Colorimetry (chemical method) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In physical and
In physical and
 In physical and
In physical and analytical chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute t ...
, colorimetry or colourimetry is a technique used to determine the concentration of colored compounds in solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solu ...
.
A colorimeter is a device used to test the magnitude of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light (not to be confused with the tristimulus colorimeter
A tristimulus colorimeter, colloquially shortened to ''colorimeter'' or ''colourimeter'', is used in digital imaging to profile and calibrate output devices.
It takes a limited number of wideband spectral energy readings along the visible spectru ...
used to measure colors in general).
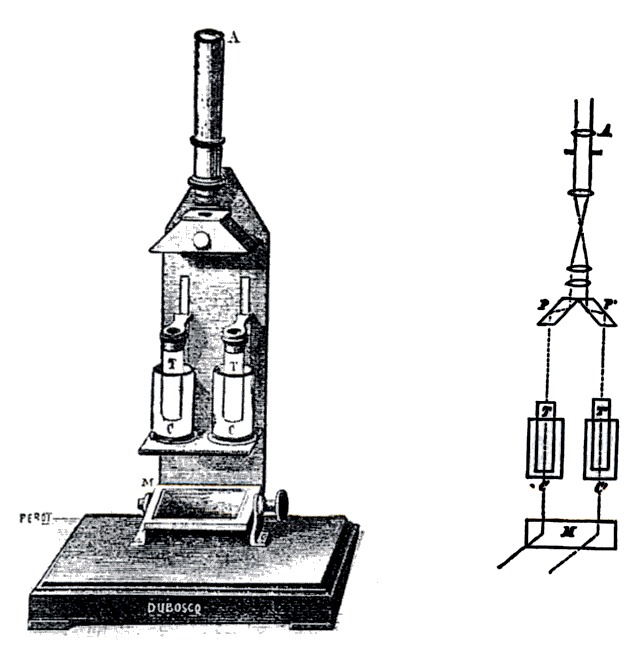
To use the colorimeter, different solutions must be made, including a control or reference of known concentration. With a visual colorimeter, for example the Duboscq colorimeter illustrated, the length of the light path through the solutions can be varied while filtered light transmitted through them is compared for a visual match. The concentration times path length is taken to be equal when the colors match, so the concentration of the unknown can be determined by simple proportions. Nessler tubes work on the same principle.
There are also electronic automated colorimeters; before these machines are used, they must be calibrated with a cuvette
In laboratories, a cuvette () is a small tube-like container with straight sides and a circular or square cross-section. It is sealed at one end, and made of a clear, transparent material such as plastic, glass, or fused quartz. Cuvettes are des ...
containing the control solution. The concentration of a sample can be calculated from the intensity of light before and after it passes through the sample by using the Beer–Lambert law
The Beer–Bouguer–Lambert (BBL) extinction law is an empirical relationship describing the attenuation in intensity of a radiation beam passing through a macroscopically homogenous medium with which it interacts. Formally, it states that the ...
. Photoelectric analyzers came to dominate in the 1960s.
The color or wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the filter chosen for the colorimeter is extremely important, as the wavelength of light that is transmitted by the colorimeter has to be the same as that absorbed by the substance being measured. For example, the filter on a colorimeter might be set to red if the liquid is blue.
Absorption colorimeter
A colorimeter is a device used to test the concentration of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light. To use this device, differentsolution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solu ...
s must be made, and a control (usually a mixture of distilled water
Distilled water is water that has been purified by boiling it into vapor then condensing it back into liquid in a separate container. Impurities in the original water that do not boil below or near the boiling point of water remain in the origin ...
and another solution) is first filled into a cuvette
In laboratories, a cuvette () is a small tube-like container with straight sides and a circular or square cross-section. It is sealed at one end, and made of a clear, transparent material such as plastic, glass, or fused quartz. Cuvettes are des ...
and placed inside a colorimeter to calibrate the machine. Only after the device has been calibrated you can use it to find the densities and/or concentrations of the other solutions. You do this by repeating the calibration, except with cuvettes filled with the other solutions.
The filter on a colorimeter must be set to red if the liquid is blue. The size of the filter initially chosen for the colorimeter is extremely important, as the wavelength of light that is transmitted by the colorimeter has to be same as that absorbed by the substance.
Colorimetric assays
Colorimetric assays use reagents that undergo a measurable color change in the presence of theanalyte
An analyte, component (in clinical chemistry), titrand (in titrations), or chemical species is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. The remainder of the sample is called the matrix. The procedure ...
. They are widely used in biochemistry to test for the presence of enzymes, specific compounds, antibodies, hormones and many more analytes. For example,
* para-Nitrophenylphosphate is converted into a yellow product by alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryo ...
enzyme.
* Coomassie Blue is an aromatic dye that binds to aromatic proteins and positively charged amino acid residues within the protein structure. The binding interaction results in a spectrum shift, enabling quantitative measurement of the protein concentration. A similar colorimetric assay, the Bicinchoninic acid assay
The bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA assay), also known as the Smith assay, after its inventor, Paul K. Smith at the Pierce Chemical Company, is a biochemical assay for determining the total concentration of protein in a solution (0.5 μg/mL to 1.5& ...
, uses a chemical reaction to determine protein concentration.
*The Biuret assay utilizes a biuret reagent which turns purple in the presence of proteins due to the chelation of copper salts in an alkaline solution.
* Enzyme linked immunoassays use enzyme-complexed-antibodies to detect antigens. Binding of the antibody is often inferred from the color change of reagents such as TMB TMB may refer to:
Organizations
*Tamilnad Mercantile Bank Limited, India
*Texas Medical Board
* Thai Military Bank
* Transports Metropolitans de Barcelona, Spain
Places
*Kendall-Tamiami Executive Airport near Miami, Florida, US, IATA code
*Tsing M ...
.
See also
*Jules Duboscq
Louis Jules Duboscq (March 5, 1817 – September 24, 1886) was a French instrument maker, inventor, and pioneering photographer. He was known in his time, and is remembered today, for the high quality of his optical instruments.
Life and wo ...
* Permanganometry Permanganometry is one of the techniques used in chemical quantitative analysis. It is a redox titration that involves the use of permanganates to measure the amount of analyte present in unknown chemical samples. It involves two steps, namely the t ...
* Lovibond colorimeter
* Turbidimetry Turbidimetry (the name being derived from ''turbidity'') is the process of measuring the loss of intensity of transmitted light due to the scattering effect of particles suspended in it. Light is passed through a filter creating a light of known wav ...
References
{{Authority control Analytical chemistry Absorption spectroscopy