Dioscoreales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Dioscoreales are an order of
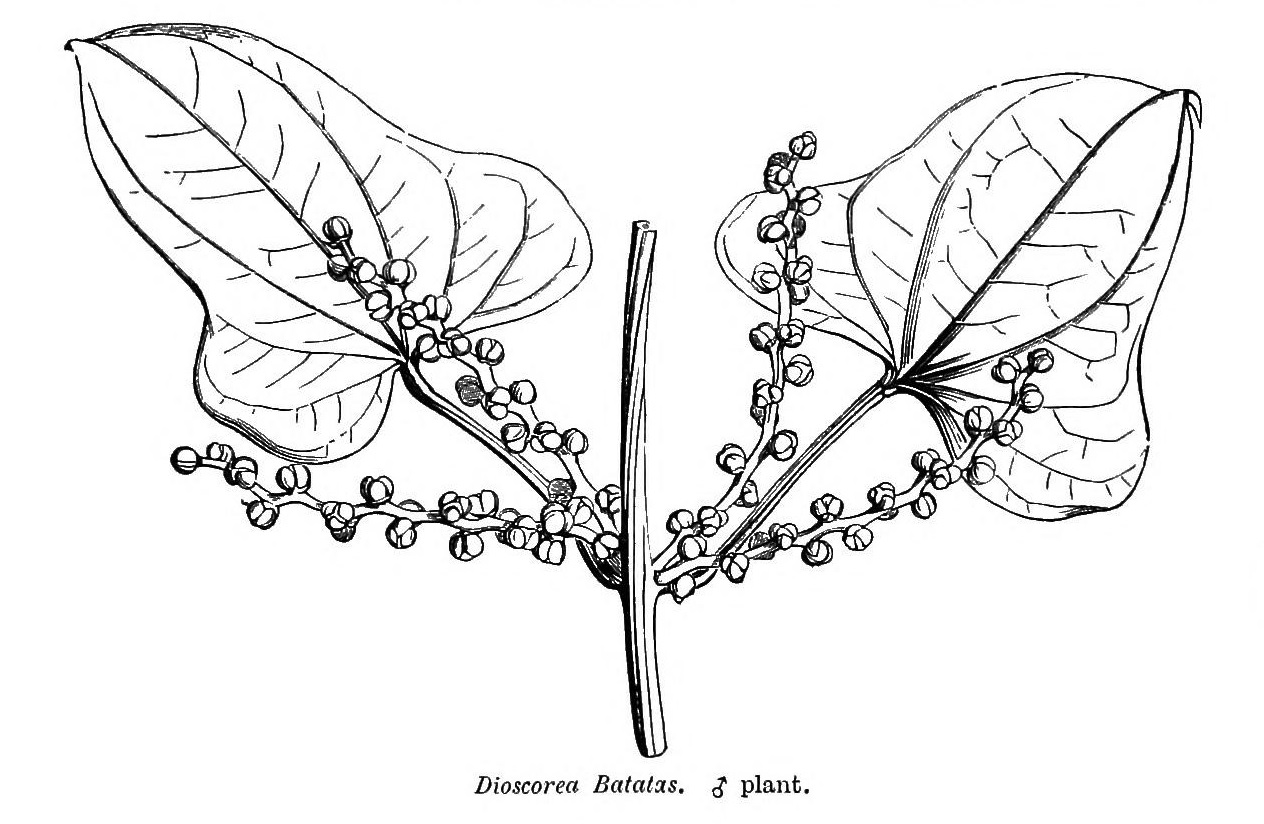 While Lindley did not use the term "Dioscoreales", he placed the family Dioscoraceae together with four other families in what he referred to as an Alliance (the equivalent of the modern Order) called Dictyogens. He reflected the uncertainty as to the place of this Alliance by placing it as a class of its own between Endogens (monocots) and Exogens (dicots) The
While Lindley did not use the term "Dioscoreales", he placed the family Dioscoraceae together with four other families in what he referred to as an Alliance (the equivalent of the modern Order) called Dictyogens. He reflected the uncertainty as to the place of this Alliance by placing it as a class of its own between Endogens (monocots) and Exogens (dicots) The
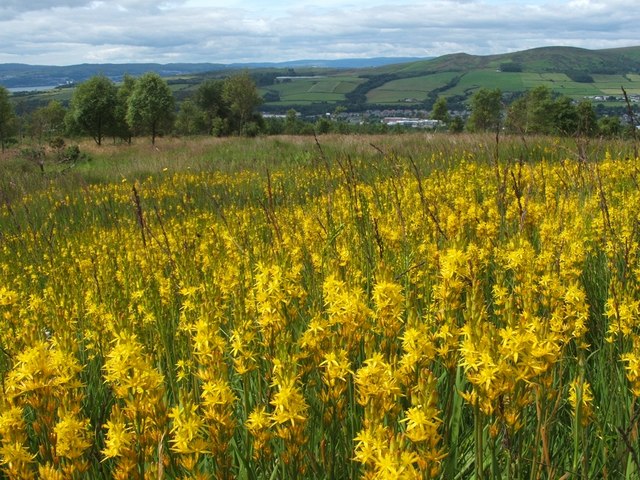 The three families included in order Dioscoreales also represent three different ecological groups of plants.
The three families included in order Dioscoreales also represent three different ecological groups of plants.
Excerpts
* * * * * * * * * * * * , In * * *
Kress WJ. Dioscoreales. Encyclopædia Britannica 2016
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Angiosperm orders Extant Aptian first appearances
monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
ous flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s in modern classification systems Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes.
It may also refer to:
Business, organiza ...
, such as the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish a consensus on the taxonomy of flowering plants (angiosperms) that reflects new knowledge about plant relationships disco ...
and the Angiosperm Phylogeny Web. Within the monocots Dioscoreales are grouped in the lilioid monocots
Lilioid monocots (lilioids, liliid monocots, petaloid monocots, petaloid lilioid monocots) is an informal name used for a grade (grouping of taxa with common characteristics) of five monocot orders (Petrosaviales, Dioscoreales, Pandanales, L ...
where they are in a sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
relationship with the Pandanales
Pandanales, the pandans or screw-pines, is an order of flowering plants placed in the monocot clade in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group and Angiosperm Phylogeny Web systems. Within the monocots Pandanales are grouped in the lilioid monocots wh ...
. The Dioscoreales must contain the family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
Dioscoreaceae
Dioscoreaceae () is a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants, with about 715 known species in nine genera. The best-known member of the family is the yam (some species of ''Dioscorea'').
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) both ...
which includes the yam ('' Dioscorea'') which is an important food source in many regions. Older systems tended to place all lilioid monocots with reticulate veined leaves (such as Smilacaceae
Smilacaceae, the greenbriers, is a family of flowering plants. While they were often assigned to a more broadly defined family Liliaceae, most recent botanists have accepted the two as distinct families, diverging around 55 million years ago dur ...
and Stemonaceae together with Dioscoraceae) in Dioscoreales. As currently circumscribed
In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter and its radius is called the circumradius.
Not every polyg ...
by phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
using combined morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
and molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
methods, Dioscreales contains many reticulate veined vines
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselv ...
in Dioscoraceae, it also includes the myco-heterotrophic
Myco-heterotrophy (from Greek μύκης , "fungus", ἕτερος ', "another", "different" and τροφή ', "nutrition") is a symbiotic relationship between certain kinds of plants and fungi, in which the plant gets all or part of its food fro ...
Burmanniaceae
Burmanniaceae is a family of flowering plants, consisting of 99 species of herbaceous plants in eight genera.
Description
These plants are annual or perennial herbs, with generally unbranched stems, some lacking leaves. Some members of this fam ...
and the autotrophic
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Works", ...
Nartheciaceae
Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:
* ''Aletr ...
. The order consists of three families, 22 genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
and about 850 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
.
Description
Dioscoreales arevines
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselv ...
or herbaceous
Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials.
Definitions of "herb" and "herbaceous"
The fourth edition of t ...
forest floor plants. They may be achlorophyllous
Myco-heterotrophy (from Greek μύκης , "fungus", ἕτερος ', "another", "different" and τροφή ', "nutrition") is a symbiotic relationship between certain kinds of plants and fungi, in which the plant gets all or part of its food fro ...
or saprophytic
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi ( ...
. Synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have ...
include tuberous roots, glandular hairs, seed coat
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm p ...
characteristics and the presence of calcium oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate ...
crystals
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
. Other characteristics of the order include the presence of saponin
Saponins (Latin "sapon", soap + "-in", one of), also selectively referred to as triterpene glycosides, are bitter-tasting usually toxic plant-derived organic chemicals that have a foamy quality when agitated in water. They are widely distributed ...
steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
, annular vascular bundles
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in the stem, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will includ ...
that are found in both the stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
and leaf
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, ste ...
. The leaves are often unsheathed at the base, have a distinctive petiole and reticulate veined lamina. Alternatively they may be small and scale-like with a sheathed base. The flowers
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechani ...
are actinomorphic
Floral symmetry describes whether, and how, a flower, in particular its perianth, can be divided into two or more identical or mirror-image parts.
Uncommonly, flowers may have no axis of symmetry at all, typically because their parts are spirall ...
, and may be bisexual
Bisexuality is a romantic or sexual attraction or behavior toward both males and females, or to more than one gender. It may also be defined to include romantic or sexual attraction to people regardless of their sex or gender identity, whi ...
or dioecious
Dioecy (; ; adj. dioecious , ) is a characteristic of a species, meaning that it has distinct individual organisms (unisexual) that produce male or female gametes, either directly (in animals) or indirectly (in seed plants). Dioecious reproductio ...
, while the flowers or inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed o ...
bear glandular hairs. The perianth
The perianth (perigonium, perigon or perigone in monocots) is the non-reproductive part of the flower, and structure that forms an envelope surrounding the sexual organs, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and the corolla (petals) or tepals when ...
may be conspicuous or reduced and the style
Style is a manner of doing or presenting things and may refer to:
* Architectural style, the features that make a building or structure historically identifiable
* Design, the process of creating something
* Fashion, a prevailing mode of clothing ...
is short with well developed style branches. The tepals
A tepal is one of the outer parts of a flower (collectively the perianth). The term is used when these parts cannot easily be classified as either sepals or petals. This may be because the parts of the perianth are undifferentiated (i.e. of very ...
persist in the development of the fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
, which is a dry capsule or berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, raspb ...
. In the seed, the endotegmen is tanniferous and the embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
short.
All of the species except the genera placed in Nartheciaceae
Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:
* ''Aletr ...
express simultaneous microsporogenesis. Plants in Nartheciaceae
Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:
* ''Aletr ...
show successive microsporogenesis which is one of the traits indicating that the family is sister to all the other members included in the order.
Taxonomy
Pre-Darwinian
For the early history from Lindley (1853) onwards, see Caddick ''et al.'' (2000) Table 1, Caddick et al. (2002a) Table 1 and Table 2 in Bouman (1995). Thetaxonomic
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
classification of Dioscoreales has been complicated by the presence of a number of morphological features reminiscent of the dicotyledons
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, t ...
, leading some authors to place the order as intermediate between the monocotyledons and the dicotyledons.
 While Lindley did not use the term "Dioscoreales", he placed the family Dioscoraceae together with four other families in what he referred to as an Alliance (the equivalent of the modern Order) called Dictyogens. He reflected the uncertainty as to the place of this Alliance by placing it as a class of its own between Endogens (monocots) and Exogens (dicots) The
While Lindley did not use the term "Dioscoreales", he placed the family Dioscoraceae together with four other families in what he referred to as an Alliance (the equivalent of the modern Order) called Dictyogens. He reflected the uncertainty as to the place of this Alliance by placing it as a class of its own between Endogens (monocots) and Exogens (dicots) The botanical authority
In botanical nomenclature, author citation is the way of citing the person or group of people who validly published a botanical name, i.e. who first published the name while fulfilling the formal requirements as specified by the '' International Co ...
is given to von Martius
Carl Friedrich Philipp (Karl Friedrich Philipp) von Martius (17 April 1794 – 13 December 1868) was a German botanist and explorer.
Life
Martius was born at Erlangen, the son of Prof Ernst Wilhelm Martius, court apothecary.
He graduated PhD ...
(1835) by APG for his description of the family Dioscoreae or ''Ordo'', while other sources cite Hooker (Dioscoreales Hook.f.
Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker (30 June 1817 – 10 December 1911) was a British botanist and explorer in the 19th century. He was a founder of geographical botany and Charles Darwin's closest friend. For twenty years he served as director of ...
) for his use of the term "Dioscorales" in 1873 with a single family, Dioscoreae. However, in his more definitive work, the ''Genera plantara'' (1883), he simply placed Dioscoraceae in the Epigynae "Series".
Post-Darwinian
AlthoughCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
's Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
(1859) preceded Bentham and Hooker's publication, the latter project was commenced much earlier and George Bentham
George Bentham (22 September 1800 – 10 September 1884) was an English botanist, described by the weed botanist Duane Isely as "the premier systematic botanist of the nineteenth century". Born into a distinguished family, he initially studi ...
was initially sceptical of Darwinism
Darwinism is a scientific theory, theory of Biology, biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of smal ...
. The new phyletic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
approach changed the way that taxonomists considered plant classification, incorporating evolutionary
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
information into their schemata, but this did little to further define the circumscription
Circumscription may refer to:
*Circumscribed circle
* Circumscription (logic)
*Circumscription (taxonomy)
*Circumscription theory, a theory about the origins of the political state in the history of human evolution proposed by the American anthrop ...
of Dioscoreaceae. The major works in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century employing this approach were in the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
literature. Authors such as Eichler, Engler and Wettstein Wettstein is a Swiss surname. Bearers of the name include:
* Carla Wettstein (born 1946), Swiss and Australian chess master
*Fritz von Wettstein (1895–1945), Austrian botanist
*Johann Jakob Wettstein (1693–1754), Swiss theologian
* Johann Rudol ...
placed this family in the Liliiflorae
Lilianae (also known as Liliiflorae) is a botanical name for a superorder (that is, a rank higher than that of order) of flowering plants. Such a superorder of necessity includes the type family Liliaceae (and usually the type order Liliales). ...
, a major subdivision of monocotyledons. it remained to Hutchinson (1926) to resurrect the Dioscoreales to group Dioscoreaceae and related families together. Hutchinson's circumscription of Dioscoreales included three other families in addition to Dioscoreaceae, Stenomeridaceae, Trichopodaceae and Roxburghiaceae. Of these only Trichopodaceae was included in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish a consensus on the taxonomy of flowering plants (angiosperms) that reflects new knowledge about plant relationships disco ...
(APG) classification (see below), but was subsumed into Dioscoraceae. Stenomeridaceae, as '' Stenomeris'' was also included in Dioscoreaceae as subfamily Stenomeridoideae, the remaining genera being grouped in subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoologi ...
Dioscoreoideae. Roxburghiaceae on the other hand was segregated in the sister order Pandanales
Pandanales, the pandans or screw-pines, is an order of flowering plants placed in the monocot clade in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group and Angiosperm Phylogeny Web systems. Within the monocots Pandanales are grouped in the lilioid monocots wh ...
as Stemonaceae. Most taxonomists in the twentieth century (the exception was the 1981 Cronquist system
The Cronquist system is a taxonomic classification system of flowering plants. It was developed by Arthur Cronquist in a series of monographs and texts, including ''The Evolution and Classification of Flowering Plants'' (1968; 2nd edition, 1988) a ...
which placed most such plants in order Liliales, subclass Liliidae
Liliidae is a botanical name at the rank of subclass. Circumscription of the subclass will vary with the taxonomic system being used (there are many such systems); the only requirement being that it includes the family Liliaceae.
Liliidae in Tak ...
, class Liliopsida
Liliopsida Batsch (synonym: Liliatae) is a botanical name for the class containing the family Liliaceae (or Lily Family). It is considered synonymous (or nearly synonymous) with the name monocotyledon. Publication of the name is credited to Scopol ...
=monocotyledons, division Magnoliophyta
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants t ...
=angiosperms) recognised Dioscoreales as a distinct order, but demonstrated wide variations in its composition.
Dahlgren, in the second version of his taxonomic classification (1982) raised the Liliiflorae to a superorder and placed Dioscoreales as an order within it. In his system, Dioscoreales contained only three families, Dioscoreaceae, Stemonaceae (''i.e.'' Hutchinson's Roxburghiaceae) and Trilliaceae
Trilliaceae was a family of flowering plants. The family has been recognised as distinct since 1846 when it was recognized; this tablfor a summarizes the placement of these taxa. The family has been recognized by taxonomists such as Takhtajan, ...
. The latter two families had been treated as a separate order ( Stemonales, or Roxburghiales) by other authors, such as Huber
Huber is a German-language surname. It derives from the German word ''Hube'' meaning hide, a unit of land a farmer might possess, granting them the status of a free tenant. It is in the top ten most common surnames in the German-speaking world, ...
(1969). The APG would later assign these to Pandanales and Liliales respectively. Dahlgren's construction of Dioscoreaceae included the Stenomeridaceae and Trichopodaceae, doubting these were distinct, and Croomiaceae in Stemonaceae. Furthermore, he expressed doubts about the order's homogeneity, especially Trilliaceae. The Dioscoreales at that time were marginally distinguishable from the Asparagales
Asparagales (asparagoid lilies) is an order (biology), order of plants in modern classification systems such as the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) and the Angiosperm Phylogeny Web. The order takes its name from the type (biology), type family ...
. In his examination of Huber's Stemonales, he found that the two constituent families had as close an affinity to Dioscoreaceae as to each other, and hence included them. He also considered closely related families and their relationship to Dioscoreales, such as the monogeneric
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispec ...
Taccaceae, then in its own order, Taccales. Similar considerations were discussed with respect to two Asparagales families, Smilacaceae and Petermanniaceae.
In Dahlgren's third and final version (1985) that broader circumscription of Dioscoreales was created within the superorder Lilianae
Lilianae (also known as Liliiflorae) is a botanical name for a superorder (that is, a rank higher than that of order) of flowering plants. Such a superorder of necessity includes the type family Liliaceae (and usually the type order Liliales). ...
, subclass Liliidae
Liliidae is a botanical name at the rank of subclass. Circumscription of the subclass will vary with the taxonomic system being used (there are many such systems); the only requirement being that it includes the family Liliaceae.
Liliidae in Tak ...
(monocotyledons), class Magnoliopsida
Magnoliopsida is a valid botanical name for a class of flowering plants. By definition the class will include the family Magnoliaceae, but its circumscription can otherwise vary, being more inclusive or less inclusive depending upon the classif ...
(angiosperms) and comprised the seven families Dioscoreaceae
Dioscoreaceae () is a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants, with about 715 known species in nine genera. The best-known member of the family is the yam (some species of ''Dioscorea'').
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) both ...
, Petermanniaceae, Smilacaceae
Smilacaceae, the greenbriers, is a family of flowering plants. While they were often assigned to a more broadly defined family Liliaceae, most recent botanists have accepted the two as distinct families, diverging around 55 million years ago dur ...
, Stemonaceae, Taccaceae
The genus ''Tacca'', which includes the batflowers and arrowroot, consists of flowering plants in the order Dioscoreales, native to tropical regions of South America, Africa, Australia, Southeast Asia, and various oceanic islands. In older text ...
, Trichopodaceae and Trilliaceae
Trilliaceae was a family of flowering plants. The family has been recognised as distinct since 1846 when it was recognized; this tablfor a summarizes the placement of these taxa. The family has been recognized by taxonomists such as Takhtajan, ...
. Thismiaceae has either been treated as a separate family closely related to Burmanniaceae
Burmanniaceae is a family of flowering plants, consisting of 99 species of herbaceous plants in eight genera.
Description
These plants are annual or perennial herbs, with generally unbranched stems, some lacking leaves. Some members of this fam ...
or as a tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English language, English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in p ...
(Thismieae) within a more broadly defined Burmanniaceae, forming a separate order, Burmanniales
Burmanniales Mart. (Burmanniales Blume, Burmanniales Heintze) was an order of monocotyledons, subsequently discontinued.
Description
Small perennial or annual mycorrhizal herbs that are achlorophyllous (lacking chlorophyll) and mycotrophic ...
, in the Dahlgren system. The related Nartheciaceae
Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:
* ''Aletr ...
were treated as tribe Narthecieae within the Melanthiaceae
Melanthiaceae, also called the bunchflower family, is a family of flowering herbaceous perennial plants native to the Northern Hemisphere. Along with many other lilioid monocots, early authors considered members of this family to belong to t ...
in a third order, the Melanthiales
Melanthiales Link (melanthoid lilies) was an order of monocotyledons, whose name and botanical authority is derived by typification from the description of the type family, Melanthiaceae by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in 1829.
In Rolf Dahlgr ...
, by Dahlgren. Dahlgren considered the Dioscoreales to most strongly resemble the ancestral monocotyledons, and hence sharing "dicotyledonous" characteristics, making it the most central monocotyledon order. Of these seven families, Bouman considered Dioscoreaceae, Trichopodaceae, Stemonaceae and Taccaceae to represent the "core" families of the order. However, that study also indicated both a clear delineation of the order from other orders particularly Asparagales, and a lack of homogeneity within the order.
Molecular phylogenetics and the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
The increasing availability ofmolecular phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
methods in addition to morphological characteristics in the 1990s led to major reconsiderations of the relationships within the monocotyledons. In that large multi-institutional examination of the seed plants
A spermatophyte (; ), also known as phanerogam (taxon Phanerogamae) or phaenogam (taxon Phaenogamae), is any plant that produces seeds, hence the alternative name seed plant. Spermatophytes are a subset of the embryophytes or land plants. They inc ...
using the plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosy ...
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
''rbc''L the authors used Dahlgren's system as their basis, but followed Thorne (1992) in altering the suffixes
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry g ...
of the superorders from "''-iflorae''" to "''-anae''". This demonstrated that the Lilianae comprised three lineages corresponding to Dahlgren's orders Dioscoreales, Liliales, and Asparagaless.
Under the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish a consensus on the taxonomy of flowering plants (angiosperms) that reflects new knowledge about plant relationships disco ...
system
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, ...
of 1998, which took Dahlgren's system as a basis, the order was placed in the monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
and comprised the five families Burmanniaceae
Burmanniaceae is a family of flowering plants, consisting of 99 species of herbaceous plants in eight genera.
Description
These plants are annual or perennial herbs, with generally unbranched stems, some lacking leaves. Some members of this fam ...
, Dioscoreaceae, Taccaceae, Thismiaceae and Trichopodaceae.
In APG II
The APG II system (Angiosperm Phylogeny Group II system) of plant classification is the second, now obsolete, version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy that was published in April 2003 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Gr ...
(2003), a number of changes were made to Dioscoreales, as a result of an extensive study by Caddick and colleagues (2002), using an analysis of three genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
, ''rbc''L, ''atp''B and 18S rDNA
18S ribosomal RNA (abbreviated 18S rRNA) is a part of the ribosomal RNA. The S in 18S represents Svedberg units. 18S rRNA is an SSU rRNA, a component of the eukaryotic ribosomal small subunit ( 40S). 18S rRNA is the structural RNA for the small ...
, in addition to morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
. These studies resulted in a re-examination of the relationships between most of the genera within the order. Thismiaceae was shown to be a sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
to Burmanniaceae, and so was included in it. The monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispec ...
families Taccaceae and Trichopodaceae were included in Dioscoreaceae, while Nartheciaceae
Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:
* ''Aletr ...
could also be grouped within Dioscoreales. APG III APG is an abbreviation with several different meanings:
* Aberdeen Proving Ground, a United States Army installation in Aberdeen, Maryland, also
** Phillips Army Airfield, the airfield of the above, from its IATA airport code
* Aboriginal Provisiona ...
(2009) did not change this, so the order now comprises three families Burmanniaceae, Dioscoreaceae and Nartheciaceae.
Although further research on the deeper relationships within Dioscoreales continues, the APG IV
The APG IV system of flowering plant classification is the fourth version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy for flowering plants (angiosperms) being developed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). It was publishe ...
(2016) authors felt it was still premature to propose a restructuring of the order. Specifically these issues involve conflicting information as to the relationship between ''Thismia
''Thismia'' is a genus of myco-heterotrophic plants in family Burmanniaceae, first described as a genus in 1845. It is native to East and Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Australia, New Zealand, and the Americas.
; Species
* '' Thismia abei'' Hatu ...
'' and Burmanniaceae, and hence whether Thismiaceae should be subsumed in the latter, or reinstated.
Phylogeny
Molecular phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
in Dioscoreales poses special problems due to the absence of plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosy ...
genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
in mycoheterotrophs. Dioscoreales is monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
and is placed as a sister order to Pandanales
Pandanales, the pandans or screw-pines, is an order of flowering plants placed in the monocot clade in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group and Angiosperm Phylogeny Web systems. Within the monocots Pandanales are grouped in the lilioid monocots wh ...
, as shown in Cladogram I.
Evolution
The data for the evolution of the order is collected from molecular analyses since there are no such fossils found. It is estimated that Dioscoreales and its sister cladePandanales
Pandanales, the pandans or screw-pines, is an order of flowering plants placed in the monocot clade in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group and Angiosperm Phylogeny Web systems. Within the monocots Pandanales are grouped in the lilioid monocots wh ...
split up around 121 million years ago during Early Cretaceous when the stem group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. ...
was formed. Then it took 3 to 6 million years for the crown group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. ...
to differentiate in Mid Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
.
Subdivision
The three families of Dioscreales constitutes about 22 genera and about 849 species making it one of the smaller monocot orders. Of these, the largest group is '' Dioscorea'' (yams) with about 450 species. By contrast the second largest genus is '' Burmannia'' with about 60 species, and most have only one or two. Some authors, preferring the original APG (1998)families, continue to treat Thismiaceae separately from Burmanniaceae and Taccaceae from Dioscoreaceae. But in the 2015 study of Hertwerk and colleagues, seven genera representing all three families were examined with an eight gene dataset. Dioscoreales was monophyletic and three subclades were represented corresponding to the APG families. Dioscoreaceae and Burmanniaceae were in a sister group relationship.Etymology
Named after thetype genus
In biological taxonomy, the type genus is the genus which defines a biological family and the root of the family name.
Zoological nomenclature
According to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, "The name-bearing type of a nominal f ...
'' Dioscorea'', which in turn was named by Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
in 1753 to honour the Greek physician and botanist Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of ''De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vol ...
.
Distribution and habitat
Species from this order are distributed across all of the continents exceptAntarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
. They are mainly tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
or subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
representatives, but some members of families Dioscoreaceae
Dioscoreaceae () is a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants, with about 715 known species in nine genera. The best-known member of the family is the yam (some species of ''Dioscorea'').
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) both ...
and Nartheciaceae
Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:
* ''Aletr ...
are found in cooler regions of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. Order Dioscoreales contains plants that are able to form an underground organ for reservation of nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficient n ...
s as many other monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
s. An exception is the family Burmanniaceae
Burmanniaceae is a family of flowering plants, consisting of 99 species of herbaceous plants in eight genera.
Description
These plants are annual or perennial herbs, with generally unbranched stems, some lacking leaves. Some members of this fam ...
which is entirely myco-heterotrophic and contains species that lack photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in c ...
abilities.
Ecology
 The three families included in order Dioscoreales also represent three different ecological groups of plants.
The three families included in order Dioscoreales also represent three different ecological groups of plants. Dioscoreaceae
Dioscoreaceae () is a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants, with about 715 known species in nine genera. The best-known member of the family is the yam (some species of ''Dioscorea'').
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) both ...
contains mainly vines ('' Dioscorea'') and other crawling species ('' Epipetrum''). Nartheciaceae
Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:
* ''Aletr ...
on the other hand is a family composed of herbaceous plants with a rather lily-like appearance (''Aletris
''Aletris'', the colicroot, colicweed, crow corn, or unicorn root, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Nartheciaceae, native to North America and to eastern and southeastern Asia, especially China. It was used as a component in Lydia P ...
'') while Burmanniaceae
Burmanniaceae is a family of flowering plants, consisting of 99 species of herbaceous plants in eight genera.
Description
These plants are annual or perennial herbs, with generally unbranched stems, some lacking leaves. Some members of this fam ...
is entirely myco-heterotrophic
Myco-heterotrophy (from Greek μύκης , "fungus", ἕτερος ', "another", "different" and τροφή ', "nutrition") is a symbiotic relationship between certain kinds of plants and fungi, in which the plant gets all or part of its food fro ...
group.
Uses
Many members ofDioscoreaceae
Dioscoreaceae () is a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants, with about 715 known species in nine genera. The best-known member of the family is the yam (some species of ''Dioscorea'').
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) both ...
produce tuberous
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure used as storage organs for nutrients in some plants. They are used for the plant's perennation (survival of the winter or dry months), to provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growin ...
starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
y root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the sur ...
s ( yams) which form staple foods
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and ...
in tropical regions. They have also been the source of steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
for the pharmaceutical industry
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. ...
, including the production of oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or or ...
contraceptives.
Notes
References
Bibliography
Articles and chapters
* , In * , In *Excerpts
* * * * * * * * * * * * , In * * *
Books and symposia
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Databases
* * * *APG
* * * *External links
Kress WJ. Dioscoreales. Encyclopædia Britannica 2016
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Angiosperm orders Extant Aptian first appearances