|
Aquila (constellation)
Aquila is a constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for 'eagle' and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greco-Roman mythology, Greek-Roman mythology. Its brightest star, Altair, is one vertex of the Summer Triangle asterism (astronomy), asterism. The constellation is best seen in the northern summer, as it is located along the Milky Way. Because of this location, many clusters and planetary nebula, nebulae are found within its borders, but they are dim and galaxies are few. History Aquila was one of the 48 constellations described by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy. It had been earlier mentioned by Eudoxus of Cnidus, Eudoxus in the fourth century BC and Aratus in the third century BC. It is now one of the 88 constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. The constellation was also known as ''Vultur volans'' (the flying vulture) to the Ancient Rome, Romans, not to be confused with ''Vultur cadens'' which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
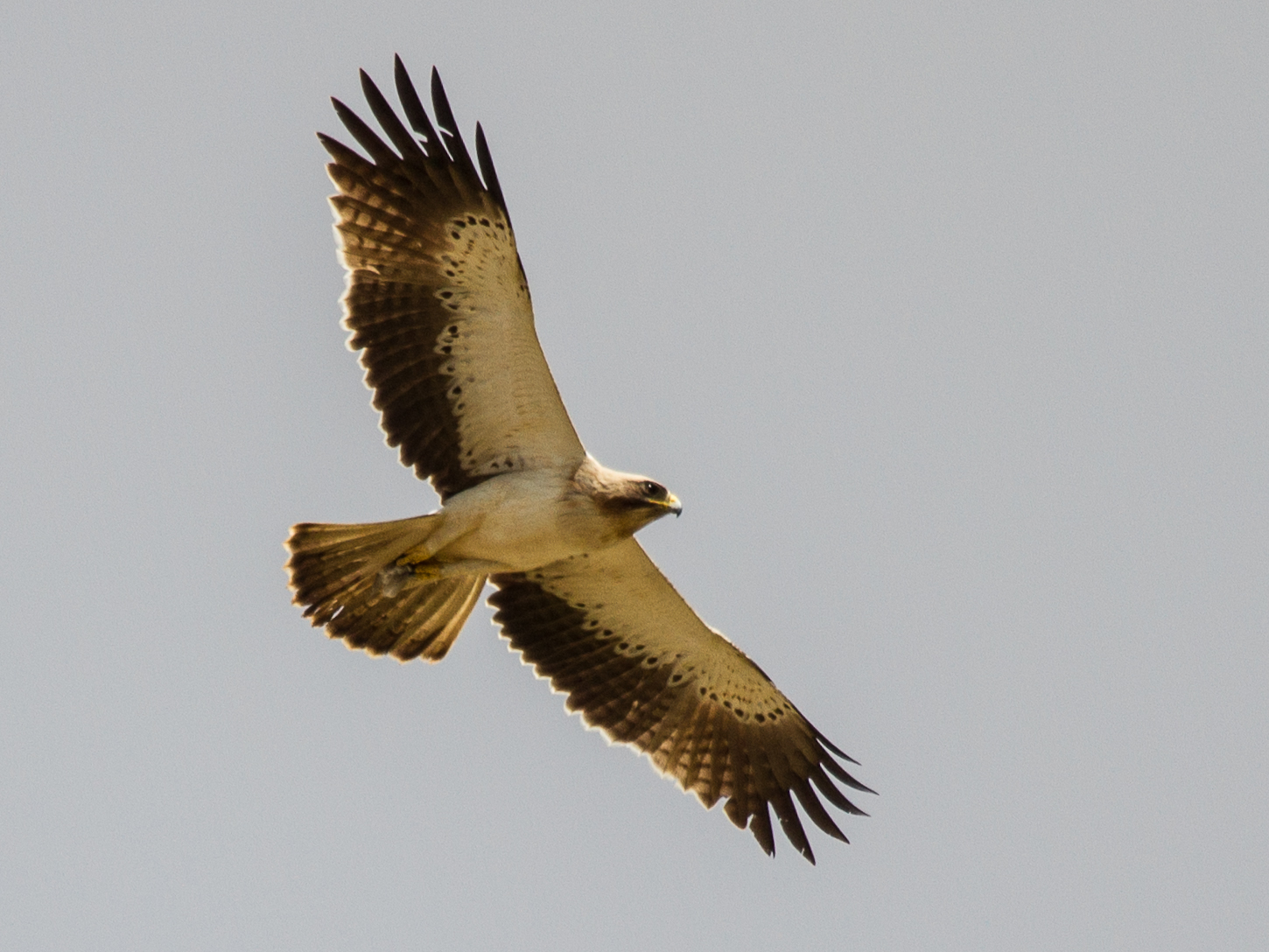
Eagle
Eagle is the common name for the golden eagle, bald eagle, and other birds of prey in the family of the Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of Genus, genera, some of which are closely related. True eagles comprise the genus ''Aquila (bird), Aquila''. Most of the 68 species of eagles are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—two in North America, nine in Central and South America, and three in Australia. Eagles are not a natural group but denote essentially any kind of bird of prey large enough to hunt sizeable (about 50 cm long or more overall) vertebrates. Etymology The word "eagle" is borrowed into English from and , both derived ultimately from ("eagle"). It is cognate with terms such as , and . It is broadly synonymous with the less common English term "erne" or "earn", deriving from , from , in which it acts as the usual word for the bird. The Old English term is turn derived from and is cognate with other synonymous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
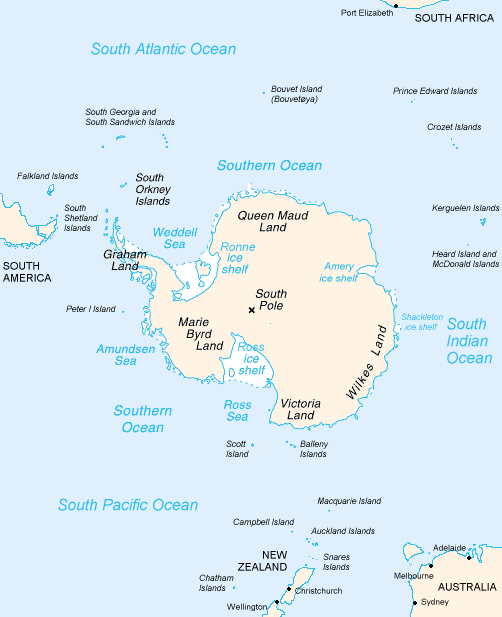
75th Parallel South
Following are circles of latitude between the 55th parallel south and the 80th parallel south. The 55th parallel south, crossing the southernmost point of Chile, is the last line of latitude moving southward to touch any part of any continent other than Antarctica, other than minor outlying islands. 56th parallel south The 56th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 56 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. No land lies on the parallel — it crosses nothing but ocean. At this latitude the sun is visible for 17 hours, 37 minutes during the December solstice and 6 hours, 57 minutes during the June solstice. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 56° south passes through: : 57th parallel south The 57th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 57 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. No land lies on the parallel — it crosses nothing but ocean. At this latitude the sun is visible for 17 hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
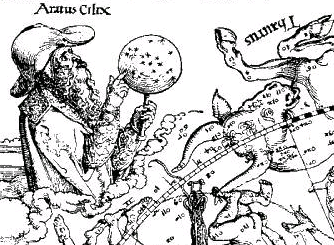
Aratus
Aratus (; ; c. 315/310 240 BC) was a Greek didactic poet. His major extant work is his hexameter poem ''Phenomena'' (, ''Phainómena'', "Appearances"; ), the first half of which is a verse setting of a lost work of the same name by Eudoxus of Cnidus. It describes the constellations and other celestial phenomena. The second half is called the ''Diosemeia'' (Διοσημεῖα "Forecasts"), and is chiefly about weather lore. Although Aratus was somewhat ignorant of Greek astronomy, his poem was very popular in the Greek and Roman world, as is proven by the large number of commentaries and Latin translations, some of which survive. Life There are several accounts of Aratus's life by anonymous Greek writers, and the Suda and Eudocia also mention him. From these it appears that he was a native of Soli in Cilicia (although one authority says Tarsus). He is known to have studied with Menecrates in Ephesus and Philitas in Cos. As a disciple of the Peripatetic philosopher Praxipha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudoxus Of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus (; , ''Eúdoxos ho Knídios''; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek Ancient Greek astronomy, astronomer, Greek mathematics, mathematician, doctor, and lawmaker. He was a student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original works are lost, though some fragments are preserved in Hipparchus' ''Commentaries on the Phenomena of Aratus and Eudoxus''. ''Theodosius' Spherics, Spherics'' by Theodosius of Bithynia may be based on a work by Eudoxus. Life Eudoxus, son of Aeschines, was born and died in Cnidus (also transliterated Knidos), a city on the southwest coast of Anatolia. The years of Eudoxus' birth and death are not fully known but Diogenes Laertius, Diogenes Laërtius gave several biographical details, mentioned that Apollodorus of Athens, Apollodorus said he reached his wikt:acme#English, acme in the 103rd Olympiad (368–), and claimed he died in his 53rd year. From this 19th century mathematical historians reconstructed dates of 408–, but 20th century schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Nebula
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives. The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The term originates from the planet-like round shape of these nebulae observed by astronomers through early telescopes. The first usage may have occurred during the 1780s with the English astronomer William Herschel who described these nebulae as resembling planets; however, as early as January 1779, the French astronomer Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix described in his observations of the Ring Nebula, "very dim but perfectly outlined; it is as large as Jupiter and resembles a fading planet". Though the modern interpretation is different, the old term is still used. All planetary nebulae form at the end of the life of a star of intermediate mass, about 1-8 solar masses. It is expected that the Sun will form a planetary nebula at the end of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observational astronomy, observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified star pattern, and therefore are a more general concept than the IAU designated constellations, 88 formally defined constellations. Constellations are based upon asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations are defined regions with official boundaries which together encompass the entire sky. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. The patterns of stars seen in asterisms are not necessarily a product of any physical association between the stars, but are rather the result of the particular perspectives of their observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Triangle
The Summer Triangle is an astronomical asterism in the northern celestial hemisphere. The defining vertices of this imaginary triangle are at Altair, Deneb, and Vega, each of which is the brightest star of its constellation ( Aquila, Cygnus, and Lyra, respectively). The greatest declination is +45° and lowest is +9° meaning the three can be seen from all places in the Northern Hemisphere and from the home of most people resident in the Southern Hemisphere. The two stars in Aquila and Cygnus represent the head of an eagle and tail of a swan that looks east inscribed into the triangle and forming the altitude of the triangle. Two small constellations, Sagitta and Vulpecula, lie between Aquila in the south of the triangle and Cygnus and Lyra to the north. History The term was popularized by the American author H. A. Rey and the British astronomer Patrick Moore in the 1950s. The name can be found in constellation guidebooks as far back as 1913. The Austrian astronomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Roman Mythology
Classical mythology, also known as Greco-Roman mythology or Greek and Roman mythology, is the collective body and study of myths from the ancient Greeks and ancient Romans. Mythology, along with philosophy and political thought, is one of the major survivals of classical antiquity throughout later, including modern, Western culture. The Greek word ''mythos'' refers to the spoken word or speech, but it also denotes a tale, story or narrative. As late as the Roman conquest of Greece during the last two centuries Before the Common Era and for centuries afterwards, the Romans, who already had gods of their own, adopted many mythic narratives directly from the Greeks while preserving their own Roman (Latin) names for the gods. As a result, the actions of many Roman and Greek deities became equivalent in storytelling and literature in modern Western culture. For example, the Roman sky god Jupiter or Jove became equated with his Greek counterpart Zeus; the Roman fertility goddess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
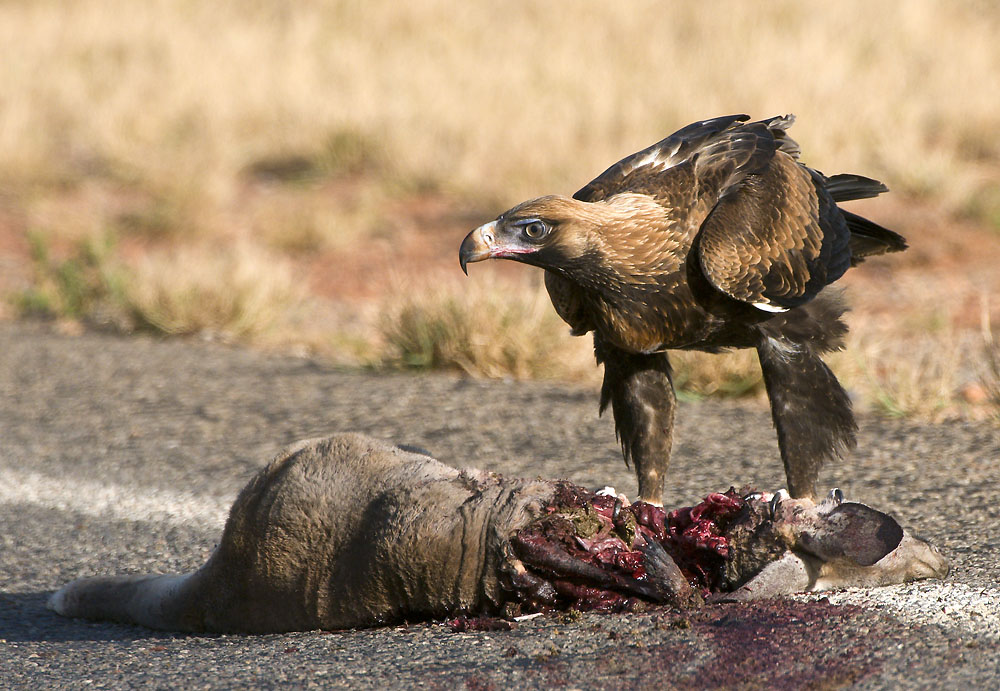
Eagle
Eagle is the common name for the golden eagle, bald eagle, and other birds of prey in the family of the Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of Genus, genera, some of which are closely related. True eagles comprise the genus ''Aquila (bird), Aquila''. Most of the 68 species of eagles are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—two in North America, nine in Central and South America, and three in Australia. Eagles are not a natural group but denote essentially any kind of bird of prey large enough to hunt sizeable (about 50 cm long or more overall) vertebrates. Etymology The word "eagle" is borrowed into English from and , both derived ultimately from ("eagle"). It is cognate with terms such as , and . It is broadly synonymous with the less common English term "erne" or "earn", deriving from , from , in which it acts as the usual word for the bird. The Old English term is turn derived from and is cognate with other synonymous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |