Edward I, King Of England on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was
 Edward was born at the
Edward was born at the
King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers Constitutional monarchy, regula ...
from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland (), sometimes referred to retrospectively as Anglo-Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of Kingdom of England, England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Normans in Ireland, Anglo ...
, and from 1254 to 1306 ruled Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
as Duke of Aquitaine
The duke of Aquitaine (, , ) was the ruler of the medieval region of Aquitaine (not to be confused with modern-day Aquitaine) under the supremacy of Frankish, English, and later French kings.
As successor states of the Visigothic Kingdom ( ...
in his capacity as a vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
of the French king
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I, king of the Fra ...
. Before his accession to the throne, he was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. The eldest son of Henry III, Edward was involved from an early age in the political intrigues of his father's reign. In 1259, he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford
The Provisions of Oxford ( or ''Oxoniae'') were constitutional reforms to the government of late medieval England adopted during the Oxford Parliament of 1258 to resolve a dispute between Henry III of England and his barons. The reforms were de ...
. After reconciling with his father, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Second Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in Kingdom of England, England between the forces of barons led by Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of Henry III of England, King Hen ...
. After the Battle of Lewes
The Battle of Lewes was one of two main battles of the conflict known as the Second Barons' War. It took place at Lewes in Sussex, on 14 May 1264. It marked the high point of the career of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, and made ...
, Edward was held hostage
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seized—such as a relative, employer, law enforcement, or government—to act, o ...
by the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and defeated the baronial leader Simon de Montfort at the Battle of Evesham
The Battle of Evesham (4 August 1265) was one of the two main battles of 13th century England's Second Barons' War. It marked the defeat of Simon de Montfort, Earl of Leicester, and the rebellious barons by the future King Edward I, who led t ...
in 1265. Within two years, the rebellion was extinguished and, with England pacified, Edward left to join the Ninth Crusade
Lord Edward's Crusade, sometimes called the Ninth Crusade, was a military expedition to the Holy Land under the command of Edward I of England, Prince Edward Longshanks (later king as Edward I) in 1271 – 1272. In practice an extension of t ...
to the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
in 1270. He was on his way home in 1272 when he was informed of his father's death. Making a slow return, he reached England in 1274 and was crowned at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British m ...
.
Edward spent much of his reign reforming royal administration and common law
Common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law primarily developed through judicial decisions rather than statutes. Although common law may incorporate certain statutes, it is largely based on prece ...
. Through an extensive legal inquiry, he investigated the tenure of several feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
liberties. The law was reformed through a series of statute
A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wil ...
s regulating criminal
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a State (polity), state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definiti ...
and property law
Property law is the area of law that governs the various forms of ownership in real property (land) and personal property. Property refers to legally protected claims to resources, such as land and personal property, including intellectual prope ...
, but the King's attention was increasingly drawn towards military affairs. After suppressing a minor conflict in Wales in 1276–77, Edward responded to a second one in 1282–83 by conquering Wales. He then established English rule, built castles and towns in the countryside and settled them with English people
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common ancestry, history, and culture. The Engl ...
. After the death of the heir to the Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
throne, Edward was invited to arbitrate a succession dispute. He claimed feudal suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
over Scotland and invaded the country, and the ensuing First Scottish War of Independence continued after his death. Simultaneously, Edward found himself at war with France (a Scottish ally) after King PhilipIV confiscated the Duchy of Gascony. The duchy was eventually recovered but the conflict relieved English military pressure against Scotland. By the mid-1290s, extensive military campaigns required high levels of taxation and this met with both lay
Lay or LAY may refer to:
Places
*Lay Range, a subrange of mountains in British Columbia, Canada
* Lay, Loire, a French commune
*Lay (river), France
* Lay, Iran, a village
* Lay, Kansas, United States, an unincorporated community
* Lay Dam, Alaba ...
and ecclesiastical opposition in England. In Ireland, he had extracted soldiers, supplies and money, leaving decay, lawlessness and a revival of the fortunes of his enemies in Gaelic territories. When the King died in 1307, he left to his son EdwardII a war with Scotland and other financial and political burdens.
Edward's temperamental nature and height () made him an intimidating figure. He often instilled fear in his contemporaries, although he held the respect of his subjects for the way he embodied the medieval ideal of kingship as a soldier, an administrator, and a man of faith. Modern historians are divided in their assessment of Edward; some have praised him for his contribution to the law and administration, but others have criticised his uncompromising attitude towards his nobility. Edward is credited with many accomplishments, including restoring royal authority after the reign of Henry III and establishing Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
as a permanent institution, which allowed for a functional system for raising taxes and reforming the law through statutes. At the same time, he is often condemned for vindictiveness, opportunism and untrustworthiness in his dealings with Wales and Scotland, coupled with a colonialist approach to their governance and to Ireland, and for antisemitic policies leading to the expulsion of the Jews from England in 1290.
Early years, 1239–1263
Childhood and marriage
 Edward was born at the
Edward was born at the Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and is located in London, England. It is commonly called the Houses of Parliament after the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two legislative ch ...
on the night of 17–18 June 1239, to King Henry III and Eleanor of Provence
Eleanor of Provence ( 1223 – 24/25 June 1291) was a Provence, Provençal noblewoman who became List of English royal consorts, Queen of England as the wife of King Henry III of England, Henry III from 1236 until his death in 1272. She served ...
., . Edward
Edward is an English male name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-S ...
, an Anglo-Saxon name
Germanic given names are traditionally dithematic; that is, they are formed from two elements ( stems), by joining a prefix and a suffix. For example, King Æþelred's name was derived from ', meaning "noble", and ', meaning "counsel". The ind ...
, was not commonly given among the aristocracy of England after the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
, but Henry was devoted to the veneration of Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was King of England from 1042 until his death in 1066. He was the last reigning monarch of the House of Wessex.
Edward was the son of Æthelred the Unready and Emma of Normandy. He succeede ...
and decided to name his firstborn son after the saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the ...
. Edward's birth was widely celebrated at the royal court and throughout England, and he was baptised
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water eit ...
three days later at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British m ...
. He was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward until his accession to the throne in 1272. Among his childhood friends was his cousin Henry of Almain
Henry of Almain ( Anglo-Norman: ''Henri d'Almayne''; 2 November 1235 – 13 March 1271), also called Henry of Cornwall, was the eldest son of Richard, Earl of Cornwall, afterwards King of the Romans, by his first wife Isabel Marshal. His surnam ...
, son of King Henry's brother Richard of Cornwall
Richard (5 January 1209 – 2 April 1272) was an English prince who was King of the Romans from 1257 until his death in 1272. He was the second son of John, King of England, and Isabella, Countess of Angoulême. Richard was nominal Count of ...
.. Henry of Almain remained a close companion of the prince for the rest of his life. Edward was placed in the care of Hugh Giffard – father of the future Chancellor
Chancellor () is a title of various official positions in the governments of many countries. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the (lattice work screens) of a basilica (court hall), which separa ...
Godfrey Giffard
Godfrey Giffard ( 12351302) was Chancellor of the Exchequer of England, Lord Chancellor of England and Bishop of Worcester.
Early life
Giffard was a son of Hugh Giffard of Boyton in Wiltshire, Nonetheless, he grew up to become a strong, athletic, and imposing man. At he towered over most of his contemporaries, hence his
 Edward remained in captivity until March 1265, and after his release was kept under strict surveillance. In
Edward remained in captivity until March 1265, and after his release was kept under strict surveillance. In
 Edward pledged himself to undertake a crusade in an elaborate ceremony on 24 June 1268, with his brother
Edward pledged himself to undertake a crusade in an elaborate ceremony on 24 June 1268, with his brother
 Llywelyn ap Gruffudd enjoyed a temporary advantage after the Barons' War. The 1267 Treaty of Montgomery recognised his ownership of land he had conquered in the Four Cantrefs of Perfeddwlad and his title of Prince of Wales. However, his administration was heavy-handed and unpopular, especially among Welshmen on the Marches, where Llywelyn resorted to hostage-taking and intimidation to retain his domination. He also entered into a damaging conflict with the Welsh church, further undermining his authority. Armed conflicts continued on the March. In 1272 Llywelyn suffered a major defeat to the Earl of Gloucester, Gilbert de Clare, and was forced to evacuate south-east Wales. This setback triggered a failed attempt to assassinate the prince, exposing divisions in his principality. The chief suspects, his younger brother Dafydd and Gruffudd ap Gwenwynwyn of Powys, fled to take refuge at the English court. Citing ongoing hostilities and Edward's harbouring of his enemies, Llywelyn refused to do homage to the King. For Edward, a further provocation came from Llywelyn's planned marriage to Eleanor, daughter of Simon de Montfort the Elder. Llywelyn was also suspected of planting a Montfortian spy, Nicholas Waltham, at Edward’s court, and intriguing with Eleanor’s brothers, Simon the Younger and Guy.
In November 1276, Edward declared war. Initial operations were under the captaincy of Mortimer, Edward's brother Edmund, Earl of Lancaster, and
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd enjoyed a temporary advantage after the Barons' War. The 1267 Treaty of Montgomery recognised his ownership of land he had conquered in the Four Cantrefs of Perfeddwlad and his title of Prince of Wales. However, his administration was heavy-handed and unpopular, especially among Welshmen on the Marches, where Llywelyn resorted to hostage-taking and intimidation to retain his domination. He also entered into a damaging conflict with the Welsh church, further undermining his authority. Armed conflicts continued on the March. In 1272 Llywelyn suffered a major defeat to the Earl of Gloucester, Gilbert de Clare, and was forced to evacuate south-east Wales. This setback triggered a failed attempt to assassinate the prince, exposing divisions in his principality. The chief suspects, his younger brother Dafydd and Gruffudd ap Gwenwynwyn of Powys, fled to take refuge at the English court. Citing ongoing hostilities and Edward's harbouring of his enemies, Llywelyn refused to do homage to the King. For Edward, a further provocation came from Llywelyn's planned marriage to Eleanor, daughter of Simon de Montfort the Elder. Llywelyn was also suspected of planting a Montfortian spy, Nicholas Waltham, at Edward’s court, and intriguing with Eleanor’s brothers, Simon the Younger and Guy.
In November 1276, Edward declared war. Initial operations were under the captaincy of Mortimer, Edward's brother Edmund, Earl of Lancaster, and  By the 1284
By the 1284
 The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne
The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne
 Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper,. and he could be intimidating; one story tells how the
Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper,. and he could be intimidating; one story tells how the
 Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the troubled reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the designation of Robert Burnell as chancellor in 1274, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. The same year as Burnell's appointment, Edward replaced most local officials, such as the
Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the troubled reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the designation of Robert Burnell as chancellor in 1274, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. The same year as Burnell's appointment, Edward replaced most local officials, such as the
 Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279.. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting
Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279.. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting  Edward's frequent military campaigns put a great financial strain on the nation. There were several ways through which the King could raise money for war, including customs duties, loans and lay subsidies, which were taxes collected at a certain fraction of the moveable property of all laymen who held such assets. In 1275, Edward negotiated an agreement with the domestic merchant community that secured a permanent duty on wool, England's primary export. In 1303, a similar agreement was reached with foreign merchants, in return for certain rights and privileges. The revenues from the customs duty were handled by the Riccardi, a group of bankers from
Edward's frequent military campaigns put a great financial strain on the nation. There were several ways through which the King could raise money for war, including customs duties, loans and lay subsidies, which were taxes collected at a certain fraction of the moveable property of all laymen who held such assets. In 1275, Edward negotiated an agreement with the domestic merchant community that secured a permanent duty on wool, England's primary export. In 1303, a similar agreement was reached with foreign merchants, in return for certain rights and privileges. The revenues from the customs duty were handled by the Riccardi, a group of bankers from
 Edward's policy towards the
Edward's policy towards the
 Edward believed that he had completed the conquest of Scotland when he left the country in 1296, but resistance soon emerged under the leadership of
Edward believed that he had completed the conquest of Scotland when he left the country in 1296, but resistance soon emerged under the leadership of
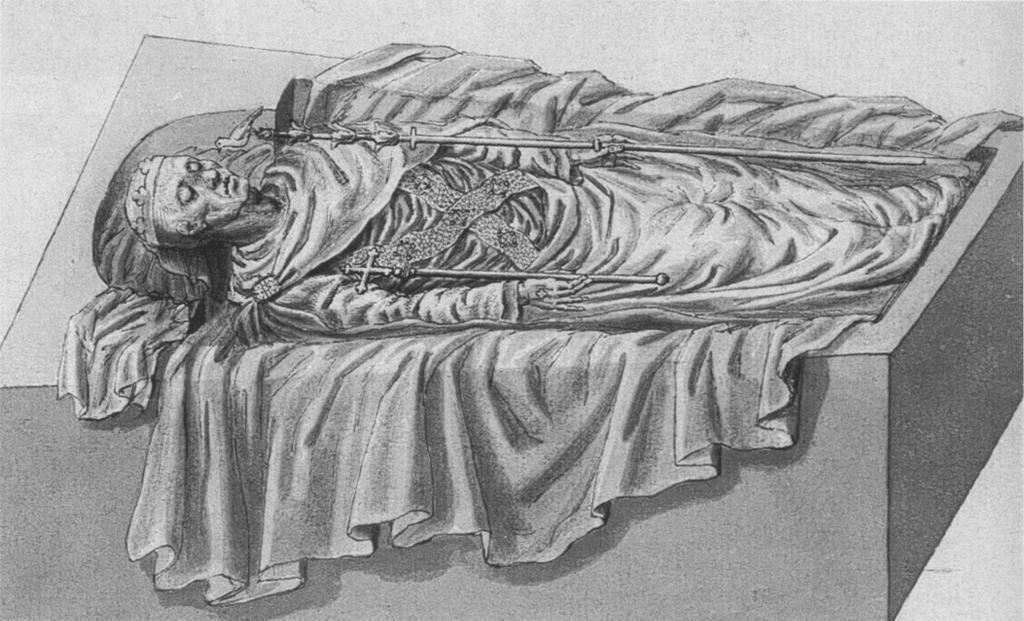 In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the
In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the
 The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the
The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the
epithet
An epithet (, ), also a byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) commonly accompanying or occurring in place of the name of a real or fictitious person, place, or thing. It is usually literally descriptive, as in Alfred the Great, Suleima ...
"Longshanks", meaning "long legs" or "long shins". The historian Michael Prestwich
Michael Charles Prestwich OBE (born 30 January 1943) is an English historian and academic, specialising on the history of medieval England, in particular the reign of Edward I. He is retired, having been Professor of Medieval History at Durham ...
states that his "long arms gave him an advantage as a swordsman, long thighs one as a horseman. In youth, his curly hair was blond; in maturity it darkened, and in old age it turned white. The regularity of his features was marred by a drooping left eyelid ... His speech, despite a lisp, was said to be persuasive."
In 1254, English fears of a Castilian invasion of the English-held province of Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
induced King Henry to arrange a politically expedient marriage between fifteen-year-old Edward and thirteen-year-old Eleanor
Eleanor () is a feminine given name, originally from an Old French adaptation of the Old Provençal name ''Aliénor''. It was the name of a number of women of royalty and nobility in western Europe during the High Middle Ages">Provençal dialect ...
, the half-sister of King Alfonso X of Castile
Alfonso X (also known as the Wise, ; 23 November 1221 – 4 April 1284) was King of Castile, Kingdom of León, León and Kingdom of Galicia, Galicia from 1 June 1252 until his death in 1284. During the April 1257 Imperial election, election of 1 ...
. They were married on 1 November 1254 in the Abbey of Santa María la Real de Las Huelgas
The Abbey of Santa María la Real de Las Huelgas is a monastery of Cistercian nuns located approximately 1.5 km west of the city of Burgos in Spain. The word , which usually refers to "labour strikes" in modern Spanish, refers in this case ...
in Castile. As part of the marriage agreement, Alfonso X gave up his claims to Gascony, and Edward received grants of land worth 15,000 marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks
A collective trademark, collective trade mark, or collective mark is a trademark owned by an organization (such ...
a year. The marriage eventually led to the English acquisition of Ponthieu
Ponthieu (; ; ) was one of six feudal counties that eventually merged to become part of the Province of Picardy, in northern France.Dunbabin.France in the Making. Ch.4. The Principalities 888-987 Its chief town is Abbeville.
History
Ponthieu p ...
in 1279 upon Eleanor's inheritance of the county. Henry made sizeable endowments to Edward in 1254, including Gascony; most of Ireland, which was granted to Edward, while making the claim for the first time that dominion of Ireland would never be separated from the English crown; and much land in Wales and England, including the Earldom of Chester
The Earldom of Chester () was one of the most powerful earldoms in medieval England, extending principally over the counties of Cheshire and Flintshire. Since 1301 the title has generally been granted to heirs apparent to the English throne, ...
. They offered Edward little independence, for Henry retained much control over the land, particularly in Ireland, and benefited from most of the income from those lands. Split control caused problems. Between 1254 and 1272, eleven different Justiciar
Justiciar is the English form of the medieval Latin term or (meaning "judge" or "justice"). The Chief Justiciar was the king's chief minister, roughly equivalent to a modern Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
The Justiciar of Ireland was ...
s were appointed to head the Irish government, encouraging further conflict and instability; corruption rose to very high levels. In Gascony, Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, 1st Earl of Chester ( – 4 August 1265), also known as Simon V de Montfort, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of the Peerage of England, English peerage, who led the baronial opposi ...
, had been appointed as royal lieutenant in 1253 and drew its income, so Edward derived neither authority nor revenue from this province. Around the end of November 1254, Edward and Eleanor left Castile and entered Gascony, where they were warmly received by the populace. Here, Edward styled himself as "ruling Gascony as prince and lord", a move that the historian J. S. Hamilton states was a show of his blooming political independence.
From 1254 to 1257, Edward was under the influence of his mother's relatives, known as the Savoyards, the most notable of whom was Peter II of Savoy
Peter II (c. 120315 May 1268), called the Little Charlemagne, was Count of Savoy from 1263 until his death in 1268. He was also holder of the Honour of Richmond, Yorkshire in England, and the English lands of the Honour of the Eagle also known a ...
, the Queen's uncle. After 1257, Edward became increasingly close to the Lusignan
The House of Lusignan ( ; ) was a royal house of French origin, which at various times ruled several principalities in Europe and the Levant, including the kingdoms of Jerusalem, Cyprus, and Armenia, from the 12th through the 15th centuries du ...
faction – the half-brothers of his father Henry III – led by such men as William de Valence. The two groups of privileged foreigners were resented by the established English aristocracy, who would be at the centre of the ensuing years' baronial reform movement. Edward's ties to his Lusignan kinsmen were viewed unfavourably by contemporaries,> including the chronicler
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, ...
Matthew Paris
Matthew Paris, also known as Matthew of Paris (; 1200 – 1259), was an English people, English Benedictine monk, English historians in the Middle Ages, chronicler, artist in illuminated manuscripts, and cartographer who was based at St A ...
, who circulated tales of unruly and violent conduct by Edward's inner circle, raising questions about his personal qualities.
Early ambitions
Edward showed independence in political matters as early as 1255, when he sided with the Soler family in Gascony in their conflict with the Colomb family. This ran contrary to his father's policy of mediation between the local factions. In May 1258, a group ofmagnate
The term magnate, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s drew up a document for reform of the King's governmentthe so-called Provisions of Oxford
The Provisions of Oxford ( or ''Oxoniae'') were constitutional reforms to the government of late medieval England adopted during the Oxford Parliament of 1258 to resolve a dispute between Henry III of England and his barons. The reforms were de ...
largely directed against the Lusignans. Edward stood by his political allies and strongly opposed the Provisions.. The reform movement succeeded in limiting the Lusignan influence, and Edward's attitude gradually changed. In March 1259, he entered into a formal alliance with one of the main reformers, Richard de Clare, 6th Earl of Gloucester
Richard de Clare, 5th Earl of Hertford, 6th Earl of Gloucester, 2nd Lord of Glamorgan, 8th Lord of Clare (4 August 1222 – 14 July 1262) was the son of Gilbert de Clare, 4th Earl of Hertford, and Isabel Marshal.History of Tewkesbury by James B ...
, and on 15 October announced that he supported the barons' goals and their leader, the Earl of Leicester.
The motive behind Edward's change of heart could have been purely pragmatic: the Earl of Leicester was in a good position to support his cause in Gascony. When the King left for France in November, Edward's behaviour turned into pure insubordination. He made several appointments to advance the cause of the reformers, and his father believed that Edward was considering a coup d'état. When Henry returned from France, he initially refused to see his son, but through the mediation of Richard of Cornwall and Boniface, Archbishop of Canterbury, the two were eventually reconciled. Edward was sent abroad to France, and in November 1260 he again united with the Lusignans, who had been exiled there.
Back in England, early in 1262, Edward fell out with some of his former Lusignan allies over financial matters. The next year, King Henry sent him on a campaign in Wales against the Welsh prince Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ( – 11 December 1282), also known as Llywelyn II and Llywelyn the Last (), was List of rulers of Gwynedd, Prince of Gwynedd, and later was recognised as the Prince of Wales (; ) from 1258 until his death at Cilmeri in 128 ...
, but Edward's forces were besieged in northern Wales and achieved only limited results. Around the same time, Leicester, who had been out of the country since 1261, returned to England and reignited the baronial reform movement. As the King seemed ready to give in to the barons' demands, Edward began to take control of the situation. From his previously unpredictable and equivocating attitude, he changed to one of firm devotion to protection of his father's royal rights. He reunited with some of the men he had alienated the year before – including Henry of Almain and John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Seco ...
– and retook Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a List of British royal residences, royal residence at Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor in the English county of Berkshire, about west of central London. It is strongly associated with the Kingdom of England, English and succee ...
from the rebels. Through the arbitration of King Louis IX of France an agreement was made between the two parties. This Mise of Amiens
The Mise of Amiens () was a settlement given by King Louis IX of France on 23 January 1264 in the conflict between King Henry III of England and his rebellious barons, led by Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Montfort. Louis' one ...
was largely favourable to the royalist side and would cause further conflict.
Civil war and crusades, 1264–1273
Second Barons' War
From 1264 to 1267 theSecond Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in Kingdom of England, England between the forces of barons led by Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of Henry III of England, King Hen ...
was fought between baronial forces led by the Earl of Leicester
Earl of Leicester is a title that has been created seven times. The first title was granted during the 12th century in the Peerage of England. The current title is in the Peerage of the United Kingdom and was created in 1837.
History
Earl ...
and those who remained loyal to the King. Edward initiated the fighting by capturing the rebel-held city of Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
. When Robert de Ferrers, 6th Earl of Derby
Robert de Ferrers, 6th Earl of Derby (1239–1279) was an English nobleman.
He was born at Tutbury Castle in Staffordshire, England, the son of William de Ferrers, 5th Earl of Derby, by his second wife Margaret de Quincy (born 1218), a daug ...
, came to the assistance of the baronial forces, Edward negotiated a truce with the Earl. Edward later broke the terms of the agreement.. He then captured Northampton
Northampton ( ) is a town and civil parish in Northamptonshire, England. It is the county town of Northamptonshire and the administrative centre of the Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority of West Northamptonshire. The town is sit ...
from Simon de Montfort the Younger
Simon VI de Montfort (April 1240 – 1271), known as Simon de Montfort the Younger, was the second son of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester and Eleanor of England.
His father and his elder brother Henry were killed at the Battle of Eve ...
before embarking on a retaliatory campaign against Derby's lands. The baronial and royalist forces met at the Battle of Lewes
The Battle of Lewes was one of two main battles of the conflict known as the Second Barons' War. It took place at Lewes in Sussex, on 14 May 1264. It marked the high point of the career of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, and made ...
, on 14 May 1264. Edward, commanding the right wing, performed well, and soon defeated the London contingent of the Earl of Leicester's forces. Unwisely, he pursued the scattered enemy, and on his return found the rest of the royal army defeated. By the Mise of Lewes
The Mise of Lewes was a settlement made on 14 May 1264 between King Henry III of England and his rebellious barons, led by Simon de Montfort. The settlement was made on the day of the Battle of Lewes, one of the two major battles of the Second B ...
, Edward and his cousin Henry of Almain were given up as hostage
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seized—such as a relative, employer, law enforcement, or government—to act, o ...
s to Leicester.
 Edward remained in captivity until March 1265, and after his release was kept under strict surveillance. In
Edward remained in captivity until March 1265, and after his release was kept under strict surveillance. In Hereford
Hereford ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of the ceremonial county of Herefordshire, England. It is on the banks of the River Wye and lies east of the border with Wales, north-west of Gloucester and south-west of Worcester. With ...
, he escaped on 28 May while out riding and joined up with Gilbert de Clare, 7th Earl of Gloucester
Gilbert de Clare, 6th Earl of Hertford, 7th Earl of Gloucester (2 September 1243 – 7 December 1295) was a powerful English magnate. He was also known as "Red" Gilbert de Clare or "The Red Earl", probably because of his hair colour or fiery te ...
, who had recently defected to the King's side. The Earl of Leicester's support was now dwindling, and Edward retook Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Engl ...
and Gloucester with little effort. Meanwhile, Leicester had made an alliance with Llywelyn and started moving east to join forces with his son Simon. Edward made a surprise attack at Kenilworth Castle
Kenilworth Castle is a castle in the town of Kenilworth in Warwickshire, England, managed by English Heritage; much of it is in ruins. The castle was founded after the Norman Conquest of 1066; with development through to the Tudor period. It ...
, where the younger Montfort was quartered, before moving on to cut off the Earl of Leicester. The two forces then met at the Battle of Evesham
The Battle of Evesham (4 August 1265) was one of the two main battles of 13th century England's Second Barons' War. It marked the defeat of Simon de Montfort, Earl of Leicester, and the rebellious barons by the future King Edward I, who led t ...
, on 4 August 1265. The Earl of Leicester stood little chance against the superior royal forces, and after his defeat he was killed and his corpse mutilated on the field.
Through such episodes as the deception of Derby at Gloucester, Edward acquired a reputation as untrustworthy. During the summer campaign he began to learn from his mistakes and gained the respect and admiration of contemporaries through actions such as showing clemency towards his enemies. The war did not end with the Earl of Leicester's death, and Edward participated in the continued campaigning. At Christmas, he came to terms with Simon the Younger and his associates at the Isle of Axholme
The Isle of Axholme is an area of Lincolnshire, England, adjoining South Yorkshire and the East Riding of Yorkshire. It is located between Scunthorpe and Gainsborough, both of which are in the traditional West Riding of Lindsey, and Doncast ...
in Lincolnshire, and in March 1266 he led a successful assault on the Cinque Ports
The confederation of Cinque Ports ( ) is a historic group of coastal towns in south-east England – predominantly in Kent and Sussex, with one outlier (Brightlingsea) in Essex. The name is Old French, meaning "five harbours", and alludes to ...
. A contingent of rebels held out in the virtually impregnable Kenilworth Castle and did not surrender until the drafting of the conciliatory Dictum of Kenilworth
The Dictum of Kenilworth (), issued on 31 October 1266, was a pronouncement designed to reconcile the rebels of the Second Barons' War with the royal government of England. After the baronial victory at the Battle of Lewes in 1264, Simon de Mo ...
in October 1266. In April it seemed as if the Earl of Gloucester would take up the cause of the reform movement, and civil war would resume, but after a renegotiation of the terms of the Dictum of Kenilworth, the parties came to an agreement. Around this time, Edward was made steward of England and began to exercise influence in the government. He was also appointed Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports
Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports is the name of a ceremonial post in the United Kingdom. The post dates from at least the 12th century, when the title was Keeper of the Coast, but it may be older. The Lord Warden was originally in charge of the ...
in 1265. Despite this, he was little involved in the settlement negotiations following the wars as he was planning his forthcoming crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
.
Crusade and accession
Edmund Crouchback
Edmund, 1st Earl of Lancaster (16 January 12455 June 1296), also known as Edmund Crouchback, was a member of the royal Plantagenet Dynasty and the founder of the first House of Lancaster. He was Earl of Leicester (1265–1296), Lancaster (1267� ...
and cousin Henry of Almain. Some of Edward's former adversaries, such as John de Vescy and the 7th Earl of Gloucester, similarly committed themselves, although some, like Gloucester, did not ultimately participate. With the country pacified, the greatest impediment to the project was funding.. King Louis IX of France, who was the leader of the crusade, provided a loan of about £17,500.. This was not enough, and the rest had to be raised through a direct tax on the laity
In religious organizations, the laity () — individually a layperson, layman or laywoman — consists of all Church membership, members who are not part of the clergy, usually including any non-Ordination, ordained members of religious orders, e ...
, which had not been levied since 1237. In May 1270, Parliament granted a tax of one-twentieth of all movable property; in exchange the King agreed to reconfirm Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardin ...
, and to impose restrictions on Jewish money lending. On 20 August Edward sailed from Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. ...
for France. Historians have not determined the size of his accompanying force with any certainty, but it was probably fewer than 1000 men, including around 225 knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
s.
Originally, the Crusaders intended to relieve the beleaguered Christian stronghold of Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
in Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
, but King Louis and his brother Charles of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou or Charles d'Anjou, was King of Sicily from 1266 to 1285. He was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the House of Anjou-Sicily. Between 1246 a ...
, the king of Sicily
The monarchs of Sicily ruled from the establishment of the Kingdom of Sicily in 1130 until the "perfect fusion" in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816.
The origins of the Sicilian monarchy lie in the Norman conquest of southern Italy which oc ...
, decided to attack the emirate of Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casabl ...
to establish a stronghold in North Africa.. The plan failed when the French forces were struck by an epidemic which, on 25 August, killed Louis. By the time Edward arrived at Tunis, Charles had already signed the Treaty of Tunis with the Emir, and there was little to do but return to Sicily.. Further military action was postponed until the following spring, but a devastating storm off the coast of Sicily dissuaded both Charles and Philip III, Louis's successor, from any further campaigning. Edward decided to continue alone, and on 9 May 1271 he landed at Acre.
The Christian situation in the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
was precarious. Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
had been reconquered by the Muslims in 1244, and Acre was now the centre of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
. The Muslim states were on the offensive under the Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
leadership of Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari (; 1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), commonly known as Baibars or Baybars () and nicknamed Abu al-Futuh (, ), was the fourth Mamluk sultan of Egypt and Syria, of Turkic Kipchak origin, in the Ba ...
, and were threatening Acre. Edward's men were an important addition to the garrison, but they stood little chance against Baibars's superior forces, and an initial raid at nearby St Georges-de-Lebeyne in June was largely futile. An embassy to Abaqa
Abaqa Khan (27 February 1234 – 4 April 1282, , "paternal uncle", also transliterated Abaġa), was the second Mongol ruler ('' Ilkhan'') of the Ilkhanate. The son of Hulagu Khan and Lady Yesünčin and the grandson of Tolui, he reigned from 1265 ...
, the Ilkhan
Il Khan (also ''il-khan'', ''ilkhan'', ''elkhan'', etc.), in Turkic languages and Mongolian, is a title of leadership. It combines the title ''khan'' with the prefix ''el/il'', from the word ''ulus'' – 'tribe, clan', 'the people', 'nation', ' ...
of the Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
, helped bring about an attack on Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
in the north, which distracted Baibars's forces. The Mongol invasion ultimately failed. In November, Edward led a raid on Qaqun
Qaqun () was a Palestinian Arab village located northwest of the city of Tulkarm at the only entrance to Mount Nablus from the coastal Sharon plain.
Evidence of organized settlement in Qaqun dates back to the period of Assyrian rule in th ...
, which could have served as a bridgehead to Jerusalem, but this was unsuccessful. The situation in Acre grew desperate, and in May 1272 Hugh III of Cyprus
Hugh III (; – 24 March 1284), also called Hugh of Antioch-Lusignan and the Great, was the king of Cyprus (as Hugh III) from 1267 and king of Jerusalem (as Hugh I) from 1268. Born into the family of the princes of Antioch, he effectively rul ...
, the nominal king of Jerusalem
The king or queen of Jerusalem was the supreme ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, a Crusader state founded in Jerusalem by the Latin Church, Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade, when the city was Siege of Jerusalem (1099), conquered in ...
, signed a ten-year truce with Baibars. Edward was initially defiant, but in June 1272 he was the victim of an assassination attempt by a member of the Syrian Order of Assassins
The Order of Assassins (; ) were a Nizari Isma'ilism, Nizari Isma'ili order that existed between 1090 and 1275 AD, founded by Hasan-i Sabbah, Hasan al-Sabbah.
During that time, they lived in the mountains of Persia and the Levant, and held a ...
, supposedly ordered by Baibars. He managed to kill the assassin, but was struck in the arm by a dagger feared to be poisoned, and was severely weakened over the following months. This persuaded Edward to abandon the campaign.
On 24 September 1272 Edward left Acre. Shortly after arriving in Sicily, he was met with the news that his father had died on 16 November. Edward was deeply saddened by this news, but rather than hurrying home, he made a leisurely journey northwards.. This was due partly to his still-poor health, but also to a lack of urgency. The political situation in England was stable after the mid-century upheavals, and Edward was proclaimed king after his father's death, rather than at his own coronation, as had until then been customary. In Edward's absence, the country was governed by a royal council, led by Robert Burnell
Robert Burnell (sometimes spelled Robert Burnel;Harding ''England in the Thirteenth Century'' p. 159 c. 1239 – 25 October 1292) was an English bishop who served as Lord Chancellor of England from 1274 to 1292. A native of Shropshire, ...
.. Edward passed through Italy and France, visiting Pope Gregory X
Pope Gregory X (; – 10 January 1276), born Teobaldo Visconti, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1 September 1271 to his death and was a member of the Third Order of St. Francis. He was elected at the ...
and paying homage to Philip III in Paris for his French domains. Edward travelled by way of Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
to receive homage from his great-uncle Count Philip I for castles in the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
held by a treaty of 1246.
Edward then journeyed to Gascony to put down a revolt headed by Gaston de Béarn. While there, he launched an investigation into his feudal possessions, which, as Hamilton puts it, reflects "Edward's keen interest in administrative efficiency ... ndreinforced Edward's position as lord in Aquitaine and strengthened the bonds of loyalty between the king-duke and his subjects". Around the same time, the King organised political alliances with the kingdoms in Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
. His four-year-old daughter Eleanor
Eleanor () is a feminine given name, originally from an Old French adaptation of the Old Provençal name ''Aliénor''. It was the name of a number of women of royalty and nobility in western Europe during the High Middle Ages">Provençal dialect ...
was promised in marriage to Alfonso
Alphons (Latinized ''Alphonsus'', ''Adelphonsus'', or ''Adefonsus'') is a male given name recorded from the 8th century (Alfonso I of Asturias, r. 739–757) in the Christian successor states of the Visigothic Kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula. I ...
, the heir to the Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Sp ...
, and Edward's heir Henry
Henry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters
* Henry (surname)
* Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone
Arts and entertainmen ...
was betrothed to Joan, heiress to the Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre ( ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona, occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost areas originally reaching the Atlantic Ocean (Bay of Biscay), between present-day Spain and France.
The me ...
.. Neither union would come to fruition. On 2 August 1274 Edward returned to England, landing at Dover. The thirty-five-year-old king held his coronation
A coronation ceremony marks the formal investiture of a monarch with regal power using a crown. In addition to the crowning, this ceremony may include the presentation of other items of regalia, and other rituals such as the taking of special v ...
on 19 August at Westminster Abbey, alongside Queen Eleanor. Immediately after being anointed
Anointing is the ritual act of pouring aromatic oil over a person's head or entire body. By extension, the term is also applied to related acts of sprinkling, dousing, or smearing a person or object with any perfumed oil, milk, butter, or oth ...
and crowned by Robert Kilwardby
Robert Kilwardby ( c. 1215 – 11 September 1279) was an Archbishop of Canterbury in England and a cardinal. Kilwardby was the first member of a mendicant order to attain a high ecclesiastical office in the English Church.
Life
Kilwardby ...
, the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the Primus inter pares, ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the bishop of the diocese of Canterbury. The first archbishop ...
, Edward removed his crown, saying that he did not intend to wear it again until he had recovered all the crown lands that his father had surrendered during his reign..
Early reign, 1274–1296
Conquest of Wales
William de Beauchamp, 9th Earl of Warwick
William de Beauchamp, 9th Earl of Warwick ({{Circa, 1238 – 1298) was the eldest of eight children of William de Beauchamp of Elmley and his wife Isabel de Mauduit. He was an English nobleman and soldier, described as a "vigorous and innovative ...
. Support for Llywelyn was weak among his countrymen. In July 1277 Edward invaded with a force of 15,500, of whom 9,000 were Welsh.. The campaign never came to a major battle, and Llywelyn realised he had no choice but to surrender. By the Treaty of Aberconwy
The Treaty of Aberconwy was signed on the 10th of November 1277, and was made between King Edward I of England and Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, Prince of Wales. It followed Edward's invasion of Llywelyn's territories earlier that year. The treaty re-e ...
in November 1277, he was left only with the land of Gwynedd
Gwynedd () is a county in the north-west of Wales. It borders Anglesey across the Menai Strait to the north, Conwy, Denbighshire, and Powys to the east, Ceredigion over the Dyfi estuary to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The ci ...
, though he was allowed to retain the title of Prince of Wales.
War broke out again in 1282. The Welsh saw the war as being over national identity and the right to traditional Welsh law. This enjoyed wide support, provoked by attempts to abuse the English legal system to dispossess prominent Welsh landowners, many of whom were Edward's former opponents. For Edward, it became a war of conquest aimed to "put an end finally to … the malice of the Welsh". The war started with a rebellion by Dafydd, who was discontented with the reward he had received in 1277. Llywelyn and other Welsh leaders soon joined in, and initially the Welsh attack was successful. In June, Gloucester was defeated at the Battle of Llandeilo Fawr
The Battle of Llandeilo Fawr took place during the conquest of Wales by Edward I, at Llandeilo between an English army led by Gilbert de Clare, 6th Earl of Hertford, and a South Welsh army led by Rhys ap Maredudd.
Background
During the Co ...
. On 6 November, while John Peckham
John Peckham (c. 1230 – 8 December 1292) was a Franciscan friar and Archbishop of Canterbury in the years 1279–1292.
Peckham studied at the University of Paris under Bonaventure, where he later taught theology and became known as a co ...
, Archbishop of Canterbury, was conducting peace negotiations, Edward's commander of Anglesey
Anglesey ( ; ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms the bulk of the Principal areas of Wales, county known as the Isle of Anglesey, which also includes Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island () and some islets and Skerry, sker ...
, Luke de Tany
Luke de Tany (died 6 November 1282) was an English noble. He was once the Seneschal of Gascony and Constable of Tickhill Castle and Knaresborough Castle. He served Edward I during his conquest of Wales by successfully capturing Anglesey in 128 ...
, carried out a surprise attack. A pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge (or ponton bridge), also known as a floating bridge, is a bridge that uses float (nautical), floats or shallow-draft (hull), draft boats to support a continuous deck for pedestrian and vehicle travel. The buoyancy of the support ...
had been built to the mainland, but shortly after Tany and his men crossed over, they were ambushed by the Welsh and suffered heavy losses at the Battle of Moel-y-don. The Welsh advances ended on 11 December, when Llywelyn was lured into a trap and killed at the Battle of Orewin Bridge
The Battle of Orewin Bridge (also known as the Battle of Irfon Bridge) was fought between English (led by the Marcher Lords) and Welsh armies on 11 December 1282 near Builth Wells in mid-Wales. It was a decisive defeat for the Welsh beca ...
. The conquest of Gwynedd was complete with the capture in June 1283 of Dafydd, who was taken to Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , ) is a market town and civil parish in Shropshire (district), Shropshire, England. It is sited on the River Severn, northwest of Wolverhampton, west of Telford, southeast of Wrexham and north of Hereford. At the 2021 United ...
and executed as a traitor the following year; Edward ordered Dafydd's head to be publicly exhibited on London Bridge
The name "London Bridge" refers to several historic crossings that have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark in central London since Roman Britain, Roman times. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 197 ...
..
 By the 1284
By the 1284 Statute of Rhuddlan
The Statute of Rhuddlan (), also known as the Statutes of Wales ( or ''Valliae'') or as the Statute of Wales ( or ''Valliae''), was a royal ordinance by Edward I of England, which gave the constitutional basis for the government of the Principal ...
, the principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales () was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the House of Aberffraw from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267–1277. Following the conquest of Wales by Edwa ...
was incorporated into England and was given an administrative system like the English, with counties policed by sheriffs. English law was introduced in criminal cases; the Welsh were allowed to maintain their own customary laws in some cases of property disputes. After 1277, and increasingly after 1283, Edward embarked on a project of English settlement of Wales, creating new towns like Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
, Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth (; ) is a University town, university and seaside town and a community (Wales), community in Ceredigion, Wales. It is the largest town in Ceredigion and from Aberaeron, the county's other administrative centre. In 2021, the popula ...
and Rhuddlan
Rhuddlan () is a town, community, and electoral ward in Denbighshire, Wales. Its associated urban zone is mainly on the right bank of the Clwyd; it is directly south of seafront town Rhyl. It gave its name to the Welsh district of Rhuddlan ...
. Their new residents were English migrants, the local Welsh being banned from living there, and many were protected by extensive walls.
An extensive project of castle building was also initiated, under the direction of James of Saint George
Master James of Saint George (–1309; French: , Old French: Mestre Jaks, Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...: Mestre Jaks, Latin: Magister Jaco ...
,. a prestigious architect Edward had met in Savoy on his return from the crusade. These included Beaumaris
Beaumaris (; ) is a town and community (Wales), community on the Anglesey, Isle of Anglesey in Wales, of which it is the former county town. It is located at the eastern entrance to the Menai Strait, the tidal waterway separating Anglesey fro ...
, Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a List of place names with royal patronage in the United Kingdom, royal town, Community (Wales), community and port in Gwynedd, Wales. It has a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the easter ...
, Conwy
Conwy (, ), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town, community and the administrative centre of Conwy County Borough in North Wales. The walled town and castle stand on the west bank of the River Conwy, facing Deganwy ...
and Harlech
Harlech () is a seaside resort and community (Wales), community in Gwynedd, North Wales, and formerly in the Historic counties of Wales, historic county of Merionethshire. It lies on Tremadog Bay in the Snowdonia National Park. Before 1966, it ...
castles, intended to act as fortresses, royal palaces and as the new centres of civilian and judicial administration. His programme of castle building in Wales heralded the widespread introduction of arrowslit
An arrowslit (often also referred to as an arrow loop, loophole or loop hole, and sometimes a balistraria) is a narrow vertical aperture in a fortification through which an archer can launch arrows or a crossbowman can launch Crossbow bolt, bolts ...
s in castle walls across Europe, drawing on Eastern architectural influences. Also a product of the Crusades was the introduction of the concentric castle
A concentric castle is a castle with two or more concentric Curtain wall (fortification), curtain walls, such that the outer wall is lower than the inner and can be defended from it. The layout was square (at Belvoir Fortress, Belvoir and ...
, and four of the eight castles Edward founded in Wales followed this design. The castles drew on imagery associated with the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
and King Arthur
According to legends, King Arthur (; ; ; ) was a king of Great Britain, Britain. He is a folk hero and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In Wales, Welsh sources, Arthur is portrayed as a le ...
in an attempt to build legitimacy for his new rule, and they made a clear statement about Edward's intention to rule Wales permanently. The Welsh aristocracy were nearly wholly dispossessed of their lands. Edward was the greatest beneficiary of this process. Localised rebellions occurred in 1287–88, partly caused by Edward failing to reward former Welsh allies. A more serious revolt came in 1294, under the leadership of Madog ap Llywelyn
Madog ap Llywelyn (died after 1312) was the leader of the Welsh revolt of 1294–95 against English rule in Wales. The revolt was surpassed in longevity only by the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr in the 15th century. Madog belonged to a junior branch ...
, a distant relative of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd. The causes of the 1294 revolt included resentment at the occupation, poor, colonial-style governance, and very heavy taxation. This last conflict demanded the King's attention, but in both cases the rebellions were put down. The revolt was followed by immediate punitive measures including taking 200 hostages. Measures to stop the Welsh from bearing arms or living in the new boroughs probably date from this time, and the Welsh administration continued to be nearly wholly imported.
In 1284, King Edward had his son Edward (later Edward II) born at Caernarfon Castle, probably to make a statement about the new political order in Wales. In 1301 at Lincoln, the young Edward became the first English prince to be invested as Prince of Wales, when the King granted him the Earldom of Chester and lands across North Wales, hoping to give his son more financial independence. Edward began a more conciliatory policy to rebuild systems of patronage and service, particularly through his son as Prince of Wales, but Wales remained politically volatile, and a deep distrust remained between the English settlers and the Welsh.
Diplomacy and war on the Continent
Edward never again went on crusade after his return to England in 1274, but he maintained an intention to do so, and in 1287 took a vow to go on another crusade. This intention guided much of his foreign policy, until at least 1291. To stage a European-wide crusade, it was essential to prevent conflict between the sovereigns onContinental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by som ...
.. A major obstacle to this was the conflict between the French Capetian House of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou, or House of Anjou-Sicily, or House of Anjou-Naples was a royal house and cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. It is one of three separate royal houses referred to as ''Angevin'', meaning "from Anjou" in France. Foun ...
ruling southern Italy and the Crown of Aragon in Spain. In 1282, the citizens of Palermo rose up against Charles of Anjou and turned for help to Peter III of Aragon
Peter III of Aragon (In Aragonese, ''Pero''; in Catalan, ''Pere''; in Italian, ''Pietro''; November 1285) was King of Aragon, King of Valencia (as ), and Count of Barcelona (as ) from 1276 to his death. At the invitation of some rebels, he con ...
, in what has become known as the Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers (; ) was a successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out at Easter 1282 against the rule of the French-born king Charles I of Anjou. Since taking control of the Kingdom of Sicily in 1266, the Capetian House ...
. In the war that followed, Charles of Anjou's son, Charles of Salerno, was taken prisoner by the Aragonese. The French began planning an attack on Aragon, raising the prospect of a large-scale European war. To Edward, it was imperative that such a war be avoided, and in Paris in 1286 he brokered a truce between France and Aragon that helped secure Charles's release. As far as the crusades were concerned, Edward's efforts proved ineffective. A devastating blow to his plans came in 1291, when the Mamluks captured Acre, the last Christian stronghold in the Holy Land.
Edward had long been deeply involved in the affairs of his own Duchy of Gascony.. In 1278 he assigned an investigating commission to his trusted associates Otto de Grandson
Otto de Grandson (–1328), sometimes numbered Otto I to distinguish him from later members of his family with the same name, was the most prominent of the Savoyard knights in the service of King Edward I of England, to whom he was the clos ...
and the chancellor
Chancellor () is a title of various official positions in the governments of many countries. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the (lattice work screens) of a basilica (court hall), which separa ...
Robert Burnell, which caused the replacement of the seneschal
The word ''seneschal'' () can have several different meanings, all of which reflect certain types of supervising or administering in a historic context. Most commonly, a seneschal was a senior position filled by a court appointment within a royal, ...
Luke de Tany. In 1286, Edward visited the region and stayed for almost three years. On Easter Sunday 1287, Edward was standing in a tower when the floor collapsed. He fell 80 feet, broke his collarbone, and was confined to bed for several months. Several others died. Soon after he regained his health, he ordered the local Jews expelled from Gascony, seemingly as a "thank-offering" for his recovery.
The perennial problem was the status of Gascony within the Kingdom of France, and Edward's role as the French king's vassal. On his diplomatic mission in 1286, Edward had paid homage to the new king, PhilipIV. Following an outbreak of piracy and informal war between English, Gascon, Norman, and French sailors in 1293, his brother Edmund Crouchback allowed Philip IV to occupy Gascony's chief fortresses as a show of good faith that Edward had not intended the seizure of several French ships or the sacking of the French port of La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle'') is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime Departments of France, department. Wi ...
. Philip refused to release the fortresses, and declared Gascony forfeit when Edward refused to appear before him again in Paris.
Correspondence between Edward and the Mongol court of the east continued during this time.. Diplomatic channels between the two had begun during Edward's time on crusade, regarding a possible alliance to retake the Holy Land for Europe. Edward received Mongol envoys at his court in Gascony while there in 1287, and one of their leaders, Rabban Bar Sauma
Rabban Bar Ṣawma (Syriac language: , ; 1220January 1294), also known as Rabban Ṣawma or Rabban ÇaumaMantran, p. 298 ( zh, s=拉班·扫马, t=拉賓掃務瑪, p=lābīn sǎowùmǎ), was a Uygurs, Uyghur monk turned diplomat of the "Nestor ...
, recorded an extant account of the interaction. Other embassies arrived in Europe in 1289 and 1290, the former relaying Ilkhan Abaqa's offer to join forces with the crusaders and supply them with horses.. Edward responded favourably, declaring his intent to travel to the east once he obtained papal approval. This did not materialise, but the King's decision to send Geoffrey of Langley as his ambassador to the Mongols showed that he was seriously considering the prospective Mongol alliance..
Eleanor of Castile died on 28 November 1290. The couple loved each other, and like his father, Edward was very devoted to his wife and was faithful to her throughout their marriage.. He was deeply affected by her death,. and displayed his grief by ordering the construction of twelve so-called Eleanor crosses, one at each place where her funeral cortège stopped for the night.
In 1294 a war at sea flared up between English and Norman privateers. Philip the Fair exploited the conflict to confiscate Gascony, provoking Edward to renounce his homage and declare war. After the initial fighting in Gascony, both kings sought to widen the conflict by forging expensive alliances. Edward joined forces with Adolf of Nassau (the King of Germany), the Count of Flanders
The count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders, beginning in the 9th century. Later, the title would be held for a time, by the rulers of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. During the French Revolution, in 1790, the c ...
and the barons of Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté (, ; ; Frainc-Comtou dialect, Frainc-Comtou: ''Fraintche-Comtè''; ; also ; ; all ) is a cultural and Provinces of France, historical region of eastern France. It is composed of the modern departments of France, departments of Doub ...
in eastern Burgundy
Burgundy ( ; ; Burgundian: ''Bregogne'') is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. ...
. Other members of the alliance included two of his sons-in-law, the Duke of Brabant
The Duke of Brabant (, ) was the ruler of the Duchy of Brabant since 1183/1184. The title was created by the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in favor of Henry I, Duke of Brabant, Henry I of the House of Reginar, son of Godfrey III of Le ...
and the Count of Bar-le-Duc
Bar-le-Duc (), formerly known as Bar, is a commune in the Meuse département, of which it is the capital. The department is in Grand Est in northeastern France.
The lower, more modern and busier part of the town extends along a narrow valley, ...
. Edward's strategy was to attack the French on all fronts and stretch their forces to their breaking point. Most of his allies did indeed go into action and caused considerable damage in Champagne
Champagne (; ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, which demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
, Burgundy, Gascony and the Toulousaine. However, the King of Germany failed to join Edward in Flanders, obliging the allies to seek a truce in October 1297. Edward renewed his military contract with the Burgundians in March 1298, prolonging the war in Franche-Comté. This may have been an effort to distract Philip and prevent him from aiding the Scots. The war was effectively frozen by the Treaties of Montreuil in 1299, whereby Edward agreed to marry Philip's sister Margaret. As part of her dowry Philip returned the county of Ponthieu, which had been seized along with Gascony in 1294. This restored Edward's position as a vassal of the French king, although Gascony was not formally returned until the 1303 Treaty of Paris.
Great Cause
 The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne
The relationship between England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward, who was his brother-in-law, but apparently only for the lands he held in England. Problems arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. When Alexander died in 1286, he left as heir to the Scottish throne Margaret
Margaret is a feminine given name, which means "pearl". It is of Latin origin, via Ancient Greek and ultimately from Iranian languages, Old Iranian. It has been an English language, English name since the 11th century, and remained popular thro ...
, his three-year-old granddaughter and sole surviving descendant. By the Treaty of Birgham
The Treaty of Birgham, also referred to as the Treaty of Salisbury, comprised two treaties in 1289 and 1290 intended to secure the independence of Scotland after the death of Alexander III of Scotland and accession of his three-year-old granddaugh ...
, it was agreed that Margaret should marry King Edward's six-year-old son Edward of Caernarfon
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also known as Edward of Caernarfon or Caernarvon, was King of England from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir to the throne follo ...
, though Scotland would remain free of English overlordship. Margaret, by now seven, sailed from Norway for Scotland in late 1290, but fell ill on the way and died in Orkney
Orkney (), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago off the north coast of mainland Scotland. The plural name the Orkneys is also sometimes used, but locals now consider it outdated. Part of the Northern Isles along with Shetland, ...
. This left the country without an obvious heir, and led to the succession dispute known as the Great Cause.
Fourteen claimants put forward their claims to the title, of whom the foremost competitors were John Balliol
John Balliol or John de Balliol ( – late 1314), known derisively as Toom Tabard (meaning 'empty coat'), was King of Scots from 1292 to 1296. Little is known of his early life. After the death of Margaret, Maid of Norway, Scotland entered an ...
and Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale
Robert V de Brus (Robert de Brus), 5th Lord of Annandale, Dumfries and Galloway, Annandale (ca. 1215 – 31 March or 3 May 1295), was a feudal lord, justice and constable of Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of England, England, a regent ...
. The Scottish magnates made a request to Edward to conduct the proceedings and administer the outcome, but not to arbitrate in the dispute. The actual decision would be made by 104 auditors40 appointed by Balliol, 40 by Brus and the remaining 24 selected by Edward from senior members of the Scottish political community. At Birgham, with the prospect of a personal union between the two realms, the question of suzerainty had not been of great importance to Edward. Now he insisted that, if he were to settle the contest, he had to be fully recognised as Scotland's feudal overlord. The Scots were reluctant to make such a concession, and replied that since the country had no king, no one had the authority to make this decision. This problem was circumvented when the competitors agreed that the realm would be handed over to Edward until a rightful heir had been found. After a lengthy hearing, a decision was made in favour of John Balliol on 17 November 1292.
Even after Balliol's accession, Edward still asserted his authority over Scotland. Against the objections of the Scots, he agreed to hear appeals on cases ruled on by the court of guardians that had governed Scotland during the interregnum. A further provocation came in a case brought by Macduff, son of Malcolm II, Earl of Fife, in which Edward demanded that Balliol appear in person before the English Parliament
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advised th ...
to answer the charges. This the Scottish King did, but the final straw was Edward's demand that the Scottish magnates provide military service in the war against France. This was unacceptable; the Scots instead formed an alliance with France and launched an unsuccessful attack on Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England.
Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its pro ...
. Edward responded by invading Scotland in 1296 and taking the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed (), sometimes known as Berwick-on-Tweed or simply Berwick, is a town and civil parish in Northumberland, England, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, and the northernmost town in England. The 2011 United Kingdom census recor ...
which included the massacre of civilians. At the Battle of Dunbar, Scottish resistance was effectively crushed. Edward took the Stone of Destiny – the Scottish coronation stoneand brought it to Westminster, placing it in what became known as King Edward's Chair
The Coronation Chair, also known as St Edward's Chair or King Edward's Chair, is an ancient wooden chair that is used by British monarchs when they are invested with regalia and crowned at their coronation. The chair was commissioned in 1296 b ...
; he deposed Balliol and placed him in the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic citadel and castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London, England. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamle ...
, and installed Englishmen to govern the country. The campaign had been very successful, but the English triumph would be only temporary.
Government and law
Character as king
 Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper,. and he could be intimidating; one story tells how the
Edward had a reputation for a fierce and sometimes unpredictable temper,. and he could be intimidating; one story tells how the Dean of St Paul's
The dean of St Paul's is a member of, and chair of the Chapter of St Paul's Cathedral in London in the Church of England. The dean of St Paul's is also '' ex officio'' dean of the Order of the British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of th ...
, wishing to confront Edward over high taxation in 1295, fell down and died once he was in the King's presence, and one 14th-century chronicler attributed the death of Archbishop Thomas of York to the King's harsh conduct towards him.. When Edward of Caernarfon demanded an earldom for his favourite Piers Gaveston
Piers Gaveston, 1st Earl of Cornwall ( – 19 June 1312) was an English nobleman of Gascon origin, and the favourite of Edward II of England.
At a young age, Gaveston made a good impression on King Edward I, who assigned him to the househo ...
, the King erupted in anger and supposedly tore out handfuls of his son's hair. Some of his contemporaries considered Edward frightening, particularly in his early days. The '' Song of Lewes'' in 1264 described him as a leopard, an animal regarded as particularly powerful and unpredictable. At times, Edward exhibited a gentler disposition, and was known to be devoted to his large family. He was close to his daughters, and gave them expensive gifts when they visited court.
Despite his harsh disposition, Edward's English contemporaries considered him an able, even an ideal, king. Though not loved by his subjects, he was feared and respected, as reflected in the lack of armed rebellions in England during his reign. Edward is often noted as exhibiting vindictiveness towards his defeated enemies, and triumphalism in his actions. Historian R. R. Davies considered Edward's repeated and "gratuitous belittling of his opponents", to have been "one of the most consistent and unattractive features of his character as king". Examples include the seizure of fragments of the Holy Cross from Wales after its defeat in 1283, and subsequently the Stone of Scone and regalia
Regalia ( ) is the set of emblems, symbols, or paraphernalia indicative of royal status, as well as rights, prerogatives and privileges enjoyed by a sovereign, regardless of title. The word originally referred to the elaborate formal dress and ...
from Scotland after defeats in 1296. Some historians question Edward's good faith and trustworthiness in relation to his dealing with Wales and Scotland, believing him to have been capable of behaving duplicitously.
Historian Michael Prestwich believes Edward met contemporary expectations of kingship in his role as an able, determined soldier and in his embodiment of shared chivalric ideals. In religious observance he fulfilled the expectations of his age: he attended chapel regularly, gave alms
Alms (, ) are money, food, or other material goods donated to people living in poverty. Providing alms is often considered an act of Charity (practice), charity. The act of providing alms is called almsgiving.
Etymology
The word ''alms'' come ...
generously and showed a fervent devotion to the Virgin Mary
Marian devotions are external pious practices directed to the person of Mary, mother of Jesus, by members of certain Christian traditions. They are performed in Catholicism, High Church Lutheranism, Anglo-Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy and Orie ...
and Saint Thomas Becket
Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and then as Archbishop of Canterbury fr ...
. Like his father, Edward was a keen participant in the tradition of the royal touch
The royal touch (also known as the king's touch) was a form of laying on of hands, whereby List of French monarchs, French and English monarchs touched their subjects, regardless of social classes, with the intent to cure them of various diseas ...
, which was believed to cure those who were touched from scrofula. Contemporary records suggest that the King touched upwards of a thousand people each year. Despite his personal piety, Edward was frequently in conflict with the Archbishops of Canterbury who served during his reign. Relations with the Papacy were at times no better, Edward coming into conflict with Rome over the issue of ecclesiastical taxation. Edward's use of the church extended to war mobilisation including disseminating justifications for war, usually through the issue of writs to England's archbishops, who distributed his requests for services and prayers. Edward's architectural programme similarly had an element of propaganda, sometimes combining this with religious messages of piety, as with the Eleanor Crosses.
Edward took a keen interest in the stories of King Arthur, which were popular in Europe during his reign. In 1278 he visited Glastonbury Abbey
Glastonbury Abbey was a monastery in Glastonbury, Somerset, England. Its ruins, a grade I listed building and scheduled ancient monument, are open as a visitor attraction.
The abbey was founded in the 8th century and enlarged in the 10th. It wa ...
to open what was then believed to be the tomb of Arthur and Guinevere
Guinevere ( ; ; , ), also often written in Modern English as Guenevere or Guenever, was, according to Arthurian legend, an early-medieval queen of Great Britain and the wife of King Arthur. First mentioned in literature in the early 12th cen ...
, and gained " Arthur's crown" from Llywelyn after the conquest of North Wales; his castle-building campaign in Wales drew upon the Arthurian myths in their design and location. He held "Round Table" events in 1284 and 1302, involving tournaments and feasting, and chroniclers compared him and the events at his court to Arthur. In some cases Edward appears to have used the Arthurian myths to serve his own political interests, including legitimising his rule in Wales and discrediting the Welsh belief that Arthur might return as their political saviour.
Administration and the law
 Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the troubled reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the designation of Robert Burnell as chancellor in 1274, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. The same year as Burnell's appointment, Edward replaced most local officials, such as the
Soon after assuming the throne, Edward set about restoring order and re-establishing royal authority after the troubled reign of his father. To accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of administrative personnel. The most important of these was the designation of Robert Burnell as chancellor in 1274, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the King's closest associates. The same year as Burnell's appointment, Edward replaced most local officials, such as the escheat
Escheat () is a common law doctrine that transfers the real property of a person who has died without heirs to the crown or state. It serves to ensure that property is not left in "limbo" without recognized ownership. It originally applied t ...
ors and sheriffs
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland, the , which is commonly ...
. This last measure was taken in preparation for an extensive inquest covering all of England, that would hear complaints about abuse of power
Abuse of power or abuse of authority, in the form of "malfeasance in office" or "official abuse of power", is the commission of an Crime, unlawful act, done in an official capacity, which affects the performance of official duties. Malfeasan ...
by royal officers. The second purpose of the inquest was to establish what land and rights the Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive ...
had lost during the reign of Henry III.
The inquest produced a set of census documents called the Hundred Rolls {{Short description, 13th-century census of England and Wales
The Hundred Rolls are a census of England and parts of what is now Wales taken in the late thirteenth century. Often considered an attempt to produce a second Domesday Book, they are na ...
.. These have been likened to the 11th-century Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
, and they formed the basis for the later legal inquiries called the ''Quo warranto
In the English-American common law, ''quo warranto'' (Medieval Latin for "by what warrant?") is a prerogative writ issued by a court which orders someone to show what authority they have for exercising some right, power, or franchise they clai ...
'' proceedings. The purpose of these inquiries was to establish by what warrant () liberties
Liberty is the state of being free within society from oppressive restrictions imposed by authority on one's way of life, behavior, or political views. The concept of liberty can vary depending on perspective and context. In the Constitutional ...
were held. If the defendant could not produce a royal licence to prove the grant of the liberty, then it was the Crown's opinionbased on the writings of the influential 13th-century legal scholar Henry de Bracton
Henry of Bracton (c. 1210 – c. 1268), also known as Henry de Bracton, Henricus Bracton, Henry Bratton, and Henry Bretton, was an English cleric and jurist.
He is famous now for his writings on law, particularly ''De legibus et consuetudinib ...
that the liberty should revert to the King. Both the Statute of Westminster 1275
The Statute of Westminster of 1275 ( 3 Edw. 1), also known as the Statute of Westminster I, codified the existing law in England, into 51 chapters. Chapters 5 (which mandates free elections) and 50 (which provided savings for the crown) are sti ...
and Statute of Westminster 1285
The Statute of Westminster of 1285 ( 13 Edw. 1. St. 1), also known as the Statute of Westminster II or the Statute of Westminster the Second, like the Statute of Westminster 1275, is a code in itself, and contains the famous clause ''De donis ...
codified the existing law in England. By enacting the Statute of Gloucester
The Statute of Gloucester () ( 6 Edw. 1) is a piece of legislation enacted in the Parliament of England during the reign of Edward I. The statute, proclaimed at Gloucester in August 1278, was crucial to the development of English law. The Statu ...
in 1278 the King challenged baronial rights through a revival of the system of general eyres (royal justices to go on tour throughout the land) and through a significant increase in the number of pleas of quo warranto to be heard by such eyres.
This caused great consternation among the aristocracy,. who insisted that long use in itself constituted licence
A license (American English) or licence (Commonwealth English) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another part ...
. A compromise was eventually reached in 1290, whereby a liberty was considered legitimate as long as it could be shown to have been exercised since the coronation of Richard the Lionheart
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'st ...
in 1189. Royal gains from the ''Quo warranto'' proceedings were insignificant as few liberties were returned to the King, but he had nevertheless won a significant victory by establishing the principle that all liberties emanated from the Crown.
The 1290 statute of ''Quo warranto'' was only one part of a wider legislative reform, which was one of the most important contributions of Edward's reign. This era of legislative action had started already at the time of the baronial reform movement; the Statute of Marlborough
The Statute of Marlborough ( 52 Hen. 3.) is a set of laws passed by the Parliament of England during the reign of Henry III in 1267. The laws comprised 29 chapters, of which four are still in force. Those four chapters constitute the oldest pi ...
(1267) contained elements both of the Provisions of Oxford and the Dictum of Kenilworth. The compilation of the Hundred Rolls was followed shortly after by the issue of Westminster I (1275), which asserted the royal prerogative
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, Privilege (law), privilege, and immunity recognised in common law (and sometimes in Civil law (legal system), civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy) as belonging to the monarch, so ...
and outlined restrictions on liberties. The Statutes of Mortmain
The Statutes of Mortmain were two enactments, in 1279 (, 7 Edw. 1) and 1290 (, 18 Edw. 1), passed in the reign of Edward I of England, aimed at preserving the kingdom's revenues by preventing land from passing into the possession of the Church. ...
(1279) addressed the issue of land grants to the Church. The first clause of Westminster II (1285), known as ''De donis conditionalibus
or the Estates Tail Act 1285 is a chapter of the English Statutes of Westminster (1285). It originated the law of entail – forbidding a landholder to sell his land except to his heirs.
Background
A form of entail has been known befor ...
'', dealt with family settlement of land, and entail
In English common law, fee tail or entail is a form of trust, established by deed or settlement, that restricts the sale or inheritance of an estate in real property and prevents that property from being sold, devised by will, or otherwise ali ...
s. The Statute of Merchants (1285) established firm rules for the recovery of debts, and the Statute of Winchester
The Statute of Winchester of 1285 ( 13 Edw. 1. St. 2; ), also known as the Statute of Winton, was a statute enacted by King Edward I of England that reformed the system of Watch and Ward (watchmen) of the Assize of Arms of 1252, and revived th ...
(1285) dealt with security and peacekeeping on a local level by bolstering the existing police system. ''Quia emptores
is a statute passed by the Parliament of England in 1290 during the reign of Edward I of England, Edward I that prevented Tenement (law), tenants from Alienation (property law), alienating (transferring) their lands to others by subinfeudati ...
'' (1290)issued along with ''Quo warranto''set out to remedy land ownership disputes resulting from alienation of land by subinfeudation
In English law, subinfeudation is the practice by which tenants, holding land under the king or other superior lord, carved out new and distinct tenures in their turn by sub-letting or alienating a part of their lands.
The tenants were termed ...
. The age of the great statutes largely ended with the death of Robert Burnell in 1292.
Finances and Parliament
 Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279.. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting
Edward's reign saw an overhaul of the coinage system, which was in a poor state by 1279.. Compared to the coinage already circulating at the time of Edward's accession, the new coins issued proved to be of superior quality. In addition to minting pennies
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is t ...
, halfpences and farthings, a new denomination called the groat (which proved to be unsuccessful) was introduced.. The coinmaking process itself was also improved. The moneyer
A moneyer is a private individual who is officially permitted to mint money. Usually the rights to coin money are bestowed as a concession by a state or government. Moneyers have a long tradition, dating back at least to ancient Greece. They bec ...
William Turnemire introduced a novel method of minting coins that involved cutting blank coins from a silver rod, in contrast with the old practice of stamping them out from sheets; this technique proved to be efficient. The practice of minting coins with the moneyer's name on them became obsolete under Edward's rule because England's mint administration became far more centralised under the Crown's authority. During this time, English coins were frequently counterfeited on the Continent, especially the Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
, and despite a ban in 1283, English coinage was secretly exported to the European continent. In August 1280, Edward forbade the usage of the old long cross coinage, which forced the populace to switch to the newly minted versions. Records indicate that the coinage overhaul successfully provided England with a stable currency..
Lucca
Città di Lucca ( ; ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its Province of Lucca, province has a population of 383,9 ...
in Italy. This was in return for their service as moneylenders to the crown, which helped finance the Welsh Wars. When the war with France broke out, the French king confiscated the Riccardi's assets, and the bank went bankrupt. After this, the Frescobaldi
The Frescobaldi are a prominent Florentine noble family whose influence extends deeply into the political, economic, and social fabric of Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the ...
of Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
took over the role as moneylenders to the English crown. Edward also sought to reduce pressure on his finances by helping his wife Eleanor to build an independent income.
Edward held Parliament on a regular basis throughout his reign. In 1295, a significant change occurred. For this Parliament, as well as the secular and ecclesiastical lords, two knights from each county and two representatives from each borough were summoned., . The representation of commons in Parliament was nothing new; what was new was the authority under which these representatives were summoned. Whereas previously the commons had been expected to assent to decisions made by the magnates, it was now proclaimed that they should meet with the full authority (''plena potestas'') of their communities, to give assent to decisions made in Parliament. The King now had full backing for collecting lay subsidies from the entire population. Whereas Henry III had only collected four of these in his reign, Edward collected nine. This format eventually became the standard for later Parliaments, and historians have named the assembly the "Model Parliament
The Model Parliament was the 1295 Parliament of England of Edward I of England, King Edward I. Its composition became the model for later parliaments.
History
The term ''Model Parliament'' was coined by William Stubbs (1825-1901) and later use ...
", a term first introduced by the English historian William Stubbs
William Stubbs (21 June 182522 April 1901) was an English historian and Anglican bishop. He was Regius Professor of History (Oxford), Regius Professor of Modern History at the University of Oxford between 1866 and 1884. He was Bishop of Ches ...
..
Parliament and the expulsion of the Jews
 Edward's policy towards the
Edward's policy towards the English Jews
The history of the Jews in England can be traced to at least 750 CE through the Canonical Exceptions of Echbright, published by the Archbishop of York, although it is likely that there had been some Jewish presence in the Roman period and poss ...
dominated his financial relations with Parliament until 1290. Jews, unlike Christians, were allowed to charge interest on loans, known as usury
Usury () is the practice of making loans that are seen as unfairly enriching the lender. The term may be used in a moral sense—condemning taking advantage of others' misfortunes—or in a legal sense, where an interest rate is charged in e ...
. Edward faced pressure from the church, who were increasingly intolerant of Judaism and usury. The Jews were the King's personal property, and he was free to tax them at will. Over-taxation of the Jews forced them to sell their debt bonds at cut prices, which was exploited by the crown to transfer vast land wealth from indebted landholders to courtiers and his wife, Eleanor of Provence, causing widespread resentment. In 1275, facing discontent in Parliament, Edward issued the Statute of the Jewry
The Statute of the Jewry (''Statutum de Judaismo, 1275'') was a statute enacted under Edward I of England in 1275. It placed a number of restrictions on Jews of England, most notably outlawing the practice of usury.Prestwich, Michael. Edward I ...
, which outlawed loans with interest and encouraged the Jews to take up other professions. In 1279, using a crack-down on coin-clippers as a pretext, he organised the arrest of all the heads of Jewish households in England. Approximately a tenth of the Jewish population, around 300 people, were executed. Others were allowed to pay fines. At least £16,000 was raised through fines and the seizure of property from the dead. In 1280, he ordered all Jews to attend special sermons, preached by Dominican friars, with the hope of persuading them to convert, but these exhortations were not followed. By 1280, the Jews had been exploited to a level at which they were no longer of much financial use to the crown,, , . but they could still be used in political bargaining.
With the Edict of Expulsion in 1290, Edward formally expelled all Jews from England. As they crossed the Channel to France, some became victims to piracy, and many more were dispossessed or died in the October storms. The Crown disposed of their property through sales and 85 grants made to courtiers and family. The Edict appears to have been issued as part of a deal to secure a lay subsidy of £110,000 from Parliament, the largest granted in the medieval period. Although expulsions had taken place on a local, temporary basis, the English expulsion was unprecedented because it was permanent. It was eventually reversed in the 1650s. Edward claimed the Expulsion was done "in honour of the Crucified
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the condemned is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross, beam or stake and left to hang until eventual death. It was used as a punishment by the Achaemenid Empire, Persians, Carthaginians, ...
" and blamed the Jews for their treachery and criminality. He helped pay for the renovation of the tomb of Little Saint Hugh
Hugh of Lincoln (1246 – 27 August 1255) was an English boy whose death in Lincoln was falsely attributed to Jews. He is sometimes known as Little Saint Hugh or Little Sir Hugh to distinguish him from the adult saint, Hugh of Lincoln (die ...
, a child falsely claimed to have been ritually crucified by Jews, in the same style as the Eleanor crosses, to take political credit for his actions. As historian Richard Stacey notes, "a more explicit identification of the crown with the ritual crucifixion charge can hardly be imagined."
Administration in Ireland
Edward's primary interest in Ireland was as a source of resources, soldiers and funds for his wars, in Gascony, Wales, Scotland and Flanders. Royal interventions aimed to maximise economic extraction. Corruption among Edward's officials was at a high level, and despite Edward's efforts after 1272 to reform the Irish administration, record keeping was poor. Disturbances in Ireland increased during the period. The weakness and lack of direction given to the Lordship's rule allowed factional fighting to grow, reinforced by the introduction of indentured military service by Irish magnates from around 1290. The funnelling of revenue to Edward's wars left Irish castles, bridges and roads in disrepair, and alongside the withdrawal of troops to be used against Wales and Scotland and elsewhere, helped induce lawless behaviour. Resistance to 'purveyances', or forced purchase of supplies such as grain, added to lawlessness, and caused speculation and inflation in the price of basic goods. Pardons were granted to lawbreakers for service for the King in England. Revenues and removal of troops for Edward's wars left the country unable to address its basic needs, while the administration was wholly focused on providing for Edward's war demands; troops looted and fought with townspeople when on the move.Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland () was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late Prehistory of Ireland, prehistoric era until the 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Norman invasi ...
enjoyed a revival, due to the absence of English magnates and the weakness of the Lordship, assimilating some of the settlers. Edward's government was hostile to the use of Gaelic law, which it condemned in 1277 as "displeasing to God and to reason". Conflict was firmly entrenched by the time of the 1297 Irish Parliament, which attempted to create measures to counter disorder and the spread of Gaelic customs and law, while the results of the distress included many abandoned lands and villages.
Later reign, 1297–1307
Constitutional crisis
The incessant warfare of the 1290s put a great financial demand on Edward's subjects. Whereas the King had levied only three lay subsidies until 1294, four such taxes were granted in the years 1294–1297, raising over £200,000. Along with this came the burden ofprise
Purveyance, a greatly expanded form of the ancient customary right of prise, was a mediaeval prerogative right of the English Crown to purchase provisions and other necessaries, at an appraised price, and to requisition horses and vehicles for ...
s, seizure of wool and hides, and the unpopular additional duty on wool, dubbed the ''maltolt
Maltolt or "bad tax" (in Norman-French) was the name given to the new taxes on wool in England of 1294–1297. Protests against the maltolt played their part in forcing the confirmation of the charters from the Crown.
Origin
Edward I of England h ...
'' ("unjustly taken"). The fiscal demands on the King's subjects caused resentment, which eventually led to serious political opposition. The initial resistance was caused not by the lay taxes, but by clerical subsidies. In 1294, Edward made a demand of a grant of one-half of all clerical revenues. There was some resistance, but the King responded by threatening opponents with outlaw
An outlaw, in its original and legal meaning, is a person declared as outside the protection of the law. In pre-modern societies, all legal protection was withdrawn from the criminal, so anyone was legally empowered to persecute or kill them. ...
ry, and the grant was eventually made. At the time, Robert Winchelsey
Robert Winchelsey (or Winchelsea; c. 1245 – 11 May 1313) was an English Catholic theologian and Archbishop of Canterbury. He studied at the universities of Paris and Oxford, and later taught at both. Influenced by Thomas Aquinas, he was a ...
, the designated Archbishop of Canterbury, was in Italy to receive consecration. Winchelsey returned in January 1295 and had to consent to another grant that November. In 1296, his position changed when he received the papal bull
A papal bull is a type of public decree, letters patent, or charter issued by the pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the leaden Seal (emblem), seal (''bulla (seal), bulla'') traditionally appended to authenticate it.
History
Papal ...
''Clericis laicos
was a papal bull issued on February 5, 1296, by Pope Boniface VIII in an attempt to prevent the secular states of Europein particular France and Englandfrom appropriating church revenues without the express prior permission of the pope. The two ...
''. This prohibited the clergy from paying taxes to lay authorities without explicit consent from the Pope. When the clergy, with reference to the bull, refused to pay, Edward responded with outlawry. Winchelsey was presented with a dilemma between loyalty to the King and upholding the papal bull, and he responded by leaving it to every individual clergyman to pay as he saw fit. By the end of the year, a solution was offered by the new papal bull '' Etsi de statu'', which allowed clerical taxation in cases of pressing urgency. This allowed Edward to collect considerable sums by taxing the English clergy.
Opposition from the laity took longer to surface. This resistance focused on the King's right to demand military service and his right to levy taxes. At the Salisbury Parliament of February 1297, the Earl Marshal
Earl Marshal (alternatively marschal or marischal) is a hereditary royal officeholder and chivalric title under the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, sovereign of the United Kingdom used in England (then, following the Act of Union 1800, in the U ...
Roger Bigod, 5th Earl of Norfolk
Roger Bigod (c. 1245 – bf. 6 December 1306) was 5th Earl of Norfolk.
Origins
He was the son of Hugh Bigod (Justiciar), Hugh Bigod (1211–1266), Justiciar, and succeeded his father's elder brother Roger Bigod, 4th Earl of Norfolk (1209� ...
, objected to a royal summons of military service. Bigod argued that the military obligation only extended to service alongside the King; if the King intended to sail to Flanders, he could not send his subjects to Gascony. In July, Bigod and Humphrey de Bohun, 3rd Earl of Hereford
Humphrey (VI) de Bohun (c. 1249 – 31 December 1298), 3rd Earl of Hereford and 2nd Earl of Essex, was an English nobleman known primarily for his opposition to King Edward I over the ''Confirmatio Cartarum.''Fritze and Robison, (2002). He ...
and Constable of England
The Lord High Constable of England is the seventh of the Great Officers of State, ranking beneath the Lord Great Chamberlain and above the Earl Marshal. This office is now called out of abeyance only for coronations. The Lord High Constable was ...
, drew up a series of complaints known as the Remonstrances
The Remonstrances of 1297 (sometimes written in the original Anglo-Norman: Monstraunces) were a set of complaints presented by a group of nobles in 1297, against the government of King Edward I of England. Foremost among the nobles were Roger Bi ...
, in which objections to the high level of taxation were voiced. Undeterred, Edward requested another lay subsidy. This one was particularly provocative, because the King had sought consent from only a small group of magnates, rather than from representatives of the communities in Parliament. While Edward was in Winchelsea
Winchelsea () is a town in the county of East Sussex, England, located between the High Weald and the Romney Marsh, approximately south west of Rye and north east of Hastings. The current town, which was founded in 1288, replaced an earli ...
, preparing for the campaign in Flanders, Bigod and de Bohun arrived at the Exchequer to prevent the collection of the tax. As the King left the country with a greatly reduced force, the kingdom seemed to be on the verge of civil war. The English defeat by the Scots at the Battle of Stirling Bridge
The Battle of Stirling Bridge () was fought during the First War of Scottish Independence. On 11 September 1297, the forces of Andrew Moray and William Wallace defeated the combined English forces of John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey, a ...
resolved the situation. The renewed threat to the homeland gave king and magnates common cause. Edward signed the ''Confirmatio cartarum
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardinal S ...
''a confirmation of Magna Carta and its accompanying Charter of the Forest
The Charter of the Forest of 1217 re-established rights of access for free tenant, free men to the royal forest that had been eroded by King William the Conqueror and his heirs. Many of its provisions were in force for centuries afterwards. It ...
and the nobility agreed to serve with the King on a campaign in Scotland.
Edward's problems with the opposition did not end with the Scottish campaign. Over the following years he would be held to the promises he had made, in particular that of upholding the Charter of the Forest. In the Parliament of 1301, the King was forced to order an assessment of the royal forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
s, but in 1305 he obtained a papal bull that freed him from this concession. Ultimately, it was a change in personnel that spelt the end of the opposition against Edward. De Bohun died late in 1298, after returning from the Scottish campaign. In 1302 Bigod arrived at an agreement with the King that was beneficial for both: Bigod, who had no children, made Edward his heir, in return for a generous annual grant. Edward got his revenge on Winchelsey, who had been opposed to the King's policy of clerical taxation, in 1305, when Clement V
Pope Clement V (; – 20 April 1314), born Raymond Bertrand de Got (also occasionally spelled ''de Guoth'' and ''de Goth''), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 5 June 1305 to his death, in April 1314. He is reme ...
was elected pope. Clement was a Gascon sympathetic to the King, and on Edward's instigation had Winchelsey suspended from office.
Return to Scotland
 Edward believed that he had completed the conquest of Scotland when he left the country in 1296, but resistance soon emerged under the leadership of
Edward believed that he had completed the conquest of Scotland when he left the country in 1296, but resistance soon emerged under the leadership of Andrew de Moray
Andrew Moray (; ), also known as Andrew de Moray, Andrew of Moray, or Andrew Murray, was a Scots esquire, who rose to prominence during the First Scottish War of Independence. He initially raised a small band of supporters at Avoch Castle i ...
in the north and William Wallace
Sir William Wallace (, ; Norman French: ; 23 August 1305) was a Scottish knight who became one of the main leaders during the First War of Scottish Independence.
Along with Andrew Moray, Wallace defeated an English army at the Battle of St ...
in the south. On 11 September 1297, a large English force under the leadership of John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey, and Hugh de Cressingham
Sir Hugh de Cressingham (died 11 September 1297) was the treasurer of the England, English administration in Scotland from 1296 to 1297. He was an adviser to John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey at the Battle of Stirling Bridge. He suggested a f ...
was routed by a much smaller Scottish army led by Wallace and Moray at the Battle of Stirling Bridge. The defeat sent shockwaves into England, and preparations for a retaliatory campaign started immediately. Soon after Edward returned from Flanders, he headed north. On 22 July 1298, in the only major battle he had fought since Evesham in 1265, Edward defeated Wallace's forces at the Battle of Falkirk
The Battle of Falkirk (; ), on 22 July 1298, was one of the major battles in the First War of Scottish Independence. Led by Edward I of England, King Edward I of England, the English army defeated the Scottish people, Scots, led by William Wal ...
. Edward was not able to take advantage of the momentum and the next year the Scots recaptured Stirling Castle
Stirling Castle, located in Stirling, is one of the largest and most historically and architecturally important castles in Scotland. The castle sits atop an Intrusive rock, intrusive Crag and tail, crag, which forms part of the Stirling Sill ge ...
. Even though Edward campaigned in Scotland in 1300, when he successfully besieged Caerlaverock Castle
Caerlaverock Castle is a moated triangular castle first built in the 13th century. It is located on the southern coast of Scotland, south of Dumfries, on the edge of the Caerlaverock National Nature Reserve. Caerlaverock was a stronghold of t ...
and in 1301, the Scots refused to engage in open battle again, preferring instead to raid the English countryside in smaller groups.
The Scots appealed to Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII (; born Benedetto Caetani; – 11 October 1303) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 December 1294 until his death in 1303. The Caetani, Caetani family was of baronial origin with connections t ...
to assert a papal claim of overlordship to Scotland in place of the English. His papal bull addressed to King Edward in these terms was firmly rejected on Edward's behalf by the Barons' Letter of 1301
The Barons' Letter of 1301 was written by 103 English, Scottish, Norman and Welsh, earls and barons loyal to King Edward I. The letter was addressed to Pope Boniface VIII as a repudiation of his claim of feudal overlordship of Scotland (express ...
. The English managed to subdue the country by other means: in 1303, a peace agreement was reached between England and France, effectively breaking up the Franco-Scottish alliance. Robert the Bruce
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (), was King of Scots from 1306 until his death in 1329. Robert led Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the First War of Scottish Independence against Kingdom of Eng ...
, the grandson of the claimant to the crown in 1291, had sided with the English in the winter of 1301–02. In 1304, most of the other nobles of the country had also pledged their allegiance to Edward, and the English also managed to re-take Stirling Castle. A great propaganda victory was achieved in 1305 when Wallace was betrayed by Sir John de Menteith
Sir John Menteith of Ruskie and Knapdale (c. 1275 – c. 1329) was a Scottish nobleman during the Wars of Scottish Independence. He is known for his capture of Sir William Wallace in 1305 and later joined with King Robert I of Scotland and ...
and turned over to the English, who had him taken to London and publicly executed. With Scotland largely under English control, Edward installed Englishmen and collaborating Scots to govern the country.
The situation changed again on 10 February 1306, when Robert the Bruce murdered his rival John Comyn
John Comyn III of Badenoch, nicknamed the Red ( 1274 – 10 February 1306), was a leading Scottish baron and magnate who played an important role in the First War of Scottish Independence. He served as Guardian of Scotland after the forced ...
,. and a few weeks later, on 25 March, was crowned King of Scotland. Bruce now embarked on a campaign to restore Scottish independence, and this took the English by surprise. Edward was suffering ill health by this time, and instead of leading an expedition himself, he gave different military commands to Aymer de Valence, 2nd Earl of Pembroke
Aymer de Valence, 2nd Earl of Pembroke ( 1270 – 23 June 1324) was an Anglo-French nobleman. Though primarily active in England, he also had strong connections with the List of French monarchs, French royal house. One of the wealthiest and mo ...
, and Henry Percy, 1st Baron Percy
Henry de Percy, 1st Baron Percy of Alnwick (25 March 1273 – October 1314) was a medieval English magnate.
He fought under Edward I of England, King Edward I of England in Wales and Scotland and was granted extensive estates in Scotland, wh ...
, while the main royal army was led by the Prince of Wales. The English initially met with success; on 19 June, Aymer de Valence routed Bruce at the Battle of Methven
The Battle of Methven took place at Methven, Scotland on 19 June 1306, during the Wars of Scottish Independence. The battlefield was researched to be included in the Inventory of Historic Battlefields in Scotland and protected by Historic Sco ...
. Bruce was forced into hiding, and the English forces recaptured their lost territory and castles.
Edward acted with unusual brutality against Bruce's family, allies, and supporters. His sister, Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a female given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religion
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blesse ...
, was imprisoned in a cage at Roxburgh Castle
Roxburgh Castle is a ruined royal castle that overlooks the junction of the rivers Tweed and Teviot, in the Borders region of Scotland. The town and castle developed into the royal burgh of Roxburgh, which the Scots destroyed along with ...
for four years. Isabella MacDuff, Countess of Buchan
Isabella MacDuff, Countess of Buchan (probably died c. 1314), was a significant figure in the Wars of Scottish Independence.
She was the daughter of Donnchadh III, Earl of Fife, and Johanna de Clare, daughter of The 6th Earl of Hertford. She ...
, who had crowned Bruce, was held in a cage at Berwick Castle. His younger brother Neil
Neil is a masculine name of Irish origin. The name is an anglicisation of the Irish ''Niall'' which is of disputed derivation. The Irish name may be derived from words meaning "cloud", "passionate", "victory", "honour" or "champion".. As a surname ...
was executed by being hanged, drawn, and quartered
To be hanged, drawn and quartered was a method of torturous capital punishment used principally to execute men convicted of high treason in medieval and early modern Britain and Ireland. The convicted traitor was fastened by the feet to a h ...
; he had been captured after he and his garrison held off Edward's forces who had been seeking his wife
A wife (: wives) is a woman in a marital relationship. A woman who has separated from her partner continues to be a wife until their marriage is legally dissolved with a divorce judgment; or until death, depending on the kind of marriage. On t ...
, daughter
A daughter is a female offspring; a girl or a woman in relation to her parents. Daughterhood is the state, condition or quality of being someone's daughter. The male counterpart is a son. Analogously the name is used in several areas to show r ...
and sisters. Edward now regarded the struggle not as a war between two nations, but as the suppression of a rebellion of disloyal subjects. This brutality, rather than helping to subdue the Scots, had the opposite effect, and rallied growing support for Bruce.
Death and burial
 In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the
In February 1307, Bruce resumed his efforts and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Valence at the Battle of Loudoun Hill
The Battle of Loudoun Hill was fought on 10 May 1307, between a Scots force led by King Robert the Bruce and the English commanded by Aymer de Valence, Earl of Pembroke. It took place beneath Loudoun Hill, in Ayrshire, and ended in a vic ...
. Edward, who had rallied somewhat, now moved north himself. He developed dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehyd ...
on the way, and his condition deteriorated. On 6 July he encamped at Burgh by Sands
Burgh by Sands () is a village and civil parish in the Cumberland unitary authority area of Cumbria, England, situated near the Solway Firth. The parish includes the village of Burgh by Sands along with Longburgh, Dykesfield, Boustead Hill, Moor ...
, just south of the Scottish border. When his servants came the next morning to lift him up so that he could eat, the King died in their arms.
Several stories emerged about Edward's deathbed wishes; according to one tradition, he requested that his heart be carried to the Holy Land, along with an army to fight the infidels.. A more dubious story tells of how he wished for his bones to be carried along on future expeditions against the Scots. Another account of his deathbed scene is more credible; according to one chronicle, Edward gathered around him Henry de Lacy, 3rd Earl of Lincoln
Henry de Lacy, Earl of Lincoln (c. 1251February 1311), Baron of Pontefract, Lord of Bowland, Baron of Halton and hereditary Constable of Chester, was an English nobleman and confidant of King Edward I. He served Edward in Wales, France, and ...
; Guy de Beauchamp, 10th Earl of Warwick
Guy or GUY may refer to:
Personal names
* Guy (given name)
* Guy (surname)
* That Guy (...), the New Zealand street performer Leigh Hart
Places
* Guy, Alberta, a Canadian hamlet
* Guy, Arkansas, US, a city
* Guy, Indiana, US, an unin ...
; Aymer de Valence; and Robert de Clifford, 1st Baron de Clifford
Robert de Clifford, 1st Baron de Clifford (1 April 1274 – 24 June 1314), of Appleby Castle, Westmorland, feudal baron of Appleby and feudal baron of Skipton in Yorkshire, was an English soldier who became 1st Lord Warden of the Marches, ...
, and charged them with looking after his son Edward. In particular they should make sure that Piers Gaveston, whom he had banished earlier that year, was not allowed to return to the country. The new king, Edward II, ignored his father's wish, and had his favourite recalled from exile almost immediately. Edward II remained in the north until August, but then abandoned the campaign and headed south, partially due to financial limitations. He was crowned king on 25 February 1308.
Edward I's body was brought south, lying in state at Waltham Abbey
Waltham Abbey is a suburban town and civil parish in the Epping Forest District of Essex, within the London metropolitan area, metropolitan and urban area of London, England, East London, north-east of Charing Cross. It lies on the Greenwich ...
, before being buried in Westminster Abbey on 27 October., . There are few records of the funeral, which cost £473.
Edward's tomb was an unusually plain sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (: sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a coffin, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:σάρξ, σάρξ ...
of Purbeck marble
Purbeck Marble is a fossiliferous limestone found in the Isle of Purbeck, a peninsula in south-east Dorset, England. It is a variety of Purbeck stone that has been quarried since at least Roman times as a decorative building stone.
Geology
S ...
, without the customary royal effigy
An effigy is a sculptural representation, often life-size, of a specific person or a prototypical figure. The term is mostly used for the makeshift dummies used for symbolic punishment in political protests and for the figures burned in certain ...
, possibly the result of the shortage of royal funds. The Society of Antiquaries of London
The Society of Antiquaries of London (SAL) is a learned society of historians and archaeologists in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1707, received its royal charter in 1751 and is a Charitable organization, registered charity. It is based ...
opened the tomb in 1774, finding that the body had been well preserved over the preceding 467 years, and took the opportunity to determine the King's original height. Traces of the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
inscription ''Edwardus Primus Scottorum Malleus hic est, 1308. Pactum Serva'' ("Here is Edward I, Hammer of the Scots, 1308. Keep the Troth") can still be seen painted on the side of the tomb, referring to his vow to avenge the rebellion of Robert the Bruce. This resulted in Edward being given the epithet the "Hammer of the Scots" by historians, but is not contemporary in origin, having been added by the Abbot John Feckenham in the 16th century.
Legacy
 The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the
The first histories of Edward in the 16th and 17th centuries drew primarily on the works of the chronicler
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, ...
s, and made little use of the official records of the period.. They limited themselves to general comments on Edward's significance as a monarch, and echoed the chroniclers' praise for his accomplishments. In the 17th century, the lawyer Edward Coke
Sir Edward Coke ( , formerly ; 1 February 1552 – 3 September 1634) was an English barrister, judge, and politician. He is often considered the greatest jurist of the Elizabethan era, Elizabethan and Jacobean era, Jacobean eras.
Born into a ...
wrote extensively about Edward's legislation, terming the King the "English Justinian" after the Byzantine lawmaker Justinian I. Later in the century, historians used the available record as evidence to elucidate the roles of Parliament and kingship under Edward, drawing comparisons between his reign and the political strife of their own century. In the 18th century, historians depicted Edward as an able, if ruthless, monarch, conditioned by the circumstances of his time.
The influential Victorian
Victorian or Victorians may refer to:
19th century
* Victorian era, British history during Queen Victoria's 19th-century reign
** Victorian architecture
** Victorian house
** Victorian decorative arts
** Victorian fashion
** Victorian literatur ...
historian William Stubbs suggested that Edward had actively shaped national history, forming English laws and institutions, and helping England to develop a parliamentary
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
and constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
. His strengths and weaknesses as a ruler were considered to be emblematic of the English people as a whole. Stubbs's student, Thomas Tout
Thomas Frederick Tout (28 September 1855 – 23 October 1929) was a British historian of the medieval period. He was one of the founders of the Historical Association in 1906.
Early life
Born in London, he was a pupil of St. Olave's Grammar S ...
, initially adopted the same perspective, but after extensive research into Edward's royal household, and backed by the research of his contemporaries into the early Parliaments of the period, he changed his mind. Tout came to view Edward as a self-interested, conservative leader, using the parliamentary system as "the shrewd device of an autocrat, anxious to use the mass of the people as a check upon his hereditary foes among the greater baronage."
Historians in the 20th and 21st centuries have conducted extensive research on Edward and his reign. Most have concluded this was a highly significant period in English medieval history, some describing Edward as one of the great medieval kings, although most agree that his final years were less successful than his early decades in power. G. Templeman argued in his 1950 historiographical essay that "it is generally recognized that Edward I deserves a high place in the history of medieval England". Three major academic narratives of Edward have been produced during this period. F. M. Powicke
Sir Frederick Maurice Powicke (16 June 1879 – 19 May 1963) was an English medieval historian. He was a fellow of Merton College, Oxford, a professor at Queen's University, Belfast, and the Victoria University of Manchester, and from 1928 un ...
's volumes, published in 1947 and 1953, forming the standard works on Edward for several decades, were largely positive in praising the achievements of his reign, and his focus on justice and the law. In 1988, Michael Prestwich produced an authoritative biography of the King, focusing on his political career, still portraying him in sympathetic terms, but highlighting some of the consequences of his failed policies. Marc Morris's biography followed in 2008, drawing out more of the detail of Edward's personality, and generally taking a harsher view of his weaknesses and less pleasant characteristics, pointing out that modern analysts of Edward's reign denounce the King for his policies against the Jewish community in England. Considerable academic debate has taken place around the character of Edward's kingship, his political skills, and his management of his earls, and whether this was collaborative or repressive in nature.
Historians have debated how Edward I's reign should be assessed: Michael Prestwich in 1988 attempted to judge him by the standards of his time. Fred Cazel agrees with this approach, particularly regarding his lack of political "sensitivity" and uncompromising attitudes, arguing that anger was his political weapon. Prestwich concludes that "Edward was a formidable king; his reign, with both its successes and its disappointments, a great one," and he was "without doubt one of the greatest rulers of his time". G. W. S. Barrow counters that Edward's contemporaries knew the "meaning of compassion, magnanimity, justice and generosity", that he rarely rose above minimum moral standards of his time, but rather showed a highly vindictive streak, and is among the "boldest opportunists of English political history". John Gillingham
John Bennett Gillingham (born 3 August 1940) is Emeritus Professor of Medieval History at the London School of Economics and Political Science. On 19 July 2007 he was elected a Fellow of the British Academy.
Gillingham is renowned as an expert on ...
argues that Edward was an "effective bully", but "no king of England had a greater impact on the peoples of Britain than Edward I" and that "modern historians of the English state … have always recognized Edward I's reign as pivotal." In 2014, Andrew Spencer and Caroline Burt reassessed Edward's reign from an English constitutional perspective, asserting that he had a personal role in reform and a moral purpose in his leadership. Spencer concludes that Edward's reign "was indeed … a great one", and Burt claims that Edward was "innovative, … creative, focused and successful". She adds that he "played the part of a good king well … ndwith aplomb". Colin Veach asks whether "the Welsh, Scots, Irish and Jews would have agreed".
There is a great difference between English and Scottish historiography on King Edward. G.W.S.Barrow saw Edward as ruthlessly exploiting the leaderless state of Scotland to obtain feudal superiority over the kingdom and reduce it to an English possession. In his view, Edward's insistence on war and misapprehension of Scottish capacity for resistance created a "bitter antagonism … which endured for centuries". Michael Brown warns that Scottish independence should not be viewed as inevitable; Edward could have achieved his goals. Welsh historians see Edward's reign and conquest as a disaster for Welsh confidence and culture. R. R. Davies views his methods in Wales as essentially colonialist, creating deep resentment and an "apartheid-like" social structure. John Davies noted the "anti-Welsh fanaticism" of the English colonists introduced by Edward's conquest. They acknowledge Edward's attempts to rebuild some kind of co-operation with native Welsh society, but state that this was insufficient to heal the trauma of conquest. Irish historian James Lydon regarded the 13th century and Edward's reign as a turning point for Ireland, as the Lordship extracted Irish resources for his wars, failed to maintain peace, and allowed a resurgence in the fortunes of Gaelic Ireland, leading to prolonged conflict. Simon Schama
Sir Simon Michael Schama ( ; born 13 February 1945) is an English historian and television presenter. He specialises in art history, Dutch history, Jewish history, and French history. He is a professor of history and art history at Columbia Uni ...
, Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a British and Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Profes ...
, and historians from Scotland, Wales and Ireland, have tried to assess Edward's reign in the context of the development of Britain and Ireland. They emphasise the growing power of the law, centralised state and crown across Europe, and see Edward as asserting his rights within England and the other nations of Britain and Ireland. Brown adds that Edward suffered from this as a subject of the French king in Gascony. Centralisation tended to imply uniformity and increasing discrimination against peripheral identities and hostility to Irish and Welsh law. While this group of historians do not see Edward as having conducted a planned policy of expansionism, they often see the tactics and results of his policies as often having caused unnecessary division and conflict.
Barrie Dobson
Richard Barrie Dobson, (3 November 1931 – 29 March 2013) was an English historian who was a leading authority on the legend of Robin Hood as well as a scholar of ecclesiastical and Jewish history. He served as Professor of Medieval History ...
says that Edward I's actions towards the Jewish minority often appear to be the most relevant part of his reign for a modern audience, while in 1992 Colin Richmond expressed dismay that Edward had not received a wider re-evaluation. Paul Hyams sees his "sincere religious bigotry" as central to his actions against Jews, Richmond sees him as a "pioneering antisemite", and Robert Stacey regards him as the first English monarch to operate a state policy of antisemitism. Robert Moore emphasises that antisemitism was developed by church leaders and acted on by figures including Edward, rather than being a facet of popular prejudice. Studies of medieval antisemitism identify Henry III and Edward's reigns, along with the Expulsion, as developing a persistent English antisemitism, based on the idea of the English superseding the Jews as God's chosen people, and on England's uniqueness as a country free of Jews.
Family
First marriage
By his first wife Eleanor of Castile, Edward had at least fourteen children, perhaps as many as sixteen. Of these, five daughters survived into adulthood, but only one son outlived his father, becoming King Edward II (). Edward's children with Eleanor were: # Katherine (1261 or 1263–1264). # Joan (1265–1265) # John (1266–1271) #Henry
Henry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters
* Henry (surname)
* Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone
Arts and entertainmen ...
(1268–1274)
# Eleanor
Eleanor () is a feminine given name, originally from an Old French adaptation of the Old Provençal name ''Aliénor''. It was the name of a number of women of royalty and nobility in western Europe during the High Middle Ages">Provençal dialect ...
(1269–1298)
# Unnamed daughter (1271–1271 or 1272)
# Joan (1272–1307)
# Alphonso
Alphons (Latinized ''Alphonsus'', ''Adelphonsus'', or ''Adefonsus'') is a male given name recorded from the 8th century (Alfonso I of Asturias, r. 739–757) in the Christian successor states of the Visigothic Kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula. I ...
(1273–1284)
# Margaret
Margaret is a feminine given name, which means "pearl". It is of Latin origin, via Ancient Greek and ultimately from Iranian languages, Old Iranian. It has been an English language, English name since the 11th century, and remained popular thro ...
(1275–1333)
# Berengaria (1276–1277 or 1278)
# Unnamed child (1278–1278)
# Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a female given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religion
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blesse ...
(1278–1332)
# Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Empress Elisabeth (disambiguation), lists various empresses named ''Elisabeth'' or ''Elizabeth''
* Princess Elizabeth ...
(1282–1316)
# Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also known as Edward of Caernarfon or Caernarvon, was King of England from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir to the throne follo ...
(1284–1327)
Second marriage
By Margaret of France, Edward had two sons, both of whom lived to adulthood, and a daughter who died as a child: #Thomas
Thomas may refer to:
People
* List of people with given name Thomas
* Thomas (name)
* Thomas (surname)
* Saint Thomas (disambiguation)
* Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church
* Thomas the A ...
(1300–1338)
# Edmund
Edmund is a masculine given name in the English language. The name is derived from the Old English elements ''ēad'', meaning "prosperity" or "riches", and ''mund'', meaning "protector".
Persons named Edmund include:
People Kings and nobles
*Ed ...
(1301–1330)
# Eleanor (1306–1311)
A genealogy in the Hailes Abbey
Hailes Abbey is a former Cistercian abbey, in the small village of Hailes, Gloucestershire, Hailes, two miles northeast of Winchcombe, Gloucestershire, England. It was founded in 1246 as a daughter establishment of Beaulieu Abbey. The abbey wa ...
chronicle indicates that John Botetourt may have been Edward's illegitimate son, but the claim is unsubstantiated.,
Genealogical table
See also
* List of earls in the reign of Edward I of England *Savoyard knights in the service of Edward I
Edward I of England was associated with the Savoyard faction of nobles and knights who came from the County of Savoy, and were favoured in England. Savoy became linked to the Plantaganet monarchy of England with the marriage of Edward I's pare ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * *: *: * * * * * * * *: *: * * * * * * * * * *: *: * * * * *: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *: * *: *: *: * * * * * *: *: * * * * *: * *: *: *: *: *: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *: *: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *: *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Edward 01 Of England 1239 births 1307 deaths 13th-century English monarchs 13th-century peers of France 14th-century English monarchs 14th-century peers of France Antisemitism in England Burials at Westminster Abbey Children of Henry III of England Christians of Lord Edward's crusade Competitors for the Crown of Scotland Deaths from dysentery Earls of Chester English people of the Wars of Scottish Independence High sheriffs of Bedfordshire High sheriffs of Buckinghamshire House of Plantagenet Jure uxoris counts Lords Warden of the Cinque Ports Medieval governors of Guernsey People from Westminster People of the Barons' Wars People with ptosis (eyelid) People with speech disorders Royalty and nobility with disabilities Sons of kings