Cython on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cython () is a superset of the programming language Python, which allows developers to write Python code (with optional, C-inspired syntax extensions) that yields performance comparable to that of C.
Cython is a
# The argument will be converted to int or raise a TypeError.
def primes(int kmax):
# These variables are declared with C types.
cdef int n, k, i
# Another C type
cdef int p 000
# A Python type
result = []
if kmax > 1000:
kmax = 1000
k = 0
n = 2
while k < kmax:
i = 0
while i < k and n % p[i] != 0:
i = i + 1
if i k:
p = n
k = k + 1
result.append(n)
n = n + 1
return result
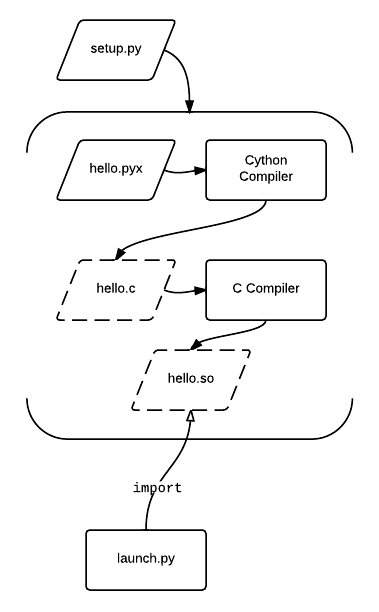 A sample hello world program for Cython is more complex than in most languages because it interfaces with the Python C API and
A sample hello world program for Cython is more complex than in most languages because it interfaces with the Python C API and
# hello.pyx - Python module, this code will be translated to C by Cython.
def say_hello():
print("Hello World!")
# launch.py - Python stub loader, loads the module that was made by Cython.
# This code is always interpreted, like normal Python.
# It is not compiled to C.
import hello
hello.say_hello()
# setup.py - unnecessary if not redistributing the code, see below
from setuptools import setup
from Cython.Build import cythonize
setup(name = "Hello world app",
ext_modules = cythonize("*.pyx"))
These commands build and launch the program:
$ python setup.py build_ext --inplace
$ python launch.py
In %load_ext Cython
In %%cython
...: def f(n):
...: a = 0
...: for i in range(n):
...: a += i
...: return a
...:
...: cpdef g(int n):
...: cdef long a = 0
...: cdef int i
...: for i in range(n):
...: a += i
...: return a
...:
In %timeit f(1000000)
10 loops, best of 3: 26.5 ms per loop
In %timeit g(1000000)
1000 loops, best of 3: 279 µs per loop
which gives a 95 times improvement over the pure-python version. More details on the subject in the official quickstart page.
compiled language
Compiled language categorizes a programming language as used with a compiler and generally implies not used with an interpreter. But, since any language can theoretically be compiled or interpreted the term lacks clarity. In practice, for some lan ...
that is typically used to generate CPython
CPython is the reference implementation of the Python programming language. Written in C and Python, CPython is the default and most widely used implementation of the Python language.
CPython can be defined as both an interpreter and a comp ...
extension modules. Annotated Python-like code is compiled to C and then automatically wrapped in interface code, producing extension modules that can be loaded and used by regular Python code using the import statement, but with significantly less computational overhead at run time. Cython also facilitates wrapping independent C or C++ code into python-importable modules.
Cython is written in Python and C and works on Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
, macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
, and Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, producing C source files compatible with CPython 2.6, 2.7, and 3.3 and later versions. The Cython source code that Cython compiles (to C) can use both Python 2 and Python 3 syntax, defaulting to Python 2 syntax in Cython 0.x and Python 3 syntax in Cython 3.x. The default can be overridden (e.g. in source code comment) to Python 3 (or 2) syntax. Since Python 3 syntax has changed in recent versions, Cython may not be up to date with the latest additions. Cython has "native support for most of the C++ language" and "compiles almost all existing Python code".
Cython 3.0.0 was released on 17 July 2023.
Design
Cython works by producing a standard Python module. However, the behavior differs from standard Python in that the module code, originally written in Python, is translated into C. While the resulting code is fast, it makes many calls into the CPython interpreter and CPython standard libraries to perform actual work. Choosing this arrangement saved considerably on Cython's development time, but modules have a dependency on the Python interpreter and standard library. Although most of the code is C-based, a small stub loader written in interpreted Python is usually required (unless the goal is to create a loader written entirely in C, which may involve work with the undocumented internals of CPython). However, this is not a major problem due to the presence of the Python interpreter. Cython has a foreign function interface for invoking C/ C++ routines and the ability to declare thestatic type
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a ''type'' (for example, integer, floating point, string) to every '' term'' (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Usu ...
of subroutine parameters and results, local variables, and class attributes.
A Cython program that implements the same algorithm as a corresponding Python program may consume fewer computing resources such as core memory and processing cycles due to differences between the CPython and Cython execution models. A basic Python program is loaded and executed by the CPython virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
, so both the runtime and the program itself consume computing resources. A Cython program is compiled to C code, which is further compiled to machine code, so the virtual machine is used only briefly when the program is loaded.
Cython employs:
* Optimistic optimizations
* Type inference
Type inference, sometimes called type reconstruction, refers to the automatic detection of the type of an expression in a formal language. These include programming languages and mathematical type systems, but also natural languages in some bran ...
(optional)
* Low overhead in control structures
* Low function call overhead
Performance depends both on what C code is generated by Cython and how that code is compiled by the C compiler.
History
Cython is a derivative of the Pyrex language, but it supports more features and optimizations than Pyrex. Cython was forked from Pyrex in 2007 by developers of the Sage computer algebra package, because they were unhappy with Pyrex's limitations and could not get patches accepted by Pyrex's maintainer Greg Ewing, who envisioned a much smaller scope for his tool than the Sage developers had in mind. They then forked Pyrex as SageX. When they found people were downloading Sage just to get SageX, and developers of other packages (including Stefan Behnel, who maintains theXML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
library ) were also maintaining forks of Pyrex, SageX was split off the Sage project and merged with .pyx extension. At its most basic, Cython code looks exactly like Python code. However, whereas standard Python is dynamically typed
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a ''type'' (for example, integer, floating point, string) to every '' term'' (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Usua ...
, in Cython, types can optionally be provided, allowing for improved performance, allowing loops to be converted into C loops where possible. For example:
Example
 A sample hello world program for Cython is more complex than in most languages because it interfaces with the Python C API and
A sample hello world program for Cython is more complex than in most languages because it interfaces with the Python C API and setuptools or other PEP517-compliant extension building facilities. At least three files are required for a basic project:
* A setup.py file to invoke the setuptools build process that generates the extension module
* A main python program to load the extension module
* Cython source file(s)
The following code listings demonstrate the build and launch process:
Using in IPython/Jupyter notebook
A more straightforward way to start with Cython is through command-line IPython (or through in-browser python console called Jupyternotebook
A notebook (also known as a notepad, writing pad, drawing pad, or legal pad) is a book or stack of paper pages that are often ruled and used for purposes such as note-taking, journaling or other writing, drawing, or scrapbooking and more.
...
):
Uses
Cython is particularly popular among scientific users of Python, where it has "the perfect audience" according to Python creator Guido van Rossum. Of particular note: * Thefree software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribut ...
SageMath computer algebra system depends on Cython, both for performance and to interface with other libraries.
* Significant parts of the scientific computing libraries SciPy, pandas and scikit-learn
scikit-learn (formerly scikits.learn and also known as sklearn) is a free and open-source machine learning library for the Python programming language.
It features various classification, regression and clustering algorithms including support ...
are written in Cython.
* Some high-traffic websites such as Quora use Cython.
Cython's domain is not limited to just numerical computing. For example, the XML toolkit is written mostly in Cython, and like its predecessor Pyrex, Cython is used to provide Python bindings for many C and C++ libraries such as the messaging library ZeroMQ. Cython can also be used to develop parallel programs for multi-core processor
A multi-core processor (MCP) is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit (IC) with two or more separate central processing units (CPUs), called ''cores'' to emphasize their multiplicity (for example, ''dual-core'' or ''quad-core''). Ea ...
machines; this feature makes use of the OpenMP
OpenMP is an application programming interface (API) that supports multi-platform shared-memory multiprocessing programming in C, C++, and Fortran, on many platforms, instruction-set architectures and operating systems, including Solaris, ...
library.
See also
* PyPy * Numba * pybindReferences
External links
* * {{Python (programming language) Articles with example Python (programming language) code Python (programming language) Python (programming language) implementations Software using the Apache license Source-to-source compilers