Gausebeck–Levchin Test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Completely Automated Public Turing Test to tell Computers and Humans Apart (CAPTCHA) ( ) is a type of challenge–response
 CAPTCHAs based on reading text—or other visual-perception tasks—prevent blind or
CAPTCHAs based on reading text—or other visual-perception tasks—prevent blind or
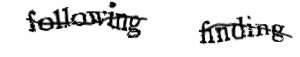 There was not a systematic methodology for designing or evaluating early CAPTCHAs. As a result, there were many instances in which CAPTCHAs were of a fixed length and therefore automated tasks could be constructed to successfully make educated guesses about where segmentation should take place. Other early CAPTCHAs contained limited sets of words, which made the test much easier to game. Still others made the mistake of relying too heavily on background confusion in the image. In each case, algorithms were created that were successfully able to complete the task by exploiting these design flaws. However, light changes to the CAPTCHA could thwart them. Modern CAPTCHAs like
There was not a systematic methodology for designing or evaluating early CAPTCHAs. As a result, there were many instances in which CAPTCHAs were of a fixed length and therefore automated tasks could be constructed to successfully make educated guesses about where segmentation should take place. Other early CAPTCHAs contained limited sets of words, which made the test much easier to game. Still others made the mistake of relying too heavily on background confusion in the image. In each case, algorithms were created that were successfully able to complete the task by exploiting these design flaws. However, light changes to the CAPTCHA could thwart them. Modern CAPTCHAs like
Telling humans and computers apart (automatically)
. ''Communications of the ACM'', 47(2):57–60.
Moni Naor, 1996.
Inaccessibility of CAPTCHA: Alternatives to Visual Turing Tests on the Web
a
CAPTCHA History
from PARC.
Reverse Engineering CAPTCHAs
Abram Hindle, Michael W. Godfrey, Richard C. Holt, 2009-08-24 {{Authority control Turing tests Internet forum terminology Computer vision 2003 neologisms 20th-century inventions Authentication Computer security Internet bots Human-based computation Social information processing
turing test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1949,. Turing wrote about the ‘imitation game’ centrally and extensively throughout his 1950 text, but apparently retired the term thereafter. He referred to ‘ iste ...
used in computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
to determine whether the user is human in order to deter bot attacks and spam.
The term was coined in 2003 by Luis von Ahn
Luis von Ahn (; born 19 August 1978) is a Guatemalan-American entrepreneur and software developer. He is the founder of the company reCAPTCHA, which was sold to Google in 2009, and the co-founder and CEO of Duolingo. For these projects and othe ...
, Manuel Blum
Manuel Blum (born 26 April 1938) is a Venezuelan-born American computer scientist who received the Turing Award in 1995 "In recognition of his contributions to the foundations of computational complexity theory and its application to cryptography ...
, Nicholas J. Hopper, and John Langford. It is a contrived acronym for "Completely Automated Public Turing test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1949,. Turing wrote about the ‘imitation game’ centrally and extensively throughout his 1950 text, but apparently retired the term thereafter. He referred to ‘ iste ...
to tell Computers and Humans Apart." A historically common type of CAPTCHA (displayed as reCAPTCHA v1
reCAPTCHA Inc. is a CAPTCHA system owned by Google. It enables web hosts to distinguish between human and automated access to websites. The original version asked users to decipher hard-to-read text or match images. Version 2 also asked users ...
) was first invented in 1997 by two groups working in parallel. This form of CAPTCHA requires entering a sequence of letters or numbers from a distorted image. Because the test is administered by a computer, in contrast to the standard Turing test that is administered by a human, CAPTCHAs are sometimes described as reverse Turing test
A reverse Turing test is a Turing test in which failure suggests that the test-taker is human, while success suggests the test-taker is automated.
Conventionally, the Turing test is conceived as having a few computer AI subjects communicate wit ...
s.
Two widely used CAPTCHA services are Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
's reCAPTCHA
reCAPTCHA Inc. is a CAPTCHA system owned by Google. It enables web hosts to distinguish between human and automated access to websites. The original version asked users to decipher hard-to-read text or match images. Version 2 also asked users ...
and the independent hCaptcha. It takes the average person approximately 10 seconds to solve a typical CAPTCHA. With the rising usage of AI, CAPTCHA scams are increasing and may be at risk of being circumvented.
Purpose
The purpose of CAPTCHAs is to prevent spam on websites, such as promotion spam, registration spam, and data scraping. Many websites use CAPTCHA effectively to prevent bot raiding. CAPTCHAs are designed so that humans can complete them, while most robots cannot. Newer CAPTCHAs look at the user's behaviour on the internet, to prove that they are a human. A normal CAPTCHA test only appears if the user acts like a bot, such as when they request webpages, or click links too fast.History
Since the 1980s–1990s, users have wanted to make text illegible to computers. The first such people werehackers
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who achieves goals and solves problems by non-standard means. The term has become associated in popular culture with a security hackersomeone with knowledge of bugs or exploits to break ...
, posting about sensitive topics to Internet forums they thought were being automatically monitored on keywords. To circumvent such filters, they replaced a word with look-alike characters. ''HELLO'' could become or , and others, such that a filter could not detect ''all'' of them. This later became known as leet
Leet (or "1337"), also known as eleet or leetspeak, or simply hacker speech, is a system of modified spellings used primarily on the Internet. It often uses character replacements in ways that play on the similarity of their glyphs via refle ...
speak.
One of the earliest commercial uses of CAPTCHAs was in the Gausebeck–Levchin test. In 2000, idrive.com began to protect its signup page with a CAPTCHA and prepared to file a patent. In 2001, PayPal
PayPal Holdings, Inc. is an American multinational financial technology company operating an online payments system in the majority of countries that support E-commerce payment system, online money transfers; it serves as an electronic alter ...
used such tests as part of a fraud prevention strategy in which they asked humans to "retype distorted text that programs have difficulty recognizing." PayPal co founder and CTO Max Levchin
Maksymilian Rafailovych "Max" Levchin (born July 11, 1975) is a Ukrainian-American software engineer and businessman. In 1998, he co-founded the company that eventually became PayPal. Levchin made contributions to PayPal's anti-fraud efforts ...
helped commercialize this use.
A popular deployment of CAPTCHA technology, reCAPTCHA
reCAPTCHA Inc. is a CAPTCHA system owned by Google. It enables web hosts to distinguish between human and automated access to websites. The original version asked users to decipher hard-to-read text or match images. Version 2 also asked users ...
, was acquired by Google in 2009. In addition to preventing bot fraud for its users, Google used reCAPTCHA and CAPTCHA technology to digitize the archives of ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' and books from Google Books in 2011.
Characteristics
CAPTCHAs are automated, requiring little human maintenance or intervention to administer, producing benefits in cost and reliability. Modern text-based CAPTCHAs are designed such that they require the simultaneous use of three separate abilities—invariant recognition, segmentation, and parsing to complete the task. * Invariant recognition refers to the ability to recognize letters despite a large amount of variation in their shapes. * Segmentation is the ability to separate one letter from another, made difficult in CAPTCHAs. * Parsing refers to the ability to understand the CAPTCHA holistically, in order to correctly identify each character. Each of these problems poses a significant challenge for a computer, even in isolation. Therefore, these three techniques in tandem make CAPTCHAs difficult for computers to solve. Whilst primarily used for security reasons, CAPTCHAs can also serve as a benchmark task for artificial intelligence technologies. According to an article by Ahn, Blum and Langford, "any program that passes the tests generated by a CAPTCHA can be used to solve a hard unsolved AI problem." They argue that the advantages of usinghard AI
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks.
Some researchers argue that sta ...
problems as a means for security are twofold. Either the problem goes unsolved and there remains a reliable method for distinguishing humans from computers, or the problem is solved and a difficult AI problem is resolved along with it.
Accessibility
 CAPTCHAs based on reading text—or other visual-perception tasks—prevent blind or
CAPTCHAs based on reading text—or other visual-perception tasks—prevent blind or visually impaired
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
users from accessing the protected resource. Because CAPTCHAs are designed to be unreadable by machines, common assistive technology
Assistive technology (AT) is a term for assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices for Disability, people with disabilities and the elderly. Disabled people often have difficulty performing activities of daily living (ADLs) independently, ...
tools such as screen readers
A screen reader is a form of assistive technology (AT) that renders text and image content as speech or braille output. Screen readers are essential to blindness, blind people, and are useful to visually impaired people, Illiteracy, illiterate, ...
cannot interpret them. The use of CAPTCHA thus excludes a small percentage of users from using significant subsets of such common Web-based services as PayPal, Gmail, Orkut, Yahoo!, many forum and weblog systems, etc. In certain jurisdictions, site owners could become targets of litigation if they are using CAPTCHAs that discriminate against certain people with disabilities. For example, a CAPTCHA may make a site incompatible with Section 508
In 1998, the U.S. Congress amended the Rehabilitation Act to require federal agencies to make their electronic and information technology accessible to people with disabilities. Section 508 was enacted to eliminate barriers in information tech ...
in the United States.
CAPTCHAs do not have to be visual. Any hard artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
problem, such as speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
, can be used as CAPTCHA. Some implementations of CAPTCHAs permit users to opt for an audio CAPTCHA, such as reCAPTCHA, though a 2011 paper demonstrated a technique for defeating the popular schemes at the time.
A method of improving CAPTCHA to ease the work with it was proposed by ProtectWebForm and named "Smart CAPTCHA". Developers are advised to combine CAPTCHA with JavaScript. Since it is hard for most bots to parse and execute JavaScript, a combinatory method which fills the CAPTCHA fields and hides both the image and the field from human eyes was proposed.
One alternative method involves displaying to the user a simple mathematical equation and requiring the user to enter the solution as verification. Although these are much easier to defeat using software, they are suitable for scenarios where graphical imagery is not appropriate, and they provide a much higher level of accessibility for blind users than the image-based CAPTCHAs. These are sometimes referred to as MAPTCHAs (M = "mathematical"). However, these may be difficult for users with a cognitive disorder, such as dyscalculia
Dyscalculia () is a learning disability resulting in difficulty learning or comprehending arithmetic, such as difficulty in understanding numbers, numeracy, learning how to manipulate numbers, performing mathematical calculations, and learning f ...
.
Challenges such as a logic puzzle, or trivia question can also be used as a CAPTCHA. There is research into their resistance against countermeasures.
Circumvention
Two main ways to bypass CAPTCHA include using cheap human labor to recognize them, and usingmachine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
to build an automated solver. According to former Google "click fraud
Click fraud is a type of ad fraud that occurs on the Internet in pay per click (PPC) online advertising. In this type of advertising, the owners of websites that post the ads are paid based on how many site visitors click on the ads. Fraud occurs ...
czar" Shuman Ghosemajumder
Shuman Ghosemajumder (born 1974) is a Canadian technologist, entrepreneur, and author. He is the former click fraud czar at Google, the author of works on technology and business including the Open Music Model, and co-founder of TeachAids. He wa ...
, there are numerous services which solve CAPTCHAs automatically.
Machine learning–based attacks
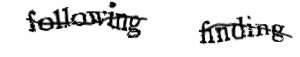 There was not a systematic methodology for designing or evaluating early CAPTCHAs. As a result, there were many instances in which CAPTCHAs were of a fixed length and therefore automated tasks could be constructed to successfully make educated guesses about where segmentation should take place. Other early CAPTCHAs contained limited sets of words, which made the test much easier to game. Still others made the mistake of relying too heavily on background confusion in the image. In each case, algorithms were created that were successfully able to complete the task by exploiting these design flaws. However, light changes to the CAPTCHA could thwart them. Modern CAPTCHAs like
There was not a systematic methodology for designing or evaluating early CAPTCHAs. As a result, there were many instances in which CAPTCHAs were of a fixed length and therefore automated tasks could be constructed to successfully make educated guesses about where segmentation should take place. Other early CAPTCHAs contained limited sets of words, which made the test much easier to game. Still others made the mistake of relying too heavily on background confusion in the image. In each case, algorithms were created that were successfully able to complete the task by exploiting these design flaws. However, light changes to the CAPTCHA could thwart them. Modern CAPTCHAs like reCAPTCHA
reCAPTCHA Inc. is a CAPTCHA system owned by Google. It enables web hosts to distinguish between human and automated access to websites. The original version asked users to decipher hard-to-read text or match images. Version 2 also asked users ...
rely on present variations of characters that are collapsed together, making them hard to segment, and they have warded off automated tasks.
In October 2013, artificial intelligence company Vicarious
Vicarious may refer to:
* Vicariousness, experiencing through another person
* Vicarious learning, observational learning
In law
* Vicarious liability, a term in common law
* Vicarious liability (criminal), a term in criminal law
Religion
* Subst ...
claimed that it had developed a generic CAPTCHA-solving algorithm that was able to solve modern CAPTCHAs with character recognition rates of up to 90%. However, Luis von Ahn
Luis von Ahn (; born 19 August 1978) is a Guatemalan-American entrepreneur and software developer. He is the founder of the company reCAPTCHA, which was sold to Google in 2009, and the co-founder and CEO of Duolingo. For these projects and othe ...
, a pioneer of early CAPTCHA and founder of reCAPTCHA, said: "It's hard for me to be impressed since I see these every few months." 50 similar claims to that of Vicarious had been made since 2003.
In August 2014 at Usenix WoOT conference, Bursztein et al. presented the first generic CAPTCHA-solving algorithm based on reinforcement learning and demonstrated its efficiency against many popular CAPTCHA schemas.
In October 2018 at ACM CCS'18 conference, Ye et al. presented a deep learning-based attack that could consistently solve all 11 text captcha schemes used by the top-50 popular websites in 2018. An effective CAPTCHA solver can be trained using as few as 500 real CAPTCHAs.
Human labor
It is possible to subvert CAPTCHAs by relaying them to asweatshop
A sweatshop or sweat factory is a cramped workplace with very poor and/or illegal working conditions, including little to no breaks, inadequate work space, insufficient lighting and ventilation, or uncomfortably or dangerously high or low temperat ...
of human operators who are employed to decode CAPTCHAs. A 2005 paper from a W3C
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working together in ...
working group said that they could verify hundreds per hour. In 2010, the University of California at San Diego
The University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego in communications material, formerly and colloquially UCSD) is a public land-grant research university in San Diego, California, United States. Established in 1960 near the pre-existing Sc ...
conducted a large scale study of CAPTCHA farms. The retail price for solving one million CAPTCHAs was as low as $1,000.
Another technique consists of using a script to re-post the target site's CAPTCHA as a CAPTCHA to the attacker's site, which unsuspecting humans visit and solve within a short while for the script to use.
In 2023, ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like re ...
tricked a TaskRabbit worker into solving a CAPTCHA by telling the worker it was not a robot and had impaired vision.
Outsourcing to paid services
There are multiple Internet companies like ''2Captcha'' and ''DeathByCaptcha'' that offer human and machine backed CAPTCHA solving services for as low as US$0.50 per 1000 solved CAPTCHAs. These services offer APIs and libraries that enable users to integrate CAPTCHA circumvention into the tools that CAPTCHAs were designed to block in the first place.Insecure implementation
Howard Yeend has identified two implementation issues with poorly designed CAPTCHA systems: reusing the session ID of a known CAPTCHA image, and CAPTCHAs residing on shared servers. Sometimes, if part of the software generating the CAPTCHA is client-side (the validation is done on a server but the text that the user is required to identify is rendered on the client side), then users can modify the client to display the un-rendered text. Some CAPTCHA systems useMD5
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. MD5 was designed by Ronald Rivest in 1991 to replace an earlier hash function MD4, and was specified in 1992 as Request for Comments, RFC 1321.
MD5 ...
hashes stored client-side, which may leave the CAPTCHA vulnerable to a brute-force attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack or exhaustive key search is a cryptanalytic attack that consists of an attacker submitting many possible keys or passwords with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. This strategy can theoretically be ...
.
Alternative CAPTCHAs
Some researchers have proposed alternatives including image recognition CAPTCHAs which require users to identify simple objects in the images presented. The argument in favor of these schemes is that tasks like object recognition are more complex to perform than text recognition and therefore should be more resilient to machine learning based attacks. Chew et al. published their work in the 7th International Information Security Conference, ISC'04, proposing three different versions of image recognition CAPTCHAs, and validating the proposal with user studies. It is suggested that one of the versions, the anomaly CAPTCHA, is best with 100% of human users being able to pass an anomaly CAPTCHA with at least 90% probability in 42 seconds. Datta et al. published their paper in the ACMMultimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms, such as Text (literary theory), writing, Sound, audio, images, animations, or video, into a single presentation. T ...
'05 Conference, named IMAGINATION (IMAge Generation for INternet AuthenticaTION), proposing a systematic way to image recognition CAPTCHAs. Images are distorted so image recognition approaches cannot recognise them.
Microsoft (Jeremy Elson, John R. Douceur, Jon Howell, and Jared Saul) claim to have developed Animal Species Image Recognition for Restricting Access (ASIRRA) which ask users to distinguish cats from dogs. Microsoft had a beta version of this for websites to use. They claim "Asirra is easy for users; it can be solved by humans 99.6% of the time in under 30 seconds. Anecdotally, users seemed to find the experience of using Asirra much more enjoyable than a text-based CAPTCHA." This solution was described in a 2007 paper to Proceedings of 14th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS). It was closed in October 2014.
See also
*Bot prevention
Bot prevention refers to the methods used by web services to prevent access by automated processes.
Types of bots
Studies suggest that over half of the traffic on the internet is bot activity, of which over half is further classified as 'bad ...
* Defense strategy (computing)
In computing, defense strategy is a concept and practice used by computer designers, users, and IT personnel to reduce computer security risks.
Common strategies
Boundary protection
Boundary protection employs security measures and devices to p ...
* Proof of personhood
Proof of personhood (PoP) is a means of resisting malicious attacks on peer to peer networks, particularly, attacks that utilize multiple fake identities, otherwise known as a Sybil attack. Decentralized online platforms are particularly vulnerable ...
* Proof of work
Proof of work (also written as proof-of-work, an abbreviated PoW) is a form of cryptographic proof in which one party (the ''prover'') proves to others (the ''verifiers'') that a certain amount of a specific computational effort has been expended ...
* reCAPTCHA
reCAPTCHA Inc. is a CAPTCHA system owned by Google. It enables web hosts to distinguish between human and automated access to websites. The original version asked users to decipher hard-to-read text or match images. Version 2 also asked users ...
References
Further references
* von Ahn, L; M. Blum and J. Langford. (2004)Telling humans and computers apart (automatically)
. ''Communications of the ACM'', 47(2):57–60.
External links
Moni Naor, 1996.
Inaccessibility of CAPTCHA: Alternatives to Visual Turing Tests on the Web
a
W3C
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working together in ...
Working Group Note.
CAPTCHA History
from PARC.
Reverse Engineering CAPTCHAs
Abram Hindle, Michael W. Godfrey, Richard C. Holt, 2009-08-24 {{Authority control Turing tests Internet forum terminology Computer vision 2003 neologisms 20th-century inventions Authentication Computer security Internet bots Human-based computation Social information processing