Deutsche Länderbank on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
I. G. Farbenindustrie AG, commonly known as IG Farben, was a German
 With the world market for synthetic dyes and other chemical products dominated by the German industry, German firms competed vigorously for market shares. Although
With the world market for synthetic dyes and other chemical products dominated by the German industry, German firms competed vigorously for market shares. Although
 Following a contract signed by all concerned parties on November 21, 1925, IG Farben was founded on December 2, 1925 as a merger of six companies:
Following a contract signed by all concerned parties on November 21, 1925, IG Farben was founded on December 2, 1925 as a merger of six companies:  In 1926, IG Farben had a
In 1926, IG Farben had a
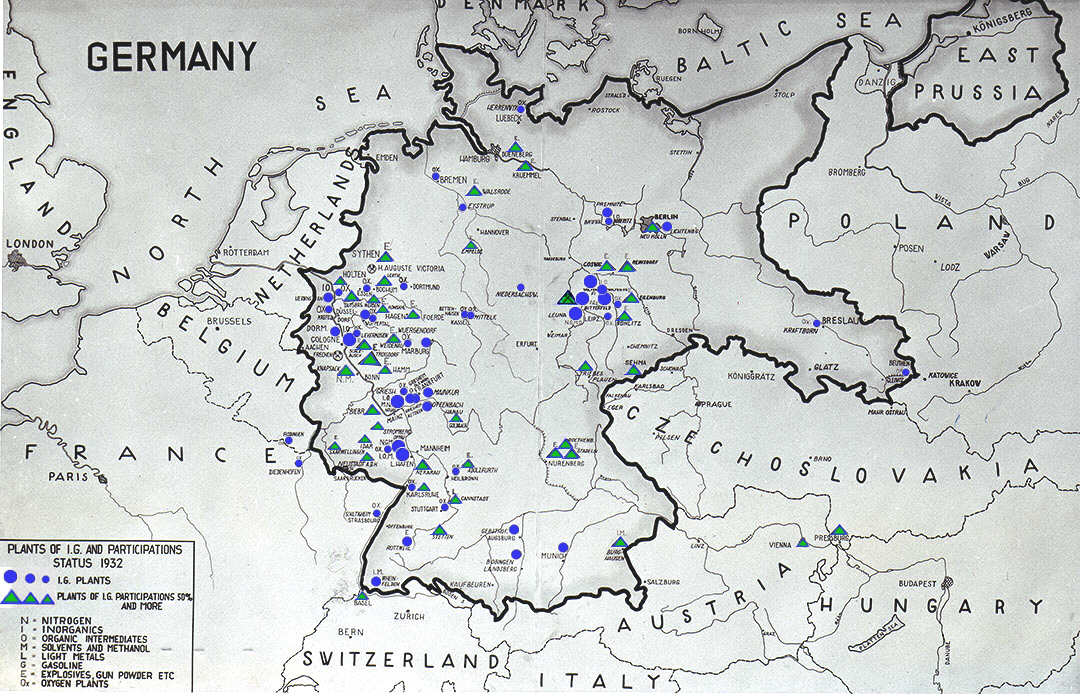 IG Farben's products included
IG Farben's products included
 The company destroyed most of its records as it became clear that Germany was losing the war. In September 1944, Fritz ter Meer, a member of IG Farben's supervisory board and future chair of Bayer's board of directors, and Ernst Struss, secretary of the company's managing board, are said to have made plans to destroy company files in Frankfurt in the event of an American invasion. As the
The company destroyed most of its records as it became clear that Germany was losing the war. In September 1944, Fritz ter Meer, a member of IG Farben's supervisory board and future chair of Bayer's board of directors, and Ernst Struss, secretary of the company's managing board, are said to have made plans to destroy company files in Frankfurt in the event of an American invasion. As the
 Of the 24 defendants arraigned, one fell ill and his case was discontinued. The
Of the 24 defendants arraigned, one fell ill and his case was discontinued. The
 In 2001, IG Farben announced that it would formally wind up its affairs in 2003. It had been continually criticized over the years for failing to pay compensation to the former labourers; its stated reason for its continued existence after 1952 was to administer its claims and pay its debts. The company, in turn, blamed ongoing legal disputes with the former captive labourers for its inability to be legally dissolved and have the remaining assets distributed as reparations."IG Farben to be dissolved"
In 2001, IG Farben announced that it would formally wind up its affairs in 2003. It had been continually criticized over the years for failing to pay compensation to the former labourers; its stated reason for its continued existence after 1952 was to administer its claims and pay its debts. The company, in turn, blamed ongoing legal disputes with the former captive labourers for its inability to be legally dissolved and have the remaining assets distributed as reparations."IG Farben to be dissolved"
BBC News, 17 September 2001. On 10 November 2003, its liquidators filed for
Stock Market Prices
of IG Farben * {{Authority control 1925 establishments in Germany 1951 disestablishments in West Germany Auschwitz concentration camp Chemical companies established in 1925 Chemical companies of Germany Companies involved in the Holocaust Conglomerate companies disestablished in 1951 Conglomerate companies established in 1925 Defunct companies of Germany Infrastructure of the Holocaust
chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
and pharmaceutical
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...
conglomerate. It was formed on December 2, 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies: Agfa
Agfa-Gevaert N.V. (Agfa) is a Belgian-German multinational corporation that develops, manufactures, and distributes Analog photography, analogue and digital imaging products, software, and systems.
The company began as a dye manufacturer in 1867 ...
, BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
, Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
, Griesheim-Elektron, Hoechst, and Weiler-ter-Meer. It was seized by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and split into its constituent companies; parts in East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
were nationalized.
IG Farben was once the largest company in Europe and the largest chemical and pharmaceutical company in the world. IG Farben scientists made fundamental contributions to all areas of chemistry and the pharmaceutical industry. Otto Bayer
Otto Bayer (4 November 1902 – 1 August 1982) was a German industrial chemist at IG Farben who was head of the research group that in 1937 discovered the polyaddition for the synthesis of polyurethanes out of poly-isocyanate and polyol.
Ba ...
discovered the polyaddition for the synthesis of polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term ...
in 1937, and three company scientists became Nobel laureates
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in th ...
: Carl Bosch
Carl Bosch (; 27 August 1874 – 26 April 1940) was a German chemist and engineer and Nobel Laureate in Chemistry. He was a pioneer in the field of high-pressure industrial chemistry and founder of IG Farben, at one point the world's largest ...
and Friedrich Bergius in 1931 "for their contributions to the invention and development of chemical high pressure methods", and Gerhard Domagk
Gerhard Johannes Paul Domagk (; 30 October 1895 – 24 April 1964) was a German pathologist and bacteriologist.
He is credited with the discovery of Sulfonamide (medicine), sulfonamidochrysoidine (KL730) as an antibiotic for which he received th ...
in 1939 "for the discovery of the antibacterial effects of prontosil
Prontosil is an antibacterial drug of the sulfonamide group. It has a relatively broad effect against gram-positive cocci but not against enterobacteria. One of the earliest antimicrobial drugs, it was widely used in the mid-20th century but is ...
".
In the 1920s, the company had ties to the liberal nationalist German People's Party
The German People's Party (German: , DVP) was a conservative-liberal political party during the Weimar Republic that was the successor to the National Liberal Party of the German Empire. Along with the left-liberal German Democratic Party (DDP), ...
and was accused by the Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
of being an "international capitalist Jewish company". A decade later, it was a Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party ( or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor ...
donor and, after the Nazi takeover of Germany in 1933, a major government contractor, providing significant material for the German war effort. Throughout that decade it purged itself of its Jewish employees; the remainder left in 1938. Described as "the most notorious German industrial concern during the Third Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
", in the 1940s the company relied on slave labour from concentration camps
A concentration camp is a prison or other facility used for the internment of political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or ethnic minority groups, on the grounds of national security, or for exploit ...
, including 30,000 from Auschwitz
Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It consisted of Auschw ...
, and was involved in medical experiments on inmates at both Auschwitz and Mauthausen. One
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
of its subsidiaries
A subsidiary, subsidiary company, or daughter company is a company completely or partially owned or controlled by another company, called the parent company or holding company, which has legal and financial control over the subsidiary company. Unl ...
supplied the poison gas Zyklon B
Zyklon B (; translated Cyclone B) was the trade name of a cyanide-based pesticide invented in Germany in the early 1920s. It consists of hydrogen cyanide (prussic acid), as well as a cautionary eye irritant and one of several adsorbents such ...
, which killed over one million people in gas chamber
A gas chamber is an apparatus for killing humans or animals with gas, consisting of a sealed chamber into which a poisonous or asphyxiant gas is introduced. Poisonous agents used include hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide.
History
Donatie ...
s during the Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
.
The Allies seized the company at the end of the war in 1945 and the US authorities put its directors on trial. Held from 1947 to 1948 as one of the subsequent Nuremberg trials, the IG Farben trial saw 23 IG Farben directors tried for war crimes and 13 convicted. However, by 1951 all of them were released from prison early after the U.S. military instituted good time credits in its war crime program. What remained of IG Farben in the West was split in 1951 into its six constituent companies, then again into three: BASF, Bayer, and Hoechst. These companies continued to operate as an informal cartel and played a major role in the West German ''Wirtschaftswunder
The ''Wirtschaftswunder'' (, "economic miracle"), also known as the Miracle on the Rhine, was the rapid reconstruction and development of the Economy, economies of West Germany and Austria after World War II. The expression was first used to re ...
''. Following several later mergers the main successor companies are Agfa, BASF, Bayer and Sanofi
Sanofi S.A. is a French Multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. The corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 200 ...
. In 2004, the University of Frankfurt, housed in the former IG Farben head office, set up a permanent exhibition on campus, the Norbert Wollheim memorial
A memorial is an object or place which serves as a focus for the memory or the commemoration of something, usually an influential, deceased person or a historical, tragic event. Popular forms of memorials include landmark objects such as home ...
, for the slave labourers and those killed by Zyklon B.
Early history
Background
At the beginning of the 20th century, the German chemical industry dominated the world market for syntheticdye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
s. Three major firms BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
, Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
and Hoechst, produced several hundred different dyes. Five smaller firms, Agfa
Agfa-Gevaert N.V. (Agfa) is a Belgian-German multinational corporation that develops, manufactures, and distributes Analog photography, analogue and digital imaging products, software, and systems.
The company began as a dye manufacturer in 1867 ...
, Cassella, , Chemische Fabrik Griesheim-Elektron and Chemische Fabrik vorm. Weiler-ter Meer, concentrated on high-quality specialty dyes. In 1913, these eight firms produced almost 90 percent of the world supply of dyestuffs and sold about 80 percent of their production abroad. The three major firms had also integrated upstream into the production of essential raw materials, and they began to expand into other areas of chemistry such as pharmaceuticals
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...
, photographic film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the ...
, agricultural chemicals
An agrochemical or agrichemical, a contraction of ''agricultural chemical'', is a chemical product used in industrial agriculture. Agrichemical typically refers to biocides (pesticides including insecticides, herbicides, fungicides and nematicid ...
and electrochemicals. Contrary to other industries, the founders and their families had little influence on the top-level decision-making of the leading German chemical firms, which was in the hands of professional salaried managers. Because of this unique situation, the economic historian Alfred Chandler called the German dye companies "the world's first truly managerial industrial enterprises".
 With the world market for synthetic dyes and other chemical products dominated by the German industry, German firms competed vigorously for market shares. Although
With the world market for synthetic dyes and other chemical products dominated by the German industry, German firms competed vigorously for market shares. Although cartel
A cartel is a group of independent market participants who collaborate with each other as well as agreeing not to compete with each other in order to improve their profits and dominate the market. A cartel is an organization formed by producers ...
s were attempted, they lasted at most for a few years. Others argued for the formation of a profit pool or ''Interessen-Gemeinschaft'' (abbr. IG, lit. "community of interest"). In contrast, the chairman of Bayer, Carl Duisberg
Friedrich Carl Duisberg (29 September 1861 – 19 March 1935) was a German chemist and industrialist.
Life
Duisberg was born in Barmen, Germany. From 1879 to 1882, he studied at the Georg August University of Göttingen and Friedrich Schiller U ...
, argued for a merger. During a trip to the United States in the spring of 1903, he had visited several of the large American trusts
A trust is a legal relationship in which the owner of property, or any transferable right, gives it to another to manage and use solely for the benefit of a designated person. In the English common law, the party who entrusts the property is k ...
such as Standard Oil
Standard Oil Company was a Trust (business), corporate trust in the petroleum industry that existed from 1882 to 1911. The origins of the trust lay in the operations of the Standard Oil of Ohio, Standard Oil Company (Ohio), which had been founde ...
, U.S. Steel
The United States Steel Corporation is an American steel company based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It maintains production facilities at several additional locations in the U.S. and Central Europe.
The company produces and sells steel products, ...
, International Paper
The International Paper Company is an American pulp and paper company, the largest such company in the world. It has approximately 39,000 employees, and is headquartered in Memphis, Tennessee.
History
The company was incorporated January 31 ...
and Alcoa
Alcoa Corporation (an acronym for "Aluminum Company of America") is an American industrial corporation. It is the world's eighth-largest producer of aluminum. Alcoa conducts operations in 10 countries. Alcoa is a major producer of primary alu ...
. In 1904, after returning to Germany, he proposed a nationwide merger of the producers of dye and pharmaceuticals in a memorandum to Gustav von Brüning, the senior manager at Hoechst.
Hoechst and several pharmaceutical firms refused to join. Instead, Hoechst and Cassella made an alliance based on mutual equity stakes in 1904. This prompted Duisberg and Heinrich von Brunck, chairman of BASF, to accelerate their negotiations. In October 1904 an ''Interessen-Gemeinschaft'' between Bayer, BASF and Agfa was formed, also known as the ''Dreibund'' or little IG. Profits of the three firms were pooled, with BASF and Bayer getting 43 percent each and Agfa 14 percent of all profits. The two alliances were loosely connected with each other through an agreement between BASF and Hoechst to jointly exploit the patent on the Heumann-Pfleger indigo synthesis.
Within the ''Dreibund'', Bayer and BASF concentrated on dye, while Agfa increasingly concentrated on photographic film. Although there was some cooperation between the technical staff in production and accounting, there was little cooperation between the firms in other areas. Neither were production or distribution facilities consolidated nor did the commercial staff cooperate. In 1908 Hoechst and Cassella acquired 88 percent of the shares of Chemische Fabrik Kalle. As Hoechst, Cassella and Kalle were connected by mutual equity shares and were located close to each other in the Frankfurt area, this allowed them to cooperate more successfully than the ''Dreibund'', although they also did not rationalize or consolidate their production facilities.
Foundation
 Following a contract signed by all concerned parties on November 21, 1925, IG Farben was founded on December 2, 1925 as a merger of six companies:
Following a contract signed by all concerned parties on November 21, 1925, IG Farben was founded on December 2, 1925 as a merger of six companies: BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
(27.4 percent of equity capital); Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
(27.4 percent); Hoechst, including Cassella and Chemische Fabrik Kalle (27.4 percent); Agfa
Agfa-Gevaert N.V. (Agfa) is a Belgian-German multinational corporation that develops, manufactures, and distributes Analog photography, analogue and digital imaging products, software, and systems.
The company began as a dye manufacturer in 1867 ...
(9 percent); Chemische Fabrik Griesheim-Elektron (6.9 percent); and Chemische Fabrik vorm. Weiler Ter Meer (1.9 percent). The supervisory board members became widely known as, and were said to call themselves jokingly, the "Council of Gods" (''Rat der Götter''). The designation was used as the title of an East German
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from its formation on 7 October 1949 until its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally vie ...
film, ''The Council of the Gods
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
'' (1950).
 In 1926, IG Farben had a
In 1926, IG Farben had a market capitalization
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.
Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by ...
of (equivalent to billion euros) and a workforce of 100,000, of which 2.6 percent were university educated, 18.2 percent were salaried professionals and 79.2 percent were workers. BASF was the nominal survivor; all shares were exchanged for BASF shares. Similar mergers took place in other countries. In the United Kingdom Brunner Mond Brunner may refer to:
Places
* Brunner, New Zealand
* Lake Brunner, New Zealand
* Brunner Mine, New Zealand
* Brunner, Houston, United States
* Brunner (crater), lunar crater
Other uses
* Brunner (surname)
* Brunner the Bounty Hunter, a cha ...
, Nobel Industries, United Alkali Company
United Alkali Company Limited was a British chemical company formed in 1890, employing the Leblanc process to produce soda ash for the glass, textile, soap, and paper industries. It became one of the top four British chemical companies merged in ...
and British Dyestuffs merged to form Imperial Chemical Industries
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British Chemical industry, chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was listed on the London Stock Exchange ...
in September 1926. In France Établissements Poulenc Frères and Société Chimique des Usines du Rhône merged to form Rhône-Poulenc
Rhône-Poulenc () was a French chemical and pharmaceutical company founded in 1928. In 1999, it merged with Hoechst AG to form Aventis. As of 2015, the pharmaceutical operations of Rhône-Poulenc are part of Sanofi and the chemicals divisions ...
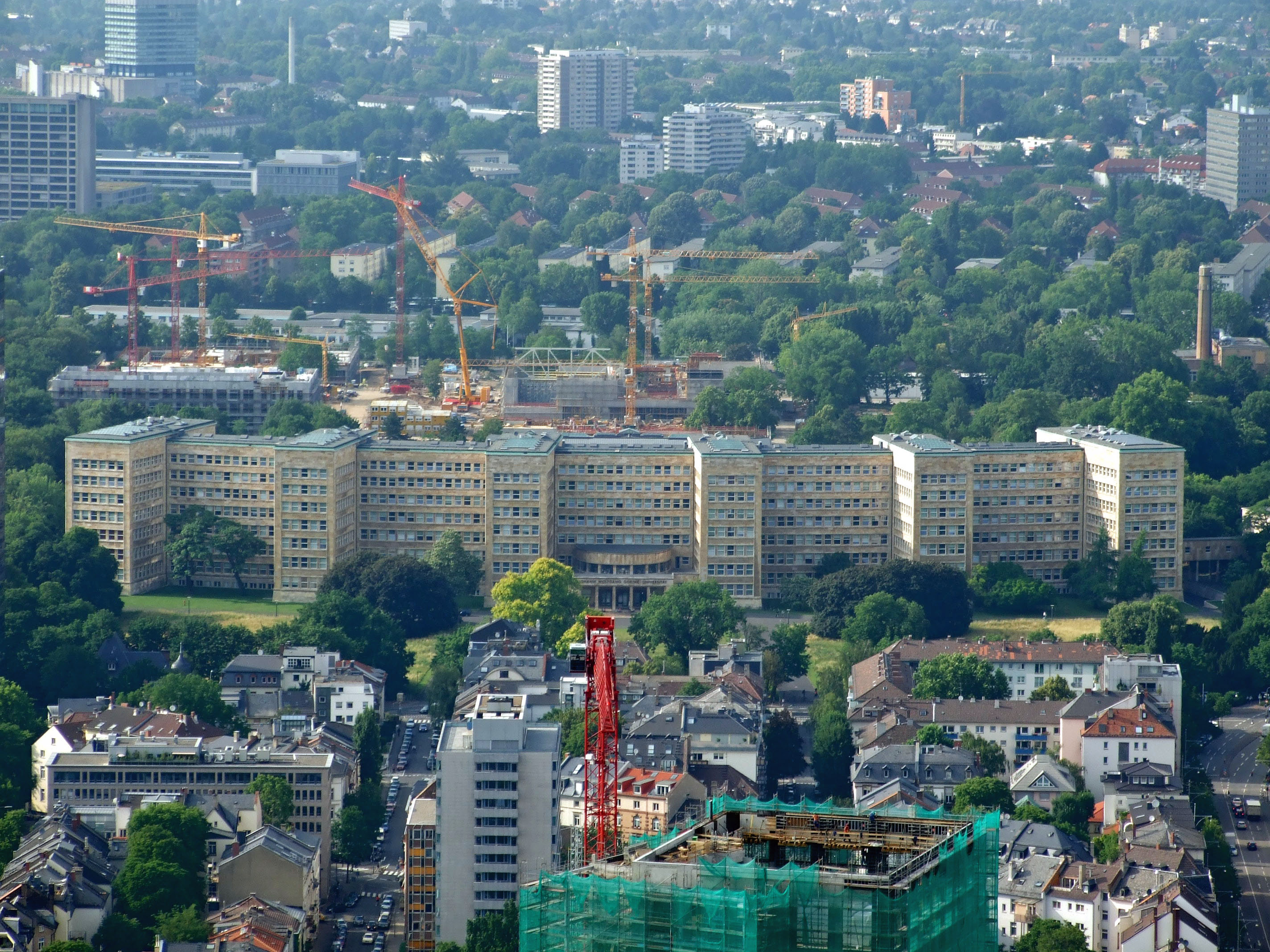
in 1928. The IG Farben Building
The I.G. Farben Building – also known as the Poelzig Building and the Abrams Building, formerly informally called The Pentagon of Europe – is a building complex in Frankfurt, Germany, which currently serves as the main structure of the West ...
, headquarters for the conglomerate in Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, Germany, was completed in 1931. In 1938, the company had 218,090 employees.
IG Farben was controversial on both the far left and far right, partly for the same reasons, related to the size and international nature of the conglomerate and the Jewish background of several of its key leaders and major shareholders . Far-right newspapers of the 1920s and early 1930s, accused it of being an "international capitalist Jewish company". The liberal and business-friendly German People's Party
The German People's Party (German: , DVP) was a conservative-liberal political party during the Weimar Republic that was the successor to the National Liberal Party of the German Empire. Along with the left-liberal German Democratic Party (DDP), ...
was its most pronounced supporter. Not a single member of the management of IG Farben before 1933 supported the Nazi Party; four members, or a third, of the IG Farben supervisory board were themselves Jewish.
Throughout the 1930s, the company underwent a process of Aryanization
Aryanization () was the Nazi term for the seizure of property from Jews and its transfer to non-Jews, and the forced expulsion of Jews from economic life in Nazi Germany, Axis powers, Axis-aligned states, and their occupied territories. It enta ...
, and the company ended up being the "largest single contribution" to the successful Nazi election campaign of 1933; there is also evidence of "secret contributions" to the party in 1931 and 1932.
By 1938 the Jews on the board had resigned and the remaining Jewish employees had been dismissed after Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician, aviator, military leader, and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which gov ...
issued a decree, as part of the Nazis' Four Year Plan (announced in 1936), that the German government would make foreign exchange available to German firms to fund construction or purchases overseas only if certain conditions were met, which included making sure the company employed no Jews.
Products
 IG Farben's products included
IG Farben's products included synthetic dyes
A Colourant, colorant is any substance that changes the spectral transmittance or reflectance of a material. Synthetic colorants are those created in a laboratory or industrial setting. The production and improvement of colorants was a driver of th ...
, nitrile rubber
Nitrile rubber, also known as nitrile butadiene rubber, NBR, Buna-N, and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, is a synthetic rubber derived from acrylonitrile (ACN) and butadiene. Trade names include Perbunan, Nipol, Krynac and Europrene. This rubber is ...
, polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term ...
, prontosil
Prontosil is an antibacterial drug of the sulfonamide group. It has a relatively broad effect against gram-positive cocci but not against enterobacteria. One of the earliest antimicrobial drugs, it was widely used in the mid-20th century but is ...
, and chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types ...
. The nerve agent
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemistry, organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (ACh ...
Sarin
Sarin (NATO designation GB nerve_agent#G-series.html" ;"title="hort for nerve agent#G-series">G-series, "B" is an extremely toxic organophosphorus compound.poison gas
Many gases have toxic properties, which are often assessed using the LC50 (median lethal concentration) measure. In the United States, many of these gases have been assigned an NFPA 704 health rating of 4 (may be fatal) or 3 (may cause serious ...
Zyklon B
Zyklon B (; translated Cyclone B) was the trade name of a cyanide-based pesticide invented in Germany in the early 1920s. It consists of hydrogen cyanide (prussic acid), as well as a cautionary eye irritant and one of several adsorbents such ...
. One product crucial to the operations of the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
was synthetic fuel
Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes Fuel gas, gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by ...
, made from lignite
Lignite (derived from Latin ''lignum'' meaning 'wood'), often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35% and is considered the lowest ...
using the coal liquefaction
Coal liquefaction is a process of converting coal into liquid hydrocarbons: liquid fuels and petrochemicals. This process is often known as "coal to X" or "carbon to X", where X can be many different hydrocarbon-based products. However, the most c ...
process.
IG Farben scientists made fundamental contributions to all areas of chemistry. Otto Bayer
Otto Bayer (4 November 1902 – 1 August 1982) was a German industrial chemist at IG Farben who was head of the research group that in 1937 discovered the polyaddition for the synthesis of polyurethanes out of poly-isocyanate and polyol.
Ba ...
discovered the polyaddition for the synthesis of polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term ...
in 1937. Several IG Farben scientists were awarded a Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
. Carl Bosch
Carl Bosch (; 27 August 1874 – 26 April 1940) was a German chemist and engineer and Nobel Laureate in Chemistry. He was a pioneer in the field of high-pressure industrial chemistry and founder of IG Farben, at one point the world's largest ...
and Friedrich Bergius were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
in 1931 "in recognition of their contributions to the invention and development of chemical high pressure methods".; Gerhard Domagk
Gerhard Johannes Paul Domagk (; 30 October 1895 – 24 April 1964) was a German pathologist and bacteriologist.
He is credited with the discovery of Sulfonamide (medicine), sulfonamidochrysoidine (KL730) as an antibiotic for which he received th ...
was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, acco ...
in 1939 "for the discovery of the antibacterial effects of prontosil
Prontosil is an antibacterial drug of the sulfonamide group. It has a relatively broad effect against gram-positive cocci but not against enterobacteria. One of the earliest antimicrobial drugs, it was widely used in the mid-20th century but is ...
".;
World War II and the Holocaust
Growth and slave labour
IG Farben has been described as "the most notorious German industrial concern during theThird Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
". When World War II began, it was the fourth largest corporation in the world and the largest in Europe. In February 1941, Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician and military leader who was the 4th of the (Protection Squadron; SS), a leading member of the Nazi Party, and one of the most powerful p ...
signed an order supporting the construction of an IG Farben Buna-N
Nitrile rubber, also known as nitrile butadiene rubber, NBR, Buna-N, and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, is a synthetic rubber derived from acrylonitrile (ACN) and butadiene. Trade names include Perbunan, Nipol, Krynac and Europrene. This rubber is ...
(synthetic rubber) plant—known as Monowitz Buna Werke (or Buna)—near the Monowitz concentration camp
Monowitz (also known as Monowitz-Buna, Buna and Auschwitz III) was a Nazi concentration camp and labor camp (''Arbeitslager'') run by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland from 1942–1945, during World War II and the Holocaust. For most of its existe ...
, part of the Auschwitz concentration camp
Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 Nazi concentration camps, concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) d ...
complex in German-occupied Poland. (Monowitz came to be known as Auschwitz III; Auschwitz I was the administrative centre and Auschwitz II-Birkenau the extermination camp.) The IG Farben plant's workforce consisted of slave labour from Auschwitz, leased to the company by the SS for a low daily rate. One of IG Farben's subsidiaries supplied the poison gas, Zyklon B
Zyklon B (; translated Cyclone B) was the trade name of a cyanide-based pesticide invented in Germany in the early 1920s. It consists of hydrogen cyanide (prussic acid), as well as a cautionary eye irritant and one of several adsorbents such ...
, that killed over one million people in gas chambers.
Company executives said after the war that they had not known what was happening inside the camps. According to the historian Peter Hayes, "the killings were an open secret within Farben, and people worked at not reflecting upon what they knew."
In 1978, Joseph Borkin, who investigated the company as a United States Justice Department lawyer, quoted an American report: "Without I.G.'s immense productive facilities, its far-reaching research, varied technical expertise and overall concentration of economic power, Germany would not have been in a position to start its aggressive war in September 1939." The company placed its resources, technical capabilities and overseas contacts at the German government's disposal. The minutes of a meeting of the Commercial Committee on 10 September 1937 noted:
This message was repeated by Wilhelm Rudolf Mann
Wilhelm Rudolf Mann (4 April 1894 – 10 March 1992) was a German business executive for IG Farben and later with Bayer. He was a supporter and member of the Nazi Party, and was involved in financing the human medical experiments of Josef Mengel ...
, who chaired a meeting of the Bayer division board of directors on 16 February 1938, and who in an earlier meeting had referred to the "miracle of the birth of the German nation": "The chairman points out our incontestable being in line with the National Socialist attitude in the association of the entire 'Bayer' pharmaceutica and insecticides; beyond that, he requests the heads of the offices abroad to regard it as their self-evident duty to collaborate in a fine and understanding manner with the functionaries of the Party, with the DAF (German Workers' Front), et cetera. Orders to that effect again are to be given to the leading German gentlemen so that there may be no misunderstanding in their execution."
By 1943, IG Farben was manufacturing products worth three billion mark
Mark may refer to:
In the Bible
* Mark the Evangelist (5–68), traditionally ascribed author of the Gospel of Mark
* Gospel of Mark, one of the four canonical gospels and one of the three synoptic gospels
Currencies
* Mark (currency), a currenc ...
s in 334 facilities in occupied Europe; almost half its workforce of 330,000 men and women consisted of slave labour or conscripts, including 30,000 Auschwitz prisoners. Altogether its annual net profit was around (equivalent to billion euros). In 1945, according to Raymond G. Stokes, it manufactured all the synthetic rubber and methanol in Germany, 90 percent of its plastic and "organic intermediates", 84 percent of its explosives, 75 percent of its nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
and solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s, around 50 percent of its pharmaceuticals, and around 33 percent of its synthetic fuel
Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes Fuel gas, gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by ...
.
Medical experiments
Staff of theBayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
group at IG Farben conducted medical experiments on concentration-camp inmates at Auschwitz and at the Mauthausen concentration camp
Mauthausen was a German Nazi concentration camp on a hill above the market town of Mauthausen, Upper Austria, Mauthausen (roughly east of Linz), Upper Austria. It was the main camp of a group with List of subcamps of Mauthausen, nearly 100 f ...
.
At Auschwitz they were led by Bayer employee Helmuth Vetter, an Auschwitz camp physician and SS captain, and Auschwitz physicians Friedrich Entress and Eduard Wirths. Most of the experiments were conducted in Birkenau in Block 20, the women's camp hospital. The patients were suffering from, and in many cases had been deliberately infected with, typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella enterica'' serotype Typhi bacteria, also called ''Salmonella'' Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often ther ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacteria, bacterium ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild Course (medicine), clinical course, but in some outbreaks, the mortality rate approaches 10%. Signs a ...
and other diseases, then were given preparations named Rutenol, Periston, B-1012, B-1034, B-1036, 3582 and P-111. According to prisoner-physicians who witnessed the experiments, after being given the drugs the women would experience circulation problems, bloody vomiting, and painful diarrhea "containing fragments of mucus membrane". Of the 50 typhoid sufferers given 3852, 15 died; 40 of the 75 tuberculosis patients given Rutenol died.
For one experiment, which tested an anaesthetic, Bayer had 150 women sent from Auschwitz to its own facility. They paid RM 150 per woman, all of whom died as a result of the research; the camp had asked for RM 200 per person, but Bayer had said that was too high. A Bayer employee wrote to Rudolf Höss
Rudolf Franz Ferdinand Höss (also Höß, Hoeß, or Hoess; ; 25 November 1901 – 16 April 1947) was a German SS officer and the commandant of the Auschwitz concentration camp. After the defeat of Nazi Germany and the end of World War II, he w ...
, the Auschwitz commandant: "The transport of 150 women arrived in good condition. However, we were unable to obtain conclusive results because they died during the experiments. We would kindly request that you send us another group of women to the same number and at the same price."
Zyklon B
Between 1942 and 1945, acyanide
In chemistry, cyanide () is an inorganic chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom.
Ionic cyanides contain the cyanide anion . This a ...
-based pesticide, Zyklon B
Zyklon B (; translated Cyclone B) was the trade name of a cyanide-based pesticide invented in Germany in the early 1920s. It consists of hydrogen cyanide (prussic acid), as well as a cautionary eye irritant and one of several adsorbents such ...
, was used to kill over one million people, mostly Jews, in gas chamber
A gas chamber is an apparatus for killing humans or animals with gas, consisting of a sealed chamber into which a poisonous or asphyxiant gas is introduced. Poisonous agents used include hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide.
History
Donatie ...
s in Europe, including in the Auschwitz II
Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 Nazi concentration camps, concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) d ...
and Majdanek
Majdanek (or Lublin) was a Nazi concentration and extermination camp built and operated by the SS on the outskirts of the city of Lublin during the German occupation of Poland in World War II. It had three gas chambers, two wooden gallows, ...
extermination camps in German-occupied Poland. The poison gas was supplied by an IG Farben subsidiary, Degesch
The Deutsche Gesellschaft für Schädlingsbekämpfung mbH (), often shortened to Degesch, was a German chemical corporation which manufactured pesticides. Degesch held the patent on the infamous pesticide Zyklon, a variant of which was used to ex ...
(Deutsche Gesellschaft für Schädlingsbekämpfung MbH, or German Company for Pest Control). Degesch originally supplied the gas to Auschwitz to fumigate clothing that was infested with lice, which carried typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
. Fumigation took place within a closed room, but it was a slow process, so Degesch recommended building small gas chambers, which heated the gas to over 30 °C and killed the lice within one hour. The idea was that the inmates would be shaved and showered while their clothes were being fumigated. The gas was first used on human beings in Auschwitz (650 Soviet POWs and 200 others) in September 1941.
Peter Hayes compiled the following table showing the increase in Zyklon B ordered by Auschwitz (figures with an asterisk are incomplete). One ton of Zyklon B was enough to kill around 312,500 people.
Several IG Farben executives said after the war that they did not know about the gassings, despite the increase in sales of Zyklon B to Auschwitz. IG Farben owned 42.5 percent of Degesch shares, and three members of Degesch's 11-person executive board, Wilhelm Rudolf Mann
Wilhelm Rudolf Mann (4 April 1894 – 10 March 1992) was a German business executive for IG Farben and later with Bayer. He was a supporter and member of the Nazi Party, and was involved in financing the human medical experiments of Josef Mengel ...
, Heinrich Hörlein
Philipp Heinrich Hörlein (5 June 1882 – 23 May 1954), was a German entrepreneur, scientist, lecturer, and Nazi ''Wehrwirtschaftsführer''. He was tried for War crime, war crimes for his involvement in the Holocaust and his knowledge of Nazi hu ...
and Carl Wurster
Carl Wurster (2 December 1900, in Stuttgart – 14 December 1974, in Frankenthal) was a German chemist and '' Wehrwirtschaftsführer'' (war economy leader) during the Third Reich. He subsequently became one of the leading figures in post-war Ge ...
, were directors of IG Farben. Mann, who had been an SA-Sturmführer
''Sturmführer'' (, "storm leader") was a paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party which began as a title used by the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA) in 1925 and became an actual SA rank in 1928. Translated as "storm leader or assault leader", the origins o ...
, was the chair of Degesch's board. Peter Hayes writes that the board did not meet after 1940, and that although Mann "continued to review the monthly sales figures for Degesch, he could not necessarily have inferred from them the uses to which the Auschwitz camp was putting the product". IG Farben executives did visit Auschwitz where only a smaller gas chamber existed, but not Auschwitz II-Birkenau, where the industrial gas chambers were located.
Other IG Farben staff appear to have known. Ernst Struss, secretary of the IG Farben's managing board, testified after the war that the company's chief engineer at Auschwitz had told him about the gassings. The general manager of Degesch is said to have learned about the gassings from Kurt Gerstein of the SS. According to the post-war testimony of Rudolf Höss
Rudolf Franz Ferdinand Höss (also Höß, Hoeß, or Hoess; ; 25 November 1901 – 16 April 1947) was a German SS officer and the commandant of the Auschwitz concentration camp. After the defeat of Nazi Germany and the end of World War II, he w ...
, the Auschwitz commandant, he was asked by , technical manager of the IG Farben Auschwitz plant, whether it was true that Jews were being cremated at Auschwitz. Höss replied that he could not discuss it and thereafter assumed that Dürrfeld knew. Dürrfeld, a friend of Höss, denied knowing about it.
Hayes writes that the inmates of Auschwitz III, which supplied the slave labour for IG Farben, were well aware of the gas chambers, in part because of the stench from the Auschwitz II crematoria, and in part because IG Farben supervisors in the camp spoke about the gassings, including using the threat of them to make the inmates work harder. Charles Coward, a British POW who had been held at Auschwitz III, told the IG Farben trial:
Mann, Hörlein and Wurster (directors of both IG Farben and Degesch) were acquitted at the IG Farben trial in 1948 of having supplied Zyklon B for the purpose of mass extermination. The judges ruled that the prosecution had not shown that the defendants or executive board "had any persuasive influence on the management policies of Degesch or any significant knowledge as to the uses to which its production was being put". In 1949, Mann became head of pharmaceutical sales at Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
. Hörlein became chair of Bayer's supervisory board. Wurster became chair of the IG Farben board, helped to reestablish BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
as a separate company, and became an honorary professor at the University of Heidelberg
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg (; ), is a public university, public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Founded in 1386 on instruction of Pope Urban VI, Heidelberg is List ...
. Dürrfeld was sentenced to eight years, but had his sentence commuted to time served in 1951 by John McCloy, the US High Commissioner for Germany, under massive political pressure, after which he joined the management or supervisory boards of several chemical companies.
Seizure by the Allies
 The company destroyed most of its records as it became clear that Germany was losing the war. In September 1944, Fritz ter Meer, a member of IG Farben's supervisory board and future chair of Bayer's board of directors, and Ernst Struss, secretary of the company's managing board, are said to have made plans to destroy company files in Frankfurt in the event of an American invasion. As the
The company destroyed most of its records as it became clear that Germany was losing the war. In September 1944, Fritz ter Meer, a member of IG Farben's supervisory board and future chair of Bayer's board of directors, and Ernst Struss, secretary of the company's managing board, are said to have made plans to destroy company files in Frankfurt in the event of an American invasion. As the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
approached Auschwitz in January 1945 to liberate it, IG Farben reportedly destroyed the company's records inside the camp, and in the spring of 1945, the company burned and shredded 15 tons of paperwork in Frankfurt.
The Americans seized the company's property under "General Order No. 2 pursuant to Military Government Law No. 52", 2 July 1945, which allowed the US to disperse "ownership and control of such of the plants and equipment seized under this order as have not been transferred or destroyed". The French followed suit in the areas they controlled. On 30 November 1945, Allied Control Council
The Allied Control Council (ACC) or Allied Control Authority (), also referred to as the Four Powers (), was the governing body of the Allies of World War II, Allied Allied-occupied Germany, occupation zones in Germany (1945–1949/1991) and Al ...
Law No. 9, "Seizure of Property owned by I.G. Farbenindustrie and the Control Thereof", formalized the seizure for "knowingly and prominently ... building up and maintaining German war potential".
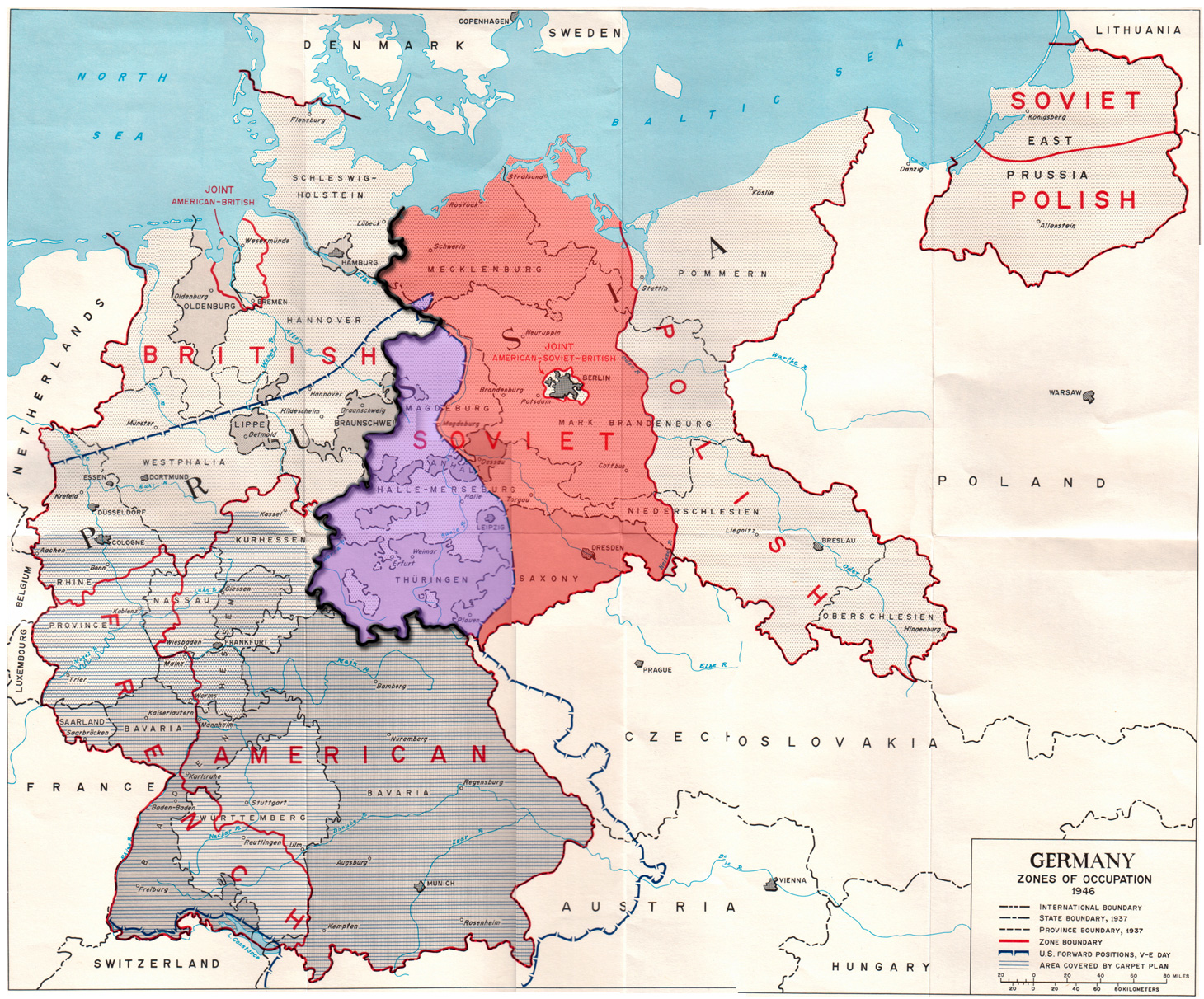
The division of property followed the division of Germany into four zones: American, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
, French and Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
.
In the Western occupation zone, the idea of destroying the company was abandoned as the policy of denazification
Denazification () was an Allied initiative to rid German and Austrian society, culture, press, economy, judiciary, and politics of the Nazi ideology following the Second World War. It was carried out by removing those who had been Nazi Par ...
evolved, in part because of a need for industry to support reconstruction, and in part because of the company's entanglement with American companies, notably the successors of Standard Oil
Standard Oil Company was a Trust (business), corporate trust in the petroleum industry that existed from 1882 to 1911. The origins of the trust lay in the operations of the Standard Oil of Ohio, Standard Oil Company (Ohio), which had been founde ...
. In 1951, the company was split into its original constituent companies. The four largest quickly bought the smaller ones. In January 1955, the Allied High Commission
The Allied High Commission (also known as the High Commission for Occupied Germany, HICOG; in German ''Alliierte Hohe Kommission'', ''AHK'') was established by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France after the 1948 breakdown of the Alli ...
issued the I.G. Liquidation Conclusion Law, naming IG Farben's legal successor as ''IG Farbenindustrie AG in Abwicklung'' (IGiA) ("I.G. Farbenindustrie AG in Liquidation).
IG Farben trial
In 1947, the American government put IG Farben's directors on trial. ''The United States of America vs. Carl Krauch, et al.'' (1947–1948), also known as the IG Farben trial, was the sixth of 12 trials forwar crime
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hostage ...
s the US authorities held in their occupation zone in Germany (Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
) against leading industrialists of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
. There were five counts against the IG Farben directors:
 Of the 24 defendants arraigned, one fell ill and his case was discontinued. The
Of the 24 defendants arraigned, one fell ill and his case was discontinued. The indictment
An indictment ( ) is a formal accusation that a person has committed a crime. In jurisdictions that use the concept of felonies, the most serious criminal offense is a felony; jurisdictions that do not use that concept often use that of an ind ...
was filed on 3 May 1947; the trial lasted from 27 August 1947 until 30 July 1948. The judges were Curtis Grover Shake (presiding), James Morris, Paul M. Hebert, and Clarence F. Merrell as an alternate judge. Telford Taylor
Telford Taylor (February 24, 1908 – May 23, 1998) was an American lawyer and professor. Taylor was known for his role as lead counsel in the prosecution of war criminals after World War II, his opposition to McCarthyism in the 1950s, and his o ...
was the chief counsel for the prosecution. Thirteen defendants were found guilty, with sentences ranging from 18 months to eight years. All were cleared of the first count of waging war. The heaviest sentences went to those involved with Auschwitz, which was IG Farben's Upper Rhine
Upper Rhine ( ; ; kilometres 167 to 529 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between the Middle Bridge, Basel, Middle Bridge in Basel, Switzerland, and the Rhine knee in Bingen am Rhein, Bingen, Germany. It is surrounded by the Upper Rhine P ...
group. Ambros, Bütefisch, Dürrfeld, Krauch and ter Meer were convicted of "participating in ... enslavement and deportation for slave labor".
All defendants who were sentenced to prison received early release. Most were quickly restored to their directorships and other positions in post-war companies, and some were awarded the Federal Cross of Merit
The Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany (, or , BVO) is the highest state decoration, federal decoration of the Federal Republic of Germany. It may be awarded for any field of endeavor. It was created by the first List of president ...
. Those who served prison sentences included:
Those acquitted
In common law jurisdictions, an acquittal means that the criminal prosecution has failed to prove that the accused is guilty beyond a reasonable doubt of the charge presented. It certifies that the accused is free from the charge of an o ...
included:
Liquidation
Agfa
Agfa-Gevaert N.V. (Agfa) is a Belgian-German multinational corporation that develops, manufactures, and distributes Analog photography, analogue and digital imaging products, software, and systems.
The company began as a dye manufacturer in 1867 ...
, BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
and Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
remained in business; Hoechst spun off its chemical business in 1999 as Celanese AG before merging with Rhône-Poulenc
Rhône-Poulenc () was a French chemical and pharmaceutical company founded in 1928. In 1999, it merged with Hoechst AG to form Aventis. As of 2015, the pharmaceutical operations of Rhône-Poulenc are part of Sanofi and the chemicals divisions ...
to form Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. The corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Synthélabo merg ...
, which later merged with Sanofi-Synthélabo to form Sanofi
Sanofi S.A. is a French Multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. The corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 200 ...
. Two years earlier, another part of Hoechst was sold in 1997 to the chemical spin-off of Sandoz, the Muttenz (Switzerland) based Clariant
Clariant AG is a Swiss multinational speciality chemical company, formed in 1995 as a spin-off from Novartis#Sandoz, Sandoz. Headquartered in Muttenz, Switzerland, the public company encompasses 68 subsidiaries in 36 countries (2023). Major manu ...
. The successor companies remain some of the world's largest chemical and pharmaceutical companies.
Although IG Farben was officially put into liquidation
Liquidation is the process in accounting by which a Company (law), company is brought to an end. The assets and property of the business are redistributed. When a firm has been liquidated, it is sometimes referred to as :wikt:wind up#Noun, w ...
in 1952, this did not end the company's legal existence. The purpose of a corporation's continuing existence, being "in liquidation", is to ensure an orderly wind-down of its affairs. As almost all its assets and all its activities had been transferred to the original constituent companies, IG Farben was from 1952, largely a shell company with no real activity.
 In 2001, IG Farben announced that it would formally wind up its affairs in 2003. It had been continually criticized over the years for failing to pay compensation to the former labourers; its stated reason for its continued existence after 1952 was to administer its claims and pay its debts. The company, in turn, blamed ongoing legal disputes with the former captive labourers for its inability to be legally dissolved and have the remaining assets distributed as reparations."IG Farben to be dissolved"
In 2001, IG Farben announced that it would formally wind up its affairs in 2003. It had been continually criticized over the years for failing to pay compensation to the former labourers; its stated reason for its continued existence after 1952 was to administer its claims and pay its debts. The company, in turn, blamed ongoing legal disputes with the former captive labourers for its inability to be legally dissolved and have the remaining assets distributed as reparations."IG Farben to be dissolved"BBC News, 17 September 2001. On 10 November 2003, its liquidators filed for
insolvency
In accounting, insolvency is the state of being unable to pay the debts, by a person or company ( debtor), at maturity; those in a state of insolvency are said to be ''insolvent''. There are two forms: cash-flow insolvency and balance-sheet i ...
, but this did not affect the existence of the company as a legal entity. While it did not join a national compensation fund set up in 2001 to pay the victims, it contributed 500,000 DM (£160,000 stg or €255,646) towards a foundation for former captive labourers under the Nazi regime. The remaining property, worth DM 21 million (£6.7 million or €10.7 million), went to a buyer. Each year, the company's annual meeting in Frankfurt was the site of demonstrations by hundreds of protesters. Its stock (denominated in Reichsmark
The (; sign: ℛ︁ℳ︁; abbreviation: RM) was the currency of Germany from 1924 until the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945, and in the American, British and French occupied zones of Germany, until 20 June 1948. The Reichsmark was then replace ...
s) traded on German markets until early 2012. , it still existed as a corporation in liquidation. The company's shares were delisted from German stock exchanges in March 2012, and it was removed from the commercial register in Frankfurt am Main on October 31, 2012, marking the formal end of its legal existence.
IG Farben in media
Film and television * IG Farben is the company said to be supporting German terror activities and research of uranium ores in Brazil after World War II inAlfred Hitchcock
Sir Alfred Joseph Hitchcock (13 August 1899 – 29 April 1980) was an English film director. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in the history of cinema. In a career spanning six decades, he directed over 50 featu ...
's film noir
Film noir (; ) is a style of Cinema of the United States, Hollywood Crime film, crime dramas that emphasizes cynicism (contemporary), cynical attitudes and motivations. The 1940s and 1950s are generally regarded as the "classic period" of Ameri ...
'' Notorious'' (1946).
* ''The Council of the Gods
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
'' (1951), produced by (DEFA
DEFA (''Deutsche Film-Aktiengesellschaft'') was the state-owned film studio of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) throughout the country's existence. Since 2019, DEFA's film heritage has been made accessible and licensable on the PR ...
director Kurt Maetzig
Kurt Maetzig (25 January 1911 – 8 August 2012) was a German film director who had a significant effect on the film industry in East Germany. He was one of the most respected filmmakers of the GDR. After his retirement he lived in Wildkuh ...
), is an East German film about IG Farben's role in World War II and the subsequent trial.
* IG Farben is the name of the arms dealer played by Dennis Hopper
Dennis Lee Hopper (May 17, 1936 – May 29, 2010) was an American actor, filmmaker, photographer and visual artist. He was considered one of the key figures of New Hollywood. He earned prizes from the Cannes Film Festival and Venice Internatio ...
in the 1987 independent film
An independent film, independent movie, indie film, or indie movie is a feature film or short film that is film production, produced outside the Major film studios, major film studio system in addition to being produced and distributed by independ ...
'' Straight to Hell'' directed by Alex Cox.
* In one of the deleted scenes from Repo Man, repo man Bud uses a phony business card with IG Farben as a company name to distract a man while his daughter's car is repossessed.
* In ''Foyle's War'' series eight, episode 1 (" High Castle"), Foyle tours Monowitz as part of his investigation of the murder of a London University professor, who as a translator for the Nuremberg Trials #REDIRECT Nuremberg trials
{{redirect category shell, {{R from other capitalisation{{R from move ...
becomes involved with an American industrialist who owns a petroleum company, and a German war criminal named Linz, who also turns up dead, in his cell. Linz's firm, IG Farben, had hired from the SS forced laborers incarcerated at Monowitz.
Literature
* IG Farben plays a prominent role in Thomas Pynchon
Thomas Ruggles Pynchon Jr. ( , ; born May 8, 1937) is an American novelist noted for his dense and complex novels. His fiction and non-fiction writings encompass a vast array of subject matter, Literary genre, genres and Theme (narrative), th ...
's novel ''Gravity's Rainbow
''Gravity's Rainbow'' is a 1973 novel by the American writer Thomas Pynchon. The narrative is set primarily in Europe at the end of World War II and centers on the design, production and dispatch of V-2 rockets by the German military. In partic ...
'', primarily as the manufacturer of the elusive and mysterious plastic product "Imipolex G."
* The company also plays a prominent role in Philip K. Dick's alternative history
Alternate history (also referred to as alternative history, allohistory, althist, or simply A.H.) is a subgenre of speculative fiction in which one or more historical events have occurred but are resolved differently than in actual history. As ...
novel '' The Man in the High Castle''.
* IG Farben is the German consortium that buys Du Pont in the Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut ( ; November 11, 1922 – April 11, 2007) was an American author known for his Satire, satirical and darkly humorous novels. His published work includes fourteen novels, three short-story collections, five plays, and five nonfict ...
novel ''Hocus Pocus''.
Games
* In ''the Hearts of Iron series'' (developed by Paradox Interactive
Paradox Interactive AB is a video game publisher based in Stockholm, Sweden. The company started out as the video game division of Target Games and then Paradox Entertainment (now Cabinet Entertainment) before being spun out into an independ ...
), IG Farben is one of several Design Companies that may be selected to provide a bonus to technology research for Germany; other options include Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the positi ...
and Krupp
Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer dur ...
.
See also
* American IG *Bernard Bernstein
Bernard Bernstein (30 November 1908 – 6 February 1990) was an American economist and public official.
Background
Bernard Bernstein was born on November 30, 1908, in New York City. He had at least one brother and one sister. He receiv ...
* Interhandel (I.G. Chemie)
* Nuremberg Trials bibliography
References
Notes
Citations
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
Books and articles * * * * * * *Du Bois, Josiah Ellis; Johnson, Edward (1953). ''Generals in Grey Suits: The Directors of the International 'I. G. Farben' Cartel, Their Conspiracy and Trial at Nuremberg''. London: Bodley Head. * * * * * * * * * * * Tenfelde, Klaus (2007). ''Stimmt die Chemie? : Mitbestimmung und Sozialpolitik in der Geschichte des Bayer-Konzerns''. Essen: Klartext. * * *External links
* * of the IG Farben successorBASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
* of the IG Farben successor Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
* of the IG Farben successor Hoechst (now Sanofi-Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. The corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Synthélabo merg ...
)
Stock Market Prices
of IG Farben * {{Authority control 1925 establishments in Germany 1951 disestablishments in West Germany Auschwitz concentration camp Chemical companies established in 1925 Chemical companies of Germany Companies involved in the Holocaust Conglomerate companies disestablished in 1951 Conglomerate companies established in 1925 Defunct companies of Germany Infrastructure of the Holocaust