Cheng Ho on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zheng He (also romanized Cheng Ho; 1371–1433/1435) was a Chinese
 Eventually, he gained the confidence and trust of the prince. Ma was also known as "Sanbao" during his service in the household of the Prince of Yan, a reference to the Buddhist
Eventually, he gained the confidence and trust of the prince. Ma was also known as "Sanbao" during his service in the household of the Prince of Yan, a reference to the Buddhist
 The
The  While Zheng He's fleet was unprecedented, the routes were not. His fleet followed long-established, well-mapped routes of trade between China and the
While Zheng He's fleet was unprecedented, the routes were not. His fleet followed long-established, well-mapped routes of trade between China and the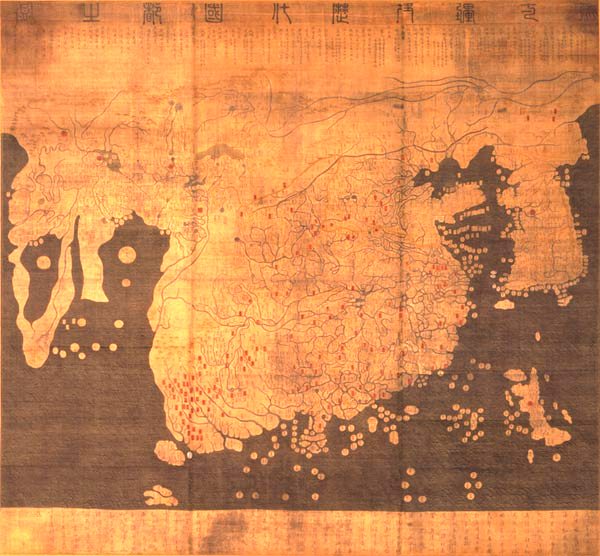  The fleet did not engage in conquest or colonization; though it included troops, their purpose was to demonstrate the Middle Kingdom's strength. However, a contemporary reported that Zheng He "walked like a tiger" and did not shrink from violence when he considered it necessary to impress foreign peoples with China's military might. He ruthlessly suppressed pirates, who had long plagued Chinese and Southeast Asian waters. For example, he defeated Chen Zuyi, one of the most feared and respected pirate captains, and returned him to China for execution. He also waged a land war against the
The fleet did not engage in conquest or colonization; though it included troops, their purpose was to demonstrate the Middle Kingdom's strength. However, a contemporary reported that Zheng He "walked like a tiger" and did not shrink from violence when he considered it necessary to impress foreign peoples with China's military might. He ruthlessly suppressed pirates, who had long plagued Chinese and Southeast Asian waters. For example, he defeated Chen Zuyi, one of the most feared and respected pirate captains, and returned him to China for execution. He also waged a land war against the

 Zheng He's sailing charts, the
Zheng He's sailing charts, the
 Edward L. Dreyer claims that Luo Maodeng's novel is unsuitable as historical evidence. The novel contains a number of fantasy element; for example the ships were "constructed with divine help by the immortal Lu Ban".
One explanation for the seemingly-inefficient size of the colossal ships was that the 44 ''zhang'' treasure ships were used only by the Emperor and imperial bureaucrats to travel along the Yangtze for court business, including reviewing Zheng He's expedition fleet. The Yangtze river, with its calmer waters, may have been navigable by these treasure ships. Zheng He, a court eunuch, would not have had the privilege in rank to command the largest of the ships, seaworthy or not. The main ships of Zheng He's fleet were instead six-masted 2000-liao ships.Xin Yuanou: ''Guanyu Zheng He baochuan chidu de jishu fenxi (A Technical Analysis of the Size of Zheng He's Ships).'' Shanghai 2002, p. 8 That would give burthen of 500 tons and a displacement tonnage of about 800 tons.
Traditional and popular accounts of Zheng He's voyages have described a great fleet of gigantic ships far larger than any other wooden ships in history. The most grandiose claims for Zheng He's 1405 fleet are entirely based on a calculation derived from an account that was written three centuries later and was accepted as fact by one modern writer; rejected by numerous naval experts. There are even some sources that claim some of the treasure ships might have been as long as . The claims that the Chinese treasure ships reached such size is disputed because other 17th century Ming records stated that European
Edward L. Dreyer claims that Luo Maodeng's novel is unsuitable as historical evidence. The novel contains a number of fantasy element; for example the ships were "constructed with divine help by the immortal Lu Ban".
One explanation for the seemingly-inefficient size of the colossal ships was that the 44 ''zhang'' treasure ships were used only by the Emperor and imperial bureaucrats to travel along the Yangtze for court business, including reviewing Zheng He's expedition fleet. The Yangtze river, with its calmer waters, may have been navigable by these treasure ships. Zheng He, a court eunuch, would not have had the privilege in rank to command the largest of the ships, seaworthy or not. The main ships of Zheng He's fleet were instead six-masted 2000-liao ships.Xin Yuanou: ''Guanyu Zheng He baochuan chidu de jishu fenxi (A Technical Analysis of the Size of Zheng He's Ships).'' Shanghai 2002, p. 8 That would give burthen of 500 tons and a displacement tonnage of about 800 tons.
Traditional and popular accounts of Zheng He's voyages have described a great fleet of gigantic ships far larger than any other wooden ships in history. The most grandiose claims for Zheng He's 1405 fleet are entirely based on a calculation derived from an account that was written three centuries later and was accepted as fact by one modern writer; rejected by numerous naval experts. There are even some sources that claim some of the treasure ships might have been as long as . The claims that the Chinese treasure ships reached such size is disputed because other 17th century Ming records stated that European
''Huangming Zuxun'' and Zheng He’s Voyages to the Western Oceans
. ''Journal of Chinese Studies'', No. 51 (July 2010). Retrieved 17 October 2012.
Cheng Ho and Islam in Southeast Asia
'. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, 2009. . The temples of the cult, called after either of his names, Cheng Hoon or Sam Po, are peculiar to overseas Chinese except for a single temple in Hongjian originally constructed by a returned Filipino Chinese in the Ming dynasty and rebuilt by another Filipino Chinese after the original was destroyed during the
Blacks in Pre-Modern China
', pp. 121–132. On his travels, Zheng He built mosques and also spread the worship of
File:Zheng He's tomb, Nanjing.jpg, Zheng He's tomb in
"Shipping News: Zheng He's Sexcentenary"
''China Heritage Newsletter'', June 2005, . Published by the China Heritage Project of The Australian National University. *
World History Encyclopedia – The Seven Voyages of Zheng He
Zheng He – The Chinese Muslim Admiral
(archived)
BBC radio programme "Swimming Dragons".
TIME magazine special feature on Zheng He (August 2001)
from elibraryhub.com
at peopledaily.com (25 September 2006) *
Newsletter, in Chinese, on academic research on the Zheng He voyages
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zheng, He 1371 births 1430s deaths 14th-century Chinese people 15th-century Chinese diplomats 15th-century Chinese military personnel 15th-century explorers Burials at sea Chinese admirals Chinese explorers Explorers of Africa Explorers of Asia Explorers of China Explorers of South Asia History of Kerala Hui people Geographers from Imperial China Ming dynasty eunuchs Ming dynasty Muslims Ming treasure voyages Naval history of China People from Kunming Scientists from Yunnan Travel writers of the medieval Islamic world Year of death uncertain Yongle Emperor
eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2 ...
, admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in many navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force. Admiral is ranked above vice admiral and below admiral of ...
and diplomat from the early Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
, who is often regarded as the greatest admiral in Chinese history
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
. Born into a Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
family as Ma He, he later adopted the surname Zheng conferred onto him by the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
().
Between 1405 and 1433, Zheng commanded seven treasure voyages
The Ming treasure voyages were maritime expeditions undertaken by Ming China's treasure fleet between 1405 and 1433. The Yongle Emperor ordered the construction of the fleet in 1403. The grand project resulted in seven far-reaching ocean vo ...
across Asia under the commission of the Yongle Emperor and the succeeding Xuande Emperor (). According to legend, Zheng's largest ships were almost twice as long as any wooden ship ever recorded, and carried hundreds of sailors on four decks.
A favorite of the Yongle Emperor, whom Zheng assisted in the Jingnan campaign that overthrew the previous Jianwen Emperor
The Jianwen Emperor (5 December 1377 – probably 13 July 1402), personal name Zhu Yunwen, also known by his temple name as the Emperor Huizong of Ming and by his posthumous name as the Emperor Hui of Ming, was the second emperor of the Ming d ...
in 1402, Zheng He rose to the top of the Ming imperial hierarchy and served as commander of the southern capital Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
.
Early life and family
Zheng was born Ma He to a Muslim family of Kunyang,Kunming
Kunming is the capital and largest city of the province of Yunnan in China. The political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province, Kunming is also the seat of the provincial government. During World War II, Kunming was a Ch ...
, Yunnan, then under the rule of the Principality of Liang loyal to the Northern Yuan
The Northern Yuan was a dynastic state ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen people, Jurchen-led ...
dynasty. He had an older brother and four sisters. The Liujiagang and Changle inscriptions suggest that devotion to Tianfei, the patron goddess of sailors and seafarers, was the dominant faith to which he adhered, reflecting the goddess's central role to the treasure fleet. John Guy mentions, "When Zheng He, the Muslim eunuch leader of the great expeditions to the 'Western Ocean' (Indian Ocean) in the early fifteenth century, embarked on his voyages, it was from the Divine Woman that he sought protection, as well as at the tombs of the Muslim saints on Lingshan Hill, above the city of Quanzhou."
Zheng He was a great-great-great-grandson of Sayyid Ajjal Shams al-Din Omar, who served in the administration of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
and was the governor of Yunnan during the early Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
. His great-grandfather Bayan may have been stationed at a Mongol garrison in Yunnan. Zheng He's grandfather carried the title ''hajji
Hajji (; sometimes spelled Hajjeh, Hadji, Haji, Alhaji, Al-Hadj, Al-Haj or El-Hajj) is an honorific title which is given to a Muslim who has successfully completed the Hajj to Mecca.
Etymology
''Hajji'' is derived from the Arabic ' (), which i ...
'', and his father had the sinicized
Sinicization, sinofication, sinification, or sinonization (from the prefix , 'Chinese, relating to China') is the process by which non-Chinese societies or groups are acculturated or assimilated into Chinese culture, particularly the language, ...
surname Ma and the title ''hajji'', which suggests that they had made the pilgrimage to Mecca
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
.
In the autumn of 1381, a Ming army invaded and conquered Yunnan, which was then ruled by the Mongol prince Basalawarmi
Basalawarmi (, , died January 6, 1382), commonly known by his hereditary noble title, the Prince of Liang, was a Yuan dynasty prince and loyalist who fought against the Ming dynasty. He was a descendant of Khökhechi, the fifth son of Kublai Kha ...
, Prince of Liang. In 1381, Ma Hajji, Zheng He's father, died in the fighting between the Ming armies and Mongol forces. Dreyer states that Zheng He's father died at 39 while resisting the Ming conquest, while Levathes states that Zheng He's father died at 37, but it is unclear if he was helping the Mongol Army or was just caught in the onslaught of battle. Wenming, the oldest son, buried their father outside Kunming. In his capacity as Admiral, Zheng He had an epitaph engraved in honour of his father, composed by the Minister of Rites Li Zhigang on 1 June 1405, which was Duanwu Festival.
Capture and service
Zheng He was captured by the Ming armies in Yunnan in 1381. General Fu Youde saw Ma He on a road and approached him to inquire about the location of the Mongol pretender. Ma He responded defiantly by saying that the Mongol pretender had jumped into a lake. Then the general took him prisoner. He was castrated between the ages of 10 and 14, and placed in the service of the Prince of Yan. Ma He was sent to serve in the household of Zhu Di, the Prince of Yan, who later became theYongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
. Zhu Di was 11 years older than Ma. Enslaved as a eunuch servant, Ma He eventually gained the confidence of Zhu Di, who, as his benefactor, gained the allegiance and loyalty of the young eunuch. The prince had been governing Beiping (modern Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
) since 1380. It was near the northern frontier with hostile Mongol tribes. Ma spent his early life as a soldier on the northern frontier and often participated in Zhu Di's military campaigns against the Mongols. On 2 March 1390, Ma accompanied the prince when he commanded his first expedition, which was a great victory, as the Mongol commander Naghachu surrendered as soon as he realized he had fallen into a trap.
Three Jewels
In Buddhism, refuge or taking refuge refers to a religious practice which often includes a prayer or recitation performed at the beginning of the day or of a practice session. Its object is typically the Three Jewels (also known as the Triple ...
. Ma received a proper education at Beiping, which he would not have had if he had been placed in the imperial capital of Nanjing as the Hongwu Emperor, the father of Zhu Di, did not trust eunuchs and believed that it was better to keep them illiterate. The Hongwu Emperor purged and exterminated much of the original Ming leadership and gave his enfeoffed sons more military authority, especially those in the north, like the Prince of Yan.
Adulthood and military career
Zheng He's appearance as an adult was recorded: he was seven '' chi'' tall, had a waist that was five ''chi'' in circumference, cheeks and a forehead that was high, a small nose, glaring eyes, teeth that were white and well-shaped as shells, and a voice that was as loud as a bell. It is also recorded that he had great knowledge about warfare and was well-accustomed to battle. The young eunuch eventually became a trusted adviser to the prince and assisted him when theJianwen Emperor
The Jianwen Emperor (5 December 1377 – probably 13 July 1402), personal name Zhu Yunwen, also known by his temple name as the Emperor Huizong of Ming and by his posthumous name as the Emperor Hui of Ming, was the second emperor of the Ming d ...
's hostility to his uncle's feudal bases prompted the 13991402 Jingnan Campaign, which ended with the emperor's apparent death and the ascension of Zhu Di, Prince of Yan, as the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
. In 1393, the Crown Prince had died, thus the deceased prince's son became the new heir apparent. By the time the emperor died (24 June 1398), the Prince of Qin and the Prince of Jin had perished, which left Zhu Di, the Prince of Yan, as the eldest surviving son of the emperor. However, Zhu Di's nephew succeeded the imperial throne as the Jianwen Emperor
The Jianwen Emperor (5 December 1377 – probably 13 July 1402), personal name Zhu Yunwen, also known by his temple name as the Emperor Huizong of Ming and by his posthumous name as the Emperor Hui of Ming, was the second emperor of the Ming d ...
. In 1398, he issued a policy known as ''xuēfān'' (), or "reducing the feudatories", which entailed eliminating all princes by stripping their power and military forces. In August 1399, Zhu Di openly rebelled against his nephew. In 1399, Ma He successfully defended Beiping's city reservoir, Zhenglunba, against the imperial armies. In January 1402, Zhu Di began with his military campaign to capture the imperial capital, Nanjing. Zheng He would be one of his commanders during that campaign.
In 1402, Zhu Di's armies defeated the imperial forces and marched into Nanjing on 13 July 1402. Zhu Di accepted the elevation to emperor four days later. After ascending the throne as the Yongle Emperor, Zhu Di promoted Ma He as the Grand Director (, ''tàijiān'') of the Directorate of Palace Servants (). During the Chinese New Year
Chinese New Year, or the Spring Festival (see also #Names, § Names), is a festival that celebrates the beginning of a New Year, new year on the traditional lunisolar calendar, lunisolar Chinese calendar. It is one of the most important holi ...
on 11 February 1404, the Yongle Emperor conferred the surname "Zheng" to Ma He, because he had distinguished himself defending the city reservoir against imperial forces in 1399. Another reason was that the eunuch commander also distinguished himself during the 1402 campaign to capture the capital, Nanjing.
In the new administration, Zheng He served in the highest posts as Grand Director and later as Chief Envoy () during his sea voyages. Over the next three decades he conducted seven of the voyages on behalf of the emperor, trading and collecting tribute in the western Pacific and Indian Oceans.
In 1424, Zheng He traveled to Palembang
Palembang (, Palembang: ''Pelémbang'', Mandarin: 巨港 (Jùgǎng), Hokkien: 舊港 (Kū-káng), Jawi: ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of South Sumatra. The city proper covers on both banks of the Musi River in the ea ...
in Sumatra to confer an official seal and letter of appointment upon Shi Jisun, who was placed in the office of Pacification Commissioner. The ''Taizong Shilu'' 27 February 1424 entry reports that Shi Jisun had sent Qiu Yancheng as envoy to petition the approval of the succession from his father Shi Jinqing, who was the Pacification Commissioner of Palembang, and was given permission from the Yongle Emperor. When Zheng He returned from Palembang, he found that the Yongle Emperor had died during his absence. On 7 September 1424, Zhu Gaozhi had inherited the throne as the Hongxi Emperor after the death of the Yongle Emperor on 12 August 1424.
On 7 September 1424, the Hongxi Emperor
The Hongxi Emperor (16 August 1378 – 29 May 1425), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Renzong of Ming, personal name Zhu Gaochi, was the fourth emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1424 to 1425. He was the eldest son of the Y ...
terminated the undertaking of further treasure voyages. On 24 February 1425, he appointed Zheng He as the defender of Nanjing and ordered him to continue his command over the treasure fleet for the city's defense. On 25 March 1428, the Xuande Emperor ordered Zheng He and others to take over the supervision for the rebuilding and repair of the Great Bao'en Temple at Nanjing. He completed the construction of the temple in 1431.
On 15 May 1426, the Xuande Emperor ordered the Directorate of Ceremonial to send a letter to Zheng He to reprimand him for a transgression. Earlier, an official petitioned the emperor to reward workmen who had built temples in Nanjing. The Xuande Emperor responded negatively to the official for charging the costs to the court instead of the monks themselves, but he realised that Zheng He and his associates had instigated the official. According to , the nature of the emperor's words indicated that Zheng He's behaviour in the situation was the last straw, but there is too little information about what had happened earlier. Nevertheless, the Xuande Emperor would eventually come to trust Zheng He.
In 1430, the new Xuande Emperor appointed Zheng He to command over a seventh and final expedition into the "Western Ocean" (Indian Ocean). In 1431, Zheng He was bestowed with the title ''Sanbao Taijian'' (), using his informal name Sanbao and the title of Grand Director.
Expeditions
 The
The Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
and the expanding Sino-Arab trade during the 14th century had gradually expanded Chinese knowledge of the world since "universal" maps previously displaying only China and its surrounding seas began to expand farther and farther southwest, with much more accurate depictions of the extent of Arabia and Africa. Between 1405 and 1433, the Ming government sponsored seven naval expeditions. The Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
, disregarding the Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328– 24 June 1398), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Ming, personal name Zhu Yuanzhang, courtesy name Guorui, was the List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, founding emperor of the Ming dyna ...
's expressed wishes, designed them to establish a Chinese presence and impose imperial control over the Indian Ocean trade, impress foreign peoples in the Indian Ocean basin, and extend the empire's tributary system. It has also been inferred from passages in the ''History of Ming
The ''History of Ming'' is the final official Chinese history included in the '' Twenty-Four Histories''. It consists of 332 volumes and covers the history of the Ming dynasty from 1368 to 1644. It was written by a number of officials commissio ...
'' that the initial voyages were launched as part of the emperor's attempt to capture his escaped predecessor, which would have made the first voyage the "largest-scale manhunt on water in the history of China."
Zheng He was placed as the admiral in control of the huge fleet and armed forces that undertook the expeditions. Wang Jinghong was appointed as second in command. Preparations were thorough and wide-ranging, including the use of so many linguists that a foreign language institute was established at Nanjing. Zheng He's first voyage departed 11 July 1405, from Suzhou
Suzhou is a major prefecture-level city in southern Jiangsu province, China. As part of the Yangtze Delta megalopolis, it is a major economic center and focal point of trade and commerce.
Founded in 514 BC, Suzhou rapidly grew in size by the ...
and consisted of a fleet of 317 ships holding almost 28,000 crewmen.
Zheng He's fleets visited Brunei
Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. Apart from its coastline on the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak, with ...
, Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, Siam
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
(Thailand), Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, India, the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, and Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, dispensing and receiving goods along the way. Zheng He presented gifts of gold, silver, porcelain
Porcelain (), also called china, is a ceramic material made by heating Industrial mineral, raw materials, generally including kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The greater strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to oth ...
, and silk, and in return, China received such novelties as ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds. Two living species are recognised, the common ostrich, native to large parts of sub-Saharan Africa, and the Somali ostrich, native to the Horn of Africa.
They are the heaviest and largest living birds, w ...
es, zebra
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), the plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. ...
s, camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
s, and ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
from the Swahili Coast
The Swahili coast () is a coastal area of East Africa, bordered by the Indian Ocean and inhabited by the Swahili people. It includes Sofala (located in Mozambique); Mombasa, Gede, Kenya, Gede, Pate Island, Lamu, and Malindi (in Kenya); and Dar es ...
. The giraffe
The giraffe is a large Fauna of Africa, African even-toed ungulate, hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the Largest mammals#Even-toed Ungulates (Artiodactyla), tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on ...
that he brought back from Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban centr ...
was considered to be a ''qilin
The qilin ( ; ) is a legendary hooved chimerical creature that appears in Chinese mythology, and is said to appear with the imminent arrival or death of a sage or illustrious ruler. Qilin are a specific type of the mythological family of o ...
'' and taken as proof of the Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven ( zh, t=天命, p=Tiānmìng, w=, l=Heaven's command) is a Chinese ideology#Political ideologies, political ideology that was used in History of China#Ancient China, Ancient China and Chinese Empire, Imperial China to legit ...
upon the administration. The Daxuexi Alley Mosque in Xi'an has a stele dating to January 1523, inscribed with Zheng He's fourth maritime voyage to Tianfang, Arabian Peninsula.
 While Zheng He's fleet was unprecedented, the routes were not. His fleet followed long-established, well-mapped routes of trade between China and the
While Zheng He's fleet was unprecedented, the routes were not. His fleet followed long-established, well-mapped routes of trade between China and the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
that had been used since at least the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
. That fact, along with the use of a more-than-abundant number of crew members who were regular military personnel, leads some to speculate that the expeditions may have been geared at least partially at spreading China's power through expansion. During the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dyna ...
Period, the king of Wu sent a 20-year diplomatic mission led by Zhu Ying and Kang Tai along the coast of Asia, which reached as far as the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
. After centuries of disruption, the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
restored large-scale maritime trade from China in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans and reached as far as the Arabian Peninsula and East Africa. When his fleet first arrived at Malacca
Malacca (), officially the Historic State of Malacca (), is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the Peninsular Malaysia#Other features, southern region of the Malay Peninsula, facing the Strait of Malacca ...
, there was already a sizable Chinese community. The ''General Survey of the Ocean Shores'' (, ''Yíngyá Shènglǎn''), composed by the translator Ma Huan in 1416, gives very detailed accounts of his observations of people's customs and lives in the ports that they visited. He referred to the expatriate Chinese as " Tang" people ().
 The fleet did not engage in conquest or colonization; though it included troops, their purpose was to demonstrate the Middle Kingdom's strength. However, a contemporary reported that Zheng He "walked like a tiger" and did not shrink from violence when he considered it necessary to impress foreign peoples with China's military might. He ruthlessly suppressed pirates, who had long plagued Chinese and Southeast Asian waters. For example, he defeated Chen Zuyi, one of the most feared and respected pirate captains, and returned him to China for execution. He also waged a land war against the
The fleet did not engage in conquest or colonization; though it included troops, their purpose was to demonstrate the Middle Kingdom's strength. However, a contemporary reported that Zheng He "walked like a tiger" and did not shrink from violence when he considered it necessary to impress foreign peoples with China's military might. He ruthlessly suppressed pirates, who had long plagued Chinese and Southeast Asian waters. For example, he defeated Chen Zuyi, one of the most feared and respected pirate captains, and returned him to China for execution. He also waged a land war against the Kingdom of Kotte
The Kingdom of Kotte (, ), named after its capital, Kotte, was a Sinhalese kingdom that flourished in Sri Lanka during the 15th century.
Founded by Parakramabahu VI with the help of the Ming, the Kingdom managed to conquer the Jaffna ki ...
on Ceylon
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, and he made displays of military force when local officials threatened his fleet in Arabia and East Africa. From his fourth voyage, he brought envoys from 30 states, who traveled to China and paid their respects at the Ming court.
In 1424, the Yongle Emperor died. His successor, the Hongxi Emperor
The Hongxi Emperor (16 August 1378 – 29 May 1425), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Renzong of Ming, personal name Zhu Gaochi, was the fourth emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1424 to 1425. He was the eldest son of the Y ...
(r. 14241425), stopped the voyages during his short reign. Zheng He made one more voyage during the reign of Hongxi's son, the Xuande Emperor (r. 1426–1435) but, the voyages of the Chinese treasure ship fleets then ended. Xuande believed his father's decision to halt the voyages had been meritorious and thus "there would be no need to make a detailed description of his grandfather's sending Zheng He to the Western Ocean." The voyages "were contrary to the rules stipulated in the Huang Ming Zuxun" (), the dynastic foundation documents laid down by the Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328– 24 June 1398), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Ming, personal name Zhu Yuanzhang, courtesy name Guorui, was the List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, founding emperor of the Ming dyna ...
:
Some far-off countries pay their tribute to me at much expense and through great difficulties, all of which are by no means my own wish. Messages should be forwarded to them to reduce their tribute so as to avoid high and unnecessary expenses on both sides.They further violated longstanding Confucian principles. They were only made possible by (and therefore continued to represent) a triumph of the Ming's eunuch faction over the administration's
scholar-bureaucrat
The scholar-officials, also known as literati, scholar-gentlemen or scholar-bureaucrats (), were government officials and prestigious scholars in Chinese society, forming a distinct social class.
Scholar-officials were politicians and governmen ...
s. Upon Zheng He's death and his faction's fall from power, his successors sought to minimize him in official accounts, along with continuing attempts to destroy all records related to the Jianwen Emperor or the manhunt to find him.
Although unmentioned in the official dynastic histories, Zheng He probably died during the treasure fleet's last voyage. Although he has a tomb in China, it is empty since he was buried at sea.
Zheng He led seven expeditions to the "Western" or Indian Ocean. Zheng He brought back to China many trophies and envoys from more than thirty kingdoms, including King Vira Alakeshwara of Ceylon
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, who came to China as a captive to apologize to the Emperor for offenses against his mission.
Zheng He wrote of his travels:
We have traversed more than 100,000 '' li'' of immense water spaces and have beheld in the ocean huge waves like mountains rising in the sky, and we have set eyes on barbarian regions far away hidden in a blue transparency of light vapors, while our sails, loftily unfurled like clouds day and night, continued their course s rapidlyas a star, traversing those savage waves as if we were treading a public thoroughfare....
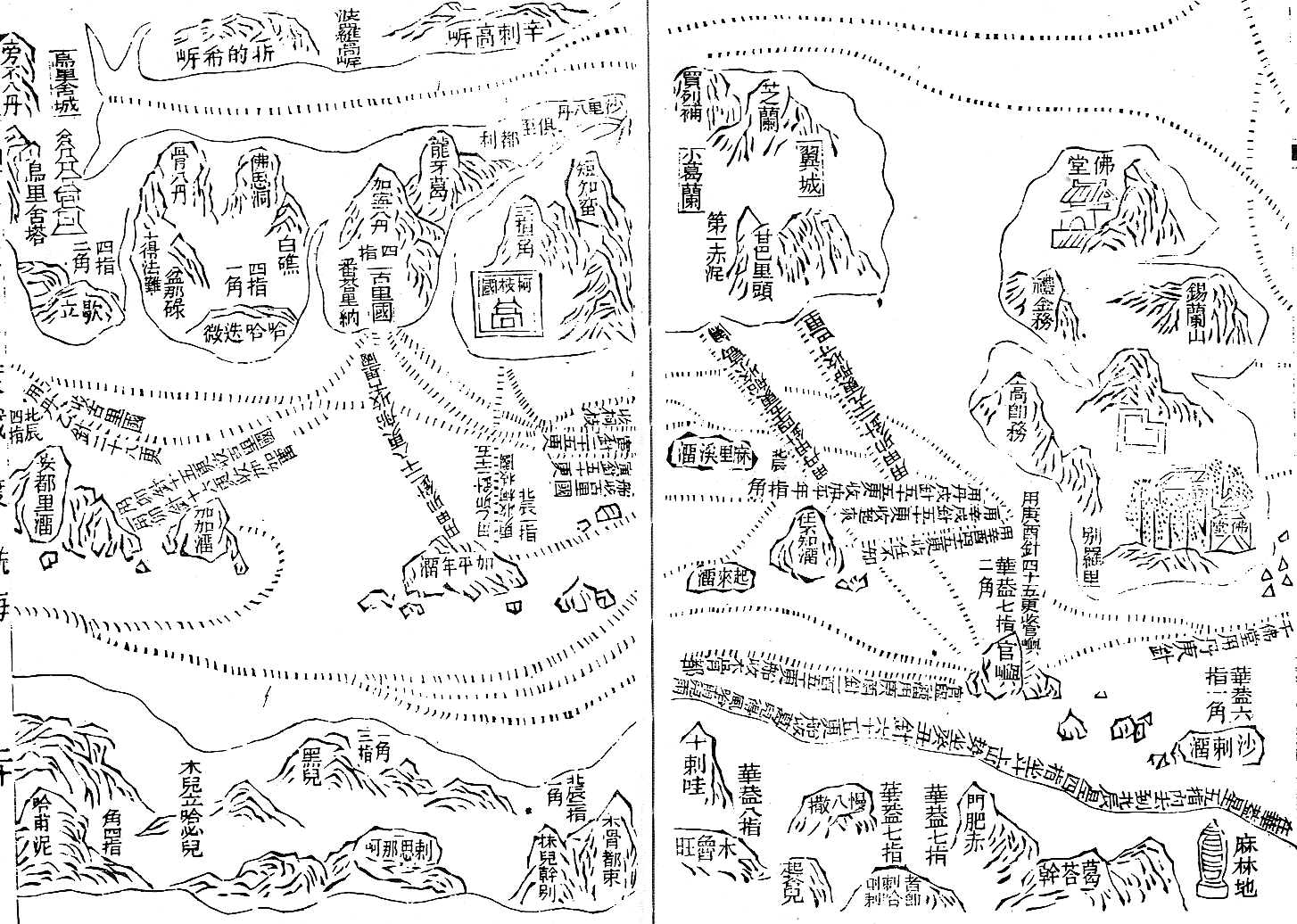
Sailing charts

 Zheng He's sailing charts, the
Zheng He's sailing charts, the Mao Kun map
Mao Kun map, usually referred to in modern Chinese sources as Zheng He's Navigation Map (), is a set of navigation charts published in the Ming dynasty military treatise '' Wubei Zhi''. The book was compiled by in 1621 and published in 1628; the ...
, were published in a book entitled the '' Wubei Zhi'' (''A Treatise on Armament Technology'') written in 1621 and published in 1628 but traced back to Zheng He's and earlier voyages. It was originally a strip map 20.5 cm by 560 cm that could be rolled up, but was divided into 40 pages which vary in scale from 7 miles/inch in the Nanjing area to 215 miles/inch in parts of the African coast.
Investigation into folios 19V to 20R of the Mao Kun Map, which cover the Indian Ocean including South India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and East Africa, suggests that the map is a composite of four maps, one for Sri Lanka, one for South India one for the Maldives and one for around 400 km of the East African coast, no further south than 6 degrees south of the Equator. Each of these maps is positioned at a different orientation to fit with the ocean currents and winds required of a sailing chart, rather than a formal map. The analysis also suggests that Arabic-speaking pilots with a detailed knowledge of the African coast were involved in the cartography.
There is little attempt to provide an accurate 2-D representation; instead, the sailing instructions are given using a 24-point compass system with a Chinese symbol for each point, together with a sailing time or distance, which takes account of the local currents and winds. Sometimes depth soundings are also provided. It also shows bays, estuaries, capes and islands, ports and mountains along the coast, important landmarks such as pagoda
A pagoda is a tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Thailand, Cambodia, Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhist, but some ...
s and temples, and shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and Earth science, geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank (geography), bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body ...
rocks. Of 300 named places outside China, more than 80% can be confidently located. There are also fifty observations of stellar altitude.
Size of ships
According to 's novel ''Sanbao Taijian Xia Xiyang Ji Tongsu Yanyi Sanbao (三宝) may refer to:
* Literally meaning Three Treasures (disambiguation), in various cultural and religious settings
* Sanbao Subdistrict, Beipiao, Liaoning
* Sanbao Township, Guangxi, in Tian'e County
* Sanbao Township, Heilongjiang, in ...
'' (''Eunuch Sanbao Western Records Popular Romance'', published 1597), the first expedition had:
* " Treasure ships" (, ''Bǎo Chuán'') nine-masted, 44.4 by 18 ''zhang'', about long and wide.
* Equine ships (, ''Mǎ Chuán''), carrying horses and tribute goods and repair material for the fleet, eight-masted, 37 by 15 ''zhang'', about long and wide.
* Supply ships (, ''Liáng Chuán''), containing staple for the crew, seven-masted, 28 by 12 ''zhang'', about long and wide.
* Transport ships (, ''Zuò Chuán''), six-masted, 24 by 9.4 ''zhang'', about long and wide.
* Warships (, ''Zhàn Chuán''), five-masted, 18 by 6.8 ''zhang'', about long.
On the ships were navigators, explorers, sailors, doctors, workers, and soldiers, along with the translator and diarist Gong Zhen. Six more expeditions took place from 1407 to 1433, with fleets thought to be of comparable size.
Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
and Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
both described multi-masted ships carrying 500 to 1,000 passengers in their translated accounts. Niccolò de' Conti Niccolò is an Italian male given name, derived from the Greek Nikolaos meaning "Victor of people" or "People's champion".
There are several male variations of the name: Nicolò, Niccolò, Nicolas, and Nicola. The female equivalent is Nicole (name), ...
, a contemporary of Zheng He, was also an eyewitness of ships in Southeast Asia, claiming to have seen five-masted junks weighing about 2,000 ''vegetes'', that is Venetian butt. Christopher Wake estimated a burthen of 1300 tons. The ship of Conti may have been a Burmese or Indonesian jong.
The largest ships in the fleet, the Chinese treasure ships described in Chinese chronicles, would have been nearly twice as long as any other wooden ship recorded thereafter until the 20th century, surpassing Admiral Nelson's HMS ''Victory'', long, which was launched in 1765, and the ''Vasa'' of 1627. The first ships to attain long were 19th century steamers with iron hulls. Many scholars consider it unlikely that any of Zheng He's ships were in length and have proposed much shorter lengths, as low as . Zhao Zhigang claimed that he has solved the debate of the size difference, and stated that Zheng He's largest ship was about in length.
Disputes of historical records of length
 Edward L. Dreyer claims that Luo Maodeng's novel is unsuitable as historical evidence. The novel contains a number of fantasy element; for example the ships were "constructed with divine help by the immortal Lu Ban".
One explanation for the seemingly-inefficient size of the colossal ships was that the 44 ''zhang'' treasure ships were used only by the Emperor and imperial bureaucrats to travel along the Yangtze for court business, including reviewing Zheng He's expedition fleet. The Yangtze river, with its calmer waters, may have been navigable by these treasure ships. Zheng He, a court eunuch, would not have had the privilege in rank to command the largest of the ships, seaworthy or not. The main ships of Zheng He's fleet were instead six-masted 2000-liao ships.Xin Yuanou: ''Guanyu Zheng He baochuan chidu de jishu fenxi (A Technical Analysis of the Size of Zheng He's Ships).'' Shanghai 2002, p. 8 That would give burthen of 500 tons and a displacement tonnage of about 800 tons.
Traditional and popular accounts of Zheng He's voyages have described a great fleet of gigantic ships far larger than any other wooden ships in history. The most grandiose claims for Zheng He's 1405 fleet are entirely based on a calculation derived from an account that was written three centuries later and was accepted as fact by one modern writer; rejected by numerous naval experts. There are even some sources that claim some of the treasure ships might have been as long as . The claims that the Chinese treasure ships reached such size is disputed because other 17th century Ming records stated that European
Edward L. Dreyer claims that Luo Maodeng's novel is unsuitable as historical evidence. The novel contains a number of fantasy element; for example the ships were "constructed with divine help by the immortal Lu Ban".
One explanation for the seemingly-inefficient size of the colossal ships was that the 44 ''zhang'' treasure ships were used only by the Emperor and imperial bureaucrats to travel along the Yangtze for court business, including reviewing Zheng He's expedition fleet. The Yangtze river, with its calmer waters, may have been navigable by these treasure ships. Zheng He, a court eunuch, would not have had the privilege in rank to command the largest of the ships, seaworthy or not. The main ships of Zheng He's fleet were instead six-masted 2000-liao ships.Xin Yuanou: ''Guanyu Zheng He baochuan chidu de jishu fenxi (A Technical Analysis of the Size of Zheng He's Ships).'' Shanghai 2002, p. 8 That would give burthen of 500 tons and a displacement tonnage of about 800 tons.
Traditional and popular accounts of Zheng He's voyages have described a great fleet of gigantic ships far larger than any other wooden ships in history. The most grandiose claims for Zheng He's 1405 fleet are entirely based on a calculation derived from an account that was written three centuries later and was accepted as fact by one modern writer; rejected by numerous naval experts. There are even some sources that claim some of the treasure ships might have been as long as . The claims that the Chinese treasure ships reached such size is disputed because other 17th century Ming records stated that European East Indiamen
East Indiamen were merchant ships that operated under charter or licence for European Trading company, trading companies which traded with the East Indies between the 17th and 19th centuries. The term was commonly used to refer to vessels belon ...
and galleon
Galleons were large, multi-decked sailing ships developed in Spain and Portugal.
They were first used as armed cargo carriers by Europe, Europeans from the 16th to 18th centuries during the Age of Sail, and they were the principal vessels dr ...
s were 30, 40, 50, and 60 ''zhang'' (90, 120, 150, and 180 m) in length.
It is also possible that the measure of ''zhang'' (丈) used in the conversions was mistaken. The length of a Dutch ship recorded in the ''History of Ming'' was 30 ''zhang''. If the ''zhang'' is taken to be 3.2 m, the Dutch ship would be 96 m long. Also the Dutch ''Hongyi'' cannon was recorded to be more than 2 ''zhang'' (6.4 m) long. Comparative study by Hu Xiaowei (2018) concluded that 1 ''zhang'' would be equal to 1.5–1.6 m, this means the Dutch ship would be 45–48 m long and the cannon would be 3–3.2 m long. Taking 1.6 m for 1 ''zhang'', Zheng He's 44 ''zhang'' treasure ship would be long and wide, or 22 ''zhang'' long and 9 ''zhang'' wide if the ''zhang'' is taken to be 3.2 m. It is known that the measure unit during the Ming era was not unified: A measurement of East and West Pagoda in Quanzhou resulted in a ''zhang'' unit of 2.5–2.56 m. According to Chen Cunren, one ''zhang'' in the Ming Dynasty is only half a ''zhang'' in modern times.
Treasure Shipyard excavation
From 2003 to 2004, the Treasure Shipyard was excavated in northwesternNanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
(the former capital of the Ming Dynasty), near the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
. Despite the site being referred to as the "Longjiang Treasure Shipyard" (龍江寶船廠) in the official names, the site is distinct from the actual Longjiang Shipyard, which was located on a different site and produced different types of ships. The Treasure Shipyard, where Zheng He's fleet is believed to have been built in the Ming Dynasty, once consisted of thirteen basins (based on a 1944 map), most of which have now been covered by the construction of buildings in the 20th century. The basins are believed to have been connected to the Yangtze via a series of gates. Three long basins survive, each with wooden structures inside, interpreted to be frames onto which the ships to be built on. The largest basin extends for a length of . While they were long enough to accommodate the largest claimed Zheng He treasure ship, they were not wide enough to fit even a ship half the claimed size. The basin was only wide at most, with only a width showing evidence of structures. They were also not deep enough, being only deep. Other remains of ships in the site indicate that the ships were only slightly larger than the frames that supported them. Moreover, the basin structures were grouped into clusters with large gaps between them, if each cluster was interpreted as a ship framework, then the largest ship would not exceed at most, probably less.
The 2003–2004 excavation also recovered two complete wooden rudderposts from the Treasure Shipyard, in addition to another recovered in 1957. They are made of teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panic ...
and measure
around in length. Zhou Shide (1962) claimed that the first rudderpost recovered was proof of the enormous dimensions of the ships based on his calculations on how big the rudderblade would be. However Church (2010) points out that Zhou was using calculations based on modern steel propeller-driven ships, not wooden ships; as well as the fact that Zhou's hypothetical rudder shape was based on the flat-bottomed ''shachuan'' (沙船) ship type, not the sea-going ''fuchuan'' (福船). The rudderposts cannot be used to infer the actual size of the rudder blades. Church notes that in traditional wooden Chinese ships, rudderposts were necessarily long in order for them to extend from the water level up unto the ship deck, where it was controlled by the tiller. Church compares it with modern wooden junks built in the traditional ''Lümeimao'' ("green eyebrow", 綠眉毛) style, which also have rudderposts that are long, but are only in overall length.
Death
One theory is that Admiral Zheng He died in 1433, during or shortly after his seventh voyage. Another is that Zheng He continued to serve as the defender of Nanjing, and died in 1435. A tomb was built for Zheng He at the southern slope of Cattle Head Hill,Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
. The original tomb was a horseshoe-shaped grave. It is a cenotaph
A cenotaph is an empty grave, tomb or a monument erected in honor of a person or group of people whose remains are elsewhere or have been lost. It can also be the initial tomb for a person who has since been reinterred elsewhere. Although t ...
believed to contain his clothes and headgear. In 1985, the tomb was rebuilt following a Muslim style.
Legacy
Zheng's voyages were long neglected in official Chinese histories but have become well known in China and abroad since the publication ofLiang Qichao
Liang Qichao (Chinese: 梁啓超; Wade–Giles: ''Liang2 Chʻi3-chʻao1''; Yale romanization of Cantonese, Yale: ''Lèuhng Kái-chīu''; ) (February 23, 1873 – January 19, 1929) was a Chinese politician, social and political activist, jour ...
's ''Biography of Our Homeland's Great Navigator, Zheng He'' in 1904.Hui Chun Hing.''Huangming Zuxun'' and Zheng He’s Voyages to the Western Oceans
. ''Journal of Chinese Studies'', No. 51 (July 2010). Retrieved 17 October 2012.
Imperial China
In the decades after the last voyage, Imperial officials minimized the importance of Zheng He and his expeditions throughout the many regnal and dynastic histories they compiled. The information in the Yongle and Xuande Emperors' official annals was incomplete and even erroneous, and other official publications omitted them completely. Although some have seen that as a conspiracy seeking to eliminate memories of the voyages, it is likely that the records were dispersed throughout several departments and the expeditions, unauthorized by and in fact counter to the injunctions of the dynastic founder, presented a kind of embarrassment to the dynasty. State-sponsored Ming naval efforts declined dramatically after Zheng's voyages. Starting in the early 15th century, China experienced increasing pressure from the surviving Yuan Mongols from the north. The relocation of the capital to Beijing in the north exacerbated this threat dramatically. At considerable expense, China launched annual military expeditions from Beijing to weaken the Mongolians. The expenditures necessary for the land campaigns directly competed with the funds necessary to continue naval expeditions. Further, in 1449, Mongolian cavalry ambushed a land expedition personally led by theZhengtong Emperor
, succession = Emperor of the Ming dynasty
, reign-type = First reign
, reign = 31 January 1435 – 22 September 1449
, coronation = 7 February 1435
, cor-type = Enthronement
, regent =
, reg-type = Regents
, ...
at Tumu Fortress, less than a day's march from the walls of the capital. The Mongolians wiped out the Chinese army and captured the emperor. The battle had two salient effects. Firstly, it demonstrated the clear threat posed by the northern nomads. Secondly, the Mongols caused a political crisis in China when they released the emperor after his half-brother had already ascended and declared the new Jingtai era. Not until 1457 and the restoration of the former emperor would political stability return. Upon his return to power, China abandoned the strategy of annual land expeditions and instead embarked upon a massive and expensive expansion of the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' long wall") is a series of fortifications in China. They were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against vario ...
. In that environment, funding for naval expeditions was simply absent.
However, missions from Southeastern Asia continued to arrive for decades. Depending on local conditions, they could reach such frequency that the court found it necessary to restrict them. The ''History of Ming
The ''History of Ming'' is the final official Chinese history included in the '' Twenty-Four Histories''. It consists of 332 volumes and covers the history of the Ming dynasty from 1368 to 1644. It was written by a number of officials commissio ...
'' records imperial edicts forbade Java, Champa, and Siam from sending their envoys more often than once every three years.
Southeast Asia
Veneration
Among theChinese diaspora
Overseas Chinese people are people of Chinese origin who reside outside Greater China (mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan). As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese. As of 2023, there were 10.5 million people livin ...
in Southeast Asia, Zheng He became a figure of folk veneration. Even some of his crew members who happened to stay in some port sometimes did so as well, such as "Poontaokong" on Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilaya' sin Lupa' Sūg''; ), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago.
It was part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamoro Autonomous R ...
.Tan Ta Sen & al. Cheng Ho and Islam in Southeast Asia
'. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, 2009. . The temples of the cult, called after either of his names, Cheng Hoon or Sam Po, are peculiar to overseas Chinese except for a single temple in Hongjian originally constructed by a returned Filipino Chinese in the Ming dynasty and rebuilt by another Filipino Chinese after the original was destroyed during the
Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a Social movement, sociopolitical movement in the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). It was launched by Mao Zedong in 1966 and lasted until his de ...
.
Malacca
The oldest and most important Chinese temple in Malacca is the 17th-century Cheng Hoon Teng, dedicated toGuanyin
Guanyin () is a common Chinese name of the bodhisattva associated with Karuṇā, compassion known as Avalokiteśvara (). Guanyin is short for Guanshiyin, which means " he One WhoPerceives the Sounds of the World". Originally regarded as m ...
. During Dutch colonial rule, the head of the Cheng Hoon Temple was appointed as chief over the community's Chinese inhabitants.
Following Zheng He's arrival, the sultan and the sultana of Malacca visited China at the head of over 540 of their subjects, bearing ample tribute. Sultan Mansur Shah (r. 1459–1477) later dispatched Tun Perpatih Putih as his envoy to China, carrying a letter from the sultan to the Ming emperor. The letter requested the hand of an imperial daughter in marriage. Malay (but not Chinese) annals record that in 1459, a princess named Hang Li Po or Hang Liu was sent from China to marry the sultan. She came with 500 high-ranking young men and a few hundred handmaidens as her entourage. They eventually settled in Bukit Cina. It is believed that a significant number of them married into the local populace, creating the descendants now known as the Peranakan
The Peranakan Chinese () are an ethnic group defined by their genealogical descent from the first waves of Southern Chinese settlers to maritime Southeast Asia, known as Nanyang (region), Nanyang (), namely the British Empire, British, Portugu ...
. Owing to this supposed lineage, the Peranakan still use special honorifics: '' Baba'' for the men and '' Nyonya'' for the women.
Indonesia
The Chinese Indonesian community have established temples dedicated to Zheng He inJakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
, Cirebon
Cirebon (, formerly rendered Cheribon or Chirebon in English) is a port city on the northern coast of the Indonesian island of Java. It is the only coastal city of West Java, located about 40 km west of the provincial border with Central J ...
, Surabaya
Surabaya is the capital city of East Java Provinces of Indonesia, province and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. Located on the northeastern corner of Java island, on the Madura Strai ...
, and Semarang
Semarang (Javanese script, Javanese: , ''Kutha Semarang'') is the capital and largest city of Central Java province in Indonesia. It was a major port during the Netherlands, Dutch Dutch East Indies, colonial era, and is still an important regio ...
.
In 1961, the Indonesian Islamic leader and scholar Hamka credited Zheng He for playing an important role in the development of Islam in Indonesia. The ''Brunei Times'' credits Zheng He with building Chinese Muslim communities in Palembang
Palembang (, Palembang: ''Pelémbang'', Mandarin: 巨港 (Jùgǎng), Hokkien: 舊港 (Kū-káng), Jawi: ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of South Sumatra. The city proper covers on both banks of the Musi River in the ea ...
and along the shores of Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
, and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
. These Muslims allegedly followed the Hanafi
The Hanafi school or Hanafism is the oldest and largest Madhhab, school of Islamic jurisprudence out of the four schools within Sunni Islam. It developed from the teachings of the Faqīh, jurist and theologian Abu Hanifa (), who systemised the ...
school in the Chinese language.
West Asia
There is a monument to Zheng He inSalalah
Salalah () is the capital and largest city of the southern Omani Governorates of Oman, governorate of Dhofar Governorate, Dhofar. It has a population close to 331,949.
Salalah is the third-largest city in the Sultanate of Oman, and the largest ...
, Oman.
Western scholarship
In the 1950s, historians such as John Fairbank andJoseph Needham
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (; 9 December 1900 – 24 March 1995) was a British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science and technology, initia ...
popularized the idea that after Zheng He's voyages China turned away from the seas due to the ''Haijin
The Haijin () or sea ban were a series of related policies in China restricting private maritime trading during much of the Ming dynasty and early Qing dynasty. The sea ban was an anomaly in Chinese history as such restrictions were unknown durin ...
'' edict and was isolated from European technological advancements. Modern historians point out that Chinese maritime commerce did not totally stop after Zheng He, that Chinese ships continued to participate in Southeast Asian commerce until the 19th century, and that active Chinese trading with India and East Africa continued long after the time of Zheng. Moreover, revisionist historians such as Jack Goldstone argue that the Zheng He voyages ended for practical reasons that did not reflect the technological level of China. Although the Ming dynasty prohibited shipping with the ''Haijin'' edict, it was a policy of the Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328– 24 June 1398), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Ming, personal name Zhu Yuanzhang, courtesy name Guorui, was the List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, founding emperor of the Ming dyna ...
that long preceded Zheng He and the ban, so obviously disregarded by the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
, was eventually lifted entirely. However, the ban on maritime shipping forced countless numbers of people into smuggling and piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
. Neglect of the imperial navy and Nanjing dockyards after Zheng He's voyages left the coast highly vulnerable to Japanese wokou
''Wokou'' ( zh, c=, p=Wōkòu; ; Hepburn romanization, Hepburn: ; ; literal Chinese translation: "dwarf bandits"), which translates to "Japanese pirates", were pirates who raided the coastlines of China and Korea from the 13th century to the 17 ...
during the 16th century.
Richard von Glahn, a UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the C ...
professor of Chinese history, commented that most treatments of Zheng He present him wrongly, "offer counterfactual arguments," and "emphasize China's missed opportunity" by focusing on failures, instead of accomplishments. In contrast, Glahn asserts that "Zheng He reshaped Asia" because maritime history in the 15th century was essentially the Zheng He story and the effects of his voyages.
Cultural influence
Despite the official neglect, the adventures of the fleet captured the imagination of some Chinese with some writing novelisations of the voyages, such as the ''Romance of the Three-Jeweled Eunuch'' in 1597.Blacks in Pre-Modern China
', pp. 121–132. On his travels, Zheng He built mosques and also spread the worship of
Mazu
Mazu or Matsu is a sea goddess in Chinese folk religion, Chinese Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism. She is also known by several other names and titles. Mazu is the deified form of Lin Moniang (), a shamaness from Fujian who is said to ...
. He apparently never found time for a pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a travel, journey to a holy place, which can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) w ...
to Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
but sent sailors there on his last voyage. He played an important part in developing relations between China and Islamic countries. Zheng He also visited Muslim shrines of Islamic holy men in the Fujian
Fujian is a provinces of China, province in East China, southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefe ...
.
In modern times, interest in Zheng He has revived substantially. In Vernor Vinge's 1999 science fiction novel '' A Deepness in the Sky'', an interstellar society of commercial traders in human space are named the Qeng Ho, after the admiral. The expeditions featured prominently in Heather Terrell's 2005 novel ''The Map Thief''. For the 600th anniversary of Zheng He's voyages in 2005, China Central Television
China Central Television (CCTV) is the State media, national television broadcaster of China, established in 1958. CCTV is operated by the National Radio and Television Administration which reports directly to the Publicity Department of th ...
produced a special television series, '' Zheng He Xia Xiyang'', starring Gallen Lo as Zheng He. He is also mentioned in part of the main storyline of the first-person shooter game Far Cry 3. The Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the Star Trek: The Original Series, series of the same name and became a worldwide Popular culture, pop-culture Cultural influence of ...
series ''Picard
Picard may refer to:
Places
* Picard, Quebec, Canada
* Picard, California, United States
* Picard (crater), a lunar impact crater in Mare Crisium
People and fictional characters
* Picard (name), a list of people and fictional characters with th ...
'' further featured an advanced starship named USS ''Zheng He''. There was even a US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
boat that was acquired for picket duty during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
that was named ''Cheng Ho'' by its previous owner.
Relics
* Zheng He built the Tianfei Palace (), a temple in honour of thegoddess
A goddess is a female deity. In some faiths, a sacred female figure holds a central place in religious prayer and worship. For example, Shaktism (one of the three major Hinduism, Hindu sects), holds that the ultimate deity, the source of all re ...
Mazu
Mazu or Matsu is a sea goddess in Chinese folk religion, Chinese Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism. She is also known by several other names and titles. Mazu is the deified form of Lin Moniang (), a shamaness from Fujian who is said to ...
, in Nanjing after the fleet returned from its first western voyage in 1407.
* The "Deed of Foreign Connection and Exchange" () or "Tongfan Deed Stele" is located in the Tianfei Palace in Liuhe, Taicang, whence the expeditions first departed. The stele
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
was submerged and lost but has been rebuilt.
* To thank the Celestial Wife for her blessings, Zheng He and his colleagues rebuilt the Tianfei Palace in Nanshan, Changle County, Fujian Province as well before they left on their last voyage. At the renovated temple, they raised a stele, "A Record of Tianfei Showing Her Presence and Power" (), discussing their earlier voyages.
* The Galle Trilingual Inscription
The Galle Trilingual Inscription is a stone tablet with an inscription in three languages, Chinese, Tamil and Persian, located in Galle, Sri Lanka. Dated 15 February 1409, it was installed by the Chinese admiral Zheng He in Galle during his ...
in Sri Lanka was discovered in the city of Galle
Galle (, ; , ) (formerly ) is a major city on the southwestern tip of Sri Lanka, south of Colombo. Galle is the provincial capital and largest city of Southern Province, Sri Lanka and is the capital of Galle District.
Galle was known as ''Gi ...
in 1911 and is preserved at the National Museum of Colombo. The three languages used in the inscription were Chinese, Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
People, culture and language
* Tamils, an ethno-linguistic group native to India, Sri Lanka, and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka
** Myanmar or Burmese Tamils, Tamil people of Ind ...
, and Persian. The inscription praises Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
and describes the fleet's donations to the famous Tenavarai Nayanar temple of Tondeswaram frequented by both Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
and Buddhists
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth ...
.
* Zheng He's tomb in Nanjing has been repaired and a small museum built next to it, but his body was buried at sea off the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast () is the southwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. It generally refers to the West Coast of India, western coastline of India stretching from Konkan to Kanyakumari. Geographically, it comprises one of the wettest regio ...
near Calicut, in western India. However, his sword and other personal possessions were interred in a Muslim tomb inscribed in Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
. The tomb of Zheng He's assistant Hong Bao was recently unearthed in Nanjing as well.
* Seven large sunken ships were found in the sea near Dongsha Island, which were confirmed to belong to Zheng He's fleet. The types of the seven sunken ships were Shachuan (沙船), Fuchuan (福船), and Zhanzuochuan (戰座船).
Commemoration
In the People's Republic of China, 11 July is Maritime Day (, ''Zhōngguó Hánghǎi Rì'') and is devoted to the memory of Zheng He's first voyage. Initially Kunming Changshui International Airport was to be named Zheng He International Airport. In 2015, Emotion Media Factory dedicated a special multimedia show "Zheng He is coming" for amusement park Romon U-Park (Ningbo
Ningbo is a sub-provincial city in northeastern Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises six urban districts, two satellite county-level cities, and two rural counties, including several islands in Hangzhou Bay and the Eas ...
, China). The show became a finalist of the amusement industry prestigious Brass Rings Awards by IAAPA.
Zheng He is the namesake of the ROCS ''Cheng Ho'' missile frigate in Taiwan.
The People's Liberation Army Navy
The People's Liberation Army Navy, also known as the People's Navy, PLA Navy or simply Chinese Navy, is the naval warfare military branch, branch of the People's Liberation Army, the national military of the People's Republic of China. It i ...
ship '' Zheng He (AX-81)'' is a Chinese training ship named for him. Like her namesake, she serves as a goodwill ambassador for China, becoming the first Chinese Navy ship to visit the United States in 1989 and completing a circumnavigation of the globe in 2012.
The proposed sample-return spacecraft ''Tianwen-2
''Tianwen-2'' () is a Chinese asteroid sample return and comet exploration mission that launched on 28 May 2025. China National Space Agency (CNSA) plans for the probe to return samples from asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa in 2027. After the ...
'' was originally named ''ZhengHe''. Its mission to explore Near-Earth asteroid
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit aro ...
2016 HO3 is scheduled to launch in 2025.
Named after the explorer, the Zheng He Seamount is an underwater mountain in the Arabian Sea. It is located southwest of Socotra island at .
Gallery
Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
File:Museum in honour of Zheng He in Nanjing.jpeg, Museum to honour Zheng He, Nanjing
File:Zheng He Gallery in Malacca.JPG, Gallery of Admiral Cheng Ho in Malacca
Malacca (), officially the Historic State of Malacca (), is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the Peninsular Malaysia#Other features, southern region of the Malay Peninsula, facing the Strait of Malacca ...
File:Admiral Zhenghe.jpg, Zheng He wax statue in the Quanzhou Maritime Museum
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * ** ** ** * *Further reading
* *"Shipping News: Zheng He's Sexcentenary"
''China Heritage Newsletter'', June 2005, . Published by the China Heritage Project of The Australian National University. *
External links
World History Encyclopedia – The Seven Voyages of Zheng He
Zheng He – The Chinese Muslim Admiral
(archived)
BBC radio programme "Swimming Dragons".
TIME magazine special feature on Zheng He (August 2001)
from elibraryhub.com
at peopledaily.com (25 September 2006) *
Newsletter, in Chinese, on academic research on the Zheng He voyages
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zheng, He 1371 births 1430s deaths 14th-century Chinese people 15th-century Chinese diplomats 15th-century Chinese military personnel 15th-century explorers Burials at sea Chinese admirals Chinese explorers Explorers of Africa Explorers of Asia Explorers of China Explorers of South Asia History of Kerala Hui people Geographers from Imperial China Ming dynasty eunuchs Ming dynasty Muslims Ming treasure voyages Naval history of China People from Kunming Scientists from Yunnan Travel writers of the medieval Islamic world Year of death uncertain Yongle Emperor