Bastnäsite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The mineral bastnäsite (or bastnaesite) is one of a family of three fluorocarbonate minerals, which includes bastnäsite-( Ce) with a formula of (Ce, La)CO3F, bastnäsite-( La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F, and bastnäsite-( Y) with a formula of (Y, Ce)CO3F. Some of the bastnäsites contain OH− instead of F− and receive the name of hydroxylbastnasite. Most bastnäsite is bastnäsite-(Ce), and
 Bastnäsite has
Bastnäsite has 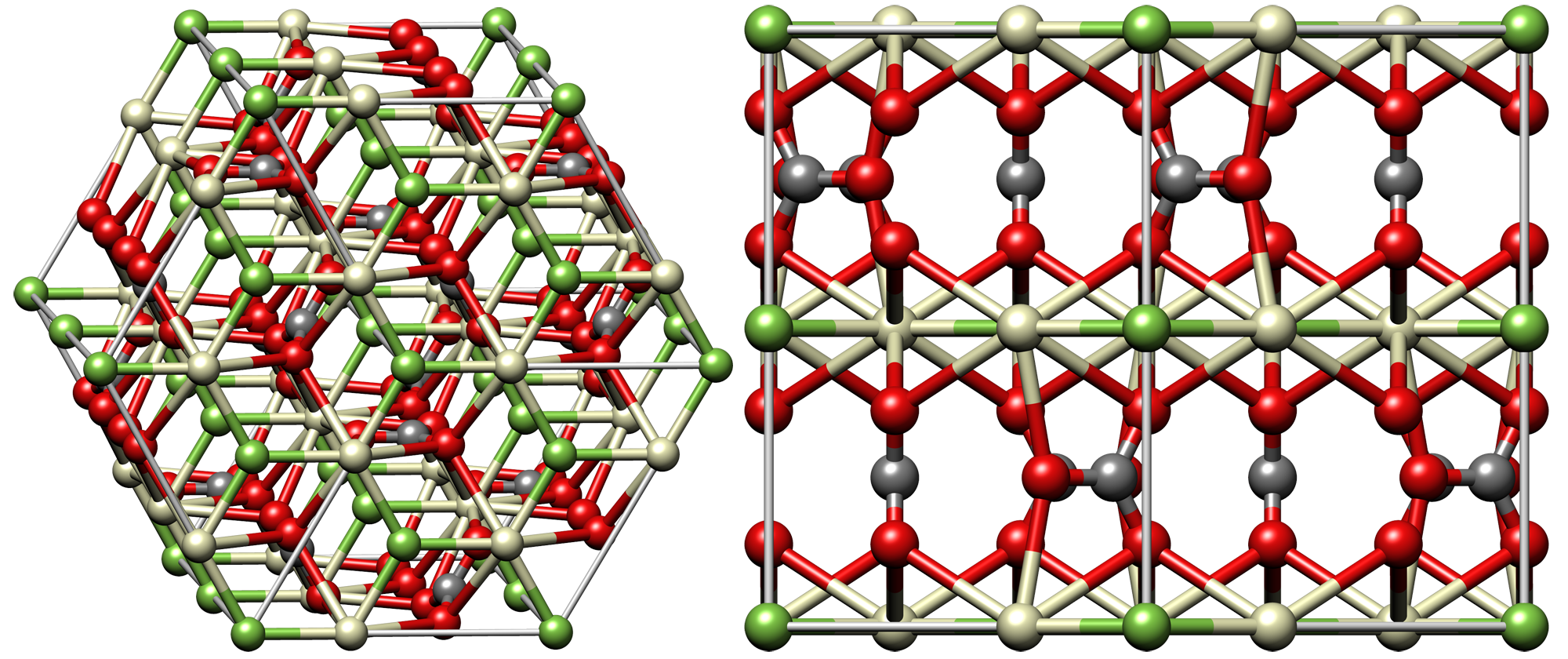 Bastnäsite is closely related to the mineral series parisite.Gupta, C. K. (2004) Extractive metallurgy of rare earths, CRC Press . The two are both rare-earth fluorocarbonates, but parisite's formula of contains
Bastnäsite is closely related to the mineral series parisite.Gupta, C. K. (2004) Extractive metallurgy of rare earths, CRC Press . The two are both rare-earth fluorocarbonates, but parisite's formula of contains
 Bastnäsite ore is typically used to produce rare-earth metals. The following steps and process flow diagram detail the rare-earth-metal extraction process from the ore.McIllree, Roderick. "Kvanefjeld Project – Major Technical Breakthrough". ''ASX Announcements''. Greenland Minerals and Energy LTD, 23 Feb. 2012. Web. 03 Mar. 2014.
# After extraction, bastnasite ore is typically used in this process, with an average of 7% REO (rare-earth oxides).
# The ore goes through
Bastnäsite ore is typically used to produce rare-earth metals. The following steps and process flow diagram detail the rare-earth-metal extraction process from the ore.McIllree, Roderick. "Kvanefjeld Project – Major Technical Breakthrough". ''ASX Announcements''. Greenland Minerals and Energy LTD, 23 Feb. 2012. Web. 03 Mar. 2014.
# After extraction, bastnasite ore is typically used in this process, with an average of 7% REO (rare-earth oxides).
# The ore goes through
cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ...
is by far the most common of the rare earths in this class of minerals. Bastnäsite and the phosphate mineral
Phosphate minerals are minerals that contain the tetrahedrally coordinated phosphate () anion, sometimes with arsenate () and vanadate () substitutions, along with chloride (Cl−), fluoride (F−), and hydroxide (OH−) anions, that also fit in ...
monazite are the two largest sources of cerium and other rare-earth element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set o ...
s.
Bastnäsite was first described by the Swedish chemist Wilhelm Hisinger in 1838. It is named for the Bastnäs mine near Riddarhyttan, Västmanland
Västmanland ( or ) is a historical Swedish province, or , in middle Sweden. It borders Södermanland, Närke, Värmland, Dalarna and Uppland.
Västmanland means "West Man Land" or, less literally, "The Land of the Western Men", where the "we ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
.
Bastnäsite also occurs as very high-quality specimens at the Zagi Mountains, Pakistan.
Bastnäsite occurs in alkali granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
and syenite and in associated pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic c ...
s. It also occurs in carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive rock, intrusive or extrusive rock, extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geoche ...
s and in associated fenites and other metasomatites.
Composition
 Bastnäsite has
Bastnäsite has cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ...
, lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element; it has symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements bet ...
and yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a "rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost a ...
in its generalized formula but officially the mineral is divided into three minerals based on the predominant rare-earth element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set o ...
.Beatty, Richard; 2007; Th℮ Lanthanides; Publish℮d by Marshall Cavendish. There is bastnäsite-(Ce) with a more accurate formula of (Ce, La)CO3F. There is also bastnäsite-(La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F. And finally there is bastnäsite-(Y) with a formula of (Y, Ce)CO3F. There is little difference in the three in terms of physical properties and most bastnäsite is bastnäsite-(Ce). Cerium in most natural bastnäsites usually dominates the others. Bastnäsite and the phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
mineral monazite are the two largest sources of cerium, an important industrial metal.
 Bastnäsite is closely related to the mineral series parisite.Gupta, C. K. (2004) Extractive metallurgy of rare earths, CRC Press . The two are both rare-earth fluorocarbonates, but parisite's formula of contains
Bastnäsite is closely related to the mineral series parisite.Gupta, C. K. (2004) Extractive metallurgy of rare earths, CRC Press . The two are both rare-earth fluorocarbonates, but parisite's formula of contains calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
(and a small amount of neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
) and a different ratio of constituent ions. Parisite could be viewed as a formula unit of calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
(CaCO3) added to two formula units of bastnäsite. In fact, the two have been shown to alter back and forth with the addition or loss of CaCO3 in natural environments.
Bastnäsite forms a series with the minerals hydroxylbastnäsite-(Ce) and hydroxylbastnäsite-(Nd). The three are members of a substitution series that involves the possible substitution of fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
(F−) ions with hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
(OH−) ions.
Name
Bastnäsite gets its name from its type locality, the Bastnäs Mine, Riddarhyttan,Västmanland
Västmanland ( or ) is a historical Swedish province, or , in middle Sweden. It borders Södermanland, Närke, Värmland, Dalarna and Uppland.
Västmanland means "West Man Land" or, less literally, "The Land of the Western Men", where the "we ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
. Ore from the Bastnäs Mine led to the discovery of several new minerals and chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
s by Swedish scientists such as Jöns Jakob Berzelius
Jöns is a Swedish given name and a surname.
Notable people with the given name include:
* Jöns Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848), Swedish chemist
* Jöns Budde (1435–1495), Franciscan friar from the Brigittine monastery in NaantaliVallis Grati ...
, Wilhelm Hisinger and Carl Gustav Mosander. Among these are the chemical elements cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ...
, which was described by Hisinger in 1803, and lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element; it has symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements bet ...
in 1839. Hisinger, who was also the owner of the Bastnäs mine, chose to name one of the new minerals ''bastnäsit'' when it was first described by him in 1838.
Occurrence
Although a scarce mineral and never in great concentrations, it is one of the more common rare-earth carbonates. Bastnäsite has been found in karstbauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
deposits in Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
and the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
region. Also found in carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive rock, intrusive or extrusive rock, extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geoche ...
s, a rare carbonate igneous intrusive rock, at the Fen Complex, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
; Bayan Obo, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
; Kangankunde, Malawi
Malawi, officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeast, and Mozambique to the east, south, and southwest. Malawi spans over and ...
; Kizilcaoren, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and the Mountain Pass rare earth mine in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, US. At Mountain Pass, bastnäsite is the leading ore mineral. Some bastnäsite has been found in the unusual granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
s of the Langesundsfjord area, Norway; Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula (; ) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk of the territory of Murmansk Oblast, it lies almost completely inside the Arctic Circle and is border ...
, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
; Mont Saint-Hilaire mines, Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, and Thor Lake deposits, Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
. Hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with th ...
sources have also been reported.
The formation of hydroxylbastnasite (NdCO3OH) can also occur via the crystallization of a rare-earth bearing amorphous precursor. With increasing temperature, the habit of NdCO3OH crystals changes progressively to more complex spherulitic or dendritic morphologies. The development of these crystal morphologies has been suggested to be controlled by the level at which supersaturation is reached in the aqueous solution during the breakdown of the amorphous precursor. At higher temperature (e.g., 220 °C) and after rapid heating (e.g. < 1 h) the amorphous precursor breaks down rapidly and the fast supersaturation promotes spherulitic growth. At a lower temperature (e.g., 165 °C) and slow heating (100 min) the supersaturation levels are approached more slowly than required for spherulitic growth, and thus more regular triangular pyramidal shapes form.
Mining history
In 1949, the huge carbonatite-hosted bastnäsite deposit was discovered atMountain Pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since mountain ranges can present formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human and animal migration t ...
, San Bernardino County, California
San Bernardino County ( ), officially the County of San Bernardino and sometimes abbreviated as S.B. County, is a County (United States), county located in the Southern California, southern portion of the U.S. state of California, and is locat ...
, US. This discovery alerted geologists to the existence of a whole new class of rare earth deposit: the rare earth containing carbonatite. Other examples were soon recognized, particularly in Africa and China. The exploitation of this deposit began in the mid-1960s after it had been purchased by Molycorp
Neo Performance Materials (formerly Molycorp Inc.) is a Canadian mining corporation headquartered in Toronto, Ontario. The corporation was formerly traded on the New York Stock Exchange, owned the Mountain Pass rare earth mine in California. I ...
(Molybdenum Corporation of America). The lanthanide composition of the ore included 0.1% europium oxide, which was needed by the color television industry, to provide the red phosphor, to maximize picture brightness. The composition of the lanthanides was about 49% cerium, 33% lanthanum, 12% neodymium, and 5% praseodymium, with some samarium and gadolinium, or distinctly more lanthanum and less neodymium and heavies as compared to commercial monazite. The europium content was at least double that of a typical monazite.
Mountain Pass bastnäsite was the world's major source of lanthanides from the 1960s to the 1980s. Thereafter, China became an increasingly important rare earth supply. Chinese deposits of bastnäsite include several in Sichuan Province
Sichuan is a Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capita ...
, and the massive deposit at Bayan Obo, Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. ...
, which had been discovered early in the 20th century, but not exploited until much later. Bayan Obo is currently (2008) providing the majority of the world's lanthanides. Bayan Obo bastnäsite occurs in association with monazite (plus enough magnetite to sustain one of the largest steel mills in China), and unlike carbonatite bastnäsites, is relatively closer to monazite lanthanide compositions, with the exception of its generous 0.2% content of europium.
Ore technology
At Mountain Pass, bastnäsite ore was finely ground, and subjected to flotation to separate the bulk of the bastnäsite from the accompanyingbarite
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate (Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
, calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
, and dolomite. Marketable products include each of the major intermediates of the ore dressing process: flotation concentrate, acid-washed flotation concentrate, calcined acid washed bastnäsite, and finally a cerium concentrate, which was the insoluble residue left after the calcined bastnäsite had been leached with hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
. The lanthanides that dissolved as a result of the acid treatment were subjected to solvent extraction
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
, to capture the europium
Europium is a chemical element; it has symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is a silvery-white metal of the lanthanide series that reacts readily with air to form a dark oxide coating. Europium is the most chemically reactive, least dense, and soft ...
, and purify the other individual components of the ore. A further product included a lanthanide mix, depleted of much of the cerium, and essentially all of samarium and heavier lanthanides. The calcination of bastnäsite had driven off the carbon dioxide content, leaving an oxide-fluoride, in which the cerium content had become oxidized to the less basic quadrivalent state. However, the high temperature of the calcination gave less-reactive oxide, and the use of hydrochloric acid, which can cause reduction of quadrivalent cerium, led to an incomplete separation of cerium and the trivalent lanthanides. By contrast, in China, processing of bastnäsite, after concentration, starts with heating with sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
.
Extraction of rare-earth metals
 Bastnäsite ore is typically used to produce rare-earth metals. The following steps and process flow diagram detail the rare-earth-metal extraction process from the ore.McIllree, Roderick. "Kvanefjeld Project – Major Technical Breakthrough". ''ASX Announcements''. Greenland Minerals and Energy LTD, 23 Feb. 2012. Web. 03 Mar. 2014.
# After extraction, bastnasite ore is typically used in this process, with an average of 7% REO (rare-earth oxides).
# The ore goes through
Bastnäsite ore is typically used to produce rare-earth metals. The following steps and process flow diagram detail the rare-earth-metal extraction process from the ore.McIllree, Roderick. "Kvanefjeld Project – Major Technical Breakthrough". ''ASX Announcements''. Greenland Minerals and Energy LTD, 23 Feb. 2012. Web. 03 Mar. 2014.
# After extraction, bastnasite ore is typically used in this process, with an average of 7% REO (rare-earth oxides).
# The ore goes through comminution
Comminution is the reduction of solid materials from one average particle size to a smaller average particle size, by crushing, grinding, cutting, vibrating, or other processes. Comminution is related to pulverization and grinding. All use m ...
using rod mills, ball mills, or autogenous mills.
# Steam is consistently used to condition the ground ore, along with soda ash fluosilicate, and usually Tail Oil C-30. This is done to coat the various types of rare earth metals with either flocculent, collectors, or modifiers for easier separation in the next step.
# Flotation using the previous chemicals to separate the gangue from the rare-earth metals.
# Concentrate the rare-earth metals and filter out large particles.
# Remove excess water by heating to ~100 °C.
# Add HCl to solution to reduce pH to < 5. This enables certain REM (rare-earth metals) to become soluble (Ce is an example).
# Oxidizing roast further concentrates the solution to approximately 85% REO. This is done at ~100 °C and higher if necessary.
# Enables solution to concentrate further and filters out large particles again.
# Reduction agents (based on area) are used to remove Ce as Ce carbonate or CeO2, typically.
# Solvents are added (solvent type and concentration based on area, availability, and cost) to help separate Eu, Sm, and Gd from La, Nd, and Pr.
# Reduction agents (based on area) are used to oxidize Eu, Sm, and Gd.
# Eu is precipitated and calcified.
# Gd is precipitated as an oxide.
# Sm is precipitated as an oxide.
# Solvent is recycled into step 11. Additional solvent is added based on concentration and purity.
# La separated from Nd, Pr, and SX.
# Nd and Pr separated. SX goes on for recovery and recycle.
# One way to collect La is adding HNO3, creating La(NO3)3. HNO3 typically added at a very high molarity (1–5 M), depending on La concentration and amount.
# Another method is to add HCl to La, creating LaCl3. HCl is added at 1 M to 5 M depending on La concentration.
# Solvent from La, Nd, and Pr separation is recycled to step 11.
# Nd is precipitated as an oxide product.
# Pr is precipitated as an oxide product.
References
Bibliography
*Palache, P.; Berman H.; Frondel, C. (1960). "''Dana's System of Mineralogy, Volume II: Halides, Nitrates, Borates, Carbonates, Sulfates, Phosphates, Arsenates, Tungstates, Molybdates, Etc. (Seventh Edition)"'' John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, pp. 289–291. {{DEFAULTSORT:Bastnasite Lanthanide minerals Radioactive gemstones Carbonate minerals Fluorine minerals Hexagonal minerals Minerals in space group 190