Castration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Castration is any action,
 Castration may have arisen in the Neolithic period in response to animal husbandry, rising populations and population specialisation.
Either surgical removal of both testicles or
Castration may have arisen in the Neolithic period in response to animal husbandry, rising populations and population specialisation.
Either surgical removal of both testicles or
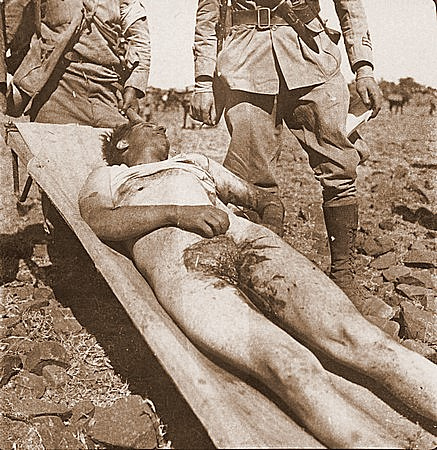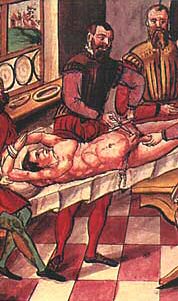
 Castration and other forms of male genital mutilation have been practiced against enemy soldiers and civilians from ancient times to the twenty-first century. Sometimes it is practiced against living boys and men and other times against corpses.
The castration of defeated enemies and the taking of body parts as trophies were traditional in
Castration and other forms of male genital mutilation have been practiced against enemy soldiers and civilians from ancient times to the twenty-first century. Sometimes it is practiced against living boys and men and other times against corpses.
The castration of defeated enemies and the taking of body parts as trophies were traditional in
by Candace Rondeaux for the Washington Post, 5 July 2006 nor is it a form of sterilization."Chemical castration – breaking the cycle of paraphiliac recidivism"
Social Justice, Spring, 1999 by Christopher Meisenkothen. With the advent of chemical castration, physical castration in humans has been widely superseded, though some have undergone the procedure voluntarily.
 Humans commonly castrate domestic animals not intended for breeding.
Domestic animals are usually castrated to avoid unwanted or uncontrolled
Humans commonly castrate domestic animals not intended for breeding.
Domestic animals are usually castrated to avoid unwanted or uncontrolled
Boar taint is only found in a small minority of pigs and can be controlled through breeding selection, diet and management. It is released when the fat is heated and has a distinct odor and flavor that is widely considered unpalatable to consumers.
Consequently, in commercial meat production, male pigs are either castrated shortly after birth or slaughtered before they reach sexual maturity. Recent research in Brazil has shown that castration of pigs is unnecessary because most pigs do not have the 'boar taint'. This is due to many breeds of pigs simply not having the heredity for the boar taint and the fact that pigs are normally slaughtered at a young market weight. In the case of pets, castration is usually called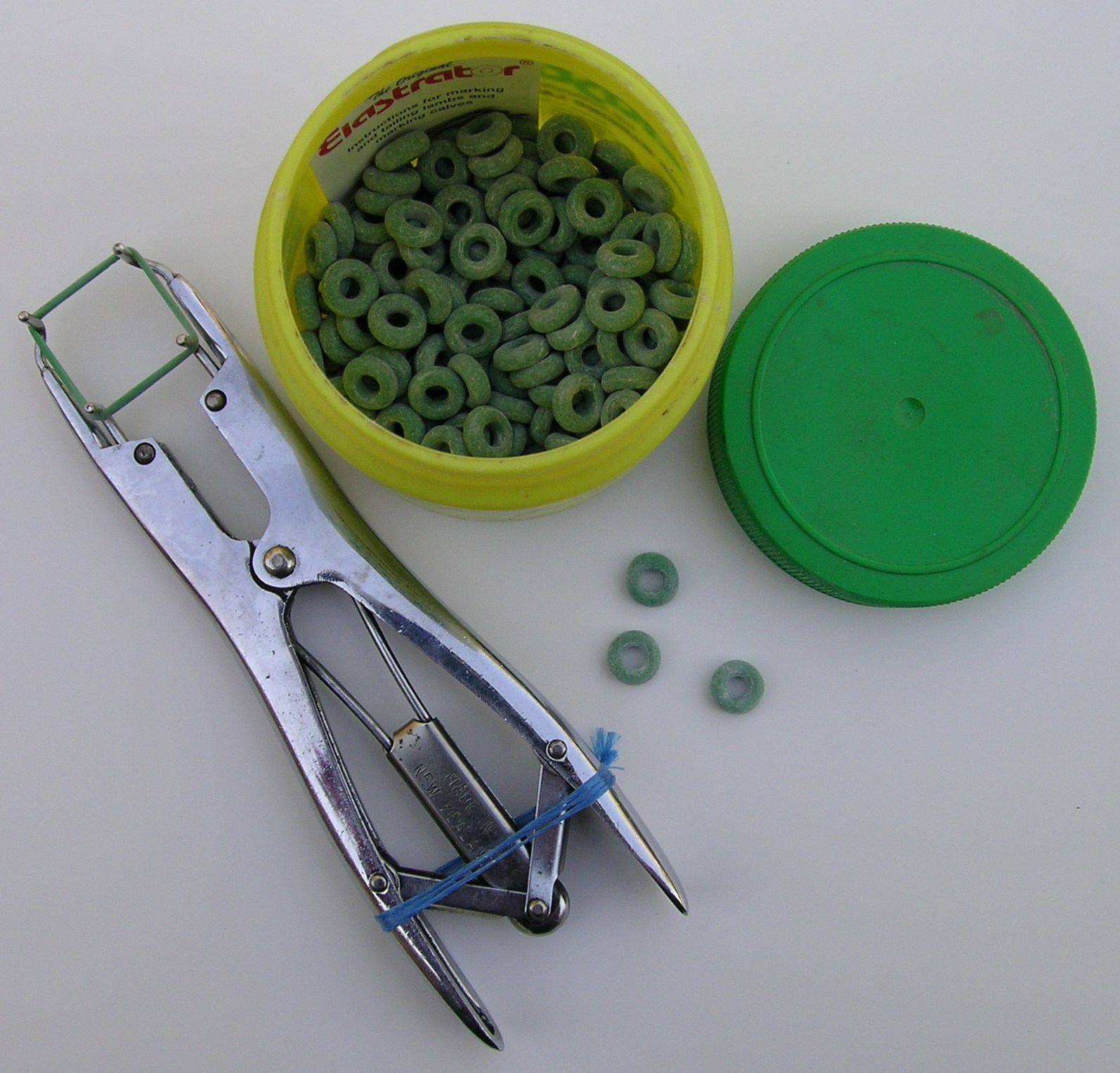 Methods of
Methods of
''Cutting Too Close for Comfort: Paul's Letter to the Galatians in Its Anatolian Cultic Context''
Reviews in Review of Biblical Literature * Theresa McCuaig,
Understanding Castration
" 2009. * * English language Abstracts of the thesis **
Research on the System of Imperial Harem in Liao Dynasty
*** **
Castration Through the Ages
The Journal of Clinical Endrocrinology and Metabolism
Neutering NOT Org
Website arguing against the castration of domestic animals
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20180429222839/http://en.castration.site/ Castration��information site {{Authority control Andrology Corporal punishments Torture Male genital modification Cybele Violence against men Sexual abuse Wartime sexual violence
surgical
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery ...
, chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
, or otherwise, by which a male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
loses use of the testicles
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
: the male gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy
Orchiectomy (also named orchidectomy) is a surgery, surgical procedure in which one or both testicles are removed. The surgery can be performed for various reasons:
*treatment for testicular cancer
*as part of gender-affirming surgery for trans ...
(excision of both testicles), while chemical castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, management of cancer, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike orchiectomy, surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision ...
uses pharmaceutical drug
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...
s to deactivate the testes. Some forms of castration cause sterilization (permanently preventing the castrated person or animal from reproducing); it also greatly reduces the production of hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s, such as testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
and estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
. Surgical castration in animals is often called neutering
Neutering, from the Latin ('of neither sex'), is the removal of a non-human animal's sex organ, reproductive organ, either all of it or a considerably large part. The male-specific term is castration, while spaying is usually reserved for female ...
.
Castration of animals is intended to favor a desired development of the animal or of its habits, as an anaphrodisiac
An anaphrodisiac (also antaphrodisiac or antiaphrodisiac) is a substance that quells or blunts the libido. It is the opposite of an aphrodisiac, something that enhances sexual appetite. The word ''anaphrodisiac'' comes from the Greek privati ...
or to prevent overpopulation
Overpopulation or overabundance is a state in which the population of a species is larger than the carrying capacity of its environment. This may be caused by increased birth rates, lowered mortality rates, reduced predation or large scale migr ...
. The parallel of castration for female animals is spaying. Castration may also refer medically to oophorectomy
Oophorectomy (; from Greek , , 'egg-bearing' and , , 'a cutting out of'), historically also called ''ovariotomy'', is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference ...
in female humans and animals.
The term ''castration'' may also be sometimes used to refer to emasculation where both the testicles ''and'' the penis are removed together. In some cultures, and in some translations, no distinction is made between the two.
History
 Castration may have arisen in the Neolithic period in response to animal husbandry, rising populations and population specialisation.
Either surgical removal of both testicles or
Castration may have arisen in the Neolithic period in response to animal husbandry, rising populations and population specialisation.
Either surgical removal of both testicles or chemical castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, management of cancer, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike orchiectomy, surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision ...
may be carried out in the case of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
. Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
-depletion treatment (either surgical removal of both testicles or chemical castration) is used to slow down the cancer. Surgical removal of one or both testicles known as orchidectomy is the most common treatment for testicular cancer.
Castration has also been used in the United States for sex offender
A sex offender (sexual offender, sex abuser, or sexual abuser) is a person who has committed a Sex and the law, sex crime. What constitutes a sex crime differs by culture and legal jurisdiction. The majority of convicted sex offenders have convi ...
s as a way of avoiding incarceration. It can greatly reduce sex drive or interest in those with sexual drives, obsessions, or behaviors, or any combination of those that may be considered deviant .
Involuntary castration appears in the history of warfare, sometimes used by one side to torture or demoralize their enemies.
Africa and the Middle East
Over the 13 centuries of the Arab slave trade in Africa, unknown numbers of Africans were enslaved and shipped to the Middle East. "The Caliphate in Baghdad at the beginning of the 10th Century had 7,000 black eunuchs and 4,000 white eunuchs in his palace." The Arab slave trade typically dealt in the sale of castrated male slaves. Black boys at the age of eight to twelve had their penises and scrota completely amputated. Reportedly, about two out of three boys died, but those who survived drew high prices.Europe
Slavery
The employment or enslavement of eunuchs (castrated men) was practiced in classical and Roman antiquity and continued into the Middle Ages. In the 10th century, slave traders in Verdun in France and in Becâne ( Pechina), Spain, castrated captives who were then enslaved as harem attendants inAl-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
.
Punishment
Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English essayist, historian, and politician. His most important work, ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1789, is known for ...
's ''Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire
''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', sometimes shortened to ''Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', is a six-volume work by the English historian Edward Gibbon. The six volumes cover, from 98 to 1590, the peak of the Ro ...
'' reports castration of defeated Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Medieval Greek, Greek-speaking Eastern Romans throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia ...
at the hands of the Frankish marquis Theobald Theobald is a Germanic dithematic name, composed from the elements '' theod-'' "people" and ''bald'' "bold". The name arrived in England with the Normans.
The name occurs in many spelling variations, including Theudebald, Diepold, Theobalt, Ty ...
of Camerino and Spoleto in the course of 10th-century wars in Italy. Gibbon also alludes to a 12th-century incident set out in William Fitzstephen
William Fitzstephen (also William fitz Stephen), (died c. 1191) was a cleric and administrator in the service of Thomas Becket. In the 1170s, he wrote a long biography of Thomas Becket – the ''Vita Sancti Thomae'' (Life of St. Thomas).
Fitzste ...
's ''Vita Sancti Thomae'' (''Life of St. Thomas'') in which Geoffrey of Anjou
Geoffrey V (24 August 1113 – 7 September 1151), called the Fair (), Plantagenet, and of Anjou, was the count of Anjou and Maine by inheritance from 1129, and also duke of Normandy by his marriage claim and conquest, from 1144.
Geoffrey m ...
castrated the members of the cathedral chapter of Sens
Sens () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yonne Departments of France, department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France, 120 km southeast from Paris.
Sens is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture and the second la ...
as a punishment for disobedience. In the medieval kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia (), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a Middle Ages, medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in Anno Domini, AD. It reached Georgian Golden Age, its Golden Age of political and economic strength during the reign ...
, the 12th-century pretender
A pretender is someone who claims to be the rightful ruler of a country although not recognized as such by the current government. The term may often be used to either refer to a descendant of a deposed monarchy or a claim that is not legitimat ...
Demna was castrated by his uncle George III of Georgia to ensure the supremacy of George's branch of the family. Another victim of castration was the 12th-century medieval French philosopher, scholar, teacher, and (later) monk Pierre Abélard. He was castrated by relatives of his lover, Héloïse. Bishop Wimund, a 12th-century English adventurer and invader of the Scottish coast, was blinded and castrated after losing a power struggle. In medieval England, men found guilty of high treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its d ...
were hanged, drawn and quartered
To be hanged, drawn and quartered was a method of torture, torturous capital punishment used principally to execute men convicted of High treason in the United Kingdom, high treason in medieval and early modern Britain and Ireland. The convi ...
, which often included emasculation (removal of the genitalia).

Modern era
Wim Deetman was criticized by the Dutch parliament for excluding evidence of castration in his report on sexual abuse by the Roman Catholic Church, where ten children were allegedly "punished" by castration in the 1950s for reporting sexual abuse by Roman Catholic priests. The Deetman Commission had rejected it as the person who reported the incident admitted it was speculative. In Spain, a law against castration was used to deny sex-reassignment surgery to transgender people until the Penal Code was reformed in 1983.China
According to legend, during the reign of the legendary Emperor Shun and Yu in China, in 2281 BC, castration was passed into law as a punishment, remaining so until the reign of Gaozu of Tang (618–626 AD). However, it was still practiced after his reign. According to historians, it was incorporated into Chinese law during the Zhou dynasty. It was one of the five physical punishments that could be legally inflicted on criminals in China. Records of castrations in China date to theShang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
(–1050 BC), when the Shang kings castrated prisoners of war.
During the reign of Mu of the Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 BC, the longest span of any dynasty in Chinese history. During the Western Zhou period (771 BC), the royal house, surnamed Ji, had military ...
(10th c. BC) the Minister of Crime, Marquis Lu, reformed the law in 950 BC to make it easier for people to be sentenced to castration instead of death. As long as the practice existed in China, not only were the testicles removed but castration included the severing of one's entire genitalia. Both organs were cut off with a knife at the same time.
Men were castrated and made into state slaves during the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng enga ...
(221–206 BC) to perform forced labor for projects such as the Terracotta Army
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting him in his aft ...
. The Qin government confiscated the property and enslaved the families of rapists who received castration as a punishment. Men punished with castration during the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
were also used as slave labor.
In the Han dynasty (206 BC–220 AD), castration continued to be used as a punishment for various offences. Chinese historian Sima Qian
Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China cov ...
was castrated by order of the Han Emperor of China for dissent. In another incident multiple people, including a chief scribe and his underlings, were subjected to castration.
During the early part of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
(1368–1644 AD), China demanded eunuchs to be sent as tribute from Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
. Some of them oversaw the Korean concubines in the harem of the Chinese Emperor.
When the Chinese overthrew Mongol rule, many Mongol captives were castrated and turned into eunuchs. When the Ming army finally captured Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
from Mongols in 1382, thousands of prisoners were killed and, according to the custom in times of war, their young sons—including Zheng He
Zheng He (also romanized Cheng Ho; 1371–1433/1435) was a Chinese eunuch, admiral and diplomat from the early Ming dynasty, who is often regarded as the greatest admiral in History of China, Chinese history. Born into a Muslims, Muslim famil ...
—were castrated.
During the Miao Rebellions (Ming dynasty), Chinese commanders castrated thousands of Miao Miao may refer to:
* Miao people, linguistically and culturally related group of people, recognized as such by the government of the People's Republic of China
* Miao script or Pollard script, writing system used for Miao languages
* Miao (Unicode ...
boys when their tribes revolted, and then distributed them as eunuch slaves as gifts to various officials.
At the end of the Ming dynasty, there were about 70,000 eunuchs (宦官 ''huànguān'', or 太監 ''tàijiàn'') employed by the emperor, with some serving inside the Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is the Chinese Empire, imperial Chinese palace, palace complex in the center of the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City in Beijing, China. It was the residence of 24 Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing dynasty L ...
.
The last imperial eunuch in China was Sun Yaoting who died in 1996.
Non-Han peoples in China
TheKhitan people
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical Eurasian nomads, nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
...
adopted the practice of using eunuchs from the Chinese and the eunuchs used were non-Khitan prisoners of war. The Khitan were a nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic Mongolic people and originally did not have eunuchs as part of their culture. When the Khitan founded the Liao dynasty they developed a harem
A harem is a domestic space that is reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic Domestic worker, servants, and other un ...
system with concubines and wives and adopted eunuchs as part of it. All of the eunuchs captured were ethnic Chinese from the Central Plains that came from two sources. The Khitan captured Chinese people who were already eunuchs at the Jin court when they invaded the Later Jin. Another source was during their war with the Chinese Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
: the Khitan would raid China, capture Han Chinese boys as prisoners of war and emasculate them to become eunuchs. The emasculation of captured Chinese boys guaranteed a continuous supply of eunuchs to serve in the Liao dynasty harem. The Empress Dowager Xiao Chuo (Chengtian) played a large role in the raids to capture and emasculate the boys.
Chengtian took power at age 30 in 982 as a regent for her son. Some reports suggest that she personally led her own army against the Song Chinese in 986. Her army defeated them in battle, fighting the retreating Chinese army. She then ordered the castration of around 100 ethnic Chinese boys she had captured in China, supplementing the Khitan's supply of eunuchs to serve at her court, among them was Wang Ji'en. The boys were all under ten years old and were selected for their good looks.
The '' History of Liao'' described and praised Empress Chengtian's capture and mass castration of the Chinese boys in a biography on Wang Ji'en.
Some legends say that the Mongol Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
was castrated by a Tangut princess using a knife, who wanted revenge against his treatment of the Tanguts and to stop him from raping her.
During the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
(1644–1911 AD), the sons and grandsons of the rebel Yaqub Beg in China were all sentenced to castration. Surviving members of Yaqub Beg's family included his four sons, four grandchildren (two grandsons and two granddaughters), and four wives. They either died in prison in Lanzhou
Lanzhou is the capital and largest city of Gansu province in northwestern China. Located on the banks of the Yellow River, it is a key regional transportation hub, connecting areas further west by rail to the eastern half of the country. His ...
, Gansu, or were killed by the Chinese. His sons Yima Kuli, K'ati Kuli, Maiti Kuli, and grandson Aisan Ahung were the only survivors in 1879. They were all underage children, and put on trial, sentenced to an agonizing death if they were complicit in their father's rebellious "sedition", or if they were innocent of their fathers crimes, were to be sentenced to castration and serving as eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2 ...
slaves to Chinese troops, when they reached 11 years old, and handed over to the Imperial Household to be executed or castrated. Although some sources assert that the sentence of castration was carried out, official sources from the US State Department and activists involved in the incident state that Yaqub Beg's son and grandsons had their sentence commuted to life imprisonment with a fund provided for their support.
Korea
The eunuchs of Korea, called (), were officials to the king and other royalty in traditional Korean society. The first recorded appearance of a Korean eunuch was inGoryeosa
''Goryeosa'' (), or ''History of Goryeo'', is an extensive historical record of the Goryeo dynasty, compiled by the officials of Goryeo's successor state, Joseon. Its compilation started during the reign of Taejo of Joseon, Taejo (the founding ...
("History of Goryeo"), a compilation about the Goryeo
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean state founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korea, Korean Peninsula until the establishment of Joseon in 1392. Goryeo achieved what has b ...
period. In 1392, with the founding of the Joseon dynasty
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom w ...
, the system was revised, and the department was renamed the "Department of " ().
The system included two ranks, those of (, "Chief of "), who held the official title of senior second rank, and (, "Common official "), both of which held rank as officers. 140 in total served the palace in Joseon dynasty period. They also took the exam on Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of li ...
every month. The system was repealed in 1894 following Gabo reform
The Kabo Reform () describes a series of sweeping reforms suggested to the government of Korea, beginning in 1894 and ending in 1896 during the reign of Gojong of Korea in response to the Donghak Peasant Revolution. Historians debate the degre ...
.
According to legend, castration consisted of daubing a boy's genitals with human feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
and having a dog bite them off. During the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
, eunuchs became a desirable commodity for tributes, and dog bites were replaced by more sophisticated surgical techniques.
Vietnam
The Vietnamese adopted the eunuch system and castration techniques from China. Records show that the Vietnamese performed castration in a painful procedure by removing the entire genitalia with both penis and testicles being cut off with a sharp knife or metal blade. The procedure was agonizing since the entire penis was cut off. The young man's thighs and abdomen would be tied, and others would pin him down on a table. The genitals would be washed with pepper water and then cut off. A tube would be then inserted into the urethra to allow urination during healing. Many Vietnamese eunuchs were products of self-castration in order to gain access to the palaces and power. In other cases, they might be paid to become eunuchs. They served in many capacities, from supervising public works, to investigating crimes, to reading public proclamations. Lý Thường Kiệt was a prominent eunuch general during theLý dynasty
The Lý dynasty (, , chữ Nôm: 茹李, chữ Hán: 朝李, Vietnamese language, Vietnamese: ''triều Lý''), officially Đại Cồ Việt (chữ Hán: 大瞿越) from 1009 to 1054 and Đại Việt (chữ Hán: 大越) from 1054 to 1225, was ...
(1009–1225).
The Trần dynasty
The Trần dynasty (Vietnamese language, Vietnamese: Nhà Trần, chữ Nôm: 茹陳; Vietnamese language, Vietnamese: triều Trần, chữ Hán: ikt:朝ikt:陳, 朝wikt:陳, 陳), officially Đại Việt (Chữ Hán: 大越), was a List ...
sent Vietnamese boy eunuchs as tribute to Ming dynasty China several times, in 1383, 1384 and 1385Tsai (1996), p. 15 Nguyen Dao, Nguyen Toan, Tru Ca, and Ngo Tin were among several Vietnamese eunuchs sent to China.
During the Fourth Chinese domination of Vietnam, the Ming Chinese under the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
castrated many young Vietnamese boys, choosing them for their handsomeness and ability, and brought them to Nanjing to serve as eunuchs. Among them were the architect-engineer Nguyễn An and Nguyen Lang (). Vietnamese were among the many eunuchs of different origins found at Yongle's court. Among the eunuchs in charge of the Capital Battalions of Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
was Xing An, a Vietnamese.
In the Lê dynasty
The Lê dynasty, also known in historiography as the Later Lê dynasty (, chữ Hán: 朝後黎, chữ Nôm: 茹後黎), officially Đại Việt (; Chữ Hán: 大越), was the longest-ruling List of Vietnamese dynasties, Vietnamese dynasty, h ...
the Vietnamese Emperor Lê Thánh Tông was aggressive in his relations with foreign countries including China. A large amount of trade between Guangdong and Vietnam happened during his reign. Early accounts recorded that the Vietnamese captured Chinese whose ships had blown off course and detained them. Young Chinese men were selected by the Vietnamese for castration to become eunuch slaves to the Vietnamese. It has been speculated by modern historians that the Chinese who were captured and castrated by the Vietnamese were involved in trade between China and Vietnam instead of actually being blown off course by the wind and they were punished as part of a crackdown on foreign trade by Vietnam.
Several Malay envoys from the Malacca sultanate
The Malacca Sultanate (; Jawi script: ) was a Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Parameswara, also known as I ...
were attacked and captured in 1469 by the Lê dynasty of Annam (Vietnam) as they were returning to Malacca from China. The Vietnamese enslaved and castrated the young from among the captured.
A 1472 entry in the Ming Shilu
The ''Ming Veritable Records'' or ''Ming Shilu'' (), contains the imperial annals of the emperors of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). It is the single largest historical source of information on the dynasty. According to modern historians, it "p ...
reported that when some Chinese from Nanhai county
Nanhai County was a former county in Guangdong Province, China, named after the South China Sea.
Its former area now makes up Chancheng and Nanhai Districts in Foshan, and Liwan District in Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Chinese postal romanizatio ...
escaped back to China after their ship had been blown off course into Vietnam, where they had been forced to serve as soldiers in Vietnam's military. The escapees also reported that they found out up to 100 Chinese men remained captives in Vietnam after they were caught and castrated by the Vietnamese after their ships were blown off course into Vietnam. The Chinese Ministry of Revenue responded by ordering Chinese civilians and soldiers to stop going abroad to foreign countries. China's relations with Vietnam during this period were marked by the punishment of prisoners by castration.
A 1499 entry in the Ming Shilu recorded that 13 Chinese men from Wenchang including a young man named Wu Rui were captured by the Vietnamese after their ship was blown off course while traveling from Hainan
Hainan is an island provinces of China, province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally mean ...
to Guangdong
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty ...
's Qin subprefecture ( Qinzhou), after which they ended up near the coast of Vietnam, during the Chenghua Emperor
The Chenghua Emperor (9 December 1447 – 9 September 1487), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Xianzong of Ming, personal name Zhu Jianshen, changed to Zhu Jianru in 1457, was the ninth emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1464 ...
's rule (1447–1487). Twelve of them were enslaved to work as agricultural laborers, while the youngest, Wu Rui was selected for castration since he was the only young man and he became a eunuch attendant at the Vietnamese imperial palace in Thang Long. After years of service, he was promoted at the death of the Vietnamese ruler in 1497 to a military position in northern Vietnam. A soldier told him of an escape route back to China and Wu Rui escaped to Longzhou. The local chief planned to sell him back to the Vietnamese, but Wu was rescued by the Pingxiang magistrate and then was sent to Beijing to work as a eunuch in the palace.
The ''Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư
The ''Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư'' ( vi-hantu, 大越史記全書; ; ''Complete Annals of Đại Việt'') is the official national chronicle of the Đại Việt, that was originally compiled by the royal historian Ngô Sĩ Liên under ...
'' records that in 1467 in An Bang province of Dai Viet (now Quảng Ninh Province) a Chinese ship blew off course onto the shore. The Chinese were detained and not allowed to return to China as ordered by Le Thanh Tong. This incident may be the same one where Wu Rui was captured.Cooke (2011), p. 109
In the Nguyễn dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (, chữ Nôm: 茹阮, chữ Hán: 朝阮) was the last List of Vietnamese dynasties, Vietnamese dynasty, preceded by the Nguyễn lords and ruling unified Vietnam independently from 1802 until French protectorate in 1883 ...
the poet Hồ Xuân Hương mocked eunuchs in her poem as a stand-in for criticizing the government.
Commoners were banned from undergoing castration in Vietnam; only adult men of high social rank could be castrated. Most eunuchs were born as such with a congenital abnormality. The Vietnamese government mandated that boys born with defective genitalia were to be reported to officials, in exchange for the town being freed from mandatory labor requirements. The boy would have the option of serving as a eunuch official or serving the palace women when he became ten years old. This law was put in place in 1838 during the Nguyễn dynasty. The only males allowed inside the Forbidden City at Huế
Huế (formerly Thừa Thiên Huế province) is the southernmost coastal Municipalities of Vietnam, city in the North Central Coast region, the Central Vietnam, Central of Vietnam, approximately in the center of the country. It borders Quảng ...
were the Emperor and his eunuchs.
The presence of eunuchs in Vietnam was used by the French colonizers to degrade the Vietnamese.
Americas
In 1778,Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
wrote a bill in Virginia reducing the punishment for rape, polygamy, or sodomy from death to castration. Over the years, several U.S. states have passed laws regarding chemical castration for sex offenders but not one state has mandatory castration. In 2016, Alabama lawmaker Steve Hurst proposed a bill requiring certain sex offenses to require the perpetrator be castrated prior to their release from state custody.
A 1969 study found that men institutionalized at the same facility in Kansas lived an extra 14 years, on average, if they were castrated.
In 1983, Judge C. Victor Pyle sentenced three men convicted of rape to choose between 30 years in prison or castration. The South Carolina Supreme Court ruled that the castration option would be cruel, however, and the men were sentenced to prison.
Prevention of crime
Chemical or surgical castration is practiced in many countries for people convicted of sex crimes as a prerequisite for their release from prison. The castration may be voluntary or mandated. The assumption is that it prevents future crimes. Reports are available from American and European countries for over 80 years (chemical for circa 30). The effectiveness and ethics of this treatment are heavily debated. A ''temporary'' "chemical castration" has been studied and developed as a preventive measure andpunishment
Punishment, commonly, is the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon an individual or group, meted out by an authority—in contexts ranging from child discipline to criminal law—as a deterrent to a particular action or beh ...
for several repeated sex crimes, such as rape or other sexually related violence. Where homosexuality has been criminalised or treated as a mental illness, chemical castration has been used on gay men, as in the case of Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer ...
.
In modern times, the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
practices surgical castration of convicted sex offenders. According to the reports compiled by Council of Europe, a human-rights forum, the central European country physically castrated at least 94 prisoners in the 10 years up to April 2008. The Czech Republic defends this procedure as voluntary and effective. According to Dr. Martin Hollý, director of the Psychiatric Hospital Bohnice in Prague, none of the nearly 100 sex offenders who had been physically castrated had committed further offences. One serial offender stated that being castrated was the "best decision" he ever made: "On the one hand you have to protect the potential victims and on the other hand I wanted to be protected from myself, I wanted to live like a normal person." Don Grubin, a professor at Newcastle University
Newcastle University (legally the University of Newcastle upon Tyne) is a public research university based in Newcastle upon Tyne, England. It has overseas campuses in Singapore and Malaysia. The university is a red brick university and a mem ...
's Institute of Neuroscience who also runs a chemical castration program backed by the UK's Ministry of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice, is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a ...
, was initially opposed to physical castration. After visiting the Czech Republic, however, he agreed that some form of castration might be of benefit to some sex offenders.
In 2020, the Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
i-controlled section of Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
passed a bill allowing for convicted child sex abusers to be chemically or surgically castrated.
In 2020, a motion calling for surgical castration of convicted rapists was defeated in the Nigerian House of Representatives
The House of Representatives (also called Green Chamber) is the lower chamber of Nigeria's bicameral National Assembly. The Senate is the upper chamber.
The Green Chamber has 360 members who are elected in single-member constituencies using t ...
. However, there remains support for the policy.
In 2024, Louisiana became the first U.S. state to allow judges to impose castration on sex offenders. Previously, in several states, convicted offenders could choose castration, including where it was a prerequisite for parole. However, should the person choose to remain in prison, they would not be forced to be castrated.
Criticism
Some criminologists argue that the reported lower recidivism rates in castrated male sex offenders compared to non-castrated ones does not conclusively prove that it is a biological effect of castration, but might be explained by other factors. One suggested factor fromgame theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed ...
is that men who are willing to accept castration to get a shorter prison sentence are those who value freedom from prison higher than men who are not willing to pay the price for freedom in the form of their testicles. This hypothesis could explain their apparent lower recidivism as a result of working harder to conceal the evidence for their crimes, and argue that their parole is a danger of releasing offenders who only hide their crimes more efficiently and are not any less likely to commit new crimes. These criminologists also argue that police investigators treating castrated men as less likely to reoffend than non-castrated men may cause an investigation bias and self-fulfilling prophecy A self-fulfilling prophecy is a prediction that comes true at least in part as a result of a person's belief or expectation that the prediction would come true. In the phenomena, people tend to act the way they have been expected to in order to mak ...
.
Torture and war crimes
 Castration and other forms of male genital mutilation have been practiced against enemy soldiers and civilians from ancient times to the twenty-first century. Sometimes it is practiced against living boys and men and other times against corpses.
The castration of defeated enemies and the taking of body parts as trophies were traditional in
Castration and other forms of male genital mutilation have been practiced against enemy soldiers and civilians from ancient times to the twenty-first century. Sometimes it is practiced against living boys and men and other times against corpses.
The castration of defeated enemies and the taking of body parts as trophies were traditional in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, and Ethiopian forces practiced castration and emasculation during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War
The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression waged by Fascist Italy, Italy against Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia, which lasted from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethiopia it is oft ...
(1935–1937). Italian aviator Tito Minniti was allegedly one victim of this practice.
One British RAF officer, G. C. Gardiner DSO DFC, is recorded as having been castrated after a crash landing in Syria. During the Mau Mau uprising
The Mau Mau rebellion (1952–1960), also known as the Mau Mau uprising, Mau Mau revolt, or Kenya Emergency, was a war in the British Kenya Colony (1920–1963) between the Kenya Land and Freedom Army (KLFA), also known as the Mau Mau, and the ...
, there were reported instances of British security forces castrating Kenyan detainees in internment camps
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simp ...
.
A video released during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
appeared to show Russian soldiers castrating a Ukrainian captive with a box cutter
A utility knife is any type of knife used for general manual work purposes.Peterson, Harold L., ''Daggers and Fighting Knives of the Western World'', London: Herbert Jenkins Ltd., , p. 1 Such knives were originally fixed-blade knives with dura ...
. This led to a wave of international condemnation against the Russian military for its use of torture in wartime. Many other cases of Russian troops castrating Ukrainian prisoners of war have also emerged. According to the prosecutors
A prosecutor is a legal representative of the prosecution in states with either the adversarial system, which is adopted in common law, or inquisitorial system, which is adopted in Civil law (legal system), civil law. The prosecution is the ...
, 101 cases of sexual violence against Ukrainian men by occupying Russian forces have been recorded, including 50 in the Kherson
Kherson (Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and , , ) is a port city in southern Ukraine that serves as the administrative centre of Kherson Oblast. Located by the Black Sea and on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, Kherson is the home to a major ship-bui ...
region. But this is almost certainly a vast undercount, since experts say men are often reluctant to report sexual violence.
When Ukrainian cities were liberated, numerous abuses by Russian forces were exposed, including castrations, in attempts to terrorize and demoralize the Ukrainian population to break their will to fight.
Music
In Europe, when women were not permitted to sing in church or cathedral choirs in the Roman Catholic Church, boys were castrated to develop a special highvoice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound produ ...
and to prevent their voices breaking at puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
. The first documents mentioning '' castrati'' are Italian church records from the 1550s.John Rosselli, "Castrato" article in ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', 2001. In the baroque and classical music eras these singers were highly appreciated by opera composers as well. Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
's ''Exultate Jubilate'', Allegri's '' Miserere'' and other pieces from this period now sung by soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hertz, Hz to A5 in Choir, choral ...
s and countertenors were written for ''castrati''. Some of the alto parts of Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
's Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
were first sung by a ''castrato''. ''Castrati'' include Farinelli
Farinelli (; 24 January 1705 – 16 September 1782) was the stage name of Carlo Maria Michelangelo Nicola Broschi (), a celebrated Italian castrato singer of the 18th century and one of the greatest singers in the history of opera. Farinelli ...
, Senesino, Carestini, and Caffarelli. The last true ''castrato'' was Alessandro Moreschi (1858–1922) who served in the Sistine Chapel Choir. It was not until the late 19th century that the Roman Catholic Church officially condemned the production of ''castrati''. In modern times, the Mexican Javier Medina is the only professional opera singer who can perform as a castrato, since he had an involuntary chemical castration, as a result of a cancer treatment that he had before he reached puberty.
Religion
Hinduism
In South Asia, many hijras live in well-defined, organized, all-hijra communities, led by a guru. The power of the hijras as a sexually ambiguous category can only be understood in the religious context of Hinduism. In some Hindu beliefs, ritual, and art, the power of the combined man/woman, or androgyne, is a frequent and significant theme. Bahuchara Mata, the main object of hijra veneration, is specifically associated withtransgender
A transgender (often shortened to trans) person has a gender identity different from that typically associated with the sex they were sex assignment, assigned at birth.
The opposite of ''transgender'' is ''cisgender'', which describes perso ...
topics.
Christianity
In theGospel of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells the story of who the author believes is Israel's messiah (Christ (title), Christ), Jesus, resurrection of Jesus, his res ...
, Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religi ...
mentions castration in a discussion about avoiding adultery and divorce that some are involuntarily castrated or born that way, while some others "make themselves eunuchs" willingly out of a desire to be chaste (). Given Jesus' frequent use of metaphor and hyperbole, e.g. , the Catholic Church has broadly discouraged any understanding of this passage as recommending literal "self-castration". That is consistent with Jesus' claims (as a rabbi) to uphold the Law given to Moses, e.g. , a Law which also discouraged literal castration . However, in his own comments Jesus had no condemnation for any of the above. In , a eunuch is baptized by Philip the Evangelist
Philip the Evangelist (, ''Philippos'') appears several times in the Acts of the Apostles. According to the work, he was one of the Seven chosen to care for the poor of the Christian community in Jerusalem (). He preached and performed miracl ...
, demonstrating acceptance of castrated individuals in his church.
The first canon of the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
in 325 AD forbade clergy members to voluntarily castrate themselves "when in perfect health", but freely accepted those who had been either castrated by others against their will, castrated due to a medical sickness or necessity, or those born as eunuchs.
Paul, arguing against self-righteousness regarding circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. T ...
in , says "As for those agitators, I wish they would go the whole way and emasculate themselves!" ( NIV)
Well-known Christian eunuchs (or alleged eunuchs) include:
* Origen
Origen of Alexandria (), also known as Origen Adamantius, was an Early Christianity, early Christian scholar, Asceticism#Christianity, ascetic, and Christian theology, theologian who was born and spent the first half of his career in Early cent ...
, who is reported by Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
to have castrated himself based on his reading of the Gospel of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells the story of who the author believes is Israel's messiah (Christ (title), Christ), Jesus, resurrection of Jesus, his res ...
and other passages in Matthew and Mark that appear to endorse voluntary amputation to avoid sin, although there is some doubt concerning this story. Schaff considers the account genuine but cites Baur ''et al.'' in opposition. Origen argues against such literal interpretations of the passages from Matthew and Mark in his First Principles.
* Bishop Melito of Sardis (d. ''ca'' 180), who was a eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2 ...
, according to the church history of Eusebius of Caesarea
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
, though, significantly the word "virgin" was substituted in Rufinus' Latin translation of Eusebius.
* Boston Corbett, who was inspired by this same verse to castrate himself (Corbett was the 19th-century American soldier who is generally believed to have fired the shot that killed John Wilkes Booth
John Wilkes Booth (May 10, 1838April 26, 1865) was an American stage actor who Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, assassinated United States president Abraham Lincoln at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., on April 14, 1865. A member of the p ...
).
* Skoptsy, a branch of the Russian Spiritual Christianity
Spiritual Christianity () is the group of belief systems held by so-called folk Protestants (), including non-Eastern Orthodox indigenous faith tribes and new religious movements that emerged in the Russian Empire. Their origins are varied: som ...
movement founded in the 1760s.
Judaism
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
strictly forbids the castration of either humans or animals. Deuteronomy 23:1 expels castrated men from the assembly of Israel; they are forbidden to marry or if married must divorce from their wives (though permitting the castrated to marry or remain married to female converts to Judaism). The laws of castration also apply to cases of irreversible or un-reversed vasectomy and all other cases where the flow of sperm is known to have been placed into a permanent state of dysfunction with either no hope or no desire to take the steps to repair.
Isaiah 56:3–5 references in a positive welcoming manner eunuchs who follow after God's laws. "Neither let the son of the stranger, that hath joined himself to the LORD, speak, saying, The LORD hath utterly separated me from his people: neither let the eunuch say, Behold, I am a dry tree. For thus saith the LORD unto the eunuchs that keep my sabbaths, and choose the things that please me, and take hold of my covenant; Even unto them will I give in mine house and within my walls a place and a name better than of sons and of daughters: I will give them an everlasting name, that shall not be cut off."
According to Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki (; ; ; 13 July 1105) was a French rabbi who authored comprehensive commentaries on the Talmud and Hebrew Bible. He is commonly known by the List of rabbis known by acronyms, Rabbinic acronym Rashi ().
Born in Troyes, Rashi stud ...
, Kham (Ham) castrated his father Noah and was cursed as a result.
In Judaism, castrated animals are deemed unfit for sacrifice
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving.
Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Gree ...
in the Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. Accord ...
(). Castrated members of the priestly caste are forbidden to enter certain parts of the temple, to approach the altar, or to make sacrifices, although they could eat their share of the offerings and receive the priestly and Levite gifts (Lev. 21:16–24).
Islam
TheMuslim conquest of Persia
As part of the early Muslim conquests, which were initiated by Muhammad in 622, the Rashidun Caliphate conquered the Sasanian Empire between 632 and 654. This event led to the decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been the official religion of ...
as well as later conquests in the Byzantine Empire and India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
brought them into contact with eunuchs. By the eighth century, the palaces of the caliphs were staffed with many eunuch slaves which sold at a premium. A regular trade in eunuchs developed with slaves being taken to locations in Spain or Africa to be castrated, as the practice of castration was forbidden for Muslims. Eunuchs were used as harem supervisors, as mediators or servile roles, but they could also rise to be trusted advisors or military commanders.
In Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, castration is considered a sin and strictly forbidden, whether one performs it on oneself or on another. In the history of slavery in the Muslim world, a fair proportion of male slaves were imported as eunuch. Levy states that according to the Quran and Islamic traditions, such emasculation was objectionable. Some jurists such as al-Baydawi
Qadi Baydawi (also known as Naṣir ad-Din al-Bayḍawi, also spelled Baidawi, Bayzawi and Beyzavi; d. June 1319, Tabriz) was a jurist, theologian, and Quran commentator. He lived during the post-Seljuk Empire, Seljuk and early Mongol Empire, Mon ...
considered castration to be mutilation, stipulating laws to prevent it. However, in practice, emasculation was frequent. In eighteenth-century Mecca, the majority of eunuchs were in the service of the mosques.
Medical consequences
A subject of castration who is altered before the onset of puberty will retain a high voice, as well as the effects of hypogonadism, which include non-muscular build, an infantile penis, a lack of a beard, more developed subcutaneous fat. He may be taller than average, with long limbs, so called "eunuchoid appearance", as the production of sex hormones in puberty—more specifically, estrogen via aromatization of testosterone—stops long bone growth in a process called osseous maturation. The subject may lack the male distribution of axillary hair, and may developpubic hair
Pubic hair (or pubes , ) is terminal hair, terminal body hair that is found in the sex organ, genital area and pubic region of adolescent and adult humans. The hair is located on and around the sex organs, and sometimes at the top of the inside ...
distributed in female pattern. They may have a low sex drive or none at all.
Castration stops the progression of male pattern baldness
Pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia (AGA)) is a hair loss condition that primarily affects the top and front of the scalp. In male-pattern hair loss (MPHL), the hair loss typically presents itself as either a receding front ...
. However, hair regrowth – if it occurs at all – may be limited to hair that was lost shortly before castration.
Historically, many eunuchs who additionally underwent a penectomy reportedly had urinary incontinence associated with the removal of the penis.
A study of 81 historical eunuchs in Korea's royal court found a 14- to 19-year increase in lifespan compared to intact men of similar socioeconomic background; these eunuchs had a centenarian
A centenarian is a person who has reached the age of 100. Because life expectancies at birth worldwide are well below 100, the term is invariably associated with longevity. The United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living centenarian ...
rate of over 3%.
Chemical castration
In the case of chemical castration, ongoing regular injections of anti-androgens are required. Chemical castration does not actually remove the testicles or ovaries of the subject,"Can Castration Be a Solution for Sex Offenders? Man Who Mutilated Himself in Jail Thinks So, but Debate on Its Effectiveness Continues in Va., Elsewhere"by Candace Rondeaux for the Washington Post, 5 July 2006 nor is it a form of sterilization."Chemical castration – breaking the cycle of paraphiliac recidivism"
Social Justice, Spring, 1999 by Christopher Meisenkothen. With the advent of chemical castration, physical castration in humans has been widely superseded, though some have undergone the procedure voluntarily.
Other animals
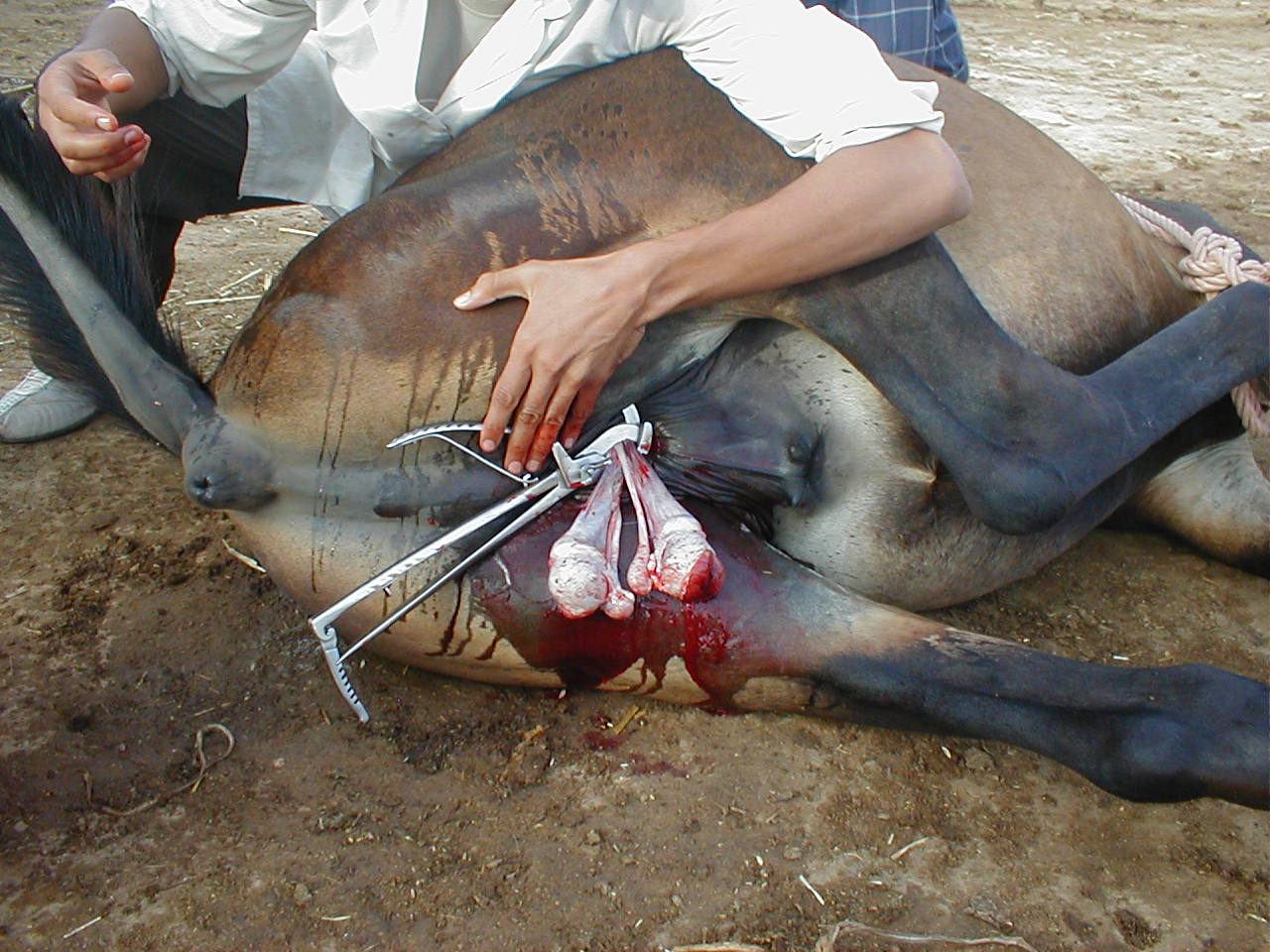
 Humans commonly castrate domestic animals not intended for breeding.
Domestic animals are usually castrated to avoid unwanted or uncontrolled
Humans commonly castrate domestic animals not intended for breeding.
Domestic animals are usually castrated to avoid unwanted or uncontrolled reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
; to reduce or prevent other manifestations of sexual behaviour such as defending the herd from humans and other threats, or intra-herd aggression (e.g. fighting between groups of entire (uncastrated) males of a species); or to reduce other consequences of sexual behavior that may make animal husbandry more difficult, such as boundary/fence/enclosure destruction when attempting to get to nearby females of the species.
Male horses are usually castrated ( gelded) using emasculators, because stallions are rather aggressive and troublesome. The same applies to male mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two ...
s, although they are sterile. Male cattle are castrated to improve fattening and docility in feedlots or for use as oxen
An ox (: oxen), also known as a bullock (in BrE, British, AusE, Australian, and IndE, Indian English), is a large bovine, trained and used as a draft animal. Oxen are commonly castration, castrated adult male cattle, because castration i ...
.
Breeding
Breeding is sexual reproduction that produces offspring, usually animals or plants. It can only occur between a male and a female animal or plant.
Breeding may refer to:
* Animal husbandry, through selected specimens such as dogs, horses, and rab ...
individuals are kept entire and used for breeding: they may fetch higher prices when sold.
Livestock may be castrated when used for food to prevent indiscriminate breeding, control aggression, and improve meat and carcass quality. In domestic pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s the undesirable odour or taint of uncastrated males, called boar taint, is caused by androstenone
Androstenone (5α-androst-16-en-3-one) is a 16-androstene class steroidal pheromone. It is found in boar's saliva, celery cytoplasm, and truffle fungus. Androstenone was the first mammalian pheromone to be identified. It is found in high concen ...
and skatole
Skatole or 3-methylindole is an organic compound belonging to the indole family. It occurs naturally in the feces of mammals and birds and is the primary contributor to fecal odor. In low concentrations, it has a flowery smell and is found in sever ...
concentrations stored in the fat tissues of the animal after sexual maturity.Genetics of Boar Taint: Implications for the Future Use of Intact MalesBoar taint is only found in a small minority of pigs and can be controlled through breeding selection, diet and management. It is released when the fat is heated and has a distinct odor and flavor that is widely considered unpalatable to consumers.
Consequently, in commercial meat production, male pigs are either castrated shortly after birth or slaughtered before they reach sexual maturity. Recent research in Brazil has shown that castration of pigs is unnecessary because most pigs do not have the 'boar taint'. This is due to many breeds of pigs simply not having the heredity for the boar taint and the fact that pigs are normally slaughtered at a young market weight. In the case of pets, castration is usually called
neutering
Neutering, from the Latin ('of neither sex'), is the removal of a non-human animal's sex organ, reproductive organ, either all of it or a considerably large part. The male-specific term is castration, while spaying is usually reserved for female ...
, and is encouraged to prevent overpopulation of the community by unwanted animals, and to reduce certain diseases such as prostate disease and testicular cancer in male dogs (oophorectomy in female pets is often called spaying). Testicular cancer is rare in dogs, and also prostate problems are somewhat common in castrated male dogs when they get older. Neutered individuals have a much higher risk of developing prostate problems in comparison to intact males. Castrated male cats are more likely to develop an obstruction in their urethra, preventing them from urinating to some degree. A specialized vocabulary has arisen for neutered animals of given species:
* Barrow (pig)
* Bullock
Bullock may refer to:
Animals
* Bullock (in British English), a castrated male cattle, bovine animal of any age
* Bullock (in American English), a young bull (an uncastrated male bovine animal)
* Bullock (in Australia, India and New Zealand), an o ...
(cattle)
* Capon (chicken)
* Gelding
A gelding (Help:IPA/English, /ˈɡɛldɪŋ/) is a castration, castrated male horse or other equine, such as a pony, donkey or a mule. The term is also used with certain other animals and livestock, such as domesticated Camelidae, camels. By compa ...
(horse)
* Gib (cat, ferret)
* Ox (cattle) (Castration performed on mature bull)
* Stag (cattle, sheep)
* Steer (cattle) (Castration performed on young calf)
* Wether (sheep, goat)
An incompletely castrated male in livestock species (horse and cattle) is known as a ''rig''.
The term ''stag'' is used for a male animal castrated after the secondary sex characteristic
A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during pubert ...
s have developed to such a point as to give him the appearance of sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans, it is related to both puberty and adulthood. ''Puberty'' is the biological process of sexual maturation, while ''adulthood'', the condition of being socially recognized ...
.
veterinary
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in non-human animals. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all animal species, both ...
castration include instant surgical
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery ...
removal, the use of an elastrator tool to secure a band around the testicles that disrupts the blood supply, the use of a Burdizzo tool or emasculators to crush the spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...
s and disrupt the blood supply, pharmacological
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between ...
injections and implants and immunological
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms.
Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and disease ...
techniques to inoculate the animal against his own sexual hormones.
Certain animals, like horses and swine
Suina (also known as Suiformes) is a suborder of omnivorous, non-ruminant artiodactyl mammals that includes the domestic pig and peccaries. A member of this clade is known as a suine. Suina includes the family Suidae, termed suids, known in ...
, are usually surgically treated with a scrotal castration (which can be done with the animal standing while sedated and after local anesthetic has been applied), while others, like dogs and cats, are anesthetised and recumbent when surgically castrated with a pre-scrotal incision in the case of dogs, or a pre-scrotal or scrotal incision used for cats.
Castration of cattle has historically been done without pain medications. All methods of castration cause pain and distress, which can be minimized by castrating as early as possible, preferably within the first week of life. The Canadian Code of Practice for the Care and Handling of Beef Cattle requires that, as of 2018, calves older than six months be castrated using pain control.Code of Practice for the Care and Handling of Beef Cattle. 2013.
www.nfacc.ca/codes-of-practice/beef-cattle
In veterinary practice an "open" castration refers to a castration in which the inguinal tunic is incised and not sutured. A "closed" castration refers to when the procedure is performed so that the inguinal tunic is sutured together after incision.
See also
* Ashley Treatment *Birth control
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
* Castration anxiety
Castration anxiety is an overwhelming fear of damage to, or loss of, the penis—a derivative of Sigmund Freud's theory of the castration complex, one of his earliest psychoanalytic theories. The term can refer to the fear of emasculation in ...
* Castrato
A castrato (Italian; : castrati) is a male singer who underwent castration before puberty in order to retain a singing voice equivalent to that of a soprano, mezzo-soprano, or contralto. The voice can also occur in one who, due to an endocrino ...
, a castrated male singer
* Chemical castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, management of cancer, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike orchiectomy, surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision ...
* Cleveland Torso Murderer, a serial killer who castrated his male victims
* Emasculation
* Emasculator
* Eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2 ...
* Gelding
A gelding (Help:IPA/English, /ˈɡɛldɪŋ/) is a castration, castrated male horse or other equine, such as a pony, donkey or a mule. The term is also used with certain other animals and livestock, such as domesticated Camelidae, camels. By compa ...
* Inguinal orchiectomy, the approach typically used to treat testicular cancer
* Spaying and neutering (for animals)
* Oophorectomy
Oophorectomy (; from Greek , , 'egg-bearing' and , , 'a cutting out of'), historically also called ''ovariotomy'', is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference ...
, the equivalent operation for ovaries
* Parasitic castration
Parasitic castration is the strategy, by a parasite, of blocking reproduction by its host, completely or in part, to its own benefit. This is one of six major strategies within parasitism.
Evolutionary strategy
The parasitic castration strateg ...
* Penectomy
* Penis removal
* Gender affirming surgery
* Vaginoplasty
* Vasectomy
Vasectomy is an elective surgical procedure that results in male sterilization, often as a means of permanent contraception. During the procedure, the male vasa deferentia are cut and tied or sealed so as to prevent sperm from entering into ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * Tuotuo. Liaoshi istory of Liao Beijing: Zhonghua shuju, 1974 (or Tuotuo, ''Liaoshi'' (Beijing: Zhonghua shuju, 1974)) * * * * * Patrick Barbier, ''The World of the Castrati: the History of an Extraordinary Operatic Phenomenon'' Souvenir, 1996, * Susan Elliott''Cutting Too Close for Comfort: Paul's Letter to the Galatians in Its Anatolian Cultic Context''
Reviews in Review of Biblical Literature * Theresa McCuaig,
Understanding Castration
" 2009. * * English language Abstracts of the thesis **
Research on the System of Imperial Harem in Liao Dynasty
*** **
External links
Castration Through the Ages
The Journal of Clinical Endrocrinology and Metabolism
Neutering NOT Org
Website arguing against the castration of domestic animals
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20180429222839/http://en.castration.site/ Castration��information site {{Authority control Andrology Corporal punishments Torture Male genital modification Cybele Violence against men Sexual abuse Wartime sexual violence