|
Tyramine
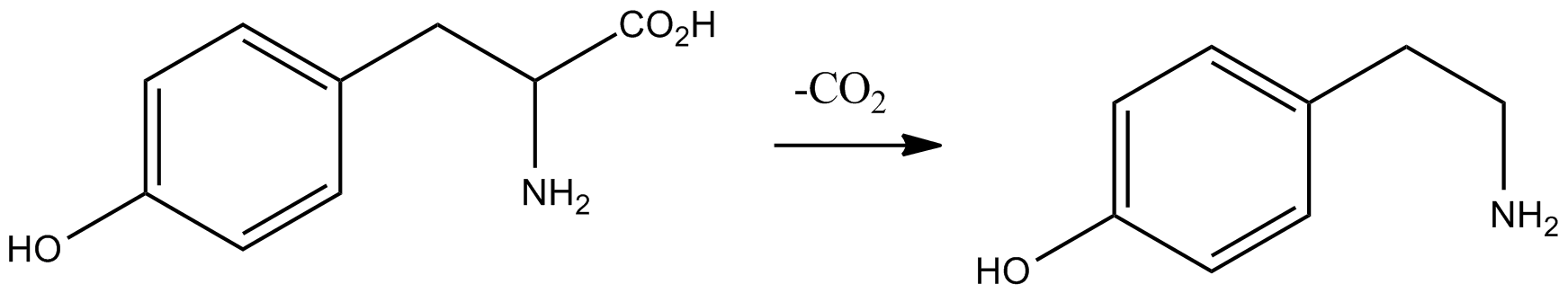
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Occurrence Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals, and is metabolized by various enzymes, including monoamine oxidases. In foods, it often is produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay. Foods that are fermented, cured, pickled, aged, or spoiled have high amounts of tyramine. Tyramine levels go up when foods are at room temperature or go past their freshness date. Specific foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include: * Strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopamine
Octopamine (OA), also known as ''para''-octopamine and norsynephrine among synonyms, is an organic chemical closely related to norepinephrine, and synthesized biologically by a homologous pathway. Octopamine is often considered the major "fight-or-flight" neurohormone of invertebrates. Its name is derived from the fact that it was first identified in the salivary glands of the octopus. In many types of invertebrates, octopamine is an important neurotransmitter and hormone. In protostomes—arthropods, molluscs, and several types of worms—it substitutes for norepinephrine and performs functions apparently similar to those of norepinephrine in mammals, functions that have been described as mobilizing the body and nervous system for action. In mammals, octopamine is found only in trace amounts (i.e., it is a trace amine), and no biological function has been solidly established for it. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange. Octopamine has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Beta-hydroxylase
Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), also known as dopamine beta-monooxygenase, is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the DBH gene. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase catalyzes the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine. The three substrates of the enzyme are dopamine, vitamin C (ascorbate), and O2. The products are norepinephrine, dehydroascorbate, and H2O. DBH is a 290 kDa copper-containing oxygenase consisting of four identical subunits, and its activity requires ascorbate as a cofactor. It is the only enzyme involved in the synthesis of small-molecule neurotransmitters that is membrane-bound, making norepinephrine the only known transmitter synthesized inside vesicles. It is expressed in noradrenergic neurons of the central nervous system (i.e. locus coeruleus) and peripheral nervous systems (i.e. sympathetic ganglia), as well as in chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. Mechanism of catalysis Based on the observations of what happens when there is no substrate, or o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trace Amine
Trace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists – and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators – that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to the classical monoamines, they are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed heterogeneously throughout the mammalian brain and peripheral nervous tissues and exhibit high rates of metabolism. Although they can be synthesized within parent monoamine neurotransmitter systems, there is evidence that suggests that some of them may comprise their own independent neurotransmitter systems. Trace amines play significant roles in regulating the quantity of monoamine neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft of monoamine neurons with TAAR1. They have well-characterized presynaptic ''amphetamine-like'' effects on these monoamine neurons via TAAR1 activation; specifically, by activating TAAR1 in neurons they promote the release and preve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase
Monoamine oxidases (MAO) () are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The first such enzyme was discovered in 1928 by Mary Bernheim in the liver and was named tyramine oxidase. The MAOs belong to the protein family of flavin-containing amine oxidoreductases. MAOs are important in the breakdown of monoamines ingested in food, and also serve to inactivate monoamine neurotransmitters. Because of the latter, they are involved in a number of psychiatric and neurological diseases, some of which can be treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) which block the action of MAOs. Subtypes and tissue distribution In humans there are two types of MAO: MAO-A and MAO-B. * Both are found in neurons and astroglia. * Outside the central nervous system: ** MAO-A is also found in the liver, pulmonary vascular end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
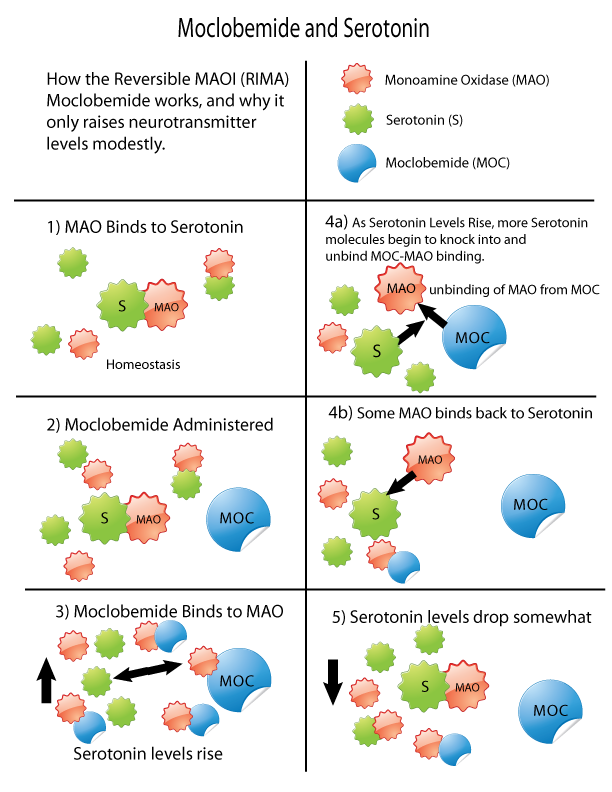
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that binding selectivity, selectively and Enzyme inhibitor#Reversible inhibitors, reversibly enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the medication, treatment of major depressive disorder, depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and many addictive drugs increase dopamine release or block its reuptake into neurons following release. Other brain dopamine pathways are involved in motor control and in controllin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-methyltyramine
''N''-Methyltyramine (NMT), also known as 4-hydroxy-''N''-methylphenethylamine, is a human trace amine and natural phenethylamine alkaloid found in a variety of plants.T. A. Smith (1977). "Phenethylamine and related compounds in plants." ''Phytochemistry'' 16 9 – 18. As the name implies, it is the N-methyl analog of tyramine, which is a well-known biogenic trace amine with which NMT shares many pharmacological properties. Biosynthetically, NMT is produced by the N-methylation of tyramine via the action of the enzyme phenylethanolamine ''N''-methyltransferase in humans and tyramine ''N''-methyltransferase in plants. Occurrence N-methyltyramine seems to be quite widely distributed in plants. NMT was isolated as a natural product for the first time, from germinating barley roots, by Kirkwood and Marion in 1950. These chemists found that 600 g of barley, after germination and 10-day growth, yielded 168 mg of N-methyltyramine.S. Kirkwood and L. Marion (1950) ''J. Am. Chem. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavin-containing Monooxygenase 3
Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), also known as dimethylaniline monooxygenase -oxide-forming3 and trimethylamine monooxygenase, is a flavoprotein enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''FMO3'' gene. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction, among others: :trimethylamine + NADPH + H+ + O2 \rightleftharpoons trimethylamine ''N''-oxide + NADP+ + H2O FMO3 is the main flavin-containing monooxygenase isoenzyme that is expressed in the liver of adult humans. The human FMO3 enzyme catalyzes several types of reactions, including: the of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines; the of nucleophilic sulfur-containing compounds; and the of the anti-cancer agent dimethylxanthenone acetic acid ( DMXAA). FMO3 is the primary enzyme in humans which catalyzes the ''N''-oxidation of trimethylamine into trimethylamine ''N''-oxide; FMO1 also does this, but to a much lesser extent than FMO3. Genetic deficiencies of the FMO3 enzyme cause primary trimethylaminuria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase B
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOB'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the flavin monoamine oxidase family. It is an enzyme located in the outer mitochondrial membrane. It catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and plays an important role in the catabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. This protein preferentially degrades benzylamine and phenethylamine. Similar to monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), MAO-B is also involved in the catabolism of dopamine. Structure and function MAO-B has a hydrophobic bipartite elongated cavity that (for the "open" conformation) occupies a combined volume close to 700 Å3. hMAO-A has a single cavity that exhibits a rounder shape and is larger in volume than the "substrate cavity" of hMAO-B. The first cavity of hMAO-B has been termed the ''entrance cavity'' (290 Å3), the second ''substrate cavity'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Releasing Agent
A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters. MRAs work by reversing the direction of the monoamine transporters (MATs), including the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and/or dopamine transporter (DAT), causing them to promote efflux of non-vesicular cytoplasmic monoamine neurotransmitter rather than reuptake of synaptic monoamine neurotransmitter. Many, but not all MRAs, also reverse the direction of the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), thereby additionally resulting in efflux of vesicular monoamine neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the Limb (anatomy), limbs and Organ (anatomy), organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into a somatic nervous system, somatic division and an autonomic nervous system, autonomic division. Each of these can further be differentiated into a sensory and a motor sector. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exceptions of the olfactory nerve and epithelia and the optic nerve (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |