|
Amylopectin
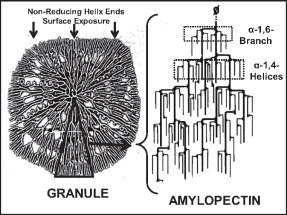
Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α-glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose. Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amyloplasts. To generate energy, the plant hydrolyzes the starch, releasing the glucose subunits. Humans and other animals that eat plant foods also use amylase, an enzyme that assists in breaking down amylopectin, to initiate the hydrolysis of starch. Starch is made of about 70–80% amylopectin by weight, though it varies depending on the source. For example, it ranges from lower percent content in long-grain rice, amylomaize, and Russet Burbank potato, russet potatoes to 100% in glutinous rice, waxy potato starch, and waxy corn. Amylopectin is highly branched, being formed of 2,000 to 200,000 glucose units. Its inner chains are formed of 20–24 glucose subunits. Starch gelatinization, Dissolved amylopectin starch has a lower tendency of retrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amylose
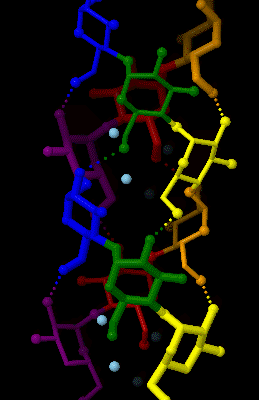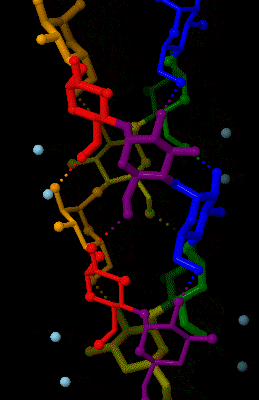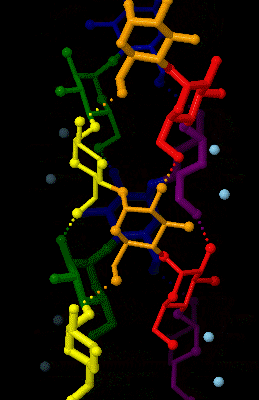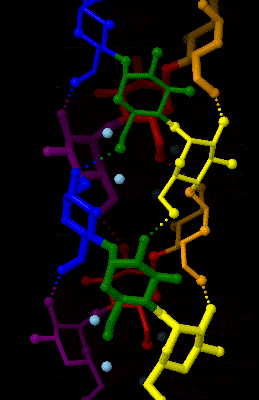
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–25% of it. Because of its tightly packed Helix, helical structure, amylose is more resistant to digestion than other starch molecules and is therefore an important form of resistant starch. Structure Amylose is made up of α(1→4) bound glucose molecules. The carbon atoms on glucose are numbered, starting at the aldehyde (C=O) carbon, so, in amylose, the 1-carbon on one glucose molecule is linked to the 4-carbon on the next glucose molecule (α(1→4) bonds). The structural formula of amylose is pictured at right. The number of repeated glucose subunits (n) is usually in the range of 300 to 3000, but can be many thousands. There are three main forms of amylose chains can take. It can exist in a disordered amorphous conformation, found both in starch granules and in hydrated amylose (when starch i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars (monosaccharides or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as hemicellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but when more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waxy Potato Starch
Waxy potato starch is a variety of commercially available starch composed almost entirely of amylopectin molecules, extracted from new potato varieties. Standard starch extracted from traditional potato varieties contains both amylose and amylopectin. Waxy potato starch, when gelatinized, has a clearer film, a stickier paste and retrogradates (thickening of starch film or paste during storage) less compared to regular potato starch. Waxy potato starch derivatives are used in textile sizing and food applications. Two types of potato plant varieties are developed using different methods: one using traditional breeding techniques and another using genetic manipulation (GMO). Amylopectin potato (traditional breeding) Through traditional breeding techniques an amylose-free mutant was obtained without genetic manipulation. Since 2005 the first natural potato variety Eliane is being cultivated and marketed by the starch company AVEBE. Amylopectin potato (genetically modified) Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch Gelatinization
Starch gelatinization is a process of breaking down of intermolecular bonds of starch molecules in the presence of water and heat, allowing the hydrogen bonding sites (the hydroxyl hydrogen and oxygen) to engage more water. This irreversibly dissolves the starch granule in water. Water acts as a plasticizer. Process Three main processes happen to the starch granule: granule swelling, crystallite and double-helical melting, and amylose leaching. *Granule swelling: During heating, water is first absorbed in the amorphous space of starch, which leads to a swelling phenomenon. *Melting of double helical structures: Water then enters via amorphous regions into the tightly bound areas of double helical structures of amylopectin. At ambient temperatures these crystalline regions do not allow water to enter. Heat causes such regions to become diffuse, the amylose chains begin to dissolve, to separate into an amorphous form and the number and size of crystalline regions decreases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helix, helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermentation, fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organelles
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bounded organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bounded organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some functional units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst (these could be referred to as membrane bound in the sense that they are attached to (or bound to) the membrane). Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organelles, particularly in eukaryotic cells. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosidic Bond
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of ether bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate. A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide (or a molecule derived from a saccharide) and the hydroxyl group of some compound such as an alcohol. A substance containing a glycosidic bond is a glycoside. The term 'glycoside' is now extended to also cover compounds with bonds formed between hemiacetal (or hemiketal) groups of sugars and several chemical groups other than hydroxyls, such as -SR (thioglycosides), -SeR (selenoglycosides), -NR1R2 (N-glycosides), or even -CR1R2R3 (C-glycosides). Particularly in naturally occurring glycosides, the compound ROH from which the carbohydrate residue has been removed is often termed the aglycone, and the carbohydrate residue itself is sometimes referred to as the 'glycone'. S-, N-, C-, and O-glycosidic bonds Glycosidic bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms of energy reserves, creatine phosphate being for very short-term, glycogen being for short-term and the triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) being for long-term storage. Protein, broken down into amino acids, is seldom used as a main energy source except during starvation and glycolytic crisis ''(see bioenergetic systems)''. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight: the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass): the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |