|
469219 Kamoʻoalewa
469219 Kamooalewa (), provisionally designated , is a very small elongated asteroid, fast rotator and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately in diameter. At present it is a quasi-satellite of Earth, and currently the second-smallest, closest, and most stable known such quasi-satellite (after ). The asteroid was discovered by Pan-STARRS at Haleakala Observatory on 27 April 2016. Numerous proposed missions have since targeted the object, including a NASA solar-sail mission,Heiligers, J., Fernandez, J. M., Stohlman, O. R., & Wilkie, W. K. (2019). Trajectory design for a solar-sail mission to asteroid 2016 HO3. Astrodynamics, 3(3), 231-246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42064-019-0061-1 a University of Colorado flyby and impact experiment, and was selected as a target for the Chinese ZhengHe project, which has developed into the Tianwen-2 mission. The chondritic simulants QLS-1, 2, and 3 have been developed by the Qian Xuesen Laboratory of Space Technology to bett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a balanced equilibrium by the fusion of hydrogen into helium at its core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. Astronomers classify it as a G-type main-sequence star. The largest objects that orbit the Sun are the eight planets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianwen-2
''Tianwen-2'' () is a Chinese asteroid sample return and comet exploration mission that launched on 28 May 2025. China National Space Agency (CNSA) plans for the probe to return samples from asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa in 2027. After the mothership drops off the sample return vessel to Earth, it is planned that it will then rendezvous with main-belt comet 311P/PANSTARRS and explore it with its 11 onboard instruments. Overview CNSA launched the ''Tianwen-2'' probe using a Long March 3B carrier rocket on 28 May 2025 from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in southwest China. The probe uses solar electric propulsion for maneuvering between its many objectives. It is planned to explore the co-orbital near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa and the main-belt comet 311P/PANSTARRS. The spacecraft will rendezvous with Kamoʻoalewa and conduct remote sensing observations in orbit, before landing on the asteroid to collect a sample of of regolith. A nano-orbiter and nano- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giordano Bruno (crater)
Giordano Bruno is a Lunar craters, lunar impact crater on the Far side of the Moon, far side of the Moon, just beyond the northeastern limb. It lies in an area that can be viewed during a favorable libration, although the area is viewed from the side and not much detail can be seen. It lies between the craters Harkhebi (crater), Harkhebi to the northwest and Szilard (crater), Szilard to the southeast. When viewed from orbit, Giordano Bruno is at the center of a symmetrical ray system of ejecta that has a higher albedo than the surrounding surface. The ray material extends for over and has not been significantly darkened by space erosion. Some of the ejecta appear to extend as far as the crater Boss (crater), Boss, over to the northwest. The outer rim of the crater is especially bright compared to its surroundings. To all appearances, this is a young formation that was created in the relatively recent past, geologically speaking. Based on photos from a lunar orbiter, the crater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Highland
The geology of the Moon (sometimes called selenology, although the latter term can refer more generally to "lunar science") is the structure and composition of the Moon, which is quite different from that of Earth. The Moon lacks a true atmosphere outside of a sparse layer of gas. Because of this, the absence of free oxygen and water eliminates erosion due to weather. Instead, the surface is eroded much more slowly through the bombardment of the lunar surface by micrometeorites. It does not have any known form of plate tectonics, along with having a lower gravity compared to Earth. Because of its small size, it cooled faster in the early days of its formation. In addition to impacts, the geomorphology of the lunar surface has been shaped by volcanism, which is now thought to have ended less than 50 million years ago. The Moon is a differentiated body, with a crust, mantle, and core. Geological studies of the Moon are based on a combination of Earth-based telescope observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Mare
The lunar maria ( ; mare ) are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by lava flowing into ancient impact basins. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich composition, and hence appear dark to the naked eye. The maria cover about 16% of the lunar surface, mostly on the side visible from Earth. The few maria on the far side are much smaller, residing mostly in very large craters. The traditional nomenclature for the Moon also includes one (ocean), as well as features with the names ('lake'), ('marsh'), and ('bay'). The last three are smaller than maria, but have the same nature and characteristics. The names of maria refer to sea features ( Mare Humorum, Mare Imbrium, Mare Insularum, Mare Nubium, Mare Spumans, Mare Undarum, Mare Vaporum, Oceanus Procellarum, Mare Frigoris), sea attributes ( Mare Australe, Mare Orientale, Mare Cognitum, Mare Marginis), or states of mind ( Mare Crisium, Mare Ingenii, Mare Serenita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
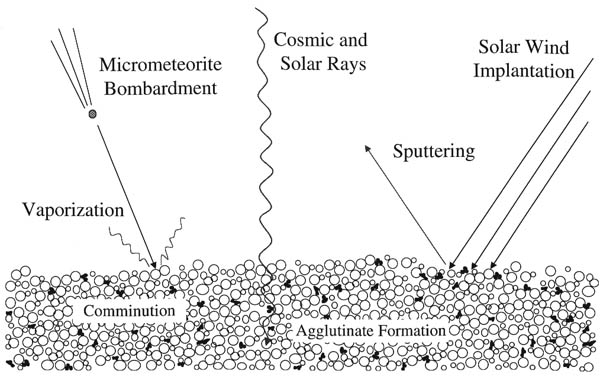
Space Weathering
Space weathering is the type of weathering that occurs to any object exposed to the harsh environment of outer space. Bodies without atmospheres (including the Moon, Mercury, the asteroids, comets, and most of the moons of other planets) take on many weathering processes: * collisions of galactic cosmic rays and solar cosmic rays, * irradiation, implantation, and sputtering from solar wind particles, and * bombardment by different sizes of meteorites and micrometeorites. Space weathering is important because these processes affect the physical and optical properties of the surface of many planetary bodies. Therefore, it is critical to understand the effects of space weathering in order to properly interpret remotely sensed data. History Much of our knowledge of the space weathering process comes from studies of the lunar samples returned by the Apollo program, particularly the lunar soils (or regolith). The constant flux of high energy particles and micrometeorites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkovsky Effect
The Yarkovsky effect is a force acting on a rotating body in space caused by the anisotropic emission of thermal photons, which carry momentum. It is usually considered in relation to meteoroids or small asteroids (about 10 cm to 10 km in diameter), as its influence is most significant for these bodies. History of discovery The effect was discovered by the Polish-Russian civil engineer Ivan Osipovich Yarkovsky (1844–1902), who worked in Russia on scientific problems in his spare time. Writing in a pamphlet around the year 1900, Yarkovsky noted that the daily heating of a rotating object in space would cause it to experience a force that, while tiny, could lead to large long-term effects in the orbits of small bodies, especially meteoroids and small asteroids. Yarkovsky's insight would have been forgotten had it not been for the Estonian astronomer Ernst J. Öpik (1893–1985), who read Yarkovsky's pamphlet sometime around 1909. Decades later, Öpik, recallin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-type Asteroid
L-type asteroids are relatively uncommon asteroids with a strongly reddish spectrum shortwards of 0.75 μm, and a featureless flat spectrum longwards of this. In comparison with the K-type, they exhibit a more reddish spectrum at visible wavelengths and a flat spectrum in the infrared. These asteroids were described as "featureless" S-types in the Tholen classification. The L-type was formally introduced in the SMASS classification, although previous studies had noted the unusual spectra of two of its members 387 Aquitania and 980 Anacostia. There are 41 asteroids classified as L-types in the SMASS taxonomy. Ld-type asteroids The Ld type is a grouping proposed in the SMASS classification for asteroids with an L-like flat spectrum longwards of 0.75 μm, but even redder in visible wavelengths, like the D-type. An example may be 728 Leonisis, although it has also been classified as an A-type. References See also * Asteroid spectral types An asteroid spectral ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejecta
Ejecta (; ) are particles ejected from an area. In volcanology, in particular, the term refers to particles including pyroclastic rock, pyroclastic materials (tephra) that came out of a explosive eruption, volcanic explosion and magma eruption volcano, volcanic vent, or volcanic crater, crater, has traveled through the air or water, and fell back to the ground surface or seabed, ocean floor. Volcanology Typically in volcanology, ejecta is a result of explosive eruptions. In an explosive eruption, large amounts of volcanic gas, gas are dissolved in extremely viscous lava; this lava froths to the surface until the material is expelled rapidly due to the trapped pressure. Sometimes in such an event a lava plug or volcanic neck forms from lava that solidifies inside a volcano's vent, causing heat and pressure to build up to an extreme with no way to escape. When the blockage breaks and cannot sustain itself any longer, a more violent eruption occurs, which allows materials to be e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction (astronomy)
In astronomy, extinction is the absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption and light scattering, scattering of electromagnetic radiation by dust and gas between an emitting astronomical object and the observation, observer. Interstellar extinction was first documented as such in 1930 by Robert Julius Trumpler. However, its effects had been noted in 1847 by Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, and its effect on the colors of stars had been observed by a number of individuals who did not connect it with the general presence of Cosmic dust, galactic dust. For stars lying near the plane of the Milky Way which are within a few thousand parsecs of the Earth, extinction in the visual band of frequencies (photometric system) is roughly 1.8 Magnitude (astronomy), magnitudes per kiloparsec. For Observatory#Ground-based_observatories, Earth-bound observers, extinction arises both from the interstellar medium and the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere; it may also arise fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |