Człuchów on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Człuchów (, ''Człochòwo'', or ''Człëchòwò''; ) is a town in the region of
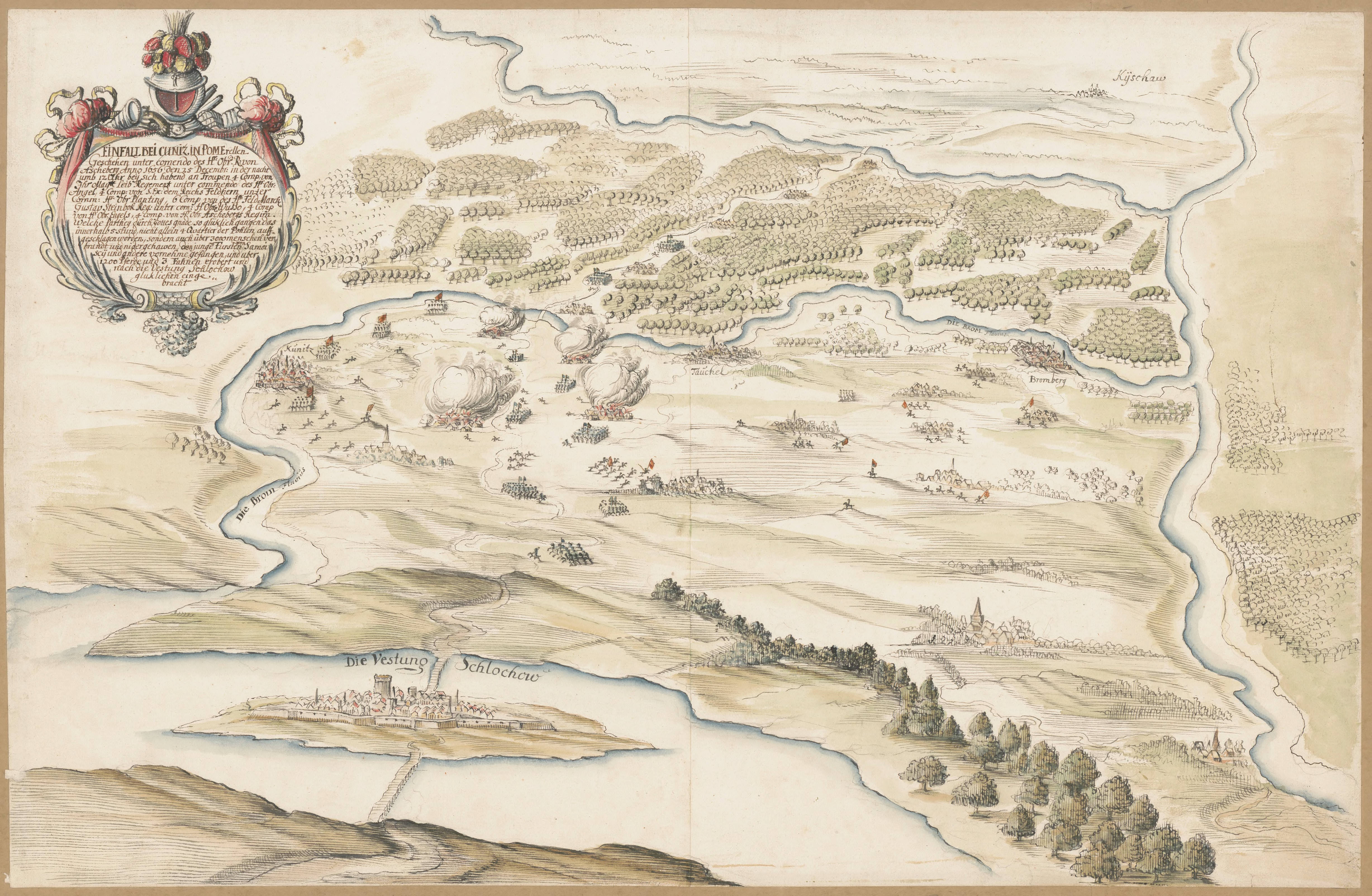 From 1655-57 during the Swedish invasion of Poland, known as the
From 1655-57 during the Swedish invasion of Poland, known as the
 The
The
City website
Gmina of Człuchów
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Pomeranian Voivodeship Człuchów County Populated lakeshore places in Poland
Gdańsk Pomerania
Gdańsk Pomerania (; ; ) is the main geographical region within Pomerelia (also known as Vistula Pomerania, Eastern Pomerania, and previously Polish Pomerania) in northern Poland, covering the bulk of Pomeranian Voivodeship. In contrast to ''Pome ...
, northern Poland, with 13,350 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is the capital of Człuchów County
__NOTOC__
Człuchów County (, ) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Pomeranian Voivodeship, northern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1 ...
in the Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship ( ; ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
The voivodeship was established on January 1, 1999, out of the former voivodeships of Gdańsk Voivo ...
.
Location
Człuchów lies in a forested area in the southwest of the Pomeranian Voivodeship, at the intersection of Highway 25 fromKoszalin
Koszalin (; ; , ) is a city in northwestern Poland, in Western Pomerania. It is located south of the Baltic Sea coast, and intersected by the river Dzierżęcinka. Koszalin is also a county-status city and capital of Koszalin County of West Pomera ...
to Bydgoszcz
Bydgoszcz is a city in northern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Kuyavia. Straddling the confluence of the Vistula River and its bank (geography), left-bank tributary, the Brda (river), Brda, the strategic location of Byd ...
and Highway 22 from Gorzów Wielkopolski
Gorzów Wielkopolski (), often abbreviated to Gorzów Wlkp. or simply Gorzów (formerly ), is a city in Geography of Poland, western Poland, located on the Warta, Warta River. It is one of the two principal cities and seats of the Lubusz Voivodes ...
to Elbląg
Elbląg (; ; ) is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 127,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg County.
Elbląg is one of the ol ...
. The nearest city is Chojnice
Chojnice (; or ; or ) is a town in northern Poland with 38,789 inhabitants, as of June 2023, near the Tuchola Forest. It is the capital of the Chojnice County in the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
Founded in , Chojnice is a former royal city of Poland ...
, to the east. There are four lakes within the town limits: Urzędowe, Miejskie, Miejskie Małe, Rychnowskie.
History
Human settlement in Człuchów dates back to prehistoric times. Several traces of the Lusatian and Pomeranian cultures were discovered duringarchaeological excavation
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be condu ...
s within the town limits. The territory became part of the emerging Polish state in the 10th century under its first historic ruler Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was Duchy of Poland (966–1025), Duke of Poland from 960 until his death in 992 and the founder of the first unified History of Poland, Polish state, the Civitas Schinesghe. A member of the Piast dynasty, he was t ...
. By the beginning of the 13th century Człuchów was a small settlement located at the intersection of two trade routes. In 1312 the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
purchased the settlement for 250 silver marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks
A collective trademark, collective trade mark, or collective mark is a trademark owned by an organization (such ...
from Nicholas of Poniec
Poniec is a town in western Poland, situated in the southern part of the Greater Poland Voivodeship. The town has 2912 inhabitants (as of 2023). It is the capital of Gmina Poniec (commune) in Gostyń County.
History
Poniec dates back to the 10th ...
, a son of the voivode
Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Mid ...
of Kalisz
Kalisz () is a city in central Poland, and the second-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship, with 97,905 residents (December 2021). It is the capital city of the Kalisz Region. Situated on the Prosna river in the southeastern part of Gr ...
. The Order began constructing a fortress
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from L ...
known as Schlochau on a hill east of the settlement; the fortress, the Order's second-largest after Marienburg (Malbork
Malbork (German: ''Marienburg'') is a town in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. It is the seat of Malbork County and has a population of 36,709 people as of 2024. The town is located on the Nogat river, in the historical region of Pomerelia.
Fo ...
), was completed in 1367. By 1323 it was used as a komtur
Commander (; ; ; ; ), or Knight Commander, is a title of honor prevalent in chivalric orders and fraternal orders.
The title of Commander occurred in the medieval military orders, such as the Knights Hospitaller, for a member senior to a Knight. ...
ei (bailiwick
A bailiwick () is usually the area of jurisdiction of a bailiff, and once also applied to territories in which a privately appointed bailiff exercised the sheriff's functions under a royal or imperial writ.
In English, the original French combi ...
) by the crusaders and consisted of three support buildings and the main castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
. The fortress was so well-developed that Grand Master Heinrich von Dusemer granted the town Kulm law
Kulm law, Culm law or Chełmno Law (; ; ) was a legal constitution for a municipal form of government used in several Central European cities in the Middle Ages and early modern period.
It was initiated on 28 December 1233 in the Monastic State o ...
in 1348. In 1454, King Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (Casimir Andrew Jagiellon; ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447 until his death in 1492. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers; under ...
reincorporated the town to the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
, and then the Teutonic Knights renounced any claims in the peace treaty
A peace treaty is an treaty, agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually country, countries or governments, which formally ends a declaration of war, state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an ag ...
of 1466. Człuchów was a county seat in the Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship ( ; ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
The voivodeship was established on January 1, 1999, out of the former voivodeships of Gdańsk Voivo ...
. The seat of local starost
Starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''старост/а'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', ) is a community elder in some Slavic lands.
The Slavic root of "starost" translates as "senior". Since the Middle Ages, it has designated an official in a leadersh ...
s was located in the castle. Many Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
immigrated to the town afterward, creating an enclosed Jewish quarter in the north of the town.
Encouraged by the Polish starosta
Starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''старост/а'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', ) is a community elder in some Slavic lands.
The Slavic root of "starost" translates as "senior". Since the Middle Ages, it has designated an official in a leadersh ...
Latal and the town's German-speaking populace, Człuchów converted to Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
in 1550 during the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
. During the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
and encouraged by the Polish government, the town's main church was reclaimed by Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
in 1609. By the end of the 16th century Człuchów had 45 houses. In the mid-17th century starost Jakub Wejher renovated the castle and founded the Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
Saint James church.
 From 1655-57 during the Swedish invasion of Poland, known as the
From 1655-57 during the Swedish invasion of Poland, known as the Deluge
A deluge is a large downpour of rain, often a flood.
The Deluge refers to the flood narrative in the biblical book of Genesis.
Deluge or Le Déluge may also refer to:
History
*Deluge (history), the Swedish and Russian invasion of the Polish-L ...
, the previously impregnable castle was captured by the Kingdom of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country by both area ...
and the town was heavily damaged.
In 1770 Człuchów had 135 houses. The town was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
in the First Partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that eventually ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The growth of power in the Russian Empire threatened the Kingdom of Prussia an ...
in 1772 and was referred to as "Schlochau", while fires in 1786 and 1793 destroyed numerous houses. King Frederick William II of Prussia
Frederick William II (; 25 September 1744 – 16 November 1797) was King of Prussia from 1786 until his death in 1797. He was also the prince-elector of Brandenburg and (through the Orange-Nassau inheritance of his grandfather) sovereign princ ...
allowed the usage of bricks from the castle during the rebuilding of the town, leaving the castle only with its keep
A keep is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residen ...
. After the administrative reorganization of Prussia in 1818, Schlochau became the seat of Landkreis Schlochau in the Regierungsbezirk Marienwerder in the Province of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and from 1878 to 1919. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonweal ...
. Between 1826-28 the town's Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
community built its chapel, which included the castle's keep as a church tower
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian comm ...
. The town began to grow economically after the completion through Schlochau of ''Reichsstraße 1'', a roadway from Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
to Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
. The town also received a boost to its development after the opening of a railway from Neustettin (Szczecinek
Szczecinek (; ) is a historic city in Middle Pomerania, northwestern Poland, capital of Szczecinek County in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, with a population of more than 40,000 (2011). The town's total area is .
The turbulent history of Szcze ...
) to Konitz (Chojnice
Chojnice (; or ; or ) is a town in northern Poland with 38,789 inhabitants, as of June 2023, near the Tuchola Forest. It is the capital of the Chojnice County in the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
Founded in , Chojnice is a former royal city of Poland ...
) in 1878. Schlochau's main street was illuminated by 1844 and businesses began to be established near the easterly-located train station. The town's hospital was established by 1865 and the district's (savings bank
A savings bank is a financial institution that is not run on a profit-maximizing basis, and whose original or primary purpose is collecting deposits on savings accounts that are invested on a low-risk basis and receive interest. Savings banks ha ...
) opened in 1871, the year Schlochau became part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
.
Resulting from the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
in 1919 following World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Schlochau became part of the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
border zone with the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
, whose began east of the town. This negatively impacted the town's trade and economy as it was cut off from much of its hinterland (East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and from 1878 to 1919. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonweal ...
), although Schlochau's population grew through immigrants from Pomeranian lands restored to Poland. In the 1920s new outlying settlements began to develop from the influx of immigrants, and the town developed a sports center and a district museum. By 1937 Schlochau had a mill
Mill may refer to:
Science and technology
* Factory
* Mill (grinding)
* Milling (machining)
* Millwork
* Paper mill
* Steel mill, a factory for the manufacture of steel
* Sugarcane mill
* Textile mill
* List of types of mill
* Mill, the arithmetic ...
, a sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes ...
, and a population of 6,029 by 1939.
After 1922 the town belonged to the Province of Posen-West Prussia, but with that province's dissolution in 1938 Schlochau became part of Province of Pomerania. In that year the Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
s built a center for 600 members of the Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth ( , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth wing of the German Nazi Party. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. From 1936 until 1945, it was th ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the Polish resistance conducted espionage of German activity in the town. The Germans operated a forced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, or violence, including death or other forms of ...
subcamp of the Stalag II-B
Stalag II-B was a German World War II prisoner-of-war camp situated west of the town of Hammerstein, Pomerania (now Czarne, Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland) on the north side of the railway line. It housed Polish, French, Belgian, Serbian, Du ...
prisoner-of-war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured as Prisoner of war, prisoners of war by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, inte ...
for over 300 Allied POWs. As the Eastern Front grew closer near the end of the war, the town's authorities began evacuating Schlochau. The Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
reached the district's borders by the end of January 1945, but German resistance prevented them from capturing Schlochau until 17 February 1945, with the town 60% destroyed in the process. Its remaining German-speaking population was expelled to Germany after the war in accordance with the Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement () was the agreement among three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe that was signed on 1 August 1945 and published the following day. A ...
as the town became again part of Poland under its historic Polish name ''Człuchów''.
From 1975 to 1998 it was administratively located in the Słupsk Voivodeship
Słupsk Voivodeship () was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland from 1975 to 1998, previously part of Szczecin Voivodeship (1945–50) and Koszalin Voivodeship (1950–75), superseded (since 1999) by Pomeranian Voiv ...
.
Gmina and population
 The
The gmina
The gmina (Polish: , plural ''gminy'' ) is the basic unit of the administrative division of Poland, similar to a municipality. , there were 2,479 gminy throughout the country, encompassing over 43,000 villages. 940 gminy include cities and tow ...
Człuchów is and contains the following villages besides the town:
Notable people
* Ulrich von Jungingen (c.1360–1410) the 26th Grand Master of theTeutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
, 1407-1410
* Friedrich Kasiski
Major Friedrich Wilhelm Kasiski (29 November 1805 – 22 May 1881) was a German infantry officer, cryptographer and archeologist. Kasiski was born in Schlochau, Kingdom of Prussia (now Człuchów, Poland).
Military service
Kasiski enlisted in E ...
(1805–1881) a German infantry officer, cryptographer and archeologist
* Martin Grase (1891–1963) a German general during World War II
* Joachim Wandel (1914–1942) a Luftwaffe ace
* Karl Nitz (born 1932) a German judoka
* Archbishop Eugeniusz Popowicz (born 1961) a Polish Ukrainian Greek Catholic hierarch
* Ted Pietka (born 1967) a Polish businessman
* Ariel Jakubowski (born 1977) a Polish footballer, over 300 pro games
* Marcin Kobierski (born 1977) a Polish sprint canoer, competed in the 1996 Summer Olympics
The 1996 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXVI Olympiad, also known as Atlanta 1996 and commonly referred to as the Centennial Olympic Games) were an international multi-sport event held from July 19 to August 4, 1996, in Atlanta, ...
* Marta Żmuda Trzebiatowska
Marta Żmuda Trzebiatowska (born 26 July 1984, in Człuchów) is a Polish film, television and theater actress.
She is best known for playing the role of Marta Orkisz in Polish TV series ''Teraz albo nigdy!'' and Monika Miller in ''Julia (Polish ...
(born 1984) a Polish film, television and theater actress.
* Paweł Kaczmarek (born 1995) a Polish sprint kayaker, competed at the 2016 Summer Olympics
The 2016 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXXI Olympiad () and officially branded as Rio 2016, were an international multi-sport event held from 5 to 21 August 2016 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, with preliminary events i ...
International relations
Człuchów is twinned with:See also
* Człuchów (PKP station)References
External links
City website
Gmina of Człuchów
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Pomeranian Voivodeship Człuchów County Populated lakeshore places in Poland