Colt Manufacturing Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Colt's Manufacturing Company, LLC (CMC, formerly Colt's Patent Firearms Manufacturing Company) is an American firearms manufacturer, founded in 1855 by

166
and two U.S. patents in 1836, one on February 25 (later numbere
U.S. Patent 9430X
and another on August 29 (). That same year, he founded his first corporation for its manufacture, the Patent Arms Manufacturing Company of Paterson, New Jersey, Colt's Patent.. The first firearm manufactured at the new Paterson plant, however, was the
166–169
Production had ended at the New Jersey corporation by 1842. Colt made another attempt at revolver production in 1846 and submitted a prototype to the US government. During the
 The New York Daily Tribune denounced Colt and his company by asserting, “the traitors have found sympathizers among us, men base enough to sell arms when they knew they would be... in the hands of the deadly enemies of the Union... Col. Colt’s manufactory can turn probably 1,000 a week and has been doing so for the past four months for the South.”Hosley, William N. Colt : The Making of an American Legend. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, 1996. 96. This article even chided the Federal Government for not taking action against Colt: “Every man who makes arms should be watched, and if he will not work for a fair equivalent for the Government, his manufactory should be taken away from him.” Despite secession and growing tensions between the North and the South, “Colt’s sales to Alabama, Virginia, Georgia, and Mississippi in 1860 alone were at least $61,000 (today’s equivalent of about 3.35 million).” Until just days before the first shot at Fort Sumter, Colt received orders from various states, some participating in secession. In his memoir on Colt, written in 1866, Henry Barnard reported, “before the rebellion broke out, Col. Colt, foreseeing that his weapons must ere long be in double demand, had made all preparations to extend his factory.”
The
The New York Daily Tribune denounced Colt and his company by asserting, “the traitors have found sympathizers among us, men base enough to sell arms when they knew they would be... in the hands of the deadly enemies of the Union... Col. Colt’s manufactory can turn probably 1,000 a week and has been doing so for the past four months for the South.”Hosley, William N. Colt : The Making of an American Legend. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, 1996. 96. This article even chided the Federal Government for not taking action against Colt: “Every man who makes arms should be watched, and if he will not work for a fair equivalent for the Government, his manufactory should be taken away from him.” Despite secession and growing tensions between the North and the South, “Colt’s sales to Alabama, Virginia, Georgia, and Mississippi in 1860 alone were at least $61,000 (today’s equivalent of about 3.35 million).” Until just days before the first shot at Fort Sumter, Colt received orders from various states, some participating in secession. In his memoir on Colt, written in 1866, Henry Barnard reported, “before the rebellion broke out, Col. Colt, foreseeing that his weapons must ere long be in double demand, had made all preparations to extend his factory.”
The
 Colt continued to produce the .41 Short derringer after the acquisition, as an effort to help break into the metallic-cartridge gun market, but also introduced its own three Colt Derringer Models, all of them also chambered in a .41 rimfire unique cartridge. The last model to be in production, the third Colt Derringer, was not dropped until 1912. The first metallic cartridge breech-loading weapons sold by Colt's were those Derringers, in 1870, that were formerly conceived by the National Arms Company, but Colt's also started developing its own rear-loading guns and cartridges.
In 1871, Colt's introduced its first revolver models using rear-loaded metallic cartridges: the .41 caliber Colt House Revolver (also known as the Cloverleaf for its four-round cylinder configuration) and the .22 cal Colt Open Top Pocket Model Revolver. However, Colt's wanted a more powerful practical handgun loaded with metallic cartridges so the company put forward William Mason, who in 1871 began work on Colt's first .44 caliber metallic-cartridge revolver: the Colt Model 1871-72 Open Top. The company registered two patents for the Open Top, one in 1871, the other in 1872, the same patents mentioned in the markings of Colt Single Action Army revolvers, a nowadays legendary and long produced model, improved and based on the Open Top. Production of the Open Top started in 1872 and stopped in 1873 when the Single Action Army model started to be delivered to the US Army. However, the Open Top was already a completely new design. The parts, for example, would not interchange with the older percussion pistols. Mason moved the rear sight to the rear of the barrel as opposed to the hammer or the breechblock of the earlier efforts. The caliber was .44 rimfire and it was submitted to the
Colt continued to produce the .41 Short derringer after the acquisition, as an effort to help break into the metallic-cartridge gun market, but also introduced its own three Colt Derringer Models, all of them also chambered in a .41 rimfire unique cartridge. The last model to be in production, the third Colt Derringer, was not dropped until 1912. The first metallic cartridge breech-loading weapons sold by Colt's were those Derringers, in 1870, that were formerly conceived by the National Arms Company, but Colt's also started developing its own rear-loading guns and cartridges.
In 1871, Colt's introduced its first revolver models using rear-loaded metallic cartridges: the .41 caliber Colt House Revolver (also known as the Cloverleaf for its four-round cylinder configuration) and the .22 cal Colt Open Top Pocket Model Revolver. However, Colt's wanted a more powerful practical handgun loaded with metallic cartridges so the company put forward William Mason, who in 1871 began work on Colt's first .44 caliber metallic-cartridge revolver: the Colt Model 1871-72 Open Top. The company registered two patents for the Open Top, one in 1871, the other in 1872, the same patents mentioned in the markings of Colt Single Action Army revolvers, a nowadays legendary and long produced model, improved and based on the Open Top. Production of the Open Top started in 1872 and stopped in 1873 when the Single Action Army model started to be delivered to the US Army. However, the Open Top was already a completely new design. The parts, for example, would not interchange with the older percussion pistols. Mason moved the rear sight to the rear of the barrel as opposed to the hammer or the breechblock of the earlier efforts. The caliber was .44 rimfire and it was submitted to the  The revolver was chosen by the Army in 1872, with the first order, for 8000 revolvers, shipping in the summer of 1873: The
The revolver was chosen by the Army in 1872, with the first order, for 8000 revolvers, shipping in the summer of 1873: The  In the new market of metallic cartridge rear-loading pocket revolvers, Colt's not only introduced its three Derringer Models (as of 1870) or the Colt House and the Open Top Pocket (the last two as of 1871) but also introduced in 1873 a subsequent design called its "
In the new market of metallic cartridge rear-loading pocket revolvers, Colt's not only introduced its three Derringer Models (as of 1870) or the Colt House and the Open Top Pocket (the last two as of 1871) but also introduced in 1873 a subsequent design called its "

 During
During
 At the beginning of
At the beginning of
 The 1960s were boom years for Colt with the escalation of the
The 1960s were boom years for Colt with the escalation of the
 The 1990s brought the end of
The 1990s brought the end of
 Colt has entered in several US contracts with mixed results. For example, Colt had an entry in the
Colt has entered in several US contracts with mixed results. For example, Colt had an entry in the
 *
*

 * Colt M1900 (1900)
* Colt M1902 (1902)
*
* Colt M1900 (1900)
* Colt M1902 (1902)
*
 * Colt 1855 Revolving carbine/rifle
* Colt 1878 Hammer Shotgun
*
* Colt 1855 Revolving carbine/rifle
* Colt 1878 Hammer Shotgun
*
Colt official site
The Colt Revolver in the American West
Colt Automatic Pistols Home Page
* Jarvis-Robinson Family Papers. Yale Collection of Western Americana, Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library. * Most of the following are filed under 36-150 Huyshope Avenue, 17-170 Van Dyke Avenue, 49 Vredendale Avenue, Hartford, Hartford County, CT: * * * * * * * * * Firearm manufacturers of the United States Historic American Engineering Record in Connecticut Military in Connecticut 1836 establishments in Connecticut Manufacturing companies established in 1836 Companies that filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2015 {{coord, 41.7385145, -72.722959, display=title
Samuel Colt
Samuel Colt (; July 19, 1814 – January 10, 1862) was an American inventor, industrialist, and businessman who established Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Manufacturing Company and made the mass production of revolvers commercially viable.
Col ...
that has become a subsidiary of Czech holding company Colt CZ Group. It is the successor corporation to Colt's earlier firearms-making efforts, which started in 1836. Colt is known for the engineering, production, and marketing of firearms, especially during the century from 1850 through World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, when it dominated its industry and was a seminal influence on manufacturing technology. Colt's earliest designs played a major role in the popularization of the revolver
A revolver is a repeating handgun with at least one barrel and a revolving cylinder containing multiple chambers (each holding a single cartridge) for firing. Because most revolver models hold six cartridges before needing to be reloaded, ...
and the shift away from single-shot
In firearm designs, the term single-shot refers to guns that can hold only a single round of ammunition inside and thus must be reloaded manually after every shot. Compared to multi-shot repeating firearms ("repeaters"), single-shot designs have ...
pistols. Although Samuel Colt did not invent the revolver, his designs resulted in the first very successful model.
The most famous Colt products include the Colt Walker
The Colt Walker, sometimes known as the Walker Colt, is a single-action revolver with a revolving cylinder holding six charges of black powder behind six bullets (typically .44 caliber lead balls). It was designed in 1846 by American firearms in ...
, made in 1847 in the facilities of Eli Whitney Jr., the Colt Single Action Army
The Colt Single Action Army (also known as the SAA, Model P, Peacemaker, or M1873) is a Trigger (firearms)#Single-action, single-action revolver handgun. It was designed for the U.S. government service revolver trials of 1872 by Colt's Patent Fi ...
, the Colt Python
The Colt Python is a double action/single action revolver chambered for the .357 Magnum cartridge. It was first introduced in 1955 by the Colt's Manufacturing Company. Dougherty, Martin ''Small Arms: From the Civil War to the Present Day'', Ne ...
, and the Colt M1911
The Colt M1911 (also known as 1911, Colt 1911, Colt .45, or Colt Government in the case of Colt-produced models) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered primarily for the .45 ACP cartridge.
History
Early hist ...
pistol, which is the longest-standing military and law enforcement service handgun in the world and is still used. Though they did not develop it, for a long time Colt was also primarily responsible for all AR-15 and M16 rifle
The M16 (officially Rifle, Caliber 5.56 mm, M16) is a family of assault rifles adapted from the ArmaLite AR-15 rifle for the United States Armed Forces, United States military. The original M16 was a 5.56×45mm NATO, 5.56×45mm automatic ...
production, as well as many derivatives of those firearms. The most successful and famous of these are numerous M16 carbines, including the Colt Commando family, and the M4 carbine
The M4 carbine (officially Carbine, Caliber 5.56 mm, M4) is a 5.56×45mm NATO assault rifle developed in the United States during the 1980s. It is a shortened version of the M16A2 assault rifle. The M4 is extensively used by the US mi ...
.
In 2002, Colt Defense was split off from Colt's Manufacturing Company. Colt's Manufacturing Company served the civilian market, while Colt Defense served the law enforcement, military, and private security markets worldwide. The two companies remained in the same West Hartford, Connecticut
West Hartford is a town in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States, west of downtown Hartford, Connecticut, Hartford. The town is part of the Capitol Planning Region, Connecticut, Capitol Planning Region. The population was 64,083 at the 20 ...
location cross-licensing certain merchandise before reuniting in 2013. Following the loss of its M4 contract in 2013, the reunited Colt was briefly in Chapter 11
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code ( Title 11 of the United States Code) permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, w ...
bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the deb ...
, starting in 2015 and emerging in January 2016. The company was bought by Česká zbrojovka Group in 2021. In April 2022, Česká zbrojovka Group announced it had changed its name to Colt CZ Group.
History
19th century
1830s–1850s

Samuel Colt
Samuel Colt (; July 19, 1814 – January 10, 1862) was an American inventor, industrialist, and businessman who established Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Manufacturing Company and made the mass production of revolvers commercially viable.
Col ...
received a British patent on his improved design for a revolver in 1835,, p166
and two U.S. patents in 1836, one on February 25 (later numbere
U.S. Patent 9430X
and another on August 29 (). That same year, he founded his first corporation for its manufacture, the Patent Arms Manufacturing Company of Paterson, New Jersey, Colt's Patent.. The first firearm manufactured at the new Paterson plant, however, was the
Colt First Model Ring Lever rifle
The Colt first model ring lever rifle and Colt second model ring lever rifle are two early Caplock mechanism, caplock revolving rifles that were produced by the Colt's Manufacturing Company, Patent Arms Manufacturing Company between 1837 and 1841. ...
beginning in 1837. This was followed shortly thereafter in late 1837 by the introduction of the Colt Paterson
The Colt Paterson revolver was the first commercial repeating firearm employing a revolving cylinder with multiple chambers aligned with a single, stationary barrel. Its design was patented by Samuel Colt on February 25, 1836, in the United ...
. This corporation suffered quality problems in production. Making firearms with interchangeable parts
Interchangeable parts are parts (wikt:component#Noun, components) that are identical for practical purposes. They are made to specifications that ensure that they are so nearly identical that they will fit into any assembly of the same type. One ...
was still rather new (it had reached commercial viability only about a decade before), and it was not yet easy to replicate across different factories. Interchangeability was not complete in the Paterson works, and traditional gunsmithing techniques did not fill the gap entirely there. The Colt Paterson
The Colt Paterson revolver was the first commercial repeating firearm employing a revolving cylinder with multiple chambers aligned with a single, stationary barrel. Its design was patented by Samuel Colt on February 25, 1836, in the United ...
revolver found patchy success and failure; some worked well, while others had problems. The United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionar ...
and United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
reported quality problems with these earliest Colt revolvers., pp166–169
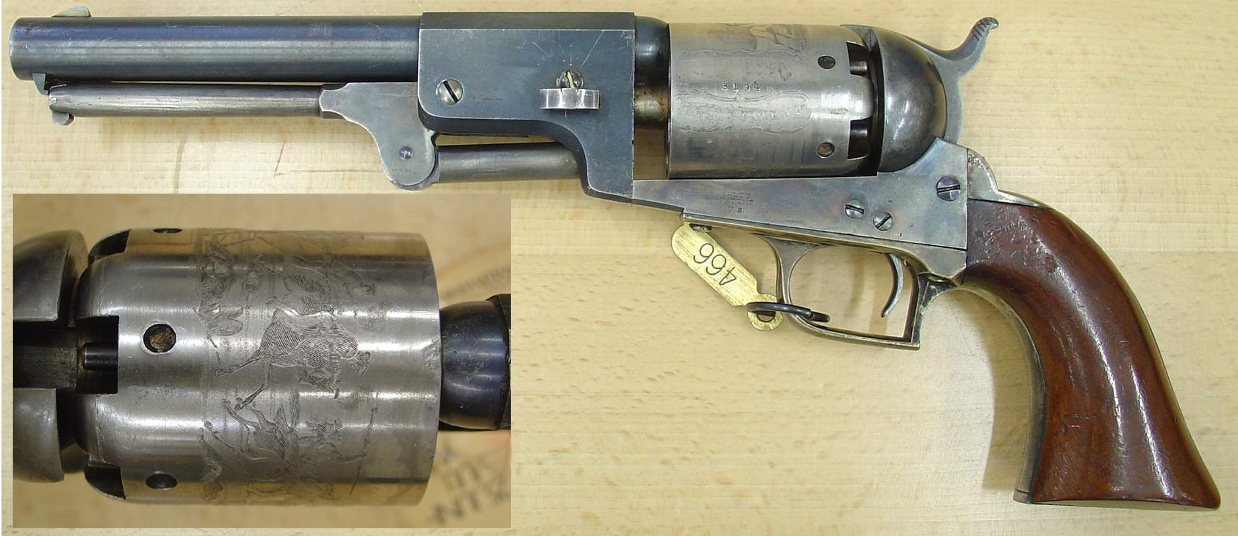
Production had ended at the New Jersey corporation by 1842. Colt made another attempt at revolver production in 1846 and submitted a prototype to the US government. During the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
(1846–1848), this prototype was seen by Captain Samuel Hamilton Walker who made some suggestions to Colt about making it in a larger caliber. Having no factory or machinery to produce the pistols, Samuel Colt collaborated with the Whitney armory of Whitneyville, Connecticut. This armory was run by the family of Eli Whitney
Eli Whitney Jr. (December 8, 1765January 8, 1825) was an American inventor, widely known for inventing the cotton gin in 1793, one of the key inventions of the Industrial Revolution that shaped the economy of the Antebellum South.
Whitney's ...
. Eli Whitney Jr (born 1820), the son of the cotton-gin-developer patriarch, was the head of the family armory and a successful arms maker and innovator of the era. Colt used a combination of renting the Whitney firm's facilities and subcontracting parts to the firm to continue his pursuit of revolver manufacture.
Colt's new revolvers found favor with Texan volunteers (the progenitors of later Texas Rangers cavalry groups), and they placed an order for 1,000 revolvers that became known as the Colt Walker
The Colt Walker, sometimes known as the Walker Colt, is a single-action revolver with a revolving cylinder holding six charges of black powder behind six bullets (typically .44 caliber lead balls). It was designed in 1846 by American firearms in ...
, ensuring Colt's continuance in manufacturing revolvers. In 1848, Colt was able to start again with a new business of his own, and 1855, he converted it into a corporation under the name of Colt's Patent Firearms Manufacturing Company in Hartford, Connecticut.
Colt purchased a large tract of land beside the Connecticut River
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges into Long Isl ...
, where he built his first factory in 1848, a larger factory called the Colt Armory
The Colt Armory is a historic factory complex for the manufacture of firearms, created by Samuel Colt. It is located in Hartford, Connecticut along the Connecticut River, and as of 2008 is part of the Coltsville Historic District, named a Natio ...
in 1855, a manor that he called Armsmear
Armsmear ("meadow of arms"), also known as the Samuel Colt Home, is a historic house located at 80 Wethersfield Avenue in Hartford, Connecticut. It was the family home of firearm manufacturer Samuel Colt. Armsmear was listed as a National Histo ...
in 1856, and employee tenement housing. He established a ten-hour day for employees, installed washing stations in the factory, mandated a one-hour lunch break, and built the Charter Oak Hall, a club where employees could enjoy games, newspapers, and discussion rooms. Colt ran his plant with a military-like discipline, he would fire workers for tardiness, sub-par work or even suggesting improvements to his designs.
In an attempt to attract skilled German workers to his plant, Colt built a village near the factory away from the tenements which he named Coltsville and modeled the homes after a village near Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
. In an effort to stem the flooding from the river he planted German osiers, a type of willow tree in a 2-mile long dike. He subsequently built a factory to manufacture wicker furniture made from these trees.
The 1850s were a decade of phenomenal success for the new Colt corporation. Colt was the first to widely commercialize the total use of interchangeable parts throughout a product. It was a leader in assembly line
An assembly line, often called ''progressive assembly'', is a manufacturing process where the unfinished product moves in a direct line from workstation to workstation, with parts added in sequence until the final product is completed. By mechan ...
practice. It was a major innovator and training ground in manufacturing technology in this decade (and several after).. Soon after establishing his Hartford factory, Colt set out to establish a factory in Europe and chose London, England. He organized a large display of his firearms at the Great Exhibition of 1851
Great may refer to:
Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
* Artel Great (bo ...
at Hyde Park, London
Hyde Park is a , historic Listed building#Heritage protection, Grade I-listed urban park in Westminster, Greater London. A Royal Parks of London, Royal Park, it is the largest of the parks and green spaces that form a chain from Kensington P ...
and ingratiated himself by presenting cased engraved Colt revolvers to such appropriate officials as Britain's Master General of the Ordnance. At one exhibit Colt disassembled ten guns and reassembled ten guns using different parts from different guns. As the world's leading proponent of mass production techniques, Colt went on to deliver a lecture on the subject to the Institution of Civil Engineers
The Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) is an independent professional association for civil engineers and a Charitable organization, charitable body in the United Kingdom. Based in London, ICE has over 92,000 members, of whom three-quarters ar ...
in London. The membership rewarded his efforts by awarding him the Telford Gold Medal.
Colt's presence in the British market caused years of acrimony and lawsuits among British arms makers, who doubted the validity of Colt's British patent and the desirability of the American system of manufacturing
The American system of manufacturing was a set of manufacturing methods that evolved in the 19th century. The two notable features were the extensive use of interchangeable parts and mechanization for production, which resulted in more efficient u ...
. It took many more years and a UK government commission before the point became universally accepted that such manufacture was possible and economical.. Colt opened his London plant on the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
at Pimlico and began production on January 1, 1853. Many English people saw Colt's advanced steam-powered machinery as proof of America's growing position as a leader in modern industrial production. On a tour of the factory, Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English novelist, journalist, short story writer and Social criticism, social critic. He created some of literature's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by ...
was so impressed with the facilities that he recorded his favorable comments of Colt's revolvers in an 1854 edition of ''Household Words
''Household Words'' was an English weekly magazine edited by Charles Dickens in the 1850s. It took its name from the line in Shakespeare's '' Henry V'': "Familiar in his mouth as household words."
History
During the planning stages, titles orig ...
''. Most significant, the Colt factory's machines mass-produced interchangeable parts that could be easily and cheaply put together on assembly lines using standardized patterns and gauges by unskilled labor as opposed to England's top gunmakers.
In 1854 the British Admiralty ordered 4,000 Navy Model Colt revolvers. In 1855 the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
placed an order for 5,000 of these revolvers for army issue. Despite a following order later in the year for an additional 9,000 revolvers, Colt failed to convince the British to adopt his revolver as the issue sidearm for the army. Colt began to realize that British sales were failing to meet his expectations. Unable to justify the London factory's expenses, Colt closed the London factory in 1856. Over the next few months his workmen crated and shipped the machinery and disassembled firearms back to America.
Though the U.S. was not directly involved in the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
(1854–1856), Colt's weapons were used by both sides. In 1855 Colt unveiled new state-of-the-art armories in the Hartford and London factories stocked with the latest machine tool
A machine tool is a machine for handling or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, Boring (manufacturing), boring, grinding (abrasive cutting), grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformations. Machine tools employ some s ...
s (some of which were of Colt's devising), many built by Francis A. Pratt and Amos Whitney, who would found the original Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of RTX Corporation (formerly Raytheon Technologies). Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation (especially ...
tool building firm a few years later. For example, the Lincoln miller debuted to industry at these armories.
Colt had set up libraries and educational programs within the plants for his employees. Colt's armories in Hartford were seminal training grounds for several generations of toolmakers and other machinist
A machinist is a tradesperson or trained professional who operates machine tools, and has the ability to set up tools such as milling machines, grinders, lathes, and drilling machines.
A competent machinist will generally have a strong mechan ...
s, who had great influence in other manufacturing efforts of the next half century. Prominent examples included F. Pratt and A. Whitney (as mentioned above); Henry Leland
Henry Martyn Leland (February 16, 1843 – March 26, 1932) was an American machinist, inventor, engineer, and automotive entrepreneur. He founded the two premier American luxury automotive marques, Cadillac and Lincoln.
Early years
Henry M. Le ...
(who would end up at Cadillac and Lincoln); Edward Bullard Sr of the Bullard firm; and, through Pratt & Whitney, Worcester R. Warner and Ambrose Swasey (of Warner & Swasey).
In 1852 an employee of Colt's, Rollin White, came up with the idea of having the revolver cylinder bored through to accept metallic cartridges. He took this idea to Colt who flatly rejected it and ended up firing White within a few years. Colt historian RL Wilson has described this as the major blunder of Sam Colt's professional life. Rollin White left Colt's in December 1854 and registered a patent on April 3, 1855, in Hartford, Connecticut, as patent number 12,648: ''Improvement in Repeating Fire-arms''. On November 17, 1856, White signed an agreement with Smith & Wesson
Smith & Wesson Brands, Inc. (S&W) is an American Firearms manufacturer, firearm manufacturer headquartered in Maryville, Tennessee, United States.
Smith & Wesson was founded by Horace Smith (inventor), Horace Smith and Daniel B. Wesson as the ...
for the exclusive use of his patent. The contract stipulated that White would be paid 25 cents for every revolver, but that it was up to him to defend his patent against infringement as opposed to Smith & Wesson.
During the 1850s and 1860s, Rollin White had been permanently trying to keep control on his breech-loading system patent, bringing a lawsuit to any breech-loaded manufactured gun. He nevertheless obtained an advance against royalties for using his patent from Smith & Wesson, a company that not only introduced its first revolver in 1857 ( Smith & Wesson Model 1, a rear-loader) but also started, as of 1858, to convert cap & ball percussion guns into rear-loaders, even with formerly Colt manufactured revolvers. But the Colt's company itself was prevented by American laws from infringing the Rollin White patent and all along the 1850s and 1860s continued manufacturing percussion guns. In 1860 it produced a new revolver model for the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
.. This Colt Army Model 1860 appeared just in time for the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
.
1860–1865: American Civil War
 The New York Daily Tribune denounced Colt and his company by asserting, “the traitors have found sympathizers among us, men base enough to sell arms when they knew they would be... in the hands of the deadly enemies of the Union... Col. Colt’s manufactory can turn probably 1,000 a week and has been doing so for the past four months for the South.”Hosley, William N. Colt : The Making of an American Legend. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, 1996. 96. This article even chided the Federal Government for not taking action against Colt: “Every man who makes arms should be watched, and if he will not work for a fair equivalent for the Government, his manufactory should be taken away from him.” Despite secession and growing tensions between the North and the South, “Colt’s sales to Alabama, Virginia, Georgia, and Mississippi in 1860 alone were at least $61,000 (today’s equivalent of about 3.35 million).” Until just days before the first shot at Fort Sumter, Colt received orders from various states, some participating in secession. In his memoir on Colt, written in 1866, Henry Barnard reported, “before the rebellion broke out, Col. Colt, foreseeing that his weapons must ere long be in double demand, had made all preparations to extend his factory.”
The
The New York Daily Tribune denounced Colt and his company by asserting, “the traitors have found sympathizers among us, men base enough to sell arms when they knew they would be... in the hands of the deadly enemies of the Union... Col. Colt’s manufactory can turn probably 1,000 a week and has been doing so for the past four months for the South.”Hosley, William N. Colt : The Making of an American Legend. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, 1996. 96. This article even chided the Federal Government for not taking action against Colt: “Every man who makes arms should be watched, and if he will not work for a fair equivalent for the Government, his manufactory should be taken away from him.” Despite secession and growing tensions between the North and the South, “Colt’s sales to Alabama, Virginia, Georgia, and Mississippi in 1860 alone were at least $61,000 (today’s equivalent of about 3.35 million).” Until just days before the first shot at Fort Sumter, Colt received orders from various states, some participating in secession. In his memoir on Colt, written in 1866, Henry Barnard reported, “before the rebellion broke out, Col. Colt, foreseeing that his weapons must ere long be in double demand, had made all preparations to extend his factory.”
The American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
was a boon to firearms manufacturers such as Colt's, and the company thrived during the conflict. Sam Colt had carefully developed contacts within the ordnance department, signing the very first government contract for 25,000 rifles. Colt's Factory was described as "an industrial palace topped by a blue dome", powered by a 250-horsepower steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
.Kinard (2004) p.154 During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, Colt had 1,500 employees who produced 150,000 muskets and pistols a year. In 1861 and 1863, the company sold 107,000 of the Colt Army Model 1860 alone, with production reaching 200,500 by the end of the war in 1865.
During the war, Colt's was still prevented by the American laws from infringing Rollin White's patent. Nevertheless, the war made a huge fortune for the company, allowing Sam Colt to become America's first manufacturing tycoon, though he did not live to see the end of the war; he died of rheumatic fever
Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammation#Disorders, inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a Streptococcal pharyngitis, streptococcal throat infection. Si ...
on January 10, 1862. His close friend and firearms engineer, Elisha K. Root, took over as Colt's company president. On February 4, 1864, a fire destroyed most of the factory, including arms, machinery, plans, and factory records. On September 1, 1865, Root died, leaving the company in the hands of Samuel Colt's brother-in-law, Richard Jarvis. The company's vice-president was William B. Franklin, who had recently left the Army at the end of the Civil War. With the Civil War over and having no new military contracts, Colt's Manufacturing was forced to lay off over 800 employees.Kinard (2004) p.124
The company found itself in a precarious situation. The original revolver patents had expired, allowing other companies to produce copies of his designs. Additionally, metallic cartridge revolvers were gaining in popularity, but Colt could not produce any because of the Rollin White patent held by rival Smith & Wesson
Smith & Wesson Brands, Inc. (S&W) is an American Firearms manufacturer, firearm manufacturer headquartered in Maryville, Tennessee, United States.
Smith & Wesson was founded by Horace Smith (inventor), Horace Smith and Daniel B. Wesson as the ...
. Likewise, Colt had been so protective of its own patents that other companies had been unable to make revolvers similar to their design. As the Rollin White patent neared expiration, Colt moved to develop its own metallic cartridge revolver.
1865–1880s: Post–Civil War
It was 1868 when Colt's first effort toward a metallic cartridge revolver was by conversion of existing percussion revolvers. The first of these conversions was patented on September 15, 1868, by Colt engineer, F. Alexander Thuer as patent number 82258. The Thuer conversion was made by milling off the rear of the receiver and replacing it with a breechplate containing six internal firing pins. The cartridges were loaded through the mouths of the chambers. Colt made 5000 of these but they were not well accepted. Colt found the mechanism so complex it included a spare percussion cylinder with each revolver. Colt tasked its superintendent of engineering, Charles Richards, to come up with a solution. The Richards conversion was performed on the Colt 1860 Army revolver. The caliber was .44 Colt and the loading lever was replaced by an ejector rod. This conversion added a breech plate with a firing pin and a rear sight mounted on the breechplate. Cartridges were loaded into the cylinder one at a time via a loading gate. Colt manufactured 9000 of these revolvers between 1873 and 1878. In 1873, Colt performed the same conversion on the M1851 and M1861 revolvers for the US Navy in .38 rimfire. Another of Colt's engineers,William Mason William, Willie, or Willy Mason may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*William Mason (poet) (1724–1797), English poet, editor and gardener
*William Mason (architect) (1810–1897), New Zealand architect
*William Mason (composer) (1829–1908), Ame ...
, improved this conversion by placing the rear sight on the hammer and, along with Richards, he was granted patents in 1871 to convert percussion revolvers into rear-loading metallic-cartridge revolvers. Those converted revolvers are identified as the "Richards-Mason conversion". There were approximately 2100 Richards-Mason M1860 Army conversions made from 1877 to 1878 in a serial-number range 5800 to 7900.
In November 1865, Franklin had attempted to purchase a license to the Rollin White patent from competitor Smith & Wesson. White and Smith & Wesson would take no less than $1.1 million, but Franklin and Colt's directors decided it was too large an investment on a patent that would expire in 1868. In the meantime, Colt turned its attention to manufacturing goods other than firearms, such as watches, sewing machines, typewriters and bicycles. In 1868 Rollin White requested an extension to his patent, but the request was rejected. He then turned to the Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
, but the request was again rejected, this time by the Senate and on the initiative of President Ulysses Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as commanding general, Grant led the Union Army to victory in the American Civil War ...
, in January 1870. This led the patent to expire, allowing competitors to develop their own breech-loading guns and metallic cartridges. Following this, on that same year of 1870, Colt's bought the National Arms Company, a Brooklyn, New York
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelv ...
company known for manufacturing derringer
A derringer or deringer is a small handgun that is neither a revolver, semi-automatic pistol, nor machine pistol. It is not to be confused with mini-revolvers or pocket pistols, although some later derringers were manufactured with the pepp ...
s and for circumventing the Rollin White patent by utilizing a unique cartridge. Colt continued to produce the .41 Short derringer after the acquisition, as an effort to help break into the metallic-cartridge gun market, but also introduced its own three Colt Derringer Models, all of them also chambered in a .41 rimfire unique cartridge. The last model to be in production, the third Colt Derringer, was not dropped until 1912. The first metallic cartridge breech-loading weapons sold by Colt's were those Derringers, in 1870, that were formerly conceived by the National Arms Company, but Colt's also started developing its own rear-loading guns and cartridges.
In 1871, Colt's introduced its first revolver models using rear-loaded metallic cartridges: the .41 caliber Colt House Revolver (also known as the Cloverleaf for its four-round cylinder configuration) and the .22 cal Colt Open Top Pocket Model Revolver. However, Colt's wanted a more powerful practical handgun loaded with metallic cartridges so the company put forward William Mason, who in 1871 began work on Colt's first .44 caliber metallic-cartridge revolver: the Colt Model 1871-72 Open Top. The company registered two patents for the Open Top, one in 1871, the other in 1872, the same patents mentioned in the markings of Colt Single Action Army revolvers, a nowadays legendary and long produced model, improved and based on the Open Top. Production of the Open Top started in 1872 and stopped in 1873 when the Single Action Army model started to be delivered to the US Army. However, the Open Top was already a completely new design. The parts, for example, would not interchange with the older percussion pistols. Mason moved the rear sight to the rear of the barrel as opposed to the hammer or the breechblock of the earlier efforts. The caliber was .44 rimfire and it was submitted to the
Colt continued to produce the .41 Short derringer after the acquisition, as an effort to help break into the metallic-cartridge gun market, but also introduced its own three Colt Derringer Models, all of them also chambered in a .41 rimfire unique cartridge. The last model to be in production, the third Colt Derringer, was not dropped until 1912. The first metallic cartridge breech-loading weapons sold by Colt's were those Derringers, in 1870, that were formerly conceived by the National Arms Company, but Colt's also started developing its own rear-loading guns and cartridges.
In 1871, Colt's introduced its first revolver models using rear-loaded metallic cartridges: the .41 caliber Colt House Revolver (also known as the Cloverleaf for its four-round cylinder configuration) and the .22 cal Colt Open Top Pocket Model Revolver. However, Colt's wanted a more powerful practical handgun loaded with metallic cartridges so the company put forward William Mason, who in 1871 began work on Colt's first .44 caliber metallic-cartridge revolver: the Colt Model 1871-72 Open Top. The company registered two patents for the Open Top, one in 1871, the other in 1872, the same patents mentioned in the markings of Colt Single Action Army revolvers, a nowadays legendary and long produced model, improved and based on the Open Top. Production of the Open Top started in 1872 and stopped in 1873 when the Single Action Army model started to be delivered to the US Army. However, the Open Top was already a completely new design. The parts, for example, would not interchange with the older percussion pistols. Mason moved the rear sight to the rear of the barrel as opposed to the hammer or the breechblock of the earlier efforts. The caliber was .44 rimfire and it was submitted to the US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United Stat ...
for testing in 1872. The Army rejected the pistol and asked for a more powerful caliber with a stronger frame. Mason redesigned the frame to incorporate a topstrap, similar to the Remington revolvers, and placed the rear sight on the rear of the frame; he consulted with Richards on some other improvements. The first prototype of the new gun was still chambered in .44 rimfire, but the first model was in the newest caliber known as the .45 Colt.
 The revolver was chosen by the Army in 1872, with the first order, for 8000 revolvers, shipping in the summer of 1873: The
The revolver was chosen by the Army in 1872, with the first order, for 8000 revolvers, shipping in the summer of 1873: The Colt Single Action Army
The Colt Single Action Army (also known as the SAA, Model P, Peacemaker, or M1873) is a Trigger (firearms)#Single-action, single-action revolver handgun. It was designed for the U.S. government service revolver trials of 1872 by Colt's Patent Fi ...
or "Peacemaker", also known as the Colt Model 1873, was born. This revolver was one of the most prevalent firearms in the American West
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Western States, the Far West, the Western territories, and the West) is census regions United States Census Bureau
As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the mea ...
during the end of the 19th century and Colt still produces it, in six different calibers, two finishes and three barrel lengths.
 In the new market of metallic cartridge rear-loading pocket revolvers, Colt's not only introduced its three Derringer Models (as of 1870) or the Colt House and the Open Top Pocket (the last two as of 1871) but also introduced in 1873 a subsequent design called its "
In the new market of metallic cartridge rear-loading pocket revolvers, Colt's not only introduced its three Derringer Models (as of 1870) or the Colt House and the Open Top Pocket (the last two as of 1871) but also introduced in 1873 a subsequent design called its "New Line
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995
* "New" (Daya song), 2017
* "New" (No Doubt song), 1 ...
" revolver models, based on William Mason's patents.
After the success of the Colt Single Action Army and Colt's conversion of existing percussion revolvers to Richards-Mason conversions, Mason went on to design Colt's first Double-action revolver, the Colt M1877. Following this, he once again teamed up with Richards to produce a larger-framed version, the Colt M1878 Frontier. It was Colt's first large-frame, double-action revolver. It combined the front end of the Single Action Army revolver with a double-action, 6-shot frame mechanism. It was available commercially in numerous calibers.
The 1870s and 1880s provided sales opportunity to the Colt company via the spread of European-American society ever further westward across the continent, and the demand for firearms that it engendered in various ways. As white Americans displaced Indians from the Indian Territory
Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, ...
, both sides were eager for firearms. On the white side, both the U.S. Army and civilians were customers of Colt. The Army carried Colt revolvers through the last of its Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, was a conflict initially fought by European colonial empires, the United States, and briefly the Confederate States of America and Republic of Texas agains ...
. On the Indian side, Colt weapons were captured when possible, or bought from whoever was selling. Even among whites in towns where Indians had been vanquished, a thriving demand for guns existed, from the criminals to the police to self-defending civilians. Memoirs of Americans including Walter Chrysler
Walter Percy Chrysler (April 2, 1875 – August 18, 1940) was an American industrial pioneer in the automotive industry, automotive industry executive, and the founder and namesake of American Chrysler, Chrysler Corporation.
Childhood
Chrysler ...
and Jack Black
Thomas Jacob "Jack" Black (born August 28, 1969) is an American actor, comedian, and musician. He is known for roles in family and comedy films, in addition to his voice work in animated films. His awards include a Children's and Family Emmy ...
speak of what it was like growing up in Western towns where most people had guns and open carry
In the United States, open carry refers to the practice of visibly carrying a firearm in public places, as distinguished from Concealed carry in the United States, concealed carry, where firearms cannot be seen by the casual observer. To "carry ...
was common (such as in Kansas and Missouri, which were considered "out West" at the time—now considered the Old West
The American frontier, also known as the Old West, and popularly known as the Wild West, encompasses the geography, history, folklore, and culture associated with the forward wave of American expansion in mainland North America that bega ...
).
1890s
Colt finally left the "loading gate concept" for a swing-out cylinder on its revolvers with the Colt M1889 Navy revolver, which resembled the Colt M1878 and was based on another design by Mason. The model was produced for three years between 1889 and 1892 and eclipsed by the Colt M1892 chambered in .38 Long Colt. The M1892 was replaced by the New Service Double Action revolver in 1899. In caliber .45 Colt, the New Service was accepted by the U.S. Military as the Model 1909 .45 revolver. The New Service revolver was available in other calibers such as .38 Special and, later in the 20th century, .45 ACP (as the M1917 revolver) and .357 Magnum. Under a contract with the U.S. Army, Colt Arms built the Model 1895 ten-barrel variant of theGatling Gun
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling of North Carolina. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon.
The Gatling gun's operatio ...
, capable of firing 800–900 .30 Army rounds per minute and used with great effect at the Battle of San Juan Hill
The Battle of San Juan Hill (), also known as the Battle for the San Juan Heights, was a major battle of the Spanish–American War fought between an American force under the command of William Rufus Shafter and Joseph Wheeler against a Span ...
.. The M1895 Colt–Browning machine gun
The Colt–Browning M1895, nicknamed "potato digger" because of its unusual operating mechanism, is an air-cooled, belt-fed, gas-operated machine gun that fires from a closed bolt with a cyclic rate of 450 rounds per minute. Based on an 1889 desi ...
or "Potato Digger" was built by Colt. The Colt–Browning was one of the first gas-operated machine guns, originally invented by John Browning. It became the first automatic machine gun adopted by the United States and saw limited use by the U.S. Marine Corps at the invasion of Guantánamo Bay and by the 1st Volunteer Infantry in the Santiago campaign during the Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
. In 1901, Elizabeth Jarvis Colt sold the company to a group of outside investors based in New York and Boston.
20th century
1900–1920s
 During
During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Colt surpassed all previous production achievements. John Browning
John Moses Browning (January 23, 1855 – November 26, 1926) was an American firearm designer who developed many varieties of military and civilian firearms, cartridges, and gun mechanisms, many of which are still in use around the world. He ...
worked for Colt for a time and came up with a design for a semiautomatic pistol, which debuted as the Colt M1900 pistol and eventually evolved into the M1911
The Colt M1911 (also known as 1911, Colt 1911, Colt .45, or Colt Government in the case of Colt-produced models) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered primarily for the .45 ACP cartridge.
History
Early hist ...
. Prior to America's entry into the war, orders from Canada and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
swelled the backlog of orders to three years. Colt hired 4,000 more workers, making a total of 10,000 employees—and its stock's price increased by 400%. By 1918, Colt had produced and sold 425,500 of the famous Browning-designed M1911
The Colt M1911 (also known as 1911, Colt 1911, Colt .45, or Colt Government in the case of Colt-produced models) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered primarily for the .45 ACP cartridge.
History
Early hist ...
. Because the factory could not keep up with demand for this pistol, the US Military decided to accept Colt New Service revolvers in caliber .45 ACP, called the M1917 revolver, as a substitute weapon. Competing manufacturer Smith & Wesson
Smith & Wesson Brands, Inc. (S&W) is an American Firearms manufacturer, firearm manufacturer headquartered in Maryville, Tennessee, United States.
Smith & Wesson was founded by Horace Smith (inventor), Horace Smith and Daniel B. Wesson as the ...
made double-action revolvers in .45 ACP, which were accepted and issued by the U.S. military under the same name. Colt produced 151,700 revolvers during the war as well as 13,000 Maxim-Vickers machine guns and 10,000 Browning machine guns with an additional 100,000 under subcontract to other companies.
Since Auto-Ordnance had no tooling for production of the newly developed Thompson submachine gun, John T. Thompson, in August 1920, entered into contract with Colt's to manufacture 15,000 Thompson 1921 submachine guns. The contract was signed on August 18, 1920. Colt's tooled up and produced the 15,000 units between April 1921 and March 1922.
The stock market crash of 1929 and the ensuing Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
resulted in a slowing down of production for Colt. In anticipation of this, company presidents William C. Skinner and Samuel M. Stone implemented a diversification program similar to that done at the close of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. Colt acquired contracts for business machines, calculators, dishwashers, motorcycles, and automobiles; all marketed under a name other than Colt. Samuel Stone acquired a firm that manufactured plastics and renamed it "Colt rock" as well as a company that manufactured electrical products. Colt weathered the financial crises of the time by cutting the work week, reducing salaries, and keeping more employees on the payroll than they needed. These measures kept the company in business but ate up the cash surplus they had acquired during the World War I years.
1930s: Great Depression
In 1935, after employees voted to disband alabor union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
, 1,000 workers went on strike for 13 weeks. Strikers became violent, attacking workers and detonating a bomb in front of company president Samuel M. Stone's house. The company set up a barracks, dining room, and recreation room for workers within the Colt Armory
The Colt Armory is a historic factory complex for the manufacture of firearms, created by Samuel Colt. It is located in Hartford, Connecticut along the Connecticut River, and as of 2008 is part of the Coltsville Historic District, named a Natio ...
during the strike. On June 3, 1935, the National Recovery Administration
The National Recovery Administration (NRA) was a prime agency established by U.S. president Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) in 1933. The goal of the administration was to eliminate "cut throat competition" by bringing industry, labor, and governmen ...
ruled that the company was within its rights not to deal with the union and the strike ended. In the year following the strike, the factory was hit by a hurricane and flood. Many company shipping records and historical documents were lost as a result.
1939–1945: World War II
 At the beginning of
At the beginning of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Colt ceased production of the Single Action Army revolver to devote more time to filling orders for the war. During the war Colt manufactured over 629,000 M1911A1 pistols as well as a large number of M1917 water-cooled machineguns. The company had a workforce of 15,000 men and women in three factories and production ran on three shifts, 24 hours a day, and won the Army-Navy rating of "E" for excellence. Colt ranked 99th among United States corporations in the value of World War II military production contracts. However, the company was losing money every year due to mismanagement, an embittered workforce that had been stretched to its limits, and manufacturing methods which were becoming obsolete.
1945–1950s
As the war ended and demand for military arms came to a halt, production literally ceased. Many long-time workers and engineers retired from the company and nothing was built from 1945 to 1947. Mismanagement of funds during the war had a serious impact as the 105-year-old firm faced possible bankruptcy. In September 1955 the board of directors voted to merge Colt with an upstart conglomerate called Penn-Texas, which had acquired Pratt & Whitney Machine Tool the same year. Also in 1955, Colt released one of the most famous revolvers in history, theColt Python
The Colt Python is a double action/single action revolver chambered for the .357 Magnum cartridge. It was first introduced in 1955 by the Colt's Manufacturing Company. Dougherty, Martin ''Small Arms: From the Civil War to the Present Day'', Ne ...
. In 1958 Penn-Texas merged with Fairbanks-Morse
Fairbanks, Morse and Company was an American manufacturing company in the late 19th and early 20th century. Founded in 1823 as a manufacturer of weighing scale, weighing scales, it later diversified into pumps, engines, windmills, coffee grinder ...
to form the Fairbanks-Whitney Corporation and in 1964 the conglomerate reorganized as Colt Industries. In 1956 Colt resumed production of the Single Action Army revolver and in 1961 began making commemorative versions of their classic models.
1960s–1970s
 The 1960s were boom years for Colt with the escalation of the
The 1960s were boom years for Colt with the escalation of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
, Robert McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara (; June 9, 1916 – July 6, 2009) was an American businessman and government official who served as the eighth United States secretary of defense from 1961 to 1968 under presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson ...
shutting down the Springfield Armory
The Springfield Armory, more formally known as the United States Armory and Arsenal at Springfield located in the city of Springfield, Massachusetts, was the primary center for the manufacture of United States military firearms from 1777 until ...
, and the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United Stat ...
's subsequent adoption of the M16, for which Colt held the production rights and would sell over 5 million units worldwide. Colt would capitalize on this with a range of AR-15 derivative carbines. They developed AR-15-based Squad Automatic Weapons, and the Colt SCAMP, an early PDW design. The Colt XM148 grenade launcher was created by Colt's design project engineer, gun designer Karl R. Lewis. The May 1967 "Colt's Ink" newsletter announced that he had won a national competition for his selection and treatment of materials in the design. The newsletter stated in part "In only 47 days, he wrote the specifications, designed the launcher, drew all the original prints, and had a working model built". At the end of the 1970s, there was a program run by the Air Force to replace the M1911A1. The Beretta 92S won, but this was contested by the Army. The Army ran their own trials, leading eventually to the Beretta 92F being selected as the M9.
In the early 1960s, Colt threatened legal action against Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball league composed of 30 teams, divided equally between the National League (baseball), National League (NL) and the American League (AL), with 29 in the United States and 1 in Canada. MLB i ...
's new Houston franchise, the Colt .45s, citing trademark infringement. In December 1964 the team backed down, renaming itself the Astros.
1980s–1990s
The 1980s were fairly good years for Colt, but the coming end of the Cold War would change all that. Colt had long left innovation in civilian firearms to their competitors, feeling that the handgun business could survive on their traditional revolver and M1911 designs. Instead, Colt focused on the military market, where they held the primary contracts for the production of rifles for the US military. This strategy dramatically failed for Colt through a series of events in the 1980s. In 1984, the U.S. military standardized on the Beretta 92F. This was not much of a loss for Colt's current business, as M1911A1 production had stopped in 1945. Meanwhile, the military rifle business was growing because the U.S. military had a major demand for more upgraded M16s; the M16A2 model had just been adopted and the military needed hundreds of thousands of them. In 1985, Colt's workers, members of theUnited Auto Workers
The United Auto Workers (UAW), fully named International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America, is an American labor union that represents workers in the United States (including Puerto Rico) and sou ...
went on strike for higher wages. This strike would ultimately last for five years and was one of the longest-running labor strikes in American history. With replacement workers running production, the quality of Colt's firearms began to decline. Dissatisfied with Colt's production, in 1988 the U.S. military awarded the contract for future M16 production to Fabrique Nationale
, trading as FN Herstal and often referred to as Fabrique Nationale, or simply FN, is a leading firearms manufacturer based in Herstal, Belgium, and former vehicle manufacturer. It was the largest exporter of military small arms in Europe .
FN ...
. The strike finally ended when an agreement was reached on 22 March 1990.
Some criticized Colt's range of handgun products in the late 1980s as out of touch with the demands of the market, and their once-vaunted reputation for quality had suffered during the UAW strike. Colt's stable of double-action revolvers and single-action pistols was seen as old-fashioned by a marketplace that was captivated by the new generation of " wondernines" – higher capacity handguns chambered in 9×19mm Parabellum
The 9×19mm Parabellum (also known as 9mm Luger, 9mm NATO or simply 9mm) is a Rim (firearms)#Rimless, rimless, Centerfire ammunition, centerfire, tapered cartridge (firearms), firearms cartridge.
Originally designed by Austrian firearm designer ...
, as typified by the Glock 17
Glock (; stylized as GLOCK) is a brand of polymer- framed, short-recoil-operated, striker-fired, locked-breech semi-automatic pistols designed and produced by Austrian manufacturer Glock Ges.m.b.H.
The firearm entered Austrian military an ...
. Realizing that the future of the company was at stake, labor and management agreed to end the strike in an arrangement that resulted in Colt being sold to a group of private investors, the State of Connecticut, and the UAW itself.
The new Colt first attempted to address some of the demands of the market with the production in 1989 of the '' Double Eagle'', a double-action pistol heavily based on the M1911 design, which was seen as an attempt to "modernize" the classic Browning design. Colt followed this up in 1992 with the '' Colt All American 2000'', which was unlike any other handgun Colt had produced before—being a polymer-framed, rotating-barrel, 9×19mm handgun with a magazine capacity of 15 rounds. It was designed by Reed Knight, with parts manufactured by outside vendors and assembled by Colt; its execution was disastrous. Early models were plagued with inaccuracy and unreliability and suffered from the poor publicity of a product recall. The product launch failed and production of the All American 2000 ended in 1994. This series of events led to the company's Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code ( Title 11 of the United States Code) permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, w ...
in 1992.
In 1992, the creditors, state and shareholders enlisted the aid of turnaround specialist RC (Ron) Whitaker to overcome the bankruptcy challenge. He developed a new team to address the company's situation. In addition to creating a positive working relationship with the UAW to introduce new techniques like cellular manufacturing, operator quality assurance and single-piece flow, they developed a renewed focus on product development. This resulted in the M4 carbine and Colt 22 pistol, two of the most successful new product offerings in the late 1990s, capturing 50% market shares in the first year of production.
 The 1990s brought the end of
The 1990s brought the end of Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, which resulted in a large downturn for the entire defense industry. Colt was hit by this downturn, though it would be made worse later in the 1990s by a boycott by the shooting public in America. In 1994, the assets of Colt were purchased by Zilkha & Co, a financial group owned by Donald Zilkha. It was speculated that Zilkha's financial backing of the company enabled Colt to begin winning back military contracts. In fact, during the time period it won only one contract, the M4 carbine
The M4 carbine (officially Carbine, Caliber 5.56 mm, M4) is a 5.56×45mm NATO assault rifle developed in the United States during the 1980s. It is a shortened version of the M16A2 assault rifle. The M4 is extensively used by the US mi ...
. However, the U.S. military had been purchasing Colt carbines for the past 30 years (See Colt Commando). During a 1998 ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'', locally known as ''The'' ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'' or ''WP'', is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C., the national capital. It is the most widely circulated newspaper in the Washington m ...
'' interview, CEO
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a chief executive or managing director, is the top-ranking corporate officer charged with the management of an organization, usually a company or a nonprofit organization.
CEOs find roles in variou ...
Ron Stewart stated that he would favor a federal permit system with training and testing for gun ownership. This led to massive grassroots boycotts
A boycott is an act of nonviolent resistance, nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organisation, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for Morality, moral, society, social, politics, political, or Environmenta ...
of Colt's products by gun stores and US gun owners.
Zilkha replaced Stewart with Steven Sliwa and focused the remainder of Colt's handgun design efforts into "smart gun
A smart gun, also called a smart-gun, or smartgun, is a firearm that can detect its authorized user(s) or something that is normally only possessed by its authorized user(s). The term is also used in science fiction to refer to various types of se ...
s," a concept favored politically, but that had little interest or support among handgun owners or police departments. This research never produced any meaningful results due to the limited technology at the time. Colt announced the termination of its production of double-action revolvers in October 1999.
21st century
2002–present
The boycott of Colt gradually faded out after William M. Keys, a retired U.S. Marine Lt. General, took the helm of the company in 2002. Keys salvaged Colt's reputation and brought Colt from the brink of bankruptcy to an international leader in Defense production. In 2010 Gerald R. Dinkel replaced Keys as CEO of Colt Defense LLC, while Keys remained on the board of directors for Colt Defense. Colt has to compete with other companies that make M1911-style pistols such as Kimber and AR-15 rifles such as Bushmaster. Bushmaster has subsequently overtaken Colt in the number of AR-15s sold on the civilian market. Colt suffered a legal defeat in court when it sued Bushmaster fortrademark infringement
Trademark infringement is a violation of the exclusive rights attached to a trademark without the authorization of the trademark owner or any licensees (provided that such authorization was within the scope of the licence). Infringement may occ ...
claiming that "M4" was a trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a form of intellectual property that consists of a word, phrase, symbol, design, or a combination that identifies a Good (economics and accounting), product or Service (economics), service f ...
that it owned. The judge ruled that since the term M4 is a generic designation that Colt does not specifically own, Colt had to pay monetary reimbursement to Bushmaster to recoup Bushmaster's legal fees. The M4 designation itself comes from the U.S. military designation system, whose terms are in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
.
 Colt has entered in several US contracts with mixed results. For example, Colt had an entry in the
Colt has entered in several US contracts with mixed results. For example, Colt had an entry in the Advanced Combat Rifle
The Advanced Combat Rifle (ACR) was a United States Army program, started in 1986, to find a replacement for the M16 assault rifle. Under the stress of battle the average soldier with an M16 may shoot a target at 45 meters, but hit probability i ...
(ACR) program of the 1980s, but along with other contestants failed to replace the M16A2. Colt and many other makers entered the US trials for a new pistol in the 1980s, though the Beretta entry would win and become the M9 Pistol
The Beretta M9, officially the Pistol, Semiautomatic, 9mm, M9, is the designation for the Beretta 92FS semi-automatic pistol used by the United States Armed Forces. The M9 was adopted by the United States military as their service pistol in 19 ...
. The Colt OHWS handgun was beaten by H&K for what became the MK23 SOCOM, it was lighter than the H&K entry but lost in performance. Colt did not get to compete for the XM8 since it was not an open competition. Current M16 rifles have been made primarily by FN USA
, trading as FN Herstal and often referred to as Fabrique Nationale, or simply FN, is a leading firearms manufacturer based in Herstal, Belgium, and former vehicle manufacturer. It was the largest exporter of military small arms in Europe .
FN H ...
since 1988. However, Colt remained the sole source for M4 carbines for the US military. Under their license agreement with Colt, the US military could not legally award second-source production contracts for the M4 until July 1, 2009. In 2007 Colt won a contract to produce M4 carbines for the US military worth $71 million. In 2008 this was followed by a $151 million order for 89,000 M4 carbine rifles.
In a 2002 restructuring, Colt's Manufacturing Company, Inc, spun off Colt Defense, LLC, to supply military, law enforcement and security markets. Colt's Manufacturing Company itself become a subsidiary of New Colt Holding Corp, LLC. In 2013 Colt Defense acquired New Colt Holding Corp., in part to protect a licensing agreement set to expire in 2014, where Colt's Manufacturing sold sporting rifles marketed to consumers that were manufactured by Colt Defense. This formed a single company to develop, manufacture and sell firearms under the Colt name for all markets for the first time since the 2003 completion of the restructuring.
In 2013, Dennis R. Veilleux assumed the role of president & chief executive officer for Colt Holding Co. LLC and president & chief executive officer of Colt Defense LLC. Mr. Veilleux previously occupied the position of Principal at Sturm, Ruger & Co., Inc., Principal at General Electric Co., president & chief executive officer at Colt's Manufacturing Co. LLC and president & chief executive officer at New Colt Holding Corp.
Following persistent reliability problems, the reunited Colt lost its contract with the US military for M4 rifles in 2013. Parent company Colt Defense, LLC, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code ( Title 11 of the United States Code) permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, w ...
protection on June 15, 2015, citing both assets and debts in the $100 million to $500 million range. According to analysts, Colt's problems were due to the loss of the contract and low demand for its civilian handguns. In January 2016, Colt announced that the bankruptcy court had approved its restructuring plan.
After restructuring, a reinvigorated Colt introduced several new versions of its 1911 pistols, including stainless-steel competition and target models. In 2017, Colt returned to the production of double-action revolvers with the .38 Colt Cobra, followed in 2019 by an improved version of the 1999 .357 ''Magnum Carry'', the King Cobra
The king cobra (''Ophiophagus hannah'') is a species complex of snakes Endemism, endemic to Asia. With an average of and a record length of , it is the world's longest venomous snake and among the heaviest. Under the genus ''Ophiophagus'', i ...
. In 2020, Colt reintroduced a modernized Colt Python
The Colt Python is a double action/single action revolver chambered for the .357 Magnum cartridge. It was first introduced in 1955 by the Colt's Manufacturing Company. Dougherty, Martin ''Small Arms: From the Civil War to the Present Day'', Ne ...
in stainless steel, followed by the reintroduction of 6- and 8-inch stainless steel versions of the Colt Anaconda in 2021- and a 4.25-inch Anaconda in 2023.
In 2021, Colt was purchased by the Česká zbrojovka Group (CZG), which would rename itself Colt CZ Group in 2022. Lubomír Kovařík, the chairman of the CZG, stated that the acquisition would allow for co-operative research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage ...
between the two companies, and specified that Colt products would continue to be manufactured in the United States.
Presidents
 *
* Samuel Colt
Samuel Colt (; July 19, 1814 – January 10, 1862) was an American inventor, industrialist, and businessman who established Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Manufacturing Company and made the mass production of revolvers commercially viable.
Col ...
(1855–1862)
* Elisha K. Root (1862–1865)
* Richard Jarvis (1865–1901)
* John Hall (1901–1902)
* Lewis C. Grover (1902–1909)
* William C. Skinner (1909–1911)
* Col. Charles L.F. Robinson (1911–1916)
* William C. Skinner (1916–1921)
* Samuel M. Stone (1921–1944)
* Graham H. Anthony (1944–1949)
* B. Franklin Conner (1949–1955)
* Chester Bland (1955–1958)
* Fred A. Roff Jr. (1958–1962)
* David C. Scott (1962–1963)
* Paul A. Benke (1963–1968)
* David I. Margolis (1968–1990)
* Richard F. Gamble (1990)
* Ronald E. Stilwell (1990–1992)
* Ronald C. Whitaker (1992–1995)
* John F. Jastrem (1995–1996)
* Donald Zilkha (1996)
* Ronald L. Stewart (1996–1999)
* Steven Sliwa (1999)
* William M. Keys (1999–2013)
* Dennis R. Veilleux (2013–present)
Archives
The company's factory collection was donated to the Museum of Connecticut History in 1957. At the same time, the company's business records were donated to theConnecticut State Library
The Connecticut State Library is the state library for the U.S. state of Connecticut and is also an executive branch agency of the state. It is located in Hartford, Connecticut, Hartford, Connecticut directly across the street from the Connecticu ...
.
Samuel Colt's personal firearm collection resides at the Wadsworth Atheneum Museum of Art. A collection of his personal papers is owned by the Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library
The Beinecke Rare Book & Manuscript Library () is the rare book library and literary archive of the Yale University Library in New Haven, Connecticut. It is one of the largest buildings in the world dedicated to rare books and manuscripts and ...
at Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
.
Products
Handguns
The years in parentheses indicate the year when production started, not the year of the model's patent.Percussion revolvers
*Colt Paterson
The Colt Paterson revolver was the first commercial repeating firearm employing a revolving cylinder with multiple chambers aligned with a single, stationary barrel. Its design was patented by Samuel Colt on February 25, 1836, in the United ...
(1836)
* Colt Walker
The Colt Walker, sometimes known as the Walker Colt, is a single-action revolver with a revolving cylinder holding six charges of black powder behind six bullets (typically .44 caliber lead balls). It was designed in 1846 by American firearms in ...
(1847)
* Colt Dragoon (1848)
* Colt Model 1849 Pocket Revolver (1849)
* Colt 1851 Navy (1851)
* Colt 1855 Sidehammer (1855)
* Colt 1860 Army (1860)
* Colt 1861 Navy (1861)
* Colt Model 1862 Pocket Police
The family of Colt Pocket Percussion Revolvers evolved from the earlier commercial revolvers marketed by the Patent Arms Manufacturing Company of Paterson, N.J. The smaller versions of Colt's first revolvers are also called "Baby Patersons" by co ...
(1862)
Metallic cartridge revolvers
* Colt House (1871) * Colt Open Top Pocket Model Revolver (1871) * Colt Model 1871-72 Open Top (1872) *Colt Single Action Army
The Colt Single Action Army (also known as the SAA, Model P, Peacemaker, or M1873) is a Trigger (firearms)#Single-action, single-action revolver handgun. It was designed for the U.S. government service revolver trials of 1872 by Colt's Patent Fi ...
"Peacemaker" (1873)
* Colt New Line (1873)
* Colt Lightning, Thunderer and Rainmaker (1877)
* Colt Model 1878 Frontier (1878)
* Colt M1889 (1889)
* Colt M1892 (1892 to 1903)
* Colt New Police Revolver (1896–1905)
* Colt New Service (1898)
* Colt M1905 New Marine
* Colt M1917
* Colt Anaconda (AA frame)
* Colt Police Positive (D frame)
* Colt Police Positive Special / Viper (D frame)
* Colt Detective Special (D frame)
* Colt Cobra (D frame)
* Colt Diamondback (D frame)
* Colt Official Police
The Colt Official Police is a medium frame, double-action revolver with a six-round cylinder, primarily chambered for the .38 Special cartridge, and manufactured by the Colt's Manufacturing Company. Released in 1908 as the Colt Army Special ...
revolver
* Colt SF VI
* Colt Python
The Colt Python is a double action/single action revolver chambered for the .357 Magnum cartridge. It was first introduced in 1955 by the Colt's Manufacturing Company. Dougherty, Martin ''Small Arms: From the Civil War to the Present Day'', Ne ...
(I frame)
* Colt Trooper
The Colt Trooper is a medium Receiver (firearms), frame, double-action revolver featuring a six-round cylinder, Chamber (firearms), chambered for .22 Long Rifle, .22 Winchester Magnum Rimfire, .38 Special, and .357 Magnum caliber Cartridge (firearm ...
(I frame)
* Colt King Cobra (V frame)
Semi-automatic pistols

 * Colt M1900 (1900)
* Colt M1902 (1902)
*
* Colt M1900 (1900)
* Colt M1902 (1902)
* Colt Model 1903 Pocket Hammerless
The Colt Model 1903 Pocket Hammerless is a .32 ACP, .32 ACP (7.65mm Browning) caliber, self-loading, semi-automatic pistol designed by John Browning and built by Colt's Manufacturing Company, Colt Patent Firearms Manufacturing Company of Hartford ...
(Model M, 1903)
* Colt Model 1908 Vest Pocket (Model N, 1908)
* Colt M1911
The Colt M1911 (also known as 1911, Colt 1911, Colt .45, or Colt Government in the case of Colt-produced models) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered primarily for the .45 ACP cartridge.
History
Early histor ...
(Model O, 1911)
* Colt M1911A1
The Colt M1911 (also known as 1911, Colt 1911, Colt .45, or Colt Government in the case of Colt-produced models) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered primarily for the .45 ACP cartridge.
History
Early histor ...
* Colt 2000
* Colt Cadet 22
* Colt Target Model 22
* Colt Mustang
* Colt Mustang Plus II
* Colt Mustang XSP
* Colt Delta Elite
* Colt Double Eagle
* Colt New Agent
* Colt Officer's ACP
* Colt Woodsman
The Colt Woodsman is a semi-automatic sporting pistol manufactured by the U.S. Colt's Manufacturing Company from 1915 to 1977. It was designed by John Moses Browning. The frame design changed over time, in three distinct series: series one being ...
(Model S)
* Colt T-4 (prototype)
* Colt Commander
* Colt Defender
Machine pistols
* Colt SCAMPLong guns
 * Colt 1855 Revolving carbine/rifle
* Colt 1878 Hammer Shotgun
*
* Colt 1855 Revolving carbine/rifle
* Colt 1878 Hammer Shotgun
* Colt-Burgess rifle
The Colt-Burgess rifle, also known as the 1883 Burgess rifle or simply the Burgess rifle, is a lever-action repeating rifle produced by Colt's Patent Firearms Manufacturing Company between 1883 and 1885. The Burgess rifle was Colt's only entra ...
* Colt–Browning M1895 machine gun
* Colt Lightning Carbine
The Colt Lightning Carbine or Colt Lightning Rifle was a Pump-action, slide-action (pump-action) rifle manufactured by Colt's Manufacturing Company, Colt from 1884 until 1904 and was originally chambered in .44-40 caliber. Colt eventually ...
* Colt Stagecoach .22 LR semi-automatic rifle
* Colt ACR
* Colt Double rifle
* ArmaLite AR-15 type rifles
* Colt Monitor – produced under license
* Thompson SMG – produced under license
Cartridges
* .25 ACP * .32 ACP * .32 Short Colt * .32 Long Colt * .38 ACP * .38 Super * .380 ACP * .38 Short Colt * .38 Long Colt * .41 Long Colt * .44 Colt * .45 ACP * .45 ColtSee also
* List of modern armament manufacturers *Sodium silicate
Sodium silicate is a generic name for chemical compounds with the formula or ·, such as sodium metasilicate (), sodium orthosilicate (), and sodium pyrosilicate (). The anions are often polymeric. These compounds are generally colorless tra ...
, used as a cement for paper cartridges used in early Colt revolvers during the American Civil War
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
Colt official site
The Colt Revolver in the American West
Colt Automatic Pistols Home Page
* Jarvis-Robinson Family Papers. Yale Collection of Western Americana, Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library. * Most of the following are filed under 36-150 Huyshope Avenue, 17-170 Van Dyke Avenue, 49 Vredendale Avenue, Hartford, Hartford County, CT: * * * * * * * * * Firearm manufacturers of the United States Historic American Engineering Record in Connecticut Military in Connecticut 1836 establishments in Connecticut Manufacturing companies established in 1836 Companies that filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2015 {{coord, 41.7385145, -72.722959, display=title