BĂĄnsĂĄg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Banat (, ; hu, BĂĄnsĂĄg; sr, ĐанаŃ, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles
 Banat is defined as the part of the Pannonian Basin bordered by the Danube to the south, the Tisza to the west, the MureČ to the north and the Southern Carpathians to the east. The historical Banat totals an area of 28,526 km². Various sources indicate figures slightly different from this. When the province was divided in 1920, Romania was assigned an area of 18,966 km² (approximately â
of the total), the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes 9,276 km² (approximately â
of the total), and Hungary 284 km² (approximately 1% of the total).
The Romanian Banat is mountainous in the south and southeast, while in the north, west and southwest it is flat and in some places marshy. Some Banat mountain massifs constitute the western branch of the Southern Carpathians, i.e., Čarcu Mountains and Cerna Mountains. The Poiana RuscÄ Mountains and Banat Mountains with the Semenic, Anina, Dognecea, AlmÄj and Locva divisions are part of the Western Carpathians. The western pre-mountainous hills make up about a third of the historical Banat territory. Their altitude varies between 200 and 400 meters. The high plain (with altitudes of over 100 meters, up to 140 meters) is represented by the plains of Vinga, BuziaČ, GÄtaia and FizeČ. The plains with intermediate altitudes, between 100 and 130 meters, are the plains of Hodoni, Duboz, Tormac, Jamu Mare, Arad and Sânnicolau Mare, and the low plain (with altitudes below 100 meters) is represented by the river meadows, the floodplains before the extensive regularization works. These plains, components of the Pannonian Plain, represent another third of the Banat area. Worth mentioning are the two extinct volcanoes from LucareČ and GÄtaia: Piatra RoČie (211 m) and Čumigu (200 m), respectively.
The relief of Serbian Banat is monotonous, except for a few morphological units: the VrĹĄac Mountains, the Bela Crkva basin and the east Banat alluvium. The largest stretch of sand in Europe, today stabilized and covered with vegetation, '' Deliblatska PeĹĄÄara'', also lies in Serbian Banat.
Banat is defined as the part of the Pannonian Basin bordered by the Danube to the south, the Tisza to the west, the MureČ to the north and the Southern Carpathians to the east. The historical Banat totals an area of 28,526 km². Various sources indicate figures slightly different from this. When the province was divided in 1920, Romania was assigned an area of 18,966 km² (approximately â
of the total), the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes 9,276 km² (approximately â
of the total), and Hungary 284 km² (approximately 1% of the total).
The Romanian Banat is mountainous in the south and southeast, while in the north, west and southwest it is flat and in some places marshy. Some Banat mountain massifs constitute the western branch of the Southern Carpathians, i.e., Čarcu Mountains and Cerna Mountains. The Poiana RuscÄ Mountains and Banat Mountains with the Semenic, Anina, Dognecea, AlmÄj and Locva divisions are part of the Western Carpathians. The western pre-mountainous hills make up about a third of the historical Banat territory. Their altitude varies between 200 and 400 meters. The high plain (with altitudes of over 100 meters, up to 140 meters) is represented by the plains of Vinga, BuziaČ, GÄtaia and FizeČ. The plains with intermediate altitudes, between 100 and 130 meters, are the plains of Hodoni, Duboz, Tormac, Jamu Mare, Arad and Sânnicolau Mare, and the low plain (with altitudes below 100 meters) is represented by the river meadows, the floodplains before the extensive regularization works. These plains, components of the Pannonian Plain, represent another third of the Banat area. Worth mentioning are the two extinct volcanoes from LucareČ and GÄtaia: Piatra RoČie (211 m) and Čumigu (200 m), respectively.
The relief of Serbian Banat is monotonous, except for a few morphological units: the VrĹĄac Mountains, the Bela Crkva basin and the east Banat alluvium. The largest stretch of sand in Europe, today stabilized and covered with vegetation, '' Deliblatska PeĹĄÄara'', also lies in Serbian Banat.
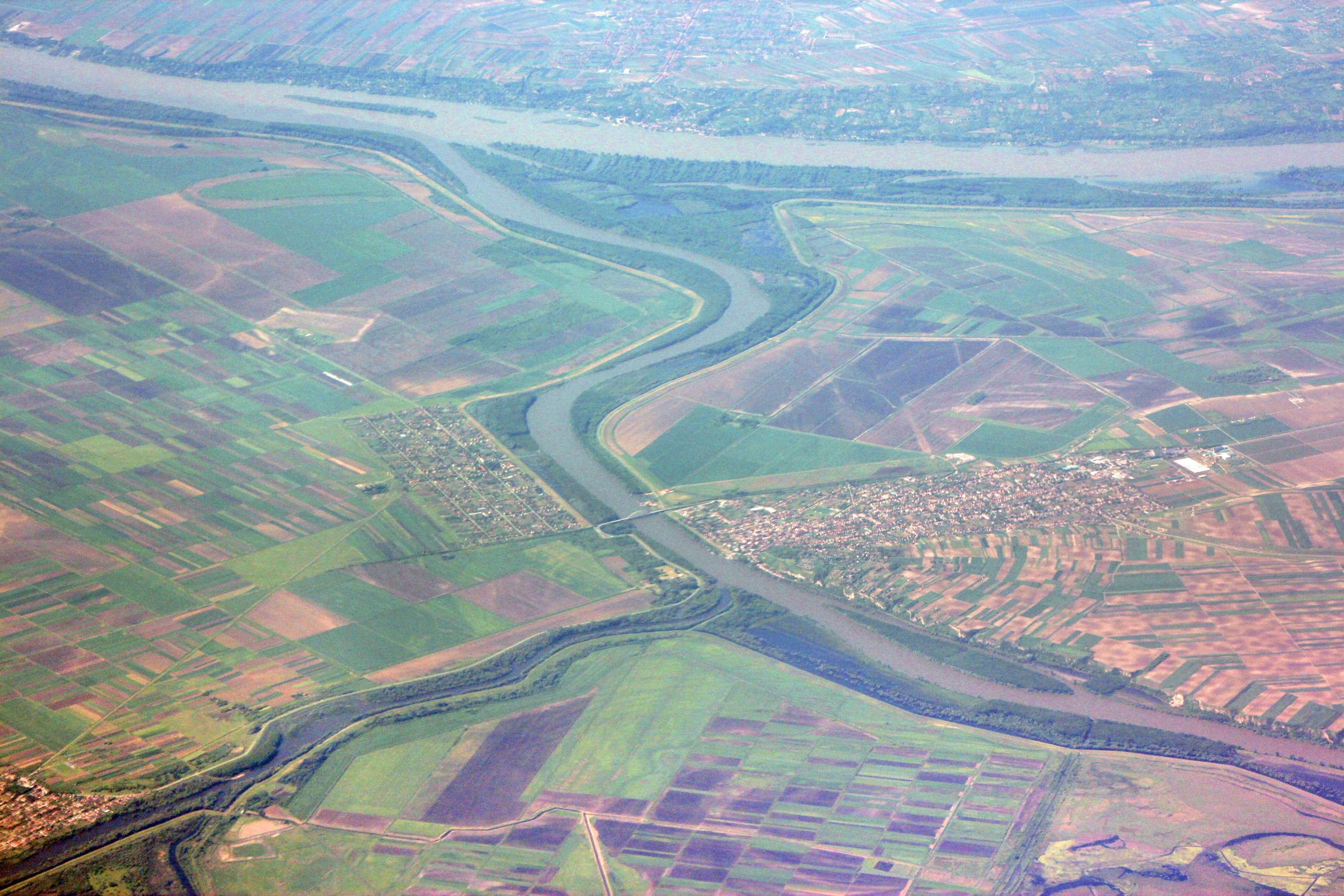 Considering the low and undesiccated land, there is a relatively large number of watercourses in Banat. The rivers bordering the area and delimiting it from the rest of the territories are MureČ, Tisza and Danube. With the exception of some small local tributaries, the MureČ does not have a very large area. The other rivers that have their source in Banat are direct or indirect tributaries of the Tisza and the Danube. The Danube forms between
Considering the low and undesiccated land, there is a relatively large number of watercourses in Banat. The rivers bordering the area and delimiting it from the rest of the territories are MureČ, Tisza and Danube. With the exception of some small local tributaries, the MureČ does not have a very large area. The other rivers that have their source in Banat are direct or indirect tributaries of the Tisza and the Danube. The Danube forms between
File:Indo Europeans Vojvodina map.png, Ancient Indo-European peoples in Banat
File:Roman cities Vojvodina.png, Ancient Roman cities in Banat
 The Goths were forced out by the Huns, who organized their ruling center in the Pannonian Basin (the Pannonian Plain), an area that included the northwestern part of today's Banat. After the death of
The Goths were forced out by the Huns, who organized their ruling center in the Pannonian Basin (the Pannonian Plain), an area that included the northwestern part of today's Banat. After the death of
 Banat was administered by the
Banat was administered by the
File:Salan glad01.png, Duchy of
 The Ottoman Empire took over the area and incorporated Banat in 1552. It was absorbed as an Ottoman
The Ottoman Empire took over the area and incorporated Banat in 1552. It was absorbed as an Ottoman
File:Patriarchate of PeÄ in the 16th and 17th century.png, Jurisdiction of Serbian Patriarchate in the 16th and 17th centuries
File:Ottoman vojvodina01.png, Eyalet of TemeĹvar and Banate of Lugoj and CaransebeČ in 1568
File:Banatski_ustanak.png, Uprising in Banat in 1594
File:Elayet of temesvar.png, Eyalet of TemeĹvar in the mid-17th century
File:Central_europe_1683.png, Eyalet of TemeĹvar and the surrounding regions in 1683
File:Eyalet of temesvar1699.png, Eyalet of TemeĹvar, from 1699 to 1716


 At the beginning of the next
At the beginning of the next
File:Vojvodina03.png, Proclaimed borders of Serbian Vojvodina in 1848 (including Western Banat)
File:Map of Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar (1849-1860).png,
File:Banat republic.png, Self-proclaimed

 In 1938, the counties of TimiČ-Torontal, CaraČ, Severin, Arad and Hunedoara were joined to form
In 1938, the counties of TimiČ-Torontal, CaraČ, Severin, Arad and Hunedoara were joined to form

 The region was claimed by the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between 1918 and 1922 (as the province of Banat, BaÄka and Baranja between 1918 and 1919) and from 1922 to 1929 it was divided between Belgrade oblast and Podunavlje oblast. In 1929, most of the region was incorporated into the
The region was claimed by the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between 1918 and 1922 (as the province of Banat, BaÄka and Baranja between 1918 and 1919) and from 1922 to 1929 it was divided between Belgrade oblast and Podunavlje oblast. In 1929, most of the region was incorporated into the
Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of TimiČ, CaraČ-Severin, Arad south of the MureČ river, and the western part of MehedinČi); the western part of Banat is in northeastern Serbia (mostly included in Vojvodina, except for a small part included in the Belgrade Region
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 mil ...
); and a small northern part lies within southeastern Hungary ( CsongrĂĄd-CsanĂĄd County).
The region's historical ethnic diversity was severely affected by the events of World War II. Today, Banat is mostly populated by ethnic Romanians, Serbs and Hungarians, but small populations of other ethnic groups also live in the region. Nearly all are citizens of either Serbia, Romania or Hungary.
Name
During the Middle Ages, the term " banate" designated a frontier province led by a military governor who was called a ''ban
Ban, or BAN, may refer to:
Law
* Ban (law), a decree that prohibits something, sometimes a form of censorship, being denied from entering or using the place/item
** Imperial ban (''Reichsacht''), a form of outlawry in the medieval Holy Roman ...
''. Such provinces existed mainly in South Slavic, Hungarian and Romanian lands. In South Slavic and other regional languages, terms for "banate" were: Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
â йанОвина/''banovina'', Hungarian â ''bĂĄnsĂĄg'', Romanian â ''banat'' and Latin â ''banatus''. Several theories have been proposed for the etymological origin of the regionym "Banat". A first theory claims that it comes from the root of a verb found in several Germanic peoples, namely ''ban''. This term means "to proclaim" or "to announce". From there it passed into medieval Latin, under the form ''bannum'', which means â among the Frankish peoples, for example â "proclamation", but also the district on which the said proclamation was to have effects. Another theory puts forward the Persian origin of the word "ban"; in Persian ''ban'' () means "master". From this language, it would have been taken over by the Avars and brought to Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
, where they ruled in the 6thâ8th centuries. Another interpretation is also related to Avars, according to which the origin of the word "ban" would come from the name of the first khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, đ°´đ°đ°Ł ), or , tr, KaÄan or ; ug, ŮاغاŮ, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, ؎اŮا٠''KhÄqÄn'', alternatively spelled KaÄan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
of the Avar Khaganate
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, ÎÎąĎĎονίĎÎľĎ, VarchonĂtes), or Pseudo-Avars ...
, Bayan I. These views are contradicted by those who believe that "ban" comes from an old Proto-Indo-European root, ''bha'', which means "to speak".
At the time of the medieval Hungarian kingdom, the territory of modern Banat appeared in written sources as ''TemeskĂśz'' (first mentioned in 1374). The Hungarian name mainly referred to the lowland areas between the MureČ, Tisza and Danube rivers. Its Ottoman name was " Eyalet of TemeĹvar" (later "Eyalet of Yanova"). During the Turkish occupation, the territory of TemeskĂśz (Banat) was also called "Rascia" ("the country of the Serbs", 1577). For Romanians, the region was also known as ''TemiČana''.
In the early modern period, there were two banates that partially or entirely included the territory of what is referred to in the current era as Banat: the Banate of Lugoj and CaransebeČ in the 16thâ17th centuries and the Banate of Temeswar in the 18thâ19th centuries. The word "Banat" without any other qualification typically refers to the historical Banate of Temeswar, which acquired this title after the 1718 Treaty of Passarowitz. The name was also used from 1941 to 1944, during Axis occupation, for the short-lived political entity (see: Banat (1941â44)
Banat (, ; hu, BĂĄnsĂĄg; sr, ĐанаŃ, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of ...
), which covered only today's Serbian part of the historical Banat.
The name "Banat" is similar in different languages of the region; ro, Banat, Serbo-Croatian: ĐанаŃ/''Banat'', hu, BĂĄnsĂĄg or ''BĂĄnĂĄt'', bg, ĐанаŃ, cs, BanĂĄt, german: Banat, el, ÎινΏĎÎż/''VanĂĄto'', sk, BanĂĄt, tr, Banat, uk, ĐанаŃ. Some of these languages would also have other terms, from their own frame of reference, to describe this historical and geographic region.
Geography
 Banat is defined as the part of the Pannonian Basin bordered by the Danube to the south, the Tisza to the west, the MureČ to the north and the Southern Carpathians to the east. The historical Banat totals an area of 28,526 km². Various sources indicate figures slightly different from this. When the province was divided in 1920, Romania was assigned an area of 18,966 km² (approximately â
of the total), the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes 9,276 km² (approximately â
of the total), and Hungary 284 km² (approximately 1% of the total).
The Romanian Banat is mountainous in the south and southeast, while in the north, west and southwest it is flat and in some places marshy. Some Banat mountain massifs constitute the western branch of the Southern Carpathians, i.e., Čarcu Mountains and Cerna Mountains. The Poiana RuscÄ Mountains and Banat Mountains with the Semenic, Anina, Dognecea, AlmÄj and Locva divisions are part of the Western Carpathians. The western pre-mountainous hills make up about a third of the historical Banat territory. Their altitude varies between 200 and 400 meters. The high plain (with altitudes of over 100 meters, up to 140 meters) is represented by the plains of Vinga, BuziaČ, GÄtaia and FizeČ. The plains with intermediate altitudes, between 100 and 130 meters, are the plains of Hodoni, Duboz, Tormac, Jamu Mare, Arad and Sânnicolau Mare, and the low plain (with altitudes below 100 meters) is represented by the river meadows, the floodplains before the extensive regularization works. These plains, components of the Pannonian Plain, represent another third of the Banat area. Worth mentioning are the two extinct volcanoes from LucareČ and GÄtaia: Piatra RoČie (211 m) and Čumigu (200 m), respectively.
The relief of Serbian Banat is monotonous, except for a few morphological units: the VrĹĄac Mountains, the Bela Crkva basin and the east Banat alluvium. The largest stretch of sand in Europe, today stabilized and covered with vegetation, '' Deliblatska PeĹĄÄara'', also lies in Serbian Banat.
Banat is defined as the part of the Pannonian Basin bordered by the Danube to the south, the Tisza to the west, the MureČ to the north and the Southern Carpathians to the east. The historical Banat totals an area of 28,526 km². Various sources indicate figures slightly different from this. When the province was divided in 1920, Romania was assigned an area of 18,966 km² (approximately â
of the total), the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes 9,276 km² (approximately â
of the total), and Hungary 284 km² (approximately 1% of the total).
The Romanian Banat is mountainous in the south and southeast, while in the north, west and southwest it is flat and in some places marshy. Some Banat mountain massifs constitute the western branch of the Southern Carpathians, i.e., Čarcu Mountains and Cerna Mountains. The Poiana RuscÄ Mountains and Banat Mountains with the Semenic, Anina, Dognecea, AlmÄj and Locva divisions are part of the Western Carpathians. The western pre-mountainous hills make up about a third of the historical Banat territory. Their altitude varies between 200 and 400 meters. The high plain (with altitudes of over 100 meters, up to 140 meters) is represented by the plains of Vinga, BuziaČ, GÄtaia and FizeČ. The plains with intermediate altitudes, between 100 and 130 meters, are the plains of Hodoni, Duboz, Tormac, Jamu Mare, Arad and Sânnicolau Mare, and the low plain (with altitudes below 100 meters) is represented by the river meadows, the floodplains before the extensive regularization works. These plains, components of the Pannonian Plain, represent another third of the Banat area. Worth mentioning are the two extinct volcanoes from LucareČ and GÄtaia: Piatra RoČie (211 m) and Čumigu (200 m), respectively.
The relief of Serbian Banat is monotonous, except for a few morphological units: the VrĹĄac Mountains, the Bela Crkva basin and the east Banat alluvium. The largest stretch of sand in Europe, today stabilized and covered with vegetation, '' Deliblatska PeĹĄÄara'', also lies in Serbian Banat.Climate
The climate of Banat is predominantly temperate ( Cfb, according to KĂśppen classification), with a northeastward increase of continental and orographic effects ( Dfb). Frequent cyclones from the Mediterranean cause positive precipitation anomalies especially in the western parts and, due to the maritime influence, winters are mild and short, but when northeastern conditions prevail, harshfrost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
s may occur. Mean annual temperatures range between 12 °C (with average summer temperatures above 22 °C in July) and 6 °C towards the eastern highlands. Besides, temperature inversions occur in the valleys and in the depressions of the Banat Hills, the bottom being colder than the slopes. The thermal and dynamic convection produced on the slopes causes greater cloudiness throughout the year; humidity and precipitation are higher.
Hydrography
 Considering the low and undesiccated land, there is a relatively large number of watercourses in Banat. The rivers bordering the area and delimiting it from the rest of the territories are MureČ, Tisza and Danube. With the exception of some small local tributaries, the MureČ does not have a very large area. The other rivers that have their source in Banat are direct or indirect tributaries of the Tisza and the Danube. The Danube forms between
Considering the low and undesiccated land, there is a relatively large number of watercourses in Banat. The rivers bordering the area and delimiting it from the rest of the territories are MureČ, Tisza and Danube. With the exception of some small local tributaries, the MureČ does not have a very large area. The other rivers that have their source in Banat are direct or indirect tributaries of the Tisza and the Danube. The Danube forms between BaziaČ
Socol ( ro, Socol, sr, ХОкОН/Sokol, or ХОкОНОваŃ/Sokolovac, hu, NĂŠrasolymos) is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, Romania (in the ''Clisura DunÄrii'' area of Banat). In 2011, the population of the commune numbered 1,873 people ...
and PorČile de Fier
The Iron Gates ( ro, PorČile de Fier; sr, / or / ; Hungarian language, Hungarian: ''Vaskapu-szoros'') is a Canyon, gorge on the river Danube. It forms part of the boundary between Serbia (to the south) and Romania (north). In the broad ...
, over a distance of 140 km, the so-called Iron Gates
The Iron Gates ( ro, PorČile de Fier; sr, / or / ; Hungarian: ''Vaskapu-szoros'') is a gorge on the river Danube. It forms part of the boundary between Serbia (to the south) and Romania (north). In the broad sense it encompasses a rou ...
. Tisza is the river that separates the Banat from the Hungarian areas to the west and divides the current Vojvodina into two parts. A wide river that meanders through the plain that bears its name.
The TimiČ/TamiĹĄ is the largest inland river of Banat, which has its sources on the eastern slopes of the Semenic Mountains, in CaraČ-Severin County. The river is formed at the confluence of three branches: Semenic, GrÄdiČte and Brebu. It crosses the entire TimiČ County, then passes into Serbia, where it flows into the Danube, at PanÄevo
PanÄevo (Serbian Cyrillic: ĐĐ°Đ˝ŃовО, ; german: Pantschowa; hu, Pancsova; ro, Panciova; sk, PĂĄnÄevo) is a city and the administrative center of the South Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is located on ...
. The most important cities through which TimiČ passes are CaransebeČ, Lugoj and PanÄevo
PanÄevo (Serbian Cyrillic: ĐĐ°Đ˝ŃовО, ; german: Pantschowa; hu, Pancsova; ro, Panciova; sk, PĂĄnÄevo) is a city and the administrative center of the South Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is located on ...
.
The Bega/Begej springs from the Poiana RuscÄ Mountains, crosses the area of FÄget and Lugoj, passes through TimiČoara, then descends through a channel
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
, flowing into the Tisza, at Titel. Bega and Aranca/Zlatica flow into the Tisza, and TimiČ with its tributaries, such as PogÄniČ, Bârzava/Brzava, CaraČ/KaraĹĄ and Nera, flow into the Danube.
There are no large natural lakes. In the past, there were many lakes, ponds and swamps in Banat, which were drained by land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamati ...
carried out at the end of the 18th century and the beginning of the 19th century. There are bigger lakes only south of Zrenjanin.
History
The first known inhabitants of present-day Banat were the Neolithic populations. In the 4th century BC,Celtic tribes
This is a list of Celtic tribes, organized in order of the likely ethnolinguistic kinship of the peoples and tribes.
In Classical antiquity, Celts were a large number and a significant part of the population in many regions of Western Europe, ...
settled in this area. Various Hallstatt and La Tène objects were found in this area. The most important tribes were the Scordisci and the Taurisci. The Scordisci, who formed a powerful state even minted their own coins, imitating the Macedonian tetradrachm. The Scordisci subdued as all the other tribes in the region to the getic ruler Burebista, therefore their region was part of the Dacian kingdom under Burebista in the first century BC, but the balance of power in the area partially changed during the campaigns of Augustus. At the beginning of the 2nd century AD, Trajan led two wars against the Dacians: the campaigns of 101â102, and 105â106. Eventually, the territory of Banat fell under Roman rule. It became an important link between Dacia province and the other parts of the Empire. Roman rule had a significant impact: castra
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
and guard stations were established and roads and public buildings built. The public bath establishments of Ad Aquas Herculis, modern-day BÄile Herculane were also established. Some of the important Roman settlements in Banat were: Arcidava
Argidava (''Argidaua'', ''Arcidava'', ''Arcidaua'', ''Argedava'', ''Argedauon'', ''Argedabon'', ''Sargedava'', ''Sargedauon'', ''Zargedava'', ''Zargedauon'', grc, áźĎγίδιĎ
Îą, ÎĎγξδιĎ
ον, ÎĎγξδιβον, ÎŁÎąĎγξδιĎ
ον) ...
(today VÄrÄdia), Centum Putea (today Surducu Mare
Forotic ( hu, Forotik) is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, Banat, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. ...
), Berzobis (today Berzovia), Tibiscum (today Jupa), Agnaviae (today ZÄvoi
ZÄvoi (until 1950 ''ZÄvoiu''; hu, ZĂĄvoly) is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, western Romania with a population of 3,946 people. It is composed of seven villages: 23 August, MÄgura (until 1960 ''Crâjma''; ''Korcsoma''), MÄru (''Almafa'') ...
), Ad Pannonios (today Teregova), Praetorium (today Mehadia), and Dierna (today OrČova).
In 273 AD Emperor Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited t ...
withdrew the Roman Army from Dacia. The area fell into the hands of foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign stat ...
such as the Sarmatians ( Iazyges, Roxolani
The Roxolani or RhoxolÄni ( grc, ΥοΞοΝινοΚ , ; la, RhoxolÄnÄŤ) were a Sarmatian people documented between the 2nd century BC and the 4th century AD, first east of the Borysthenes (Dnieper) on the coast of Lake Maeotis (Sea of Azov), a ...
, Limigantes) and later the Goths, who also took control of other parts of Dacia.
Migration Period and Early Middle Ages
 The Goths were forced out by the Huns, who organized their ruling center in the Pannonian Basin (the Pannonian Plain), an area that included the northwestern part of today's Banat. After the death of
The Goths were forced out by the Huns, who organized their ruling center in the Pannonian Basin (the Pannonian Plain), an area that included the northwestern part of today's Banat. After the death of Attila
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European traditio ...
, the Hunnic empire disintegrated in days. The previously subjected Gepids formed a new kingdom in the area, only to be defeated 100 years later by the Avars.
One governing center of the Avars was formed in the region, which played an important role in the AvarâByzantine wars. An inscription on one of the vessels from the Treasure of Sânnicolau Mare
Treasure (from la, thesaurus from Greek language ''thÄsauros'', "treasure store") is a concentration of wealth â often originating from ancient history â that is considered lost and/or forgotten until rediscovered. Some jurisdictions leg ...
(which origin is disputed) recorded names of two local rulers, Butaul Butaul (also spelled ''Buta-ul'', with possible meaning "the son of Buta") is a name mentioned in an inscription contained in a treasure trove of gold artifacts found in 1799 in Sânnicolau Mare, in northern Banat (then under administration of Habs ...
and Buyla
The Buyla inscription is a 9-word, 56-character inscription written in the Greek alphabet but in a non-Greek language. It is found on a golden buckled bowl (vessel), bowl or cup which is among the pieces of the Treasure of NagyszentmiklĂłs which ...
, who bore Slavic ruling titles of Ĺžupan. The Avar rule over the area lasted until the 9th century, until Charlemagne's campaigns. Banat region became part of the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, йНŃгаŃŃŃкО ŃŃŁŃĐ°ŃŃŃŃвиѼ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, ĐŃŃвО ĐąŃНгаŃŃкО ŃĐ°ŃŃŃвО) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europ ...
a few decades later. Archaeological evidence shows the Avars and Gepids lived here until the middle of the 10th century. The Avar rule had triggered considerable Slavic migration to the southern Pannonian plain and to the Balkans.
In 895, the Hungarians living in EtelkĂśz entered the Byzantine-Bulgarian war as allies of Byzantium, and defeated the Bulgars. Because of this, the Bulgarians allied with the Pechenegs, who attacked the Hungarian settlements. This led to the process of what is known as the Hungarian conquest of the Pannonian basin, referred to by them as "hometaking" (') in Hungarian. This also resulted in the loss of part of the territories north of the Danube for the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, ĐŃНгаŃŃкО ŃĐ°ŃŃŃвО, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
.
According to ''Gesta Hungarorum'' chronicle, a local ruler known as Glad ruled over Banat and his army was formed by Vlachs, Bulgarians, and Cumans. Ahtum was another early-11th-century ruler in the territory now known as Banat. His primary source is the Long Life of Saint Gerard, a 14th-century hagiography. Chanadinus, Ahtum's former commander-in-chief, defeated and killed Ahtum, occupying his realm.
Hungarian administration (11thâ16th centuries)
 Banat was administered by the
Banat was administered by the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, йНŃгаŃŃŃкО ŃŃŁŃĐ°ŃŃŃŃвиѼ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, ĐŃŃвО ĐąŃНгаŃŃкО ŃĐ°ŃŃŃвО) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europ ...
from the 9th to the 11th century, but that control gradually migrated to the Kingdom of Hungary which administered it from the 11th century up until 1552, when the region of TemesvĂĄr (today TimiČoara) was captured by the Ottoman Empire.
The area of the TimiČ river was not the land of the Hungarian royal tribe. When nomadic Hungarians came to Transylvania there was no direct Bulgarian political rule there. In the eastern part of the Carpathian basin the Byzantine rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
Th ...
became more influential after Ajtony's ( la, Ahtum) conversion to Christianity. This was halted with the establishment of the Kingdom of Hungary. IstvĂĄn I reasserted dominance over the last local leader, Ajtony. He was a semi-independent ruler of Banat and an Orthodox Christian who constructed a Byzantine monastery at Morisena. His vassal CsanĂĄd defeated him by the will of King Stephen I of Hungary. The territory of the modern Banat did not form a separate territorial unit in medieval Kingdom of Hungary, it was an integral part of it. The territory was shared by KrassĂł, Keve
Keve, the son of Csele of the ZemĂŠny clan, was a legendary Hun leader in the 4th century. Keve was captain of a group of soldiers who headed west into Pannonia in the late 4th century. They fought against the armies of Prince Macrinus from Lomb ...
, Temes, CsanĂĄd, Arad and TorontĂĄl counties.
In 1233, under the Kingdom of Hungary administration, the Banate of Severin, a military frontier area was formed, including some eastern parts of the modern Banat. In the 14th century, the region became of priority concern to the Kingdom, as the southern border of Banat was the most important defensive line against Ottoman expansion from the southeast.
Glad
Glad may refer to:
*Glad (Norse mythology), a horse ridden by the gods in Norse mythology
People
*Emil Glad (1929â2009), Croatian actor
*Ingrid Kristine Glad (born 1965), Norwegian statistician
*John Glad (1941â2015), an American academic, ...
, 9th century
File:Ahtum sermon03 01.png, Duchy of Ahtum, 11th century
File:Koh administrative 1370 01.png, Counties of the Kingdom of Hungary in present-day Banat in the 14th century
File:Banate of severin.png, Banate of Severin
Ottoman administration (1552â1716)
 The Ottoman Empire took over the area and incorporated Banat in 1552. It was absorbed as an Ottoman
The Ottoman Empire took over the area and incorporated Banat in 1552. It was absorbed as an Ottoman eyalet
Eyalets ( Ottoman Turkish: اŰاŮŘŞ, , English: State), also known as beylerbeyliks or pashaliks, were a primary administrative division of the Ottoman Empire.
From 1453 to the beginning of the nineteenth century the Ottoman local government ...
(province) named the Eyalet of TemeĹvar. The Banat region was mainly populated by Rascians ( Serbs) in the west, and Vlachs ( Romanians) in the east. Thus, in some historical sources, the region of Banat was referred to as ''Rascia'', while in others as ''Wallachia''. Numerous Ottoman Muslims settled in the area, living mostly in the cities and associated with trade and administration.
Not all of Banat fell immediately under Turkish rule. Eastern regions around Lugoj and CaransebeČ came under the rule of Princes of Transylvania. In that area, a new banate was formed, known as the Banate of Lugoj and CaransebeČ.
In the spring of 1594, shortly after the beginning of the Austro-Turkish War (1593-1606), local Serbian Christians, in the Eyalet of TemeĹvar, started an uprising against Turkish rule. The local Romanians also participated in this uprising. At first, rebels were successful. They took the city of VrĹĄac and various other towns in Banat and started negotiations with Prince of Transylvania. One of the leaders of the uprising was local Serbian Orthodox Bishop Theodore.
In the middle of the 17th century, the territory of Banate of Lugoj and CaransebeČ finally fell under Turkish rule and was incorporated into Eyalet of TemeĹvar.
During Austro-Turkish War (1683â1699), local Serbian uprisings broke out in various parts of Eyalet of TemeĹvar. Austrian armies and Serbian militia tried to drive out sultans army from the province, but Turks succeeded in holding the fort of TemesvĂĄr. In 1689, Serbian patriarch Arsenije III sided with Austrians. His jurisdiction (including the province) was officially recognized by the charters of emperor Leopold I in 1690, 1691 and 1695. Under the Treaty of Karlowitz (1699), northern parts of the Eyalet of TemeĹvar were incorporated into the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, but the territory of Banat remained under Turkish rule.
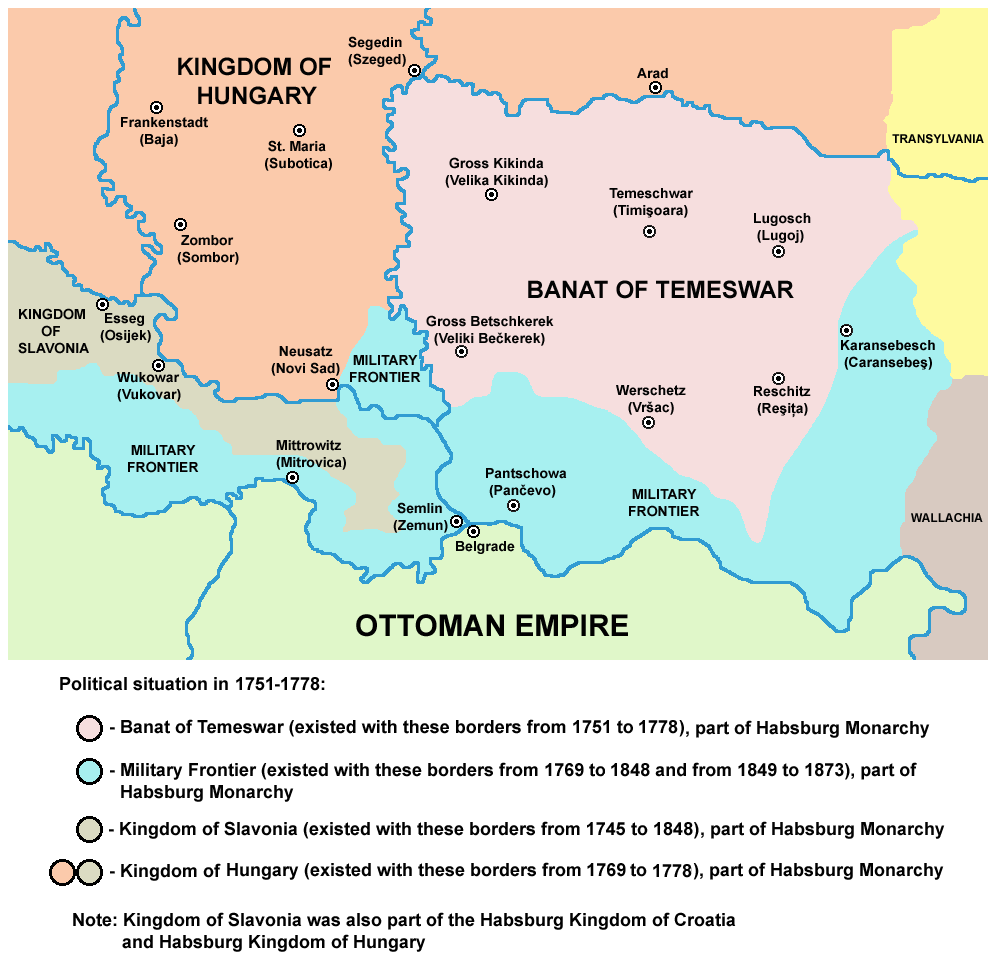
Habsburg administration (1716â1867)



 At the beginning of the next
At the beginning of the next Austro-Turkish War (1716â1718)
The Austro-Turkish War (1716â1718) was fought between Habsburg monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. The 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz was not an acceptable permanent agreement for the Ottoman Empire. Twelve years after Karlowitz, it began the long- ...
, Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene Francis of SavoyâCarignano, (18 October 1663 â 21 April 1736) better known as Prince Eugene, was a Generalfeldmarschall, field marshal in the army of the Holy Roman Empire and of the Austrian Habsburg dynasty during the 17th a ...
took the Banat region from the Turks. After the Treaty of Passarowitz (1718), the region became a province of the Habsburg Monarchy. It was not incorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary. Special provincial administration was established, centered in TemesvĂĄr.
In 1738, over 50 Romanian villages from Serbia and Banat were destroyed and dwellers murdered by Austrians and Serb militia during a revolt of Romanians. Also governor of the province was not given the title of "ban", the region became known as the ''Banate of Temes'' or Banat of Temeswar. It remained a separate province within the Habsburg monarchy and under military administration until 1751, when Empress Maria Theresa of Austria reorganized the province, dividing it between military and civil administration. The Banat of Temeswar province was abolished in 1778, when civilian part of the region was incorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary and divided into counties. The southern part of the Banat region remained within the Military Frontier ( Banat Krajina) until the Frontier was abolished in 1871.
During the Ottoman rule, parts of Banat had a low population density due to years of warfare, and some local residents also lost their lives during Habsburg-Ottoman wars and Prince Eugene of Savoy's conquest. Much of the area had reverted to nearly uninhabited marsh, heath and forest. Count Claudius Mercy (1666â1734), who was appointed governor of the Banat of Temeswar in 1720, took numerous measures for the regeneration of Banat. He recruited German artisans and especially farmers from Bavaria and other southern areas as colonists, allowing them privileges such as keeping their language and religion in their settlements. Farmers brought their families and belongings on rafts down the Danube River, and were encouraged to restore farming in the area. They cleared the marshes near the Danube and Tisa
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza be ...
rivers, helped build roads and canals, and re-established agriculture. Trade was also encouraged.
Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 â 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position ''suo jure'' (in her own right). ...
also took a direct interest in Banat; she colonized the region with large numbers of German farmers, who were admired for their agricultural skills. She encouraged the exploitation of the mineral wealth of the country, and generally developed the measures that were introduced by Count Mercy. German settlers arrived from Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
, Alsace and Bavaria, as did German-speaking colonists from Austria. Many settlements in the eastern Banat were developed by Germans and had ethnic-German majorities. The ethnic Germans in the Banat region became known as the Danube Swabians, or ''Donauschwaben''. After years of separation from their original German provinces, their language was markedly different, preserving historic characteristics.
Similarly, a minority coming from French-speaking or linguistically mixed communes in Lorraine maintained the French language for several generations, and developed a specific ethnic identity, later known as Banat French, ''Français du Banat''.
In 1779, the Banat region was incorporated into the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary, and the three counties of Torontal, Temes and Karasch were created. In 1848, after the May Assembly, the western Banat became part of the Serbian Vojvodina, a Serbian autonomous region within the Habsburg Monarchy. During the Revolutions of 1848â1849, Banat was respectively held by Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
and Hungarian troops.
After the Revolution of 1848â1849, Banat (together with Syrmia
Syrmia ( sh, Srem/ĐĄŃоП or sh, Srijem/ĐĄŃиŃоП, label=none) is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is divided between Serbia and Croatia. Most of the region is flat, with the exce ...
and BaÄka) was designated as a separate Austrian crownland known as the Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banat
, conventional_long_name = Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banate
, common_name = Serbia and Banat
, subdivision = Crownland
, nation = the Austrian Empire
, year_start = 1849
, date_start = 18 November
, year_end = 1860
, date_end = ...
. In 1860 this province was abolished and most of its territory was incorporated into the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary.
The Serbian Banat (Western Banat) was part of Serbian Vojvodina (1848â1849) and part of the Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banat
, conventional_long_name = Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banate
, common_name = Serbia and Banat
, subdivision = Crownland
, nation = the Austrian Empire
, year_start = 1849
, date_start = 18 November
, year_end = 1860
, date_end = ...
(1849â1860). After 1860, later Serbian Banat was part of Torontal and Temes counties of Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary. The center of Torontal county was GroĂbetschkerek (Hungarian: Nagybecskerek, Serbian: Veliki BeÄkerek), the current Zrenjanin.
Hungarian administration (1867â1918)
In 1867, after the Austro-Hungarian compromise the territory returned again to Hungarian administration. After 1871, the former Military Frontier, located in southern parts of Banat, came under civil administration and was incorporated into Banat's counties. KrassĂł and SzĂśrĂŠny were united into KrassĂł-SzĂśrĂŠny in 1881.Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banat
, conventional_long_name = Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banate
, common_name = Serbia and Banat
, subdivision = Crownland
, nation = the Austrian Empire
, year_start = 1849
, date_start = 18 November
, year_end = 1860
, date_end = ...
(1849â1860)
File:Vojvodina10.png, Counties in Banat, BaÄka and Syrmia
Syrmia ( sh, Srem/ĐĄŃоП or sh, Srijem/ĐĄŃиŃоП, label=none) is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is divided between Serbia and Croatia. Most of the region is flat, with the exce ...
from 1881 to 1918
The Banat Question at the end of First World War
In 1918, theBanat Republic
The Banat Republic (german: Banater Republik, hu, BĂĄnĂĄti KĂśztĂĄrsasĂĄg or ''BĂĄnsĂĄgi KĂśztĂĄrsasĂĄg'', ro, Republica bÄnÄČeanÄ or ''Republica Banatului'', sr, ĐанаŃŃка ŃопŃйНика, ) was a short-lived state proclaimed ...
was proclaimed in TimiČoara in October, and the government of Hungary recognized its independence. However, it was short-lived. After just two weeks, Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
troops invaded the region and took control. From November 1918 to March 1919, western and central parts of Banat were governed by Serbian administration from Novi Sad, as part of the Banat, BaÄka and Baranja province of the Kingdom of Serbia and newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (which was later renamed as Yugoslavia).
In the wake of the Declaration of Union of Transylvania with Romania on December 1, 1918, and the Declaration of Unification of Banat, BaÄka and Baranja with Serbia on November 25, 1918, most of Banat was (on July 26, 1919) divided between Romania ( KrassĂł-SzĂśrĂŠny completely, two-thirds of Temes, and a small part of TorontĂĄl) and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (most of TorontĂĄl, and one-third of Temes). A small area near Szeged was assigned to the newly independent Hungary. These borders were confirmed by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles and the 1920 Treaty of Trianon.
At the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the delegates of the Romanian and some German communities voted for union with Romania during the Great National Assembly of Alba Iulia; the delegates of the Serbian, Bunjevac and other Slavic and non-Slavic communities (including some Germans) voted for union with Serbia during the Great People's Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs in Banat, BaÄka and Baranja
The Great People's Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs in Banat, BaÄka and Baranja () or Novi Sad Assembly () was an assembly held in Novi Sad on 25 November 1918, which proclaimed the unification of Banat, BaÄka and Baranya with the Kin ...
; while the Hungarian minority remained loyal to the government in Budapest. Besides these declarations, no other plebiscite was held.
Banat Republic
The Banat Republic (german: Banater Republik, hu, BĂĄnĂĄti KĂśztĂĄrsasĂĄg or ''BĂĄnsĂĄgi KĂśztĂĄrsasĂĄg'', ro, Republica bÄnÄČeanÄ or ''Republica Banatului'', sr, ĐанаŃŃка ŃопŃйНика, ) was a short-lived state proclaimed ...
in 1918
File:Banat backa baranja 02 map.png, Situation around Banat in 1918
File:Banat backa baranja 01 map.png, Situation around Banat in 1919â1921
File:Banat2 en.png, Division of Banat in 1919â1923
Romanian Banat since the First World War

Činutul TimiČ
Činutul TimiČ was one of the ten Romanian ''Činuturi'' ("lands"), founded in 1938 after King Carol II initiated an institutional reform by modifying the 1923 Constitution and the law of territorial administration. It comprised the Romanian ...
, which roughly encompassed the area typically called Banat in Romania.
On 6 September 1950, the province was replaced by the TimiČoara Region (formed by the present-day counties of TimiČ and CaraČ-Severin). In 1956, the southern half of the existing Arad Region was incorporated to the TimiČoara Region. In December 1960, the TimiČoara Region was renamed the Banat Region.
On 17 February 1968, a new territorial division was made and today's TimiČ, CaraČ-Severin and Arad counties were formed.
Since 1998, Romania has been divided into eight development regions, acting as divisions that coordinate and implement regional development. The Vest development region is composed of four counties: Arad, TimiČ, Hunedoara and CaraČ-Severin; thus it has almost same borders as the TimiČ Province (''Činutul TimiČ'') of 1938. The Vest development region is also a part of the Danube-CriČ-MureČ-Tisa Euroregion
In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two (or more) contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border region. ...
.
Serbian Banat since the First World War

 The region was claimed by the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between 1918 and 1922 (as the province of Banat, BaÄka and Baranja between 1918 and 1919) and from 1922 to 1929 it was divided between Belgrade oblast and Podunavlje oblast. In 1929, most of the region was incorporated into the
The region was claimed by the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between 1918 and 1922 (as the province of Banat, BaÄka and Baranja between 1918 and 1919) and from 1922 to 1929 it was divided between Belgrade oblast and Podunavlje oblast. In 1929, most of the region was incorporated into the Danube Banovina
Danube Banovina or Danube Banate ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Dunavska banovina, ĐŃнавŃка йанОвина), was a banovina (or province) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of the geographical ...
(Danubian Banat), a province of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, while the city of PanÄevo
PanÄevo (Serbian Cyrillic: ĐĐ°Đ˝ŃовО, ; german: Pantschowa; hu, Pancsova; ro, Panciova; sk, PĂĄnÄevo) is a city and the administrative center of the South Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is located on ...
was incorporated into self-governed Belgrade district.
During World War II, the Axis Powers occupied this area and partitioned it. Nazi Germany had been intent on expanding into eastern Europe to incorporate what it called the '' Volksdeutsche'', people of ethnic German descent. They established the political entity known as Banat in 1941. It included only the western part of the historical Banat region, which was formerly part of Yugoslavia. It was formally under the control of the Serbian puppet Government of National Salvation in Belgrade led by Milan NediÄ. It theoretically had limited jurisdiction over all of the territory under German Military Administration in Serbia, but in practice the local minority of ethnic Germans (Danube Swabian
The Danube Swabians (german: Donauschwaben ) is a collective term for the ethnic German-speaking population who lived in various countries of central-eastern Europe, especially in the Danube River valley, first in the 12th century, and in grea ...
s or Shwoveh
The Danube Swabians (german: Donauschwaben ) is a collective term for the ethnic German-speaking population who lived in various countries of central-eastern Europe, especially in the Danube River valley, first in the 12th century, and in grea ...
) held the political power within Banat. The regional civilian commissioner was Josef Lapp. The head of the ethnic German group was Sepp Janko. Following the ousting of Axis forces in 1944, this German-ruled region was dissolved. As a consequence, much of the local Germans fled from the region together with defeated German army in 1944. Most of its territory was included in the Vojvodina, one of the two autonomous provinces of Serbia within the new SFR Yugoslavia. Following WWII, most ethnic Germans were expelled from Banat and eastern Europe. Those Germans who remained in the country were sent to prison camps run by the new communist authorities. After prison camps were dissolved (in 1948), most of the remaining German population left Serbia because of economic reasons. Many went to Germany; others emigrated to western Europe and the United States.
Since 1944â1945, the Serbian Banat (together with BaÄka and Syrmia
Syrmia ( sh, Srem/ĐĄŃоП or sh, Srijem/ĐĄŃиŃоП, label=none) is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is divided between Serbia and Croatia. Most of the region is flat, with the exce ...
), has been part of the Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, first as part of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and then as part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, CŃйиŃĐ° и ĐŚŃна ĐĐžŃĐ°, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yu ...
. Since 2006, it has been part of an independent Serbia.
Hungarian Banat since the First World War
The Hungarian Banat consists of a small northern part of the region, which is part of the CsongrĂĄd-CsanĂĄd County of Hungary and is made up of seven villages and the district of Szeged, Ăjszeged. The Hungarian part of Banat used to be the northernmost region of the TorontĂĄl County in the Kingdom of Hungary.Administrative organization
In Romania, Banat includes all of TimiČ and CaraČ-Severin counties (with the exception ofBÄuČar
BÄuČar ( hu, AlsĂłbaucĂĄr) is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, western Romania with a population of 2,604 people as of 2011. It is composed of four villages: BÄuČar, Bucova (''Bukova''), CorniČoru (''Strimba''), and Preveciori.
The commun ...
), Arad County
Arad County () is an administrative division ( judeĹŁ) of Romania roughly translated into county in the western part of the country on the border with Hungary, mostly in the region of CriČana and few villages in Banat. The administrative center ...
(only the part south of the MureČ), the MehedinČi panhandle
A salient (also known as a panhandle or bootheel) is an elongated protrusion of a geopolitical entity, such as a subnational entity or a sovereign state.
While similar to a peninsula in shape, a salient is most often not surrounded by water on ...
(several localities from the traditional Banat area disappeared under the waters of the PorČile de Fier reservoir) and Hunedoara County (only the villages of Pojoga and SÄlciva).
The Serbian Banat includes the part located east of the Tisza in Vojvodina: North Banat District, Central Banat District
The Central Banat District ( sr, ĐĄŃодŃОйанаŃŃки ОкŃŃĐł, Srednjobanatski okrug, ; hu, KĂśzĂŠp-bĂĄnsĂĄgi kĂśrzet) is one of seven administrative districts of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It lies in the geogr ...
and South Banat District, as well as a part of Central Serbia
Central Serbia ( sr, ŃонŃŃаНна ĐĄŃйиŃĐ° / centralna Srbija), also referred to as Serbia proper ( sr, link=no, ŃМа ĐĄŃйиŃĐ° / uĹža Srbija), is the region of Serbia lying outside the autonomous province of Vojvodina to the nort ...
(the area called ''PanÄevaÄki Rit
PanÄevaÄki Rit ( sr-cyr, ĐĐ°Đ˝ŃоваŃки ŃиŃ) is a small geographical area in south-western Banat, Serbia. It is situated between the rivers Danube and TamiĹĄ, in Belgrade's municipality of Palilula.
Features
Its wetland was const ...
'', forming the left part of the Danube in the municipality of Palilula, included in the Belgrade metropolitan area).
In Hungary, there is only a small part of CsongrĂĄd-CsanĂĄd County, namely the part located in the southern angle formed by the Tisza and MureČ rivers, up to the state border with Romania and Serbia.Largest cities
The following table lists the cities in Banat with a population greater than 10,000 (2011). Some cities that are not historically part of Banat expanded into this region during the 20th century, so that today some districts lie in the historical Banat: Arad (Aradu Nou),Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
( Palilula) and Szeged (Ăjszeged).
Demographics
Romanian Banat
Romanians form a clear majority in the south, center and east of Banat since historical times. Their share increased, after 1930, also in the TimiČ Plain (where they were a minority) through immigration from Transylvania, Moldavia and Oltenia. In some settlements the majority is made up of other peoples: Serbs make up the absolute majority inPojejena
Pojejena ( ro, Pojejena, ; Serbian: ĐОМоМона or ''PoĹžeĹžena''; hu, AlsĂłpozsgĂĄs) is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, Romania. The commune is located in the geographical area known as Clisura DunÄrii (''Banatska Klisura'' in Serbian) ...
(ĐОМоМона) and SviniČa
SviniČa ( ro, SviniČa, sr, ХвиŃиŃĐ° or Svinjica, hu, Szinice) is a commune in MehedinČi County, Romania, located on the Danube (in the area of the Banat known as Clisura DunÄrii â ''Banatska Klisura'' in Serbian). It is composed of a ...
(ХвиŃиŃĐ°), and the relative majority in Socol
Socol ( ro, Socol, sr, ХОкОН/Sokol, or ХОкОНОваŃ/Sokolovac, hu, NĂŠrasolymos) is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, Romania (in the ''Clisura DunÄrii'' area of Banat). In 2011, the population of the commune numbered 1,873 pe ...
(ХОкОНОваŃ); Croats (KraĹĄovani
The Krashovani ( ro, CaraČoveni, hr, KraĹĄovani) are a Croat community inhabiting CaraČova and Lupac in the CaraČ-Severin County within Romanian Banat. They are Catholic by faith and speak the Torlakian dialect. Glottolog lists "Karashevski ...
) make up the majority in CaraČova (''KaraĹĄevo'') and Lupac
Lupac (Romanian: ''Lupac''; Croatian: ''Lupak''; hu, KiskrassĂł) is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, Banat, Romania. In 2002, its population numbered 3,023 people and was mostly made up of Krashovani Croats. It is composed of four villages: C ...
(''Lupak''); Bulgarians make up the majority in DudeČtii Vechi (''StĂĄr BiĹĄnov''); while Ukrainians make up the majority in Čtiuca
Čtiuca (Romanian for " pike"; hu, CsukĂĄs; german: Ebendorf; uk, ĐŠŃка or ШŃŃка) is a commune in TimiČ County, Romania. It is composed of four villages: DragomireČti, OloČag, Čtiuca and ZgribeČti. Name
History
The first menti ...
(ĐŠŃка) and CopÄcele
CopÄcele is a commune in CaraČ-Severin County, western Romania with a population of 1,087 people. It is composed of four villages: CopÄcele, Ohaba-Mâtnic, Ruginosu and Zorile. At the 2011 census, 61.1% of inhabitants were Ukrainians and 38.4% ...
(ĐОпаŃиНŃ).
Serbian Banat
In most cities and municipalities of the Serbian Banat, the majority population is Serbian. Hungarians make up the majority of the population in Äoka (''CsĂłka''), andSlovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, SlovĂĄci, singular: ''SlovĂĄk'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
make up the relative majority in the ethnically mixed municipality of KovaÄica. Romanians make up the majority in certain settlements, and Czechs in ÄeĹĄko Selo
ÄeĹĄko Selo (, ) is a village located in the Bela Crkva municipality, in the South Banat District of Serbia. It is situated in the autonomous province of Vojvodina. The village has a Czech ethnic majority (84.78%) and a population of 46 people ( ...
.Hungarian Banat
In the Hungarian part of Banat, the majority population is Hungarian, but in some villages in the region ( Deszk/ĐĐľŃка, SzĹreg/ХиŃиг, ĂjszentivĂĄn/ĐОви ХонŃиван) there is also a Serbian minority.Symbols
The traditional heraldic symbol of Banat is alion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
, which is nowadays present in both the coat of arms of Romania and the coat of arms of Vojvodina. It is assumed that the Banat lion has its origin in the Cuman lion.
The current coat of arms of the Romanian Banat was designed in 1921, after the union of the Banat with the Kingdom of Romania, by the heraldist by combining some elements from the coats of arms of Temes and KrassĂł counties from 1779 to represent the "Romanian Banat of Severin". It consists of a red shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of a ...
in which is represented a golden lion rampant emerging from a golden bridge with two arched openings, built of carved stone, over an azure river. According to its author, "the lion is the old (Cuman) element, the bridge is the new element, Trajan's Bridge over the Danube". The coat of arms from 1921 was modified in 1992 by adding a sabre in the right paw, recalling the backsword of PĂĄl Kinizsi, count of Temes.
Serbs use the seal of the Velika Kikinda District of 1774 to represent Banat. It also features a golden lion rampant with a sabre in the right paw and a severed Turkish head in the left one.Nota