
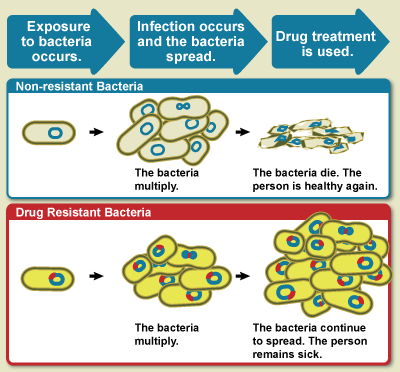
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when
microbe
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
s evolve mechanisms that protect them from
antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat
infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s.
This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
(antibiotic resistance),
viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almo ...
(antiviral resistance),
parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
(antiparasitic resistance), and
fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
(antifungal resistance). Together, these adaptations fall under the AMR umbrella, posing significant challenges to healthcare worldwide.
Misuse and improper management of antimicrobials are primary drivers of this resistance, though it can also occur naturally through genetic mutations and the spread of resistant genes.
Antibiotic resistance, a significant AMR subset, enables
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
to survive
antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
treatment, complicating infection management and treatment options.
Resistance arises through spontaneous mutation,
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
, and increased selective pressure from
antibiotic overuse, both in medicine and agriculture, which accelerates resistance development.
The burden of AMR is immense, with nearly 5 million annual deaths associated with resistant infections.
Infections from AMR microbes are more challenging to treat and often require costly alternative therapies that may have more severe side effects.
Preventive measures, such as using
narrow-spectrum antibiotic
A narrow-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that is only able to kill or inhibit limited species of bacteria. Examples of narrow-spectrum antibiotics include fidaxomicin and sarecycline
Sarecycline, sold under the brand name Seysara, is a ...
s and improving hygiene practices, aim to reduce the spread of resistance.
Microbes resistant to multiple drugs are termed
multidrug-resistant (MDR) and are sometimes called superbugs.
The
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) claims that AMR is one of the top global public health and development threats, estimating that bacterial AMR was directly responsible for 1.27 million global deaths in 2019 and contributed to 4.95 million deaths. Moreover, the WHO and other international bodies warn that AMR could lead to up to 10 million deaths annually by 2050 unless actions are taken. Global initiatives, such as calls for international AMR treaties, emphasize coordinated efforts to limit misuse, fund research, and provide access to necessary antimicrobials in developing nations. However, the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
redirected resources and scientific attention away from AMR, intensifying the challenge.
Definition
Antimicrobial resistance means a microorganism's
resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism.
A person cannot become resistant to antibiotics. Resistance is a property of the microbe, not a person or other organism infected by a microbe. All types of microbes can develop drug resistance. Thus, there are
antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
,
antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as ...
,
antiviral
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
and
antiparasitic
Antiparasitics are a class of medications which are indicated for the treatment of parasitic diseases, such as those caused by helminths, amoeba, ectoparasites, parasitic fungi, and protozoa, among others. Antiparasitics target the parasitic ...
resistance.
Antibiotic resistance is a subset of antimicrobial resistance. This more specific resistance is linked to bacteria and thus broken down into two further subsets, microbiological and clinical. Microbiological resistance is the most common and occurs from genes,
mutated
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral rep ...
or inherited, that allow the bacteria to resist the mechanism to kill the microbe associated with certain antibiotics. Clinical resistance is shown through the failure of many therapeutic techniques where the bacteria that are normally susceptible to a treatment become resistant after surviving the outcome of the treatment. In both cases of acquired resistance, the bacteria can pass the genetic catalyst for resistance through horizontal gene transfer: conjugation,
transduction, or
transformation
Transformation may refer to:
Science and mathematics
In biology and medicine
* Metamorphosis, the biological process of changing physical form after birth or hatching
* Malignant transformation, the process of cells becoming cancerous
* Trans ...
. This allows the resistance to spread across the same species of
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
or even similar bacterial pathogens.
Overview
WHO report released April 2014 stated, "this serious threat is no longer a prediction for the future, it is happening right now in every region of the world and has the potential to affect anyone, of any age, in any country. Antibiotic resistance—when bacteria change so antibiotics no longer work in people who need them to treat infections—is now a major threat to public health."
["WHO's first global report on antibiotic resistance reveals serious, worldwide threat to public health"](_blank)
Retrieved 2 May 2014.
Each year, nearly 5 million deaths are associated with AMR globally.
In 2019, global deaths attributable to AMR numbered 1.27 million in 2019. That same year, AMR may have contributed to 5 million deaths and one in five people who died due to AMR were children under five years old.
In 2018, WHO considered antibiotic resistance to be one of the biggest threats to global health,
food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
and development.
Deaths attributable to AMR vary by area:
The
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) is an agency of the European Union (EU) whose mission is to strengthen Europe's defences against infectious diseases. It covers a wide spectrum of activities, such as: surveillance, e ...
calculated that in 2015 there were 671,689 infections in the EU and
European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Asso ...
caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, resulting in 33,110 deaths. Most were acquired in healthcare settings. In 2019 there were 133,000 deaths caused by AMR.
Causes
AMR is driven largely by the
misuse and overuse of antimicrobials.
Yet, at the same time, many people around the world do not have access to essential antimicrobials.
This leads to microbes either evolving a defense against drugs used to treat them, or certain strains of microbes that have a natural resistance to antimicrobials becoming much more prevalent than the ones that are easily defeated with medication. While antimicrobial resistance does occur naturally over time, the use of antimicrobial agents in a variety of settings both within the healthcare industry and outside of has led to antimicrobial resistance becoming increasingly more prevalent.
Although many microbes develop resistance to antibiotics over time through natural mutation, overprescribing and inappropriate prescription of antibiotics have accelerated the problem. It is possible that as many as 1 in 3 prescriptions written for antibiotics are unnecessary.
Every year, approximately 154 million prescriptions for antibiotics are written. Of these, up to 46 million are unnecessary or inappropriate for the condition that the patient has.
Microbes may naturally develop resistance through genetic mutations that occur during cell division, and although random mutations are rare, many microbes reproduce frequently and rapidly, increasing the chances of members of the population acquiring a mutation that increases resistance.
Many individuals stop taking antibiotics when they begin to feel better. When this occurs, it is possible that the microbes that are less susceptible to treatment still remain in the body. If these microbes are able to continue to reproduce, this can lead to an infection by bacteria that are less susceptible or even resistant to an antibiotic.
Natural occurrence

AMR is a naturally occurring process.
Antimicrobial resistance can evolve naturally due to continued exposure to antimicrobials.
Natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
means that organisms that are able to adapt to their environment, survive, and continue to produce offspring.
As a result, the types of microorganisms that are able to survive over time with continued attack by certain antimicrobial agents will naturally become more prevalent in the environment, and those without this resistance will become obsolete.
Some contemporary antimicrobial resistances have also evolved naturally before the use of antimicrobials of human clinical uses. For instance,
methicillin
Methicillin ( USAN), also known as meticillin ( INN), is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.
Methicillin was discovered in 1960.
Medical uses
Compared to other penicillins that face antimicrobial resistance ...
-resistance evolved as a pathogen of
hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are 17 species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introduction. The ...
s, possibly as a
co-evolutionary adaptation of the pathogen to hedgehogs that are infected by a
dermatophyte
Dermatophyte (from Greek '' derma'' "skin" ( GEN ''dermatos'') and ''phyton'' "plant") is a common label for a group of fungus of '' Arthrodermataceae'' that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. Traditionally, these anamorphic ( ...
that naturally produces antibiotics.
Also, many
soil fungi and bacteria are natural competitors and the original antibiotic
penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
discovered by
Alexander Fleming
Sir Alexander Fleming (6 August 1881 – 11 March 1955) was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in 1928 of wha ...
rapidly lost clinical effectiveness in treating humans and, furthermore, none of the other natural penicillins (F, K, N, X, O, U1 or U6) are currently in clinical use.
Antimicrobial resistance can be acquired from other microbes through swapping genes in a process termed
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
. This means that once a gene for resistance to an antibiotic appears in a microbial community, it can then spread to other microbes in the community, potentially moving from a non-disease causing microbe to a disease-causing microbe. This process is heavily driven by the
natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
processes that happen during antibiotic use or misuse.
Over time, most of the strains of bacteria and infections present will be the type resistant to the antimicrobial agent being used to treat them, making this agent now ineffective to defeat most microbes. With the increased use of antimicrobial agents, there is a speeding up of this natural process.
Self-medication
In the vast majority of countries, antibiotics can only be prescribed by a doctor and supplied by a pharmacy.
Self-medication
Self-medication, sometime called do-it-yourself (DIY) medicine, is a human behavior in which an individual uses a substance or any exogenous influence to self-administer treatment for physical or psychological conditions, for example headaches or ...
by consumers is defined as "the taking of medicines on one's own initiative or on another person's suggestion, who is not a certified medical professional", and it has been identified as one of the primary reasons for the evolution of antimicrobial resistance.
Self-medication with antibiotics is an unsuitable way of using them but a common practice in resource-constrained countries. The practice exposes individuals to the risk of bacteria that have developed antimicrobial resistance.
Many people resort to this out of necessity, when access to a physician is unavailable, or when patients have a limited amount of time or money to see a doctor. This increased access makes it extremely easy to obtain antimicrobials. An example is India, where in the state of
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
73% of the population resorted to treating their minor health issues and chronic illnesses through self-medication.
Self-medication is higher outside the hospital environment, and this is linked to higher use of antibiotics, with the majority of antibiotics being used in the community rather than hospitals. The prevalence of self-medication in
low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) ranges from 8.1% to 93%. Accessibility, affordability, and conditions of health facilities, as well as the health-seeking behavior, are factors that influence self-medication in low- and middle-income countries.
Two significant issues with self-medication are the lack of knowledge of the public on, firstly, the dangerous effects of certain antimicrobials (for example
ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
which can cause
tendonitis
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tenn ...
,
tendon rupture
Tendon rupture is a condition in which a tendon separates in whole or in part from tissue to which it is attached, or is itself torn or otherwise divided in whole or in part.
Examples include:
* Achilles tendon rupture
* Biceps tendon rupture
* A ...
and
aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of agonizing ches ...
) and, secondly, broad microbial resistance and when to seek medical care if the infection is not clearing. In order to determine the public's knowledge and preconceived notions on antibiotic resistance, a screening of 3,537 articles published in Europe, Asia, and North America was done. Of the 55,225 total people surveyed in the articles, 70% had heard of antibiotic resistance previously, but 88% of those people thought it referred to some type of physical change in the human body.
Clinical misuse
Clinical misuse by healthcare professionals is another contributor to increased antimicrobial resistance. Studies done in the US show that the indication for treatment of antibiotics, choice of the agent used, and the duration of therapy was incorrect in up to 50% of the cases studied.
In 2010 and 2011 about a third of antibiotic prescriptions in
outpatient settings in the United States were not necessary. Another study in an intensive care unit in a major hospital in France has shown that 30% to 60% of prescribed antibiotics were unnecessary.
These inappropriate uses of antimicrobial agents promote the evolution of antimicrobial resistance by supporting the bacteria in developing genetic alterations that lead to resistance.
According to research conducted in the US that aimed to evaluate physicians' attitudes and knowledge on antimicrobial resistance in ambulatory settings, only 63% of those surveyed reported antibiotic resistance as a problem in their local practices, while 23% reported the aggressive prescription of antibiotics as necessary to avoid failing to provide adequate care. This demonstrates that many doctors underestimate the impact that their own prescribing habits have on antimicrobial resistance as a whole. It also confirms that some physicians may be overly cautious and prescribe antibiotics for both medical or legal reasons, even when clinical indications for use of these medications are not always confirmed. This can lead to unnecessary antimicrobial use, a pattern which may have worsened during the
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
pandemic.
Studies have shown that common misconceptions about the effectiveness and necessity of antibiotics to treat common mild illnesses contribute to their overuse.
Important to the conversation of antibiotic use is the
veterinary medical system. Veterinary oversight is required by law for all medically important antibiotics. Veterinarians use the
Pharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific subs ...
/pharmacodynamic model (PK/PD) approach to ensuring that the correct dose of the drug is delivered to the correct place at the correct timing.
Pandemics, disinfectants and healthcare systems
Increased antibiotic use during the early waves of the COVID-19 pandemic may exacerbate this
global health challenge. Moreover, pandemic burdens on some healthcare systems may contribute to antibiotic-resistant infections. The use of
disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than ...
s such as alcohol-based hand sanitizers, and antiseptic hand wash may also have the potential to increase antimicrobial resistance. Extensive use of disinfectants can lead to mutations that induce antimicrobial resistance. On the other hand, "increased hand hygiene, decreased international travel, and decreased elective hospital procedures may have reduced AMR pathogen selection and spread in the short term" during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A 2024
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
High-Level Meeting on AMR has pledged to reduce deaths associated with bacterial AMR by 10% over the next six years.
In their first major declaration on the issue since 2016, global leaders also committed to raising $100 million to update and implement AMR action plans. However, the final draft of the declaration omitted an earlier target to reduce antibiotic use in animals by 30% by 2030, due to opposition from meat-producing countries and the farming industry. Critics argue this omission is a major weakness, as livestock accounts for around 73% of global sales of antimicrobial agents, including
antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s,
antivirals
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
, and
antiparasitic
Antiparasitics are a class of medications which are indicated for the treatment of parasitic diseases, such as those caused by helminths, amoeba, ectoparasites, parasitic fungi, and protozoa, among others. Antiparasitics target the parasitic ...
s.
Environmental pollution
Considering the complex interactions between humans, animals and the environment, it is also important to consider the environmental aspects and contributors to antimicrobial resistance. Although there are still some knowledge gaps in understanding the mechanisms and transmission pathways,
environmental pollution is considered a significant contributor to antimicrobial resistance.
Important contributing factors are through "antibiotic residues", "industrial effluents", "
agricultural runoffs", "heavy metals", "
biocide
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a sli ...
s and
pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s" and "sewage and wastewater" that create reservoirs for resistant genes and bacteria that facilitates the transfer of human pathogens.
Unused or expired antibiotics, if not disposed of properly, can enter water systems and soil.
Discharge from pharmaceutical manufacturing and other industrial companies can also introduce antibiotics and other chemicals into the environment.
These factors allow for creating selective pressure for resistant bacteria.
Antibiotics used in livestock and
aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
can contaminate soil and water, which promotes resistance in environmental microbes.
Heavy metals such as
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, copper and
mercury, and also biocides and pesticides, can co- select for antibiotic resistance,
enhancing their speed.
Inadequate
treatment of sewage and wastewater allows resistant bacteria and genes to spread through water systems.
Food production
Livestock

The antimicrobial resistance crisis also extends to the food industry, specifically with food producing animals. With an ever-increasing human population, there is constant pressure to intensify productivity in many agricultural sectors, including the production of meat as a source of protein. Antibiotics are fed to livestock to act as growth supplements, and a preventive measure to decrease the likelihood of infections.
Farmers typically use antibiotics in animal feed to improve growth rates and prevent infections. However, this is illogical as antibiotics are used to treat infections and not prevent infections. 80% of antibiotic use in the U.S. is for agricultural purposes and about 70% of these are medically important.
Overusing antibiotics gives the bacteria time to adapt leaving higher doses or even stronger antibiotics needed to combat the infection. Though antibiotics for growth promotion were banned throughout the EU in 2006, 40 countries worldwide still use antibiotics to promote growth.
This can result in the transfer of resistant bacterial strains into the food that humans eat, causing potentially fatal transfer of disease. While the practice of using antibiotics as growth promoters does result in better yields and
meat
Meat is animal Tissue (biology), tissue, often muscle, that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted and farmed other animals for meat since prehistory. The Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of vertebrates, including chickens, sheep, ...
products, it is a major issue and needs to be decreased in order to prevent antimicrobial resistance. Though the evidence linking antimicrobial usage in livestock to antimicrobial resistance is limited, the World Health Organization Advisory Group on Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance strongly recommended the reduction of use of medically important antimicrobials in livestock. Additionally, the Advisory Group stated that such antimicrobials should be expressly prohibited for both growth promotion and disease prevention in food producing animals.
By mapping antimicrobial consumption in livestock globally, it was predicted that in 228 countries there would be a total 67% increase in consumption of antibiotics by livestock by 2030. In some countries such as Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa it is predicted that a 99% increase will occur.
Several countries have restricted the use of antibiotics in livestock, including Canada, China, Japan, and the US. These restrictions are sometimes associated with a reduction of the
prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of antimicrobial resistance in humans.
In the United States the
Veterinary Feed Directive went into practice in 2017 dictating that ''All medically important antibiotics to be used in feed or water for food animal species require a veterinary feed directive (VFD) or a prescription.''
Pesticides
Most
pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s protect crops against insects and plants, but in some cases antimicrobial pesticides are used to protect against various microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, algae, and protozoa. The overuse of many pesticides in an effort to have a higher yield of crops has resulted in many of these microbes evolving a tolerance against these antimicrobial agents. Currently there are over 4000 antimicrobial pesticides registered with the US
Environmental Protection Agency
Environmental Protection Agency may refer to the following government organizations:
* Environmental Protection Agency (Queensland), Australia
* Environmental Protection Agency (Ghana)
* Environmental Protection Agency (Ireland)
* Environmenta ...
(EPA) and sold to market, showing the widespread use of these agents. It is estimated that for every single meal a person consumes, 0.3 g of pesticides is used, as 90% of all pesticide use is in agriculture. A majority of these products are used to help defend against the spread of infectious diseases, and hopefully protect public health. But out of the large amount of pesticides used, it is also estimated that less than 0.1% of those antimicrobial agents, actually reach their targets. That leaves over 99% of all pesticides used available to contaminate other resources. In soil, air, and water these antimicrobial agents are able to spread, coming in contact with more microorganisms and leading to these microbes evolving mechanisms to tolerate and further resist pesticides. The use of antifungal
azole
Azoles are a class of five-membered heterocyclic compounds containing a nitrogen atom and at least one other non-carbon atom (i.e. nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen) as part of the ring.
Their names originate from the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature. Th ...
pesticides that drive environmental azole resistance have been linked to azole resistance cases in the clinical setting. The same issues confront the novel antifungal classes (e.g.
orotomides) which are again being used in both the clinic and agriculture.
Wild birds
Wildlife, including wild and
migratory birds
Bird migration is a seasonal movement of birds between breeding and wintering grounds that occurs twice a year. It is typically from north to south or from south to north. Migration is inherently risky, due to predation and mortality.
The ...
, serve as a reservoir for zoonotic disease and antimicrobial-resistant organisms. Birds are a key link between the transmission of zoonotic diseases to human populations. By the same token, increased contact between wild birds and human populations (including domesticated animals), has increased the amount of anti-microbial resistance (AMR) to the bird population.
The introduction of AMR to wild birds positively correlates with human pollution and increased human contact. Additionally, wild birds can participate in
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
with bacteria, leading to the transmission of antibiotic-resistant genes (ARG).
For simplicity, wild bird populations can be divided into two major categories, wild sedentary birds and wild migrating birds. Wild sedentary bird exposure to AMR is through increased contact with densely populated areas, human waste, domestic animals, and domestic animal/livestock waste. Wild migrating birds interact with sedentary birds in different environments along their migration route. This increases the rate and diversity of AMR across varying ecosystems.
Neglect of wildlife in the global discussions surrounding
health security
Health security is a concept that encompasses activities and measures across sovereign boundaries that mitigates public health incidents to ensure the health of populations. It is an evolving paradigm within the fields of international relations a ...
and AMR, creates large barriers to true AMR surveillance. The surveillance of anti-microbial resistant organisms in wild birds is a potential metric for the rate of AMR in the environment. This surveillance also allows for further investigation into the transmission routs between different ecosystems and human populations (including domesticated animals and livestock).
Such information gathered from wild bird biomes, can help identify patterns of diseased transmission and better target interventions. These targeted interventions can inform the use of antimicrobial agents and reduce the persistence of multi-drug resistant organisms.
Gene transfer from ancient microorganisms

Permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
is a term used to refer to any ground that remained frozen for two years or more, with the oldest known examples continuously frozen for around 700,000 years.
In the recent decades, permafrost has been rapidly thawing due to
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
[Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xiao, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, S.S. Drijfhout, T.L. Edwards, N.R. Golledge, M. Hemer, R.E. Kopp, G. Krinner, A. Mix, D. Notz, S. Nowicki, I.S. Nurhati, L. Ruiz, J.-B. Sallée, A.B.A. Slangen, and Y. Yu, 2021]
Chapter 9: Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change
. I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1211–1362, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.011. The cold preserves any organic matter inside the permafrost, and it is possible for microorganisms to resume their life functions once it thaws. While some common
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s such as
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
,
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
or the bacteria associated with
pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
have failed to survive intentional attempts to revive them,
more cold-adapted microorganisms such as
anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis'' or ''Bacillus cereus'' biovar ''anthracis''. Infection typically occurs by contact with the skin, inhalation, or intestinal absorption. Symptom onset occurs between one ...
, or several ancient
plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
and
amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by ...
viruses, have successfully survived prolonged thaw.
Some scientists have argued that the inability of known
causative agent
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
s of
contagious disease
A contagious disease is an infectious disease that can be spread rapidly in several ways, including direct contact, indirect contact, and droplet contact.
These diseases are caused by organisms such as parasites, bacteria, fungi, and viruses. ...
s to survive being frozen and thawed makes this threat unlikely. Instead, there have been suggestions that when modern pathogenic bacteria interact with the ancient ones, they may, through
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
, pick up
genetic sequence
Genetic may refer to:
*Genetics, in biology, the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms
**Genetic, used as an adjective, refers to genes
*** Genetic disorder, any disorder caused by a genetic mutation, whether inherited or de no ...
s which are associated with antimicrobial resistance, exacerbating an already difficult issue.
Antibiotics to which permafrost bacteria have displayed at least some resistance include
chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
,
streptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, ''Burkholderia'' i ...
,
kanamycin
Kanamycin A, often referred to simply as kanamycin, is an antibiotic used to treat severe bacterial infections and tuberculosis. It is not a first line treatment. It is used by mouth, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle. Kanamy ...
,
gentamicin
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis amo ...
,
tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
,
spectinomycin and
neomycin
Neomycin, also known as framycetin, is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against ...
.
However, other studies show that resistance levels in ancient bacteria to modern antibiotics remain lower than in the contemporary bacteria from the
active layer of thawed ground above them,
which may mean that this risk is "no greater" than from any other soil.
Prevention

There have been increasing public calls for global collective action to address the threat, including a proposal for an international treaty on antimicrobial resistance. Further detail and attention is still needed in order to recognize and measure trends in resistance on the international level; the idea of a global tracking system has been suggested but implementation has yet to occur. A system of this nature would provide insight to areas of high resistance as well as information necessary for evaluating programs, introducing interventions and other changes made to fight or reverse antibiotic resistance.
Duration of antimicrobials
Delaying or minimizing the use of antibiotics for certain conditions may help safely reduce their use.
Antimicrobial treatment duration should be based on the infection and other health problems a person may have.
For many infections once a person has improved there is little evidence that stopping treatment causes more resistance.
Some, therefore, feel that stopping early may be reasonable in some cases.
Other infections, however, do require long courses regardless of whether a person feels better.
Delaying antibiotics for ailments such as a sore throat and otitis media may have no difference in the rate of complications compared with immediate antibiotics, for example.
When treating
respiratory tract infection
Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are infectious diseases involving the lower or upper respiratory tract. An infection of this type usually is further classified as an upper respiratory tract infection (URI or URTI) or a lower respiratory tract ...
s, clinical judgement is required as to the appropriate treatment (delayed or immediate antibiotic use).
The study, "Shorter and Longer Antibiotic Durations for Respiratory Infections: To Fight Antimicrobial Resistance—A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study in a Secondary Care Setting in the UK," highlights the urgency of reevaluating antibiotic treatment durations amidst the global challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). It investigates the effectiveness of shorter versus longer antibiotic regimens for respiratory tract infections (RTIs) in a UK secondary care setting, emphasizing the need for evidence-based prescribing practices to optimize patient outcomes and combat AMR.
Monitoring and mapping
There are multiple national and international monitoring programs for drug-resistant threats, including
methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA),
vancomycin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (VRSA),
extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing
Enterobacterales
Enterobacterales is an order of Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, non-spore forming, Facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria with the class Gammaproteobacteria. The type genus of this order is ''Enterob ...
,
vancomycin-resistant ''Enterococcus'' (VRE), and
multidrug-resistant ''Acinetobacter baumannii'' (MRAB).
ResistanceOpen is an online global map of antimicrobial resistance developed by
HealthMap which displays aggregated data on antimicrobial resistance from publicly available and user submitted data. The website can display data for a radius from a location. Users may submit data from
antibiograms for individual hospitals or laboratories. European data is from the EARS-Net (European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network), part of the
ECDC. ResistanceMap is a website by the
Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy and provides data on antimicrobial resistance on a global level.
The WHO's AMR global action plan also recommends antimicrobial resistance surveillance in animals.
Initial steps in the EU for establishing the veterinary counterpart EARS-Vet (EARS-Net for veterinary medicine) have been made.
AMR data from pets in particular is scarce, but needed to support antibiotic stewardship in veterinary medicine.
By comparison there is a lack of national and international monitoring programs for antifungal resistance.
Limiting antimicrobial use in humans
Antimicrobial stewardship programmes appear useful in reducing rates of antimicrobial resistance.
The antimicrobial stewardship program will also provide pharmacists with the knowledge to educate patients that antibiotics will not work for a virus for example.
Excessive antimicrobial use has become one of the top contributors to the evolution of antimicrobial resistance. Since the beginning of the antimicrobial era, antimicrobials have been used to treat a wide range of infectious diseases. Overuse of antimicrobials has become the primary cause of rising levels of antimicrobial resistance. The main problem is that doctors are willing to prescribe antimicrobials to ill-informed individuals who believe that antimicrobials can cure nearly all illnesses, including viral infections like the common cold. In an analysis of drug prescriptions, 36% of individuals with a cold or an
upper respiratory infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, ...
(both usually viral in origin) were given prescriptions for antibiotics. These prescriptions accomplished nothing other than increasing the risk of further evolution of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Using antimicrobials without prescription is another driving force leading to the overuse of antibiotics to self-treat diseases like the common cold, cough, fever, and dysentery resulting in an epidemic of antibiotic resistance in countries like Bangladesh, risking its spread around the globe. Introducing strict antibiotic stewardship in the outpatient setting to reduce inappropriate prescribing of antibiotics may reduce the emerging bacterial resistance.
The
WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) guidance and antibiotic book has been introduced to guide antibiotic choice for the 30 most common infections in adults and children to reduce inappropriate prescribing in primary care and hospitals.
Narrow-spectrum antibiotic
A narrow-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that is only able to kill or inhibit limited species of bacteria. Examples of narrow-spectrum antibiotics include fidaxomicin and sarecycline
Sarecycline, sold under the brand name Seysara, is a ...
s are preferred due to their lower resistance potential, and
broad-spectrum antibiotic
A broad-antimicrobial spectrum, spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are ...
s are only recommended for people with more severe symptoms. Some antibiotics are more likely to confer resistance, so are kept as reserve antibiotics in the AWaRe book.
Various diagnostic strategies have been employed to prevent the overuse of antifungal therapy in the clinic, proving a safe alternative to empirical antifungal therapy, and thus underpinning antifungal stewardship schemes.
At the hospital level
Antimicrobial stewardship
Antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) refers to coordinated efforts to promote the optimal use of antimicrobial agents, including drug choice, dosing, route, and duration of administration. AMS has been an organized effort of specialists in infectious d ...
teams in hospitals are encouraging optimal use of antimicrobials. The goals of antimicrobial stewardship are to help practitioners pick the right drug at the right dose and duration of therapy while preventing misuse and minimizing the development of resistance. Stewardship interventions may reduce the length of stay by an average of slightly over 1 day while not increasing the risk of death. Dispensing, to discharged in-house patients, the exact number of antibiotic pharmaceutical units necessary to complete an ongoing treatment can reduce antibiotic leftovers within the community as community pharmacies can have antibiotic package inefficiencies.
At the primary care level
Given the volume of care provided in primary care (general practice), recent strategies have focused on reducing unnecessary antimicrobial prescribing in this setting. Simple interventions, such as written information explaining when taking antibiotics is not necessary, for example in common infections of the upper respiratory tract, have been shown to reduce antibiotic prescribing. Various tools are also available to help professionals decide if prescribing antimicrobials is necessary.
Parental expectations, driven by the worry for their children's health, can influence how often children are prescribed antibiotics. Parents often rely on their clinician for advice and reassurance. However a lack of plain language information and not having adequate time for consultation negatively impacts this relationship. In effect parents often rely on past experiences in their expectations rather than reassurance from the clinician. Adequate time for consultation and plain language information can help parents make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary antibiotic use.
Parents play a critical role in reducing unnecessary antibiotic use, particularly during cold and flu season when children frequently experience respiratory illnesses. Many of these illnesses are caused by viruses, such as colds or the flu, which antibiotics cannot treat. Misusing antibiotics in these situations not only fails to benefit the child but also contributes to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a broader public health threat. To address parental concerns and reduce inappropriate prescribing, healthcare providers can offer plain-language explanations about the difference between bacterial and viral infections, alongside clear guidance on managing viral illnesses without antibiotics. Vaccinations also play a vital role in reducing the incidence of serious bacterial infections that may require antibiotic treatment, thereby helping to preserve the effectiveness of existing antibiotics. Schools further amplify the spread of infections due to close contact and shared surfaces, underscoring the importance of hygiene practices like regular handwashing, covering coughs, and staying home when unwell. These preventive measures not only reduce the need for antibiotics but also lower the overall risk of resistant bacteria spreading within communities.
The prescriber should closely adhere to the five rights of drug administration: the right patient, the right drug, the right dose, the right route, and the right time. Microbiological samples should be taken for culture and sensitivity testing before treatment when indicated and treatment potentially changed based on the susceptibility report.
Health workers and pharmacists can help tackle antibiotic resistance by: enhancing infection prevention and control; only prescribing and dispensing antibiotics when they are truly needed; prescribing and dispensing the right antibiotic(s) to treat the illness.
A unit dose system implemented in community pharmacies can also reduce antibiotic leftovers at households.
Despite these, written guideline intervention for prescriber to do history taking and provision of advice and knowledge of pharmacists and non‐pharmacists may not reduce the sales of non‐prescription antimicrobial drugs in community pharmacies, drugstores, and other medicine outlets.
At the individual level
People can help tackle resistance by using antibiotics only when infected with a bacterial infection and prescribed by a doctor; completing the full prescription even if the user is feeling better, never sharing antibiotics with others, or using leftover prescriptions.
Taking antibiotics when not needed won't help the user, but instead give bacteria the option to adapt and leave the user with the side effects that come with the certain type of antibiotic.
The CDC recommends that you follow these behaviors so that you avoid these negative side effects and keep the community safe from spreading drug-resistant bacteria.
Practicing basic bacterial infection prevention courses, such as hygiene, also helps to prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Country examples
* The
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
has the lowest rate of antibiotic prescribing in the
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
, at a rate of 11.4
defined daily dose
The defined daily dose (DDD) is a statistical measure of pharmaceutical drug, drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. It is defined in combination with the Anatomical T ...
s (DDD) per 1,000 people per day in 2011. The defined daily dose (DDD) is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization (WHO).
*
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
also have lower prescribing rates, with Sweden's rate having been declining since 2007.
*
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
,
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
have high prescribing rates for antibiotics of more than 28 DDD.
Water, sanitation, hygiene
Infectious disease control through improved
water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) infrastructure needs to be included in the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) agenda. The "Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance" stated in 2018 that "the spread of pathogens through unsafe water results in a high burden of gastrointestinal disease, increasing even further the need for antibiotic treatment."
[IACG (2018]
Reduce unintentional exposure and the need for antimicrobials, and optimize their use IACG Discussion Paper
, Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance
public consultation process
at WHO, Geneva, Switzerland This is particularly a problem in
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
where the spread of infectious diseases caused by inadequate WASH standards is a major driver of antibiotic demand.
Growing usage of antibiotics together with persistent infectious disease levels have led to a dangerous cycle in which reliance on antimicrobials increases while the efficacy of drugs diminishes.
The proper use of infrastructure for water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) can result in a 47–72 percent decrease of diarrhea cases treated with antibiotics depending on the type of intervention and its effectiveness.
A reduction of the diarrhea disease burden through improved infrastructure would result in large decreases in the number of diarrhea cases treated with antibiotics. This was estimated as ranging from 5 million in Brazil to up to 590 million in India by the year 2030.
The strong link between increased consumption and resistance indicates that this will directly mitigate the accelerating spread of AMR.
Sanitation and water for all by 2030 is
Goal Number 6 of the
Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
.
An increase in
hand washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap, soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to th ...
compliance by hospital staff results in decreased rates of resistant organisms.
Water supply and sanitation infrastructure in health facilities offer significant co-benefits for combatting AMR, and investment should be increased.
There is much room for improvement: WHO and UNICEF estimated in 2015 that globally 38% of health facilities did not have a source of water, nearly 19% had no toilets and 35% had no water and soap or alcohol-based hand rub for handwashing.
Industrial wastewater treatment
Manufacturers of antimicrobials need to improve the treatment of their wastewater (by using
industrial wastewater treatment
Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for Wastewater treatment, treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater (or effluent) may be reus ...
processes) to reduce the release of residues into the environment.
Limiting antimicrobial use in animals and farming
It is established that the use of
antibiotics in animal husbandry can give rise to AMR resistances in bacteria found in food animals to the antibiotics being administered (through injections or medicated feeds). For this reason only antimicrobials that are deemed "not-clinically relevant" are used in these practices.
Unlike resistance to antibacterials, antifungal resistance can be driven by
arable farming
Arable land (from the , "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for the purposes of a ...
, currently there is no regulation on the use of similar antifungal classes in agriculture and the clinic.
Recent studies have shown that the prophylactic use of "non-priority" or "non-clinically relevant" antimicrobials in feeds can potentially, under certain conditions, lead to co-selection of environmental AMR bacteria with resistance to medically important antibiotics.
The possibility for co-selection of AMR resistances in the food chain pipeline may have far-reaching implications for human health.
Country examples
= Europe
=
In 1997, European Union health ministers voted to ban
avoparcin and four additional antibiotics used to promote animal growth in 1999. In 2006 a ban on the use of antibiotics in European feed, with the exception of two antibiotics in poultry feeds, became effective. In Scandinavia, there is evidence that the ban has led to a lower prevalence of antibiotic resistance in (nonhazardous) animal bacterial populations. As of 2004, several European countries established a decline of antimicrobial resistance in humans through limiting the use of antimicrobials in agriculture and food industries without jeopardizing animal health or economic cost.
= United States
=
The
United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and producti ...
(USDA) and the
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) collect data on antibiotic use in humans and in a more limited fashion in animals.
About 80% of antibiotic use in the U.S. is for agriculture purposes, and about 70% of these are medically important.
This gives reason for concern about the antibiotic resistance crisis in the U.S. and more reason to monitor it. The FDA first determined in 1977 that there is evidence of emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains in livestock. The long-established practice of permitting OTC sales of antibiotics (including penicillin and other drugs) to lay animal owners for administration to their own animals nonetheless continued in all states.
In 2000, the FDA announced their intention to revoke approval of
fluoroquinolone
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well ...
use in poultry production because of substantial evidence linking it to the emergence of fluoroquinolone-resistant ''
Campylobacter
''Campylobacter'' is a type of bacteria that can cause a diarrheal disease in people. Its name means "curved bacteria", as the germ typically appears in a comma or "s" shape. According to its scientific classification, it is a genus of gram-negat ...
'' infections in humans. Legal challenges from the food animal and pharmaceutical industries delayed the final decision to do so until 2006.
Fluroquinolones have been banned from extra-label use in food animals in the USA since 2007. However, they remain widely used in companion and exotic animals.
Global action plans and awareness
At the 79th United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting on AMR on 26 September 2024, world leaders approved a political declaration committing to a clear set of targets and actions, including reducing the estimated 4.95 million human deaths associated with bacterial AMR annually by 10% by 2030.
The increasing interconnectedness of the world and the fact that new classes of antibiotics have not been developed and approved for more than 25 years highlight the extent to which antimicrobial resistance is a global health challenge. A global action plan to tackle the growing problem of resistance to antibiotics and other antimicrobial medicines was endorsed at the Sixty-eighth
World Health Assembly
The World Health Assembly (WHA) is the forum through which the World Health Organization (WHO) is governed by its 194 World Health Organization#Membership, member states. It is the world's highest health policy setting body and is composed of h ...
in May 2015.
One of the key objectives of the plan is to improve awareness and understanding of antimicrobial resistance through effective communication, education and training. This global action plan developed by the World Health Organization was created to combat the issue of antimicrobial resistance and was guided by the advice of countries and key stakeholders. The WHO's global action plan is composed of five key objectives that can be targeted through different means, and represents countries coming together to solve a major problem that can have future health consequences.
These objectives are as follows:
* improve awareness and understanding of antimicrobial resistance through effective communication, education and training.
* strengthen the knowledge and evidence base through surveillance and research.
* reduce the incidence of infection through effective sanitation, hygiene and infection prevention measures.
* optimize the use of antimicrobial medicines in human and animal health.
* develop the economic case for sustainable investment that takes account of the needs of all countries and to increase investment in new medicines, diagnostic tools, vaccines and other interventions.
Steps towards progress
* React based in Sweden has produced informative material on AMR for the general public.
* Videos are being produced for the general public to generate interest and awareness.
* The Irish Department of Health published a National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance in October 2017. The Strategy for the Control of Antimicrobial Resistance in Ireland (SARI), Iaunched in 2001 developed Guidelines for Antimicrobial Stewardship in Hospitals in Ireland in conjunction with the Health Protection Surveillance Centre, these were published in 2009. Following their publication a public information campaign 'Action on Antibiotics' was launched to highlight the need for a change in antibiotic prescribing. Despite this, antibiotic prescribing remains high with variance in adherence to guidelines.
* The United Kingdom published a 20-year vision for antimicrobial resistance that sets out the goal of containing and controlling AMR by 2040. The vision is supplemented by a 5-year action plan running from 2019 to 2024, building on the previous action plan (2013–2018).
* The World Health Organization has published the 2024 Bacterial Priority Pathogens List which covers 15 families of antibiotic-resistant bacterial pathogens. Notable among these are
gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
resistant to last-resort antibiotics, drug-resistant
mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
, and other high-burden resistant pathogens such as
Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
,
Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram negative, facultatively anaerobic, non–spore-forming, nonmotile, rod shaped, and is genetically nested within ''Escherichia''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who discovered it in 1 ...
,
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular) or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria first isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. An obligate human pathog ...
,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...
, and
Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
. The inclusion of these pathogens in the list underscores their global impact in terms of burden, as well as issues related to transmissibility, treatability, and prevention options. It also reflects the R&D pipeline of new treatments and emerging resistance trends.
Antibiotic Awareness Week
The World Health Organization has promoted the first World Antibiotic Awareness Week running from 16 to 22 November 2015. The aim of the week is to increase global awareness of antibiotic resistance. It also wants to promote the correct usage of antibiotics across all fields in order to prevent further instances of antibiotic resistance.
World Antibiotic Awareness Week has been held every November since 2015. For 2017, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Health Organization (WHO) and the
World Organisation for Animal Health
The World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), formerly the (OIE), is an intergovernmental organisation founded in 1924, coordinating, supporting and promoting animal disease control. The primary objective of WOAH is to control epizootic dis ...
(OIE) are together calling for responsible use of antibiotics in humans and animals to reduce the emergence of antibiotic resistance.
United Nations
In 2016 the Secretary-General of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
convened the Interagency Coordination Group (IACG) on Antimicrobial Resistance.
The IACG worked with international organizations and experts in human, animal, and plant health to create a plan to fight antimicrobial resistance.
Their report released in April 2019 highlights the seriousness of antimicrobial resistance and the threat it poses to world health. It suggests five recommendations for member states to follow in order to tackle this increasing threat. The IACG recommendations are as follows:
* Accelerate progress in countries
* Innovate to secure the future
* Collaborate for more effective action
* Invest for a sustainable response
* Strengthen accountability and global governance
One Health Approach
The One Health approach recognizes that human, animal, and environmental health are interconnected in the development and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Key strategies include:
Integrated Surveillance
* Monitoring antibiotic use and resistance trends across human medicine, agriculture, and environmental sectors.
* For example, 73% of the world's antibiotics are used in livestock, often for non-therapeutic purposes like growth promotion.
Policy Interventions
* Banning non-therapeutic antibiotics in agriculture (e.g., European Union's 2006 growth promoter ban).
* Incentivizing development of new antibiotics and alternatives (e.g., vaccines, bacteriophages).
Environmental Mitigation
* Reducing pharmaceutical waste in water systems and soil through improved waste management.
* Addressing resistance genes in wastewater from hospitals, farms, and drug manufacturing sites.
Mechanisms and organisms
Bacteria
The five main mechanisms by which bacteria exhibit resistance to antibiotics are:
# Drug inactivation or modification: for example, enzymatic deactivation of
penicillin G in some penicillin-resistant bacteria through the production of
β-lactamases. Drugs may also be chemically modified through the addition of
functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
s by
transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved ...
enzymes; for example,
acetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
,
phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
, or
adenylation are common resistance mechanisms to
aminoglycoside
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer ...
s. Acetylation is the most widely used mechanism and can affect a number of
drug class
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestio ...
es.
# Alteration of target- or binding site: for example, alteration of
PBP—the binding target site of penicillins—in
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. ...
and other penicillin-resistant bacteria. Another protective mechanism found among bacterial species is ribosomal protection proteins. These proteins protect the bacterial cell from antibiotics that target the cell's ribosomes to inhibit protein synthesis. The mechanism involves the binding of the ribosomal protection proteins to the ribosomes of the bacterial cell, which in turn changes its conformational shape. This allows the ribosomes to continue synthesizing proteins essential to the cell while preventing antibiotics from binding to the ribosome to inhibit protein synthesis.
# Alteration of metabolic pathway: for example, some
sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the Chemical structure, structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this gro ...
-resistant bacteria do not require
para-aminobenzoic acid
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as ''para''-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the ''para'' position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA ...
(PABA), an important precursor for the synthesis of
folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
and
nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s in bacteria inhibited by sulfonamides, instead, like mammalian cells, they turn to using preformed folic acid.
# Reduced drug accumulation: by decreasing drug
permeability or increasing active
efflux (pumping out) of the drugs across the cell surface. These
multidrug efflux pumps within the cellular membrane of certain bacterial species are used to pump antibiotics out of the cell before they are able to do any damage. They are often activated by a specific substrate associated with an antibiotic, as in
fluoroquinolone
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well ...
resistance.
# Ribosome splitting and recycling: for example, drug-mediated stalling of the ribosome by
lincomycin
Lincomycin is a lincosamide antibiotic that comes from the actinomycete ''Streptomyces lincolnensis''. A related compound, clindamycin, is derived from lincomycin by using thionyl chloride to replace the 7-hydroxy group with a chlorine atom with ...
and
erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used ...
unstalled by a heat shock protein found in ''Listeria monocytogenes'', which is a homologue of HflX from other bacteria. Liberation of the ribosome from the drug allows further translation and consequent resistance to the drug.

There are several different types of germs that have developed a resistance over time.
The six pathogens causing most deaths associated with resistance are ''Escherichia coli'', ''Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii'', and ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. They were responsible for 929,000 deaths attributable to resistance and 3.57 million deaths associated with resistance in 2019.
Penicillinase-producing ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' developed a resistance to penicillin in 1976. Another example is Azithromycin-resistant ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', which developed a resistance to azithromycin in 2011.
In
gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
, plasmid-mediated resistance genes produce proteins that can bind to
DNA gyrase
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-po ...
, protecting it from the action of quinolones. Finally, mutations at key sites in DNA gyrase or
topoisomerase IV
Topoisomerase IV is one of two Type II topoisomerases in bacteria, the other being DNA gyrase. Like gyrase, topoisomerase IV is able to pass one double-strand of DNA through another double-strand of DNA, thereby changing the linking number of DNA ...
can decrease their binding affinity to quinolones, decreasing the drug's effectiveness.
Some bacteria are naturally resistant to certain antibiotics; for example, gram-negative bacteria are resistant to most
β-lactam antibiotics due to the presence of
β-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide Multiple drug resistance, multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem ...
. Antibiotic resistance can also be acquired as a result of either genetic mutation or
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
. Although mutations are rare, with spontaneous mutations in the
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
occurring at a rate of about 1 in 10
5 to 1 in 10
8 per chromosomal replication, the fact that bacteria reproduce at a high rate allows for the effect to be significant. Given that lifespans and production of new generations can be on a timescale of mere hours, a new (de novo) mutation in a parent cell can quickly become an
inherited mutation of widespread prevalence, resulting in the
microevolution
Microevolution is the change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population. This change is due to four different processes: mutation, selection ( natural and artificial), gene flow and genetic drift. This change happens over ...
of a fully resistant colony. However, chromosomal mutations also confer a cost of fitness. For example, a ribosomal mutation may protect a bacterial cell by changing the binding site of an antibiotic but may result in slower growth rate. Moreover, some adaptive mutations can propagate not only through inheritance but also through
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
. The most common mechanism of horizontal gene transfer is the transferring of
plasmids
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and ...
carrying antibiotic resistance genes between bacteria of the same or different species via
conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
*Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change o ...
. However, bacteria can also acquire resistance through
transformation
Transformation may refer to:
Science and mathematics
In biology and medicine
* Metamorphosis, the biological process of changing physical form after birth or hatching
* Malignant transformation, the process of cells becoming cancerous
* Trans ...
, as in ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' uptaking of naked fragments of extracellular DNA that contain antibiotic resistance genes to streptomycin, through
transduction, as in the bacteriophage-mediated transfer of tetracycline resistance genes between strains of ''S. pyogenes'', or through
gene transfer agents, which are particles produced by the host cell that resemble bacteriophage structures and are capable of transferring DNA.
Antibiotic resistance can be introduced artificially into a microorganism through laboratory protocols, sometimes used as a
selectable marker
A selectable marker is a gene introduced into cell (biology), cells, especially bacteria or cells in cell culture, culture, which confers one or more traits suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory micr ...
to examine the mechanisms of gene transfer or to identify individuals that absorbed a piece of DNA that included the resistance gene and another gene of interest.
Recent findings show no necessity of large populations of bacteria for the appearance of antibiotic resistance. Small populations of ''
Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'' in an antibiotic gradient can become resistant. Any heterogeneous environment with respect to nutrient and antibiotic gradients may facilitate antibiotic resistance in small bacterial populations. Researchers hypothesize that the mechanism of resistance evolution is based on four SNP mutations in the genome of ''E. coli'' produced by the gradient of antibiotic.
In one study, which has implications for space microbiology, a non-pathogenic strain ''E. coli'' MG1655 was exposed to trace levels of the broad spectrum antibiotic
chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
, under simulated microgravity (LSMMG, or Low Shear Modeled Microgravity) over 1000 generations. The adapted strain acquired resistance to not only chloramphenicol, but also cross-resistance to other antibiotics; this was in contrast to the observation on the same strain, which was adapted to over 1000 generations under LSMMG, but without any antibiotic exposure; the strain in this case did not acquire any such resistance. Thus, irrespective of where they are used, the use of an antibiotic would likely result in persistent resistance to that antibiotic, as well as cross-resistance to other antimicrobials.
In recent years, the emergence and spread of
β-lactamases called
carbapenemases has become a major health crisis. One such carbapenemase is
New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1
NDM-1 is an enzyme that makes bacteria Antibiotic resistance, resistant to a broad range of beta-lactam antibiotics. These include the antibiotics of the carbapenem family, which are a mainstay for the treatment of antibiotic-resistant bacterial ...
(NDM-1),
an
enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
that makes
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
resistant to a broad range of
beta-lactam antibiotics. The most common bacteria that make this enzyme are gram-negative such as ''E. coli'' and ''
Klebsiella pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose- fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar.
Although found in the normal flora of the mo ...
'', but the gene for NDM-1 can spread from one strain of bacteria to another by
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
.
Viruses
Specific
antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s are used to treat some viral infections. These drugs prevent viruses from reproducing by inhibiting essential stages of the virus's replication cycle in infected cells. Antivirals are used to treat
HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
,
hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
,
hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include ...
,
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
,
herpes viruses including
varicella zoster virus
Varicella zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting children and young adults, and shingles (herpes zos ...
,
cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherp ...
and
Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), also known as human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4), is one of the nine known Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human herpesvirus types in the Herpesviridae, herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in ...
. With each virus, some strains have become resistant to the administered drugs.
Antiviral drugs typically target key components of viral reproduction; for example,
oseltamivir
Oseltamivir, sold under the brand name Tamiflu among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B, viruses that cause the flu. Many medical organizations recommend it in people who have complicati ...
targets influenza
neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glycosidic linkag ...
, while guanosine analogs inhibit viral DNA polymerase. Resistance to antivirals is thus acquired through mutations in the genes that encode the protein targets of the drugs.
Resistance to HIV antivirals is problematic, and even multi-drug resistant strains have evolved. One source of resistance is that many current HIV drugs, including NRTIs and NNRTIs, target
reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobi ...
; however, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is highly error prone and thus mutations conferring resistance arise rapidly. Resistant strains of the HIV virus emerge rapidly if only one antiviral drug is used. Using three or more drugs together, termed
combination therapy
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are ...
, has helped to control this problem, but new drugs are needed because of the continuing emergence of drug-resistant HIV strains.
Fungi
Infections by fungi are a cause of high morbidity and mortality in
immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affe ...
persons, such as those with HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis or receiving
chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
. The fungi
''Candida'', ''
Cryptococcus neoformans
''Cryptococcus neoformans'' is an encapsulated basidiomycetous yeast belonging to the class Tremellomycetes and an obligate aerobe that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is a filamentous fungus, formerly referred to ''Filob ...
'' and ''
Aspergillus fumigatus
''Aspergillus fumigatus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus'', and is one of the most common ''Aspergillus'' species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency.
''Aspergillus fumigatus'', a saprotroph widespread in ...
'' cause most of these infections and antifungal resistance occurs in all of them. Multidrug resistance in fungi is increasing because of the widespread use of antifungal drugs to treat infections in immunocompromised individuals and the use of some agricultural antifungals.
Antifungal resistant disease is associated with increased mortality.
Some fungi (e.g.
Candida krusei and
fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. These include candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and tinea versicolor. It is also used to pr ...
) exhibit intrinsic resistance to certain antifungal drugs or classes, whereas some species develop antifungal resistance to external pressures. Antifungal resistance is a
One Health concern, driven by multiple extrinsic factors, including extensive fungicidal use, overuse of clinical antifungals,
environmental change
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism ...
and host factors.
In the USA
fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. These include candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and tinea versicolor. It is also used to pr ...
-resistant Candida species and azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus have been highlighted as a growing threat.
More than 20 species of ''Candida'' can cause
candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any species of the genus '' Candida'' (a yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the ...
infection, the most common of which is ''
Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
''. ''Candida'' yeasts normally inhabit the skin and mucous membranes without causing infection. However, overgrowth of ''Candida'' can lead to candidiasis. Some ''Candida'' species (e.g. ''
Candida glabrata)'' are becoming resistant to first-line and second-line
antifungal agents such as
echinocandin
Echinocandins are a class of antifungal drugs that inhibit the synthesis of β-glucan in the fungal cell wall via noncompetitive inhibition of the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase. The class has been dubbed the "penicillin of antifungals," along w ...
s and
azoles.
The emergence of ''Candida auris'' as a potential human pathogen that sometimes exhibits multi-class antifungal drug resistance is concerning and has been associated with several outbreaks globally. The WHO has released a priority fungal pathogen list, including pathogens with antifungal resistance.
The identification of antifungal resistance is undermined by limited classical diagnosis of infection, where a culture is lacking, preventing susceptibility testing.
National and international surveillance schemes for fungal disease and antifungal resistance are limited, hampering the understanding of the disease burden and associated resistance.
The application of molecular testing to identify genetic markers associating with resistance may improve the identification of antifungal resistance, but the diversity of mutations associated with resistance is increasing across the fungal species causing infection. In addition, a number of resistance mechanisms depend on up-regulation of selected genes (for instance reflux pumps) rather than defined mutations that are amenable to molecular detection.
Due to the limited number of antifungals in clinical use and the increasing global incidence of antifungal resistance, using the existing antifungals in combination might be beneficial in some cases but further research is needed. Similarly, other approaches that might help to combat the emergence of antifungal resistance could rely on the development of host-directed therapies such as
immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
or vaccines.
Parasites
The
protozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
n parasites that cause the diseases
malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
,
trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis or trypanosomosis is the name of several diseases in vertebrates caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosomes of the genus ''Trypanosoma''. In humans this includes African trypanosomiasis and Chagas disease. A number of other disea ...
,
toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or month ...
,
cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by ''Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the ileum, distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tr ...
and
leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by protozoal parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of Phlebotominae, phlebotomine Sandfly, sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' an ...
are important human pathogens.
Malarial parasites that are resistant to the drugs that are currently available to infections are common and this has led to increased efforts to develop new drugs. Resistance to recently developed drugs such as
artemisinin
Artemisinin () and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum''. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for he ...
has also been reported. The problem of drug resistance in malaria has driven efforts to develop vaccines.
Trypanosomes
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek language, Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of ...
are parasitic protozoa that cause
African trypanosomiasis
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma bru ...
and
Chagas disease
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. It is spread mostly by insects in the subfamily Triatominae, known as "kissing bugs". The symptoms change throughout the ...
(American trypanosomiasis). There are no vaccines to prevent these infections so drugs such as
pentamidine
Pentamidine is an antimicrobial medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, '' Balamuthia'' infections, babesiosis, and to prevent and treat pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in people with poor immune function. In African trypa ...
and
suramin
Suramin is a medication used to treat African sleeping sickness and river blindness. It is the treatment of choice for sleeping sickness without central nervous system involvement. It is given by injection into a vein.
Suramin causes a fai ...
,
benznidazole
Benznidazole is an antiparasitic medication used in the treatment of Chagas disease. While it is highly effective in early disease, the effectiveness decreases in those who have long-term infection. It is the first-line treatment given its mod ...
and
nifurtimox are used to treat infections. These drugs are effective but infections caused by resistant parasites have been reported.
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by protozoal parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of Phlebotominae, phlebotomine Sandfly, sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' an ...
is caused by protozoa and is an important public health problem worldwide, especially in sub-tropical and tropical countries. Drug resistance has "become a major concern".
Global and genomic data


In 2022, genomic epidemiologists reported results from a
global
Global may refer to:
General
*Globe, a spherical model of celestial bodies
*Earth, the third planet from the Sun
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 198 ...
survey of antimicrobial resistance via genomic
wastewater-based epidemiology, finding large regional variations, providing maps, and suggesting resistance genes are also
passed on between microbial species that are not closely related.
The
WHO
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 15 ...
provides the Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) reports which summarize annual (e.g. 2020's) data on international AMR, also including an interactive dashboard.
Epidemiology
United Kingdom
Public Health England
Public Health England (PHE) was an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in England which began operating on 1 April 2013 to protect and improve health and wellbeing and reduce health inequalities. Its formation came as a ...
reported that the total number of antibiotic resistant infections in England rose by 9% from 55,812 in 2017 to 60,788 in 2018, but antibiotic consumption had fallen by 9% from 20.0 to 18.2 defined daily doses per 1,000 inhabitants per day between 2014 and 2018.
United States
The
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
reported that more than 2.8 million cases of antibiotic resistance have been reported. However, in 2019 overall deaths from antibiotic-resistant infections decreased by 18% and deaths in hospitals decreased by 30%.
The
COVID pandemic
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fev ...
caused a reversal of much of the progress made on attenuating the effects of antibiotic resistance, resulting in more antibiotic use, more resistant infections, and less data on preventive action. Hospital-onset infections and deaths both increased by 15% in 2020, and significantly higher rates of infections were reported for 4 out of 6 types of healthcare associated infections.
History
The 1950s to 1970s represented the golden age of antibiotic discovery, where countless new classes of antibiotics were discovered to treat previously incurable diseases such as tuberculosis and syphilis. However, since that time the discovery of new classes of antibiotics has been almost nonexistent, and represents a situation that is especially problematic considering the resiliency of bacteria shown over time and the continued misuse and overuse of antibiotics in treatment.
Already in 1940, in their letter to the editor of Nature journal,
Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
and
Chain
A chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. A ...
identified the enzyme
penicillinase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapenem ...
as responsible for the deactivation of penicillin in penicillin-resistant bacteria. This discovery was the first step in understanding the mechanisms of microbial resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. The phenomenon of antimicrobial resistance caused by overuse of antibiotics was predicted as early as 1945 by
Alexander Fleming
Sir Alexander Fleming (6 August 1881 – 11 March 1955) was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in 1928 of wha ...
who said "The time may come when penicillin can be bought by anyone in the shops. Then there is the danger that the ignorant man may easily under-dose himself and by exposing his microbes to nonlethal quantities of the drug make them resistant." Without the creation of new and stronger antibiotics an era where common infections and minor injuries can kill, and where complex procedures such as surgery and chemotherapy become too risky, is a very real possibility. Antimicrobial resistance can lead to epidemics of enormous proportions if preventive actions are not taken. In this day and age current antimicrobial resistance leads to longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality.
Society and culture
Innovation policy
Since the mid-1980s pharmaceutical companies have invested in medications for cancer or chronic disease that have greater potential to make money and have "de-emphasized or dropped development of antibiotics".
On 20 January 2016 at the
World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-governmental organization, international advocacy non-governmental organization and think tank, based in Cologny, Canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded on 24 January 1971 by German ...
in
Davos
Davos (, ; or ; ; Old ) is an Alpine resort town and municipality in the Prättigau/Davos Region in the canton of Graubünden, Switzerland. It has a permanent population of (). Davos is located on the river Landwasser, in the Rhaetian ...
,
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, more than "80 pharmaceutical and diagnostic companies" from around the world called for "transformational commercial models" at a global level to spur research and development on antibiotics and on the "enhanced use of diagnostic tests that can rapidly identify the infecting organism".
A number of countries are considering or implementing delinked payment models for new antimicrobials whereby payment is based on value rather than volume of drug sales. This offers the opportunity to pay for valuable new drugs even if they are reserved for use in relatively rare drug resistant infections.
Legal frameworks
Some global health scholars have argued that a global, legal framework is needed to prevent and control antimicrobial resistance.
For instance, binding global policies could be used to create antimicrobial use standards, regulate antibiotic marketing, and strengthen global surveillance systems.
Ensuring compliance of involved parties is a challenge.
Global antimicrobial resistance policies could take lessons from the environmental sector by adopting strategies that have made international environmental agreements successful in the past such as: sanctions for non-compliance, assistance for implementation, majority vote decision-making rules, an independent scientific panel, and specific commitments.
United States
For the
United States 2016 budget,
U.S. president
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
proposed to nearly double the amount of federal funding to "combat and prevent" antibiotic resistance to more than $1.2 billion. Many international funding agencies like USAID, DFID,
SIDA and
Gates Foundation
The Gates Foundation is an American private foundation founded by Bill Gates and Melinda French Gates. Based in Seattle, Washington, it was launched in 2000 and is reported to be the third largest charitable foundation in the world, holding $ ...
have pledged money for developing strategies to counter antimicrobial resistance.
On 27 March 2015, the
White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
released a comprehensive plan to address the increasing need for agencies to combat the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The Task Force for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria developed ''The National Action Plan for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria'' with the intent of providing a roadmap to guide the US in the antibiotic resistance challenge and with hopes of saving many lives. This plan outlines steps taken by the Federal government over the next five years needed in order to prevent and contain outbreaks of antibiotic-resistant infections; maintain the efficacy of antibiotics already on the market; and to help to develop future diagnostics, antibiotics, and vaccines.
The Action Plan was developed around five goals with focuses on strengthening health care, public health veterinary medicine, agriculture, food safety and research, and manufacturing. These goals, as listed by the White House, are as follows:
* Slow the Emergence of Resistant Bacteria and Prevent the Spread of Resistant Infections
* Strengthen National One-Health Surveillance Efforts to Combat Resistance
* Advance Development and use of Rapid and Innovative Diagnostic Tests for Identification and Characterization of Resistant Bacteria
* Accelerate Basic and Applied Research and Development for New Antibiotics, Other Therapeutics, and Vaccines
* Improve International Collaboration and Capacities for Antibiotic Resistance Prevention, Surveillance, Control and Antibiotic Research and Development
The following are goals set to meet by 2020:
* Establishment of antimicrobial programs within acute care hospital settings
* Reduction of inappropriate antibiotic prescription and use by at least 50% in outpatient settings and 20% inpatient settings
* Establishment of State Antibiotic Resistance (AR) Prevention Programs in all 50 states
* Elimination of the use of medically important antibiotics for growth promotion in food-producing animals.
Current Status of AMR in the U.S.
As of 2023, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains a significant public health threat in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's 2023 Report on Antibiotic Resistance Threats, over 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur in the U.S. each year, leading to at least 35,000 deaths annually.
Among the most concerning resistant pathogens are Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and Clostridioides difficile (C. diff), all of which continue to be responsible for severe healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a significant disruption in healthcare, with an increase in the use of antibiotics during the treatment of viral infections. This rise in antibiotic prescribing, coupled with overwhelmed healthcare systems, contributed to a resurgence in AMR during the pandemic years. A 2021 CDC report identified a sharp increase in HAIs caused by resistant pathogens in COVID-19 patients, a trend that has persisted into 2023.
Recent data suggest that although antibiotic use has decreased since the pandemic, some resistant pathogens remain prevalent in healthcare settings.
The CDC has also expanded its Get Ahead of Sepsis campaign in 2023, focusing on raising awareness of AMR's role in sepsis and promoting the judicious use of antibiotics in both healthcare and community settings.
This initiative has reached millions through social media, healthcare facilities, and public health outreach, aiming to educate the public on the importance of preventing infections and reducing antibiotic misuse.
Under the administration of
Donald
Donald is a Scottish masculine given name. It is derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinter ...
J. Trump, severe federal funding cuts in 2025 at the
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
(NIH) and many other research entities in the United States are expected to impede progress in combating antimicrobial resistance. Public health experts believe these budget reductions will adversely affect the development of new antibiotics as well as advances in diagnostics and treatment strategies, thus undermining efforts currently underway to address AMR. The
Infectious Diseases Society of America
The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) is a medical association representing physicians, scientists, and other health care professionals who specialize in infectious diseases. It was founded in 1963 and is based in Arlington, Virginia. ...
(IDSA) is but one organization that has expressed grave concern regarding the negative consequences of such extreme budget measures on antimicrobial stewardship, and, as a result, on global health security overall.
Policies
According to
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, policymakers can help tackle resistance by strengthening resistance-tracking and laboratory capacity and by regulating and promoting the appropriate use of medicines.
Policymakers and industry can help tackle resistance by: fostering innovation and research and development of new tools; and promoting cooperation and information sharing among all stakeholders.
The U.S. government continues to prioritize AMR mitigation through policy and legislation. In 2023, the National Action Plan for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (CARB) 2023-2028 was released, outlining strategic objectives for reducing antibiotic-resistant infections, advancing infection prevention, and accelerating research on new antibiotics.
The plan also emphasizes the importance of improving antibiotic stewardship across healthcare, agriculture, and veterinary settings.
Furthermore, the PASTEUR Act (Pioneering Antimicrobial Subscriptions to End Upsurging Resistance) has gained momentum in Congress. If passed, the bill would create a subscription-based payment model to incentivize the development of new antimicrobial drugs, while supporting antimicrobial stewardship programs to reduce the misuse of existing antibiotics.
This legislation is considered a critical step toward addressing the economic barriers to developing new antimicrobials.
Policy evaluation
Measuring the costs and benefits of strategies to combat AMR is difficult and policies may only have effects in the distant future. In other infectious diseases this problem has been addressed by using mathematical models. More research is needed to understand how AMR develops and spreads so that mathematical modelling can be used to anticipate the likely effects of different policies.
Further research
Rapid testing and diagnostics

Distinguishing infections requiring antibiotics from self-limiting ones is clinically challenging. In order to guide appropriate use of antibiotics and prevent the evolution and spread of antimicrobial resistance, diagnostic tests that provide clinicians with timely, actionable results are needed.
Acute febrile illness is a common reason for seeking medical care worldwide and a major cause of morbidity and mortality. In areas with decreasing malaria incidence, many febrile patients are inappropriately treated for malaria, and in the absence of a simple diagnostic test to identify alternative causes of fever, clinicians presume that a non-malarial febrile illness is most likely a bacterial infection, leading to inappropriate use of antibiotics. Multiple studies have shown that the use of malaria rapid diagnostic tests without reliable tools to distinguish other fever causes has resulted in increased antibiotic use.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) can facilitate a
precision medicine
Precision, precise or precisely may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Precision'' (march), the official marching music of the Royal Military College of Canada
* "Precision" (song), by Big Sean
* ''Precisely'' (sketch), a dramatic sketch by the Eng ...
approach to treatment by helping clinicians to prescribe more effective and targeted antimicrobial therapy. At the same time with traditional phenotypic AST it can take 12 to 48 hours to obtain a result due to the time taken for organisms to grow on/in culture media.
Rapid testing, possible from
molecular diagnostics
Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical tests, medical testing. In medicine th ...
innovations, is defined as "being feasible within an 8-h working shift".
There are several commercial Food and Drug Administration-approved assays available which can detect AMR genes from a variety of specimen types. Progress has been slow due to a range of reasons including cost and regulation. Genotypic AMR characterisation methods are, however, being increasingly used in combination with machine learning algorithms in research to help better predict phenotypic AMR from organism genotype.
Optical techniques such as phase contrast microscopy in combination with single-cell analysis are another powerful method to monitor bacterial growth. In 2017, scientists from Uppsala University in Sweden published a method that applies principles of
microfluidics
Microfluidics refers to a system that manipulates a small amount of fluids (10−9 to 10−18 liters) using small channels with sizes of ten to hundreds of micrometres. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves molecular analysis, molecular bi ...
and cell tracking, to monitor bacterial response to antibiotics in less than 30 minutes overall manipulation time. This invention was awarded the 8M£ Longitude Prize on AMR in 2024. Recently, this platform has been advanced by coupling microfluidic chip with
optical tweezing in order to isolate bacteria with altered phenotype directly from the analytical matrix.
Rapid diagnostic methods have also been trialled as antimicrobial stewardship interventions to influence the healthcare drivers of AMR. Serum
procalcitonin measurement has been shown to reduce mortality rate, antimicrobial consumption and antimicrobial-related side-effects in patients with respiratory infections, but impact on AMR has not yet been demonstrated. Similarly, point of care serum testing of the inflammatory biomarker
C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin ...
has been shown to influence antimicrobial prescribing rates in this patient cohort, but further research is required to demonstrate an effect on rates of AMR. Clinical investigation to rule out bacterial infections are often done for patients with pediatric acute respiratory infections. Currently it is unclear if rapid viral testing affects antibiotic use in children.
Vaccines
Vaccines are an essential part of the response to reduce AMR as they prevent infections, reduce the use and overuse of antimicrobials, and slow the emergence and spread of drug-resistant pathogens.
Microorganisms usually do not develop
resistance to vaccines because vaccines reduce the spread of the infection and target the pathogen in multiple ways in the same host and possibly in different ways between different hosts. Furthermore, if the use of vaccines increases, there is evidence that antibiotic resistant strains of pathogens will decrease; the need for antibiotics will naturally decrease as vaccines prevent infection before it occurs. A 2024 report by WHO finds that vaccines against 24 pathogens could reduce the number of antibiotics needed by 22% or 2.5 billion defined daily doses globally every year.
If vaccines could be rolled out against all the evaluated pathogens, they could save a third of the hospital costs associated with AMR.
Vaccinated people have fewer infections and are protected against potential complications from secondary infections that may need antimicrobial medicines or require admission to hospital.
However, there are well documented cases of vaccine resistance, although these are usually much less of a problem than antimicrobial resistance.
While theoretically promising, antistaphylococcal vaccines have shown limited efficacy, because of immunological variation between ''Staphylococcus'' species, and the limited duration of effectiveness of the antibodies produced. Development and testing of more effective vaccines is underway.
Two registrational trials have evaluated vaccine candidates in active immunization strategies against ''S. aureus'' infection. In a phase II trial, a bivalent vaccine of capsular proteins 5 & 8 was tested in 1804 hemodialysis patients with a primary fistula or synthetic graft vascular access. After 40 weeks following vaccination a protective effect was seen against ''S. aureus'' bacteremia, but not at 54 weeks following vaccination. Based on these results, a second trial was conducted which failed to show efficacy.
Merck tested V710, a vaccine targeting IsdB, in a blinded randomized trial in patients undergoing median sternotomy. The trial was terminated after a higher rate of multiorgan system failure–related deaths was found in the V710 recipients. Vaccine recipients who developed ''S. aureus'' infection were five times more likely to die than control recipients who developed ''S. aureus'' infection.
Numerous investigators have suggested that a multiple-antigen vaccine would be more effective, but a lack of biomarkers defining human protective immunity keep these proposals in the logical, but strictly hypothetical arena.
Antibody therapy
Antibodies are promising against antimicrobial resistance. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) target bacterial virulence factors, aiding in bacterial destruction through various mechanisms. Three FDA-approved antibodies target ''B. anthracis'' and ''C. difficile'' toxins.
Innovative strategies include DSTA4637S, an antibody-antibiotic conjugate, and MEDI13902, a bispecific antibody targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa components.
Alternating therapy
Alternating therapy is a proposed method in which two or three antibiotics are taken in a rotation versus taking just one antibiotic such that bacteria resistant to one antibiotic are killed when the next antibiotic is taken. Studies have found that this method reduces the rate at which antibiotic resistant bacteria emerge in vitro relative to a single drug for the entire duration.
Studies have found that bacteria that evolve antibiotic resistance towards one group of antibiotic may become more sensitive to others. This phenomenon can be used to select against resistant bacteria using an approach termed collateral sensitivity cycling, which has recently been found to be relevant in developing treatment strategies for chronic infections caused by ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. Despite its promise, large-scale clinical and experimental studies revealed limited evidence of susceptibility to antibiotic cycling across various pathogens.
Development of new drugs
Since the discovery of antibiotics,
research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage ...
(R&D) efforts have provided new drugs in time to treat bacteria that became resistant to older antibiotics, but in the 2000s there has been concern that development has slowed enough that seriously ill people may run out of treatment options. Another concern is that practitioners may become reluctant to perform routine surgeries because of the increased risk of harmful infection.
Backup treatments can have serious side-effects; for example, antibiotics like
aminoglycoside
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer ...
s (such as
amikacin
Amikacin is an antibiotic medication used for a number of bacterial infections. This includes joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections. It is also used for the treatment of ...
,
gentamicin
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis amo ...
,
kanamycin
Kanamycin A, often referred to simply as kanamycin, is an antibiotic used to treat severe bacterial infections and tuberculosis. It is not a first line treatment. It is used by mouth, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle. Kanamy ...
,
streptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, ''Burkholderia'' i ...
, etc.) used for the treatment of
drug-resistant tuberculosis
Management of tuberculosis refers to techniques and procedures utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB), or simply a treatment plan for TB.
The medical standard for active TB is a short course treatment involving a combination of isoniazid, rifa ...
and cystic fibrosis can cause respiratory disorders, deafness and kidney failure.
The potential crisis at hand is the result of a marked decrease in industry research and development.
Poor financial investment in antibiotic research has exacerbated the situation.
The pharmaceutical industry has little incentive to invest in antibiotics because of the high risk and because the potential financial returns are less likely to cover the cost of
development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
than for other pharmaceuticals. In 2011,
Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
, one of the last major pharmaceutical companies developing new antibiotics, shut down its primary research effort, citing poor shareholder returns relative to drugs for chronic illnesses.
However, small and medium-sized pharmaceutical companies are still active in antibiotic drug research. In particular, apart from classical synthetic chemistry methodologies, researchers have developed a combinatorial synthetic biology platform on single cell level in a
high-throughput screening
High-throughput screening (HTS) is a method for scientific discovery especially used in drug discovery and relevant to the fields of biology, materials science and chemistry. Using robotics, data processing/control software, liquid handling device ...
manner to diversify novel
lanthipeptides.
In the 5–10 years since 2010, there has been a significant change in the ways new antimicrobial agents are discovered and developed – principally via the formation of public-private funding initiatives. These include
CARB-X
Combating Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) is a global nonprofit partnership focused on supporting the development of new antibacterial products. Its mission is to strengthen the pipeline of vaccines, rapid diagn ...
, which focuses on nonclinical and early phase development of novel antibiotics, vaccines, rapid diagnostics; Novel Gram Negative Antibiotic (GNA-NOW), which is part of the EU's
Innovative Medicines Initiative; and Replenishing and Enabling the Pipeline for Anti-infective Resistance Impact Fund (REPAIR). Later stage clinical development is supported by the AMR Action Fund, which in turn is supported by multiple investors with the aim of developing 2–4 new antimicrobial agents by 2030. The delivery of these trials is facilitated by national and international networks supported by the Clinical Research Network of the
National Institute for Health and Care Research
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) is the British government's major funder of clinical, public health, social care and translational research. With a budget of over £1.2 billion in 2020–21, its mission is to "impr ...
(NIHR), European Clinical Research Alliance in Infectious Diseases (ECRAID) and the recently formed ADVANCE-ID, which is a clinical research network based in Asia. The
Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership (GARDP) is generating new evidence for global AMR threats such as neonatal sepsis, treatment of serious bacterial infections and sexually transmitted infections as well as addressing global access to new and strategically important antibacterial drugs.
The discovery and development of new antimicrobial agents has been facilitated by regulatory advances, which have been principally led by the
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of pharmaceutical products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products ...
(EMA) and the
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA). These processes are increasingly aligned although important differences remain and drug developers must prepare separate documents. New development pathways have been developed to help with the approval of new antimicrobial agents that address unmet needs such as the Limited Population Pathway for Antibacterial and Antifungal Drugs (LPAD). These new pathways are required because of difficulties in conducting large definitive
phase III clinical trials
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases ...
in a timely way.
Some of the economic impediments to the development of new antimicrobial agents have been addressed by innovative reimbursement schemes that delink payment of antimicrobials from volume-based sales. In the UK, a market entry reward scheme has been pioneered by the
National Institute for Clinical Excellence
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
(NICE) whereby an annual subscription fee is paid for use of strategically valuable antimicrobial agents –
cefiderocol
Cefiderocol, sold under the brand name Fetroja (by Shionogi) among others, is an antibiotic used to treat complicated urinary tract infections when no other options are available. It is indicated for the treatment of multi-drug-resistant Gram ...
and
ceftazidime-aviabactam are the first agents to be used in this manner and the scheme is potential blueprint for comparable programs in other countries.
The available classes of antifungal drugs are still limited but as of 2021 novel classes of antifungals are being developed and are undergoing various stages of clinical trials to assess performance.
Scientists have started using advanced computational approaches with supercomputers for the development of new antibiotic derivatives to deal with antimicrobial resistance.
Biomaterials
Using antibiotic-free alternatives in bone infection treatment may help decrease the use of antibiotics and thus antimicrobial resistance.
The bone regeneration material
bioactive glass S53P4 has shown to effectively inhibit the bacterial growth of up to 50 clinically relevant bacteria including MRSA and MRSE.
Nanomaterials
During the last decades,
copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
and
silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
nanomaterials
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science ...
have demonstrated appealing features for the development of a new family of antimicrobial agents. Nanoparticles (1–100 nm) show unique properties and promise as antimicrobial agents against resistant bacteria.
Silver (AgNPs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are extensively studied, disrupting bacterial cell membranes and interfering with protein synthesis. Zinc oxide (ZnO NPs), copper (CuNPs), and silica (SiNPs) nanoparticles also exhibit antimicrobial properties. However, high synthesis costs, potential toxicity, and instability pose challenges. To overcome these, biological synthesis methods and combination therapies with other antimicrobials are explored. Enhanced biocompatibility and targeting are also under investigation to improve efficacy.
Rediscovery of ancient treatments
Similar to the situation in malaria therapy, where successful treatments based on ancient recipes have been found, there has already been some success in finding and testing ancient drugs and other treatments that are effective against AMR bacteria.
Computational community surveillance
One of the key tools identified by the WHO and others for the fight against rising antimicrobial resistance is improved surveillance of the spread and movement of AMR genes through different communities and regions. Recent advances in high-throughput
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
as a result of the
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a ...
have resulted in the ability to determine the individual microbial genes in a sample.
Along with the availability of databases of known antimicrobial resistance genes, such as the Comprehensive Antimicrobial Resistance Database (CARD) and
ResFinder, this allows the identification of all the antimicrobial resistance genes within the sample – the so-called "
resistome". In doing so, a profile of these genes within a community or environment can be determined, providing insights into how antimicrobial resistance is spreading through a population and allowing for the identification of resistance that is of concern.
Phage therapy
Phage therapy
Phage therapy, viral phage therapy, or phagotherapy is the therapeutic use of bacteriophages for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. This therapeutic approach emerged at the beginning of the 20th century but was progressively r ...
is the
therapeutic
A therapy or medical treatment is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. Both words, ''treatment'' and ''therapy'', are often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx.
As a rule, each therapy has indications an ...
use of
bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that Capsid, encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structu ...
s to treat
pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and many are beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of t ...
s.
Phage therapy has many potential applications in human medicine as well as dentistry, veterinary science, and agriculture.
Phage therapy relies on the use of naturally occurring bacteriophages to infect and lyse bacteria at the site of infection in a host. Due to current advances in genetics and biotechnology these bacteriophages can possibly be manufactured to treat specific infections. Phages can be bioengineered to target multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, and their use involves the added benefit of preventing the elimination of beneficial bacteria in the human body.
Phages destroy bacterial cell walls and membrane through the use of lytic proteins which kill bacteria by making many holes from the inside out.
Bacteriophages can even possess the ability to digest the
biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
that many bacteria develop that protect them from antibiotics in order to effectively infect and kill bacteria. Bioengineering can play a role in creating successful bacteriophages.
Understanding the mutual interactions and evolutions of bacterial and phage populations in the environment of a human or animal body is essential for rational phage therapy.
Bacteriophagics are used against antibiotic resistant bacteria in
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
(
George Eliava Institute) and in one institute in
Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
, Poland. Bacteriophage cocktails are common drugs sold over the counter in pharmacies in eastern countries.
In Belgium, four patients with severe musculoskeletal infections received bacteriophage therapy with concomitant antibiotics. After a single course of phage therapy, no recurrence of infection occurred and no severe side-effects related to the therapy were detected.
See also
References
Books
*
*
*
Journals
*
*
*
*
*
*
* 16-minute film about a post-antibiotic world. Review:
Further reading
*
*
External links
*
WHO fact sheet on antimicrobial resistanceAnimation of Antibiotic Resistance
Bracing for Superbugs: Strengthening environmental action in the One Health response to antimicrobial resistanceUNEP
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
, 2023.
CDC Guideline "Management of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings, 2006"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antibiotic Resistance
Evolutionary biology
Health disasters
Pharmaceuticals policy
Veterinary medicine
Global issues
 Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when  Antimicrobial resistance means a microorganism's resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism. A person cannot become resistant to antibiotics. Resistance is a property of the microbe, not a person or other organism infected by a microbe. All types of microbes can develop drug resistance. Thus, there are
Antimicrobial resistance means a microorganism's resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism. A person cannot become resistant to antibiotics. Resistance is a property of the microbe, not a person or other organism infected by a microbe. All types of microbes can develop drug resistance. Thus, there are  AMR is a naturally occurring process. Antimicrobial resistance can evolve naturally due to continued exposure to antimicrobials.
AMR is a naturally occurring process. Antimicrobial resistance can evolve naturally due to continued exposure to antimicrobials.  The antimicrobial resistance crisis also extends to the food industry, specifically with food producing animals. With an ever-increasing human population, there is constant pressure to intensify productivity in many agricultural sectors, including the production of meat as a source of protein. Antibiotics are fed to livestock to act as growth supplements, and a preventive measure to decrease the likelihood of infections.
Farmers typically use antibiotics in animal feed to improve growth rates and prevent infections. However, this is illogical as antibiotics are used to treat infections and not prevent infections. 80% of antibiotic use in the U.S. is for agricultural purposes and about 70% of these are medically important. Overusing antibiotics gives the bacteria time to adapt leaving higher doses or even stronger antibiotics needed to combat the infection. Though antibiotics for growth promotion were banned throughout the EU in 2006, 40 countries worldwide still use antibiotics to promote growth.
This can result in the transfer of resistant bacterial strains into the food that humans eat, causing potentially fatal transfer of disease. While the practice of using antibiotics as growth promoters does result in better yields and
The antimicrobial resistance crisis also extends to the food industry, specifically with food producing animals. With an ever-increasing human population, there is constant pressure to intensify productivity in many agricultural sectors, including the production of meat as a source of protein. Antibiotics are fed to livestock to act as growth supplements, and a preventive measure to decrease the likelihood of infections.
Farmers typically use antibiotics in animal feed to improve growth rates and prevent infections. However, this is illogical as antibiotics are used to treat infections and not prevent infections. 80% of antibiotic use in the U.S. is for agricultural purposes and about 70% of these are medically important. Overusing antibiotics gives the bacteria time to adapt leaving higher doses or even stronger antibiotics needed to combat the infection. Though antibiotics for growth promotion were banned throughout the EU in 2006, 40 countries worldwide still use antibiotics to promote growth.
This can result in the transfer of resistant bacterial strains into the food that humans eat, causing potentially fatal transfer of disease. While the practice of using antibiotics as growth promoters does result in better yields and 
 There have been increasing public calls for global collective action to address the threat, including a proposal for an international treaty on antimicrobial resistance. Further detail and attention is still needed in order to recognize and measure trends in resistance on the international level; the idea of a global tracking system has been suggested but implementation has yet to occur. A system of this nature would provide insight to areas of high resistance as well as information necessary for evaluating programs, introducing interventions and other changes made to fight or reverse antibiotic resistance.
There have been increasing public calls for global collective action to address the threat, including a proposal for an international treaty on antimicrobial resistance. Further detail and attention is still needed in order to recognize and measure trends in resistance on the international level; the idea of a global tracking system has been suggested but implementation has yet to occur. A system of this nature would provide insight to areas of high resistance as well as information necessary for evaluating programs, introducing interventions and other changes made to fight or reverse antibiotic resistance.
 There are several different types of germs that have developed a resistance over time.
The six pathogens causing most deaths associated with resistance are ''Escherichia coli'', ''Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii'', and ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. They were responsible for 929,000 deaths attributable to resistance and 3.57 million deaths associated with resistance in 2019.
Penicillinase-producing ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' developed a resistance to penicillin in 1976. Another example is Azithromycin-resistant ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', which developed a resistance to azithromycin in 2011.
In
There are several different types of germs that have developed a resistance over time.
The six pathogens causing most deaths associated with resistance are ''Escherichia coli'', ''Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii'', and ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. They were responsible for 929,000 deaths attributable to resistance and 3.57 million deaths associated with resistance in 2019.
Penicillinase-producing ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' developed a resistance to penicillin in 1976. Another example is Azithromycin-resistant ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', which developed a resistance to azithromycin in 2011.
In 
 In 2022, genomic epidemiologists reported results from a
In 2022, genomic epidemiologists reported results from a  Distinguishing infections requiring antibiotics from self-limiting ones is clinically challenging. In order to guide appropriate use of antibiotics and prevent the evolution and spread of antimicrobial resistance, diagnostic tests that provide clinicians with timely, actionable results are needed.
Acute febrile illness is a common reason for seeking medical care worldwide and a major cause of morbidity and mortality. In areas with decreasing malaria incidence, many febrile patients are inappropriately treated for malaria, and in the absence of a simple diagnostic test to identify alternative causes of fever, clinicians presume that a non-malarial febrile illness is most likely a bacterial infection, leading to inappropriate use of antibiotics. Multiple studies have shown that the use of malaria rapid diagnostic tests without reliable tools to distinguish other fever causes has resulted in increased antibiotic use.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) can facilitate a
Distinguishing infections requiring antibiotics from self-limiting ones is clinically challenging. In order to guide appropriate use of antibiotics and prevent the evolution and spread of antimicrobial resistance, diagnostic tests that provide clinicians with timely, actionable results are needed.
Acute febrile illness is a common reason for seeking medical care worldwide and a major cause of morbidity and mortality. In areas with decreasing malaria incidence, many febrile patients are inappropriately treated for malaria, and in the absence of a simple diagnostic test to identify alternative causes of fever, clinicians presume that a non-malarial febrile illness is most likely a bacterial infection, leading to inappropriate use of antibiotics. Multiple studies have shown that the use of malaria rapid diagnostic tests without reliable tools to distinguish other fever causes has resulted in increased antibiotic use.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) can facilitate a