Proposition 64, a measure pushed by Lyndon H. LaRouche to forcibly quarantine those with AIDS, and encouraged Catholics to vote against it. Joseph L. Bernardin, the Archbishop of Chicago, issued a 12-page policy paper in 1986 that outlined "sweeping pastoral initiatives" his archdiocese would be undertaking.
Present-day activism
An effective response to HIV/AIDS requires that groups of vulnerable populations have access to HIV prevention programs with information and services that are specific to them. In the present day, some AIDS activist groups and organizations that were established during the height of the epidemic are still present and working to assist people living with HIV/AIDS. They may offer any combination of the following: health education, counseling and support, or advocacy for law and policy. AIDS activist groups and organizations also continue to call for public awareness and support through participation in events like LGBT pride parades, World AIDS Day, and AIDS Walks.Current status
TheCenters for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
estimates at the end of 2019, there were 1,189,700 people aged 13 or older with diagnosed HIV infections in the United States and dependent areas. Since 2010, the number of people living with HIV/AIDS has increased, while the annual number of new HIV infections has declined over the past few years. In 2021, 36,136 people were newly diagnosed with HIV/AIDS, compared to 37,832 diagnosed in 2018. 67% of 2021 diagnoses were among men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM), 56% were among American early adolescents and young adults between the ages of 13 and 34, 40% were from the African-American population, and 7% were intravenous drug users.
The 2021 CDC HIV Surveillance Report estimates that 36,136 new cases of HIV infections were diagnosed in the United States in 2021, a rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population. This rate is an increase from the previous year's estimates, which indicated 30,585 new infections and a rate of 9.5 per 100,000 population. This increase has been peculiar among epidemiologists, since over the past few years before 2021, rates of HIV infections were decreasing overtime. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States
On December 31, 2019, China announced the discovery of a cluster of pneumonia cases in Wuhan. The first American case was reported on January 20, and United States Department of Health and Human Services, Health and Human Services Secreta ...
(2019–2022), many barriers have made getting tested for HIV/AIDS more difficult, with many who are racially and economically disadvantaged to have reduced resources in terms of testing.
Individuals in the 25–29 age range had the highest rates of new HIV infections, with a rate of 32.9 per 100,000. With regard to race and ethnicity, the highest rate of new HIV infections in 2017 occurred in the African-American population, with a rate of 4.5 per 100,000. This more than doubled the next highest rate of new HIV infections for a racial or ethnic group, which was the Hispanic/Latino population, with a rate of 3.2 per 100,000. The lowest rate of new HIV infections in 2021 occurred in the Asian American population, with a rate of 2.3 per 100,000.
According to CDC estimates, the most common transmission category of new HIV infections remained male-to-male sexual contact, which accounted for roughly 79% of all new infections in the United States in 2021. Among the proportion of new HIV-positive
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
gay and bisexual
Bisexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior toward both males and females. It may also be defined as the attraction to more than one gender, to people of both the same and different gender, or the attraction t ...
men in 2021, 40% are African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
, 29% are Hispanic/Latino Americans, and 25% are White Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
. With regard to region of residence, the highest rates of new infections in 2021 occurred in the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Cens ...
, with about 52% of new total cases being from the American South. The region identified as "American South" includes Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
, Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
, Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northea ...
, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, and West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
. The city of Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
has the highest HIV infection rate in the country.
According to CDC estimates, the majority of new HIV infections among White Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
occurred among adult men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM) aged 30–39, followed closely by those aged 40–49, while the majority of new HIV infections among African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
have occurred predominantly among early adolescent and young adult men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(aged 13–29). In the United States, men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM), described as gay and bisexual
Bisexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior toward both males and females. It may also be defined as the attraction to more than one gender, to people of both the same and different gender, or the attraction t ...
men, make up about 55% of the total HIV-positive population, and 83% of the estimated new HIV/AIDS diagnoses among all males aged 13 and older, and approximately 92% of new HIV/AIDS diagnoses among all men in their age group. 1 in 6 gay and bisexual men are therefore expected to be diagnosed with HIV/AIDS in their lifetime if current rates continue. The CDC estimates that more than 600,000 gay and bisexual men are currently living with HIV/AIDS in the United States. A review of four studies in which trans women
A trans woman or transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity and may experience gender dysphoria (distress brought upon by the discrepancy between a person's gender identity and their ...
in the United States were tested for HIV/AIDS found that 27.7% tested positive.
In 2015, a major HIV infection outbreak, Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
's largest-ever, occurred in two largely rural, economically depressed and poor counties in the southern portion of the state, due to the injection of a relatively new opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
-type drug called Opana (oxymorphone
Oxymorphone (sold under the brand names Numorphan and Opana among others) is a highly potent opioid analgesic indicated for treatment of severe pain. Pain relief after injection begins after about 5–10 minutes; after oral administration it ...
), which is designed be taken in pill form but is ground up and injected intravenously using needles. Because of the lack of HIV cases in that area beforehand and the youth of many but not all of those affected, the relative unavailability in the local area of treatment centers capable of dealing with long-term therapies, HIV/AIDS healthcare, and drug addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
during the initial phases of the outbreak, and political opposition to needle exchange programs, the outbreak expanded for months, resulting in up to 127 preventable cases. Under pressure, officials eventually declared a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state before, during, o ...
, but much of the damage had already been done. In 2025 Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
has cut much of the federal funding for HIV/AIDS research
HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
Transmission
A body of sc ...
, prevention and medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
.
See also
* Adult Industry Medical Health Care Foundation * AIDS Education and Training Centers * AIDS Project Los Angeles *Criminal transmission of HIV in the United States
The criminal transmission of HIV in the United States varies among jurisdictions. More than thirty of the fifty U.S. states have prosecuted HIV-positive individuals for exposing another person to HIV. State laws criminalize different behaviors and ...
* Hank M. Tavera
* Healthcare and the LGBT community
* HIV/AIDS and African Americans
** African-American LGBT community#HIV/AIDS
* Men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are men who engage in sexual activity with other men, regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity. The term was created by epidemiologists in the 1990s, to better study and communicate the spre ...
(MSM)
** ''Bugchasing
''Bugchasing'' (alternatively'' bug chasing'') is the rare practice of intentionally seeking human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection through sexual activity.
Bugchasers—those who eroticize HIV—are a subculture of barebackers, men ...
'', sexual subculture of HIV/AIDS fetishists
** '' Down-low'', sexual subculture of African-American MSM
** HIV and men who have sex with men
** Sexual practices between men
* President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief
The United States President's Emergency Plan For AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) is the global health funding by the United States to address the global HIV/AIDS Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS, epidemic and help save the lives of those suffering from the disease ...
International:
* AIDS education and training centers
* Elton John AIDS Foundation
* Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS
* HIV/AIDS activism
Activism, Socio-political activism to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS as well as to advance the Management of HIV/AIDS, effective treatment and care of people with AIDS (PWAs) has taken place in multiple locations since the 1980s. The evolution o ...
* HIV/AIDS activists
* HIV/AIDS global epidemic
* HIV/AIDS in North America
** HIV/AIDS in Atlanta
** HIV/AIDS in Canada
HIV/AIDS was first detected in Canada in 1982. In 2018, there were approximately 62,050 people living with HIV/AIDS in Canada. It was estimated that 8,300 people were living with undiagnosed HIV in 2018.
Mortality has decreased due to medical adv ...
** HIV/AIDS in New York City
References
Bibliography
# # # # #Further reading
*Document ID 5291
External links
AIDS.gov – The U.S. Federal Domestic HIV/AIDS Resource
AIDSVu.org – Interactive Map Illustrating HIV Prevalence in the United States
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hiv Aids In The United States 1960 establishments in the United States LGBTQ history in the United States