2006 UST Growling Tigers Men's Basketball Team on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
6 (six) is the
 A
A

 The evolution of the modern digit 6 appears to be more simple when compared with the other digits. The modern 6 can be traced back to the
The evolution of the modern digit 6 appears to be more simple when compared with the other digits. The modern 6 can be traced back to the  .
This digit resembles an inverted ''9''. To disambiguate the two on objects and documents that can be inverted, the 6 has often been underlined, both in handwriting and on printed labels.
.
This digit resembles an inverted ''9''. To disambiguate the two on objects and documents that can be inverted, the 6 has often been underlined, both in handwriting and on printed labels.

 *The sixfold
*The sixfold
The Number 6The Positive Integer 6
{{DEFAULTSORT:6 (Number) Integers 6 (number)
natural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive in ...
following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number
A composite number is a positive integer that can be formed by multiplying two smaller positive integers. Accordingly it is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Every positive integer is composite, prime numb ...
and the smallest perfect number
In number theory, a perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive proper divisors, that is, divisors excluding the number itself. For instance, 6 has proper divisors 1, 2 and 3, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6, so 6 is a perfec ...
.
In mathematics
A six-sidedpolygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure made up of line segments connected to form a closed polygonal chain.
The segments of a closed polygonal chain are called its '' edges'' or ''sides''. The points where two edges meet are the polygon ...
is a hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A regular hexagon is de ...
, one of the three regular polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either ''convex ...
s capable of tiling the plane. A hexagon also has 6 edges as well as 6 internal and external angles
In geometry, an angle of a polygon is formed by two adjacent edge (geometry), sides. For a simple polygon (non-self-intersecting), regardless of whether it is Polygon#Convexity and non-convexity, convex or non-convex, this angle is called an ...
.
6 is the second smallest composite number
A composite number is a positive integer that can be formed by multiplying two smaller positive integers. Accordingly it is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Every positive integer is composite, prime numb ...
. It is also the first number that is the sum of its proper divisors, making it the smallest perfect number
In number theory, a perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive proper divisors, that is, divisors excluding the number itself. For instance, 6 has proper divisors 1, 2 and 3, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6, so 6 is a perfec ...
. It is also the only perfect number that doesn't have a digital root
The digital root (also repeated digital sum) of a natural number in a given radix is the (single digit) value obtained by an iterative process of summing digits, on each iteration using the result from the previous iteration to compute a digit su ...
of 1. 6 is the first unitary perfect number
A unitary perfect number is an integer which is the sum of its positive proper unitary divisors, not including the number itself. (A divisor ''d'' of a number ''n'' is a unitary divisor if ''d'' and ''n''/''d'' share no common factors). The numb ...
, since it is the sum of its positive proper unitary divisor
In mathematics, a natural number ''a'' is a unitary divisor (or Hall divisor) of a number ''b'' if ''a'' is a divisor of ''b'' and if ''a'' and \frac are coprime, having no common factor other than 1. Equivalently, a divisor ''a'' of ''b'' is a un ...
s, without including itself. Only five such numbers are known to exist. 6 is the largest of the four all-Harshad numbers.
6 is the 2nd superior highly composite number
In number theory, a superior highly composite number is a natural number which, in a particular rigorous sense, has many divisors. Particularly, it is defined by a ratio between the number of divisors an integer has and that integer raised to s ...
, the 2nd colossally abundant number
In number theory, a colossally abundant number (sometimes abbreviated as CA) is a natural number that, in a particular, rigorous sense, has many divisors. Particularly, it is defined by a ratio between the sum of an integer's divisors and that ...
, the 3rd triangular number
A triangular number or triangle number counts objects arranged in an equilateral triangle. Triangular numbers are a type of figurate number, other examples being square numbers and cube numbers. The th triangular number is the number of dots in ...
, the 4th highly composite number
A highly composite number is a positive integer that has more divisors than all smaller positive integers. If ''d''(''n'') denotes the number of divisors of a positive integer ''n'', then a positive integer ''N'' is highly composite if ''d''(' ...
, a pronic number
A pronic number is a number that is the product of two consecutive integers, that is, a number of the form n(n+1).. The study of these numbers dates back to Aristotle. They are also called oblong numbers, heteromecic numbers,. or rectangular number ...
, a congruent number
In number theory, a congruent number is a positive integer that is the area of a right triangle with three rational number sides. A more general definition includes all positive rational numbers with this property.
The sequence of (integer) cong ...
, a harmonic divisor number
In mathematics, a harmonic divisor number or Ore number is a positive integer whose divisors have a harmonic mean that is an integer. The first few harmonic divisor numbers are
: 1, 6, 28, 140, 270, 496, 672, 1638, 2970, 6200, 8128, 8190 .
...
, and a semiprime
In mathematics, a semiprime is a natural number that is the product of exactly two prime numbers. The two primes in the product may equal each other, so the semiprimes include the squares of prime numbers.
Because there are infinitely many prime n ...
. 6 is also the first Granville number, or -perfect number. A Golomb ruler
In mathematics, a Golomb ruler is a set (mathematics), set of marks at integer positions along a ruler such that no two pairs of marks are the same distance apart. The number of marks on the ruler is its ''order'', and the largest distance bet ...
of length 6 is a "perfect ruler".
The six exponentials theorem
In mathematics, specifically transcendental number theory, the six exponentials theorem is a result that, given the right conditions on the exponents, guarantees the transcendence of at least one of a set of six exponentials.
Statement
: If x_1, ...
guarantees that under certain conditions one of a set of six exponentials is transcendental. The smallest non-abelian group
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is commu ...
is the symmetric group
In abstract algebra, the symmetric group defined over any set is the group whose elements are all the bijections from the set to itself, and whose group operation is the composition of functions. In particular, the finite symmetric grou ...
which has 3! = 6 elements. 6 the answer to the two-dimensional kissing number problem
In geometry, the kissing number of a mathematical space is defined as the greatest number of non-overlapping unit spheres that can be arranged in that space such that they each touch a common unit sphere. For a given sphere packing (arrangement o ...
.
 A
A cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square (geometry), square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It i ...
has 6 face
The face is the front of the head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect th ...
s. A tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tet ...
has 6 edges. In four dimensions, there are a total of six convex regular polytopes.
In the classification of finite simple groups
In mathematics, the classification of finite simple groups (popularly called the enormous theorem) is a result of group theory stating that every List of finite simple groups, finite simple group is either cyclic group, cyclic, or alternating gro ...
, twenty of twenty-six sporadic group
In the mathematical classification of finite simple groups, there are a number of groups which do not fit into any infinite family. These are called the sporadic simple groups, or the sporadic finite groups, or just the sporadic groups.
A simpl ...
s in the happy family Happy Family, The Happy Family, or A Happy Family may refer to:
Film
* ''Happy Family'' (1934 film) or ''The Merry Frinks'', an American comedy directed by Alfred E. Green
* '' A Happy Family'', a 1935 Krazy Kat animated short
* ''The Happy Fa ...
are part of three families of groups which divide the order of the friendly giant, the largest sporadic group: five ''first generation'' Mathieu group
In group theory, a topic in abstract algebra, the Mathieu groups are the five sporadic simple groups ''M''11, ''M''12, ''M''22, ''M''23 and ''M''24 introduced by . They are multiply transitive permutation groups on 11, 12, 22, 23 or 24 objec ...
s, seven ''second generation'' subquotient
In the mathematical fields of category theory and abstract algebra, a subquotient is a quotient object of a subobject. Subquotients are particularly important in abelian categories, and in group theory, where they are also known as sections, thou ...
s of the Leech lattice
In mathematics, the Leech lattice is an even unimodular lattice Λ24 in 24-dimensional Euclidean space which is one of the best models for the kissing number problem. It was discovered by . It may also have been discovered (but not published) by Er ...
, and eight ''third generation'' subgroup
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, a subset of a group G is a subgroup of G if the members of that subset form a group with respect to the group operation in G.
Formally, given a group (mathematics), group under a binary operation ...
s of the friendly giant. The remaining six sporadic groups do not divide the order of the friendly giant, which are termed the '' pariahs'' ( ''Ly'', ''O'N'', ''Ru'', ''J''4, ''J''3, and ''J''1).
6 is the smallest integer which is not an exponent of a prime number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime ...
, making it the smallest integer greater than 1 for which there does not exist a finite field
In mathematics, a finite field or Galois field (so-named in honor of Évariste Galois) is a field (mathematics), field that contains a finite number of Element (mathematics), elements. As with any field, a finite field is a Set (mathematics), s ...
of that size.
List of basic calculations
Greek and Latin word parts
'
' is classicalGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
for "six". Thus:
*"Hexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbo ...
" combines ' with the Latinate ' to name a number base
In a positional numeral system, the radix (radices) or base is the number of unique digits, including the digit zero, used to represent numbers. For example, for the decimal system (the most common system in use today) the radix is ten, becaus ...
of 16
*A hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A regular hexagon is de ...
is a regular polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either ''convex ...
with six sides
**' is a French nickname for the continental part of Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France ( or ), also known as European France (), is the area of France which is geographically in Europe and chiefly comprises #Hexagon, the mainland, popularly known as "the Hexagon" ( or ), and Corsica. This collective name for the ...
for its resemblance to a regular hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A regular hexagon is de ...
*A hexahedron
A hexahedron (: hexahedra or hexahedrons) or sexahedron (: sexahedra or sexahedrons) is any polyhedron with six faces. A cube, for example, is a regular hexahedron with all its faces square, and three squares around each vertex.
There are seven ...
is a polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (: polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional figure with flat polygonal Face (geometry), faces, straight Edge (geometry), edges and sharp corners or Vertex (geometry), vertices. The term "polyhedron" may refer ...
with six faces, with a cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square (geometry), square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It i ...
being a special case
*Hexameter
Hexameter is a metrical line of verses consisting of six feet (a "foot" here is the pulse, or major accent, of words in an English line of poetry; in Greek as well as in Latin a "foot" is not an accent, but describes various combinations of s ...
is a poetic form consisting of six feet per line
*A "hex nut" is a nut
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed
* Nut (food), a dry and edible fruit or seed, including but not limited to true nuts
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut, NUT or Nuts may also refer to:
A ...
with six sides, and a hex bolt has a six-sided head
*The prefix "" also occurs in the systematic name
A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature.
A semisystematic name or semitrivi ...
of many chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
s, such as hexane
Hexane () or ''n''-hexane is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and the molecular formula C6H14.
Hexane is a colorless liquid, odorless when pure, and with a boiling point of approximately . It is widely used as ...
which has 6 carbon atoms ().
The prefix ''sex-''
''Sex-'' is aLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the word to which it is affixed.
Prefixes, like other affixes, can b ...
meaning "six". Thus:
*''Senary'' is the ordinal adjective meaning "sixth"
*People with sexdactyly have six fingers on each hand
*The measuring instrument called a sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of cel ...
got its name because its shape forms one-sixth of a whole circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
*A group of six musicians is called a sextet
A sextet (or hexad) is a formation containing exactly six members. The former term is commonly associated with vocal ensembles (e.g. The King's Singers, Affabre Concinui) or musical instrument groups, but can be applied to any situation where six ...
*Six babies delivered in one birth are sextuplet
A multiple birth is the culmination of a multiple pregnancy, wherein the mother gives birth to two or more babies. A term most applicable to vertebrate species, multiple births occur in most kinds of mammals, with varying frequencies. Such births ...
s
*Sexy prime
In number theory, sexy primes are prime numbers that differ from each other by . For example, the numbers and are a pair of sexy primes, because both are prime and 11 - 5 = 6.
The term "sexy prime" is a pun stemming from the Latin word for six ...
pairs – Prime pairs differing by six are ''sexy'', because sex is the Latin word for six.
The SI prefix
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official st ...
for 10006 is exa-
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The pre ...
(E), and for its reciprocal atto-
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The pre ...
(a).
Evolution of the Hindu-Arabic digit

 The evolution of the modern digit 6 appears to be more simple when compared with the other digits. The modern 6 can be traced back to the
The evolution of the modern digit 6 appears to be more simple when compared with the other digits. The modern 6 can be traced back to the Brahmi numerals
Brahmi numerals are a numeral system attested in the Indian subcontinent from the 3rd century BCE. It is the direct graphic ancestor of the modern Hindu–Arabic numeral system. However, the Brahmi numeral system was conceptually distinct from ...
of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, which are first known from the Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 2 ...
. It was written in one stroke like a cursive lowercase e rotated 90 degrees clockwise. Gradually, the upper part of the stroke (above the central squiggle) became more curved, while the lower part of the stroke (below the central squiggle) became straighter. The Arabs dropped the part of the stroke below the squiggle. From there, the European evolution to our modern 6 was very straightforward, aside from a flirtation with a glyph that looked more like an uppercase G.
On the seven-segment display
A seven-segment display is a display device for Arabic numerals, less complex than a device that can show more characters such as dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, ...
s of calculators and watches, 6 is usually written with six segments. Some historical calculator models use just five segments for the 6, by omitting the top horizontal bar. This glyph variant has not caught on; for calculators that can display results in hexadecimal, a 6 that looks like a "b" is not practical.
Just as in most modern typeface
A typeface (or font family) is a design of Letter (alphabet), letters, Numerical digit, numbers and other symbols, to be used in printing or for electronic display. Most typefaces include variations in size (e.g., 24 point), weight (e.g., light, ...
s, in typefaces with text figures
Text figures (also known as non-lining, lowercase, old style, ranging, hanging, medieval, billing, or antique figures or numerals) are numerals designed with varying heights in a fashion that resembles a typical line of running text, hence the ...
the character for the digit 6 usually has an ascender, as, for example, in 
Chemistry
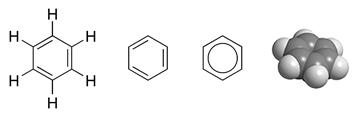
 *The sixfold
*The sixfold symmetry
Symmetry () in everyday life refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, the term has a more precise definition and is usually used to refer to an object that is Invariant (mathematics), invariant und ...
of snowflake
A snowflake is a single ice crystal that is large enough to fall through the Earth's atmosphere as snow.Knight, C.; Knight, N. (1973). Snow crystals. Scientific American, vol. 228, no. 1, pp. 100–107.Hobbs, P.V. 1974. Ice Physics. Oxford: C ...
s arises from the hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A regular hexagon is de ...
al crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat ...
of ordinary ice.
Anthropology
*Acoffin
A coffin or casket is a funerary box used for viewing or keeping a corpse, for burial, entombment or cremation. Coffins are sometimes referred to as caskets, particularly in American English.
A distinction is commonly drawn between "coffins" a ...
is traditionally buried six feet under the ground; thus, the phrase "six feet under" means that a person (or thing, or concept) is dead.
*Six is a lucky number in Chinese culture.
*"Six" is used as an informal slang term for the British Secret Intelligence Service
The Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), commonly known as MI6 (MI numbers, Military Intelligence, Section 6), is the foreign intelligence service of the United Kingdom, tasked mainly with the covert overseas collection and analysis of Human i ...
, MI6.
See also
*Six degrees (disambiguation) Six degrees of separation is the theory that anyone on Earth can be connected to any other person on the planet through a chain of acquaintances that has no more than five intermediaries
Six degrees or Six degrees of separation may also refer to:
...
.
References
* *''A Property of the Number Six'', Chapter 6, P Cameron, JH v. Lint, ''Designs, Graphs, Codes and their Links'' *Wells, D. ''The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Numbers'' London: Penguin Group. (1987): 67 - 69External links
The Number 6
{{DEFAULTSORT:6 (Number) Integers 6 (number)