Enterprise Service Bus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An enterprise service bus (ESB) implements a communication system between mutually interacting software applications in a
An enterprise service bus (ESB) implements a communication system between mutually interacting software applications in a
"Lasting concept or latest buzzword?"
(Nicolas Farges, 2003)
(July 22, 2005)
JSR-208: Java Business Integration
(August 2005)
The Role of the Enterprise Service Bus (InfoQ - Video Presentation)
(October 23, 2006)
ESB Roundup Part One: Defining the ESB (InfoQ)
(July 13, 2006)
ESB Roundup Part Two: Use Cases (InfoQ)
(July 5, 2006)
"Services Fabric—Fine Fabrics for New Era Systems"
(Binildas A. Christudas, 2007)
(Dennis Byron, September 20, 2007)
Aggregate Services in ServiceMix JBI ESB: PACKT Publishers
(Binildas A. Christudas, November 30, 2007)
ESB Topology alternatives
(InfoQ, A. Louis, May 23, 2008)
Rethinking the ESB: Building a Simple, Secure, Scalable Service Bus with a SOA Gateway
(Computerworld, J. Ryan, 2011) *
(IBM developer Works, Greg Flurry and Kim Clark, May 2011) {{DEFAULTSORT:Enterprise Service Bus Enterprise application integration Message-oriented middleware Service-oriented (business computing) Software architecture 2002 neologisms
service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. SOA is a good choice for system integration. By consequence, it is also applied in the field ...
(SOA). It represents a software architecture
Software architecture is the set of structures needed to reason about a software system and the discipline of creating such structures and systems. Each structure comprises software elements, relations among them, and properties of both elements a ...
for distributed computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers.
The components of a distributed system commu ...
, and is a special variant of the more general client-server model, wherein any application may behave as server or client. ESB promotes agility and flexibility with regard to high-level protocol communication between applications. Its primary use is in enterprise application integration (EAI) of heterogeneous and complex service landscapes.
Architecture
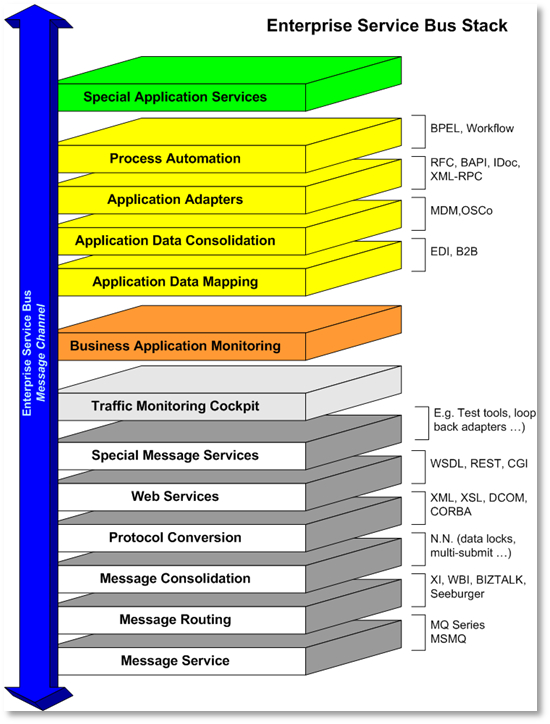
The concept of the enterprise service bus is analogous to the bus concept found in computer hardware architecture combined with the modular and concurrent design of high-performance computer operating systems. The motivation for the development of the architecture was to find a standard, structured, and general purpose concept for describing implementation of loosely coupled software components (called services) that are expected to be independently deployed, running, heterogeneous, and disparate within a network. ESB is also a common implementation pattern forservice-oriented architecture
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. SOA is a good choice for system integration. By consequence, it is also applied in the field ...
, including the intrinsically adopted network design of the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
.
No global standards exist for enterprise service bus concepts or implementations. Most providers of message-oriented middleware
Message-oriented middleware (MOM) is software or hardware infrastructure supporting sending and receiving messages between distributed systems. Message-oriented middleware is in contrast to streaming-oriented middleware where data is communicate ...
have adopted the enterprise service bus concept as ''de facto'' standard for a service-oriented architecture. The implementations of ESB use event-driven and standards-based message-oriented middleware in combination with message queue
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components typically used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter- thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the ...
s as technology frameworks. However, some software manufacturers relabel existing middleware and communication solutions as ESB without adopting the crucial aspect of a bus concept.
Functions
An ESB applies the design concept of modernoperating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s to independent services running within networks of disparate and independent computers. Like concurrent operating systems, an ESB provides commodity services in addition to adoption, translation and routing of client requests to appropriate answering services.
The primary duties of an ESB are:
* Route messages between services
* Monitor and control routing of message exchange between services
* Resolve contention between communicating service components
* Control deployment and versioning of services
* Marshal use of redundant services
* Provide commodity services like event handling, data transformation and mapping, message and event queuing and sequencing, security or exception handling
In computing and computer programming, exception handling is the process of responding to the occurrence of ''exceptions'' – anomalous or exceptional conditions requiring special processing – during the execution of a program. In general, an ...
, protocol conversion and enforcing proper quality of communication service.
History
The first published usage of the term "enterprise service bus" is attributed to Roy W. Schulte from the Gartner Group 2002 and the book ''The Enterprise Service Bus'' by David Chappell. Although a number of companies take credit for coining the phrase, in an interview, Schulte said that the first time he heard the phrase was from a company named Candle and went on to say: "The most direct ancestor to the ESB was Candle’s Roma product from 1998" whose Chief Architect and patent application holder was Gary Aven. Roma was first sold in 1998 making it the first commercial ESB in the market, but that Sonic's product from 2002 was also one of the early ESBs on the market. * Service - denotes non-iterative and autonomously executing programs that communicate with other services through message exchange * Bus - is used in analogy to a computer hardware bus * Enterprise - the concept has been originally invented to reduce complexity of enterprise application integration within an enterprise; the restriction has become obsolete since modern Internet communication is no longer limited to a corporate entityESB as software
The ESB is implemented in software that operates between the business applications, and enables communication among them. Ideally, the ESB should be able to replace all direct contact with the applications on the bus, so that all communication takes place via the ESB. To achieve this objective, the ESB must encapsulate the functionality offered by its component applications in a meaningful way. This typically occurs through the use of an enterprise message model. The message model defines a standard set of messages that the ESB transmits and receives. When the ESB receives a message, it routes the message to the appropriate application. Often, because that application evolved without the same message model, the ESB has to transform the message into a format that the application can interpret. A software adapter fulfills the task of effecting these transformations, analogously to a physicaladapter
An adapter or adaptor is a device that converts attributes of one electrical device or system to those of an otherwise incompatible device or system. Some modify power or signal attributes, while others merely adapt the physical form of one co ...
.
ESBs rely on accurately constructing the enterprise message model and properly designing the functionality offered by applications. If the message model does not completely encapsulate the application functionality, then other applications that desire that functionality may have to bypass the bus, and invoke the mismatched applications directly. Doing so violates the principles of the ESB model, and negates many of the advantages of using this architecture.
The beauty of the ESB lies in its platform-agnostic nature and the ability to integrate with anything at any condition. It is important that Application Lifecycle Management
Application lifecycle management (ALM) is the product lifecycle management (governance, development, and maintenance) of computer programs. It encompasses requirements management, software architecture, computer programming, software testing, ...
vendors truly apply all the ESB capabilities in their integration products while adopting SOA. Therefore, the challenges and opportunities for EAI vendors are to provide an integration solution that is low-cost, easily configurable, intuitive, user-friendly, and open to any tools customers choose.

Characteristics
¹ ''Some do not regard process choreography as an ESB function. For example, see M.Richards. ² ''While process choreography supports implementation of complex business processes that require coordination of multiplebusiness
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
services (usually using BPEL), service orchestration enables coordination of multiple implementation services (most suitably exposed as an aggregate service) to serve individual requests.''
These solutions often focus on low-level ESB functions, such as connectivity, routing and transformation, and require coding or scripting to implement orchestration. Developers operating at a project or tactical level, e.g., just trying to fix a problem, often gravitate toward lightweight service bus technologies, but there is often ongoing tension between these initiatives and an enterprise architecture whose goal it is to optimize infrastructure across multiple projects.
If the message broker, the ESB software, translates a message from one format to another, then as with any translation, there is the issue of semantics of the message. For example, a record can be translated from JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced or ) is an open standard file format and electronic data interchange, data interchange format that uses Human-readable medium and data, human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consi ...
to XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
, but the same set of fields can be interpreted differently by different applications, specifically in the case of the various corner cases that are usually known only to developers that have extensive experience with the application that is connected to the ESB. For the known corner cases the number of tests that cover all corner cases increases exponentially with every application that is connected to the ESB, because every ESB-connected application must be tested against every other application that is connected to the ESB.
Key benefits
* Scales from point-solutions to enterprise-wide deployment (distributed bus) * More configuration rather than integration coding * No central rules-engine, no central broker * Easy plug-in and plug-out and loosely coupling systemKey disadvantages
* Slower communication speed, especially for those already compatible services *Single point of failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that would Cascading failure, stop the entire system from working if it were to fail. The term single point of failure implies that there is not a backup or redundant option that would enab ...
, can bring down all communications in the Enterprise
* High configuration and maintenance complexity
Products
Notable products include: * Proprietary **IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
App Connect, formerly IBM Integration Bus and IBM WebSphere ESB
** InterSystems Ensemble
** Information Builders iWay Service Manager
**Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure, or just Azure ( /ˈæʒər, ˈeɪʒər/ ''AZH-ər, AY-zhər'', UK also /ˈæzjʊər, ˈeɪzjʊər/ ''AZ-ure, AY-zure''), is the cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft. It has management, access and development of ...
Service Bus
** Microsoft BizTalk Server
**Mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two ...
ESB
** Oracle Enterprise Service Bus
**Progress Software
Progress Software Corporation is an American public company that produces software for creating and deploying business applications. Founded in Burlington, Massachusetts with offices in 16 countries, the company posted revenues of $531.3 mill ...
Sonic ESB (acquired by Trilogy
A trilogy is a set of three distinct works that are connected and can be seen either as a single work or as three individual works. They are commonly found in literature, film, and video games. Three-part works that are considered components of ...
)
** SAP Process Integration
** TIBCO Software ActiveMatrix BusinessWorks
** webMethods enterprise service bus (acquired by Software AG
Software GmbH, trading as Software AG, is a German multinational software corporation that develops enterprise software for business process management, integration, and big data analytics. Founded in 1969, the company is headquartered in Darmstad ...
)
** Sonic ESB from Aurea
*Open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software an ...
** Apache Camel
** Fuse ESB from Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North ...
** JBoss ESB
** NetKernel
** Open ESB
** Petals ESB
** Spring Integration
** UltraESB
** WSO2 ESB
See also
* Enterprise Integration Patterns * Event-driven messaging * Java Business Integration *Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to Business process discovery, discover, Business process modeling, model, Business analysis, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and Business process auto ...
* Universal Integration Platform
* Enterprise application integration
* Business Service Provider
* Medical integration environment
* Message Oriented Middleware
Message-oriented middleware (MOM) is software or hardware infrastructure supporting sending and receiving messages between distributed systems. Message-oriented middleware is in contrast to streaming-oriented middleware where data is communicate ...
* Complex event processing
* Event Stream Processing
* Event-driven programming
In computer programming, event-driven programming is a programming paradigm in which the Control flow, flow of the program is determined by external Event (computing), events. User interface, UI events from computer mouse, mice, computer keyboard, ...
* Comparison of Business Integration Software
* Comparison of BPEL engines
* Comparison of BPMN 2.0 Engines
* Composite application
In computing, a composite application is a software application built by combining multiple existing functions into a new application. The technical concept can be compared to mashups. However, composite applications use business sources (e.g., ex ...
* Event-driven SOA
* Integration Platform as a service (iPaaS)
References
Further reading
* David Chappell, "Enterprise Service Bus" (O’Reilly: June 2004, ) * Binildas A. Christudas, "Service-oriented Java Business Integration" (Packt Publishers: February 2008, ; ) * Michael Bell, "Service-Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and Architecture" (2008 Wiley & Sons, )External links
"Lasting concept or latest buzzword?"
(Nicolas Farges, 2003)
(July 22, 2005)
JSR-208: Java Business Integration
(August 2005)
The Role of the Enterprise Service Bus (InfoQ - Video Presentation)
(October 23, 2006)
ESB Roundup Part One: Defining the ESB (InfoQ)
(July 13, 2006)
ESB Roundup Part Two: Use Cases (InfoQ)
(July 5, 2006)
"Services Fabric—Fine Fabrics for New Era Systems"
(Binildas A. Christudas, 2007)
(Dennis Byron, September 20, 2007)
Aggregate Services in ServiceMix JBI ESB: PACKT Publishers
(Binildas A. Christudas, November 30, 2007)
ESB Topology alternatives
(InfoQ, A. Louis, May 23, 2008)
Rethinking the ESB: Building a Simple, Secure, Scalable Service Bus with a SOA Gateway
(Computerworld, J. Ryan, 2011) *
(IBM developer Works, Greg Flurry and Kim Clark, May 2011) {{DEFAULTSORT:Enterprise Service Bus Enterprise application integration Message-oriented middleware Service-oriented (business computing) Software architecture 2002 neologisms