French Royal Domain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The

crown land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. ...
s, crown estate, royal domain or (in French) ''domaine royal'' (from demesne
A demesne ( ) or domain was all the land retained and managed by a lord of the manor under the feudal system for his own use, occupation, or support. This distinguished it from land sub-enfeoffed by him to others as sub-tenants. The concept or ...
) of France were the lands, fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an Lord, overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a for ...
s and rights directly possessed by the kings of France. While the term eventually came to refer to a territorial unit, the royal domain originally referred to the network of "castles, villages and estates, forests, towns, religious houses and bishoprics, and the rights of justice, tolls and taxes" effectively held by the king or under his domination. In terms of territory, before the reign of Henry IV, the ''domaine royal'' did not encompass the entirety of the territory of the kingdom of France and for much of the Middle Ages significant portions of the kingdom were the direct possessions of other feudal lords.
In the tenth and eleventh centuries, the first Capetians—while being the kings of France—were among the least powerful of the great feudal lords of France in terms of territory possessed. Patiently, through the use of feudal law (and, in particular, the confiscation of fiefs from rebellious vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
s), conquest, annexation, skillful marriages with heiresses of large fiefs, and even by purchase, the kings of France were able to increase the royal domain. By the time of Philip IV, the meaning of "royal domain" began to shift from a mere collection of lands and rights to a fixed territorial unit, and by the sixteenth century the "royal domain" began to coincide with the entire kingdom. However, the medieval system of appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; french: apanage ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a sovereign, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture. It was common in much o ...
(a concession of a fief with its land rights by the sovereign to his younger sons, which reverts to the crown upon the extinction of the male line of the original holder) alienated large territories from the royal domain and sometimes created dangerous rivals (especially the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
from the 14th to the 15th centuries).
During the Wars of Religion
A religious war or a war of religion, sometimes also known as a holy war ( la, sanctum bellum), is a war which is primarily caused or justified by differences in religion. In the modern period, there are frequent debates over the extent to wh ...
, the alienation of lands and fiefs from the royal domain was frequently criticized. The Edict of Moulins
Moulins (; oc, Molins) is a commune in central France, capital of the Allier department. It is located on the river Allier.
Among its many tourist attractions are the Maison Mantin, the Anne de Beaujeu Museum and The National Center of Co ...
(1566) declared that the royal domain (defined in the second article as all the land controlled by the crown for more than ten years) could not be alienated, except in two cases: by interlocking, in the case of financial emergency, with a perpetual option to repurchase the land; and to form an appanage, which must return to the crown in its original state on the extinction of the male line.
Traditionally, the king was expected to survive from the revenues generated from the royal domain, but fiscal necessity, especially in times of war, led the kings to enact "exceptional" taxes, like the ''taille
The ''taille'' () was a direct land tax on the French peasantry and non-nobles in ''Ancien Régime'' France. The tax was imposed on each household and was based on how much land it held, and was directly paid to the state.
History
Originally o ...
'', upon the whole of the kingdom (the ''taille'' became permanent in 1439).
Chronology of the formation of the royal domain

House of Capet
Reign of Hugh Capet
At the beginning ofHugh Capet
Hugh Capet (; french: Hugues Capet ; c. 939 – 14 October 996) was the King of the Franks from 987 to 996. He is the founder and first king from the House of Capet. The son of the powerful duke Hugh the Great and his wife Hedwige of Saxony, ...
's reign, the crown estate was extremely small and consisted essentially of scattered possessions in the Île-de-France
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 = +01:00
, timezone1_DST = CEST
, utc_offset1_DST = +02:00
, blank_name_sec1 = Gross regional product
, blank_info_sec1 = Ranked 1st
, bla ...
and Orléanais
The Duchy of Orléanais () is a former province of France, which was created during the Renaissance by merging four former counties and towns. However after the French Revolution, the province was dissolved in 1791 and succeeded by five ''départm ...
regions (Senlis
Senlis () is a commune in the northern French department of Oise, Hautes de France.
The monarchs of the early French dynasties lived in Senlis, attracted by the proximity of the Chantilly forest. It is known for its Gothic cathedral and other ...
, Poissy
Poissy () is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, from the centre of Paris. Inhabitants are called ''Pisciacais'' in French.
Poissy is one of ...
, Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and Attigny. These lands were largely the inheritance of the
 * 1034: the king gives the
* 1034: the king gives the
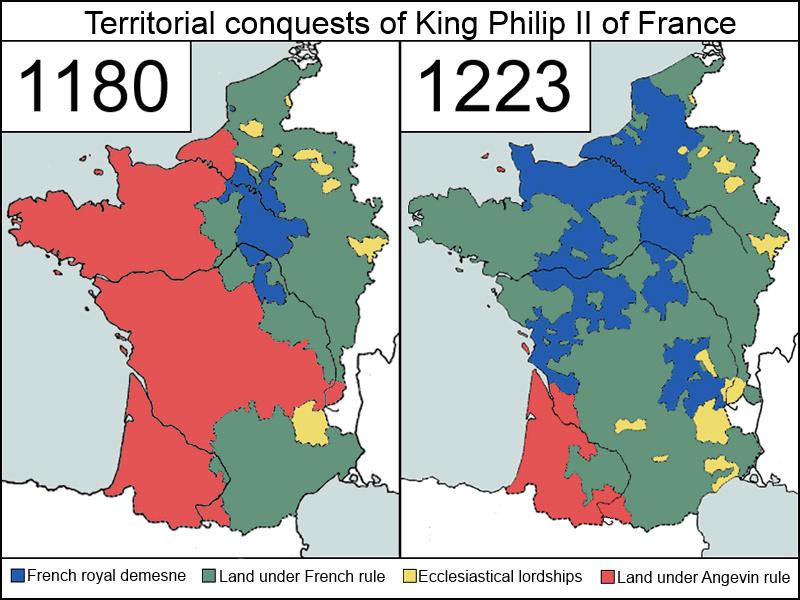 * 1184: granted
* 1184: granted
 *1392: the appanage of
*1392: the appanage of
 * 1461–1472: the king gives the
* 1461–1472: the king gives the
(US) and Attigny. These lands were largely the inheritance of the
Robertians
The Robertians (sometimes called the Robertines in modern scholarship) are the proposed Frankish family which was ancestral to the Capetian dynasty, and thus to the royal families of France and of many other countries. The Capetians appear first ...
, the direct ancestors of the Capetians.
* 988: Montreuil-sur-Mer
Montreuil (; also nl, Monsterole), also known as Montreuil-sur-Mer (; pcd, Montreu-su-Mér or , literally ''Montreuil on Sea''), is a sub-prefecture in the Pas-de-Calais department, northern France. It is located on the Canche river, not far fr ...
, the first port held by the Capetians, is acquired through the marriage of the crown prince Robert (future Robert II the Pious) with Rozala, the widow of the Arnulf II, Count of Flanders
Arnulf II (960 or 961 – 30 March 987) was Count of Flanders from 965 until his death.
Life
He was the son of Baldwin III of Flanders and Mathilde Billung of Saxony, daughter of Herman, Duke of Saxony.Detlev Schwennicke, '' Europäische Stammt ...
.
Reign of Robert II
*1016: acquisition of theDuchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
. The king was the nephew of Duke Henry of Burgundy, who died without heirs.
* Robert gains the counties of Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, Dreux
Dreux () is a commune in the Eure-et-Loir department in northern France.
Geography
Dreux lies on the small river Blaise, a tributary of the Eure, about 35 km north of Chartres. Dreux station has rail connections to Argentan, Paris and Granvi ...
and Melun
Melun () is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region, north-central France. It is located on the southeastern outskirts of Paris, about from the centre of the capital. Melun is the prefecture of the Seine-et-Ma ...
, and negotiates the ultimate acquisition (1055) of a part of Sens
Sens () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yonne Departments of France, department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France, 120 km from Paris.
Sens is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture and the second city of the d ...
.
Reign of
Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the ...
Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
to his brother Robert
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
(the duchy would remain with his descendants until 1361; see House of Burgundy
The House of Burgundy () was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty, descending from Robert I, Duke of Burgundy, a younger son of King Robert II of France. The House ruled the Duchy of Burgundy from 1032–1361 and achieved the recognized title ...
)
* 1055: annexation of the County of Sens.
Reign of
Philip I Philip(p) I may refer to:
* Philip I of Macedon (7th century BC)
* Philip I Philadelphus (between 124 and 109 BC–83 or 75 BC)
* Philip the Arab (c. 204–249), Roman Emperor
* Philip I of France (1052–1108)
* Philip I (archbishop of Cologne) (1 ...
* 1068: acquisition of Gâtinais
Gâtinais () or Gâtine () was a province of France, containing the area around the valley of the Loing, corresponding roughly to the northeastern part of the département of Loiret, and the south of the present department of Seine-et-Marne. Unde ...
and Château-Landon
Château-Landon () is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. The commune contains within it the Souppes-sur-Loing quarry, where the bright white travertine stones for construction of the ...
from Fulk IV, Count of Anjou Fulk is an old European personal name, probably deriving from the Germanic ''folk'' ("people" or "chieftain"). It is cognate with the French Foulques, the German Volk, the Italian Fulco and the Swedish Folke, along with other variants such as F ...
* 1077: annexation of the French Vexin
Vexin () is an historical county of northwestern France. It covers a verdant plateau on the right bank (north) of the Seine running roughly east to west between Pontoise and Romilly-sur-Andelle (about 20 km from Rouen), and north to south ...
* 1081: acquisition of Moret-sur-Loing
Moret-sur-Loing (, literally ''Moret on Loing'') is a former commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. It is situated on the river Loing, close to its confluence with the Seine. Moret–Veneu ...
* 1101: acquisition of the Viscounty of Bourges
Bourges () is a commune in central France on the river Yèvre. It is the capital of the department of Cher, and also was the capital city of the former province of Berry.
History
The name of the commune derives either from the Bituriges, t ...
and the ''seigneury
''Seigneur'' is an originally feudal title in France before the Revolution, in New France and British North America until 1854, and in the Channel Islands to this day. A seigneur refers to the person or collective who owned a ''seigneurie'' (o ...
'' of Dun-sur-Auron
Dun-sur-Auron (, literally ''Dun on Auron'') is a commune in the Cher department in the Centre-Val de Loire region of France.
Geography
A farming area comprising a small town and a couple of hamlets situated by the banks of both the Auron and ...
from Odo Arpin of Bourges
Reign of Louis VI
* the king spends much of his reign pacifying and consolidating the royal domain by battling certain feudal lords (lords ofMontlhéry
Montlhéry () is a Communes of France, commune in the Essonne Departments of France, department in Île-de-France in northern France. It is located from Paris.
History
Montlhéry lay on the strategically important road from Paris to Orléans. U ...
, of Coucy, of Puiset, of Crécy...)
* from Fulk, Viscount of Gâtinais
Gâtinais () or Gâtine () was a province of France, containing the area around the valley of the Loing, corresponding roughly to the northeastern part of the département of Loiret, and the south of the present department of Seine-et-Marne. Unde ...
, Louis bought Moret, Le Châtelet-en-Brie
Le Châtelet-en-Brie () is a Communes of France, commune in the Seine-et-Marne Departments of France, department in the Île-de-France Regions of France, region in north-central France.
Demographics
The inhabitants are called ''Châtelains''.
Se ...
, Boësses, Yèvre-le-Châtel and Chambon
A chambon is a piece of horse tack. It is a strap that runs forward from the bottom of the girth or surcingle, and forks. The forks continue to a ring on either side of the bridle or halter, at the base of the crownpiece. Running through those ...
.
*Other additions to the royal domain include: Montlhéry
Montlhéry () is a Communes of France, commune in the Essonne Departments of France, department in Île-de-France in northern France. It is located from Paris.
History
Montlhéry lay on the strategically important road from Paris to Orléans. U ...
and Châteaufort, Chevreuse
Chevreuse () is a commune in the French department of Yvelines, administrative region of Île-de-France, north-central France.
Geography
Chevreuse is located south of Paris, in the middle of a regional natural park, Parc naturel régional de l ...
, Corbeil Corbeil may refer to:
Places
* Corbeil, Ontario, Canada
* Corbeil, Marne, a commune in the Marne département in north-eastern France
* Corbeil-Cerf, a commune in the département of Oise in northern France
* Corbeil-Essonnes, a commune in the so ...
, Meung-sur-Loire
Meung-sur-Loire () is a commune in the Loiret department, north-central France.
It was the site of the Battle of Meung-sur-Loire in 1429.
Geography
Meung-sur-Loire lies 15 km to the west of Orléans on the north bank of the river Loire at ...
, Châteaurenard
Châteaurenard (; Provençal oc, Castèurainard; ) is a commune in the Arles arrondissement, in the Bouches-du-Rhône department, in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, in southern France.
Population
Twin towns
Châteaurenard is twinne ...
and Saint-Brisson.
Reign of Louis VII
* 1137: marriage of Louis withEleanor of Aquitaine
Eleanor ( – 1 April 1204; french: Aliénor d'Aquitaine, ) was Queen of France from 1137 to 1152 as the wife of King Louis VII, Queen of England from 1154 to 1189 as the wife of King Henry II, and Duchess of Aquitaine in her own right from ...
, Duchess of Aquitaine and Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
and Countess of Poitou. By this marriage, Louis hopes to attach most of South-West France to the royal domain.
* 1137: Louis gives Dreux
Dreux () is a commune in the Eure-et-Loir department in northern France.
Geography
Dreux lies on the small river Blaise, a tributary of the Eure, about 35 km north of Chartres. Dreux station has rail connections to Argentan, Paris and Granvi ...
to his brother Robert
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
.
* 1151: separation of Louis VII and of Eleanor of Aquitaine, who in 1152 weds Henry Plantagenet, Count of Anjou
The Count of Anjou was the ruler of the County of Anjou, first granted by Charles the Bald in the 9th century to Robert the Strong. Ingelger and his son, Fulk the Red, were viscounts until Fulk assumed the title of Count of Anjou. The Robertians ...
, Count of Maine
This is a list of counts and dukes of Maine. The capital of Maine was Le Mans. In the thirteenth century it was annexed by France to the royal domain.
Dukes of Maine (''duces Cenomannici'')
* Charivius ( fl. 723) – appears as ''dux'' in a docu ...
and Duke of Normandy
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western Kingdom of France, France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles the Simple, Charles III in ...
, who becomes in 1154, King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiw ...
. Eleanor's lands come to Henry in her dowry.
* 1160: gives Norman Vexin
Vexin () is an historical county of northwestern France. It covers a verdant plateau on the right bank (north) of the Seine running roughly east to west between Pontoise and Romilly-sur-Andelle (about 20 km from Rouen), and north to south ...
to his daughter Margaret
Margaret is a female first name, derived via French () and Latin () from grc, μαργαρίτης () meaning "pearl". The Greek is borrowed from Persian.
Margaret has been an English name since the 11th century, and remained popular througho ...
as a dowry. Margaret is later forced to surrender her dowry.
Reign of
Philip II Augustus
Philip II (21 August 1165 – 14 July 1223), byname Philip Augustus (french: Philippe Auguste), was King of France from 1180 to 1223. His predecessors had been known as kings of the Franks, but from 1190 onward, Philip became the first French ...
 * 1184: granted
* 1184: granted Montargis
Montargis () is a communes of France, commune in the Loiret Departments of France, department, Centre-Val de Loire, France.
Montargis is the seventh most populous commune in the Loiret, after Orléans and its suburbs. It is near a large forest, ...
.
* 1185: by the Treaty of Boves, gains Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of ...
and Montdidier, Roye, Choisy-au-Bac, and Thourotte
Thourotte () is a commune in the Oise department in northern France.
See also
* Communes of the Oise department
The following is a list of the 679 communes of the Oise department of France.
The communes cooperate in the following intercommu ...
and rights to the inheritance of Vermandois and Valois.
* 1187: seizes Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Euromet ...
from the bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
.
* confiscates Meulan
Meulan-en-Yvelines (; formerly just ''Meulan'') is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. It hosted part of the sailing events for the 1900 Summer Olympics held in neighboring Paris, and would d ...
, Gisors
Gisors () is a Communes of France, commune of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy, France. It is located northwest from the Kilometre Zero, centre of Paris.
Gisors, together with the neighbouring communes of Trie-Château and Trie-la-Vill ...
, and other castles.
* 1191: at the death of Philip of Alsace, Count of Flanders, the County of Artois
The County of Artois (, ) was a historic province of the Kingdom of France, held by the Dukes of Burgundy from 1384 until 1477/82, and a state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1493 until 1659.
Present Artois lies in northern France, on the border ...
and its dependencies, the inheritance of the queen Isabelle of Hainaut
Isabella of Hainault (5 April 1170 – 15 March 1190) (Also spelled: Ysabella de Hainault, Ysabelle de Hainaut or Ysabeau de Hainaut) was a Queen of France as the first wife of King Philip II. She was also formally ruling Countess of Artois ''de ...
, are given to prince Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
. These areas would not become integrated into the royal domain until 1223 when Louis becomes king.
* 1191: the County of Vermandois
Vermandois was a kingdom of France, French county that appeared in the Merovingian dynasty, Merovingian period. Its name derives from that of an ancient tribe, the Viromandui. In the 10th century, it was organised around two castellan domains: S ...
is acquired by the king, after the death of Elisabeth of Vermandois
Elisabeth (French: ''Élisabeth''), also known as Isabelle Mabille (1143 – Arras, 28 March 1183), was ruling Count of Vermandois, Countess of Vermandois from 1168 to 1183, and also List of countesses of Flanders by marriage, Countess of Flanders ...
, the inheritor of the County. Confirmed in 1213, by Eléonore of Vermandois sister of Elisabeth. Philip also gains Valois.
* 1200: the Norman Vexin
Vexin () is an historical county of northwestern France. It covers a verdant plateau on the right bank (north) of the Seine running roughly east to west between Pontoise and Romilly-sur-Andelle (about 20 km from Rouen), and north to south ...
is annexed
* 1200 the County of Évreux
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
and Issoudun
Issoudun () is a commune in the Indre department, administrative region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is also referred to as ''Issoundun'', which is the ancient name.
Geography Location
Issoudun is a sub-prefecture, located in the east o ...
are annexed, in exchange for the king's recognition of John of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Emp ...
as king of England.
* 1204: confiscation of the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
, the Touraine
Touraine (; ) is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher, Indre and Vie ...
, Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
, Saintonge
Saintonge may refer to:
*County of Saintonge, a historical province of France on the Atlantic coast
*Saintonge (region), a region of France corresponding to the historical province
Places
*Saint-Genis-de-Saintonge, a commune in the Charente-Mari ...
and, temporarily, of the Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
from John of England.
* 1208: La Ferté-Macé
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figur ...
confiscated from Guillaume IV of Ferté-Macé
* 1220: the County of Alençon
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
is reunited to the royal domain in the absence of a male heir to Count Robert IV (the county is sold by the vicomtesse of Châtellerault).
Reign of
Louis VIII
Louis VIII (5 September 1187 – 8 November 1226), nicknamed The Lion (french: Le Lion), was King of France from 1223 to 1226. As prince, he invaded England on 21 May 1216 and was excommunicated by a papal legate on 29 May 1216. On 2 June 1216 ...
* 1223: Philip Hurepel
Philip I of Boulogne (Philip Hurepel) (1200–1235) was a French prince, Count of Clermont-en-Beauvaisis in his own right, and Count of Boulogne, Mortain, Aumale, and Dammartin-en-Goële ''jure uxoris''.
Philip was born in September 1200, the son ...
, half-brother of the king, received in appanage the Counties of Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
(Boulogne-sur-Mer
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
), and of Clermont (Clermont-en-Beauvaisis
Clermont () is a commune in the Oise department in northern France. Clermont-de-l'Oise station has rail connections to Amiens, Creil and Paris.
History
Clermont was also known as Clermont-en-Beauvaisis or Clermont-de-l'Oise. The town is built ...
), as well as the fiefs of Domfront, Mortain
Mortain () is a former commune in the Manche department in Normandy in north-western France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Mortain-Bocage.
Geography
Mortain is situated on a rocky hill rising above the gorge of the C ...
and Aumale
Aumale (), formerly known as Albemarle," is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region in north-western France. It lies on the River Bresle.
History
The town's Latin name was ''Alba Marla''. It was raised by William th ...
.
* Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
, Saintonge
Saintonge may refer to:
*County of Saintonge, a historical province of France on the Atlantic coast
*Saintonge (region), a region of France corresponding to the historical province
Places
*Saint-Genis-de-Saintonge, a commune in the Charente-Mari ...
, Angoumois
Angoumois (), historically the County of Angoulême, was a county and province of France, originally inferior to the parent duchy of Aquitaine, similar to the Périgord to its east but lower and generally less forested, equally with occasional vin ...
, Périgord
Périgord ( , ; ; oc, Peiregòrd / ) is a natural region and former province of France, which corresponds roughly to the current Dordogne department, now forming the northern part of the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is div ...
and a part of the Bordelais were confiscated from the king of England.
* following the Albigensian Crusade
The Albigensian Crusade or the Cathar Crusade (; 1209–1229) was a military and ideological campaign initiated by Pope Innocent III to eliminate Catharism in Languedoc, southern France. The Crusade was prosecuted primarily by the French crown ...
(1209–1229) against the Cathars
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Fol ...
and the Count of Toulouse
The count of Toulouse ( oc, comte de Tolosa, french: comte de Toulouse) was the ruler of county of Toulouse, Toulouse during the 8th to 13th centuries. Originating as vassals of the kingdom of the Franks, Frankish kings,
the hereditary counts ru ...
, the king annexed the County of Toulouse
The County of Toulouse ( oc, Comtat de Tolosa) was a territory in southern France consisting of the city of Toulouse and its environs, ruled by the Count of Toulouse from the late 9th century until the late 13th century.
The territory is the ...
the heiress of which, Joan of Toulouse
Joan (1220 – 25 August 1271) was Count of Toulouse, Countess of Toulouse from 1249 until her death. She was the only child of Raymond VII, Count of Toulouse by his first wife Sancha of Aragon, Countess of Toulouse.
Biography
Joan was born at th ...
, married Alphonse, Count of Poitou, son of the king, in 1237.
* 1225: in his will, Louis grants the appanages of Artois
Artois ( ; ; nl, Artesië; English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht'') ...
and his mother's inheritance to his second son Robert; Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
and Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auverg ...
to his third son Alphonse; and Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
and Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
to his fourth son John (due to John's death, these possessions would go to Louis' seventh son Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
).
Reign of
Louis IX
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the d ...
* 1229: Raymond VII, Count of Toulouse
Raymond VII (July 1197 – 27 September 1249) was Count of Toulouse, Duke of Narbonne and Marquis of Provence from 1222 until his death.
Family and marriages
Raymond was born at the Château de Beaucaire, the son of Raymond VI of Toulouse ...
cedes to the king the ''sénéchaussées'' of Nîmes
Nîmes ( , ; oc, Nimes ; Latin: ''Nemausus'') is the prefecture of the Gard department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. Located between the Mediterranean Sea and Cévennes, the commune of Nîmes has an estimated population of 148,5 ...
– Beaucaire and of Béziers
Béziers (; oc, Besièrs) is a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Hérault Departments of France, department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region of Southern France. Every August Béziers hos ...
–Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
(Treaty of Paris (1229)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as Treaty of Meaux, was signed on 12 April 1229 between Raymond VII of Toulouse and Louis IX of France in Meaux near Paris. Louis was still a minor, and it was his mother Blanche of Castile, as regent, who was inst ...
)
* 1237: the king confirms the appanage grant of the County of Artois
The County of Artois (, ) was a historic province of the Kingdom of France, held by the Dukes of Burgundy from 1384 until 1477/82, and a state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1493 until 1659.
Present Artois lies in northern France, on the border ...
for his brother Robert I of Artois
Robert I (25 September 1216 – 8 February 1250), called the Good, was the first Count of Artois. He was the fifth (and second surviving) son of King Louis VIII of France and Blanche of Castile.
Life
He received Artois as an appanage, in accordan ...
.
* 1241: the king confirms the appanage grant of Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
for his brother Alfonso, Count of Poitou.
* 1249: Alfonso, Count of Poitou, by right of his wife succeeds Raymond VII of Toulouse.
* 1255: the County of Beaumont-le-Roger
Beaumont-le-Roger () is a commune in the department of Eure in Normandy region in northern France.
Geography
The commune is located in the valley of the Risle on the edge of the forest with which it shares its name. It is crossed by the Pari ...
is bought back from Raoul of Meulan.
* 1258: the king renounces the Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; ca, Rosselló ; oc, Rosselhon ) is a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of the reg ...
and Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the north ...
; in exchange the king of Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
renounces Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
and Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (; , ; oc, Lengadòc ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately ...
(Treaty of Corbeil (1258)
The Treaty of Corbeil was an agreement signed on 11 May 1258, in Corbeil (today Corbeil-Essonnes, in the region of Île-de-France) between Louis IX of France and James I of Aragon.
The French king, as the heir of Charlemagne, renounced the claims ...
)
* 1259: seigneuries of Domfront and of Tinchebray
Tinchebray () is a former commune in the Orne department in the Lower Normandy region in north-western France. On 1 January 2015, Tinchebray and six other communes merged becoming one commune called Tinchebray-Bocage.
History
It was the scene of ...
acquired.
* 1259: the king gives to the king of England Henry III the Duchy of Aquitaine
The Duchy of Aquitaine ( oc, Ducat d'Aquitània, ; french: Duché d'Aquitaine, ) was a historical fiefdom in western, central, and southern areas of present-day France to the south of the river Loire, although its extent, as well as its name, fluc ...
, and promises him Saintonge
Saintonge may refer to:
*County of Saintonge, a historical province of France on the Atlantic coast
*Saintonge (region), a region of France corresponding to the historical province
Places
*Saint-Genis-de-Saintonge, a commune in the Charente-Mari ...
, Charente
Charente (; Saintongese: ''Chérente''; oc, Charanta ) is a department in the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine, south western France. It is named after the river Charente, the most important and longest river in the department, an ...
and Agenais
Agenais (), or Agenois (), was an ancient region that became a county (Old French: ''conté'' or ''cunté'') of France, south of Périgord.Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Agenais". '' Webster's Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. 9th ed. Sprin ...
in the case of the death without heir of the Count of Toulouse Alfonso of Poitiers (Treaty of Paris (1259)
The Treaty of Paris (also known as the Treaty of Albeville) was a treaty between Louis IX of France and Henry III of England, agreed to on 4 December 1259, ending 100 years of conflicts between the Capetian and Plantagenet dynasties.
History
...
)
* 1268 the king gives the County of Alençon
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
and Perche
Perche () (French: ''le Perche'') is a former province of France, known historically for its forests and, for the past two centuries, for the Percheron draft horse breed. Until the French Revolution, Perche was bounded by four ancient territorie ...
to his son Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a sur ...
.
* the king grants as appanage the County of Valois
The Valois ( , also , ; originally ''Pagus Valensis'') was a region in the valley of the Oise river in Picardy in the north of France. It was a fief in West Francia and subsequently the Kingdom of France until its counts furnished a line of king ...
to his son John Tristan and Clermont-en-Beauvaisis
Clermont () is a commune in the Oise department in northern France. Clermont-de-l'Oise station has rail connections to Amiens, Creil and Paris.
History
Clermont was also known as Clermont-en-Beauvaisis or Clermont-de-l'Oise. The town is built ...
to his son Robert.
Reign of Philip III
* 1271: reversion of the County of Toulouse,Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
and Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auverg ...
, the Comtat Venaissin
The Comtat Venaissin (; Provençal: , Mistralian norm: , classical norm: ; 'County of Venaissin'), often called the for short, was a part of the Papal States (1274‒1791) in what is now the region of France.
The entire region was an enclav ...
, appanages of Alfonso, Count of Poitou, to the royal domain
* 1274: purchase of the County of Nemours
* 1274: the king cedes half of the Comtat Venaissin
The Comtat Venaissin (; Provençal: , Mistralian norm: , classical norm: ; 'County of Venaissin'), often called the for short, was a part of the Papal States (1274‒1791) in what is now the region of France.
The entire region was an enclav ...
to pope Gregory X
Pope Gregory X ( la, Gregorius X; – 10 January 1276), born Teobaldo Visconti, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1 September 1271 to his death and was a member of the Secular Franciscan Order. He was ...
* 1283: Perche
Perche () (French: ''le Perche'') is a former province of France, known historically for its forests and, for the past two centuries, for the Percheron draft horse breed. Until the French Revolution, Perche was bounded by four ancient territorie ...
and the County of Alençon
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
are inherited from the king's brother Pierre I of Alençon.
* 1284: purchase of the County of Chartres.
* the king makes appanage grants of Valois to his second son Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
and Beaumont-en-Oise to his third son Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
.
Reigns of Philip IV, the Fair and his sons
* 1284: marriage of Philip the Fair, the future king of France, with QueenJoan I of Navarre
Joan I (14 January 1273 – 31 March/2 April 1305) ( eu, Joana) was Queen of Navarre and Countess of Champagne from 1274 until 1305; she was also Queen of France by marriage to King Philip IV. She founded the College of Navarre in Paris in 130 ...
, Countess of Champagne. The County of Champagne is reunited to the royal domain (made official in 1361)
* 1285–1295: purchase of the County of Guînes The County of Guînes, was a Flemish fief and later French fief in the Middle Ages.
The county was split from the County of Boulogne in about 988.
Counts
*?-c.965 - Siegfried, Count of Guînes
**Although he never seemed to be formally design ...
from Count Arnould III who needed money to pay a ransom.
* 1286: purchase of the County of Chartres from Jeanne of Blois-Châtillon, widow of her uncle Pierre
Pierre is a masculine given name. It is a French form of the name Peter. Pierre originally meant "rock" or "stone" in French (derived from the Greek word πέτρος (''petros'') meaning "stone, rock", via Latin "petra"). It is a translation ...
* 1292: Ostrevant
* 1295: the king gives up a part of the County of Guines.
* as they reverted to the crown, Philip IV makes appanage grants of Alençon
Alençon (, , ; nrf, Alençoun) is a commune in Normandy, France, capital of the Orne department. It is situated west of Paris. Alençon belongs to the intercommunality of Alençon (with 52,000 people).
History
The name of Alençon is firs ...
, Chartres
Chartres () is the prefecture of the Eure-et-Loir department in the Centre-Val de Loire region in France. It is located about southwest of Paris. At the 2019 census, there were 170,763 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Chartres (as d ...
and Perche
Perche () (French: ''le Perche'') is a former province of France, known historically for its forests and, for the past two centuries, for the Percheron draft horse breed. Until the French Revolution, Perche was bounded by four ancient territorie ...
to his brother Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
and Évreux
Évreux () is a commune in and the capital of the department of Eure, in the French region of Normandy.
Geography
The city is on the Iton river.
Climate
History
In late Antiquity, the town, attested in the fourth century CE, was named ...
to his brother Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
. By his marriage, Charles also acquires Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
and Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
. To his sons, Philip gives the appanages of Poitiers
Poitiers (, , , ; Poitevin: ''Poetàe'') is a city on the River Clain in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and the historical centre of Poitou. In 2017 it had a population of 88,291. Its agglomerat ...
to Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularize ...
, and La Marche and Angoulême
Angoulême (; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Engoulaeme''; oc, Engoleime) is a communes of France, commune, the Prefectures of France, prefecture of the Charente Departments of France, department, in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of southwestern Franc ...
to Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
.Hallam, 250.
* 1308: purchase of the County of Angoulême
Angoumois (), historically the County of Angoulême, was a county and province of France, originally inferior to the parent duchy of Aquitaine, similar to the Périgord to its east but lower and generally less forested, equally with occasional vin ...
, of Fougères
Fougères (; br, Felger; Gallo: ''Foujerr'') is a commune and a sub-prefecture of the Ille-et-Vilaine department in the region of Brittany in northwestern France.
As of 2017, Fougères had 20,418 inhabitants. The Fougères area comprises appr ...
and of Lusignan
The House of Lusignan ( ; ) was a royal house of French origin, which at various times ruled several principalities in Europe and the Levant, including the kingdoms of Jerusalem, Cyprus, and Armenia, from the 12th through the 15th centuries du ...
from Yolande of Lusignan
* 1313: Confiscation of Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Euromet ...
– which is however a land belonging to the Empire – from Marie de Mortagne.
* 1322: the County of Bigorre
The County of Bigorre was a small feudatory of the Duchy of Gascony in the ninth through 15th centuries. Its capital was Tarbes.
The county was constituted out of the dowry of Faquilène, an Aquitainian princess, for her husband Donatus Lupus ...
is incorporated into the royal domain at the crowning of the king Charles IV, who held it from his mother Joan I of Navarre
Joan I (14 January 1273 – 31 March/2 April 1305) ( eu, Joana) was Queen of Navarre and Countess of Champagne from 1274 until 1305; she was also Queen of France by marriage to King Philip IV. She founded the College of Navarre in Paris in 130 ...
House of Valois
Reign of
Philip VI of Valois
Philip VI (french: Philippe; 1293 – 22 August 1350), called the Fortunate (french: le Fortuné, link=no) or the Catholic (french: le Catholique, link=no) and of Valois, was the first king of France from the House of Valois, reigning from 1328 ...
* the appanages of the new king ( Valois, Anjous, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
, Chartres
Chartres () is the prefecture of the Eure-et-Loir department in the Centre-Val de Loire region in France. It is located about southwest of Paris. At the 2019 census, there were 170,763 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Chartres (as d ...
and Alençon
Alençon (, , ; nrf, Alençoun) is a commune in Normandy, France, capital of the Orne department. It is situated west of Paris. Alençon belongs to the intercommunality of Alençon (with 52,000 people).
History
The name of Alençon is firs ...
) are reunited to the royal domain.
* 1336: conquest of the County of Ponthieu
Ponthieu (, ) was one of six feudal counties that eventually merged to become part of the Province of Picardy, in northern France.Dunbabin.France in the Making. Ch.4. The Principalities 888-987 Its chief town is Abbeville.
History
Ponthieu play ...
, given to the king of England in 1360.
* 1343–1349: the Dauphiné
The Dauphiné (, ) is a former province in Southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was originally the Dauphiné of Viennois.
In the 12th centu ...
is sold to the kingdom of France by the Dauphin of Viennois
* 1349: purchase for the kingdom of France of the seigneurie of Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the Departments of ...
from James III of Majorca
James III ( – ), known as James the Rash (or the Unfortunate), was King of Majorca from 1324 to 1344. He was the son of Ferdinand of Majorca and Isabella of Sabran.
Life
James was born in Catania, Sicily. Margaret of Villehardouin, James's ...
, the dispossessed king of Majorca, for 120 000 écu
The term ''écu'' () or crown may refer to one of several French coins. The first ''écu'' was a gold coin (the ''écu d'or'') minted during the reign of Louis IX of France, in 1266. ''Écu'' (from Latin ''scutum'') means shield, and the coin ...
s.
Reign of
John II John II may refer to:
People
* John Cicero, Elector of Brandenburg (1455–1499)
* John II Casimir Vasa of Poland (1609–1672)
* John II Comyn, Lord of Badenoch (died 1302)
* John II Doukas of Thessaly (1303–1318)
* John II Komnenos (1087–1 ...
* 1350–1360: after the death of Raoul II of Brienne, Count of Guînes, and connétable of France (decapitated for treason), the County of Guînes The County of Guînes, was a Flemish fief and later French fief in the Middle Ages.
The county was split from the County of Boulogne in about 988.
Counts
*?-c.965 - Siegfried, Count of Guînes
**Although he never seemed to be formally design ...
is confiscated. It will be ceded to the English by the Treaty of Brétigny.
* 1360: by the Treaty of Brétigny
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty, drafted on 8 May 1360 and ratified on 24 October 1360, between Kings Edward III of England and John II of France. In retrospect, it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' ...
, Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January ...
(1/3 of the kingdom) is given to the king of England, to obtain the release of the French king, prisoner since the Battle of Poitiers (1356)
The Battle of Poitiers was fought on 19September 1356 between a French army commanded by King JohnII and an Anglo- Gascon force under Edward, the Black Prince, during the Hundred Years' War. It took place in western France, south of Poiti ...
.
* 1360: John, Duke of Berry
John of Berry or John the Magnificent (French: ''Jean de Berry'', ; 30 November 1340 – 15 June 1416) was Duke of Berry and Auvergne and Count of Poitiers and Montpensier. He was Regent of France during the minority of his nephew 1380-1388 ...
receives the Duchy of Berry
Duke of Berry (french: Duc de Berry) or Duchess of Berry (french: Duchesse de Berry) was a title in the Peerage of France. The Berry, France, Duchy of Berry, centred on Bourges, was originally created as an appanage for junior members of the Hous ...
as appanage. He is also made Count of Poitiers
Among the people who have borne the title of Count of Poitiers (or ''Poitou'', in what is now France but in the Middle Ages became part of Aquitaine) are:
*Bodilon
* Warinus (638–677), son of Bodilon
*Hatton (735-778)
Carolingian Counts
...
(1357–1416), Count of Mâcon
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
(c. 1360–1372), Count of Angoulême
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
and Saintonge
Saintonge may refer to:
*County of Saintonge, a historical province of France on the Atlantic coast
*Saintonge (region), a region of France corresponding to the historical province
Places
*Saint-Genis-de-Saintonge, a commune in the Charente-Mari ...
(bef. 1372–1374) and Count of Étampes
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
(1399–1416). At his death, these lands return to the royal domain. He is also given the Duchy of Auvergne
This is a list of the various rulers of Auvergne.
History
In the 7th century Auvergne was disputed between the Franks and Aquitanians. It was later conquered by the Carolingians, and was integrated for a time into the kingdom of Aquitaine. The ...
.
* 1361: the king gives Touraine
Touraine (; ) is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher, Indre and Vie ...
in appanage to his son Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularize ...
.
* 1361: the king successfully claims the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
as the heir by proximity of blood.
Reign of
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
* Thanks to Du Guesclin
Bertrand du Guesclin ( br, Beltram Gwesklin; 1320 – 13 July 1380), nicknamed "The Eagle of Brittany" or "The Black Dog of Brocéliande", was a Breton knight and an important military commander on the French side during the Hundred Years' ...
, the king recovers the Duchy of Aquitaine
The Duchy of Aquitaine ( oc, Ducat d'Aquitània, ; french: Duché d'Aquitaine, ) was a historical fiefdom in western, central, and southern areas of present-day France to the south of the river Loire, although its extent, as well as its name, fluc ...
.
* 27 May 1364: the city of Montivilliers
Montivilliers ( or ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Seine-Maritime Departments of France, department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy region in northern France.
Geography
A large light industry, light industrial and farm ...
is detached from the County of Longueville
Count of Longueville is a French noble title, whose holder had the fiefdom of the County of Longueville. The County was erected into a Duchy in 1505.
Origins
The Lordship of Longueville was a fief that belonged to the Giffard family. Willia ...
and attached to the royal domain.
* 1364: Philip the Bold
Philip II the Bold (; ; 17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404) was Duke of Burgundy and '' jure uxoris'' Count of Flanders, Artois and Burgundy. He was the fourth and youngest son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg.
Philip II was ...
receives in appanage the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
* 1371: purchase of the County of Auxerre
The County of Auxerre is a former state of current central France, with capital in Auxerre.
History
The first count attested by the sources is one Ermenaud, a companion of Charlemagne who reigned around 770. In 859 Charles the Bald handed over t ...
* 1377: Dreux
Dreux () is a commune in the Eure-et-Loir department in northern France.
Geography
Dreux lies on the small river Blaise, a tributary of the Eure, about 35 km north of Chartres. Dreux station has rail connections to Argentan, Paris and Granvi ...
returns to the royal domain
Reign of Charles VI
Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and Louis I de Valois, Duke of Orléans Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis ( ...
, brother of the king. He also becomes (US) and Louis I de Valois, Duke of Orléans Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis ( ...
Count of Valois
The Valois ( , also , ; originally ''Pagus Valensis'') was a region in the valley of the Oise river in Picardy in the north of France. It was a fief in West Francia and subsequently the Kingdom of France until its counts furnished a line of kings ...
(1386?), Duke of Touraine {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2022
Duke of Touraine was a title in the Peerage of France, relating to Touraine.
It was first created in 1360 for Philip the Bold, youngest son of King John II of France. He returned the duchy to the Crown in 1363 on b ...
(1386), Count of Blois
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
(1397; the county is sold by Guy II, Count of Blois
Guy II of Châtillon, Count of Blois (died 22 December 1397), the youngest son of Louis I of Châtillon and Joan of Avesnes, was Count of Blois and Soissons, and lord of Avesnes, Schoonhoven, and Gouda 1381–1397, and lord of Beaumont and Ch ...
at the death of his only son), Angoulême
Angoulême (; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Engoulaeme''; oc, Engoleime) is a communes of France, commune, the Prefectures of France, prefecture of the Charente Departments of France, department, in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of southwestern Franc ...
(1404), Périgord
Périgord ( , ; ; oc, Peiregòrd / ) is a natural region and former province of France, which corresponds roughly to the current Dordogne department, now forming the northern part of the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is div ...
, Dreux
Dreux () is a commune in the Eure-et-Loir department in northern France.
Geography
Dreux lies on the small river Blaise, a tributary of the Eure, about 35 km north of Chartres. Dreux station has rail connections to Argentan, Paris and Granvi ...
and Soissons
Soissons () is a commune in the northern French department of Aisne, in the region of Hauts-de-France. Located on the river Aisne, about northeast of Paris, it is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital ...
.
*1416: the appanage of the Duchy of Berry
Duke of Berry (french: Duc de Berry) or Duchess of Berry (french: Duchesse de Berry) was a title in the Peerage of France. The Berry, France, Duchy of Berry, centred on Bourges, was originally created as an appanage for junior members of the Hous ...
comes back to the royal domain after the death of Jean, Duke of Berry, the uncle of the king.
*1416: the king recreates the appanage of Berry for his son Jean
Jean may refer to:
People
* Jean (female given name)
* Jean (male given name)
* Jean (surname)
Fictional characters
* Jean Grey, a Marvel Comics character
* Jean Valjean, fictional character in novel ''Les Misérables'' and its adaptations
* Jea ...
who dies in 1417.
*1417: the king gives the appanage of Berry to his son Charles VII of France
Charles VII (22 February 1403 – 22 July 1461), called the Victorious (french: le Victorieux) or the Well-Served (), was King of France from 1422 to his death in 1461.
In the midst of the Hundred Years' War, Charles VII inherited the throne of F ...
.
Reign of Charles VII
* 1424: Duchy of Touraine granted to Archibald Douglas, 4th Earl of Douglas, killed later that year at Verneuil. * 1434:Amboise
Amboise (; ) is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France. Today a small market town, it was once home of the French royal court.
Geography
Amboise lies on the banks of the river Loire, east of Tours. It is also about away ...
is confiscated from Louis of Amboise (who had plotted against Georges de la Trémoille Georges may refer to:
Places
*Georges River, New South Wales, Australia
*Georges Quay (Dublin)
*Georges Township, Fayette County, Pennsylvania
Other uses
*Georges (name)
* ''Georges'' (novel), a novel by Alexandre Dumas
* "Georges" (song), a 1977 ...
, a favorite of the king) and reunited with the crown.
* 1453: at the death of Mathieu of Foix
Mathieu de Grailly or Mathieu de Foix (died 1453) was Count of Comminges between 1419 and 1443.
He was the fourth son of Archambaud de Grailly, captal de Buch and Isabella, Countess of Foix.
Biography
He was knighted in 1413 and became a mem ...
, the County of Comminges
This is a list of counts of the County of Comminges.
Counts of Comminges
House of Comminges
House of Lescun
''In 1462, the king of France Louis XI detached the county of Comminges from the royal domain and gave it to his friend.''
* 1462 ...
is incorporated into the royal domain
Reign of
Louis XI
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (french: le Prudent), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII.
Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revol ...
 * 1461–1472: the king gives the
* 1461–1472: the king gives the Duchy of Berry
Duke of Berry (french: Duc de Berry) or Duchess of Berry (french: Duchesse de Berry) was a title in the Peerage of France. The Berry, France, Duchy of Berry, centred on Bourges, was originally created as an appanage for junior members of the Hous ...
in appanage to his brother Charles of France. Dissatisfied, Charles joins with other feudal nobles in the League of the Public Weal
The War of the Public Weal (French: ''La guerre du Bien public'') was a conflict between the king of France and an alliance of feudal nobles, organized in 1465 in defiance of the centralized authority of King Louis XI of France. It was masterminded ...
. At the Treaty of Conflans
The Treaty of Conflans (or the Peace of Conflans) was signed on 5 October 1465 between King Louis XI of France and Count Charles of Charolais. This treaty was signed months after the Battle of Montlhéry (13 July 1465), where the French dukes of ...
in 1465, Charles of France exchanges Berry for the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
(1465–1469). In 1469, Charles is forced to exchange Normandy for the Duchy of Guyenne
Guyenne or Guienne (, ; oc, Guiana ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of '' Aquitania Secunda'' and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transformation of ...
(1486–1472).
* 1462: the king alienates the County of Comminges
This is a list of counts of the County of Comminges.
Counts of Comminges
House of Comminges
House of Lescun
''In 1462, the king of France Louis XI detached the county of Comminges from the royal domain and gave it to his friend.''
* 1462 ...
from the royal domain, giving it to Jean de Lescun Jean de Lescun d'Armagnac (died 1473?), known as "the bastard of Armagnac", was an ally of king Louis XI of France from before the latter's accession to the throne.
He was the illegitimate son of Arnaud Guillaume of Lescun, Bishop of Aire, and An ...
.
* 1477: the County of Ponthieu
Ponthieu (, ) was one of six feudal counties that eventually merged to become part of the Province of Picardy, in northern France.Dunbabin.France in the Making. Ch.4. The Principalities 888-987 Its chief town is Abbeville.
History
Ponthieu play ...
is definitively reattached to the royal domain.
* 1478: the County of Boulogne
The County of Boulogne was a county within the Kingdom of France during the 9th to 15th centuries, centred on the city of Boulogne-sur-Mer. It was ruled by the counts of Flanders in the 10th century, but a separate House of Boulogne emerged durin ...
is acquired by exchange.
* 1481: Charles IV, Duke of Anjou
Charles IV, Duke of Anjou, also Charles of Maine, Count of Le Maine and Guise (1446 – 10 December 1481) was the son of the Angevin prince Charles of Le Maine, Count of Maine and Isabelle of Luxembourg.
He succeeded his father as Count of Maine ...
, Count of Maine
This is a list of counts and dukes of Maine. The capital of Maine was Le Mans. In the thirteenth century it was annexed by France to the royal domain.
Dukes of Maine (''duces Cenomannici'')
* Charivius ( fl. 723) – appears as ''dux'' in a docu ...
, Guise
Guise (; nl, Wieze) is a commune in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. The city was the birthplace of the noble family of Guise, Dukes of Guise, who later became Princes of Joinville.
Population
Sights
The remains ...
, Mortain
Mortain () is a former commune in the Manche department in Normandy in north-western France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Mortain-Bocage.
Geography
Mortain is situated on a rocky hill rising above the gorge of the C ...
and Gien
Gien () is a commune in the Loiret department in north-central France.
Gien is on the river Loire, from Orléans. Gien station has rail connections to Montargis, Nevers and Paris. The town was bought for the royal domain by Philip II of Franc ...
, who succeeded his uncle René I of Anjou
René ('' born again'' or ''reborn'' in French) is a common first name in French-speaking, Spanish-speaking, and German-speaking countries. It derives from the Latin name Renatus.
René is the masculine form of the name (Renée being the feminin ...
as Duke of Anjou
The Count of Anjou was the ruler of the County of Anjou, first granted by Charles the Bald in the 9th century to Robert the Strong. Ingelger and his son, Fulk the Red, were viscounts until Fulk assumed the title of Count of Anjou. The Robertians ...
and Count of Provence
The land of Provence has a history quite separate from that of any of the larger nations of Europe. Its independent existence has its origins in the frontier nature of the dukedom in Merovingian Gaul. In this position, influenced and affected by ...
and Forcalquier
Forcalquier (; oc, Forcauquier, ) is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in southeastern France.
Forcalquier is located between the Lure and Luberon mountain ranges, about south of Sisteron and west of the Durance river. Dur ...
, dies, bequeathing his lands to his cousin Louis XI of France.
* 1482: by the Treaty of Arras, the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
and Picardy
Picardy (; Picard and french: Picardie, , ) is a historical territory and a former administrative region of France. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region of Hauts-de-France. It is located in the northern part of France.
Hi ...
are reattached to the domain.
* 1482: acquisition of the viscounty of Châtellerault
Châtellerault (; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Châteulrô/Chateleràud''; oc, Chastelairaud) is a commune in the Vienne department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in France. It is located in the northeast of the former province Poitou, and the re ...
.
Reign of Charles VIII
* 1483: the seigneuries ofChâtel-sur-Moselle
Châtel-sur-Moselle (, literally ''Châtel on Moselle'') is a commune in the Vosges department in Grand Est in northeastern France.
History
With its commanding position alongside the River Moselle, located at the junction of the three main Rom ...
and Bainville are taken from the Duchy of Bar
The County of Bar, later Duchy of Bar, was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire encompassing the '' pays de Barrois'' and centred on the city of Bar-le-Duc. It was held by the House of Montbéliard from the 11th century. Part of the county, t ...
.
* 1491: the marriage of the king to Duchess Anne of Brittany
Anne of Brittany (; 25/26 January 1477 – 9 January 1514) was reigning Duchess of Brittany from 1488 until her death, and Queen of France from 1491 to 1498 and from 1499 to her death. She is the only woman to have been queen consort of France ...
begins the personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
of the Duchy of Brittany
The Duchy of Brittany ( br, Dugelezh Breizh, ; french: Duché de Bretagne) was a medieval feudal state that existed between approximately 939 and 1547. Its territory covered the northwestern peninsula of Europe, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
and the kingdom.
Reign of
Louis XII
Louis XII (27 June 14621 January 1515), was King of France from 1498 to 1515 and King of Naples from 1501 to 1504. The son of Charles, Duke of Orléans, and Maria of Cleves, he succeeded his 2nd cousin once removed and brother in law at the tim ...
* 1498: the crowning of the new king brings his appanages Valois (alienated in 1386?) and Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and county of Blois The County of Blois was a feudal principality centred on Blois, south of Paris, France. It was created just after king Clovis I conquered Roman Gaul around AD 500. Between the 8th and the 13th centuries, it was amongst the most powerful vassa ...
is integrated into the royal domain for the first time.
* 1498: the second marriage of the king with the Duchess (US) and county of Blois The County of Blois was a feudal principality centred on Blois, south of Paris, France. It was created just after king Clovis I conquered Roman Gaul around AD 500. Between the 8th and the 13th centuries, it was amongst the most powerful vassa ...
Anne of Brittany
Anne of Brittany (; 25/26 January 1477 – 9 January 1514) was reigning Duchess of Brittany from 1488 until her death, and Queen of France from 1491 to 1498 and from 1499 to her death. She is the only woman to have been queen consort of France ...
continues the personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
of Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
to the kingdom which had been interrupted when Anne, as widow, asserted the independence of Brittany.
* 1498: at the death of Odet of Aydie, the County of Comminges
This is a list of counts of the County of Comminges.
Counts of Comminges
House of Comminges
House of Lescun
''In 1462, the king of France Louis XI detached the county of Comminges from the royal domain and gave it to his friend.''
* 1462 ...
(alienated in 1462) returns to the crown.
* 1499: the king gives the Duchy of Berry
Duke of Berry (french: Duc de Berry) or Duchess of Berry (french: Duchesse de Berry) was a title in the Peerage of France. The Berry, France, Duchy of Berry, centred on Bourges, was originally created as an appanage for junior members of the Hous ...
to his former wife Joan of France.
* 1504–1512: the Duchy of Nemours Duke of Nemours was a title in the Peerage of France. The name refers to Nemours in the Île-de-France region of north-central France.
History
In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Lordship of Nemours, in the Gatinais, France, was a possession of th ...
reverts to the royal domain. In 1507, it is given to Gaston of Foix, but reverts at his death in 1512.
Reign of
Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
* 1515: Nemours
Nemours () is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France.
Geography
Nemours is located on the Loing and its canal, c. south of Melun, on the Moret–Lyon railway. Nemours – Saint-Pierre ...
is given to Giuliano di Lorenzo de' Medici
Giuliano di Lorenzo de' Medici KG (12 March 1479 – 17 March 1516) was an Italian nobleman, the third son of Lorenzo the Magnificent, and a ruler of Florence.
Biography
Born in Florence, he was raised with his brothers Piero and Giovanni d ...
. The duchy passes in 1524 to Francis' mother, Louise of Savoy
Louise of Savoy (11 September 1476 – 22 September 1531) was a French noble and regent, Duchess ''suo jure'' of Auvergne and Bourbon, Duchess of Nemours, and the mother of King Francis I. She was politically active and served as the regent of Fra ...
and will remain with the house of Savoy until 1659.
*1531: possessions of the disgraced Charles III, Duke of Bourbon
Charles III, Duke of Bourbon (17 February 1490 – 6 May 1527) was a French military leader, the count of Montpensier, Clermont and Auvergne, and dauphin of Auvergne from 1501 to 1523, then duke of Bourbon and Auvergne, count of Clermont-e ...
are confiscated: Bourbonnais
Bourbonnais () was a historic province in the centre of France that corresponds to the modern ''département'' of Allier, along with part of the ''département'' of Cher. Its capital was Moulins.
History
The title of the ruler of Bourbonnais ...
, Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auverg ...
, Counties of Montpensier
The French lordship of Montpensier (named after the village of Montpensier, département of Puy-de-Dôme), located in historical Auvergne, became a countship in the 14th century.
It changed hands from the House of Thiern, to the House of Beau ...
, of Clermont, of Mercœur and Forez
Forez is a former province of France, corresponding approximately to the central part of the modern Loire ''département'' and a part of the Haute-Loire and Puy-de-Dôme ''départements''.
The final "z" in Forez () is not pronounced in the Loire ...
From the reign of Francis I, the concept of "royal domain" begins to coincide with the French kingdom in general; the appanage of the House of Bourbon however remains alienated.
* 1532: union of the Duchy of Brittany
The Duchy of Brittany ( br, Dugelezh Breizh, ; french: Duché de Bretagne) was a medieval feudal state that existed between approximately 939 and 1547. Its territory covered the northwestern peninsula of Europe, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
to France, the inheritance of Claude of France
Claude of France (13 October 1499 – 20 July 1524) was Queen of France by marriage to King Francis I. She was also ruling Duchess of Brittany from 1514 until her death in 1524. She was a daughter of King Louis XII of France and his second wife ...
daughter of Anne of Brittany
Anne of Brittany (; 25/26 January 1477 – 9 January 1514) was reigning Duchess of Brittany from 1488 until her death, and Queen of France from 1491 to 1498 and from 1499 to her death. She is the only woman to have been queen consort of France ...
. The Dauphin becomes the Duke of Brittany but dies before he ascends to the throne of France.
Reign of Henry II
*1547: for the first time the title Duke of Brittany and King of France is held by the same male primogeniture descendant. This marks the final step in the personal union of Brittany with France. *1548: Duchy of Châtellerault conferred uponJames Hamilton, 2nd Earl of Arran
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
.
*1558: French reconquest and incorporation of Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
into the Crown lands under the leadership of Henry II, which ended 150 years of English rule.
House of Bourbon
Reign of Henry IV
* 1589: Henry III of Navarre becomes king Henry IV of France, succeeding his cousin Henry III after his assassination. On accession to the thrones of Navarre and France, Henry ruled over a vast territory including appanages suzerain to the king of France, such as theCounty of Soissons This is a list of those who bore the title Count of Soissons (french: Comte de Soissons) and ruled Soissons and its '' civitas'' or diocese as a county in the Middle Ages. The title continued in use into modern times, but without ties to the actual ...
, the duchies of Alençon
Alençon (, , ; nrf, Alençoun) is a commune in Normandy, France, capital of the Orne department. It is situated west of Paris. Alençon belongs to the intercommunality of Alençon (with 52,000 people).
History
The name of Alençon is firs ...
, Vendôme
Vendôme (, ) is a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Departments of France, department of Loir-et-Cher, France. It is also the department's third-biggest Communes of France, commune with 15,856 inhabitants (2019).
It is one of the ...
, Beaumont
Beaumont may refer to:
Places Canada
* Beaumont, Alberta
* Beaumont, Quebec
England
* Beaumont, Cumbria
* Beaumont, Essex
** Beaumont Cut, a canal closed in the 1930s
* Beaumont Street, Oxford
France (communes)
* Beaumont, Ardèche
* ...
, the Viscounty of Limoges
Limoges (, , ; oc, Lemòtges, locally ) is a city and Communes of France, commune, and the prefecture of the Haute-Vienne Departments of France, department in west-central France. It was the administrative capital of the former Limousin region ...
, the County of Périgord
Périgord ( , ; ; oc, Peiregòrd / ) is a natural region and former province of France, which corresponds roughly to the current Dordogne department, now forming the northern part of the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is div ...
, the County of Rodez, the Duchy of Albret, the viscounties of Lomagne, Marsan
Marsan (; oc, Marçan, link=no, ) is a commune in the Gers department, southwestern France.
Geography
Population
There exists a Swedish vanilla sauce product called , the name inspired by a visit by the owner to Marsan, Gers in the 1920s. ...
, Gabardan, and Tursan
Tursan, first a Vin délimité de qualité supérieure (VDQS) for wine in South West France since 1958 (decree of 11 July 1958, last modified 26 February 2003), has been granted AOC status in 2011.
Presentation
Its production zone covers potent ...
, as well as the counties of Fézensac, Quatre-Vallées
Quatre-Vallées (i.e. "Four Valleys") ( Gascon: ''Quate-Vaths'') was a small province of France located in the southwest of France. It was made up of four constituent parts: Aure valley (Gascon: ''Aura''), Barousse valley (Gascon: ''Varossa''), ...
, Gaure, Armagnac
Armagnac (, ) is a distinctive kind of brandy produced in the Armagnac region in Gascony, southwest France. It is distilled from wine usually made from a blend of grapes including Baco 22A, Colombard, Folle blanche and Ugni blanc, traditionally ...
, Foix
Foix (; oc, Fois ; ca, Foix ) is a commune, the former capital of the County of Foix. It is the capital of the department of Ariège as it is the seat of the Préfecture of that department. Foix is located in the Occitanie region of south ...
, and Bigorre
Bigorre ({{IPA-fr, biɡɔʁ; Gascon: ''Bigòrra'') is a region in southwest France, historically an independent county and later a French province, located in the upper watershed of the Adour, on the northern slopes of the Pyrenees, part of t ...
.
* 1589: The Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre (; , , , ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona (), was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, alongside the Atlantic Ocean between present-day Spain and France.
The medieval state took ...
(Basse-Navarre
Lower Navarre ( eu, Nafarroa Beherea/Baxenabarre; Gascon/Bearnese: ''Navarra Baisha''; french: Basse-Navarre ; es, Baja Navarra) is a traditional region of the present-day French ''département'' of Pyrénées-Atlantiques. It corresponds to the ...
and the principality of Béarn) remains independent but in personal union with France.
Reign of
Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown ...
* 1620: The king leads an army over Béarn and issues an edict at Pau, incorporating the Kingdom of Navarre and Béarn to the crown of France. From then on, while some prerogatives and the name were kept, the Kingdom of Navarre (Basse Navarre) with Béarn was no longer sovereign.
See also
*Appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; french: apanage ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a sovereign, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture. It was common in much o ...
* Feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
* Territorial formation of France
* Crown Estate
The Crown Estate is a collection of lands and holdings in the United Kingdom belonging to the British monarch as a corporation sole, making it "the sovereign's public estate", which is neither government property nor part of the monarch's priva ...
– for similar holdings in the UK
References
*''This article is based on a translation of the equivalent article from theFrench Wikipedia
The French Wikipedia (french: Wikipédia en français) is the French-language edition of Wikipedia, the free online encyclopedia. This edition was started on 23 March 2001, two months after the official creation of Wikipedia. It has article ...
, retrieved on 13 September 2008.''
* Elizabeth M. Hallam. ''Capetian France: 987–1328''. London: Longman, 1980.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Crown Lands Of France
Ancien Régime
French monarchy
Geography of France
Land registration
Monarchy and money