giraffes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the
 Giraffids like '' Palaeotragus'', '' Shansitherium'' and '' Samotherium'' appeared 14 mya and lived throughout Africa and Eurasia. These animals had broader skulls with reduced frontal cavities. ''Paleotragus'' resembled the okapi and may have been its ancestor. Others find that the okapi lineage diverged earlier, before ''Giraffokeryx''. ''Samotherium'' was a particularly important
Giraffids like '' Palaeotragus'', '' Shansitherium'' and '' Samotherium'' appeared 14 mya and lived throughout Africa and Eurasia. These animals had broader skulls with reduced frontal cavities. ''Paleotragus'' resembled the okapi and may have been its ancestor. Others find that the okapi lineage diverged earlier, before ''Giraffokeryx''. ''Samotherium'' was a particularly important
 The
The
 Fully grown giraffes stand tall, with males taller than females. The average weight is for an adult male and for an adult female. Despite its long neck and legs, its body is relatively short. The skin is mostly gray or tan, and can reach a thickness of . The long tail ends in a long, dark tuft of hair and is used as a defense against insects.
The
Fully grown giraffes stand tall, with males taller than females. The average weight is for an adult male and for an adult female. Despite its long neck and legs, its body is relatively short. The skin is mostly gray or tan, and can reach a thickness of . The long tail ends in a long, dark tuft of hair and is used as a defense against insects.
The
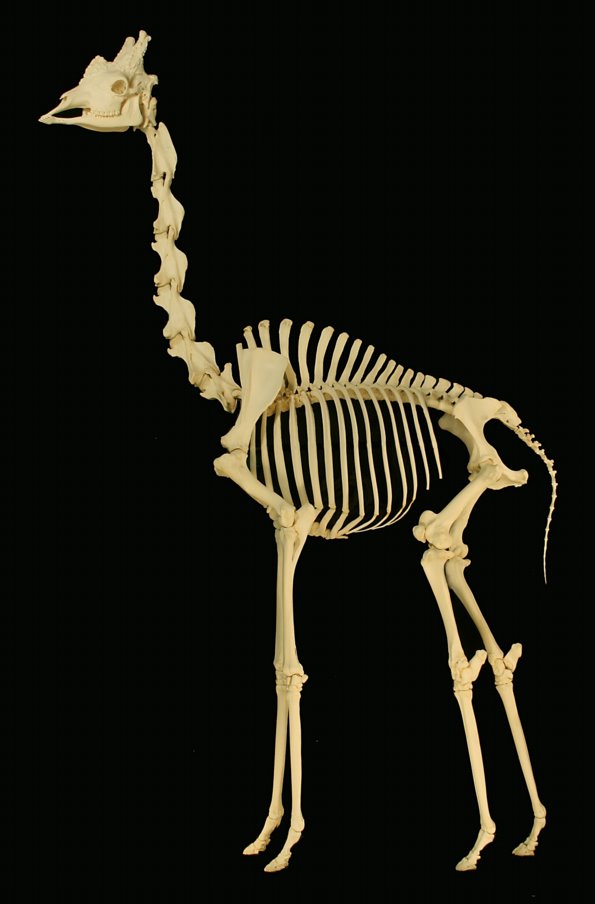
 The giraffe's neck vertebrae have
The giraffe's neck vertebrae have
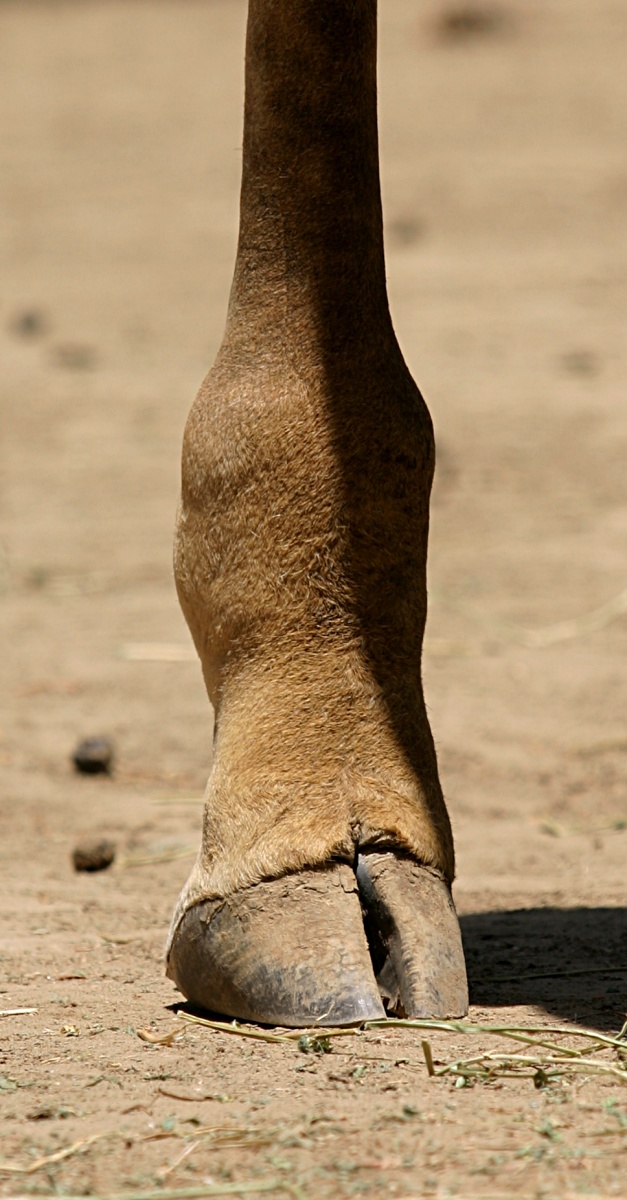 The front legs tend to be longer than the hind legs, and males have proportionally longer front legs than females, which gives them better support when swinging their necks during fights. The leg bones lack first, second and fifth metapodials. It appears that a suspensory ligament allows the lanky legs to support the animal's great weight. The hooves of large male giraffes reach in diameter. The fetlock of the leg is low to the ground, allowing the hoof to better support the animal's weight. Giraffes lack
The front legs tend to be longer than the hind legs, and males have proportionally longer front legs than females, which gives them better support when swinging their necks during fights. The leg bones lack first, second and fifth metapodials. It appears that a suspensory ligament allows the lanky legs to support the animal's great weight. The hooves of large male giraffes reach in diameter. The fetlock of the leg is low to the ground, allowing the hoof to better support the animal's weight. Giraffes lack
 In mammals, the left
In mammals, the left  The giraffe's
The giraffe's
 Male giraffes use their necks as
Male giraffes use their necks as
 Some parasites feed on giraffes. They are often hosts for ticks, especially in the area around the genitals, which have thinner skin than other areas. Tick species that commonly feed on giraffes are those of genera '' Hyalomma'', '' Amblyomma'' and '' Rhipicephalus''. Red-billed and yellow-billed oxpeckers clean giraffes of ticks and alert them to danger. Giraffes host numerous species of internal parasites and are susceptible to various diseases. They were victims of the (now eradicated) viral illness
Some parasites feed on giraffes. They are often hosts for ticks, especially in the area around the genitals, which have thinner skin than other areas. Tick species that commonly feed on giraffes are those of genera '' Hyalomma'', '' Amblyomma'' and '' Rhipicephalus''. Red-billed and yellow-billed oxpeckers clean giraffes of ticks and alert them to danger. Giraffes host numerous species of internal parasites and are susceptible to various diseases. They were victims of the (now eradicated) viral illness
 Giraffes were depicted in art throughout the African continent,. The Kiffians were responsible for a life-size rock engraving of two giraffes, dated 8,000 years ago, that has been called the "world's largest rock art petroglyph". Judging from evidence including incised clay pots, archaeologists now believe that, in the ancient Kushite societies located in
Giraffes were depicted in art throughout the African continent,. The Kiffians were responsible for a life-size rock engraving of two giraffes, dated 8,000 years ago, that has been called the "world's largest rock art petroglyph". Judging from evidence including incised clay pots, archaeologists now believe that, in the ancient Kushite societies located in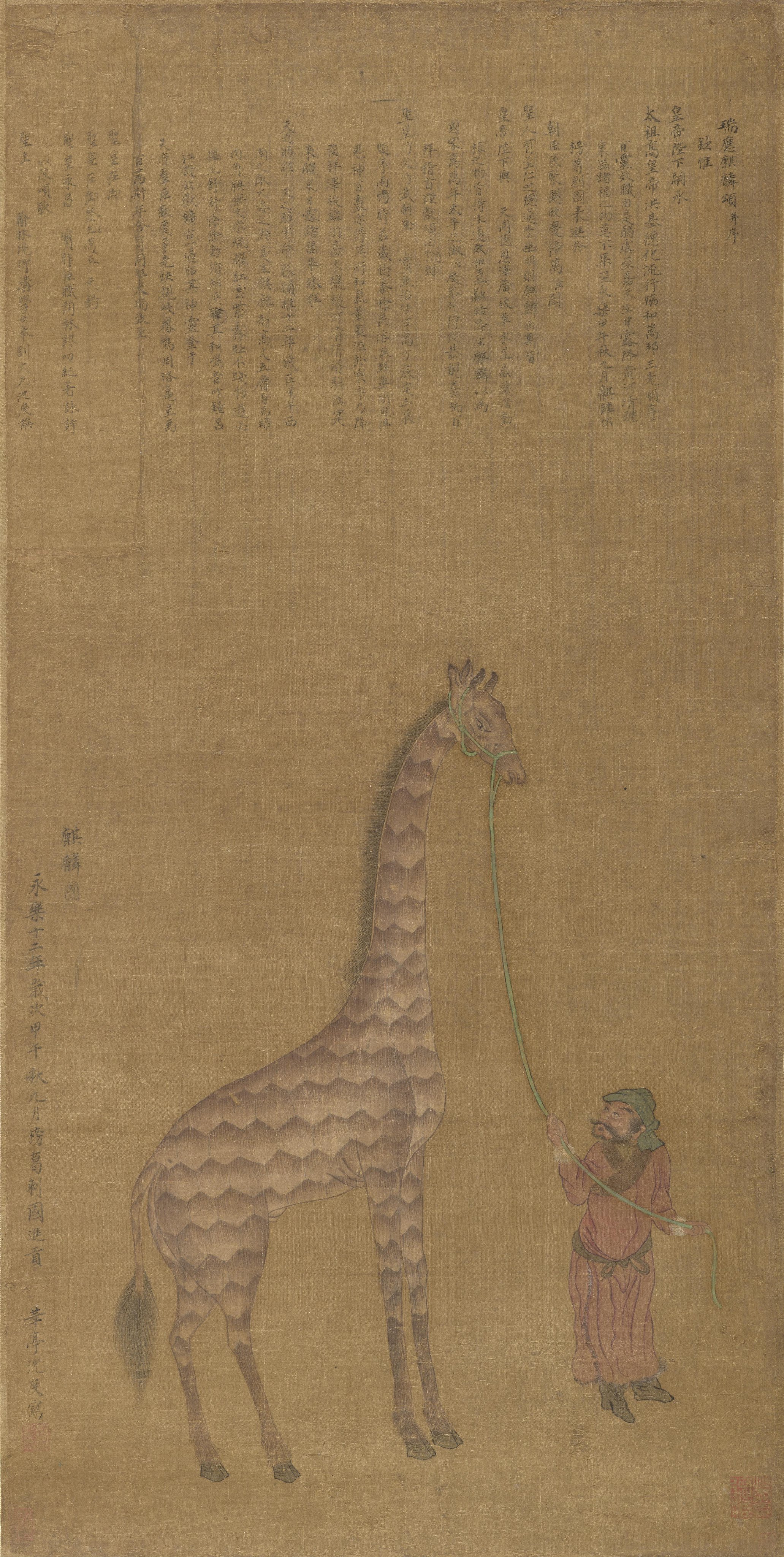 
 The primary causes for giraffe population declines are
The primary causes for giraffe population declines are
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
''Giraffa.'' It is the tallest living terrestrial animal
Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land (e.g. cats, chickens, ants, most spiders), as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water (e.g. fish, lobsters, octopuses), ...
and the largest ruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. It is classified under the family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Giraffidae, along with its closest extant relative, the okapi. Traditionally, giraffes have been thought of as one species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, '' Giraffa camelopardalis'', with nine subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
. Most recently, researchers proposed dividing them into four extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species which can be distinguished by their fur coat
A coat is typically an outer garment for the upper body, worn by any gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front, and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners (AKA velcro), ...
patterns. Six valid extinct species of ''Giraffa'' are known from the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
record.
The giraffe's distinguishing characteristics are its extremely long neck and legs, horn-like ossicones, and spotted coat patterns. Its scattered range extends from Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
in the north to South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
in the south and from Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
in the west to Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
in the east. Giraffes usually inhabit savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
s and woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
s. Their food source is leaves, fruits, and flowers of woody plants, primarily acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
species, which they browse at heights most other ground-based herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat ...
s cannot reach. Lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
s, leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
s, spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
s, and African wild dogs may prey
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not ki ...
upon giraffes. Giraffes live in herds of related females and their offspring or bachelor herds of unrelated adult males but are gregarious and may gather in large groups. Males establish social hierarchies through "necking", combat bouts where the neck is used as a weapon. Dominant males gain mating access to females, which bear sole responsibility for rearing the young.
The giraffe has intrigued various ancient and modern cultures for its peculiar appearance and has often been featured in paintings, books, and cartoons. It is classified by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
(IUCN) as vulnerable to extinction. It has been extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
from many parts of its former range. Giraffes are still found in many national park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
s and game reserve
A game reserve (also known as a game park) is a large area of land where wild animals are hunted in a controlled way for sport. If hunting is prohibited, a game reserve may be considered a nature reserve; however, the focus of a game reserve ...
s, but estimates as of 2016 indicate there are approximately 97,500 members of ''Giraffa'' in the wild. More than 1,600 were kept in zoos in 2010.
Etymology
The name "giraffe" has its earliest known origins in theArabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
word (), of an ultimately unclear Sub-Saharan African language origin. The Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
and early Modern English
Early Modern English (sometimes abbreviated EModEFor example, or EMnE) or Early New English (ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transit ...
spellings, and , derive from the Arabic form-based Spanish and Portuguese ''girafa''. The modern English form developed around 1600 from the French .
"Camelopard" () is an archaic English name for the giraffe; it derives from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
(), from (), "camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
", and (), "leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
", referring to its camel-like shape and leopard-like colouration.
Taxonomy
Evolution
The giraffe is one of only two living genera of the family Giraffidae in the orderArtiodactyla
Artiodactyls are placental mammals belonging to the order (biology), order Artiodactyla ( , ). Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes (the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof ...
, the other being the okapi. They are ruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
s of the clade Pecora
Pecora is an Order (biology), infraorder of Artiodactyla, even-toed hoofed mammals with ruminant digestion. Most members of Pecora have cranial appendages projecting from their frontal bones; only two extant genera lack them, ''Hydropotes'' and ...
, along with Antilocapridae ( pronghorns), Cervidae (deer), Bovidae
The Bovidae comprise the family (biology), biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes Bos, cattle, bison, Bubalina, buffalo, antelopes (including Caprinae, goat-antelopes), Ovis, sheep and Capra (genus), goats. A member o ...
(cattle, antelope, goats and sheep) and Moschidae (musk deer). A 2019 genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
study (cladogram below) finds that Giraffidae are a sister taxon to Antilocapridae, with an estimated split of over 20 million years ago.
The family Giraffidae was once much more extensive, with over 10 fossil genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
described. The elongation of the neck appears to have started early in the giraffe lineage. Comparisons between giraffes and their ancient relatives suggest vertebrae close to the skull lengthened earlier, followed by lengthening of vertebrae further down. One early giraffid ancestor was '' Canthumeryx'', which has been dated variously to have lived , 17–15 mya or 18–14.3 mya and whose deposits have been found in Libya. This animal resembled an antelope
The term antelope refers to numerous extant or recently extinct species of the ruminant artiodactyl family Bovidae that are indigenous to most of Africa, India, the Middle East, Central Asia, and a small area of Eastern Europe. Antelopes do ...
and had a medium-sized, lightly built body. '' Giraffokeryx'' appeared 15–12 mya on the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
and resembled an okapi or a small giraffe, and had a longer neck and similar ossicones. ''Giraffokeryx'' may have shared a clade with more massively built giraffids like '' Sivatherium'' and '' Bramatherium''.
 Giraffids like '' Palaeotragus'', '' Shansitherium'' and '' Samotherium'' appeared 14 mya and lived throughout Africa and Eurasia. These animals had broader skulls with reduced frontal cavities. ''Paleotragus'' resembled the okapi and may have been its ancestor. Others find that the okapi lineage diverged earlier, before ''Giraffokeryx''. ''Samotherium'' was a particularly important
Giraffids like '' Palaeotragus'', '' Shansitherium'' and '' Samotherium'' appeared 14 mya and lived throughout Africa and Eurasia. These animals had broader skulls with reduced frontal cavities. ''Paleotragus'' resembled the okapi and may have been its ancestor. Others find that the okapi lineage diverged earlier, before ''Giraffokeryx''. ''Samotherium'' was a particularly important transitional fossil
A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross ...
in the giraffe lineage, as the length and structure of its cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
were between those of a modern giraffe and an okapi, and its neck posture was likely similar to the former's. '' Bohlinia'', which first appeared in southeastern Europe and lived 9–7 mya, was likely a direct ancestor of the giraffe. ''Bohlinia'' closely resembled modern giraffes, having a long neck and legs and similar ossicones and dentition.
''Bohlinia'' colonised China and northern India and produced the ''Giraffa'', which, around , reached Africa. Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
s led to the extinction of the Asian giraffes, while the African giraffes survived and radiated into new species. Living giraffes appear to have arisen around in eastern Africa during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
. Some biologists suggest the modern giraffes descended from '' G. jumae''; others find '' G. gracilis'' a more likely candidate. ''G. jumae'' was larger and more robust, while ''G. gracilis'' was smaller and more slender.
The changes from extensive forests to more open habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
s, which began 8 mya, are believed to be the main driver for the evolution of giraffes. During this time, tropical plants disappeared and were replaced by arid C4 plants, and a dry savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
emerged across eastern and northern Africa and western India. Some researchers have hypothesised that this new habitat, coupled with a different diet, including acacia species, may have exposed giraffe ancestors to toxins that caused higher mutation rates and a higher rate of evolution. The coat patterns of modern giraffes may also have coincided with these habitat changes. Asian giraffes are hypothesised to have had more okapi-like colourations.
The giraffe genome is around 2.9 billion base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s in length, compared to the 3.3 billion base pairs of the okapi. Of the proteins in giraffe and okapi genes, 19.4% are identical. The divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the rate that the vector field alters the volume in an infinitesimal neighborhood of each point. (In 2D this "volume" refers to ...
of giraffe and okapi lineages dates to around 11.5 mya. A small group of regulatory genes in the giraffe appears responsible for the animal's height and associated circulatory adaptations.
Species and subspecies
 The
The International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
(IUCN) currently recognises only one species of giraffe with nine subspecies.
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
originally classified living giraffes as one species in 1758. He gave it the binomial name ''Cervus
''Cervus'' is a genus of deer that primarily are native to Eurasia, although one species occurs in northern Africa and another in North America. In addition to the species presently placed in this genus, it has included a whole range of other s ...
camelopardalis''. Mathurin Jacques Brisson
Mathurin Jacques Brisson (; 30 April 1723 – 23 June 1806) was a French zoologist and natural philosophy, natural philosopher.
Brisson was born on 30 April 1723 at Fontenay-le-Comte in the Vendée department of western France. Note that page 14 ...
coined the generic name ''Giraffa'' in 1762. During the 1900s, various taxonomies with two or three species were proposed. A 2007 study on the genetics of giraffes using mitochondrial DNA suggested at least six lineages could be recognised as species. A 2011 study using detailed analyses of the morphology of giraffes, and application of the phylogenetic species concept, described eight species of living giraffes. A 2016 study also concluded that living giraffes consist of multiple species. The researchers suggested the existence of four species, which have not exchanged genetic information between each other for one to two million years.
A 2020 study showed that depending on the method chosen, different taxonomic hypotheses recognizing from two to six species can be considered for the genus ''Giraffa''. That study also found that multi-species coalescent methods can lead to taxonomic over-splitting, as those methods delimit geographic structures rather than species. The three-species hypothesis, which recognises ''G''. ''camelopardalis'', ''G''. ''giraffa'', and ''G''. ''tippelskirchi'', is highly supported by phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
analyses and also corroborated by most population genetic and multi-species coalescent analyses. A 2021 whole genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing or just genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's ...
study suggests the existence of four distinct species and seven subspecies, which was supported by a 2024 study of cranial morphology. A 2024 study found a higher amount of ancient gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
than expected between populations.
The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
below shows the phylogenetic relationship between the four proposed species and seven subspecies based on a 2021 genome analysis. The eight lineages correspond to eight traditional subspecies in the one-species hypothesis. The Rothschild giraffe is subsumed into ''G. camelopardalis camelopardalis''.
The following table compares the different hypotheses for giraffe species. The description column shows the traditional nine subspecies in the one-species hypothesis.
The first extinct species to be described was '' Giraffa sivalensis'' from Pakistan, the holotype of which was reevaluated as a vertebra of separate species within the genus that was initially described as a fossil of the living giraffe. Another extinct species ''Giraffa punjabiensis'' is known from Pakistan. Four other valid extinct species of ''Giraffa'' known from Africa are ''Giraffa gracilis'', '' Giraffa jumae'', '' Giraffa pygmaea'' and '' Giraffa stillei''. "''G.''" ''pomeli'' from Algeria and Tunisia is not a species of Giraffinae, but a species of Palaeotraginae related to ''Mitilanotherium''.
Anatomy
 Fully grown giraffes stand tall, with males taller than females. The average weight is for an adult male and for an adult female. Despite its long neck and legs, its body is relatively short. The skin is mostly gray or tan, and can reach a thickness of . The long tail ends in a long, dark tuft of hair and is used as a defense against insects.
The
Fully grown giraffes stand tall, with males taller than females. The average weight is for an adult male and for an adult female. Despite its long neck and legs, its body is relatively short. The skin is mostly gray or tan, and can reach a thickness of . The long tail ends in a long, dark tuft of hair and is used as a defense against insects.
The coat
A coat is typically an outer garment for the upper body, worn by any gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front, and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners (AKA velcro), ...
has dark blotches or patches, which can be orange, chestnut, brown, or nearly black, surrounded by light hair, usually white or cream
Cream is a dairy product composed of the higher-fat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, the fat, which is less dense, eventually rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream, this proces ...
coloured. Male giraffes become darker as they grow old. The coat pattern has been claimed to serve as camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
in the light and shade patterns of savannah woodlands. When standing among trees and bushes, they are hard to see at even a few metres distance. However, adult giraffes move about to gain the best view of an approaching predator, relying on their size and ability to defend themselves rather than on camouflage, which may be more important for calves. Each giraffe has a unique coat pattern. Calves inherit some coat pattern traits from their mothers, and variation in some spot traits is correlated with calf survival. The skin under the blotches may regulate the animal's body temperature, being sites for complex blood vessel systems and large sweat gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial s ...
s. Spotless or solid-color giraffes are very rare, but have been observed.
The fur may give the animal chemical defense, as its parasite repellents give it a characteristic scent. At least 11 main aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugati ...
chemicals are in the fur, although indole
Indole is an organic compound with the formula . Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole ...
and 3-methylindole are responsible for most of the smell. Because males have a stronger odour than females, it may also have a sexual function.
Head
Both sexes have prominent horn-like structures called ossicones, which can reach . They are formed fromossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
, covered in skin, and fused to the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
at the parietal bone
The parietal bones ( ) are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint known as a cranial suture, form the sides and roof of the neurocranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four bord ...
s. Being vascular Vascular can refer to:
* blood vessels, the vascular system in animals
* vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex transporting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue ...
ised, the ossicones may have a role in thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, and are used in combat between males. Appearance is a reliable guide to the sex or age of a giraffe: the ossicones of females and young are thin and display tufts of hair on top, whereas those of adult males tend to be bald and knobbed on top. A lump, which is more prominent in males, emerges in the middle of the skull. Males develop calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
deposits that form bumps on their skulls as they age. Multiple sinuses lighten a giraffe's skull. However, as males age, their skulls become heavier and more club-like, helping them become more dominant in combat. The occipital condyles at the bottom of the skull allow the animal to tip its head over 90 degrees and grab food on the branches directly above them with the tongue.
With eyes located on the sides of the head, the giraffe has a broad visual field from its great height. Compared to other ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined ...
s, giraffe vision is more binocular and the eyes are larger with a greater retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
l surface area. Giraffes may see in colour, and their senses of hearing and smell are sharp. The ears are movable. The nostrils are slit-shaped, possibly to withstand blowing sand. The giraffe's tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...
is about long. It is black, perhaps to protect against sunburn, and can grasp
A grasp is an act of taking, holding or seizing firmly with (or as if with) the hand. An example of a grasp is the handshake, wherein two people grasp one of each other's like hands.
In zoology
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of an ...
foliage and delicately pick off leaves. The upper lip is flexible and hairy to protect against sharp prickles. The upper jaw has a hard palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sep ...
instead of front teeth. The molars and premolar
The premolars, also called premolar Tooth (human), teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the Canine tooth, canine and Molar (tooth), molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per dental terminology#Quadrant, quadrant in ...
s are wide with low crowns on the surface.
Neck
The giraffe has an extremely elongated neck, which can be up to in length. Along the neck is a mane made of short, erect hairs. The neck typically rests at an angle of 50–60 degrees, though juveniles are closer to 70 degrees. The long neck results from a disproportionate lengthening of thecervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
, not from the addition of more vertebrae. Each cervical vertebra is over long. They comprise 52–54 per cent of the length of the giraffe's vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
, compared with the 27–33 percent typical of similar large ungulates, including the giraffe's closest living relative, the okapi. This elongation largely takes place after birth, perhaps because giraffe mothers would have a difficult time giving birth to young with the same neck proportions as adults. The giraffe's head and neck are held up by large muscles and a nuchal ligament
The nuchal ligament is a ligament at the back of the neck that is continuous with the supraspinous ligament.
Structure
The nuchal ligament extends from the external occipital protuberance on the skull and median nuchal line to the spinous p ...
, which are anchored by long thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
spines, giving them a hump.
 The giraffe's neck vertebrae have
The giraffe's neck vertebrae have ball and socket joint
The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of ...
s. The point of articulation between the cervical and thoracic vertebrae of giraffes is shifted to lie between the first and second thoracic vertebrae (T1 and T2), unlike in most other ruminants, where the articulation is between the seventh cervical vertebra (C7) and T1. This allows C7 to contribute directly to increased neck length and has given rise to the suggestion that T1 is actually C8, and that giraffes have added an extra cervical vertebra. However, this proposition is not generally accepted, as T1 has other morphological features, such as an articulating rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
, deemed diagnostic of thoracic vertebrae, and because exceptions to the mammalian limit of seven cervical vertebrae are generally characterised by increased neurological anomalies and maladies.
There are several hypotheses regarding the evolutionary origin and maintenance of elongation in giraffe necks. Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
originally suggested the "competing browsers hypothesis", which has been challenged only recently. It suggests that competitive pressure from smaller browsers, like kudu
The kudus are two species of antelope of the genus '' Tragelaphus'':
* Lesser kudu, ''Tragelaphus imberbis'', of eastern Africa
* Greater kudu, ''Tragelaphus strepsiceros'', of eastern and southern Africa
The two species look similar, th ...
, steenbok
The steenbok (''Raphicerus campestris'') is a common small antelope of southern and eastern Africa. It is sometimes known as the steinbuck or steinbok.
Description
Steenbok resemble small oribi, standing 45–60 cm (16"–24") at the ...
and impala, encouraged the elongation of the neck, as it enabled giraffes to reach food that competitors could not. This advantage is real, as giraffes can and do feed up to high, while even quite large competitors, such as kudu, can feed up to only about high. There is also research suggesting that browsing competition is intense at lower levels, and giraffes feed more efficiently (gaining more leaf biomass with each mouthful) high in the canopy. However, scientists disagree about just how much time giraffes spend feeding at levels beyond the reach of other browsers, and a 2010 study found that adult giraffes with longer necks actually suffered higher mortality rates under drought conditions than their shorter-necked counterparts. This study suggests that maintaining a longer neck requires more nutrients, which puts longer-necked giraffes at risk during a food shortage.
Another theory, the sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ...
hypothesis, proposes that long necks evolved as a secondary sexual characteristic, giving males an advantage in "necking" contests (see below) to establish dominance and obtain access to sexually receptive females. In support of this theory, some studies have stated that necks are longer and heavier for males than females of the same age, and that males do not employ other forms of combat. However, a 2024 study found that, while males have thicker necks, females actually have proportionally longer ones, which is likely because of their greater need to find more food to sustain themselves and their dependent young. It has also been proposed that the neck serves to give the animal greater vigilance.
Legs, locomotion and posture
 The front legs tend to be longer than the hind legs, and males have proportionally longer front legs than females, which gives them better support when swinging their necks during fights. The leg bones lack first, second and fifth metapodials. It appears that a suspensory ligament allows the lanky legs to support the animal's great weight. The hooves of large male giraffes reach in diameter. The fetlock of the leg is low to the ground, allowing the hoof to better support the animal's weight. Giraffes lack
The front legs tend to be longer than the hind legs, and males have proportionally longer front legs than females, which gives them better support when swinging their necks during fights. The leg bones lack first, second and fifth metapodials. It appears that a suspensory ligament allows the lanky legs to support the animal's great weight. The hooves of large male giraffes reach in diameter. The fetlock of the leg is low to the ground, allowing the hoof to better support the animal's weight. Giraffes lack dewclaw
A dewclaw is a digit – vestigial in some animals – on the foot of many mammals, birds, and reptiles (including some extinct orders, like certain theropods). It commonly grows higher on the leg than the rest of the foot, such that in di ...
s and interdigital glands. While the pelvis is relatively short, the ilium has stretched-out crests.
A giraffe has only two gait
Gait is the pattern of Motion (physics), movement of the limb (anatomy), limbs of animals, including Gait (human), humans, during Animal locomotion, locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on s ...
s: walking and galloping. Walking is done by moving the legs on one side of the body, then doing the same on the other side. When galloping, the hind legs move around the front legs before the latter move forward, and the tail will curl up. The movements of the head and neck provide balance and control momentum while galloping. The giraffe can reach a sprint speed of up to , and can sustain for several kilometres. Giraffes would probably not be competent swimmers as their long legs would be highly cumbersome in the water, although they might be able to float. When swimming, the thorax would be weighed down by the front legs, making it difficult for the animal to move its neck and legs in harmony or keep its head above the water's surface.
A giraffe rests by lying with its body on top of its folded legs. To lie down, the animal kneels on its front legs and then lowers the rest of its body. To get back up, it first gets on its front knees and positions its backside on top of its hindlegs. It then pulls the backside upwards, and the front legs stand straight up again. At each stage, the animal swings its head for balance. If the giraffe wants to reach down to drink, it either spreads its front legs or bends its knees. Studies in captivity found the giraffe sleeps intermittently around 4.6 hours per day, mostly at night. It usually sleeps lying down; however, standing sleeps have been recorded, particularly in older individuals. Intermittent short "deep sleep" phases while lying are characterised by the giraffe bending its neck backwards and resting its head on the hip or thigh, a position believed to indicate paradoxical sleep.
Internal systems
recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recur ...
is longer than the right; in the giraffe, it is over longer. These nerves are longer in the giraffe than in any other living animal; the left nerve is over long. Each nerve cell in this path begins in the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
and passes down the neck along the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
, then branches off into the recurrent laryngeal nerve which passes back up the neck to the larynx. Thus, these nerve cells have a length of nearly in the largest giraffes. Despite its long neck and large skull, the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
of the giraffe is typical for an ungulate. Evaporative heat loss in the nasal passages keep the giraffe's brain cool. The shape of the skeleton gives the giraffe a small lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
volume relative to its mass. Its long neck gives it a large amount of dead space, though this is limited by its narrow windpipe. The giraffe also has a high tidal volume
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide.
Tidal may also refer to:
* ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple
* Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim
* TidalCycles
TidalCycles (also known as Tidal) is a live coding ...
, so the balance of dead space and tidal volume is much the same as other mammals. The animal can still provide enough oxygen for its tissues, and it can increase its respiratory rate and oxygen diffusion when running.
 The giraffe's
The giraffe's circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
has several adaptations to compensate for its great height. Its and heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
must generate approximately double the blood pressure required for a human to maintain blood flow to the brain. As such, the wall of the heart can be as thick as . Giraffes have relatively high heart rates for their size, at 150 beats per minute. When the animal lowers its head, the blood rushes down fairly unopposed and a rete mirabile in the upper neck, with its large cross-sectional area, prevents excess blood flow to the brain. When it raises again, the blood vessels constrict and push blood into the brain so the animal does not faint. The jugular veins contain several (most commonly seven) valves to prevent blood flowing back into the head from the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
and right atrium
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.
...
while the head is lowered. Conversely, the blood vessels in the lower legs are under great pressure because of the weight of fluid pressing down on them. To solve this problem, the skin of the lower legs is thick and tight, preventing too much blood from pouring into them.
Giraffes have oesophageal muscles that are strong enough to allow regurgitation of food from the stomach up the neck and into the mouth for rumination. They have four-chambered stomachs, which are adapted to their specialized diet. The intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. T ...
s of an adult giraffe measure more than in length and have a relatively small ratio of small
Small means of insignificant size
Size in general is the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or dimensions of a thing. More specifically, ''geometrical size'' (or ''spatial size'') can refer to three geometrical measures: length, area, or ...
to large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the Digestion, digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces befor ...
. The giraffe has a small, compact liver. In fetuses there may be a small gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
that vanishes before birth.
Behaviour and ecology
Habitat and feeding
Giraffes usually inhabit savannahs and openwoodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
s. They prefer areas dominated by Acacieae, ''Commiphora
''Commiphora'' is the most species-rich genus of flowering plants in the frankincense and myrrh family, Burseraceae. The genus contains approximately 190 species of shrubs and trees, which are distributed throughout the (sub-) tropical regions of A ...
'', ''Combretum
''Combretum'', the bushwillows or combretums, make up the type genus of the family Combretaceae. The genus comprises about 272 species of trees and shrubs, most of which are native to Tropics, tropical and southern Africa, about 5 to Madagascar ...
'' and '' Terminalia'' trees over '' Brachystegia'' which are more densely spaced. The Angolan giraffe can be found in desert environments. Giraffes browse on the twigs of trees, preferring those of the subfamily Acacieae and the genera ''Commiphora'' and ''Terminalia'', which are important sources of calcium and protein to sustain the giraffe's growth rate. They also feed on shrubs, grass and fruit. A giraffe eats around of plant matter daily. When stressed, giraffes may chew on large branches, stripping them of bark. Giraffes are also recorded to chew old bones.
During the wet season, food is abundant and giraffes are more spread out, while during the dry season, they gather around the remaining evergreen trees and bushes. Mothers tend to feed in open areas, presumably to make it easier to detect predators, although this may reduce their feeding efficiency. As a ruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
, the giraffe first chews its food, then swallows it for processing and then visibly passes the half-digested cud up the neck and back into the mouth to chew again. The giraffe requires less food than many other herbivores because the foliage it eats has more concentrated nutrients and it has a more efficient digestive system. The animal's faeces come in the form of small pellets. When it has access to water, a giraffe will go no more than three days without drinking.
Giraffes have a great effect on the trees that they feed on, delaying the growth of young trees for some years and giving "waistlines" to particularly tall trees. Feeding is at its highest during the first and last hours of daytime. Between these hours, giraffes mostly stand and ruminate. Rumination is the dominant activity during the night, when it is mostly done lying down.
Social life
Giraffes usually form groups that vary in size and composition according to ecological, anthropogenic, temporal, and social factors. Traditionally, the composition of these groups had been described as open and ever-changing. For research purposes, a "group" has been defined as "a collection of individuals that are less than a kilometre apart and moving in the same general direction". More recent studies have found that giraffes have long-lasting social groups or cliques based on kinship, sex or other factors, and these groups regularly associate with other groups in larger communities or sub-communities within afission–fusion society
In ethology, fission–fusion society is one in which the size and composition of the social group change as time passes and animals move throughout the environment; animals merge into a group (fusion)—e.g. sleeping in one place—or split (fissi ...
. Proximity to humans can disrupt social arrangements. Masai giraffes in Tanzania sort themselves into different subpopulations of 60–90 adult females with overlapping ranges, each of which differ in reproductive rates and calf mortality. Dispersal is male biased, and can include spatial and/or social dispersal. Adult female subpopulations are connected by males into super communities of around 300 animals.
The number of giraffes in a group can range from one up to 66 individuals. Giraffe groups tend to be sex-segregated although mixed-sex groups made of adult females and young males also occur. Female groups may be matrilineally related. Generally, females are more selective than males when deciding which individuals of the same sex they associate with. Particularly stable giraffe groups are those made of mothers and their young, which can last weeks or months. Young males also form groups and will engage in playfights. However, as they get older, males become more solitary but may also associate in pairs or with female groups. Giraffes are not territorial
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
, but they have home range
A home range is the area in which an animal lives and moves on a periodic basis. It is related to the concept of an animal's territory which is the area that is actively defended. The concept of a home range was introduced by W. H. Burt in 1943. ...
s that vary according to rainfall and proximity to human settlements. Male giraffes occasionally roam far from areas that they normally frequent.
Early biologists suggested giraffes were mute and unable to create enough air flow to vibrate their vocal fold
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when brea ...
s. This has been proved to the contrary; they have been recorded to communicate using snorts, sneezes, coughs, snores, hisses, bursts, moans, grunts, growls and flute-like sounds. During courtship, males emit loud coughs. Females call their young by bellowing. Calves will emit bleats, mooing and mewing sounds. Snorting and hissing is associated with vigilance. During nighttime, giraffes appear to hum to each other. There is some evidence that giraffes use Helmholtz resonance to create infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a Audio frequency, frequency below the lower limit of human audibility ...
. They also communicate with body language. Dominant males display to other males with an erect posture; holding the chin and head up while walking stiffly and displaying their side. The less dominant show submissiveness by dropping the head and ears, lowering the chin and fleeing.
Reproduction and parental care
Reproduction in giraffes is broadly polygamous: a few older males mate with the fertile females. Females can reproduce throughout the year and experience oestrus cycling approximately every 15 days. Female giraffes in oestrus are dispersed over space and time, so reproductive adult males adopt a strategy of roaming among female groups to seek mating opportunities, with periodic hormone-induced rutting behaviour approximately every two weeks. Males prefer young adult females over juveniles and older adults. Male giraffes assess female fertility by tasting the female's urine to detect oestrus, in a multi-step process known as the flehmen response. Once an oestrous female is detected, the male will attempt to court her. When courting, dominant males will keep subordinate ones at bay. A courting male may lick a female's tail, lay his head and neck on her body or nudge her with his ossicones. During copulation, the male stands on his hind legs with his head held up and his front legs resting on the female's sides. Giraffegestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregn ...
lasts 400–460 days, after which a single calf is normally born, although twins occur on rare occasions. The mother gives birth standing up. The calf emerges head and front legs first, having broken through the fetal membranes, and falls to the ground, severing the umbilical cord
In Placentalia, placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord i ...
. A newborn giraffe is tall. Within a few hours of birth, the calf can run around and is almost indistinguishable from a one-week-old. However, for the first one to three weeks, it spends most of its time hiding, its coat pattern providing camouflage. The ossicones, which have lain flat in the womb, raise up in a few days.
Mothers with calves will gather in nursery herds, moving or browsing together. Mothers in such a group may sometimes leave their calves with one female while they forage and drink elsewhere. This is known as a " calving pool". Calves are at risk of predation, and a mother giraffe will stand over them and kick at an approaching predator. Females watching calving pools will only alert their own young if they detect a disturbance, although the others will take notice and follow. Allo-sucking, where a calf will suckle a female other than its mother, has been recorded in both wild and captive giraffes. Calves first ruminate at four to six months and stop nursing
Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alle ...
at six to eight months. Young may not reach independence until they are 14 months old. Females are able to reproduce at four years of age, while spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
in males begins at three to four years of age. Males must wait until they are at least seven years old to gain the opportunity to mate.
Necking
weapons
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law ...
in combat, a behaviour known as "necking". Necking is used to establish dominance, and males that win necking bouts have greater reproductive success. This behaviour occurs at low or high intensity. In low-intensity necking, the combatants rub and lean on each other. The male that can keep itself more upright wins the bout. In high-intensity necking, the combatants will spread their front legs and swing their necks at each other, attempting to land blows with their ossicones. The contestants will try to dodge each other's blows and then prepare to counter. The power of a blow depends on the weight of the skull and the arc of the swing. A necking duel can last more than half an hour, depending on how well matched the combatants are. Although most fights do not lead to serious injury, there have been records of broken jaws, broken necks, and even deaths.
After a duel, it is common for two male giraffes to caress and court each other. Such interactions between males have been found to be more frequent than heterosexual coupling. In one study, up to 94 percent of observed mounting incidents took place between males. The proportion of same-sex activities varied from 30 to 75 percent. Only one percent of same-sex mounting incidents occurred between females.
Mortality and health
Giraffes have high adult survival probability, and an unusually long lifespan compared to other ruminants, up to 38 years. Adult female survival is significantly correlated with the number of social associations. Because of their size, eyesight and powerful kicks, adult giraffes are mostly safe from predation, withlion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
s being their only major threats. Calves are much more vulnerable than adults and are also preyed on by leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
s, spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
s and wild dogs. A quarter to a half of giraffe calves reach adulthood. Calf survival varies according to the season of birth, with calves born during the dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
having higher survival rates.
The local, seasonal presence of large herds of migratory wildebeests and zebra
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), the plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. ...
s reduces predation pressure on giraffe calves and increases their survival probability. In turn, it has been suggested that other ungulates may benefit from associating with giraffes, as their height allows them to spot predators from further away. Zebras were found to assess predation risk by watching giraffes and spend less time looking around when giraffes are present.
 Some parasites feed on giraffes. They are often hosts for ticks, especially in the area around the genitals, which have thinner skin than other areas. Tick species that commonly feed on giraffes are those of genera '' Hyalomma'', '' Amblyomma'' and '' Rhipicephalus''. Red-billed and yellow-billed oxpeckers clean giraffes of ticks and alert them to danger. Giraffes host numerous species of internal parasites and are susceptible to various diseases. They were victims of the (now eradicated) viral illness
Some parasites feed on giraffes. They are often hosts for ticks, especially in the area around the genitals, which have thinner skin than other areas. Tick species that commonly feed on giraffes are those of genera '' Hyalomma'', '' Amblyomma'' and '' Rhipicephalus''. Red-billed and yellow-billed oxpeckers clean giraffes of ticks and alert them to danger. Giraffes host numerous species of internal parasites and are susceptible to various diseases. They were victims of the (now eradicated) viral illness rinderpest
Rinderpest (also cattle plague or steppe murrain) was an infectious viral disease of cattle, domestic water buffalo, and many other species of even-toed ungulates, including gaurs, African Buffalo, buffaloes, large antelope, deer, giraffes, wilde ...
. Giraffes can also suffer from a skin disorder, which comes in the form of wrinkles, lesions or raw fissures. As much as 79% of giraffes have symptoms of the disease in Ruaha National Park, but it did not cause mortality in Tarangire and is less prevalent in areas with fertile soils.
Human relations
Cultural significance
With its lanky build and spotted coat, the giraffe has been a source of fascination throughout human history, and its image is widespread in culture. It has represented flexibility, far-sightedness, femininity, fragility, passivity, grace, beauty and the continent of Africa itself. Giraffes were depicted in art throughout the African continent,. The Kiffians were responsible for a life-size rock engraving of two giraffes, dated 8,000 years ago, that has been called the "world's largest rock art petroglyph". Judging from evidence including incised clay pots, archaeologists now believe that, in the ancient Kushite societies located in
Giraffes were depicted in art throughout the African continent,. The Kiffians were responsible for a life-size rock engraving of two giraffes, dated 8,000 years ago, that has been called the "world's largest rock art petroglyph". Judging from evidence including incised clay pots, archaeologists now believe that, in the ancient Kushite societies located in Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
, or what is now northern Sudan, giraffes may have featured in popular religion and women's religion, though not in elite or royal religion, and may have also had a connection to beliefs about the sun. The Tugen people of modern Kenya used the giraffe to depict their god Mda. The Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
gave the giraffe its own hieroglyph
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters. ...
; 'sr' in Old Egyptian and 'mmy' in later periods. How the giraffe got its height has been the subject of various African folktales.
Giraffes have a presence in modern Western culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompas ...
. Salvador Dalí
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol (11 May 190423 January 1989), known as Salvador Dalí ( ; ; ), was a Spanish Surrealism, surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, ...
depicted them with burning manes in some surrealist paintings. Dali considered the giraffe to be a masculine symbol. A flaming giraffe was meant to be a "masculine cosmic apocalyptic monster". Several children's books feature the giraffe, including David A. Ufer's ''The Giraffe Who Was Afraid of Heights'', Giles Andreae's ''Giraffes Can't Dance'' and Roald Dahl
Roald Dahl (13 September 1916 – 23 November 1990) was a British author of popular children's literature and short stories, a poet, screenwriter and a wartime Flying ace, fighter ace. His books have sold more than 300 million copies ...
's '' The Giraffe and the Pelly and Me''. Giraffes have appeared in animated films as minor characters in Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly referred to as simply Disney, is an American multinational mass media and entertainment industry, entertainment conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios (Burbank), Walt Di ...
's '' Dumbo'' and '' The Lion King'', and in more prominent roles in '' The Wild'' and the ''Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
'' films. Sophie the Giraffe has been a popular teether since 1961. Another famous fictional giraffe is the Toys "R" Us mascot Geoffrey the Giraffe.
The giraffe has also been used for some scientific experiments and discoveries. Scientists have used the properties of giraffe skin as a model for astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spa ...
and fighter pilot suits because the people in these professions are in danger of passing out if blood rushes to their legs. Computer scientists have modeled the coat patterns of several subspecies using reaction–diffusion mechanisms. The constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Camelopardalis, introduced in the 17th century, depicts a giraffe. The Tswana people
The Batswana (, singular ''Motswana'') are a Bantu peoples, Bantu Ethnic groups in South Africa, ethnic group native to Southern Africa that are descendants of King Looe (Lowe) who established the Hurutshi tribe in Southern Africa (linguistic ...
of Botswana traditionally see the constellation Crux
CRUX is a lightweight x86-64 Linux distribution targeted at experienced Linux users and delivered by a tar.gz-based package system with BSD-style initscripts. It is not based on any other Linux distribution. It also utilizes a ports system ...
as two giraffes— Acrux and Mimosa forming a male, and Gacrux and Delta Crucis forming the female.

Captivity
The Egyptians were among the earliest people to keep giraffes in captivity and shipped them around the Mediterranean. The giraffe was among the many animals collected and displayed by the Romans. The first one in Rome was brought in byJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
in 46 BC. With the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast ...
, the housing of giraffes in Europe declined. During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, giraffes were known to Europeans through contact with the Arabs, who revered the giraffe for its peculiar appearance.
Individual captive giraffes were given celebrity status throughout history. In 1414, a giraffe from Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban centr ...
was taken to China by explorer Zheng He
Zheng He (also romanized Cheng Ho; 1371–1433/1435) was a Chinese eunuch, admiral and diplomat from the early Ming dynasty, who is often regarded as the greatest admiral in History of China, Chinese history. Born into a Muslims, Muslim famil ...
and placed in a Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
zoo. The animal was a source of fascination for the Chinese people, who associated it with the mythical Qilin
The qilin ( ; ) is a legendary hooved chimerical creature that appears in Chinese mythology, and is said to appear with the imminent arrival or death of a sage or illustrious ruler. Qilin are a specific type of the mythological family of o ...
. The Medici giraffe was a giraffe presented to Lorenzo de' Medici
Lorenzo di Piero de' Medici (), known as Lorenzo the Magnificent (; 1 January 1449 – 9 April 1492), was an Italian statesman, the ''de facto'' ruler of the Florentine Republic, and the most powerful patron of Renaissance culture in Italy. Lore ...
in 1486. It caused a great stir on its arrival in Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
. Zarafa, another famous giraffe, was brought from Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
to Paris in the early 19th century as a gift for Charles X of France. A sensation, the giraffe was the subject of numerous memorabilia or "giraffanalia".
Giraffes have become popular attractions in modern zoos, though keeping them is difficult as they prefer large areas and need to eat large amounts of browse. Captive giraffes in North America and Europe appear to have a higher mortality rate than in the wild, the most common causes being poor husbandry, nutrition, and management. Giraffes in zoos display stereotypical behaviours, particularly the licking of inanimate objects and pacing. Zookeepers may offer various activities to stimulate giraffes, including training them to take food from visitors. Stable
A stable is a building in which working animals are kept, especially horses or oxen. The building is usually divided into stalls, and may include storage for equipment and feed.
Styles
There are many different types of stables in use tod ...
s for giraffes are built particularly high to accommodate their height.
Exploitation
Giraffes were probably common targets for hunters throughout Africa. Different parts of their bodies were used for different purposes. Their meat was used for food. The tail hairs were flyswatters, bracelets, necklaces, and threads. Shields, sandals, and drums were made using the skin, and the strings of musical instruments were from the tendons. InBuganda
Buganda is a Bantu peoples, Bantu kingdom within Uganda. The kingdom of the Baganda, Baganda people, Buganda is the largest of the List of current non-sovereign African monarchs, traditional kingdoms in present-day East Africa, consisting of Ug ...
, the smoke of burning giraffe skin was traditionally used to treat nosebleeds. The Humr people of Kordofan consume the drink Umm Nyolokh, which is prepared from the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
of giraffes. Richard Rudgley hypothesised that Umm Nyolokh might contain DMT. The drink is said to cause hallucinations of giraffes, believed to be the giraffes' ghosts, by the Humr.
Conservation status
In 2016, giraffes were assessed as Vulnerable from a conservation perspective by the IUCN. In 1985, it was estimated there were 155,000 giraffes in the wild. This declined to over 140,000 in 1999. Estimates as of 2016 indicate there are approximately 97,500 members of ''Giraffa'' in the wild. The Masai and reticulated subspecies areendangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
, and the Rothschild subspecies is near threatened
A near-threatened species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as that may be vulnerable to Endangered species, endangerment in the ne ...
. The Nubian subspecies is critically endangered
An IUCN Red List critically endangered (CR or sometimes CE) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of t ...
.
 The primary causes for giraffe population declines are
The primary causes for giraffe population declines are habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
and direct killing for bushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are Hunting, hunted for human consumption. Bushmeat represents a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity in poor and rural communities of humid tropical forest regions of the worl ...
markets. Giraffes have been extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
from much of their historic range, including Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
, Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
, Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
and Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
. They may also have disappeared from Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, and Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, but have been introduced to Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
and Eswatini
Eswatini, formally the Kingdom of Eswatini, also known by its former official names Swaziland and the Kingdom of Swaziland, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by South Africa on all sides except the northeast, where i ...
. , there were more than 1,600 in captivity at Species360-registered zoos. Habitat destruction has hurt the giraffe. In the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
, the need for firewood and grazing room for livestock has led to deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
. Normally, giraffes can coexist with livestock, since they avoid direct competition by feeding above them. In 2017, severe droughts in northern Kenya led to increased tensions over land and the killing of wildlife by herders, with giraffe populations being particularly hit.
Protected areas like national parks provide important habitat and anti-poaching
Poaching is the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set against the huntin ...
protection to giraffe populations. Community-based conservation efforts outside national parks are also effective at protecting giraffes and their habitats. Private game reserves have contributed to the preservation of giraffe populations in eastern and southern Africa. The giraffe is a protected species in most of its range. It is the national animal of Tanzania, and is protected by law, and unauthorised killing can result in imprisonment. The UN-backed Convention of Migratory Species selected giraffes for protection in 2017. In 2019, giraffes were listed under Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES
CITES (shorter acronym for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of inte ...
), which means international trade including in parts/derivatives is regulated.
Translocations are sometimes used to augment or re-establish diminished or extirpated populations, but these activities are risky and difficult to undertake using the best practices of extensive pre- and post-translocation studies and ensuring a viable founding population. Aerial survey is the most common method of monitoring giraffe population trends in the vast roadless tracts of African landscapes, but aerial methods are known to undercount giraffes. Ground-based survey methods are more accurate and can be used in conjunction with aerial surveys to make accurate estimates of population sizes and trends.
See also
*Fauna of Africa
The fauna of Africa are all the animals living in Africa and its surrounding seas and islands. The more characteristic African fauna are found in the Afrotropical realm, Afro-tropical realm. Lying almost entirely within the tropics, and stretching ...
* Giraffe Centre
* Giraffe Manor - hotel in Nairobi with giraffes
References
External links
* of the Giraffe Conservation Foundation {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Fauna of Sub-Saharan Africa Herbivorous mammals Mammal genera Mammals of Africa National symbols of Tanzania Vulnerable animals Vulnerable biota of Africa