|
Gait
Gait is the pattern of Motion (physics), movement of the limb (anatomy), limbs of animals, including Gait (human), humans, during Animal locomotion, locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to wikt:maneuver, maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gait (human)
A gait is a manner of Limb (anatomy), limb movements made during Animal locomotion, locomotion. Human gaits are the various ways in which humans can move, either naturally or as a result of specialized training. Human gait is defined as Bipedalism, bipedal Bipedal gait cycle, forward propulsion of the center of gravity of the human body, in which there are Sinuosity, sinuous movements of different segments of the body with little energy spent. Various gaits are characterized by differences in limb movement patterns, overall velocity, forces, kinetic and potential energy cycles, and changes in contact with the ground. Classification Human gaits are classified in various ways. Each gait can be generally categorized as either natural (one that humans use instinctively) or trained (a non-instinctive gait learned via training). Examples of the latter include hand walking and specialized gaits used in martial arts. Gaits can also be categorized according to whether the person remains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gait Graphs V2
Gait is the pattern of Motion (physics), movement of the limb (anatomy), limbs of animals, including Gait (human), humans, during Animal locomotion, locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to wikt:maneuver, maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
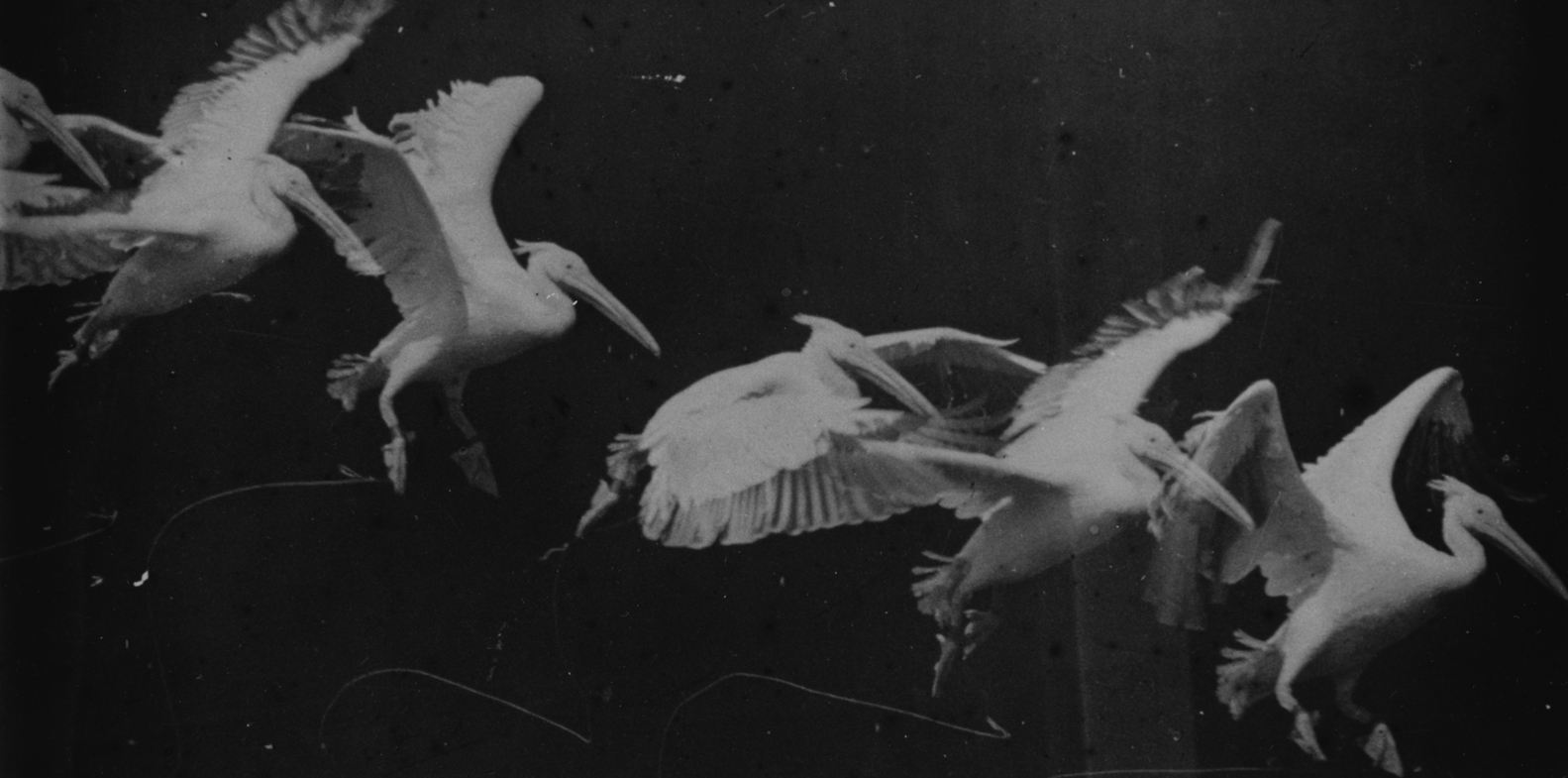
Tripod Gait
Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined as an "inverted pendulum" gait in which the body vaults over the stiff limb or limbs with each step. This applies regardless of the usable number of limbs‚ÄĒeven arthropods, with six, eight, or more limbs, walk. In humans, walking has health benefits including improved mental health and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and death. Difference from running The word ''walk'' is descended from the Old English ''wealcan'' 'to roll'. In humans and other bipeds, walking is generally distinguished from running in that only one foot at a time leaves contact with the ground and there is a period of double-support. In contrast, running begins when both feet are off the ground with each step. This distinction has the status of a formal requirement in competitive walking events. For quadrupedal specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
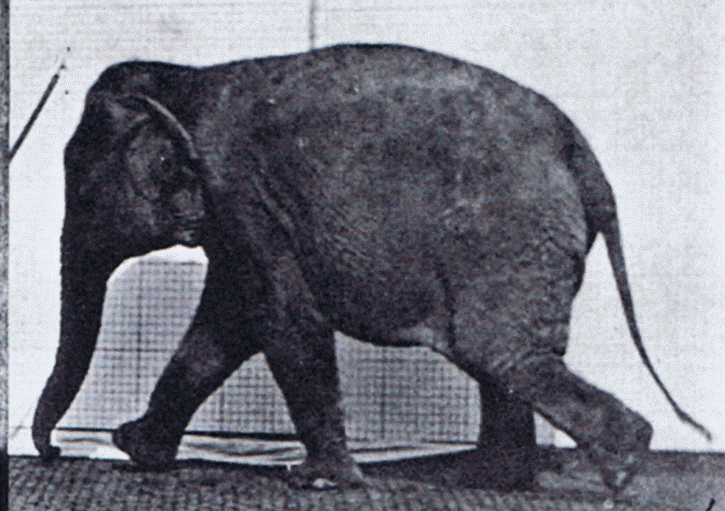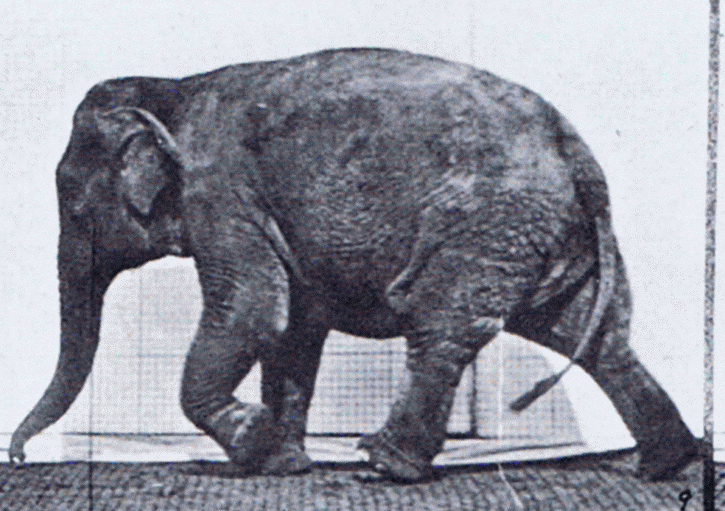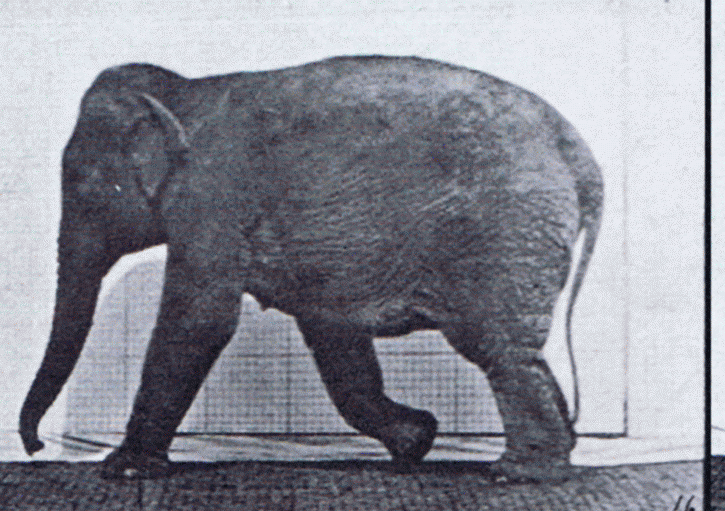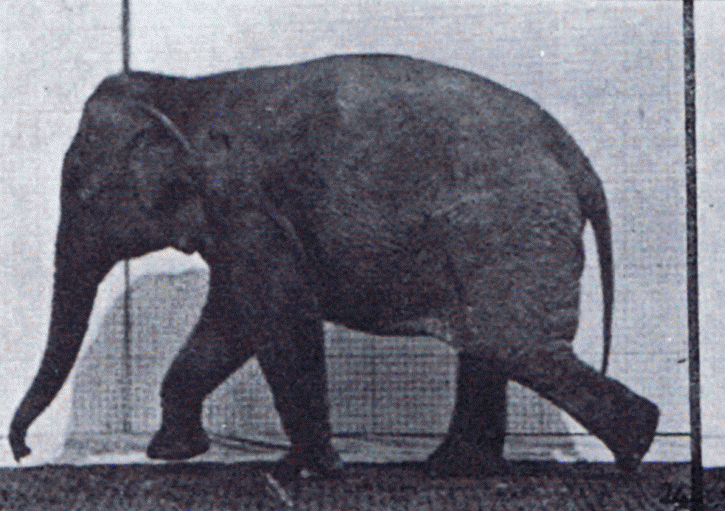
Elephant Walking
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''). They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears and convex or level backs. Elephants are scattered througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Locomotion
In ethology, animal locomotion is any of a variety of methods that animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flight, flying, hopping, soaring and gliding. There are also many animal species that depend on their environment for transportation, a type of mobility called passive locomotion, e.g., sailing (some jellyfish), ballooning (spider), kiting (spiders), rolling (some beetles and spiders) or riding other animals (phoresis). Animals move for a variety of reasons, such as to foraging, find food, a mating system, mate, a suitable microhabitat, or to escape response, escape predators. For many animals, the ability to move is essential for survival and, as a result, natural selection has shaped the locomotion methods and mechanisms used by moving organisms. For example, animal migration, migratory animals that travel vast distances (such as the Arctic tern) typically have a locomotion me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eadweard Muybridge
Eadweard Muybridge ( ; 9 April 1830 ‚Äď 8 May 1904, born Edward James Muggeridge) was an English photographer known for his pioneering work in photographic studies of motion, and early work in motion-picture Movie projector, projection. He adopted the first name "Eadweard" as the original Germanic name, Anglo-Saxon form of "Edward", and the surname "Muybridge", believing it to be similarly archaic. A photographer in the 19th century American West, he photographed Yosemite National Park, Yosemite, San Francisco, the newly acquired Alaska, Alaskan Territory, subjects involved in the Modoc War, and lighthouses on the West Coast of the United States, West Coast. He also made his early moving picture studies in California. Born in Kingston upon Thames, Surrey, England, at the age of 20 he emigrated to the United States as a bookseller, first to New York City, then to San Francisco. In 1860, he planned a return trip to Europe, but suffered serious head injuries en route in a sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
√Čtienne-Jules Marey
√Čtienne-Jules Marey (; 5 March 1830, Beaune, C√īte-d'Or ‚Äď 15 May 1904, Paris) was a French scientist, physiologist and chronophotographer. His work was significant in the development of cardiology, physical instrumentation, aviation, cinematography and the science of laboratory photography. He is widely considered to be a pioneer of photography and an influential pioneer of the history of cinema. He was also a pioneer in establishing a variety of graphical techniques for the display and interpretation of quantitative data from physiological measurement. Biography Marey started by studying blood circulation in the human body. Then he shifted to analyzing heart beats, respiration, muscles (myography), and movement of the body. To aid his studies he developed many instruments for precise measurements. For example, in 1859, in collaboration with the physiologist Auguste Chauveau and the watch manufacturer Breguet, he developed a wearable ''Sphygmograph'' to measure the puls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier's Constraint
Carrier's constraint is the observation that air-breathing vertebrates with two lungs that flex their bodies sideways during locomotion find it difficult to move and breathe at the same time, because the sideways flexing expands one lung and compresses the other, shunting stale air from lung to lung instead of expelling it completely to make room for fresh air. It was named by English paleontologist Richard Cowen for David R. Carrier, who wrote his observations on the problem in 1987. Consequences Most lizards move in short bursts, with long pauses for breath. Around the Late Triassic period, animals with Carrier's constraint were preyed on by bipedal species that evolved a more efficient stride. Solutions Workarounds Most snakes have only one lung, so Carrier's constraint does not apply. Monitor lizards increase their stamina by using bones and muscles in the throat and floor of the mouth to "gulp" air via gular pumping. Some other lizards, mainly agamids, use bipedal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathing
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or external respiration, brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where cellular respiration takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscera
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decelerating
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's second law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object ‚ÄĒ magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made ‚ÄĒ magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass. The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \mathrm). For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |