Fichtelberg, Bavaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Fichtelberg () is a
Fichtelberg () is a
 Fichtelberg () is a
Fichtelberg () is a municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
in the district of Bayreuth
Bayreuth ( or ; High Franconian German, Upper Franconian: Bareid, ) is a Town#Germany, town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtel Mountains. The town's roots date back to 11 ...
in Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. It is a state-recognised climatic spa (Luftkurort).
Geography
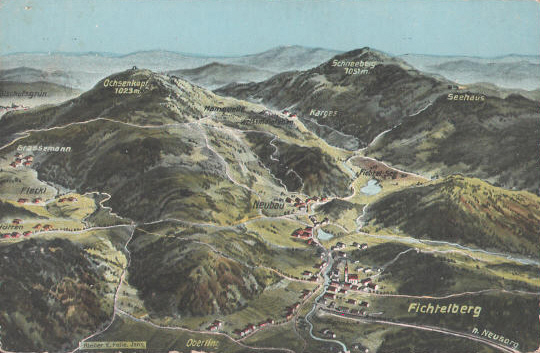
Fichtelberg lies on the southeastern slopes of the Ochsenkopf, the second highest summit of theFichtel Mountains
The Fichtel Mountains (, ; ) is a mountain range in Germany and the Czech Republic. They extend from the valley of the Red Main River in northeastern Bavaria to the Karlovy Vary Region in western Czech Republic. The Fichtel Mountains contain an ...
, and the most populous place in the Fichtel Mountain Nature Park
The Fichtel Mountain Nature Park () lies in the tri-border area of Saxony, the Czech Republic and Bavaria and has an area of . It is maintained by the ''Naturpark Fichtelgebirge e. V.'' in Wunsiedel.
Landscape
The Fichtel Mountains, with th ...
. Fichtelberg lies on a major European watershed
Watershed may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, an area of land where surface water converges (North American usage)
Music
* Watershed Music Festival, an annual country ...
. Two rivers rise above the suburb of Neubau, the White Main
The White Main ( or ''Weißmain'', not to be confused with the Weismain), is the larger and shorter of the two headstreams of the river Main. It rises in the Fichtel Mountains and merges near Steinenhausen, southwest of Kulmbach, with the left ...
, one of the two headstreams of the Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
*Main River (disambiguation), multiple rivers with the same name
*Ma'in, an ancient kingdom in modern-day Yemen
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*Spanish Main, the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territ ...
, which flows westwards to the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, and the Fichtelnaab, which flows south and enters the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
.
Since 1857 Fichtelberg has belonged to the Bavarian provinces of Upper Franconia
Upper Franconia (, ) is a (administrative 'Regierungs''region 'bezirk'' of the state of Bavaria, southern Germany. It forms part of the historically significant region of Franconia, the others being Middle Franconia and Lower Franconia, wh ...
.
Municipal divisions
* Fichtelberg * Hüttstadl * NeubauNeighbouring parish
The only parish that borders immediately on Fichtelberg is Mehlmeisel.Etymology
The origin of the name Fichtelberg, as well as the Fichtel Mountains is probably to be found in mining lore and not, as long suspected, its dense, spruce forests. At the time the name originated, pollen analysis shows that in the North Bavarian region mixed forests of beech, fir and spruce existed. It was only due to the mining and smelting industry, that hardwood species were decimated and faster-growing spruce was planted to supply wood for the mines. At first, only a mountain called ''Vythenberg'' where the St. Vitus mine was located, was mentioned in a charter of 1317; this later became the Ochsenkopf. The original name later evolved into the word ''Vichtel'' or ''Fichtel'' and was eventually used for the entire terrain of present-day Fichtel Mountains. The first written record of the ''Viechtlpergs'' dates to 1508.History
The history of the site at Fichtelberg is dominated by ore mining of themining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
company ''Erzgrube Gottesgab im Gleißingerfels am Fichtelberg''.
In 1600 the uppermost reaches of the Fichtelnaab valley near the present villages of Neubau and Fichtelberg was still covered with a rugged, forest-covered wilderness. Finds, such as a serpentine pendant in 1922 on the Ochsenkopf or a stone axe head excavated in 1935 east of Fichtelberg, suggest that the area around Fichtelberg was already inhabited in the Neolithic period, at least by hunters passing through. The absence of other finds, however, rules out any permanent settlement until the beginning of the 17th century. This was probably due to the steep slopes and significantly higher altitude along with a harsh climate and less fertile soils. Iron ore mining in the upper Fichtelnaab valley began in 1478, but only a small settlement of a few houses extended from the south up to the outskirts of what is now Fichtelberg today.
In 1602, Johann Glaser founded a company of six influential and financially powerful men, in order to work with them to begin mining on Gleißingerfels (about halfway between the modern villages of Hütten und Neubau), to search for suitable iron ore lodes, smelt them in blast furnaces using the most modern and profitable methods of the day and to process them profitably. The wood that was needed in large quantities in the furnaces, forges, hammers and foundries, was available in the extensive forests of the region. There was also enough water at first for the water wheels of the ironworks; when eventually the available water finally became insufficient, they promptly drove channels from the highest headstreams of the Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
*Main River (disambiguation), multiple rivers with the same name
*Ma'in, an ancient kingdom in modern-day Yemen
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*Spanish Main, the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territ ...
and the Steinach, and diverted the water. One example was the ''Bocksgraben''. A thriving iron industry rapidly developed. Iron ore was processed in the royal foundry. At first, the mines were open cast, because the ore veins were on the surface. But eventually these pits collected too much water and there were no powerful pumps at hand. So adits were driven to enable the water to drain out. These hand-hewn tunnels were so big, that a large man could easily walk through them.
The mine on the Gleißinger Fels was called ''Gottesgab am Fichtelberg'' as was the important mining office established later far up the Fichtelnaab valley. The first accommodation huts appeared, the beginnings of a now growing and thriving mining settlement, and four furnaces smelted the silver iron that was mined in the Fichtelberg area. At this time, the region around Fichtelberg was the most important mining operation in the Electorate of Bavaria
The Electorate of Bavaria () was a quasi-independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
The Wittelsbach dynasty which ruled the Duchy of Bavaria was the younger ...
.
Fichtelberg came under the Amberg ' and the Waldeck district court (''Landgericht'') in the Electorate of Bavaria. The mining office had the legal status of a royal estate (''Hofmark''). In 1808 the Fichtelberg Mining Office, as a border region, changed hand repeatedly between the Kingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria ( ; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingd ...
and Margrave of Bayreuth
The Principality of Bayreuth () or Margraviate of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (''Markgraftum Brandenburg-Bayreuth'') was an immediate territory of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a Franconian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty. Since Burgrave Frederic ...
. Since 1857, when the district of the then Bayreuth District Court was enlarged, it has been part of the province of Upper Franconia
Upper Franconia (, ) is a (administrative 'Regierungs''region 'bezirk'' of the state of Bavaria, southern Germany. It forms part of the historically significant region of Franconia, the others being Middle Franconia and Lower Franconia, wh ...
.
Ore mining and smelting had been ''the'' economic factor in Fichtelberg, but with the beginning of industrialization, ore mining became less and less profitable. On 26 March 1859 work ceased and, in 1862, the mining company closed. It was initially followed by an economic decline which could only be partially compensated for by quarrying of granite and 'greenstone' (''Proterobas''), which had already since been worked on the Ochsenkopf massif since the beginning of the 17th century - and which was used especially for glass production - and by the timber industry. Many residents left the area.
After the Second World War, settlers came, mainly glass blowers from Gablonz
Jablonec nad Nisou (; ) is a city in the Liberec Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 46,000 inhabitants. It is the second-largest city in the region. It is a local centre for education, and is known for its glass and jewelry production, espe ...
, and helped Fichtelberg to renewed prosperity as an industrial site based on the glass and button production.
Since then it has largely lost its industrial importance, but survives because of its scenic location on the southwestern slope of the Ochsenkopf, mainly from tourism, and its function as a winter sports centre.
The ''Gleißinger Fels'' mines are the oldest in northern Bavaria and are the only silver iron (''Silbereisen'') mine in the world, which is still accessible to the public.
Tourism
* 1,100 beds in the hotels, inns, guest houses, holiday homes and private homes * Highest campsite in northern BavariaGovernment
Parish council
The council has 14 members: *CSU
CSU may refer to:
Universities and university systems
United States
* Columbia Southern University, in Orange Beach, Alabama
* California State University system
* Colorado State University, in Fort Collins, Colorado
* Connecticut State Univers ...
5 seats
* Christlich Sozialer Förderkreis 2 seats
* Freie Wähler
Free Voters (, FW) is a political party in Germany. It originates as an umbrella organisation of several Free Voters Associations (), associations of people which participate in an election without having the status of a registered party. These ...
(independents) 2 seats
* Wählergruppe Fichtelberg 2.0 3 seats
(as at local elections in 2014)
Mayor
The mayor (''Bürgermeister'') is Sebastian Voit (CSU), elected in 2020.Culture and points of interest
*Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
mining office church (Roman Catholic) 1708 to 1711, with altar from 1730 and wood carvings. The baroque glass windows in the altar room have mining motifs. Currently they are fully restored.
* Baroque Marian column
Marian may refer to:
People
* Marian (given name), a list of people with the given name
* Marian (surname), a list of people so named
Places
* Marian, Iran (disambiguation)
* Marian, Queensland, a town in Australia
* Marian, a village in toe c ...
in 1680
* Historic greenstone glassworks on the southern slope of the Ochsenkopf (archaeological excavations)
Sport
* Fichtelsee recreation centre with nature reserve * Guided walks * Curling * Ice skating * Minigolf * Mountain biking * Kegeln * Skilift * Night langlauf trailSport
* ''Bleam'l Alm'' ski centreMuseums
* AMF car museum * ''Mühlgüt'l'' village museum * Gleißinger Felsvisitor mine
A show mine is a mine that is accessible to visitors.
A mine, i.e. an industrial facility for the underground extraction of mineral products, has three operating phases: it may be open or running, or closed or it may be a working museum. Most ...
Transport
Fichtelberg lies about 3 kilometres south of the B 303 and not far from the A 9 motorway fromBerlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
-Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
, exit Bad Berneck
Bad Berneck im Fichtelgebirge () is a spa town in the district of Bayreuth, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated on the White Main river, in the Fichtel Mountains, 13 km northeast of Bayreuth. It lies in the northern part of the Bavarian pro ...
or, from Berlin, Gefrees
Gefrees () is a town in the district of Bayreuth, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated in the Fichtel Mountains, 21 km northeast of Bayreuth. It was the site of a battle during the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict ...
,
References
Further reading
Dietmar Herrmann: Der Ochsenkopf im Fichtelgebirge, Heft 17/2009 der Schriftenreihe des Fichtelgebirgsvereins e.V.External links
* * http://www.bergwerk-fichtelberg.de/ * http://www.geopark-bayern.de/Public/Geosites/Bayreuth/GlashuetteOchsenkopf.htm * http://www.bayern-fichtelgebirge.de {{Authority control Bayreuth (district)