Decarboxylative on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Decarboxylation is a
Decarboxylation is a
 Straight-chain fatty acid synthesis occurs by recurring reactions involving decarboxylation of
Straight-chain fatty acid synthesis occurs by recurring reactions involving decarboxylation of
 Upon heating, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid decarboxylates to give the psychoactive compound Δ9-
Upon heating, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid decarboxylates to give the psychoactive compound Δ9-
 Decarboxylation is a
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
that removes a carboxyl group
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g. ...
and releases carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, is called carboxylation
Carboxylation is a chemical reaction in which a carboxylic acid is produced by treating a substrate with carbon dioxide. The opposite reaction is decarboxylation. In chemistry, the term carbonation is sometimes used synonymously with carboxylation ...
, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylase
Carboxy-lyases, also known as decarboxylases, are carbon–carbon lyases that add or remove a carboxyl group from organic compounds. These enzymes catalyze the decarboxylation of amino acids and alpha-keto acids.
Classification and nomenclature ...
s or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases
Carboxy-lyases, also known as decarboxylases, are carbon–carbon lyases that add or remove a carboxyl group from organic compounds. These enzymes catalyze the decarboxylation of amino acids and alpha-keto acids.
Classification and nomenclature
...
( EC number 4.1.1).
In organic chemistry
The term "decarboxylation" usually means replacement of acarboxyl group
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g. ...
() with a hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral hydrogen atom contains a single positively charged proton in the nucleus, and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb for ...
:
:
Decarboxylation is one of the oldest known organic reactions. It is one of the processes assumed to accompany pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
and destructive distillation
Destructive distillation is a chemical process in which decomposition of unprocessed material is achieved by heating it to a high temperature; the term generally applies to processing of organic material in the absence of air or in the presence o ...
.
Overall, decarboxylation depends upon stability of the carbanion synthon
In retrosynthetic analysis, a synthon is a hypothetical unit within a target molecule that represents a potential starting reagent in the retroactive synthesis of that target molecule. The term was coined in 1967 by E. J. Corey. He noted in 1988 ...
, although the anion may not be a true chemical intermediate. Typically, carboxylic acids decarboxylate slowly, but carboxylic acids with an α electron-withdrawing group
An electron-withdrawing group (EWG) is a Functional group, group or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms. This electron density transfer is often achieved by resonance or inductive effe ...
(e.g. βketo acid
In organic chemistry, keto acids or ketoacids (also called oxo acids or oxoacids) are organic compounds that contain a carboxylic acid group () and a ketone group ().Franz Dietrich Klingler, Wolfgang Ebertz "Oxocarboxylic Acids" in Ullmann's En ...
s, βnitriles, αnitro
Nitro may refer to:
Chemistry
*Nitrogen, a chemical element and a gas except at very low temperatures, with which many compounds are formed:
**Nitro compound, an organic compound containing one or more nitro functional groups, -NO2
**Nitro ligand ...
acids, or arylcarboxylic acids) decarboxylate easily. Decarboxylation of sodium chlorodifluoroacetate
Sodium chlorodifluoroacetate is the organofluorine compound with the formula . It is a salt formed by neutralization of chlorodifluoroacetic acid with sodium hydroxide. The compound, a white solid, is of interest as a source of difluorocarbene:
...
generates difluorocarbene
Difluorocarbene is the chemical compound with formula CF2. It has a short half-life, 0.5 and 20 ms, in solution and in the gas phase, respectively.Douglas A Jean Osteraas "Difluorocarbene Modification of Polymer and Fiber Surfaces," ''Journal ...
:
:
Decarboxylations are an important in the malonic and acetoacetic ester synthesis. The Knoevenagel condensation
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation () reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation.
A Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition o ...
and they allow keto acids serve as a stabilizing protecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In man ...
for carboxylic acid enol
In organic chemistry, enols are a type of functional group or intermediate in organic chemistry containing a group with the formula (R = many substituents). The term ''enol'' is an abbreviation of ''alkenol'', a portmanteau deriving from "-ene ...
s.
For the free acids, conditions that deprotonate the carboxyl group (possibly protonating the electron-withdrawing group to form a zwitterionic
In chemistry, a zwitterion ( ; ), also called an inner salt or dipolar ion, is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively and negatively charged functional groups.
:
(1,2-dipolar compounds, such as ylides, are sometimes excluded from t ...
tautomer
In chemistry, tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the reloca ...
) accelerate decarboxylation. A strong base is key to ketonization
Ketonic decarboxylation (also known as decarboxylative ketonization) is a type of organic reaction involving decarboxylation, converting two equivalents of a carboxylic acid () to a symmetric ketone (). The reaction typically requires heat and a ...
, in which a pair of carboxylic acids combine to the eponymous functional group:

Transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
salts, especially copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
compounds, facilitate decarboxylation via carboxylate complex intermediates. Metals that catalyze cross-coupling reaction
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important re ...
s thus treat aryl carboxylates as an aryl anion synthon; this synthetic strategy is the decarboxylative cross-coupling reaction.
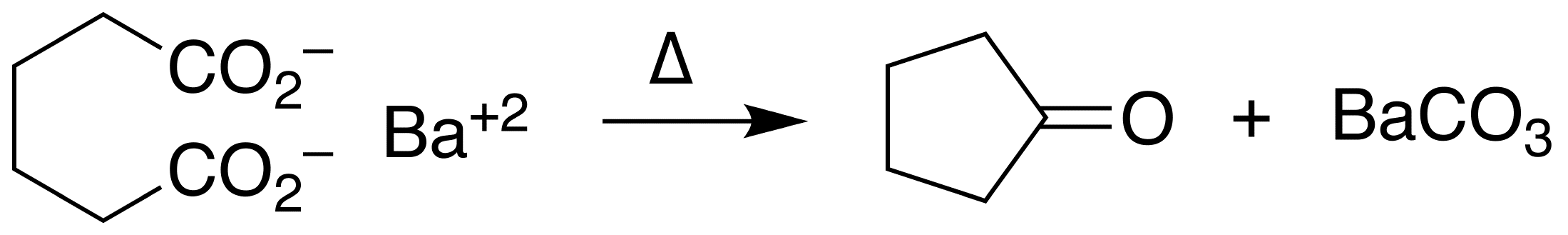
Upon heating in cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of ...
, amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s decarboxylate. In the related Hammick reaction, uncatalyzed decarboxylation of a picolinic acid
Picolinic acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a derivative of pyridine with a carboxylic acid (COOH) substituent at the 2-position. It is an isomer of nicotinic acid and isonicotinic acid, which have the carboxyl side chain at th ...
gives a stable carbene
A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is an organic molecule whose natural resonance structure has a carbon atom with incomplete octet (a carbene), but does not exhibit the tremendous instability typically associated with such moiet ...
that attacks a carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
electrophile.
Oxidative decarboxylations are generally radical reactions. These include the Kolbe electrolysis
__NOTOC__
The Kolbe electrolysis or Kolbe reaction is an organic reaction named after Hermann Kolbe. The Kolbe reaction is formally a decarboxylative dimerisation of two carboxylic acids (or carboxylate ions). The overall reaction is:
:
If a ...
and Hunsdiecker-Kochi reaction
The Kochi reaction is an organic reaction for the decarboxylation of carboxylic acids to alkyl halides with lead(IV) acetate and a lithium halide.''A New Method for Halodecarboxylation of Acids Using Lead(IV) Acetate'' Jay K. Kochi J. Am. Chem. S ...
s. The Barton decarboxylation
The Barton decarboxylation is a radical reaction in which a carboxylic acid is converted to a thiohydroxamate ester (commonly referred to as a Barton ester). The product is then heated in the presence of a radical initiator and a suitable hydrogen ...
is an unusual radical reductive decarboxylation.
As described above, most decarboxylations start with a carboxylic acid or its alkali metal salt, but the Krapcho decarboxylation starts with methyl ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
s. In this case, the reaction begins with halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
-mediated cleavage of the ester, forming the carboxylate.
In biochemistry
Decarboxylations are pervasive in biology. They are often classified according to the cofactors that catalyze the transformations.Biotin
Biotin (also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. ...
-coupled processes effect the decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.
Biosynthesis
Malonyl-CoA cannot cross membranes and there is no known malonyl-CoA import mechanism. The biosynthesis therefore takes place locally:
* cytosol: Malonyl-CoA is formed by c ...
to acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
. Thiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin – an Nutrient#Micronutrients, essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosp ...
(T:) is the active component for decarboxylation of alpha-ketoacids, including pyruvate:
:
:
Pyridoxal phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependen ...
promotes decarboxylation of amino acids. Flavin-dependent decarboxylases are involved in transformations of cysteine.
Iron-based hydroxylases operate by reductive activation of using the decarboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate as an electron donor. The decarboxylation can be depicted as such:
:
:
Decarboxylation of amino acids
Commonbiosynthetic
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme- catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve ...
oxidative decarboxylations of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s to amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s are:
* tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
to tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the firs ...
* phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
to phenylethylamine
* tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
to tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the bl ...
* histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an Amine, α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under Physiological condition, biological conditions), a carboxylic ...
to histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
* serine
Serine
(symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − ...
to ethanolamine
Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is a naturally occurring organic chemical compound with the formula or . The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorl ...
* glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ...
to GABA
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, γ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
* lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
to cadaverine
Cadaverine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5(NH2)2. Classified as a diamine, it is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is present in small quantities in living organisms but is often associated with the putrefaction of Tiss ...
* arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
to agmatine
* ornithine
Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic α-amino acid that plays a role in the urea cycle. It is not incorporated into proteins during translation. Ornithine is abnormally accumulated in the body in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, a disorder of th ...
to putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of Putrefaction, putref ...
* 5-HTP
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), used medically as oxitriptan, is a naturally occurring amino acid and chemical precursor as well as a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin.
5-HTP can be manufactured and us ...
to serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
* L-DOPA
-DOPA, also known as -3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and used medically as levodopa, is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize -DO ...
to dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
Other decarboxylation reactions from the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
include:
* pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
to acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
(see pyruvate decarboxylation)
* oxalosuccinate to α- ketoglutarate
* α- ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-coenzyme A, abbreviated as succinyl-CoA () or SucCoA, is a thioester of succinic acid and coenzyme A.
Sources
It is an important intermediate in the citric acid cycle, where it is synthesized from Alpha-Ketoglutaric acid, α-ketoglutarate ...
.
Fatty acid synthesis
malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.
Biosynthesis
Malonyl-CoA cannot cross membranes and there is no known malonyl-CoA import mechanism. The biosynthesis therefore takes place locally:
* cytosol: Malonyl-CoA is formed by c ...
.
Case studies
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of ''Cannabis'' and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) de ...
. When cannabis is heated in vacuum, the decarboxylation of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) appears to follow first order kinetics. The log fraction of THCA present decreases steadily over time, and the rate of decrease varies according to temperature. At 10-degree increments from 100 to 140 °C, half of the THCA is consumed in 30, 11, 6, 3, and 2 minutes; hence the rate constant follows Arrhenius' law, ranging between 10−8 and 10−5 in a linear log-log relationship with inverse temperature. However, modelling of decarboxylation of salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a active metabolite, metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is a plant hormone, and has been lis ...
with a water molecule had suggested an activation barrier of 150 kJ/mol for a single molecule in solvent, much too high for the observed rate. Therefore, it was concluded that this reaction, conducted in the solid phase in plant material with a high fraction of carboxylic acids, follows a pseudo first order kinetics in which a nearby carboxylic acid precipitates without affecting the observed rate constant. Two transition states corresponding to indirect and direct keto-enol routes are possible, with energies of 93 and 104 kJ/mol. Both intermediates involve protonation of the alpha carbon
In the nomenclature of organic chemistry, a locant is a term to indicate the position of a functional group or substituent within a molecule.
Numeric locants
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends the use of n ...
, disrupting one of the double bonds of the aromatic ring and permitting the beta-keto group (which takes the form of an enol
In organic chemistry, enols are a type of functional group or intermediate in organic chemistry containing a group with the formula (R = many substituents). The term ''enol'' is an abbreviation of ''alkenol'', a portmanteau deriving from "-ene ...
in THCA and THC) to participate in decarboxylation.
In beverages stored for long periods, very small amounts of benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
may form from benzoic acid
Benzoic acid () is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. The benzoyl group is often abbreviated "Bz" (not to be confused with "Bn," which ...
by decarboxylation catalyzed by the presence of ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula , originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.
Asco ...
.
The addition of catalytic amounts of cyclohexenone has been reported to catalyze the decarboxylation of amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
. However, using such catalysts may also yield an amount of unwanted by-products.
References
{{Reflist, 2 Substitution reactions