ALS Gold Medal–winning Works on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—
 It is still not fully understood why neurons die in ALS, but this
It is still not fully understood why neurons die in ALS, but this
 No single test can provide a definite diagnosis of ALS. Instead, the diagnosis of ALS is primarily made based on a physician's clinical assessment after ruling out other diseases. Physicians often obtain the person's full
No single test can provide a definite diagnosis of ALS. Instead, the diagnosis of ALS is primarily made based on a physician's clinical assessment after ruling out other diseases. Physicians often obtain the person's full 
 Physical therapy can promote functional independence through aerobic, range of motion, and stretching exercises. Occupational therapy can assist with activities of daily living through adaptive equipment. Speech therapy can assist people with ALS who have difficulty speaking. Preventing weight loss and malnutrition in people with ALS improves both survival and quality of life. Initially, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) can be managed by dietary changes and swallowing techniques. A
Physical therapy can promote functional independence through aerobic, range of motion, and stretching exercises. Occupational therapy can assist with activities of daily living through adaptive equipment. Speech therapy can assist people with ALS who have difficulty speaking. Preventing weight loss and malnutrition in people with ALS improves both survival and quality of life. Initially, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) can be managed by dietary changes and swallowing techniques. A



 Preventing
Preventing
 Descriptions of the disease date back to at least 1824 by
Descriptions of the disease date back to at least 1824 by
ALS Association Official Website
ALS Therapy Development Institute
International Alliance of ALS/MND Associations
International Symposium on ALS/MND
* {{Authority control Motor neuron diseases Rare diseases Unsolved problems in neuroscience Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system Cytoskeletal defects Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Neuromuscular disorders Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Idiopathic diseases Diseases named after patients
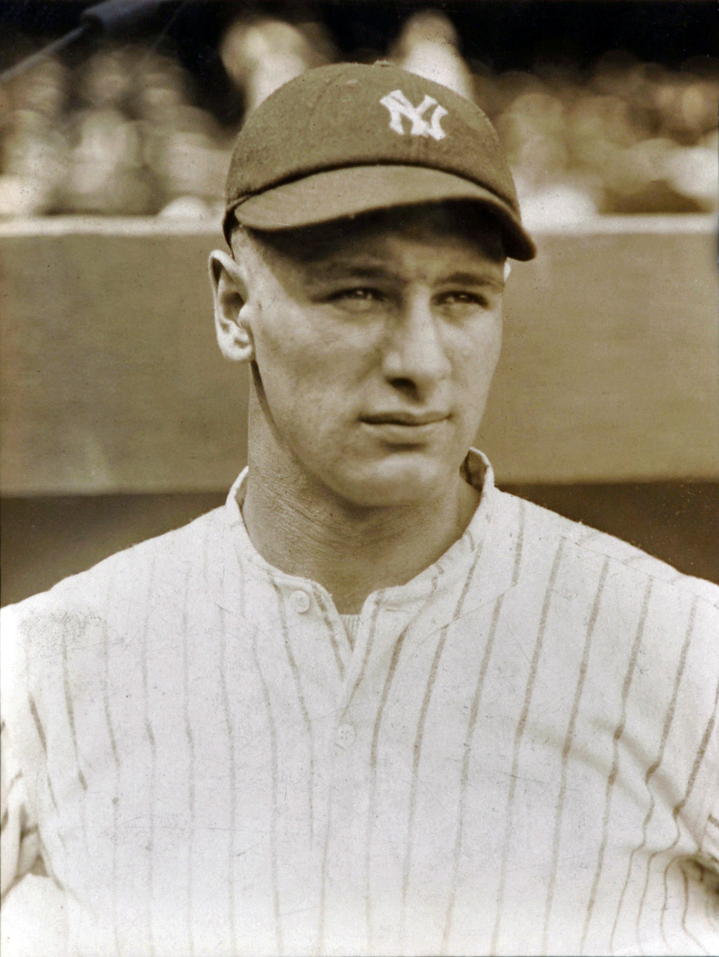
Lou Gehrig
Henry Louis Gehrig ( ; June 19, 1903June 2, 1941), also known as Heinrich Ludwig Gehrig, was an American professional baseball first baseman who played 17 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the New York Yankees (1923–1939). Gehrig was ...
's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly o ...
s that normally control voluntary muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bo ...
contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a ...
, twitches, weakness
Weakness is a symptom of many different medical conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, ...
, and wasting
In medicine, wasting, also known as wasting syndrome, refers to the process by which a debilitating disease causes muscle and fat tissue to "waste" away. Wasting is sometimes referred to as "acute malnutrition" because it is believed that epis ...
. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal lobe, frontal and tempor ...
, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, and delibe ...
and behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (begins with weakness in the arms or legs) or ''bulbar-onset'' (begins with difficulty in speaking
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, su ...
or swallowing
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific and medical contexts, is a physical process of an animal's digestive tract (e.g. that of a human body) that allows for an ingested substance (typically food) to pass from the mou ...
).
Most cases of ALS (about 90–95%) have no known cause, and are known as ''sporadic ALS''. However, both genetic and environmental factors
An environmental factor, ecological factor or eco factor is any factor, abiotic or biotic, that influences living organisms. Abiotic factors include ambient temperature, amount of sunlight, air, soil, water and pH of the water soil in which an ...
are believed to be involved. The remaining 5–10% of cases have a genetic cause, often linked to a family history of the disease, and these are known as ''familial ALS'' (hereditary). About half of these genetic cases are due to disease-causing variants in one of four specific gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s. The diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
is based on a person's signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
, with testing conducted to rule out other potential causes.
There is no known cure for ALS. The goal of treatment is to slow the disease progression, and improve symptoms. FDA-approved treatments that slow the progression of ALS include riluzole
Riluzole is a medication used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other motor neuron diseases. Riluzole delays the onset of ventilator-dependence or tracheostomy in some people and may increase survival by two to three months. Ril ...
and edaravone. Non-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alte ...
may result in both improved quality and length of life. Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
can prolong survival but does not stop disease progression. A feeding tube
A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to people who cannot obtain nutrition by mouth, are unable to swallow safely, or need nutritional supplementation. The state of being fed by a feeding tube is called gavage, enteral f ...
may help maintain weight and nutrition. Death is usually caused by respiratory failure. The disease can affect people of any age, but usually starts around the age of 60. The average survival from onset to death is two to four years, though this can vary, and about 10% of those affected survive longer than ten years.
Descriptions of the disease date back to at least 1824 by Charles Bell
Sir Charles Bell (12 November 177428 April 1842) was a Scottish surgeon, anatomist, physiologist, neurologist, artist, and philosophical theologian. He is noted for discovering the difference between sensory nerves and motor nerves in the ...
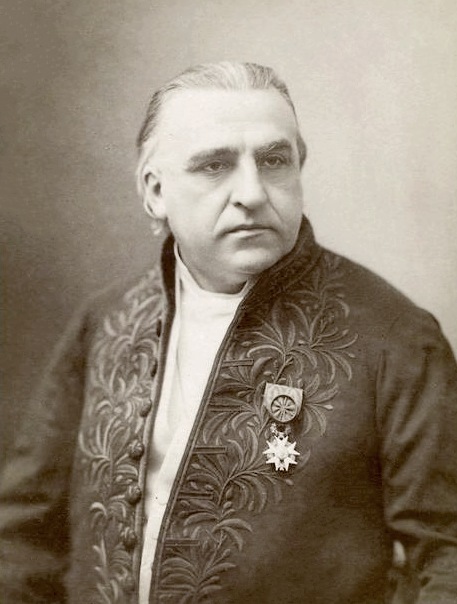
. In 1869, the connection between the symptoms and the underlying neurological problems was first described by French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot (; 29 November 1825 – 16 August 1893) was a French neurology, neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on groundbreaking work about hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise A ...
, who in 1874 began using the term ''amyotrophic lateral sclerosis''.
Classification
ALS is amotor neuron disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and low ...
, which is a group of neurological disorder
Neurological disorders represent a complex array of medical conditions that fundamentally disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerve networks, presenting unique diagnosis, treatment, and ...
s that selectively affect motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly o ...
s, the cells that control voluntary muscles of the body. Other motor neuron diseases include primary lateral sclerosis (PLS), progressive muscular atrophy (PMA), progressive bulbar palsy, pseudobulbar palsy
Pseudobulbar palsy is a medical condition characterized by the inability to control facial movements (such as chewing and speaking) and caused by a variety of neurological disorders. Patients experience difficulty chewing and swallowing, have i ...
, and monomelic amyotrophy
Hirayama disease, also known as monomelic amyotrophy (MMA), is a rare motor neuron disease first described in 1959 in Japan. Its symptoms usually appear about two years after adolescent growth spurt and is significantly more common in males, with ...
(MMA).
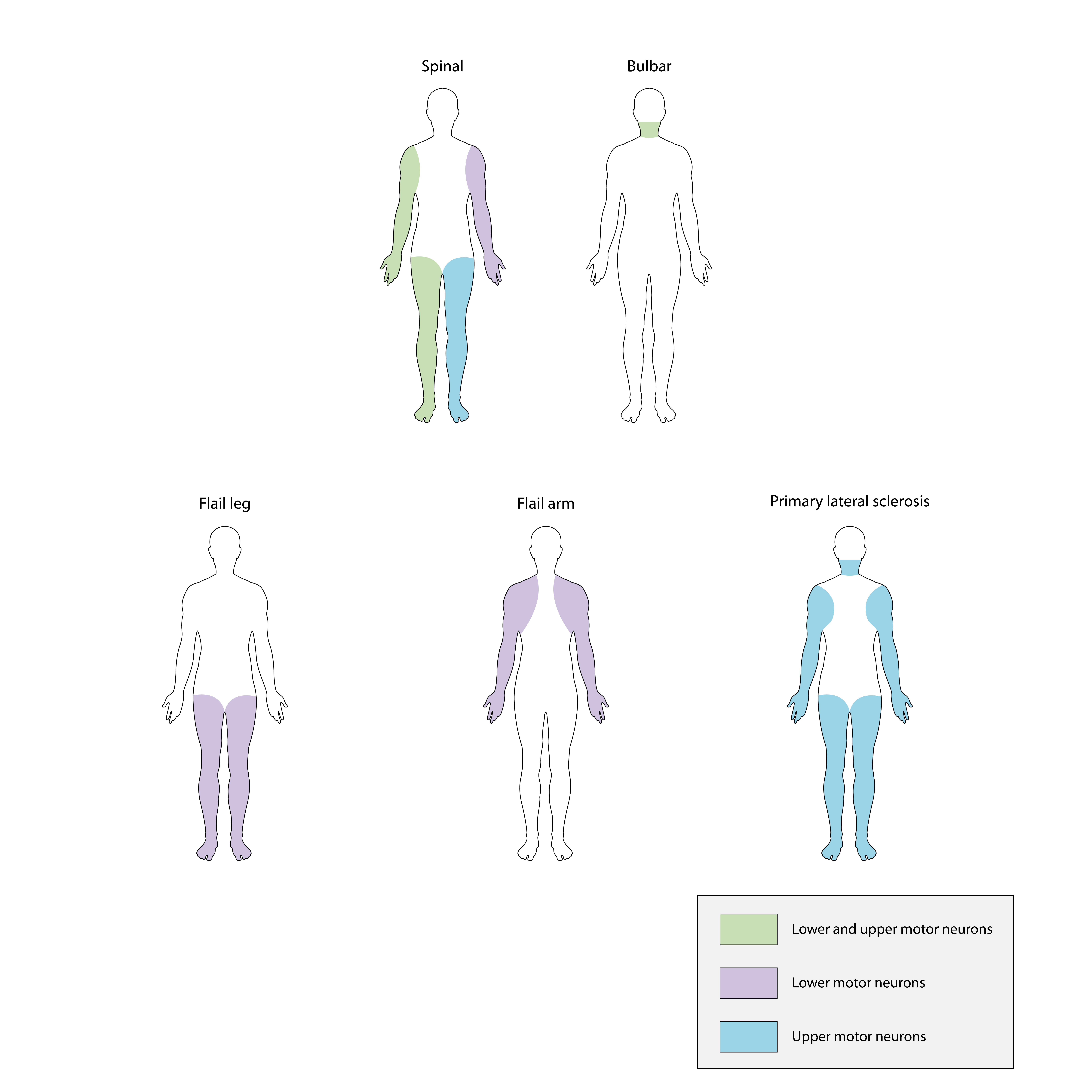
As a disease, ALS itself can be classified in a few different ways: by which part of the motor neurons are affected; by the parts of the body first affected; whether it is genetic; and by the age at which it started. Each individual diagnosed with the condition will sit at a unique place at the intersection of these complex and overlapping subtypes, which presents a challenge to diagnosis, understanding, and prognosis.
Subtypes of motor neuron disease
ALS can be classified by the types of motor neurons that are affected. To successfully control any voluntary muscle in the body, a signal must be sent from themotor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, motor control, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
in the brain down the upper motor neuron
Upper motor neurons (UMNs) is a term introduced by William Gowers in 1886. They are found in the cerebral cortex and brainstem and carry information down to activate interneurons and lower motor neurons, which in turn directly signal muscles ...
as it travels down the spinal cord. There, it connects via a synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending o ...
to the lower motor neuron
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots (spinal lower motor neurons) or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function (cranial nerve lower ...
which connects to the muscle itself. Damage to either the upper or lower motor neuron, as it makes its way from the brain to muscle, causes different types of symptoms. Damage to the upper motor neuron typically causes spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles. ...
including stiffness and increased tendon reflex
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension.
Tendons, like ligaments, are made o ...
es or clonus
Clonus is a set of involuntary and rhythmic muscular contractions and relaxations. Clonus is a sign of certain neurological conditions, particularly associated with upper motor neuron lesions involving descending motor pathways, and in many cas ...
, while damage to the lower motor neuron typically causes weakness
Weakness is a symptom of many different medical conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, ...
, muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakne ...
, and fasciculation
A fasciculation, or muscle twitch, is a spontaneous, involuntary muscle contraction and relaxation, involving fine muscle fibers. They are common, with as many as 70% of people experiencing them. They can be benign, or associated with more seriou ...
s.
Classical, or classic ALS, involves degeneration to both the upper motor neuron
Upper motor neurons (UMNs) is a term introduced by William Gowers in 1886. They are found in the cerebral cortex and brainstem and carry information down to activate interneurons and lower motor neurons, which in turn directly signal muscles ...
s in the brain and the lower motor neuron
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots (spinal lower motor neurons) or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function (cranial nerve lower ...
s in the spinal cord. Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) involves degeneration of only the upper motor neurons, and progressive muscular atrophy (PMA) involves only the lower motor neurons. There is debate over whether PLS and PMA are separate diseases or simply variants of ALS.
Classical ALS accounts for about 70% of all cases of ALS and can be subdivided into where symptoms first appear as these are usually focused to one region of the body at initial presentation before later spread. ''Limb-onset'' ALS (also known as spinal-onset) and ''bulbar-onset'' ALS. Limb-onset ALS begins with weakness in the hands, arms, feet, and/or legs and accounts for about two-thirds of all classical ALS cases. Bulbar-onset ALS begins with weakness in the muscles of speech, chewing, and swallowing and accounts for about 25% of classical ALS cases. A rarer type of classical ALS affecting around 3% of patients is respiratory-onset, in which the initial symptoms are difficulty breathing (dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
) upon exertion, at rest, or while lying flat (orthopnea
Orthopnea or orthopnoea is shortness of breath (dyspnea) that occurs when lying flat, causing the person to have to sleep propped up in bed or sitting in a chair. It is commonly seen as a late manifestation of heart failure, resulting from fluid ...
).
Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) is a subtype of the overall ALS category which accounts for about 5% of all cases and only affects the upper motor neurons in the arms, legs, and bulbar region. However, more than 75% of people with apparent PLS go on to later develop lower motor neuron signs within four years of symptom onset, meaning that a definitive diagnosis of PLS cannot be made until several years have passed. PLS has a better prognosis than classical ALS, as it progresses slower, results in less functional decline, does not affect the ability to breathe, and causes less severe weight loss than classical ALS.
Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA) is another subtype that accounts for about 5% of the overall ALS category and affects lower motor neurons in the arms, legs, and bulbar region. While PMA is associated with longer survival on average than classical ALS, it is still progressive over time, eventually leading to respiratory failure and death. As with PLS developing into classical ALS, PMA can also develop into classical ALS over time if the lower motor neuron involvement progresses to include upper motor neurons, in which case the diagnosis might be changed to classic ALS.
Rare isolated variants of ALS
Isolated variants of ALS have symptoms that are limited to a single region for at least a year; they progress more slowly than classical ALS and are associated with longer survival. These regional variants of ALS can only be considered as a diagnosis should the initial symptoms fail to spread to other spinal cord regions for an extended period of time (at least 12 months). Flail arm syndrome is characterized by lower motor neuron damage affecting the arm muscles, typically starting with the upper arms symmetrically and progressing downwards to the hands. Flail leg syndrome is characterized by lower motor neuron damage leading to asymmetrical weakness and wasting in the legs starting around the feet. Isolated bulbar palsy is characterized by upper or lower motor neuron damage in the bulbar region (in the absence of limb symptoms for at least 20 months), leading to gradual onset of difficulty with speech (dysarthria
Dysarthria is a speech sound disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor–speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes. It is a condition in which problems effectively occur with the ...
) and swallowing (dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
).

Age of onset
ALS can also be classified based on the age of onset. People with familial ALS have an age of onset about 5 years younger than those with apparently sporadic ALS. About 10% of all cases of ALS begin before age 45 ("young-onset" ALS), and about 1% of all cases begin before age 25 ("juvenile" ALS). People who develop young-onset ALS are more likely to be male, less likely to have bulbar onset of symptoms, and more likely to have a slower progression of the disease. Juvenile ALS is more likely to be genetic in origin than adult-onset ALS; the most common genes associated with juvenile ALS are '' FUS'', '' ALS2'', and '' SETX''. Although most people with juvenile ALS live longer than those with adult-onset ALS, some of them have specific mutations in '' FUS'' and ''SOD1
Superoxide dismutase u-Zn'' also known as superoxide dismutase 1 or hSod1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SOD1'' gene, located on chromosome 21. SOD1 is one of three human superoxide dismutases. It is implicated in apoptosis, fami ...
'' that are associated with a poor prognosis. Late onset (after age 65) is generally associated with a more rapid functional decline and shorter survival.
Signs and symptoms
The disorder causes muscle weakness,atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
, and muscle spasms
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder.
A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a musc ...
throughout the body due to the degeneration of the upper motor and lower motor neurons. Sensory nerves
A sensory nerve, or afferent nerve, is a nerve that contains exclusively afferent nerve fibers. Nerves containing also motor fibers are called mixed. Afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve carry sensory information toward the central nervous ...
and the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
are generally unaffected, meaning the majority of people with ALS maintain hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory sci ...
, sight
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual percept ...
, touch
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of bo ...
, smell, and taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste. Taste is the perception stimulated when a substance in the mouth biochemistry, reacts chemically with taste receptor cells l ...
.
Initial symptoms
The start of ALS may be so subtle that the symptoms are overlooked. The earliest symptoms of ALS are muscle weakness or muscle atrophy, typically on one side of the body. Other presenting symptoms include trouble swallowing or breathing, cramping, or stiffness of affected muscles; muscle weakness affecting an arm or a leg; or slurred and nasal speech. The parts of the body affected by early symptoms of ALS depend on which motor neurons in the body are damaged first. In limb-onset ALS, the first symptoms are in the arms or the legs. If the legs are affected first, people may experience awkwardness, tripping, or stumbling when walking or running; this is often marked by walking with a " dropped foot" that drags gently on the ground. If the arms are affected first, they may experience difficulty with tasks requiring manual dexterity, such as buttoning a shirt, writing, or turning a key in a lock. In bulbar-onset ALS, the first symptoms are difficulty speaking or swallowing. Speech may become slurred, nasal in character, or quieter. There may be difficulty with swallowing and loss of tongue mobility. A smaller proportion of people experience "respiratory-onset" ALS, where theintercostal muscle
The intercostal muscles comprise many different groups of muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle ...
s that support breathing are affected first.
Over time, people experience increasing difficulty moving, swallowing (dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
), and speaking or forming words (dysarthria
Dysarthria is a speech sound disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor–speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes. It is a condition in which problems effectively occur with the ...
). Symptoms of upper motor neuron involvement include tight and stiff muscles (spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles. ...
) and exaggerated reflexes (hyperreflexia
Hyperreflexia is overactive or overresponsive bodily reflexes. Examples of this include twitching and spastic tendencies, which indicate disease of the upper motor neurons and the lessening or loss of control ordinarily exerted by higher brain ...
), including an overactive gag reflex. While the disease does not cause pain directly, pain is a symptom experienced by most people with ALS caused by reduced mobility. Symptoms of lower motor neuron degeneration include muscle weakness and atrophy, muscle cramps, and fleeting twitches of muscles that can be seen under the skin (fasciculation
A fasciculation, or muscle twitch, is a spontaneous, involuntary muscle contraction and relaxation, involving fine muscle fibers. They are common, with as many as 70% of people experiencing them. They can be benign, or associated with more seriou ...
s).
Progression
Although the initial site of symptoms and subsequent rate of disability progression vary from person to person, the initially affected body region is usually the most affected over time, and symptoms usually spread to a neighbouring body region. For example, symptoms starting in one arm usually spread next to either the opposite arm or to the leg on the same side. Bulbar-onset patients most typically get their next symptoms in their arms rather than legs, arm-onset patients typically spread to the legs before the bulbar region, and leg-onset patients typically spread to the arms rather than the bulbar region. Over time, regardless of where symptoms began, most people eventually lose the ability to walk or use their hands and arms independently. Less consistently, they may lose the ability to speak and to swallow food. It is the eventual development of weakness of the respiratory muscles, with the loss of ability to cough and to breathe without support, that is ultimately life-shortening in ALS. The rate of progression can be measured using the ALS Functional Rating Scale - Revised (ALSFRS-R), a 12-item instrument survey administered as a clinical interview or self-reported questionnaire that produces a score between 48 (normal function) and 0 (severe disability). The ALSFRS-R is the most frequently used outcome measure in clinical trials and is used by doctors to track disease progression. Though the degree of variability is high and a small percentage of people have a much slower progression, on average people with ALS lose about 1 ALSFRS-R point per month. Brief periods of stabilization ("plateaus") and even small reversals in ALSFRS-R score are not uncommon, due to the fact the tool is subjective, can be affected by medication, and different forms of compensation for changes in function. However, it is rare (<1%) for these improvements to be large (i.e. greater than 4 ALSFRS-R points) or sustained (i.e. greater than 12 months). A survey-based study among clinicians showed that they rated a 20% change in the slope of the ALSFRS-R as being clinically meaningful, which is the most common threshold used to determine whether a new treatment is working in clinical trials.Late-stage disease management
Difficulties with chewing and swallowing make eating very difficult (dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
) and increase the risk of choking or of aspirating food into the lungs. In later stages of the disorder, aspiration pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of lung infection that is due to a relatively large amount of material from the stomach or mouth entering the lungs. Signs and symptoms often include fever and cough of relatively rapid onset. Complications may incl ...
can develop, and maintaining a healthy weight can become a significant problem that may require the insertion of a feeding tube. As the diaphragm and intercostal muscle
The intercostal muscles comprise many different groups of muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle ...
s of the rib cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great ve ...
that support breathing weaken, measures of lung function
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system ...
such as vital capacity
Vital capacity (VC) is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume. It is approximately equal to Force ...
and inspiratory pressure diminish. In respiratory-onset ALS, this may occur before significant limb weakness is apparent. Individuals affected by the disorder may ultimately lose the ability to initiate and control all voluntary movement, known as locked-in syndrome
Locked-in syndrome (LIS), also known as pseudocoma, is a condition in which a patient is aware but cannot move or communicate verbally due to complete paralysis of nearly all voluntary muscles in their body except for vertical eye movements and ...
. Bladder and bowel function are usually spared, meaning urinary
The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressu ...
and fecal incontinence
Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms, encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents—including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. FI is a sign or a symptom ...
are uncommon, although trouble getting to a toilet can lead to difficulties. The extraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior ...
responsible for eye movement are usually spared, meaning the use of eye tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research ...
technology to support augmentative communication is often feasible, albeit slow, and needs may change over time. Despite these challenges, many people in an advanced state of disease report satisfactory wellbeing and quality of life.
Prognosis, staging, and survival
Although respiratory support usingnon-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alte ...
can ease problems with breathing and prolong survival, it does not affect the progression rate of ALS. Most people with ALS die between two and four years after the diagnosis. Around 50% of people with ALS die within 30 months of their symptoms beginning, about 20% live between five and ten years, and about 10% survive for 10 years or longer.
The most common cause of death among people with ALS is respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a r ...
, often accelerated by pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
. Most ALS patients die at home after a period of worsening difficulty breathing, a decline in their nutritional status, or a rapid worsening of symptoms. Sudden death or acute respiratory distress are uncommon. Access to palliative care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
is recommended from an early stage to explore options, ensure psychosocial support for the patient and caregivers, and to discuss advance healthcare directive
An advance healthcare directive, also known as living will, personal directive, advance directive, medical directive or advance decision, is a document in which a person specifies what actions should be taken for their health if they are no longe ...
s.
As with cancer staging, ALS has staging systems numbered between 1 and 4 that are used for research purposes in clinical trials. Two very similar staging systems emerged around a similar time, the King's staging system and Milano-Torino (MiToS) functional staging.
Providing individual patients with a precise prognosis is not currently possible, though research is underway to provide statistical models on the basis of prognostic factors including age at onset, progression rate, site of onset, and presence of frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal lobe, frontal and tempor ...
. Those with a bulbar onset have a worse prognosis than limb-onset ALS; a population-based study found that bulbar-onset ALS patients had a median survival of 2.0 years and a 10-year survival rate of 3%, while limb-onset ALS patients had a median survival of 2.6 years and a 10-year survival rate of 13%. Those with respiratory-onset ALS had a shorter median survival of 1.4 years and 0% survival at 10 years. While astrophysicist Stephen Hawking
Stephen William Hawking (8January 194214March 2018) was an English theoretical physics, theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author who was director of research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at the University of Cambridge. Between ...
lived for 55 more years following his diagnosis, his was an unusual case.
Cognitive, emotional, and behavioral symptoms
Cognitive impairment
Cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process or different areas of cognition. Cognition, also known as cognitive function, refers to the mental processes of how a person ...
or behavioral dysfunction is present in 30–50% of individuals with ALS, and can appear more frequently in later stages of the disease. Language dysfunction, executive dysfunction
In psychology and neuroscience, executive dysfunction, or executive function deficit, is a disruption to the efficacy of the executive functions, which is a group of cognitive processes that regulate, control, and manage other cognitive processe ...
, and troubles with social cognition and verbal memory
Verbal memory is a term used in cognitive psychology which refers to memory of words and other abstractions involving language. A variety of tests is used to test verbal memory, including learning lists or pairs of words, or recalling a story after ...
are the most commonly reported cognitive symptoms in ALS. Cognitive impairment is found more frequently in patients with C9orf72 gene repeat expansions, bulbar onset, bulbar symptoms, family history
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kins ...
of ALS, and/or a predominantly upper motor neuron phenotype.
Emotional lability
In medicine and psychology, emotional lability is a Medical sign, sign or symptom typified by exaggerated changes in mood or affect (psychology), affect in quick succession. Sometimes the emotions expressed outwardly are very different from how th ...
is a symptom in which patients cry, smile, yawn, or laugh, either in the absence of emotional stimuli, or when they are feeling the opposite emotion to that being expressed; it is experienced by about half of ALS patients and is more common in those with bulbar-onset ALS. While relatively benign relative to other symptoms, it can cause increased stigma and social isolation as people around the patient struggle to react appropriately to what can be frequent and inappropriate outbursts in public.
In addition to mild changes in cognition that may only emerge during neuropsychological testing, around 10–15% of individuals have signs of frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal lobe, frontal and tempor ...
(FTD). Repeating phrases or gestures, apathy, and loss of inhibition are the most frequently reported behavioral features of ALS. ALS and FTD are now considered to be part of a common disease spectrum (ALS–FTD) because of genetic, clinical, and pathological similarities. Genetically, repeat expansions in the C9orf72 gene account for about 40% of genetic ALS and 25% of genetic FTD.
Cognitive and behavioral issues are associated with a poorer prognosis as they may reduce adherence to medical advice, and deficits in empathy and social cognition which may increase caregiver burden.
Cause
It is not known what causes sporadic ALS, hence it is described as anidiopathic disease
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin.
For some medical conditions, one or more causes are somewhat understood, but in a certain percentage of people with the condition, the cause ...
. Though its exact cause is unknown, genetic and environmental factors are thought to be of roughly equal importance. The genetic factors are better understood than the environmental factors; no specific environmental factor has been definitively shown to cause ALS. A multi-step liability threshold model
In mathematical or statistical modeling a threshold model is any model where a threshold value, or set of threshold values, is used to distinguish ranges of values where the behaviour predicted by the model varies in some important way. A particu ...
for ALS proposes that cellular damage accumulates over time due to genetic factors present at birth and exposure to environmental risks throughout life. ALS can strike at any age, but its likelihood increases with age. Most people who develop ALS are between the ages of 40 and 70, with an average age of 55 at the time of diagnosis. ALS is 20% more common in men than women, but this difference in sex distribution is no longer present in patients with onset after age 70.
Genetics and genetic testing
While they appear identical clinically and pathologically, ALS can be classified as being either familial or sporadic, depending on whether there is a known family history of the disease and/or whether an ALS-associated genetic mutation has been identified via genetic testing. Familial ALS is thought to account for 10–15% of cases overall and can include monogenic, oligogenic, andpolygenic
A polygene is a member of a group of non- epistatic genes that interact additively to influence a phenotypic trait, thus contributing to multiple-gene inheritance (polygenic inheritance, multigenic inheritance, quantitative inheritance), a type ...
modes of inheritance.
There is considerable variation among clinicians on how to approach genetic testing in ALS, and only about half discuss the possibility of genetic inheritance with their patients, particularly if there is no discernible family history of the disease. In the past, genetic counseling and testing was only offered to those with obviously familial ALS. But it is increasingly recognized that cases of sporadic ALS may also be due to disease-causing de novo mutation
A de novo mutation (DNM) is any mutation or alteration in the genome of an individual organism (human, animal, plant, microbe, etc.) that was not inherited from its parents. This type of mutation spontaneously occurs during the process of DNA repl ...
s in ''SOD1
Superoxide dismutase u-Zn'' also known as superoxide dismutase 1 or hSod1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SOD1'' gene, located on chromosome 21. SOD1 is one of three human superoxide dismutases. It is implicated in apoptosis, fami ...
'', or ''C9orf72
C9orf72 (chromosome 9 open reading frame 72) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the gene ''C9orf72''.
The human ''C9orf72'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 9 open reading frame 72, from base pair 27,546,546 to base pa ...
'', an incomplete family history, or incomplete penetrance
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant (or allele) of a gene (genotype) that also expresses an associated trait (phenotype). In medical genetics, the penetrance of a disease-causing mutation is the pr ...
, meaning that a patient's ancestors carried the gene but did not express the disease in their lifetimes. The lack of positive family history may be caused by lack of historical records, having a smaller family, older generations dying earlier of causes other than ALS, genetic non-paternity, and uncertainty over whether certain neuropsychiatric conditions (e.g. frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal lobe, frontal and tempor ...
, other forms of dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, suicide, psychosis, schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
) should be considered significant when determining a family history. There have been calls in the research community to routinely counsel and test all diagnosed ALS patients for familial ALS, particularly as there is now a licensed gene therapy ( tofersen) specifically targeted to carriers of SOD-1 ALS. A shortage of genetic counselors and limited clinical capacity to see such at-risk individuals makes this challenging in practice, as does the unequal access to genetic testing around the world.
More than 40 genes have been associated with ALS, of which four account for nearly half of familial cases, and around 5% of sporadic cases: ''C9orf72
C9orf72 (chromosome 9 open reading frame 72) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the gene ''C9orf72''.
The human ''C9orf72'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 9 open reading frame 72, from base pair 27,546,546 to base pa ...
'' (40% of familial cases, 7% sporadic), ''SOD1
Superoxide dismutase u-Zn'' also known as superoxide dismutase 1 or hSod1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SOD1'' gene, located on chromosome 21. SOD1 is one of three human superoxide dismutases. It is implicated in apoptosis, fami ...
'' (12% of familial cases, 1–2% sporadic), '' FUS'' (4% of familial cases, 1% sporadic), and ''TARDBP
Transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa (TAR DNA-binding protein 43 or TDP-43) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TARDBP'' gene.
Structure
TDP-43 is 414 amino acid residues long. It consists of four domains: an N-term ...
'' (4% of familial cases, 1% sporadic), with the remaining genes mostly accounting for fewer than 1% of either familial or sporadic cases. ALS genes identified to date explain the cause of about 70% of familial ALS and about 15% of sporadic ALS. Overall, first-degree relatives of an individual with ALS have a ~1% risk of developing ALS themselves.
Environmental and other factors
The multi-step hypothesis suggests the disease is caused by some interaction between an individual's genetic risk factors and their cumulative lifetime of exposures to environmental factors, termed theirexposome
The exposome is a concept used to describe environmental exposures that an individual encounters throughout life, and how these exposures impact biology and health. It encompasses both external and internal factors, including chemical, physical ...
. The most consistent lifetime exposures associated with developing ALS (other than genetic mutations) include heavy metals (e.g. lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
and mercury), chemicals (e.g. pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s and solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s), electric shock
An electrical injury (electric injury) or electrical shock (electric shock) is damage sustained to the skin or internal organs on direct contact with an electric current.
The injury depends on the Current density, density of the current, tissu ...
, physical injury
Injury is physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether in humans, in other animals, or in plants.
Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanically with penetration by sharp objects such as teeth or with ...
(including head injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
), and smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
(in men more than women). Overall these effects are small, with each exposure in isolation only increasing the likelihood of a very rare condition by a small amount. For instance, an individual's lifetime risk of developing ALS might go from "1 in 400" without exposure to between "1 in 300" and "1 in 200" if they were exposed to heavy metals. Some industries are heavily dependent upon the use or exposure to these environmental factors, increasing employees' susceptibility. Agricultural tasks can be intertwined with as many as 5 such risk factors excluding workers' smoking preferences.
A range of other factors have weaker evidence supporting them and include participation in professional sports
In professional sports, as opposed to amateur sports, participants receive payment for their performance. Professionalism in sport has come to the fore through a combination of developments. Mass media and increased leisure have brought larger a ...
, having a lower body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
, lower educational attainment
Educational attainment is a term commonly used by statisticians to refer to the highest degree of education an individual has completed as defined by the US Census Bureau Glossary.
See also
*Academic achievement
*Academic degree
*Bachelor's degree ...
, manual occupations, military service, exposure to Beta-N-methylamino-L-alanin (BMAA), and viral infections.
Although some personality traits, such as openness
Openness is an overarching concept that is characterized by an emphasis on transparency and collaboration. That is, openness refers to "accessibility of knowledge, technology and other resources; the transparency of action; the permeability of or ...
, agreeableness
Agreeableness is the trait theory, personality trait of being kind, Sympathy, sympathetic, cooperative, warm, honest, straightforward, and considerate. In personality psychology, agreeableness is one of the Big Five personality traits, five major ...
and conscientiousness
Conscientiousness is the personality trait of being responsible, :wikt:careful, careful, or :wikt:diligent, diligent. Conscientiousness implies a desire to do a task well, and to take obligations to others seriously. Conscientious people tend to ...
appear remarkably common among patients with ALS, it remains open whether personality can increase susceptibility to ALS directly. Instead, genetic factors giving rise to personality might simultaneously predispose people to develop ALS, or the above personality traits might underlie lifestyle choices which are in turn risk factors for ALS.
Pathophysiology
Neuropathology
Upon examination at autopsy, features of the disease that can be seen with the naked eye include skeletalmuscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakne ...
, motor cortex atrophy, sclerosis of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tract
The corticobulbar (or corticonuclear) tract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the Medullary pyramids (brainstem), medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblonga ...
s, thinning of the hypoglossal nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated b ...
s (which control the tongue), and thinning of the anterior roots of the spinal cord.
The defining feature of ALS is the death of both upper motor neurons (located in the motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, motor control, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
of the brain) and lower motor neurons (located in the brainstem and spinal cord). In ALS with frontotemporal dementia, neurons throughout the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain die as well. The pathological hallmark of ALS is the presence of inclusion bodies
Inclusion bodies are aggregates of specific types of protein found in neurons, and a number of tissue (biology), tissue cells including red blood cells, bacteria, viruses, and plants. Inclusion bodies of aggregations of multiple proteins are also ...
(abnormal aggregations of protein) known as Bunina bodies in the cytoplasm of motor neurons. In about 97% of people with ALS, the main component of the inclusion bodies is TDP-43
Transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa (TAR DNA-binding protein 43 or TDP-43) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TARDBP'' gene.
Structure
TDP-43 is 414 amino acid residues long. It consists of four domains: an N-ter ...
protein; however, in those with ''SOD1'' or ''FUS'' mutations, the main component of the inclusion bodies is SOD1 protein or FUS protein, respectively. Prion
A prion () is a Proteinopathy, misfolded protein that induces misfolding in normal variants of the same protein, leading to cellular death. Prions are responsible for prion diseases, known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSEs), w ...
-like propagation of misfolded proteins from cell to cell may explain why ALS starts in one area and spreads to others. The glymphatic system
The glymphatic system, glymphatic clearance pathway or paravascular system is an organ system for metabolic waste removal in the central nervous system (CNS) of vertebrates. According to this model, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), an ultrafiltrated ...
may also be involved in the pathogenesis
In pathology, pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes .
Descript ...
of ALS.
Biochemistry
 It is still not fully understood why neurons die in ALS, but this
It is still not fully understood why neurons die in ALS, but this neurodegeneration
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their cell death, death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sc ...
is thought to involve many different cellular and molecular processes. The genes known to be involved in ALS can be grouped into three general categories based on their normal function: protein degradation, the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
, and RNA processing. Mutant SOD1 protein forms intracellular aggregations that inhibit protein degradation. Cytoplasmic aggregations of wild-type
The wild type (WT) is the phenotype of the typical form of a species as it occurs in nature. Originally, the wild type was conceptualized as a product of the standard "normal" allele at a locus, in contrast to that produced by a non-standard, " ...
(normal) SOD1 protein are common in sporadic ALS. It is thought that misfolded mutant SOD1 can cause misfolding and aggregation of wild-type SOD1 in neighboring neurons in a prion-like manner. Other protein degradation genes that can cause ALS when mutated include '' VCP'', '' OPTN'', '' TBK1'', and ''SQSTM1
Sequestosome-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SQSTM1'' gene. Also known as the ubiquitin-binding protein p62, it is an autophagosome cargo protein that targets other proteins that bind to it for selective autophagy. By interac ...
''. Three genes implicated in ALS that are important for maintaining the cytoskeleton and for axonal transport include '' DCTN1'', '' PFN1'', and '' TUBA4A''.
Several ALS genes encode RNA-binding proteins. The first to be discovered was TDP-43 protein, a nuclear protein that aggregates in the cytoplasm of motor neurons in almost all cases of ALS; however, mutations in ''TARDBP'', the gene that codes for TDP-43, are a rare cause of ALS. ''FUS'' codes for FUS, another RNA-binding protein with a similar function to TDP-43, which can cause ALS when mutated. It is thought that mutations in ''TARDBP'' and ''FUS'' increase the binding affinity of the low-complexity domain, causing their respective proteins to aggregate in the cytoplasm. Once these mutant RNA-binding proteins are misfolded and aggregated, they may be able to misfold normal proteins both within and between cells in a prion-like manner. This also leads to decreased levels of RNA-binding protein in the nucleus, which may mean that their target RNA transcripts do not undergo normal processing. Other RNA metabolism genes associated with ALS include '' ANG'', '' SETX'', and '' MATR3''.
''C9orf72'' is the most commonly mutated gene in ALS and causes motor neuron death through a number of mechanisms. The pathogenic mutation is a hexanucleotide repeat expansion (a series of six nucleotides repeated over and over); people with up to 30 repeats are considered normal, while people with hundreds or thousands of repeats can have familial ALS, frontotemporal dementia, or sometimes sporadic ALS. The three mechanisms of disease associated with these ''C9orf72'' repeats are deposition of RNA transcripts in the nucleus, translation of the RNA into toxic dipeptide repeat proteins in the cytoplasm, and decreased levels of the normal C9orf72 protein. Mitochondrial bioenergetic dysfunction leading to dysfunctional motor neuron axonal homeostasis (reduced axonal length and fast axonal transport of mitochondrial cargo) has been shown to occur in ''C9orf72''-ALS using human induced pluripotent stem cell
Induced pluripotent stem cells (also known as iPS cells or iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from a somatic cell. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka and Kazutoshi Takahashi in Kyoto, Jap ...
(iPSC) technologies coupled with CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing, and human post-mortem spinal cord tissue examination.
Excitotoxicity
In excitotoxicity, neuron, nerve cells suffer damage or death when the levels of otherwise necessary and safe neurotransmitters such as glutamic acid, glutamate become pathologically high, resulting in excessive stimulation of cell surface recept ...
, or nerve cell death caused by high levels of intracellular calcium due to excessive stimulation by the excitatory neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
, is a mechanism thought to be common to all forms of ALS. Motor neurons are more sensitive to excitotoxicity than other types of neurons because they have a lower calcium-buffering capacity and a type of glutamate receptor (the AMPA receptor
The α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPA receptor, AMPAR, or quisqualate receptor) is an ionotropic receptor, ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) and predominantly sodium ion channel that mediates fast excitator ...
) that is more permeable to calcium. In ALS, there are decreased levels of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 ( EAAT2), which is the main transporter that removes glutamate from the synapse; this leads to increased synaptic glutamate levels and excitotoxicity. Riluzole
Riluzole is a medication used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other motor neuron diseases. Riluzole delays the onset of ventilator-dependence or tracheostomy in some people and may increase survival by two to three months. Ril ...
, a drug that modestly prolongs survival in ALS, inhibits glutamate release from pre-synaptic neurons; however, it is unclear if this mechanism is responsible for its therapeutic effect.
Diagnosis
 No single test can provide a definite diagnosis of ALS. Instead, the diagnosis of ALS is primarily made based on a physician's clinical assessment after ruling out other diseases. Physicians often obtain the person's full
No single test can provide a definite diagnosis of ALS. Instead, the diagnosis of ALS is primarily made based on a physician's clinical assessment after ruling out other diseases. Physicians often obtain the person's full medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
and conduct neurologic examinations at regular intervals to assess whether signs and symptoms such as muscle weakness, muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakne ...
, hyperreflexia
Hyperreflexia is overactive or overresponsive bodily reflexes. Examples of this include twitching and spastic tendencies, which indicate disease of the upper motor neurons and the lessening or loss of control ordinarily exerted by higher brain ...
, Babinski's sign, and spasticity are worsening. Many biomarkers are being studied for the condition, but as of 2023 are not in general medical use.
Differential diagnosis
Because symptoms of ALS can be similar to those of a wide variety of other, more treatable diseases or disorders, appropriate tests must be conducted to exclude the possibility of other conditions. One of these tests iselectromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
(EMG), a special recording technique that detects electrical activity in muscles. Certain EMG findings can support the diagnosis of ALS. Another common test measures nerve conduction velocity
In neuroscience, nerve conduction velocity (CV) is the speed at which an electrochemical impulse propagates down a neural pathway. Conduction velocities are affected by a wide array of factors, which include age, sex, and various medical conditio ...
(NCV). Specific abnormalities in the NCV results may suggest, for example, that the person has a form of peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
(damage to peripheral nerves) or myopathy
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease ( Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meaning implies that the primary defec ...
(muscle disease) rather than ALS. While a magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) is often normal in people with early-stage ALS, it can reveal evidence of other problems that may be causing the symptoms, such as a spinal cord tumor, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, a herniated disc
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
in the neck, syringomyelia
Syringomyelia is a generic term referring to a disorder in which a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord. Often, syringomyelia is used as a generic term before an etiology is determined. This cyst, called a syrinx, can expand and elongate ...
, or cervical spondylosis
Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense, it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related degeneration of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degener ...
.
Based on the person's symptoms and findings from the examination and from these tests, the physician may order tests on blood and urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
samples to eliminate the possibility of other diseases, as well as routine laboratory tests. In some cases, for example, if a physician suspects the person may have a myopathy rather than ALS, a muscle biopsy may be performed.
A number of infectious diseases can sometimes cause ALS-like symptoms, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
), human T-lymphotropic virus
The primate T-lymphotropic viruses (PTLVs) are a group of retroviruses that infect primates, using their lymphocytes to reproduce. The ones that infect humans are known as human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), and the ones that infect Old World monk ...
(HTLV), Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-borne disease caused by species of ''Borrelia'' bacteria, Disease vector, transmitted by blood-feeding ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is the most common disease spread by ticks in th ...
, and syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
. Neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis, post-polio syndrome
Post-polio syndrome (PPS, poliomyelitis sequelae) is a group of latent symptoms of poliomyelitis (polio), occurring in more than 80% of polio infections. The symptoms are caused by the damaging effects of the viral infection on the nervous syst ...
, multifocal motor neuropathy
Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) is a progressively worsening condition where muscles in the extremities gradually weaken. The disorder, a pure motor neuropathy syndrome, is sometimes mistaken for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) because of t ...
, CIDP
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is an acquired autoimmune disease of the peripheral nervous system characterized by progressive weakness and impaired sensory function in the legs and arms. The disorder is sometimes called ...
, spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common geneti ...
, and spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA), popularly known as Kennedy's disease, is a rare, adult-onset, X-linked recessive lower motor neuron disease caused by trinucleotide CAG repeat expansions in exon 1 of the androgen receptor (AR) gene, whi ...
can also mimic certain aspects of the disease and should be considered.
ALS must be differentiated from the "ALS mimic syndromes", which are unrelated disorders that may have a similar presentation and clinical features to ALS or its variants. Because the prognosis of ALS and closely related subtypes of motor neuron disease are generally poor, neurologists may carry out investigations to evaluate and exclude other diagnostic possibilities. Disorders of the neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
, such as myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, ...
(MG) and Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome
Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs. It is also known as myasthenic syndrome, Eaton–Lambert syndrome, and when related to cancer, carcinomatous myopathy.
...
, may also mimic ALS, although this rarely presents diagnostic difficulty over time. Benign fasciculation syndrome
Benign fasciculation syndrome (BFS) is characterized by fasciculation (twitching) of Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscles in the body. The twitching can occur in any voluntary muscle group but is most common in the eyelids, arms, hands, fingers, leg ...
and cramp fasciculation syndrome may also, occasionally, mimic some of the early symptoms of ALS. Nonetheless, the absence of other neurological features that develop inexorably with ALS means that, over time, the distinction will not present any difficulty to the experienced neurologist; where doubt remains, EMG may be helpful.
Management
There is no cure for ALS. Management focuses on treating symptoms and providing supportive care, to improve quality of life and prolong survival. This care is best provided by multidisciplinary teams of healthcare professionals; attending a multidisciplinary ALS clinic is associated with longer survival, fewer hospitalizations, and improved quality of life.Non-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alte ...
(NIV) is the main treatment for respiratory failure in ALS. In people with normal bulbar function, it prolongs survival by about seven months and improves the quality of life. One study found that NIV is ineffective for people with poor bulbar function while another suggested that it may provide a modest survival benefit. Many people with ALS have difficulty tolerating NIV. Invasive ventilation is an option for people with advanced ALS when NIV is not enough to manage their symptoms. While invasive ventilation prolongs survival, disease progression, and functional decline continue. It may decrease the quality of life of people with ALS or their caregivers. Invasive ventilation is more commonly used in Japan than in North America or Europe.
 Physical therapy can promote functional independence through aerobic, range of motion, and stretching exercises. Occupational therapy can assist with activities of daily living through adaptive equipment. Speech therapy can assist people with ALS who have difficulty speaking. Preventing weight loss and malnutrition in people with ALS improves both survival and quality of life. Initially, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) can be managed by dietary changes and swallowing techniques. A
Physical therapy can promote functional independence through aerobic, range of motion, and stretching exercises. Occupational therapy can assist with activities of daily living through adaptive equipment. Speech therapy can assist people with ALS who have difficulty speaking. Preventing weight loss and malnutrition in people with ALS improves both survival and quality of life. Initially, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) can be managed by dietary changes and swallowing techniques. A feeding tube
A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to people who cannot obtain nutrition by mouth, are unable to swallow safely, or need nutritional supplementation. The state of being fed by a feeding tube is called gavage, enteral f ...
should be considered if someone with ALS loses 5% or more of their body weight or if they cannot safely swallow food and water. The feeding tube is usually inserted by percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is an endoscopic medical procedure in which a tube (PEG tube) is passed into a patient's stomach through the abdominal wall, most commonly to provide a means of feeding when oral intake is not adequate ...
(PEG). There is weak evidence that PEG tubes improve survival. PEG insertion is usually performed with the intent of improving quality of life.
Palliative care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
should begin shortly after someone is diagnosed with ALS. Discussion of end-of-life issues gives people with ALS time to reflect on their preferences for end-of-life care
End-of-life care is health care provided in the time leading up to a person's death. End-of-life care can be provided in the hours, days, or months before a person dies and encompasses care and support for a person's mental and emotional needs, phy ...
and can help avoid unwanted interventions or procedures. Hospice care can improve symptom management at the end of life and increase the likelihood of a peaceful death. In the final days of life, opioids can be used to treat pain and dyspnea, while benzodiazepines can be used to treat anxiety.
Medications
Disease-slowing treatments
Riluzole
Riluzole is a medication used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other motor neuron diseases. Riluzole delays the onset of ventilator-dependence or tracheostomy in some people and may increase survival by two to three months. Ril ...
has been found to modestly prolong survival by about 2–3 months. It may have a greater survival benefit for those with bulbar-onset ALS. It may work by decreasing release of the excitatory neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
from pre-synaptic neurons. The most common side effects are nausea and a lack of energy (asthenia
Weakness is a symptom of many different medical conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, ...
). People with ALS should begin treatment with riluzole as soon as possible following their diagnosis. Riluzole is available as a tablet, liquid, or dissolvable oral film.
Edaravone has been shown to modestly slow the decline in function in a small group of people with early-stage ALS. It may work by protecting motor neurons from oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
. The most common side effects are bruising and gait disturbance. Edaravone is available as an intravenous infusion or as an oral suspension.
AMX0035 (Relyvrio) is a combination of sodium phenylbutyrate
Sodium phenylbutyrate, sold under the brand name Buphenyl among others, is a salt of an aromatic fatty acid, 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA) or 4-phenylbutyric acid. The compound is used to treat urea cycle disorders, because its metabolites offer an ...
and taurursodiol, which was initially shown to prolong the survival of patients by an average of six months. Relyvrio was withdrawn by the manufacturer in April 2024 following the completion of the Phase 3 PHOENIX trial which did not show substantial benefit to ALS patients.
Tofersen (Qalsody) is an antisense oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small fragments of nucleic aci ...
that was approved for medical use in the United States in April 2023, for the treatment of SOD1-associated ALS. In a study of 108 patients with SOD1-associated ALS there was a non-significant trend towards a slowing of progression, as well as a significant reduction in neurofilament light chain, a putative ALS biomarker thought to indicate neuronal damage. A follow-up study and open-label extension suggested that earlier treatment initiation had a beneficial effect on slowing disease progression. Tofersen is available as an intrathecal injection into the lumbar cistern
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled ...
at the base of the spine.
A 2025 phase II study published found that tetramethylpyrazine nitrone is safe for patients with ALS, but it did not show a significant advantage over placebo in the primary efficacy measure. Researchers noted that the drug may help slow the decline in grip strength, however further clinical trials are necessary to confirm its potential benefits.
Symptomatic treatments
Other medications may be used to help reduce fatigue, ease muscle cramps, control spasticity, and reduce excess saliva andphlegm
Phlegm (; , ''phlégma'', "inflammation", "humour caused by heat") is mucus produced by the respiratory system, excluding that produced by the throat nasal passages. It often refers to respiratory mucus expelled by coughing, otherwise known as ...
. Gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropath ...
, pregabalin
Pregabalin, sold under the brand name Lyrica among others, is an anticonvulsant, analgesic, and anxiolytic amino acid medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, restless legs syndrome, opioid withdrawal, generalized anx ...
, and tricyclic antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains ...
(e.g., amitriptyline
Amitriptyline, sold under the brand name Elavil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, and a variety of pain syndromes such as neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, migraine and tension headac ...
) can be used for neuropathic pain, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs), acetaminophen
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
, and opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
s can be used for nociceptive pain.
Depression can be treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs primarily work by blo ...
s (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants, while benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat co ...
can be used for anxiety. There are no medications to treat cognitive impairment/frontotemporal dementia (FTD); however, SSRIs and antipsychotics can help treat some of the symptoms of FTD. Baclofen
Baclofen, sold under the brand name Lioresal among others, is a medication used to treat muscle spasticity, such as from a spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis. It may also be used for hiccups and muscle spasms near the end of life, and ...
and tizanidine
Tizanidine, sold under the brand name Zanaflex among others, is an alpha-2 (α2) adrenergic receptor agonist, similar to clonidine, that is used to treat muscle spasticity due to spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, and spastic cerebral ...
are the most commonly used oral drugs for treating spasticity; an intrathecal
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space (sin. ''intrathecal space'') so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is useful in several applic ...
baclofen pump can be used for severe spasticity. Atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically give ...
, scopolamine
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a medication used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin a ...
, amitriptyline, or glycopyrrolate
Glycopyrronium bromide is a medication of the muscarinic anticholinergic group. It does not cross the blood–brain barrier and consequently has few to no central effects. It is given by mouth, via intravenous injection, on the skin, and via in ...
may be prescribed when people with ALS begin having trouble swallowing their saliva (sialorrhea
Hypersalivation or hypersialosis is the excessive production of saliva. It has also been defined as increased amount of saliva in the mouth, which may also be caused by decreased clearance of saliva.Medscape > HypersalivationBy Erica Brownfield. P ...
).
A 2017 review concluded that mexiletine is safe and effective for treating cramps in ALS based on a randomized controlled trial from 2016.
Breathing support
Non-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alte ...
(NIV) is the primary treatment for respiratory failure in ALS and was the first treatment shown to improve both survival and quality of life. NIV uses a face or nasal mask connected to a ventilator that provides intermittent positive pressure to support breathing. Continuous positive pressure is not recommended for people with ALS because it makes breathing more difficult. Initially, NIV is used only at night because the first sign of respiratory failure is decreased gas exchange (hypoventilation
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide ( hypercap ...
) during sleep; symptoms associated with this nocturnal hypoventilation include interrupted sleep, anxiety, morning headaches, and daytime fatigue. As the disease progresses, people with ALS develop shortness of breath when lying down, during physical activity or talking, and eventually at rest. Other symptoms include poor concentration, poor memory, confusion, respiratory tract infections, and a weak cough. Respiratory failure is the most common cause of death in ALS.
It is important to monitor the respiratory function of people with ALS every three months because beginning NIV soon after the start of respiratory symptoms is associated with increased survival. This involves asking the person with ALS if they have any respiratory symptoms and measuring their respiratory function. The most commonly used measurement is upright forced vital capacity
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is he ...
(FVC), but it is a poor detector of early respiratory failure and is not a good choice for those with bulbar symptoms, as they have difficulty maintaining a tight seal around the mouthpiece. Measuring FVC while the person is lying on their back (supine FVC) is a more accurate measure of diaphragm weakness than upright FVC. Sniff nasal inspiratory pressure (SNIP) is a rapid, convenient test of diaphragm strength that is not affected by bulbar muscle weakness. If someone with ALS has signs and symptoms of respiratory failure, they should undergo daytime blood gas analysis to look for hypoxemia
Hypoxemia (also spelled hypoxaemia) is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia is usually caused by pulmonary disease. Sometimes the concentration of oxygen in the ...
(low oxygen in the blood) and hypercapnia
Hypercapnia (from the Greek ''hyper'', "above" or "too much" and ''kapnos'', "smoke"), also known as hypercarbia and CO2 retention, is a condition of abnormally elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood. Carbon dioxide is a gaseous pro ...
(too much carbon dioxide in the blood). If their daytime blood gas analysis is normal, they should then have nocturnal pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring blood oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading of art ...
to look for hypoxemia during sleep.
Non-invasive ventilation prolongs survival longer than riluzole. A 2006 randomized controlled trial found that NIV prolongs survival by about 48 days and improves the quality of life; however, it also found that some people with ALS benefit more from this intervention than others. For those with normal or only moderately impaired bulbar function, NIV prolongs survival by about seven months and significantly improves the quality of life. For those with poor bulbar function, NIV neither prolongs survival nor improves the quality of life, though it does improve some sleep-related symptoms. Despite the clear benefits of NIV, about 25–30% of all people with ALS are unable to tolerate it, especially those with cognitive impairment or bulbar dysfunction. Results from a large 2015 cohort study suggest that NIV may prolong survival in those with bulbar weakness, so NIV should be offered to all people with ALS, even if it is likely that they will have difficulty tolerating it.
Invasive ventilation
Invasive ventilation bypasses the nose and mouth (the upper airways) by making a cut in the trachea (tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the front of the neck to open a direct airway to the trachea. The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway ...
) and inserting a tube
Tube or tubes may refer to:
* ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film
* "Tubes" (Peter Dale), performer on the Soccer AM television show
* Tube (band), a Japanese rock band
* Tube & Berger, the alias of dance/electronica producers Arndt Rör ...
connected to a ventilator. It is an option for people with advanced ALS whose respiratory symptoms are poorly managed despite continuous NIV use. While invasive ventilation prolongs survival, especially for those younger than 60, it does not treat the underlying neurodegenerative process. The person with ALS will continue to lose motor function, making communication increasingly difficult and sometimes leading to locked-in syndrome
Locked-in syndrome (LIS), also known as pseudocoma, is a condition in which a patient is aware but cannot move or communicate verbally due to complete paralysis of nearly all voluntary muscles in their body except for vertical eye movements and ...
, in which they are completely paralyzed except for their eye muscles. About half of the people with ALS who choose to undergo invasive ventilation report a decrease in their quality of life but most still consider it to be satisfactory. However, invasive ventilation imposes a heavy burden on caregivers and may decrease their quality of life. Attitudes toward invasive ventilation vary from country to country; about 30% of people with ALS in Japan choose invasive ventilation, versus less than 5% in North America and Europe.
Therapy

Physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
plays a large role in rehabilitation for individuals with ALS. Specifically, physical, occupational, and speech therapists can set goals and promote benefits for individuals with ALS by delaying loss of strength, maintaining endurance, limiting pain, improving speech and swallowing, preventing complications, and promoting functional independence.
Occupational therapy and special equipment such as assistive technology
Assistive technology (AT) is a term for assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices for Disability, people with disabilities and the elderly. Disabled people often have difficulty performing activities of daily living (ADLs) independently, ...
can also enhance people's independence and safety throughout the course of ALS. Gentle, low-impact aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise, also known as cardio, is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, involving, or requiring oxygen", and refers to the use of ...
such as performing activities of daily living, walking, swimming, and stationary bicycling can strengthen unaffected muscles, improve cardiovascular health, and help people fight fatigue and depression. Range of motion and stretching exercises can help prevent painful spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles. ...
and shortening (contracture) of muscles. Physical and occupational therapists can recommend exercises that provide these benefits without overworking muscles because muscle exhaustion can lead to a worsening of symptoms associated with ALS, rather than providing help to people with ALS. They can suggest devices such as ramps, braces, walkers, bathroom equipment (shower chairs, toilet risers, etc.), and wheelchairs that help people remain mobile. Occupational therapists can provide or recommend equipment and adaptations to enable ALS people to retain as much safety and independence in activities of daily living as possible. Since respiratory insufficiency is the primary cause of mortality, physical therapists can help improve respiratory outcomes in people with ALS by implementing pulmonary physical therapy. This includes inspiratory muscle training, lung volume recruitment training, and manual assisted cough therapy aimed at increasing respiratory muscle strength as well as increasing survival rates.
People with ALS who have difficulty speaking or swallowing may benefit from working with a speech-language pathologist. These health professionals can teach people adaptive strategies such as techniques to help them speak louder and more clearly. As ALS progresses, speech-language pathologists can recommend the use of augmentative and alternative communication
Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) encompasses the communication methods used to supplement or replace speech or writing for those with impairments in the production or comprehension of spoken or written language. AAC is used by t ...
such as voice amplifiers, speech-generating devices (or voice output communication devices), or low-tech communication techniques such as head-mounted laser pointers, alphabet boards or yes/no signals.
Nutrition
 Preventing
Preventing weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
and malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
in people with ALS improves both survival and quality of life. Weight loss in ALS is often caused by muscle wasting and increased resting energy expenditure. Weight loss may also be secondary to reduced food intake since dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
develops in about 85% of people with ALS at some point throughout their disease course. Therefore, regular periodic assessment of the weight and swallowing ability in people with ALS is very important. Dysphagia is often initially managed via dietary changes and modified swallowing techniques. People with ALS are often instructed to avoid dry or chewy foods in their diet and instead have meals that are soft, moist, and easy to swallow. Switching to thick liquids (like fruit nectar or smoothies) or adding thickeners (to thin fluids like water and coffee) may also help people facing difficulty swallowing liquids. There is tentative evidence that high-calorie diets may prevent further weight loss and improve survival, but more research is still needed.
A feeding tube
A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to people who cannot obtain nutrition by mouth, are unable to swallow safely, or need nutritional supplementation. The state of being fed by a feeding tube is called gavage, enteral f ...
should be considered if someone with ALS loses 5% or more of their body weight or if they cannot safely swallow food and water. This can take the form of a gastrostomy
A gastrostomy is the creation of an artificial external opening into the stomach for nutritional support or gastric decompression.
Typically this would include an incision in the patient's epigastrium as part of a formal operation. When originall ...
tube, in which a tube is placed through the wall of the abdomen into the stomach, or (less commonly) a nasogastric tube
Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube (nasogastric tube or NG tube) through the nose, down the esophagus, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the insertion ...
, in which a tube is placed through the nose and down the esophagus into the stomach. A gastrostomy tube is more appropriate for long-term use than a nasogastric tube, which is uncomfortable and can cause esophageal ulcers. The feeding tube is usually inserted by a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is an endoscopic medical procedure in which a tube (PEG tube) is passed into a patient's stomach through the abdominal wall, most commonly to provide a means of feeding when oral intake is not adequate ...
procedure (PEG). While there is weak evidence that PEG tubes improve survival in people with ALS, no randomized controlled trials
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical ...
(RCTs) have yet been conducted to indicate whether enteral tube feeding has benefits compared to continuation of feeding by mouth. Nevertheless, PEG tubes are still offered with the intent of improving the person's quality of life by sustaining nutrition, hydration status, and medication intake.
End-of-life care
Palliative care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
, which relieves symptoms and improves the quality of life without treating the underlying disease, should begin shortly after someone is diagnosed with ALS. Early discussion of end-of-life issues gives people with ALS time to reflect on their preferences for end-of-life care
End-of-life care is health care provided in the time leading up to a person's death. End-of-life care can be provided in the hours, days, or months before a person dies and encompasses care and support for a person's mental and emotional needs, phy ...
and can help avoid unwanted interventions or procedures. Once they have been fully informed about all aspects of various life-prolonging measures, they can fill out advance directive
An advance healthcare directive, also known as living will, personal directive, advance directive, medical directive or advance decision, is a document in which a person specifies what actions should be taken for their health if they are no longe ...
s indicating their attitude toward noninvasive ventilation, invasive ventilation, and feeding tubes. Late in the disease course, difficulty speaking due to muscle weakness (dysarthria
Dysarthria is a speech sound disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor–speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes. It is a condition in which problems effectively occur with the ...
) and cognitive dysfunction may impair their ability to communicate their wishes regarding care. Continued failure to solicit the preferences of the person with ALS may lead to unplanned and potentially unwanted emergency interventions, such as invasive ventilation. If people with ALS or their family members are reluctant to discuss end-of-life issues, it may be useful to use the introduction of gastrostomy or noninvasive ventilation as an opportunity to bring up the subject.
Hospice care
Hospice care is a type of health care that focuses on the palliation of a terminally ill patient's pain and symptoms and attending to their emotional and spiritual needs at the end of life. Hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life b ...
, or palliative care at the end of life, is especially important in ALS because it helps to optimize the management of symptoms and increases the likelihood of a peaceful death. It is unclear exactly when the end-of-life phase begins in ALS, but it is associated with significant difficulty moving, communicating, and, in some cases, thinking. Although many people with ALS fear choking to death (suffocating), they can be reassured that this occurs rarely, less than 1% of the time. Most patients die at home, and in the final days of life, opioids can be used to treat pain and dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
, while benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant, depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed t ...
s can be used to treat anxiety.
Epidemiology
ALS is the most commonmotor neuron disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and low ...
in adults and the third most common neurodegenerative disease
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
after Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
and Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
. Worldwide the number of people who develop ALS yearly is estimated to be 1.9 people per 100,000 per year, while the number of people who have ALS at any given time is estimated to be about 4.5 people per 100,000. In Europe, the number of new cases a year is about 2.6 people per 100,000, while the number affected is 7–9 people per 100,000. The lifetime risk of developing ALS is 1:350 for European men and 1:400 for European women. Men have a higher risk mainly because spinal-onset ALS is more common in men than women. The number of those with ALS in the United States in 2015 was 5.2 people per 100,000, and was higher in whites, males, and people over 60 years old. The number of new cases is about 0.8 people per 100,000 per year in East Asia and about 0.7 people per 100,000 per year in South Asia. About 80% of ALS epidemiology studies have been conducted in Europe and the United States, mostly in people of northern European descent. There is not enough information to determine the rates of ALS in much of the world, including Africa, parts of Asia, India, Russia, and South America. There are several geographic clusters in the Western Pacific where the prevalence of ALS was reported to be 50–100 times higher than in the rest of the world, including Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, the Kii Peninsula
The is the largest peninsula on the island of Honshū in Japan and is located within the Kansai region. It is named after the ancient Kii Province. The peninsula has long been a sacred place in Buddhism, Shinto, and Shugendo, and many people wou ...
of Japan, and Western New Guinea
Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, and Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the island of New Guinea, formerly Dutch and granted to Indonesia in 1962. Given the island is alternatively named Papua, the region ...
. The incidence in these areas has decreased since the 1960s; the cause remains unknown.
People of all races and ethnic backgrounds may be affected by ALS, but it is more common in whites than in Africans, Asians, or Hispanics. In the United States in 2015, the prevalence of ALS in whites was 5.4 people per 100,000, while the prevalence in blacks was 2.3 people per 100,000. The Midwest had the highest prevalence of the four US Census regions with 5.5 people per 100,000, followed by the Northeast (5.1), the South (4.7), and the West (4.4). The Midwest and Northeast likely had a higher prevalence of ALS because they have a higher proportion of whites than the South and West. Ethnically mixed populations may be at a lower risk of developing ALS; a study in Cuba found that people of mixed ancestry were less likely to die from ALS than whites or blacks. There are also differences in the genetics of ALS between different ethnic groups; the most common ALS gene in Europe is ''C9orf72'', followed by ''SOD1'', ''TARDBP'', and ''FUS'', while the most common ALS gene in Asia is ''SOD1'', followed by ''FUS'', ''C9orf72'', and ''TARDBP''.
ALS can affect people at any age, but the peak incidence is between 50 and 75 years and decreases dramatically after 80 years. The reason for the decreased incidence in the elderly is unclear. One thought is that people who survive into their 80s may not be genetically susceptible to developing ALS; alternatively, ALS in the elderly might go undiagnosed because of comorbidities (other diseases they have), difficulty seeing a neurologist, or dying quickly from an aggressive form of ALS. In the United States in 2015, the lowest prevalence was in the 18–39 age group, while the highest prevalence was in the 70–79 age group. Sporadic ALS usually starts around the ages of 58 to 63 years, while genetic ALS starts earlier, usually around 47 to 52 years. The number of ALS cases worldwide is projected to increase from 222,801 in 2015 to 376,674 in 2040, an increase of 69%. This will largely be due to the aging of the world's population, especially in developing countries.
History

 Descriptions of the disease date back to at least 1824 by
Descriptions of the disease date back to at least 1824 by Charles Bell
Sir Charles Bell (12 November 177428 April 1842) was a Scottish surgeon, anatomist, physiologist, neurologist, artist, and philosophical theologian. He is noted for discovering the difference between sensory nerves and motor nerves in the ...
. In 1850, François-Amilcar Aran
François-Amilcar Aran (12 July 1817, in Bordeaux – 22 February 1861, in Paris) was a French physician.
He studied medicine in Bordeaux and received his doctorate in Paris with a thesis on heart palpitations. In Paris he subsequently becam ...
was the first to describe a disorder he named "progressive muscular atrophy", a form of ALS in which only the lower motor neurons are affected. In 1869, the connection between the symptoms and the underlying neurological problems was first described by Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot (; 29 November 1825 – 16 August 1893) was a French neurology, neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on groundbreaking work about hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise A ...
, who initially introduced the term ''amyotrophic lateral sclerosis'' in his 1874 paper. Flail arm syndrome, a regional variant of ALS, was first described by Alfred Vulpian in 1886. Flail leg syndrome, another regional variant of ALS, was first described by Pierre Marie
Pierre Marie (9 September 1853 – 13 April 1940) was a French neurologist and political journalist close to the SFIO.
Medical career
After finishing medical school, he served as an interne (1878), working as an assistant to neurologist Jean- ...
and his student Patrikios in 1918.
Diagnostic criteria
In the 1950s,electrodiagnostic testing
Electrodiagnosis (EDX) is a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about diseases by passively recording the electrical activity of body parts (that is, their natural electrophysiology) or by measuring their response to external ele ...
(EMG) and nerve conduction velocity
In neuroscience, nerve conduction velocity (CV) is the speed at which an electrochemical impulse propagates down a neural pathway. Conduction velocities are affected by a wide array of factors, which include age, sex, and various medical conditio ...
(NCV) testing began to be used to evaluate clinically suspected ALS. In 1969 Edward H. Lambert published the first EMG/NCS diagnostic criteria for ALS, consisting of four findings he considered to strongly support the diagnosis. Since then several diagnostic criteria have been developed, which are mostly in use for research purposes for inclusion/exclusion criteria, and to stratify patients for analysis in trials. Research diagnostic criteria for ALS include the "El Escorial" in 1994, revised in 1998. In 2006, the "Awaji" criteria proposed using EMG and NCV tests to help diagnose ALS earlier, and most recently the "Gold Coast" criteria in 2019.
Name
''Amyotrophic'' comes fromGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
: ''a-'' means "no", ''myo-'' (from ''mûs'') refers to "muscle", and ''trophḗ'' means "nourishment". Therefore, '' amyotrophy'' means "muscle malnourishment" or the wasting of muscle tissue. ''Lateral'' identifies the locations in the spinal cord of the affected motor neurons. '' Sclerosis'' means "scarring" or "hardening" and refers to the death of the motor neurons in the spinal cord.
ALS is sometimes referred to as ''Charcot's disease'' (not to be confused with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is an inherited neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nerves responsible for transmitting signals between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body.
This is the most common inherited neuropath ...
or Charcot joint disease), because Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot (; 29 November 1825 – 16 August 1893) was a French neurology, neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on groundbreaking work about hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise A ...
was the first to connect the clinical symptoms with the pathology seen at autopsy. The British neurologist Russell Brain coined the term ''motor neuron disease'' in 1933 to reflect his belief that ALS, progressive bulbar palsy, and progressive muscular atrophy were all different forms of the same disease. In some countries, especially the United States, ALS is called ''Lou Gehrig's disease'' after the American baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball sport played between two team sport, teams of nine players each, taking turns batting (baseball), batting and Fielding (baseball), fielding. The game occurs over the course of several Pitch ...
player Lou Gehrig
Henry Louis Gehrig ( ; June 19, 1903June 2, 1941), also known as Heinrich Ludwig Gehrig, was an American professional baseball first baseman who played 17 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the New York Yankees (1923–1939). Gehrig was ...
, who was diagnosed with ALS in 1939.
In the United States and continental Europe, the term ''ALS'' (as well as ''Lou Gehrig's disease'' in the US) refers to all forms of the disease, including "classical" ALS, progressive bulbar palsy, progressive muscular atrophy, and primary lateral sclerosis. In the United Kingdom and Australia, the term ''motor neuron disease'' refers to all forms of the disease while ''ALS'' only refers to "classical" ALS, meaning the form with both upper and lower motor neuron involvement.
Society and culture
In addition to the baseball playerLou Gehrig
Henry Louis Gehrig ( ; June 19, 1903June 2, 1941), also known as Heinrich Ludwig Gehrig, was an American professional baseball first baseman who played 17 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the New York Yankees (1923–1939). Gehrig was ...
and the theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking
Stephen William Hawking (8January 194214March 2018) was an English theoretical physics, theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author who was director of research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at the University of Cambridge. Between ...
(who notably lived longer than any other known person with the condition), several other notable individuals have or have had ALS. Several books have been written and films have been made about patients of the disease as well. American sociology professor and ALS patient Morrie Schwartz was the subject of the memoir '' Tuesdays with Morrie'' and the film of the same name, and Stephen Hawking was the subject of the critically acclaimed biopic '' The Theory of Everything''.
In August 2014, the "Ice Bucket Challenge
The Ice Bucket Challenge, sometimes called the ALS Ice Bucket Challenge, is an activity involving the pouring of a bucket of ice water over a person's head, either by another person or self-administered, to promote awareness of the disease amyo ...
" to raise money for ALS research went viral online. Participants filmed themselves filling a bucket full of ice water and pouring it onto themselves; they then nominated other individuals to do the same. Many participants donated to ALS research at the ALS Association
The ALS Association is an American nonprofit organization that funds global amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) research, provides care services and programs to people affected by ALS through its nationwide network of clinical care centers, and w ...
, the ALS Therapy Development Institute
The ALS Therapy Development Institute (ALS TDI) is a non-profit biotechnology research organization focused on finding treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). With a staff including more than 30 scientists, it operates a research and d ...
, ALS Society of Canada, or Motor neuron Disease Association in the UK.
References
External links
ALS Association Official Website
ALS Therapy Development Institute
International Alliance of ALS/MND Associations
International Symposium on ALS/MND
* {{Authority control Motor neuron diseases Rare diseases Unsolved problems in neuroscience Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system Cytoskeletal defects Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Neuromuscular disorders Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Idiopathic diseases Diseases named after patients