Astronomical symbols on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Astronomical symbols are abstract pictorial
Astronomical symbols are abstract pictorial
File:Sun symbol (late classical and medieval mss).png, The symbol for the Sun in late Classical (4th c.) and medieval Byzantine (11th c.) manuscripts
File:Moon symbol (medieval ms).png, The symbol for the Moon in a medieval Byzantine manuscript (11th c.). The late Classical appearance was similar.
In modern academic writing, the Sun symbol is used for astronomical constants relating to the Sun. Teff☉ represents the solar
 Symbols for the
Symbols for the
File:Mercury symbol (late classical and medieval mss).png, The symbol for Mercury in late Classical (4th c.) and medieval Byzantine (11th c.) manuscripts
File:Venus symbol (late classical and medieval mss).png, The symbol for Venus in late Classical (4th c.) and medieval Byzantine (11th c.) manuscripts
File:Mars symbol (late classical and medieval mss).png, The symbol for Mars in late Classical (6th c.) and medieval Byzantine (11th c.) manuscripts
File:Jupiter symbol (late classical and medieval mss).png, The symbol for Jupiter in late Classical (4th c.) and medieval Byzantine (11th c.) manuscripts
File:Saturn symbol (late classical and medieval mss).png, The symbol for Saturn in late Classical (4th & 5th c.) and medieval Byzantine (11th c.) manuscripts – cf. kappa-rho,
The symbols for
file:Ceres and Pallas symbols, 1802.png, Symbols for Ceres and Pallas, as rendered in 1802
file:3 Juno symbol (1804).png, Symbol for Juno, as rendered in 1804 with the available type sorts of an asterisk * and a rotated
German astronomer  All these symbols are rare or obsolete in modern astronomy, though NASA has used Ceres' symbol when describing the dwarf planets, and Psyche's symbol may have influenced the design of the insignia for the '' Psyche'' mission. The major use of symbols for minor planets today is by astrologers, who have invented symbols for many more objects, though they sometimes use symbols that differ from the historical symbols for the same bodies.
The symbol for
All these symbols are rare or obsolete in modern astronomy, though NASA has used Ceres' symbol when describing the dwarf planets, and Psyche's symbol may have influenced the design of the insignia for the '' Psyche'' mission. The major use of symbols for minor planets today is by astrologers, who have invented symbols for many more objects, though they sometimes use symbols that differ from the historical symbols for the same bodies.
The symbol for

 The zodiac symbols have several astronomical interpretations. Depending on context, a zodiac symbol may denote either a constellation, or a point or interval on the ecliptic plane.
Lists of astronomical phenomena published by almanacs sometimes included conjunctions of stars and planets or the Moon; rather than print the full name of the star, a Greek letter and the symbol for the constellation of the star was sometimes used instead.
The ecliptic was sometimes divided into 12 ''signs'', each subdivided into 30 degrees,
and the ''sign'' component of ecliptic longitude was expressed either with a number from 0 to 11.
The 1834 edition of the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris'' abandoned the use of numerical signs (among other innovations); compare the representation of (ecliptic) longitude in the editions for the year
The zodiac symbols have several astronomical interpretations. Depending on context, a zodiac symbol may denote either a constellation, or a point or interval on the ecliptic plane.
Lists of astronomical phenomena published by almanacs sometimes included conjunctions of stars and planets or the Moon; rather than print the full name of the star, a Greek letter and the symbol for the constellation of the star was sometimes used instead.
The ecliptic was sometimes divided into 12 ''signs'', each subdivided into 30 degrees,
and the ''sign'' component of ecliptic longitude was expressed either with a number from 0 to 11.
The 1834 edition of the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris'' abandoned the use of numerical signs (among other innovations); compare the representation of (ecliptic) longitude in the editions for the year
1834
an
1833
or with the corresponding zodiacal symbol. In modern astronomical writing, all the constellations, including the 12 of the zodiac, have dedicated three-letter abbreviations, which specifically refer to ''constellations'' rather than ''signs''. The zodiac symbols are also sometimes used to represent points on the ecliptic, particularly the solstices and equinoxes. Each symbol is taken to represent the "first point" of each ''sign'', rather than the place in the visible ''constellation'' where the alignment is observed. Thus, ♈︎ the symbol for Aries, represents the
 ) have been used in published astronomical observations of comets. In tables of these observations, ☄ stood for the comet being discussed and
) have been used in published astronomical observations of comets. In tables of these observations, ☄ stood for the comet being discussed and  for the star of comparison relative to which measurements of the comet's position were made.
:
for the star of comparison relative to which measurements of the comet's position were made.
:
 :
:  :
:  :
:  : Lyrids
: Lyrids  :
: 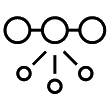 :
:  : Quadrantids
: Quadrantids  :
: 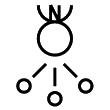
 : Ursids
: Ursids  For planetary transits of Mercury and Venus, Moskowitz proposed overlaying the respective planetary symbol on that of the Sun, extending the crossbar into an arrow:
For planetary transits of Mercury and Venus, Moskowitz proposed overlaying the respective planetary symbol on that of the Sun, extending the crossbar into an arrow:  (Mercury),
(Mercury),  (Venus). This also has some limited use.
Limited use can also be found of Moskowitz's symbol for
(Venus). This also has some limited use.
Limited use can also be found of Moskowitz's symbol for
 Astronomical symbols are abstract pictorial
Astronomical symbols are abstract pictorial symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
s used to represent astronomical object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are of ...
s, theoretical constructs and observational events in European astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
. The earliest forms of these symbols appear in Greek papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
texts of late antiquity. The Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
codices
The codex (: codices ) was the historical ancestor format of the modern book. Technically, the vast majority of modern books use the codex format of a stack of pages bound at one edge, along the side of the text. But the term ''codex'' is now r ...
in which many Greek papyrus texts were preserved continued and extended the inventory of astronomical symbols. New symbols have been invented to represent many planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s and minor planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor ...
s discovered in the 18th to the 21st centuries.
These symbols were once commonly used by professional astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galax ...
s, amateur astronomers, alchemists
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first ...
, and astrologer
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
s. While they are still commonly used in almanacs and astrological publications, their occurrence in published research and texts on astronomy is relatively infrequent, with some exceptions such as the Sun and Earth symbols appearing in astronomical constant
An astronomical constant is any of several physical constants used in astronomy. Formal sets of constants, along with recommended values, have been defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) several times: in 1964Resolution No.4 of thXII ...
s, and certain zodiacal signs used to represent the solstice
A solstice is the time when the Sun reaches its most northerly or southerly sun path, excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around 20–22 June and 20–22 December. In many countries ...
s and equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
es.
Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Char ...
has encoded many of these symbols, mainly in the Miscellaneous Symbols
Miscellaneous Symbols is a Unicode block (U+2600–U+26FF) containing glyphs representing concepts from a variety of categories: astrological, astronomical, chess, dice, musical notation, political symbols, recycling, religious symbols, trig ...
, Miscellaneous Symbols and Arrows
Miscellaneous Symbols and Arrows is a Unicode block containing arrows and geometric shapes with various fills, astrological symbols, technical symbols, intonation marks, and others.
Block
Emoji
The Miscellaneous Symbols and Arrows block co ...
, Miscellaneous Symbols and Pictographs
Miscellaneous Symbols and Pictographs is a Unicode block containing meteorological and astronomical symbols, emoji characters largely for compatibility with Japanese telephone carriers' implementations of Shift JIS, and characters originally from ...
,
and Alchemical Symbols
Alchemical symbols were used to denote chemical elements and compounds, as well as alchemy, alchemical apparatus and processes, until the 18th century. Although notation was partly standardized, style and symbol varied between alchemists. Lüdy ...
blocks.
__TOC__
Sun and Moon
The use of astronomical symbols for the Sun and Moon dates to antiquity. The forms of the symbols that appear in the original papyrus texts of Greek horoscopes are a circle with one ray () for the Sun and a crescent for the Moon. The modern Sun symbol, a circle with a dot (☉), first appeared in Europe in the Renaissance.effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
, and the luminosity, mass, and radius of stars are often represented using the corresponding solar constants (, , and , respectively) as units of measurement
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other qua ...
.
Planets
 Symbols for the
Symbols for the classical planet
A classical planet is an astronomical object that is visible to the naked eye and moves across the sky and its backdrop of fixed stars (the common stars which seem still in contrast to the planets), appearing as wandering stars. Visible to huma ...
s appear in many medieval Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
codices in which many ancient horoscopes were preserved.
The written symbols for Mercury, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
, and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
have been traced to forms found in late Greek papyrus texts.
The symbols for Jupiter and Saturn are identified as monogram
A monogram is a motif (visual arts), motif made by overlapping or combining two or more letters or other graphemes to form one symbol. Monograms are often made by combining the initials of an individual or a company, used as recognizable symbo ...
s of the corresponding Greek names, and the symbol for Mercury is a stylized caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; , ) is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was borne by other heralds like Iris (mythology), Iris, the messenger of Hera. The s ...
. According to A.S.D. Maunder, antecedents of the planetary symbols were used in art to represent the gods associated with the classical planets; ''Bianchini's planisphere
In astronomy, a planisphere () is a star chart analog computing instrument in the form of two adjustable disks that rotate on a common pivot. It can be adjusted to display the visible stars for any time and date. It is an instrument to assist i ...
'', discovered by Francesco Bianchini in the 18th century, produced in the 2nd century,
shows Greek personifications of planetary gods charged with early versions of the planetary symbols: Mercury has a caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; , ) is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was borne by other heralds like Iris (mythology), Iris, the messenger of Hera. The s ...
; Venus has, attached to her necklace, a cord connected to another necklace; Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, a spear; Jupiter, a staff; Saturn, a scythe; the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, a circlet with rays radiating from it; and the Moon, a headdress with a crescent attached.
A diagram in Byzantine astronomer Johannes Kamateros's 12th century ''Compendium of Astrology'' shows the Sun represented by the circle with a ray, Jupiter by the letter Zeta
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; , , classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter zay ...
(the initial of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, Jupiter's counterpart in Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
), Mars by a shield crossed by a spear, and the remaining classical planets by symbols resembling the modern ones, without the cross-mark at the bottom of the modern versions of the symbols for Mercury and Venus. These cross-marks first appear around the 16th century. According to Maunder, the addition of crosses appears to be "an attempt to give a savour of Christianity to the symbols of the old pagan gods."
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
were created shortly after its discovery. One symbol, , invented by J. G. Köhler and refined by Bode, was intended to represent the newly discovered metal platinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name origina ...
; since platinum, commonly called white gold, was found by chemists mixed with iron, the symbol for platinum combines the alchemical symbols for the planetary elements iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, ♂, and gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, ☉.
Another symbol, , was suggested by Joseph Jérôme Lefrançois de Lalande in 1784. In a letter to William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
, Lalande described it as ''"un globe surmonté par la première lettre de votre nom"'' (''"a globe surmounted by the first letter of your name"'').
Today, Köhler's symbol is more common among astronomers, and Lalande's among astrologers, although it is not uncommon to see each symbol in the other context.
Several symbols were proposed for Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
to accompany the suggested names for the planet. Claiming the right to name his discovery, Urbain Le Verrier
Urbain Jean Joseph Le Verrier (; 11 March 1811 – 23 September 1877) was a French astronomer and mathematician who specialized in celestial mechanics and is best known for predicting the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics. ...
originally proposed the name ''Neptune''
and the symbol of a trident
A trident (), () is a three- pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm. As compared to an ordinary spear, the three tines increase the chance that a fish will be struck and decrease the chance that a fish will b ...
,
while falsely stating that this had been officially approved by the French Bureau des Longitudes
__NOTOC__
The ''Bureau des Longitudes'' () is a French scientific institution, founded by decree of 25 June 1795 and charged with the improvement of nautical navigation, standardisation of time-keeping, geodesy and astronomical observation. Durin ...
. In October, he sought to name the planet ''Leverrier'', after himself, and he had loyal support in this from the observatory director, François Arago
Dominique François Jean Arago (), known simply as François Arago (; Catalan: , ; 26 February 17862 October 1853), was a French mathematician, physicist, astronomer, freemason, supporter of the Carbonari revolutionaries and politician.
Early l ...
,
who in turn proposed a new symbol for the planet (). However, this suggestion met with stiff resistance outside France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. French almanacs quickly reintroduced the name ''Herschel'' for ''Uranus'', after that planet's discoverer Sir William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
, and ''Leverrier'' for the new planet. Professor James Pillans of the University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under th ...
defended the name ''Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janus (''Ianu ...
'' for the new planet, and proposed a key for its symbol. Meanwhile, German-Russian astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galax ...
Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve
Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve (, trans. ''Vasily Yakovlevich Struve''; 15 April 1793 – ) was a Baltic German astronomer and geodesist. He is best known for studying double stars and initiating a triangulation survey later named Struve ...
presented the name ''Neptune'' on December 29, 1846, to the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences. In August 1847, the Bureau des Longitudes announced its decision to follow prevailing astronomical practice and adopt the choice of ''Neptune'', with Arago refraining from participating in this decision.
The International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
discourages the use of these symbols in journal articles, though they do occur. In certain cases where planetary symbols might be used, such as in the headings of tables, the ''IAU Style Manual'' permits certain one- and (to disambiguate Mercury and Mars) two-letter abbreviations for the names of the planets.
:
Asteroids
Following the discovery of Ceres in 1801 by the astronomer andCatholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
priest Giuseppe Piazzi
Giuseppe Piazzi ( , ; 16 July 1746 – 22 July 1826) was an Italian Catholic Church, Catholic priest of the Theatines, Theatine order, mathematician, and astronomer. He established an observatory at Palermo, now the ''Palermo Astronomical Ob ...
, a group of astronomers ratified the name, which Piazzi had proposed. At that time, the sickle was chosen as a symbol of the planet.
The symbol for 2 Pallas
Pallas (minor-planet designation: 2 Pallas) is the List of largest asteroids, third-largest asteroid in the Solar System by volume and mass. It is the second asteroid to have been discovered, after 1 Ceres, Ceres, and is likely a remnant ...
, the spear of Pallas Athena, was invented by Baron Franz Xaver von Zach
Baron Franz Xaver von Zach (''Franz Xaver Freiherr von Zach''; 4 June 1754 – 2 September 1832) was an Austrian astronomer born at Pest, Hungary (now Budapest in Hungary).
Biography
Zach studied physics at the Royal University of Pest, and ...
, who organized a group of twenty-four astronomers to search for a planet between the orbits of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
and Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
. The symbol was introduced by von Zach in 1802.
In a letter to von Zach, discoverer Heinrich Wilhelm Matthäus Olbers (who had discovered and named Pallas) expressed his approval of the proposed symbol, but wished that the handle of the sickle of Ceres had been adorned with a pommel instead of a crossbar, to better differentiate it from the sign of Venus.
dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually one or two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a cutting or stabbing, thrusting weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or ...
†
File:Vesta symbol, 1807.png, Symbol for Vesta, as rendered in 1807
Karl Ludwig Harding
Karl Ludwig Harding (29 September 1765 – 31 August 1834) was a German astronomer, who discovered 3 Juno, Juno, the third asteroid of the main-belt in 1804.
Life and career
Harding was born in Lauenburg. From 1786–1789, he was educated a ...
created the symbol for 3 Juno
Juno (minor-planet designation: 3 Juno) is a large asteroid in the asteroid belt. Juno was the third asteroid discovered, in 1804, by German astronomer Karl Harding. It is tied with three other asteroids as the thirteenth largest asteroid, and ...
. Harding, who discovered this asteroid in 1804, proposed the name Juno and the use of a scepter topped with a star as its astronomical symbol.
The symbol for 4 Vesta
Vesta (minor-planet designation: 4 Vesta) is one of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, with a mean diameter of . It was discovered by the German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Matthias Olbers on 29 March 1807 and is named after Vesta (mytho ...
was invented by German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observatory and ...
. Olbers, having previously discovered and named 2 Pallas, gave Gauss the honor of naming his newest discovery. Gauss decided to name the new asteroid for the goddess Vesta, and also designed the symbol (): the altar of the goddess, with the sacred fire burning on it. Other contemporaneous writers use a more elaborate symbol () instead.
Karl Ludwig Hencke
Karl Ludwig Hencke (8 April 1793 – 21 September 1866) was a German amateur astronomer and discoverer of minor planets. He is sometimes confused with Johann Franz Encke, another :German astronomers, German astronomer.
Biography
Hencke was born ...
, a German amateur astronomer, discovered the next two asteroids, 5 Astraea
5 Astraea () is an asteroid in the asteroid belt. This object is orbiting the Sun at a distance of with a period of and an orbital eccentricity of 0.19. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 5.37° to the plane of the ecliptic. It is sp ...
(in 1845) and 6 Hebe
6 Hebe () is a large main-belt asteroid, containing around 0.5% of the mass of the belt. However, due to its apparently high bulk density (greater than that of the Moon), Hebe does not rank among the top twenty asteroids by volume. This high bu ...
(in 1847). Hencke requested that the symbol for 5 Astraea be an upside-down anchor;
however, a weighing scale
A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, massometers, and weight balances.
The traditional scale consists of two plates or bowls suspended at equal d ...
was sometimes used instead. Gauss named 6 Hebe at Hencke's request, and chose a wineglass as the symbol.
As more new asteroids were discovered, astronomers continued to assign symbols to them. Thus, 7 Iris (discovered 1847) had for its symbol a rainbow with a star; 8 Flora (discovered 1847), a flower; 9 Metis
9 Metis is one of the larger main-belt asteroids. It is composed of silicates and metallic nickel-iron, and may be the core remnant of a large asteroid that was destroyed by an ancient collision. Metis is estimated to contain just under half a ...
(discovered 1848), an eye with a star;
10 Hygiea
10 Hygiea is a large asteroid located in the outer main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It was the tenth known asteroid, discovered on 12 April 1849 by Italian astronomer Annibale de Gasparis at the Astronomical Observa ...
(discovered 1849), an upright snake with a star on its head; 11 Parthenope (discovered 1850), a standing fish with a star; 12 Victoria
12 Victoria is a large main-belt asteroid, orbiting the Sun with a orbital period, period of 3.56 years and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity of 0.221. It is a S-type asteroid, stony (S-type) asteroid, about 112–124 km across wit ...
(discovered 1850), a star topped with a branch of laurel
Laurel may refer to:
Plants
* Lauraceae, the laurel family
* Laurel (plant), including a list of trees and plants known as laurel
People
* Laurel (given name), people with the given name
* Laurel (surname), people with the surname
* Laurel (mus ...
; 13 Egeria (discovered 1850), a buckler; 14 Irene
14 Irene () is a large main-belt asteroid, discovered by the English astronomer John Russell Hind on May 19, 1851. It is orbiting the Sun at a distance of with a period of and an eccentricity of 0.168. The orbital plane is tilted at an a ...
(discovered 1851), a dove carrying an olive branch with a star on its head; 15 Eunomia (discovered 1851), a heart topped with a star; 16 Psyche
16 Psyche ( ) is a large M-type asteroid, which was discovered by the Italian astronomer Annibale de Gasparis, on 17 March 1852 and named after the Greek goddess Psyche.
The prefix "16" signifies that it was the sixteenth minor plane ...
(discovered 1852), a butterfly wing with a star; 17 Thetis
17 Thetis is a stony asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 90 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 April 1852, by German astronomer Robert Luther at Bilk Observatory in Düsseldorf, Germany who deferred ...
(discovered 1852), a dolphin with a star; 18 Melpomene (discovered 1852), a dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually one or two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a cutting or stabbing, thrusting weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or ...
over a star; and 19 Fortuna (discovered 1852), a star over Fortuna's wheel.
In most cases the discovery reports only describe the symbols and do not draw them; from Hygiea onward, there are significant glyph variants as well as a significant delay between the discovery and the symbols having been communicated to the astronomical community as a whole. Consequently, astronomical publications were not always complete. The discovery reports for Melpomene and Fortuna do not even describe the symbols, which only appear in a later reference work by the discoverer; the symbols are drawn in the reports for Astraea, Hebe, and Thetis. Benjamin Apthorp Gould criticised the symbols in 1852 as being often inefficient at suggesting the bodies they represented and difficult to draw, and pointed out that the symbol that had been described for Irene had to his knowledge never actually been drawn. The same year, John Russell Hind expressed the contrary view that the symbols were easier to remember than the numbers, but also admitted that the names were more commonly used than either the numbers or the symbols.
The last edition of the Berliner Astronomisches Jahrbuch
The ''Berliner Astronomisches Jahrbuch'' (abbrev. B.A.J.) is an astronomical ephemeris almanac and one of the longest publication series in astronomy. It was a compendium of ephemerides of all large Solar System bodies and of fundamental stars wh ...
(BAJ, Berlin Astronomical Yearbook) to use asteroid symbols was for the year 1853, published in 1850: although it includes eleven asteroids up to Parthenope, it only includes symbols for the first nine (up to Metis), noting that the symbols for Hygiea and Parthenope had not yet been made definitively known. The last edition of the British ''The Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris'' to include asteroid ephemerides was that for 1855, published in 1852: despite fifteen asteroids being known (up to Eunomia), symbols are only included for the first nine.
Johann Franz Encke
Johann Franz Encke (; 23 September 179126 August 1865) was a German astronomer. Among his activities, he worked on the calculation of the periods of comets and asteroids, measured the distance from the Earth to the Sun, and made observations ...
made a major change in the BAJ for the year 1854, published in 1851. He introduced encircled numbers instead of symbols, although his numbering began with Astraea
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Astraea (; ), also spelled Astrea or Astria, is a daughter of Astraeus and Eos. She is the virgin goddess of justice, innocence, purity, and precision. She is closely associated with the Greek goddess of ...
, the first four asteroids continuing to be denoted by their traditional symbols. This symbolic innovation was adopted very quickly by the astronomical community. The following year (1852), Astraea's number was bumped up to 5, but Ceres through Vesta were not listed by their numbers until the 1867 edition. The ''Astronomical Journal'' edited by Gould adopted the symbolism in this form, with Ceres at 1 and Astraea at 5. This form had previously been proposed in an 1850 letter by Heinrich Christian Schumacher to Gauss. The circle later became a pair of parentheses, which were easier to typeset, and the parentheses were sometimes omitted altogether over the next few decades. Thus the iconic asteroid symbols fell out of use; reference works continued giving them for the next few decades, though they often noted them as being obsolete.
A few asteroids were given symbols by their discoverers after the encircled-number notation became widespread. 26 Proserpina (discovered 1853), 28 Bellona (discovered 1854), 35 Leukothea
35 Leukothea is a large, dark asteroid from the asteroid belt. It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Theodor Robert Luther on April 19, 1855, and named after Leukothea, a sea goddess in Greek mythology. Its historical symbol was a ''pha ...
(discovered 1855), and 37 Fides
37 Fides () is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Theodor Robert Luther on October 5, 1855, and named after Fides, the Roman goddess of loyalty. Fides was the last of the main-belt asteroids to be assigned ...
(discovered 1855), all discovered by German astronomer Robert Luther
Karl Theodor Robert Luther (16 April 1822, Świdnica – 15 February 1900 Düsseldorf), normally published as Robert Luther, was a German astronomer. While working at the Bilk Observatory in Düsseldorf, Germany, he searched for asteroids and di ...
, were assigned, respectively, a pomegranate with a star inside; a whip and spear; an antique lighthouse; and a cross. These symbols were drawn in the discovery reports. 29 Amphitrite
29 Amphitrite is one of the largest S-type asteroids, approximately in diameter, and probably fifth largest after 15 Eunomia, Eunomia, 3 Juno, Juno, 7 Iris, Iris and 532 Herculina, Herculina.
Discovery
Amphitrite was discovered by Albert Mart ...
was named and assigned a shell for its symbol by George Bishop, the owner of the observatory where astronomer Albert Marth
Albert Marth (5 May 1828 – 6 August 1897) was a German astronomer who worked in United Kingdom, Britain and Ireland.
Life
After studying theology at the University of Berlin, his interest in astronomy and mathematics led him to study astro ...
discovered it in 1854, though the symbol was not drawn in the discovery report.
99942 Apophis
99942 Apophis ( provisional designation ) is a near-Earth asteroid and a potentially hazardous object, 450 metres (1,480 ft) by 170 metres (560 ft) in size, that caused a brief period of concern in December 2004 when initial observatio ...
, a near-Earth asteroid
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit aro ...
discovered in 2004 that attracted interest when initial observations suggested a significant probability of an Earth impact in 2029 (a possibility since eliminated), is much later. It was designed by Denis Moskowitz, who also designed many of the dwarf-planet symbols, at a time when asteroid symbols had become extremely rare in astronomy. Nonetheless, its inclusion of a star is meant to recall the 19th-century asteroid symbols.
Table
Trans-Neptunian objects
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
's name and symbol were announced by the discoverers on May 1, 1930.
The symbol, a monogram
A monogram is a motif (visual arts), motif made by overlapping or combining two or more letters or other graphemes to form one symbol. Monograms are often made by combining the initials of an individual or a company, used as recognizable symbo ...
of the letters PL, could be interpreted to stand for Pluto or for Percival Lowell
Percival Lowell (; March 13, 1855 – November 12, 1916) was an American businessman, author, mathematician, and astronomer who fueled speculation that there were canals on Mars, and furthered theories of a ninth planet within the Solar System ...
, the astronomer who initiated Lowell Observatory
Lowell Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. Lowell Observatory was established in 1894, placing it among the oldest observatories in the United States, and was designated a National Historic Landmark ...
's search for a planet beyond the orbit of Neptune. Pluto has an alternative symbol consisting of an orb over Pluto's bident
A bident is a two-pronged implement resembling a pitchfork. In Renaissance art, the bident is associated with the Greek god Pluto (mythology), Pluto.
Etymology
The word 'bident' was brought into the English language before 1871, and is derived f ...
: it is more common in astrology than astronomy, and was popularised by the astrologer Paul Clancy, but has been used by NASA to refer to Pluto as a ''dwarf'' planet. There are a few other astrological symbols for Pluto that are used locally. Pluto also had the IAU abbreviation P when it was considered the ninth planet.
The other large trans-Neptunian objects were only discovered around the dawn of the 21st century. They were not generally thought to be planets on their discovery, and planetary symbols had in any case mostly fallen out of use among astronomers by then. Denis Moskowitz, a software engineer in Massachusetts, proposed astronomical symbols for the dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...
s Quaoar, Sedna, Orcus, Haumea, Eris, Makemake, and Gonggong. These symbols are somewhat standard among astrologers (e.g. in the program Astrolog), which is where planetary symbols are most used today. Moskowitz has also proposed symbols for Varuna
Varuna (; , ) is a Hindu god. He is one of the earliest deities in pantheon, whose role underwent a significant transformation from the Vedic to the Puranic periods. In the early Vedic era, Varuna is seen as the god-sovereign, ruling the sky ...
, Ixion
In Greek mythology, Ixion ( ; ) was king of the Lapiths, the most ancient tribe of Thessaly.
Family
Ixion was the son of Ares, or Leonteus (mythology), Leonteus, or Antion and Perimele, or the notorious evildoer Phlegyas, whose name connotes " ...
, and Salacia, and others have done so for additional TNOs, but there is little consistency between sources.
NASA has used Moskowitz's symbols for Haumea, Makemake, and Eris in an astronomical context, and Unicode labels the symbols for Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, and Orcus (added to Unicode in 2022) as "astronomy symbols".
Zodiac and other constellations

 The zodiac symbols have several astronomical interpretations. Depending on context, a zodiac symbol may denote either a constellation, or a point or interval on the ecliptic plane.
Lists of astronomical phenomena published by almanacs sometimes included conjunctions of stars and planets or the Moon; rather than print the full name of the star, a Greek letter and the symbol for the constellation of the star was sometimes used instead.
The ecliptic was sometimes divided into 12 ''signs'', each subdivided into 30 degrees,
and the ''sign'' component of ecliptic longitude was expressed either with a number from 0 to 11.
The 1834 edition of the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris'' abandoned the use of numerical signs (among other innovations); compare the representation of (ecliptic) longitude in the editions for the year
The zodiac symbols have several astronomical interpretations. Depending on context, a zodiac symbol may denote either a constellation, or a point or interval on the ecliptic plane.
Lists of astronomical phenomena published by almanacs sometimes included conjunctions of stars and planets or the Moon; rather than print the full name of the star, a Greek letter and the symbol for the constellation of the star was sometimes used instead.
The ecliptic was sometimes divided into 12 ''signs'', each subdivided into 30 degrees,
and the ''sign'' component of ecliptic longitude was expressed either with a number from 0 to 11.
The 1834 edition of the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris'' abandoned the use of numerical signs (among other innovations); compare the representation of (ecliptic) longitude in the editions for the year1834
an
1833
or with the corresponding zodiacal symbol. In modern astronomical writing, all the constellations, including the 12 of the zodiac, have dedicated three-letter abbreviations, which specifically refer to ''constellations'' rather than ''signs''. The zodiac symbols are also sometimes used to represent points on the ecliptic, particularly the solstices and equinoxes. Each symbol is taken to represent the "first point" of each ''sign'', rather than the place in the visible ''constellation'' where the alignment is observed. Thus, ♈︎ the symbol for Aries, represents the
March equinox
The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the ver ...
;
♋︎, for Cancer, the June solstice
The June solstice is the solstice on Earth that occurs annually between 20 and 22 June according to the Gregorian calendar. In the Northern Hemisphere, the June solstice is the summer solstice (the day with the longest period of daylight), while ...
;
♎︎, for Libra, the September equinox
The September equinox (or southward equinox) is the moment when the Sun appears to cross the celestial equator, heading southward. Because of differences between the calendar year and the tropical year, the September equinox may occur from ...
;
and ♑︎, for Capricorn, the December solstice
The December solstice, also known as the southern solstice, is the solstice that occurs each December – typically on 21 December, but may vary by one day in either direction according to the Gregorian calendar. In the Northern Hemisphere, the ...
.
Although the use of astrological sign
In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up ecliptic, Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the Equinox (c ...
symbols is rare, the particular symbol ♈︎ for Aries, is an exception; it is commonly used in modern astronomy to represent the location of the (slowly) moving reference point for the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
and equatorial celestial coordinate system
In astronomy, coordinate systems are used for specifying positions of celestial objects (satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, etc.) relative to a given reference frame, based on physical reference points available to a situated observer (e. ...
s.
:
Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellati ...
has been proposed as a thirteenth sign of the zodiac by astrologer Walter Berg in 1995, who gave it a symbol that has become popular in Japan.
:
None of the constellations have official symbols. However, in addition to the zodiac, occasional symbols for other modern constellations, as well as older constellations that occur in modern nomenclature, have appeared in publication. The symbols below were devised by Denis Moskowitz (except those for the 13 constellations already listed above).
: Andromeda
: Antlia
Antlia (; from Ancient Greek ''ἀντλία'') is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name means "pump" in Latin and Greek language, Greek; it represents an air pump. Originally Antlia Pneumatica, the constellation was es ...
: Apus
Apus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky. It represents a bird-of-paradise, and its name means "without feet" in Greek language, Greek because the bird-of-paradise was once wrongly believed to lack feet. ...
: Aquarius
: Aquila
: Ara
: Argo Navis
Argo Navis (the Ship Argo), or simply Argo, is one of Ptolemy's 48 constellations, now a grouping of three IAU constellations. It is formerly a single large constellation in the southern sky. The genitive is "Argus Navis", abbreviated "Arg". ...
:: Carina
Carina may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Carina, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina Heights, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina, Victoria, a locality in Mildura
Serbia
* Carina, Osečina, a village in the Kolubara District
...
:: Puppis
Puppis ("poop deck, stern") is a constellation in the southern sky. It was originally part of the Former constellations, traditional constellation of Argo Navis (the ship of Jason and the Argonauts), which was divided into three parts, the other ...
:: Vela
: Aries
: Auriga
: Boötes
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from , which comes from 'herder, herdsman' or 'plowman' (literally, 'o ...
: Caelum
Caelum is a faint constellation in the southern sky, introduced in the 1750s by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille and counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name means "chisel" in Latin, and it was formerly known as Caelum Sculptorium ("Engrave ...
: Camelopardalis
Camelopardalis is a large but faint constellation of the northern sky representing a giraffe. The constellation was introduced in 1612 or 1613 by Petrus Plancius. Some older astronomy books give Camelopardalus or Camelopardus as alternative form ...
: Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
: Canes Venatici
Canes Venatici ( ) is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and ...
: Canis Major
Canis Major is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "greater dog" in contrast to C ...
: Canis Minor
Canis Minor is a small constellation in the Celestial sphere, northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an Asterism (astronomy), asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counte ...
: Capricornus
Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat Horn (anatomy), horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is hal ...
: Cassiopeia
Cassiopeia or Cassiopea may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), queen of Aethiopia and mother of Andromeda
* Cassiopeia (wife of Phoenix), wife of Phoenix, king of Phoenicia
* Cassiopeia, wife of Epaphus, king of Egy ...
: Centaurus
Centaurus () is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the 88 modern constellations by area, largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one ...
: Cepheus
: Cetus
Cetus () is a constellation, sometimes called 'the whale' in English. The Cetus (mythology), Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology which both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water- ...
: Chamaeleon
: Circinus
: Columba
Columba () or Colmcille (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is today Scotland at the start of the Hiberno-Scottish mission. He founded the important abbey ...
: Coma Berenices
Coma Berenices is an ancient asterism in the northern sky, which has been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is in the direction of the fourth galactic quadrant, between Leo and Boötes, and it is visible in both hemispher ...
: Corona Australis
: Corona Borealis
Corona Borealis is a small constellation in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its brightest stars form a sem ...
: Corvus
''Corvus'' is a widely distributed genus of passerine birds ranging from medium-sized to large-sized in the family Corvidae. It includes species commonly known as crows, ravens, and rooks. The species commonly encountered in Europe are the car ...
: Crater
A crater is a landform consisting of a hole or depression (geology), depression on a planetary surface, usually caused either by an object hitting the surface, or by geological activity on the planet. A crater has classically been described ...
: Crux
CRUX is a lightweight x86-64 Linux distribution targeted at experienced Linux users and delivered by a tar.gz-based package system with BSD-style initscripts. It is not based on any other Linux distribution. It also utilizes a ports system ...
: Cygnus
: Delphinus
: Dorado
Dorado (, ) is a constellation in the Southern Sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the mahi-mahi (''Coryphaena hippurus''), which is known as ''dorado'' ("golden") in Sp ...
: Draco
: Equuleus
: Eridanus
: Fornax
Fornax () is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere, partly ringed by the celestial river Eridanus (constellation), Eridanus. Its name is Latin for furnace. It was named by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1756. Forna ...
: Gemini
: Grus
: Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
: Horologium
: Hydra
: Hydrus
Hydrus is a small constellation in the deep Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky. It was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first ap ...
: Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
: Lacerta
: Leo
: Leo Minor
: Lepus
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores and live solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are able to fend for themselves shortly after birth. The genu ...
: Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
: Lupus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common ...
: Lynx
A lynx ( ; : lynx or lynxes) is any of the four wikt:extant, extant species (the Canada lynx, Iberian lynx, Eurasian lynx and the bobcat) within the medium-sized wild Felidae, cat genus ''Lynx''. The name originated in Middle Engl ...
: Lyra
, from ; pronounced: ) is a small constellation. It is one of the 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the modern 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star ...
: Mensa
: Microscopium
Microscopium ("the Microscope") is a minor constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere, one of twelve created in the 18th century by French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and one of several depicting scientific instruments. The name ...
: Monoceros
Monoceros ( Greek: , "unicorn") is a faint constellation on the celestial equator. Its definition is attributed to the 17th-century cartographer Petrus Plancius. It is bordered by Orion to the west, Gemini to the north, Canis Major to the s ...
: Musca
: Norma Norma may refer to:
* Norma (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
** Norma Lizbeth Ramos, a Mexican bullying victim
Astronomy
*Norma (constellation)
* 555 Norma, a minor asteroid
* Cygnus Arm or Norma Arm, a spiral ...
: Octans
Octans is a faint constellation located in the deep southern celestial hemisphere, Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for the eighth part of a circle, but it is named after the octant (instrument), octant, a navigational instrument. Devised by kingd ...
: Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellati ...
: Orion
: Pavo
: Pegasus
Pegasus (; ) is a winged horse in Greek mythology, usually depicted as a white stallion. He was sired by Poseidon, in his role as horse-god, and foaled by the Gorgon Medusa. Pegasus was the brother of Chrysaor, both born from Medusa's blood w ...
: Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
: Phoenix
: Pictor
: Pisces
: Piscis Austrinus
Piscis Austrinus is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. The name is Latin for "the southern fish", in contrast with the larger constellation Pisces, which represents a pair of fish. Before the 20th century, it was also known as ...
: Pyxis
Pyxis is a small and faint constellation in the southern sky. Abbreviated from Pyxis Nautica, its name is Latin for a mariner's compass (contrasting with Circinus, which represents a draftsman's compasses). Pyxis was introduced by Nicolas-Louis ...
: Quadrans Muralis
: Reticulum
Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle—a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions. The constellation is best viewed b ...
: Sagitta
Sagitta is a dim but distinctive constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'arrow', not to be confused with the significantly larger constellation Sagittarius 'the archer'. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by t ...
: Sagittarius
: Scorpius
Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation whose recognition pred ...
: Sculptor
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
: Scutum
: Serpens
Serpens () is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union. It ...
:: Serpens Cauda
:: Serpens Caput
Serpens () is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations designated by the Inter ...
: Sextans
Sextans is a faint, minor constellation on the celestial equator which was introduced in 1687 by Polish astronomer Johannes Hevelius. Its name is Latin for the astronomical sextant, an instrument that Hevelius made frequent use of in his obs ...
: Taurus
: Telescopium
Telescopium is a minor constellation in the southern Celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere, one of twelve named in the 18th century by French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and one of several depicting scientific instruments. Its name i ...
: Triangulum
Triangulum is a small constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "triangle", derived from its three brightest stars, which form a long and narrow triangle. Known to the ancient Babylonians and Greeks, Triangulum was one of the 48 ...
: Triangulum Australe
Triangulum Australe is a small constellation in the far Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name is Latin for "the southern triangle", which distinguishes it from Triangulum in the northern sky and is derived from the Acute triangle, acute, almost ...
: Tucana
: Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa M ...
: Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor (, contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern celestial hemisphere, northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of ...
: Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Virgo (film), a 1970 Egyptian film
* Virgo (character), several Marvel Comics characters
* Virgo Asmita, a character in the manga ''Saint Seiya: The Lost Canvas''
* ''Virgo'' (album), by Virgo Four, ...
: Volans
: Vulpecula
Vulpecula is a faint constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "little fox", although it is commonly known simply as the fox. It was identified in the seventeenth century, and is located in the middle of the Summer Triangle (an ...
Other
Symbols for aspects and nodes appear in medieval texts, although medieval and modern usage of the node symbols differ; the modern ascending node symbol (☊) formerly stood for the descending node, and the modern descending node symbol (☋) was used for the ascending node. In describing the Keplerian elements of an orbit, ☊ is sometimes used to denote theecliptic longitude
In astronomy, the ecliptic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system commonly used for representing the apparent positions, orbits, and pole orientations of Solar System objects. Because most planets (except Mercury) and many small So ...
of the ascending node, although it is more common to use Ω (capital omega, and inverted ℧), which were originally typographical substitutes for the astronomical symbols.
The symbols for aspects first appear in Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
codices. Of the symbols for the five Ptolemaic aspects, only the three displayed here — for conjunction, opposition, and quadrature — are used in astronomy.
Symbols for a comet (☄) and a star (Meteor shower
A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at ext ...
s also have limited use of astronomical symbols in the literature, designed by Denis Moskowitz. They are based on the parent constellation symbols, with letters included to disambiguate the Aquariids and Taurids.
: Delta Aquariids  :
: Eta Aquariids
The Eta Aquariids are a meteor shower associated with Halley's Comet. The shower is visible from about April 19 to about May 28 each year with peak activity on or around May 5. Unlike most major annual meteor showers, there is no sharp peak fo ...
 :
: Geminids
The Geminids are a prolific meteor shower with 3200 Phaethon (which is thought to be an Apollo asteroid with a " rock comet" orbit.) being the parent body. Because of this, it would make this shower, along with the Quadrantids, the only ...
 :
: Leonids
The Leonids ( ) are a prolific annual meteor shower associated with the comet 55P/Tempel–Tuttle, Tempel–Tuttle, and are also known for their spectacular meteor storms that occur about every 33 years. The Leonids get their name from the loca ...
 : Lyrids
: Lyrids  :
: Orionids
The Orionids meteor shower, often shortened to the Orionids, is one of two meteor showers associated with Halley's Comet. The Orionids are so-called because the point they appear to come from, called the radiant, lies in the constellation
...
 :
: Perseids
The Perseids are a prolific meteor shower associated with the comet Swift–Tuttle that are usually visible from mid-July to late-August. The meteoroid, meteors are called the Perseids because they appear from the general direction of the const ...
 : Quadrantids
: Quadrantids  :
: Taurids
The Taurids are an annual meteor shower, associated with the comet Encke. The Taurids are actually two separate showers, with a Southern and a Northern component. The Southern Taurids originated from Comet Encke, while the Northern Taurids or ...

 : Ursids
: Ursids  For planetary transits of Mercury and Venus, Moskowitz proposed overlaying the respective planetary symbol on that of the Sun, extending the crossbar into an arrow:
For planetary transits of Mercury and Venus, Moskowitz proposed overlaying the respective planetary symbol on that of the Sun, extending the crossbar into an arrow: Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet is the only known List of periodic comets, short-period comet that is consistently visible to the naked eye from Earth, appearing every 72–80 years, though with the majority of recorded apparitions (25 of 30) occurring after ...
, : it is simply the standard comet symbol with an H.
See also
* Astrological symbols *Alchemical symbol
Alchemical symbols were used to denote chemical elements and compounds, as well as alchemy, alchemical apparatus and processes, until the 18th century. Although notation was partly standardized, style and symbol varied between alchemists. Lüdy ...
s
* List of common astronomy symbols
*Maya calendar
The Maya calendar is a system of calendars used in Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Mesoamerica and in many modern communities in the Guatemalan highlands, Veracruz, Oaxaca and Chiapas, Mexico.
The essentials of the Maya calendar are based upon ...
for the logogram
In a written language, a logogram (from Ancient Greek 'word', and 'that which is drawn or written'), also logograph or lexigraph, is a written character that represents a semantic component of a language, such as a word or morpheme. Chine ...
s used in Maya astronomy
Maya astronomy is the study of the Moon, planets, Milky Way, Sun, and astronomical phenomena by the Precolumbian Maya civilization of Mesoamerica.
The Classic Maya in particular developed some of the most accurate pre-telescope astronomy in th ...
*Solar symbol
A solar symbol is a symbol representing the Sun.
Common solar symbols include circles (with or without rays), crosses, and spirals.
In religious iconography, personifications of the Sun or solar attributes are often indicated by means of a halo ( ...
*Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
Footnotes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Astronomical Symbols Symbols, astronomicalAstronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
Heraldic charges