Cúcuta Deportivo Footballers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cúcuta (), officially San José de Cúcuta, is a
 Cúcuta was originally a
Cúcuta was originally a
 In 1541,
In 1541,
 The Battle of Cúcuta was one of the most important events of the
The Battle of Cúcuta was one of the most important events of the
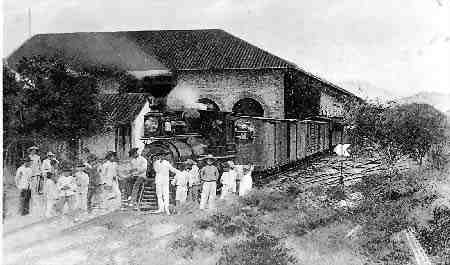 In the 19th century, the construction of a railroad set off an
In the 19th century, the construction of a railroad set off an
 Cúcuta's center, core of the city, is organized as a grid adopted from Spain in colonial times and reformed by Francisco Andrade Troconis after the devastating earthquake of 1875, with
Cúcuta's center, core of the city, is organized as a grid adopted from Spain in colonial times and reformed by Francisco Andrade Troconis after the devastating earthquake of 1875, with
 The red and black
The red and black
 The lower part of the shield displays the arms that the Congress of Cúcuta, National Congress adopted for Colombia by the Law of October 6, 1821, at its meeting in the Villa del Rosario. In the center are a quiver of spears, marked with X's, and a set of bow and arrows, tied with tricolor tape. The spears represent attributes of the Roman consuls; the X is a symbol of the right of life or death; the bow and arrows are symbols of the pre-hispanic indigenous people.
The lower part of the shield displays the arms that the Congress of Cúcuta, National Congress adopted for Colombia by the Law of October 6, 1821, at its meeting in the Villa del Rosario. In the center are a quiver of spears, marked with X's, and a set of bow and arrows, tied with tricolor tape. The spears represent attributes of the Roman consuls; the X is a symbol of the right of life or death; the bow and arrows are symbols of the pre-hispanic indigenous people.
 Many notable Colombians are from Cúcuta:
* James Rodríguez, association football, footballer, who is currently playing for Olympiacos of Pyraeus.
*
Many notable Colombians are from Cúcuta:
* James Rodríguez, association football, footballer, who is currently playing for Olympiacos of Pyraeus.
*
asapedia.com Accessed October 15, 2006 * El reverendo padre Rafael García Herreros (the founder of Minuto de Dios) * Elias M. Soto, a classical musician * Marino Vargas Villalta, civic leader and businessman, who during the 1950s and 1960s was the chairperson of the popular local soccer team, Cúcuta Deportivo * Alberto Villamizar, a former congressman and ambassador to Indonesia, Netherlands, and Cuba; Colombia's first "kidnappings czar"; and leading political figure of the nuevo liberalismo (New Liberalism) movement of Luis Carlos Galan

 The city is notable for bilateral trade and manufacturing. Its location on the border between Colombia and Venezuela has made possible strong links with the Venezuelan city of San Cristóbal, Táchira.
Its Free Zone is the most active of all those in the country and one of the most active in all Latin America, largely due to Venezuela being Colombia's second largest trade partner.
The most developed Industry (economics), industries are dairy, construction, textiles, shoes, and leather. The city is a top producer of cement and its clay and stoneware industry has the best reputation nationally for its high quality. The mining of coal also plays an important role in the local economy. The University Francisco de Paula Santander in Cucuta, the National University of Colombia in Bogotá, and the Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia in Tunja are the only ones in the country that provide for the career of Mining Engineering.
The Colombian peso, peso is the official and sole legal tender currency in the city. Owing to its proximity to
The city is notable for bilateral trade and manufacturing. Its location on the border between Colombia and Venezuela has made possible strong links with the Venezuelan city of San Cristóbal, Táchira.
Its Free Zone is the most active of all those in the country and one of the most active in all Latin America, largely due to Venezuela being Colombia's second largest trade partner.
The most developed Industry (economics), industries are dairy, construction, textiles, shoes, and leather. The city is a top producer of cement and its clay and stoneware industry has the best reputation nationally for its high quality. The mining of coal also plays an important role in the local economy. The University Francisco de Paula Santander in Cucuta, the National University of Colombia in Bogotá, and the Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia in Tunja are the only ones in the country that provide for the career of Mining Engineering.
The Colombian peso, peso is the official and sole legal tender currency in the city. Owing to its proximity to
 Law 100 of 1993 is the law governing Health in Colombia, which is regulated by the Ministry of Social Protection. In Cucuta and
Law 100 of 1993 is the law governing Health in Colombia, which is regulated by the Ministry of Social Protection. In Cucuta and

City Hall of Cúcuta
Gobernación de Norte de Santander
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cucuta Cúcuta, Municipalities of the Norte de Santander Department Colombia–Venezuela border crossings Capitals of Colombian departments
Colombian municipality
The Municipalities of Colombia are decentralized subdivisions of the Republic of Colombia. Municipalities make up most of the departments of Colombia with 1,122 municipalities (''municipios''). Each one of them is led by a mayor (''alcalde'') ...
, capital of the department of Norte de Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Ven ...
and nucleus of the Metropolitan Area of Cúcuta. The city is located in the homonymous valley, at the foot of the Eastern Ranges
The Eastern Ranges is an Australian rules football team in the NAB League, the Victorian statewide under-18s competition.
The club is a founding member of the competition (1992) and has produced several players for the Australian Football Le ...
of the Colombian Andes
The Andean region, located in central Colombia, is the most populated natural region of Colombia. With many mountains, the Andes contain most of the country's urban centers.Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
. It comprises an area of approximately 1119 km2, with an urban area of 64 km2 (divided into 10 communes) and a rural area of 1055 km2 (divided into 10 townships). The city has a population of 777,106 inhabitants, which makes it the most populous municipality in the department and the sixth most populous municipality in the country. Similarly, its metropolitan area (made up of the municipalities of Villa del Rosario, Los Patios, El Zulia
El Zulia () is a municipality of the Norte de Santander Department in Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coas ...
, San Cayetano and Puerto Santander) has an approximate population of 1,046,347.
The city was founded as a parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or ...
on June 17, 1733, by Juana Rangel de Cuéllar, resident of Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
in the area under the name of ''San José de Guasimales'', as part of an initiative of the white and mestizo locals to separate themselves from the "Indian Village of Cúcuta" (currently San Luis Quarter). Later, the name was changed to San José de Cúcuta, castellanization of «Kuku-ta», in honor of the indigenous people of the region. From its foundation in the 18th century
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave tradin ...
and throughout the Spanish viceroyalty, the parish was consolidated as one of the most important settlements of the Colombian East and Spanish America, receiving in 1792 the title of «Very Noble, Valiant and Loyal Village» by King Charles IV of Spain
Charles IV (Carlos Antonio Pascual Francisco Javier Juan Nepomuceno José Januario Serafín Diego) 11 November 1748 – 20 January 1819) was King of Spain and ruler of the Spanish Empire from 1788 to 1808.
The Spain inherited by Charles IV ...
.
The city is the political, economic, industrial, artistic, cultural, sports and tourist epicenter of Norte de Santander and constitutes, in turn, as the most important urban settlement of the Colombian-Venezuelan border along with the Venezuelan city of San Cristóbal, due to its trade dynamics and its historical importance in the consolidation of the modern states of Colombia and Venezuela as well as its diplomatic relations
Diplomacy comprises spoken or written communication by representatives of states (such as leaders and diplomats) intended to influence events in the international system.Ronald Peter Barston, ''Modern diplomacy'', Pearson Education, 2006, p. 1 ...
, hosting events such as the Battle of Cúcuta of 1813, the Congress of Cúcuta of 1821 in Villa del Rosario, in more recent times the signing of the 1941 Treaty of Limits between Colombia and Venezuela, the 1959 Treaty of Tonchalá, the charity concerts Peace Without Borders of 2008 and Venezuela Aid Live of 2019, among others. It also played a significant role during Colombian immigration to Venezuela and has recently become one of the most important transit points of the Venezuelan migration crisis.
As the capital of Norte de Santander, Cúcuta houses the main governmental bodies of departmental order such as the Government of Norte de Santander, the Assembly of Norte de Santander, the Superior Court of Cúcuta, the Judicial District of Cúcuta, the Administrative Court of Norte de Santander and the regional branches of the Superior Council of the Judiciary and the Office of the Inspector General of Colombia
The Office of the Inspector General of Colombia ( es, Procuraduría General de Colombia) is a Colombian independent, public institution overseeing the public conduct of those in authority or in charge of exercising a public office, and of overse ...
. Cúcuta is connected by road with Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the largest ...
, Bucaramanga
Bucaramanga () is the capital and largest city of the department of Santander, Colombia. Bucaramanga has the fifth-largest economy by GDP in Colombia, has the lowest unemployment rate and has the ninth-largest population in the country, with ...
, Valledupar
Valledupar () is a city and municipality in northeastern Colombia. It is the capital of Caesar Department. Its name, ''Valle de Upar'' (Valley of Upar), was established in honor of the Amerindian cacique who ruled the valley; ''Cacique Upar''. T ...
, Cartagena de Indias
Cartagena ( , also ), known since the colonial era as Cartagena de Indias (), is a city and one of the major ports on the northern coast of Colombia in the Caribbean Coast Region, bordering the Caribbean sea. Cartagena's past role as a link ...
and, by its border condition, with Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
. It has an air terminal, the Camilo Daza International Airport, and a ground terminal, the Central de Transportes de Cúcuta.
Its flagship university is the Francisco de Paula Santander University
The Francisco de Paula Santander University (Spanish: ''Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander'') is a public, coeducational, research university based primarily in the city of Cúcuta, Colombia, with regional campuses in Ocaña, Colombia, C ...
, one of the most important universities in eastern Colombia. It also has the presence of other universities of local and national renown such as the University of Pamplona
The University of Pamplona ( es, Universidad de Pamplona), is a public, departmental, coeducational research university based primarily in the city of Pamplona, Norte de Santander, Colombia. The university also has two satellite campuses in the ...
, the FESC, the Free University of Colombia
Free University of Colombia ( es, Universidad Libre), also called Unilibre, is a nonsectarian, coeducational, private and nonprofit university based in Bogota, Colombia, with six satellite campuses located in Cali, Barranquilla, Pereira, Ca ...
, the Simón Bolivar University, the University of Santander, the Saint Thomas University, among others.
Etymology
The city has a name composed in the manner of almost all the Spanish foundations in America: San José (one of the most widespread names in the continent thanks to the devotions of San José in Spain), honorsSaint Joseph
Joseph (; el, Ἰωσήφ, translit=Ioséph) was a 1st-century Jewish man of Nazareth who, according to the canonical Gospels, was married to Mary, the mother of Jesus, and was the legal father of Jesus. The Gospels also name some brothers ...
. The name of Cúcuta was taken in honor of the cacique Kuku-ta «Cúcuta in Spanish» and represents the Motilon-Bari indigenous people who inhabited the region before the conquest. Kuku-ta in the native language means "House of the Goblin". The city was known as San José de Guasimales from 1733 to 1793, when it changed to its current name.
The coat of arms of the city has the legend that it says «Muy Noble, Valerosa y Leal Villa de San José de Cúcuta» ''Very Noble, Valiant and Loyal Village of San José de Cúcuta'', title that was granted to him by means of royal card in just recognition to his laborious sons, shortly before the end of the century, by the King Charles IV of Spain
Charles IV (Carlos Antonio Pascual Francisco Javier Juan Nepomuceno José Januario Serafín Diego) 11 November 1748 – 20 January 1819) was King of Spain and ruler of the Spanish Empire from 1788 to 1808.
The Spain inherited by Charles IV ...
. This was possible thanks to the help of the lawyer of the Royal Audience José María Maldona, who was in charge of legally presenting before the Viceroy José Manuel de Ezpeleta the presentation of the title of village on behalf of the inhabitants of the city.
The city has the nicknames ''The Pearl of the North, Gate of the Border, Green City, City of Trees, The Basketball Capital of Colombia''.
History
 Cúcuta was originally a
Cúcuta was originally a pre-hispanic
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, t ...
settlement. It was entrusted to Sebastian Lorenzo by Pedro de Ursua as an encomienda
The ''encomienda'' () was a Spanish labour system that rewarded conquerors with the labour of conquered non-Christian peoples. The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military ...
in 1550. Juana Rangel de Cuellar
Juana is a Spanish female first name. It is the feminine form of Juan (English John), and thus corresponds to the English names Jane, Janet, Jean, Joan, and Joanna. Juanita is a common variant. The name Juana may refer to:
People
* Jua ...
founded Cúcuta on June 17, 1733, and donated a further . The village, centred on a church, grew considerably due to its strategic commercial location, and eventually became a city.
Several important events that forged Colombia as an independent republic took place in the city: one of these events was the Congress of 1821, where the Constitution of Cúcuta
The Constitution of Cúcuta, also known as Constitution of the Gran Colombia and Constitution of 1821, was the founding document and constitution of the Republic of Colombia (historiographically called Gran Colombia), unifying the territories ...
was written and approved. This constitution created Greater Colombia, a country embracing the present-day territories of Colombia, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
, Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar language, Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechuan ...
, and Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
. The city preserves places where these historical events took place: the Historical Church of Cúcuta
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as we ...
, the House of Santander, and the Park of Greater Colombia.
As the site of the Battle of Cúcuta (February 28, 1813), the city was the beginning of the Admirable Campaign led by Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24 July 1783 – 17 December 1830) was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and ...
. This campaign resulted in the independence of Venezuela.
16th century: First European incursions
The first European in theNorth Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Venezu ...
territories was the German conquistador Ambrosio Alfinger, who came from Santa Ana de Coro
Coro, historically known as Neu-Augsburg, is the capital of Falcón State and the second oldest city of Venezuela (after Cumaná). It was founded on July 26, 1527, by Juan de Ampíes as Santa Ana de Coro. It is established at the south of the Par ...
(Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
) in 1530 with a troop of adventurers, and invaded the unexplored eastern region of the newly created Governorate of Santa Marta.
Alfínger, in search of ''El Dorado
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the golden"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or kin ...
'', arrived in an area of indigenous settlements called Tamalameque along the Magdalena River, fighting and defeating several tribes. Alfinger was eventually killed in the outskirts of present-day Chinácota
Chinácota is a small town and municipality located in the Department of Norte de Santander in Colombia, South America. This department is located in the north-eastern region of the country, near the border with Venezuela. Chinácota has a popul ...
in a battle with Chimila and Chitarero
The Chitarero were an indigenous Chibcha-speaking people in the Andes of north-eastern Colombia and north-western Venezuela. They were responsible for the death of the German ''conquistador'' Ambrosius Ehinger in 1533 by means of poisoned arrows. ...
. With Alfínger dead, Fedro St. Martin took command of the troops and returned to Coro, passing through the territory of Cúcuta.
 In 1541,
In 1541, Hernán Pérez de Quesada
Hernán Pérez de Quesada, sometimes spelled as Quezada, (c. 1515 – 1544) was a Spanish conquistador. Second in command of the army of his elder brother, Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, Hernán was part of the first European expedition towards ...
reached the territory of Chinácota
Chinácota is a small town and municipality located in the Department of Norte de Santander in Colombia, South America. This department is located in the north-eastern region of the country, near the border with Venezuela. Chinácota has a popul ...
, but had to turn back the same year due to resistance by the indigenous people. Shortly thereafter, Alfonso Perez de Tolosa left El Tocuyo (Venezuela) and went to Salazar de Las Palmas, through Cúcuta, but also had to turn back after losing many soldiers in clashes with the natives.
In 1549, Spanish troops, commanded by Pedro de Ursúa and Ortún Velasco, invaded North Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Venezu ...
and reached the valley of Pamplona. In tribute to the Spanish city of Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
, the Spaniards founded the city of Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
. The new town soon attracted numerous people because of its agreeable climate, and gold mines that were discovered in the region. Further expeditions left this town and completed the conquest of the current territory of North Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Venezu ...
.
An expedition commanded by Diego de Montes founded the town of Salazar, but it was soon destroyed by the ''cacique
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a ...
'' Cínera. In 1583, the town was rebuilt by Alonso Esteban Rangel (great-grandfather of the founder of Cúcuta), on a site more appropriate for its defense in the event of new attacks by the natives.
The second expedition, commanded by Captain Francisco Fernández de Contreras, reached the lands of the Hacaritamas indigenous group and, on 26 July 1572, founded the city of Ocaña, calling it "Santa Ana de Hacarí". Some of his colleagues named it New Madrid, and others Santa Ana of Ocaña. The next year, Antonio Orozco, a subaltern of Fernández, founded the town of Teorama, while the Augustinian Friars
The Order of Saint Augustine, ( la, Ordo Fratrum Sancti Augustini) abbreviated OSA, is a religious mendicant order of the Catholic Church. It was founded in 1244 by bringing together several eremitical groups in the Tuscany region who were f ...
founded a convent in what is today the city of Chinácota
Chinácota is a small town and municipality located in the Department of Norte de Santander in Colombia, South America. This department is located in the north-eastern region of the country, near the border with Venezuela. Chinácota has a popul ...
.
17th century: Foundation
In the early 17th century a great part of the valley of Cúcuta belonged to Captain Christopher de Araque Ponce de Leon. The land passed through inheritance to his son Fernando Araque Ponce de Leon, who was the owner of the entire territory from the Valley of Cúcuta to the village of San Jose, the jurisdiction of the city of San Faustino. These fields had been donated to the older Araque by the Governor of the Province of New Mérida on 9 September 1630. The resistance of the Motilones indigenous group towards the whites who were taking over and controlling the valley with economic ambitions was the key factor in the request for the establishment of a Catholic parish with the name "San José." Juana Rangel de Cuéllar donated on June 17, 1733, for the construction of a church and land for Spanish families. Today, this area is the neighborhood of San Luis.19th century: Major events
Battle of Cúcuta
Spanish American wars of independence
The Spanish American wars of independence (25 September 1808 – 29 September 1833; es, Guerras de independencia hispanoamericanas) were numerous wars in Spanish America with the aim of political independence from Spanish rule during the early ...
, due to its role in the independence of Colombia and Venezuela. This battle was the beginning of the Admirable Campaign of Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24 July 1783 – 17 December 1830) was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and ...
. On February 28, 1813, Bolivar captured the city after a battle that lasted from 9:00 a.m. until early afternoon. About 400 men led by Bolivar fought 800 troops led by the Spanish general Ramon Correa. Bolivar's forces reported losses of two killed and 14 injured, whilst the royalists are said to have suffered 20 killed and 40 injured. The victory freed the city of Cúcuta and led to the Admirable Campaign.
Colonel Simón Bolívar then launched a major offensive against the Spanish forces who were on the east bank of the Magdalena River and quickly achieved resounding victories. These led him to undertake a journey to liberate the Valley of Cúcuta held by the command of royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
Colonel Ramon Correa.
Congress of Cúcuta
On August 30, 1821, the Congress of Cúcuta took place at the town of Villa del Rosario (today part of Cúcuta) in the church known today as the "Historic Temple of Cúcuta". The congress was established by Antonio Nariño and its participants includedFrancisco de Paula Santander
Francisco José de Paula Santander y Omaña ( Villa del Rosario, Norte de Santander, Colombia, April 2, 1792 – Santafé de Bogotá, Colombia, May 6, 1840), was a Colombian military and political leader during the 1810–1819 independ ...
, Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24 July 1783 – 17 December 1830) was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and ...
, and other leaders of Spanish America's struggle for independence from Spain.
The main objective of this congress was to unify the territories of New Granada ( Colombia and Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
) and Venezuela and thus create a huge state to be known as the Republic of Colombia (Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia ( Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1 ...
). Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar language, Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechuan ...
subsequently joined Gran Colombia.
At 11 am on October 3, 1821, Simón Bolívar entered the meeting room in the sacristy of the church. He took a seat next to the president of Congress and was sworn in as president of the fledgling Republic of Colombia.
Earthquake of Cúcuta
On May 18, 1875, Cúcuta was largely destroyed by theearthquake of Cúcuta
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
, also known as the "Earthquake of the Andes". The earthquake occurred at 11:15 am; it destroyed Villa del Rosario, San Antonio del Tachira and Capacho, seriously damaged the Venezuelan settlements of San Cristóbal, La Mulata, Rubio, Michelena, La Grita and Colón (among others), and was felt in Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the largest ...
and Caracas
Caracas (, ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the ...
.
Industrial Revolution
 In the 19th century, the construction of a railroad set off an
In the 19th century, the construction of a railroad set off an Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in the city. The railroad had four branches: North, East, South and West. The North branch was constructed from 1878 to 1888, and connected Cúcuta with Puerto Santander and Venezuela. Construction of the Eastern and Southern branches began in 1878; the South branch linked with Pamplona, Colombia, and ended in El Diamante. The West branch was not built owing to economic problems. The railroad company fell into bankruptcy and was closed in 1960.
Many of the city's historic buildings lie within the Park of Greater Colombia, including the House of Santander, the historic church
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as we ...
, and the historic tamarind. All these are well preserved.
Geography, climate and lay-out
Geography
The city is in the eastern part of the Department ofNorth Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Venezu ...
, in the Cordillera Oriental, close to the border with Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
. The city's area is and its elevation is above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''.
The ...
.
Rivers in Cúcuta and Norte de Santander include the Pamplonita River, Guaramito River, San Miguel River and Zulia River.
The Pamplonita River crosses the Norte de Santander Department
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Vene ...
.
Climate
Cúcuta has atropical savanna climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of ...
, bordering on a hot semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-a ...
( Köppen ''BSh''). The mean temperature is ; afternoon maximum temperatures are around . There is a sharp contrast between the wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the Rainy season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. It is the time of year where the majority of a country's or region's annual precipitation occurs. Generally, the se ...
and the dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The ...
. The driest months are January, February, June and July; the wettest are April, May, September, October and November. June and July usually however have frequent light precipitation and fog, whereas August is sunny and windy. The annual precipitation is around . Higher elevations near the city have cooler and wetter climates.
Layout
 Cúcuta's center, core of the city, is organized as a grid adopted from Spain in colonial times and reformed by Francisco Andrade Troconis after the devastating earthquake of 1875, with
Cúcuta's center, core of the city, is organized as a grid adopted from Spain in colonial times and reformed by Francisco Andrade Troconis after the devastating earthquake of 1875, with Santander Park
Santander Park ( es, Parque Santander) is located in Cúcuta, Colombia. The park is bordered by 5th and 6th Avenue and 10th and 11th Street and was previously the location of the Grand Square of San José de Guasimales, a site hosting principal ev ...
as the guiding point. More than 300 neighborhoods form the urban network. Poorer neighborhoods are in the north, north-west and south-west, many of them squatter areas. The middle class lives mostly in the central and eastern areas.
Odonymy
Minor streets (''Calles'') run from east to west, perpendicular to the city's western hills, whose numbering increases from north to south, starting from 1st Street. Major streets (''avenidas''), on the other hand, run from south to north parallel to the hills, starting from Zero Avenue. Avenues west of Zero Avenue increase their numbering from east to west, while those east of Zero Avenue increase their numbering from west to east, adding the indicative "E" (from ''Este'', east) as well (for example, 1st Avenue E, 2nd Avenue E, etc.).Symbols
Flag
North Santander Department
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Venezu ...
flag was exhibited for the first time in 1928, when the first National Olympics were held in Cali
Santiago de Cali (), or Cali, is the capital of the Valle del Cauca department, and the most populous city in southwest Colombia, with 2,227,642 residents according to the 2018 census. The city spans with of urban area, making Cali the secon ...
. However, the flag of Cúcuta was not legalized until Mayor Carlos A. Rangel issued Decree 106 on May 3, 1988.
The black section represents the rich resources hidden beneath the territory, as well as the potential capability of the local people, whereas the red section represents the sacrifices of the Spanish American wars of independence, independence heroes and the perseverance of the people in charge of reconstructing the city.
Coat of arms
The coat of arms of Cúcuta was adopted on February 3, 1958, by Decree 032, after a request by the History Academy of North Santander. The shield is a classic shape, and carries the title conferred on the city by Royal Decree of the Emperor Carlos IV: ''Very noble, valiant and loyal town of San José of Cúcuta''. The upper part depicts the arms of the city's founder Juana Rangel of Cuéllar, who donated lands for the foundation of the city on June 17, 1733. They are five silver and red fleur-de-lis in the shape of reels, on a golden background.Anthem
The anthem of Cúcuta was legalized by means of Decree 039 of February 8, 1984, by Mayor Luis Vicente Mountain Forest. The lyrics were written by Father Manuel Grillo Martínez, and the music by the master Pablo Tarazona Prada. It was chosen as the Anthem of Cúcuta by a unanimous vote in a contest held in the Theater Zulima.Demographics
Population
The metropolitan area, which includes the municipalities of Villa del Rosario, Los Patios,El Zulia
El Zulia () is a municipality of the Norte de Santander Department in Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coas ...
, San Cayetano, and Puerto Santander, has a combined population of more than 830,000 people. It is the largest metropolitan area in eastern Colombia and seventh in Colombia, behind Barranquilla, Bucaramanga
Bucaramanga () is the capital and largest city of the department of Santander, Colombia. Bucaramanga has the fifth-largest economy by GDP in Colombia, has the lowest unemployment rate and has the ninth-largest population in the country, with ...
, and Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena.
People
 Many notable Colombians are from Cúcuta:
* James Rodríguez, association football, footballer, who is currently playing for Olympiacos of Pyraeus.
*
Many notable Colombians are from Cúcuta:
* James Rodríguez, association football, footballer, who is currently playing for Olympiacos of Pyraeus.
* Francisco de Paula Santander
Francisco José de Paula Santander y Omaña ( Villa del Rosario, Norte de Santander, Colombia, April 2, 1792 – Santafé de Bogotá, Colombia, May 6, 1840), was a Colombian military and political leader during the 1810–1819 independ ...
, the first president of Colombia, known as "the man of the laws"
* Virgilio Barco, a former president of Colombia
* Fabiola Zuluaga, the most successful Colombian tennis playerAzapedia: Fabiola Zuluagaasapedia.com Accessed October 15, 2006 * El reverendo padre Rafael García Herreros (the founder of Minuto de Dios) * Elias M. Soto, a classical musician * Marino Vargas Villalta, civic leader and businessman, who during the 1950s and 1960s was the chairperson of the popular local soccer team, Cúcuta Deportivo * Alberto Villamizar, a former congressman and ambassador to Indonesia, Netherlands, and Cuba; Colombia's first "kidnappings czar"; and leading political figure of the nuevo liberalismo (New Liberalism) movement of Luis Carlos Galan
Government
The current mayor of Cúcuta is Donamaris Ramírez-Paris Lobo, who was elected for the 2011–2015 period. He represented the Green Party (Colombia), Partido Verde and achieved approximately 43% of the votation or 98,588 votes. The city is governed by the three branches of power: the executive power, represented by the Mayor and its departments; the legislative power, represented by the City Council; and the judicial power, which is formed by the tribunals and many other organisms of control. The Mayor is elected for a 4-year period and is in charge of electing each head of the administration departments. The city council is formed by 19 representatives elected by popular vote for four years. They approve or reject each decree issued by the mayor and make or correct laws regarding the city. As the capital ofNorte de Santander Department
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Vene ...
, Cúcuta houses the Department Hall and the City hall of the Metropolitan Area of Cúcuta, along with the Francisco de Paula Santander Justice Palace.
The city is divided into 10 localities (''comunas''). The Metropolitan Area of Cúcuta is formed by Cúcuta (as the main city), Villa del Rosario, Los Patios, San Cayetano, Colombia, San Cayetano, El Zulia
El Zulia () is a municipality of the Norte de Santander Department in Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coas ...
, and Puerto Santander.
Politics in Cúcuta are not defined by a single political movement. Past rivals included the Partido Liberal Colombiano, Colombian Liberal Party and the Colombian Conservative Party. Today the political landscape is shared by many political parties, none commanding majority support.
Economy

 The city is notable for bilateral trade and manufacturing. Its location on the border between Colombia and Venezuela has made possible strong links with the Venezuelan city of San Cristóbal, Táchira.
Its Free Zone is the most active of all those in the country and one of the most active in all Latin America, largely due to Venezuela being Colombia's second largest trade partner.
The most developed Industry (economics), industries are dairy, construction, textiles, shoes, and leather. The city is a top producer of cement and its clay and stoneware industry has the best reputation nationally for its high quality. The mining of coal also plays an important role in the local economy. The University Francisco de Paula Santander in Cucuta, the National University of Colombia in Bogotá, and the Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia in Tunja are the only ones in the country that provide for the career of Mining Engineering.
The Colombian peso, peso is the official and sole legal tender currency in the city. Owing to its proximity to
The city is notable for bilateral trade and manufacturing. Its location on the border between Colombia and Venezuela has made possible strong links with the Venezuelan city of San Cristóbal, Táchira.
Its Free Zone is the most active of all those in the country and one of the most active in all Latin America, largely due to Venezuela being Colombia's second largest trade partner.
The most developed Industry (economics), industries are dairy, construction, textiles, shoes, and leather. The city is a top producer of cement and its clay and stoneware industry has the best reputation nationally for its high quality. The mining of coal also plays an important role in the local economy. The University Francisco de Paula Santander in Cucuta, the National University of Colombia in Bogotá, and the Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia in Tunja are the only ones in the country that provide for the career of Mining Engineering.
The Colombian peso, peso is the official and sole legal tender currency in the city. Owing to its proximity to Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
, the Venezuelan bolívar, bolívar was accepted by the vast majority of commercial establishments until the rapid devaluation of the Venezuelan currency began after the Crisis in Venezuela, 2013 recession.
US–Colombia Free Trade Agreement, implications for Cúcuta
Colombia signed a Free trade area, Free Trade Agreement with the United States against opposition by Venezuela. Despite this opposition, industries from Venezuela are constructing their infrastructure in Cúcuta to export their products to the United States, registering their products as if they were Colombian, a strategy that allows them to export without paying certain tariffs. For that reason, Cúcuta is expected to become an industrial city. Colombian law provides tax exemptions for Venezuelan imports through the ''Zona Franca'', which, coupled with the motorway links between Cúcuta and Maracaibo, increases the possibility of exports from Maracaibo into Colombia.Telecommunications
The city's telecommunications services include payphones, WiMAX wireless networks, and mobile phone networks (GSM, CDMA, and Digital AMPS, TDMA). Telecom Colombia offers the services of local, national, and international telephone and broadband ADSL Internet. There are three mobile telephone operators: Comcel Colombia, Comcel, Movistar, and Tigo.Transport
For travel outside the city, there is a bus station called "Terminal de Transportes" (to be replaced by a new one), the Camilo Daza International Airport (Colombia) and the San Antonio Airport (Venezuela). Eighty years ago the city had the "Railroad of Cúcuta", which connected with Venezuela. The main forms of public transportation are the bus (or Bus, collective) and taxicabs. In addition, National Planning has a project to build a mass transit system, under the name "Metrobus" (Cucuta). The highway toBucaramanga
Bucaramanga () is the capital and largest city of the department of Santander, Colombia. Bucaramanga has the fifth-largest economy by GDP in Colombia, has the lowest unemployment rate and has the ninth-largest population in the country, with ...
(renovated in January 2007) connects Cúcuta with Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the largest ...
, Medellín (Colombia), Medellín, and Santiago de Cali, Cali. The highway to Ocaña, Colombia, Ocaña connects the city with Barranquilla, Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena, and Santa Marta, and the highway to San Cristóbal connects it with Caracas
Caracas (, ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the ...
.
Bridges
The city has many bridges: * Richmond-San Rafael Bridge, San Rafael Bridge – the official name is "Benito Hernández Bustos". * Francisco de Paula Andrade Troconis Bridge – the prolongation of Av. 0, connecting the city with the municipality of Los Patios. * Elías M. Soto Bridge – rebuilt and extended to 6 rails. * Louis IX of France, San Luís Bridge – imported from England. * Rafael García Herreros Bridge – part of the East Anillo Vial. Six overpasses are under construction.Health
 Law 100 of 1993 is the law governing Health in Colombia, which is regulated by the Ministry of Social Protection. In Cucuta and
Law 100 of 1993 is the law governing Health in Colombia, which is regulated by the Ministry of Social Protection. In Cucuta and North Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Venezu ...
, health is administered by the Municipal Institute of Health (IMSALUD) and the local Department of Health, respectively. Entities such as the Colombian Red Cross, Civil Defense, Colombian Civil Defense (for emergencies, calamities, and natural disasters) and the Colombian Family Welfare Institute (ICBF), are part of the social protection system.
The city has the following public health institutions (or State Social Enterprises, ESE): ESE Erasmus University Hospital Meoz, the ESE Francisco de Paula Santander (Clinical Social Security), the ESE CardioNeuroPulmonar Rehabilitation Center, the ESE Hospital of Los Patios, and ESE Hospital of Villa del Rosario. Private health centers include: San Jose Clinic, the North Clinic, Clinica Santa Ana, Lions Clinic, the Samaritan Clinic, and Profamilia (sexual and reproductive health).
The aforementioned entities are part of the network of institutions providing services to health attached to the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Municipal Health Department. The Erasmus Hospital Meoz holds fourth-level scale and specializes in performing highly complex surgeries, such as Organ transplant, transplants and reimplantations. Additionally, it offers healthcare services distributed in the different districts of the city, which deal with varying degrees of complexity. The city has a large number of health-promoting entities (SPE's), such as Colsanitas, SaludCoop, Cafesalud, etc.
Education
Basic education and high school education are in Colombian "Calendar A" for schools (from February to November).Schools
* Colegio María Reina * Colegio Sagrados Corazones * Colegio El Carmen Teresiano * Colegio Santa Teresa * Colegio Calasanz * Colegio Sagrado Corazón de Jesús * Colegio Metropolitano de San José * Colegio Instituto Técnico Nacional de Comercio * Colegio Salesiano * Colegio Hispanoamericano * Colegio La Salle * Colegio Comfaoriente * Colegio Santo Angel de la Guarda * Colegio Acoandes * Colegio Gimnasio Los Almendros * Colegio Gimnasio Domingo Savio * Colegio Cardenal Sancha * Colegio Instituto Tecnico Mercedes Abrego * Instituto Bilingüe Londres * Colegio Cooperativo San José de Peralta * Colegio Andino Bilingüe * Colegio Integrado Juan Atalaya * Colegio INEM José Eusebio Caro * Colegio Municipal * Colegio María Concepción Loperena CASD * Colegio San José de Cúcuta * Colegio Ebenezer * Colegio Comfanorte * Colegio Gimnasio El Bosque * Colegio Gremios UnidosUniversities
State Universities * Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander * Universidad de Pamplona * SENA * Unidades Tecnológicas de Santander Private Universities * FESC University, Universidad FESC * Universidad Libre de Colombia * Universidad de Santander * Universidad Antonio Nariño * Universidad Simón BolivarSports
The sport that gather people the most is Association football, football, although basketball, volleyball, and Inline speed skating are also popular. The Cúcuta Deportivo -recently relegated to the Categoría Primera A, First Division- is the main professional team of the city, and play their local matches at the Estadio General Santander, General Santander stadium. The team won their first Categoría Primera A, Championship in the 2006 season and had a well-remembered participation in the 2007 Copa Libertadores, when they reached the semi-final and lose to the multi-champion Boca Juniors; since that year, only one other Colombian team has reached the semi-final of the prestigious competition (Atletico Nacional from Medellin in 2016). Other professional teams located in the city are the Norte de Santander (Basketball team), and futsal team Cucuta Niza; Both squads play local at the Coliseo Toto Hernández. The city hosted the XIX National Games of Colombia in 2012, which helped to modernize many of the sport venues like the Coliseo Toto Hernández. The Colombian Football Federation announced that Cúcuta will be one of the venue cities to host the 2016 FIFA Futsal World Cup, an event that is celebrated every four years.Recent development
The city has recently undergone development at an historically unprecedented rate. This has included construction of six overpasses, a convention center, a new Bus station, bus terminal, a new Integrated Massive Transport network, Transportation System called "Metrobus", modernization of state-owned schools, renewal of downtown, and doubling the capacity of the General Santander Stadium. New industries are expected to come from Venezuela, which will place their factories in Cúcuta to export through the Colombia Trade Promotion Agreement between Colombia and the United States.Distances to other cities
Cities of Colombia *Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
–
* Ocaña, Norte de Santander, Ocaña –
* Bucaramanga
Bucaramanga () is the capital and largest city of the department of Santander, Colombia. Bucaramanga has the fifth-largest economy by GDP in Colombia, has the lowest unemployment rate and has the ninth-largest population in the country, with ...
–
* Barrancabermeja –
* Tunja –
* Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the largest ...
–
* Manizales –
* Armenia, Colombia, Armenia –
* Pereira, Colombia, Pereira –
* Medellín (Colombia), Medellín –
* Montería –
* Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena –
* Barranquilla –
* Santiago de Cali, Cali –
Cities of Venezuela
* San Cristóbal –
* Mérida (Venezuela), Mérida –
* Maracaibo –
* Barinas, Barinas, Barinas –
* Acarigua –
* Valencia, Carabobo, Valencia –
* Caracas
Caracas (, ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the ...
–
Landscape
Monuments
The main monuments in the city are: * The monument of the Battle of Cúcuta * The monument ofJuana Rangel de Cuellar
Juana is a Spanish female first name. It is the feminine form of Juan (English John), and thus corresponds to the English names Jane, Janet, Jean, Joan, and Joanna. Juanita is a common variant. The name Juana may refer to:
People
* Jua ...
, the founder of Cúcuta
* The monument of Camilo Daza, at the Camilo Daza International Airport.
Parks
The main parks in the city are: *Santander Park
Santander Park ( es, Parque Santander) is located in Cúcuta, Colombia. The park is bordered by 5th and 6th Avenue and 10th and 11th Street and was previously the location of the Grand Square of San José de Guasimales, a site hosting principal ev ...
(in Spanish, ''Parque Santander''), the main park of the city located in front of the city hall.
* Colón Park (in Spanish, ''Parque Colón''), constructed in honor of Cristopher Columbus (in Spanish, ''Cristobal Colón'').
* Simón Bolivar Park (in Spanish, ''Parque Simón Bolivar''), constructed in honor of Simón Bolivar and donated by the Consulate of Venezuela in Cúcuta.
Greenery
Cúcuta has more green zones than many cities in Colombia. Some consider the city an ''urban lung'', due to its greenery and lack of pollution. Cucuteños, and the legion of foreigners who reconstructed the city after the 1875 earthquake, led by engineer Francisco de Paula Andrade Troconis, led to the development of greenery in the city. The first planted trees were clemones. Soon they were replaced by acacias, peracos, and almond trees that adorned the parks and roadsides. An example of this city design is the Avenue of the Lights (based on oití, ficus, and cují), that forms a natural tunnel admired in the rest of the country and by tourists. Arecaceae, Palm trees are common in places such as Santander Park, Great Colombian Park, the Bank of the Republic, and the Department Hall ofNorte de Santander
North Santander (Spanish: Norte de Santander) () is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.
North Santander is bordered by Ven ...
.
Heritage sites
Cúcuta has several important cultural sites such as the birthplace of Eduardo Cote Lamus, an influential person in the politics of Norte de Santander and the country during the first half of the twentieth century, this building was built in 1877. Another historical site of Cúcuta is the Casa Torre de Reloj, which served at the beginning as the Compañía Eléctrica del Norte (), and later as the House of Culture in addition to office of the Department's Secretary of Culture. Another historic site is the Palacio de la Cúpula Chata, which is a building dating from 1919, part of the dome was shipped from New York City in June 1915. In 1989, part of the building was damaged by a fire, so in 1990, the project of reconstruction of the building was started based on the project of Maria Teresa Vela Viccini.International Relations
Twin towns – sister cities
* Zaragoza, Spain
References
External links
City Hall of Cúcuta
Gobernación de Norte de Santander
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cucuta Cúcuta, Municipalities of the Norte de Santander Department Colombia–Venezuela border crossings Capitals of Colombian departments