exoenzyme on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
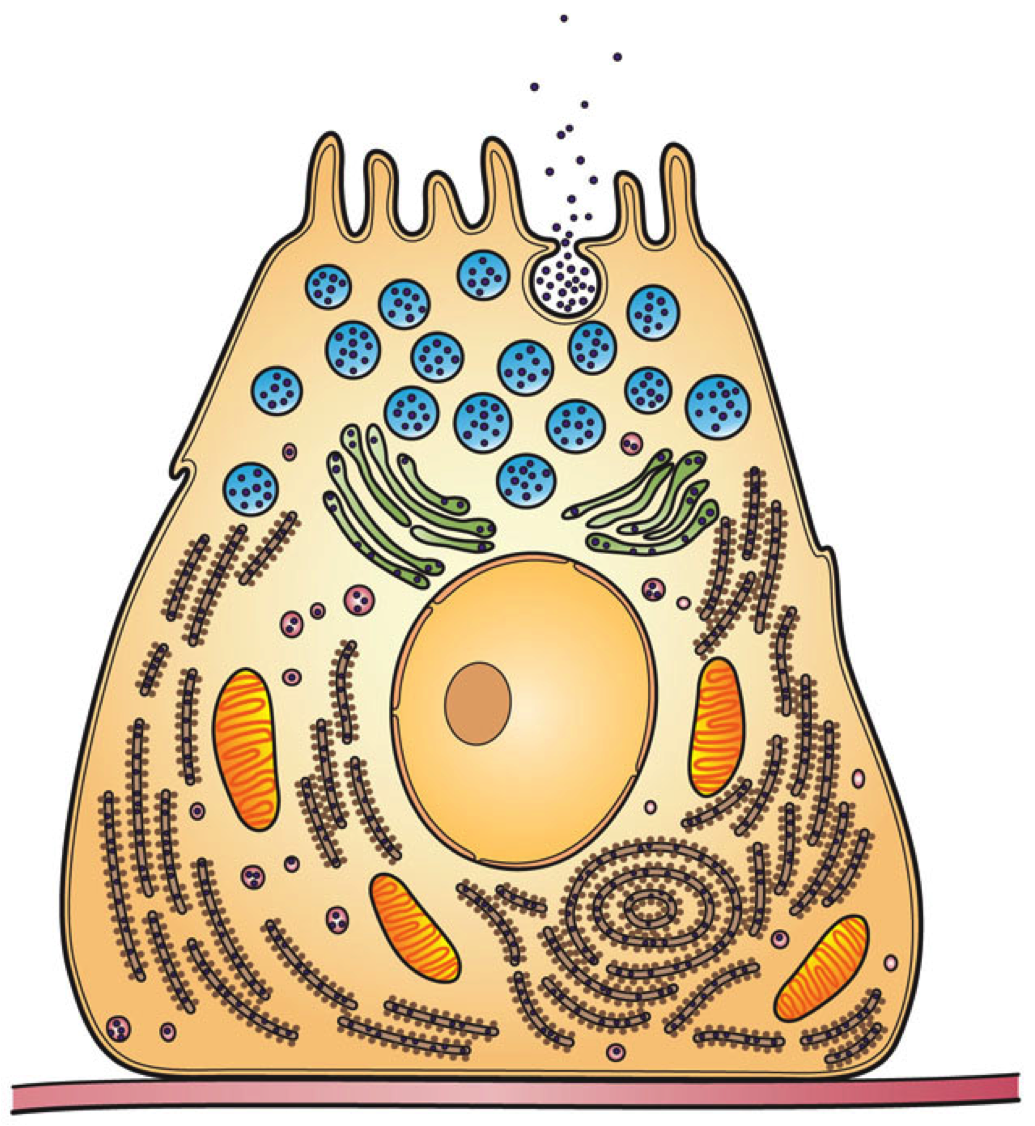 An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an
An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an


 Lipases are one of the most used exoenzymes in
Lipases are one of the most used exoenzymes in
 An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an
An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
that is secreted by a cell and functions outside that cell. Exoenzymes are produced by both prokaryotic and eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
cells and have been shown to be a crucial component of many biological processes. Most often these enzymes are involved in the breakdown of larger macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
s. The breakdown of these larger macromolecules is critical for allowing their constituents to pass through the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
and enter into the cell. For human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s and other complex organisms, this process is best characterized by the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
which breaks down solid food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
via exoenzymes. The small molecules, generated by the exoenzyme activity, enter into cells and are utilized for various cellular functions. Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
also produce exoenzymes to digest nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s in their environment, and these organisms can be used to conduct laboratory assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity ...
s to identify the presence and function of such exoenzymes. Some pathogenic species also use exoenzymes as virulence factors to assist in the spread of these disease-causing microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s. In addition to the integral roles in biological systems, different classes of microbial exoenzymes have been used by humans since pre-historic times for such diverse purposes as food production, biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from Biomass (energy), biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels such as oil. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricu ...
s, textile production and in the paper industry. Another important role that microbial exoenzymes serve is in the natural ecology and bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, wate ...
of terrestrial and marine environments.
History
Very limited information is available about the original discovery of exoenzymes. According toMerriam-Webster
Merriam-Webster, Incorporated is an list of companies of the United States by state, American company that publishes reference work, reference books and is mostly known for Webster's Dictionary, its dictionaries. It is the oldest dictionary pub ...
dictionary, the term "exoenzyme" was first recognized in the English language in 1908. The book "Intracellular Enzymes: A Course of Lectures Given in the Physiological," by Horace Vernon is thought to be the first publication using this word in that year. Based on the book, it can be assumed that the first known exoenzymes were pepsin and trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
, as both are mentioned by Vernon to have been discovered by scientists Briike and Kiihne before 1908.
Function
Inbacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, exoenzymes play an integral role in allowing the organisms to effectively interact with their environment. Many bacteria use digestive enzymes to break down nutrients in their surroundings. Once digested, these nutrients enter the bacterium, where they are used to power cellular pathways with help from endoenzymes.
Many exoenzymes are also used as virulence factors. Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s, both bacterial and fungal, can use exoenzymes as a primary mechanism with which to cause disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
. The metabolic activity of the exoenzymes allows the bacterium to invade host organisms by breaking down the host cells' defensive outer layers or by necrotizing body tissues of larger organisms. Many gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
have injectisomes, or flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr ...
-like projections, to directly deliver the virulent exoenzyme into the host cell using a type three secretion system. With either process, pathogens can attack the host cell's structure and function, as well as its nucleic DNA.
In eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
cells, exoenzymes are manufactured like any other enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
via protein synthesis, and are transported via the secretory pathway
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell (biology), cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. Th ...
. After moving through the rough endoplasmic reticulum, they are processed through the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
, where they are packaged in vesicles and released out of the cell. In human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s, a majority of such exoenzymes can be found in the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
and are used for metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
breakdown of macronutrients via hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
. Breakdown of these nutrients allows for their incorporation into other metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
s.
Examples of exoenzymes as virulence factors
Source:
Necrotizing enzymes
Necrotizing enzymes destroy cells and tissue. One of the best known examples is an exoenzyme produced by '' Streptococcus pyogenes'' that causesnecrotizing fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF), also known as flesh-eating disease, is an infection that kills the body's soft tissue. It is a serious disease that begins and spreads quickly. Symptoms include red or purple or black skin, swelling, severe pain, fever ...
in humans.
Coagulase
By binding to prothrombin, coagulase facilitates clotting in a cell by ultimately converting fibrinogen to fibrin. Bacteria such as ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' use the enzyme to form a layer of fibrin around their cell to protect against host defense mechanisms.
Kinases
The opposite of coagulase, kinases can dissolve clots. ''S. aureus'' can also produce staphylokinase, allowing them to dissolve the clots they form, to rapidly diffuse into the host at the correct time.Hyaluronidase
Similar to collagenase, hyaluronidase enables a pathogen to penetrate deep into tissues. Bacteria such as '' Clostridium'' do so by using the enzyme to dissolvecollagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
and hyaluronic acid, the protein and saccharides, respectively, that hold tissues together.
Hemolysins
Hemolysins target erythrocytes, a.k.a. red blood cells. Attacking and lysing these cells harms the host organism, and provides the microorganism, such as the fungus '' Candida albicans'', with a source of iron from the lysedhemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
. Organisms can either by alpha-hemolytic, beta-hemolytic, or gamma
Gamma (; uppercase , lowercase ; ) is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter normally repr ...
-hemolytic (non-hemolytic).
Examples of digestive exoenzymes
Amylases

Amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large ...
s are a group of extracellular enzymes ( glycoside hydrolases) that catalyze the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
into maltose. These enzymes are grouped into three classes based on their amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
sequences, mechanism of reaction, method of catalysis
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
and their structure. The different classes of amylases are α-amylases, β-amylases, and glucoamylases. The α-amylases hydrolyze starch by randomly cleaving the 1,4-a-D-glucosidic linkages between glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
units, β-amylases cleave non-reducing chain ends of components of starch such as amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–25% of it. Because of its tightly packed Helix, helical struct ...
, and glucoamylases hydrolyze glucose molecules from the ends of amylose and amylopectin. Amylases are critically important extracellular enzymes and are found in plants, animals, and microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s. In humans, amylases are secreted by the pancreas and salivary glands, with both sources of the enzyme required for complete starch hydrolysis.
Lipoprotein lipase
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) is a type of digestive enzyme that helps regulate the uptake of triacylglycerols from chylomicrons and other low-density lipoproteins from fatty tissues in the body. The exoenzymatic function allows it to break down the triacylglycerol into two free fatty acids and one molecule of monoacylglycerol. LPL can be found inendothelial cell
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and th ...
s in fatty tissues, such as adipose
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
, cardiac, and muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
. Lipoprotein lipase is downregulated by high levels of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
, and upregulated by high levels of glucagon and adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
.
Pectinase
Pectinases, also called pectolyticenzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s, are a class of exoenzymes that are involved in the breakdown of pectic substances, most notably pectin. Pectinases can be classified into two different groups based on their action against the galacturonan backbone of pectin: de-esterifying and depolymerizing. These exoenzymes can be found in both plants and microbial organisms including fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
and bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
. Pectinases are most often used to break down the pectic elements found in plants and plant-derived products.
Pepsin
Discovered in 1836, pepsin was one of the first enzymes to be classified as an exoenzyme. The enzyme is first made in the inactive form, pepsinogen by chief cells in the lining of thestomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
. With an impulse from the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
, pepsinogen is secreted into the stomach, where it mixes with hydrochloric acid to form pepsin. Once active, pepsin works to break down proteins in foods such as dairy, meat
Meat is animal Tissue (biology), tissue, often muscle, that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted and farmed other animals for meat since prehistory. The Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of vertebrates, including chickens, sheep, ...
, and eggs. Pepsin works best at the pH of gastric acid
Gastric acid or stomach acid is the acidic component – hydrochloric acid – of gastric juice, produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands of the stomach lining. In humans, the pH is between one and three, much lower than most other a ...
, 1.5 to 2.5, and is deactivated when the acid is neutralized to a pH of 7.
Trypsin
Also one of the first exoenzymes to be discovered,trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
was named in 1876, forty years after pepsin. This enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of large globular proteins and its activity is specific to cleaving the C-terminal sides of arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
and lysine amino acid residues. It is the derivative of trypsinogen, an inactive precursor that is produced in the pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
. When secreted into the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
, it mixes with enterokinase to form active trypsin. Due to its role in the small intestine, trypsin works at an optimal pH of 8.0.
Bacterial assays
The production of a particular digestive exoenzyme by a bacterial cell can be assessed using plateassay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity ...
s. Bacteria are streaked across the agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from " ogonori" and " tengusa". As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, t ...
, and are left to incubate. The release of the enzyme into the surroundings of the cell cause the breakdown of the macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
on the plate. If a reaction does not occur, this means that the bacteria does not create an exoenzyme capable of interacting with the surroundings. If a reaction does occur, it becomes clear that the bacteria does possess an exoenzyme, and which macromolecule is hydrolyzed determines its identity.
Amylase
Amylase breaks down carbohydrates into mono- and disaccharides, so astarch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
agar must be used for this assay. Once the bacteria is streaked on the agar, the plate is flooded with iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
. Since iodine binds to starch but not its digested by-product
A by-product or byproduct is a secondary product derived from a production process, manufacturing process or chemical reaction; it is not the primary product or service being produced.
A by-product can be useful and marketable or it can be cons ...
s, a clear area will appear where the amylase reaction has occurred. ''Bacillus subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'' (), known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacill ...
'' is a bacterium that results in a positive assay as shown in the picture.
Lipase
Lipase assays are done using alipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
agar with a spirit blue dye. If the bacteria has lipase, a clear streak will form in the agar, and the dye will fill the gap, creating a dark blue halo around the cleared area. '' Staphylococcus epidermidis'' results in a positive lipase assay.
Biotechnological and industrial applications
Microbiological sources of exoenzymes includingamylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large ...
s, proteases, pectinases, lipases, xylanases, and cellulases are used for a wide range of biotechnological and industrial uses including biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from Biomass (energy), biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels such as oil. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricu ...
generation, food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
production, paper manufacturing, detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with Cleanliness, cleansing properties when in Concentration, dilute Solution (chemistry), solutions. There are a large variety of detergents. A common family is the alkylbenzene sulfonate ...
s and textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
production. Optimizing the production of biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from Biomass (energy), biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels such as oil. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricu ...
s has been a focus of researchers in recent years and is centered around the use of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s to convert biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
into ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
. The enzymes that are of particular interest in ethanol production are cellobiohydrolase which solubilizes crystalline cellulose and xylanase that hydrolyzes xylan into xylose. One model of biofuel production is the use of a mixed population of bacterial strains or a consortium
A consortium () is an association of two or more individuals, companies, organizations, or governments (or any combination of these entities) with the objective of participating in a common activity or pooling their resources for achieving a ...
that work to facilitate the breakdown of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
materials into ethanol by secreting exoenzymes such as cellulases and laccases. In addition to the important role it plays in biofuel production, xylanase is utilized in a number of other industrial and biotechnology applications due to its ability to hydrolyze cellulose and hemicellulose
A hemicellulose (also known as polyose) is one of a number of heteropolymers (matrix polysaccharides), such as arabinoxylans, present along with cellulose in almost all embryophyte, terrestrial plant cell walls. Cellulose is crystalline, strong, an ...
. These applications include the breakdown of agricultural and forestry wastes, working as a feed additive to facilitate greater nutrient uptake by livestock, and as an ingredient in bread making to improve the rise and texture of the bread.
 Lipases are one of the most used exoenzymes in
Lipases are one of the most used exoenzymes in biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists ...
and industrial applications. Lipases make ideal enzymes for these applications because they are highly selective in their activity, they are readily produced and secreted by bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, their crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat ...
is well characterized, they do not require cofactors for their enzymatic activity, and they do not catalyze side reactions. The range of uses of lipases encompasses production of biopolymers, generation of cosmetics, use as a herbicide, and as an effective solvent. However, perhaps the most well known use of lipases in this field is its use in the production of biodiesel fuel. In this role, lipases are used to convert vegetable oil
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed ...
to methyl- and other short-chain alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
s by a single transesterification reaction.
Cellulases, hemicellulases and pectinases are different exoenzymes that are involved in a wide variety of biotechnological and industrial applications. In the food industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, ...
these exoenzymes are used in the production of fruit juice
Juice is a drink made from the extraction or pressing of the natural liquid contained in fruit and vegetables. It can also refer to liquids that are flavored with concentrate or other biological food sources, such as meat or seafood, such ...
s, fruit nectars, fruit purees and in the extraction of olive oil
Olive oil is a vegetable oil obtained by pressing whole olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea'', a traditional Tree fruit, tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin) and extracting the oil.
It is commonly used in cooking for frying foods, as a cond ...
among many others. The role these enzymes play in these food applications is to partially breakdown the plant cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, and functi ...
s and pectin. In addition to the role they play in food production, cellulases are used in the textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of textiles: yarn, cloth and clothing.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturing
Cotton is the world's most important natural fibre. In the year 2007, th ...
to remove excess dye from denim
Denim is a sturdy cotton warp-faced textile in which the weft passes under two or more Warp (weaving), warp threads. This twill weave produces a diagonal ribbing that distinguishes it from cotton duck. Denim, as it is recognized today, was f ...
, soften cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
fabric
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, and different types of fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is no ...
s, and restore the color brightness of cotton fabrics. Cellulases and hemicellulases (including xylanases) are also used in the paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
and pulp industry to de-ink recycled fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
s, modify coarse mechanical pulp, and for the partial or complete hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of pulp fibers. Cellulases and hemicellulases are used in these industrial applications due to their ability to hydrolyze the cellulose and hemicellulose components found in these materials.
Bioremediation applications
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, wate ...
is a process in which pollutants or contaminant
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for the physical body, natural environment, wiktionary:Workplace, workplace, etc.
Types of contamina ...
s in the environment are removed through the use of biological organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s or their products. The removal of these often hazardous pollutants is mostly carried out by naturally occurring or purposely introduced microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s that are capable of breaking down or absorbing the desired pollutant. The types of pollutants that are often the targets of bioremediation strategies are petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
products (including oil and solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s) and pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s. In addition to the microorganisms ability to digest and absorb the pollutants, their secreted exoenzymes play an important role in many bioremediation strategies.
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
have been shown to be viable organisms to conduct bioremediation and have been used to aid in the decontamination of a number of pollutants including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s, synthetic dyes, chlorophenols, explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An ex ...
s, crude oil, and many others. While fungi can breakdown many of these contaminants intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
ly, they also secrete numerous oxidative exoenzymes that work extracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
ly. One critical aspect of fungi in regards to bioremediation is that they secrete these oxidative exoenzymes from their ever elongating hyphal tips. Laccases are an important oxidative enzyme that fungi secrete and use oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
to oxidize many pollutants. Some of the pollutants that laccases have been used to treat include dye-containing effluents from the textile industry, wastewater pollutants (chlorophenols, PAHs, etc.), and sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
-containing compounds from coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
processing.
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
are also a viable source of exoenzymes capable of facilitating the bioremediation of the environment. There are many examples of the use of bacteria for this purpose and their exoenzymes encompass many different classes of bacterial enzymes. Of particular interest in this field are bacterial hydrolase
In biochemistry, hydrolases constitute a class of enzymes that commonly function as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond:
:\ce \quad \xrightarrowtext\quad \ce
This typically results in dividing a larger molecule into s ...
s as they have an intrinsic low substrate specificity and can be used for numerous pollutants including solid wastes. Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
wastes including polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term ...
s are particularly hard to degrade, but an exoenzyme has been identified in a Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
bacterium, ''Comamonas acidovorans'', that was capable of degrading polyurethane waste in the environment. Cell-free use of microbial exoenzymes as agents of bioremediation is also possible although their activity is often not as robust and introducing the enzymes into certain environments such as soil has been challenging. In addition to terrestrial based microorganisms, marine based bacteria and their exoenzymes show potential as candidate
A candidate, or nominee, is a prospective recipient of an award or honor, or a person seeking or being considered for some kind of position. For example, one can be a candidate for membership in a group (sociology), group or election to an offic ...
s in the field of bioremediation. Marine based bacteria have been utilized in the removal of heavy metals, petroleum/ diesel degradation and in the removal of polyaromatic hydrocarbons among others.
References
{{Reflist, 33em Enzymes