2006 Canadian federal election on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 2006 Canadian federal election was held on January 23, 2006, to elect members to the
 Most observers believed only the Liberals and the Conservatives were capable of forming a government in this election, although Canadian political history is not without examples of wholly unexpected outcomes, such as Ontario's provincial election in 1990. However, with the exception of the Unionist government of 1917 (which combined members of both the Conservatives and the Liberals), at the Federal stage, only Liberals or Conservatives have formed government. With the end of the campaign at hand, pollsters and pundits placed the Conservatives ahead of the Liberals.
Prime Minister Paul Martin's Liberals hoped to recapture their majority, and this appeared likely at one point during the campaign; but it would have required holding back Bloc pressure in
Most observers believed only the Liberals and the Conservatives were capable of forming a government in this election, although Canadian political history is not without examples of wholly unexpected outcomes, such as Ontario's provincial election in 1990. However, with the exception of the Unionist government of 1917 (which combined members of both the Conservatives and the Liberals), at the Federal stage, only Liberals or Conservatives have formed government. With the end of the campaign at hand, pollsters and pundits placed the Conservatives ahead of the Liberals.
Prime Minister Paul Martin's Liberals hoped to recapture their majority, and this appeared likely at one point during the campaign; but it would have required holding back Bloc pressure in
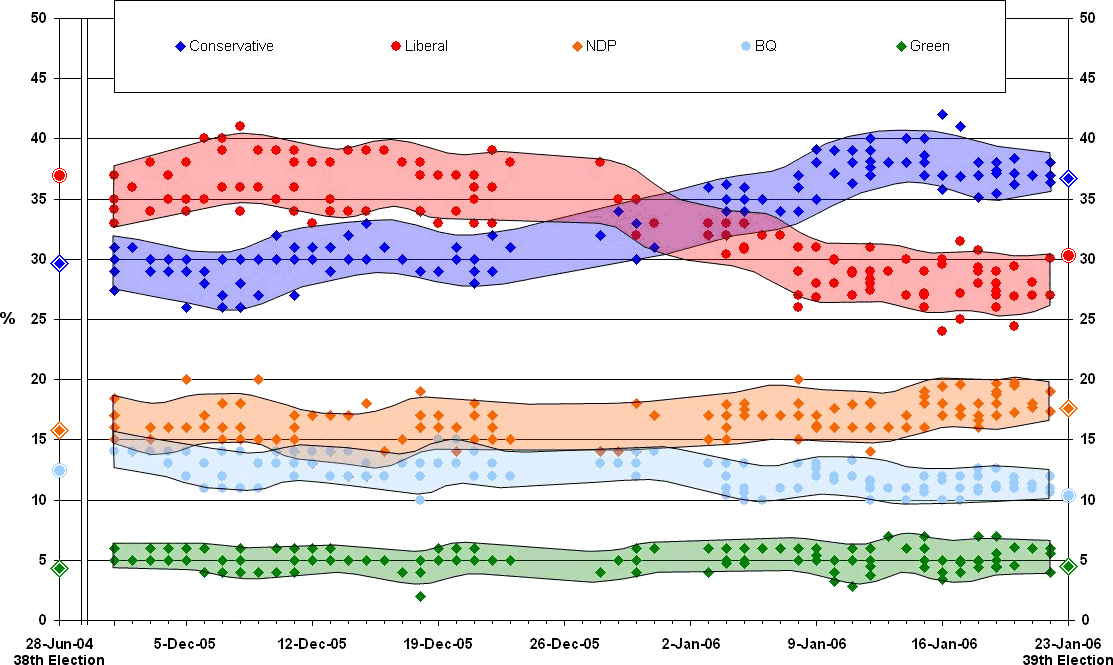 Prior to and during the election campaign,
Prior to and during the election campaign,


Election Prediction ProjectUBC Election Stock Market 2006Which party to vote for? (saplin.com)
– Vote by issue quiz
Predicting the 2006 Canadian Election
Windows Media Video streamCTV News – Election 2006The Globe and Mail – Decision 2006
by Graeme MacKay of ''The Hamilton Spectator''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Canadian federal election, 2006
House of Commons of Canada
The House of Commons of Canada () is the lower house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Monarchy of Canada#Parliament (King-in-Parliament), Crown and the Senate of Canada, they comprise the Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of Ca ...
of the 39th Parliament of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
.
New details of the sponsorship scandal
The sponsorship scandal, AdScam or Sponsorgate, was a scandal in Canada that came as a result of a federal government " sponsorship program" in the province of Quebec involving the Liberal Party of Canada, which was in power from 1993 to 2006.
...
were released through the Gomery Commission
The sponsorship scandal, AdScam or Sponsorgate, was a scandal in Canada that came as a result of a Government of Canada, federal government "Sponsor (commercial), sponsorship program" in the province of Quebec involving the Liberal Party of Can ...
, and the three opposition parties aimed to bring down Liberal Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
Paul Martin
Paul Edgar Philippe Martin (born August 28, 1938), also known as Paul Martin Jr., is a Canadian lawyer and retired politician who served as the 21st prime minister of Canada and the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2003 to 2006.
Th ...
's minority government
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in ...
, contending that it was corrupt. On November 28, 2005, Martin's government was defeated on a motion of non-confidence
A motion or vote of no confidence (or the inverse, a motion or vote of confidence) is a motion and corresponding vote thereon in a deliberative assembly (usually a legislative body) as to whether an officer (typically an executive) is deemed fit ...
. A day later, Martin met with Governor General
Governor-general (plural governors-general), or governor general (plural governors general), is the title of an official, most prominently associated with the British Empire. In the context of the governors-general and former British colonies, ...
Michaëlle Jean
Michaëlle Jean (; born September 6, 1957) is a Canadian former journalist who served as the 27th governor general of Canada from 2005 to 2010. She is the first Haitian Canadian and black person to hold this office.
Jean was the Organisation i ...
to dissolve parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
, triggering an unusual winter election.
The Conservative Party, that was formed in 2003 from the merger of the Progressive Conservative Party and the Canadian Alliance
The Canadian Alliance (), formally the Canadian Reform Conservative Alliance (), was a centre-right to right-wing federal political party in Canada that existed under that name from 2000 to 2003. The Canadian Alliance was the new name of the ...
, scored its first-ever victory as they won the greatest number of seats
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but may also refer to concentrations of power in a wider sense (i.e " seat (legal entity)"). See disambiguation.
Types of seat
The ...
in the House of Commons, winning 124 out of 308, up from 99 seats in 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and Its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 60 ...
. Due to the emerging details of the sponsorship scandal, as well as a unified right-of-centre
Centre-right politics is the set of right-wing politics, right-wing political ideologies that lean closer to the political centre. It is commonly associated with conservatism, Christian democracy, liberal conservatism, and conservative liberalis ...
party, the Tories led by Stephen Harper
Stephen Joseph Harper (born April 30, 1959) is a Canadian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Canada from 2006 to 2015. He is to date the only prime minister to have come from the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada, ser ...
went on to end over 12 years of Liberal rule. Harper formed the smallest minority government in Canadian history (in terms of proportion of seats), becoming prime minister. The New Democratic Party
The New Democratic Party (NDP; , ) is a federal political party in Canada. Widely described as social democratic,The party is widely described as social democratic:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* The Editors of ''Encyclopædia Britann ...
experienced a modest boost in support whereas the Bloc Québécois
The Bloc Québécois (, , BQ) is a centre-left politics, centre-left and list of federal political parties in Canada, federal political party in Canada devoted to Quebec nationalism, Quebecois nationalism, social democracy, and the promotion o ...
' seat count nearly stayed the same. This is the most recent election in which the winning federal party did not win New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
and Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
.
Cause of the election
This unusual wintergeneral election
A general election is an electoral process to choose most or all members of a governing body at the same time. They are distinct from By-election, by-elections, which fill individual seats that have become vacant between general elections. Gener ...
was caused by a motion of no confidence
A motion or vote of no confidence (or the inverse, a motion or vote of confidence) is a motion and corresponding vote thereon in a deliberative assembly (usually a legislative body) as to whether an officer (typically an executive) is deemed fi ...
passed by the House of Commons on November 28, 2005, with Canada's three opposition parties contending that the Liberal government of Prime Minister Paul Martin
Paul Edgar Philippe Martin (born August 28, 1938), also known as Paul Martin Jr., is a Canadian lawyer and retired politician who served as the 21st prime minister of Canada and the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2003 to 2006.
Th ...
was corrupt. The following morning Martin met with Governor General Michaëlle Jean
Michaëlle Jean (; born September 6, 1957) is a Canadian former journalist who served as the 27th governor general of Canada from 2005 to 2010. She is the first Haitian Canadian and black person to hold this office.
Jean was the Organisation i ...
, who then dissolved parliament, summoned the next parliament, and ordered the issuance of writs of election
A writ of election is a writ issued ordering the holding of an election. In Commonwealth countries writs are the usual mechanism by which general elections are called and are issued by the head of state or their representative. In the United S ...
. The last set January 23, 2006, as election day and February 13 as the date for return of the writs. The campaign was almost eight weeks in length, the longest in two decades, in order to allow time for the Christmas and New Year holidays.
Recent political events, most notably testimony to the Gomery Commission
The sponsorship scandal, AdScam or Sponsorgate, was a scandal in Canada that came as a result of a Government of Canada, federal government "Sponsor (commercial), sponsorship program" in the province of Quebec involving the Liberal Party of Can ...
investigating the sponsorship scandal
The sponsorship scandal, AdScam or Sponsorgate, was a scandal in Canada that came as a result of a federal government " sponsorship program" in the province of Quebec involving the Liberal Party of Canada, which was in power from 1993 to 2006.
...
, significantly weakened the Liberals (who, under Martin, had formed the first Liberal minority government
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in ...
since the Trudeau era) by allegations of criminal corruption in the party. The first Gomery report, released November 1, 2005, had found a "culture of entitlement" to exist within the Government. Although the next election was not legally required until 2009, the opposition had enough votes to force the dissolution of Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
earlier. While Prime Minister Martin had committed in April 2005 to dissolve Parliament within a month of the tabling of the second Gomery Report (which was released on schedule on February 1, 2006), all three opposition parties
Parliamentary opposition is a form of political opposition to a designated government, particularly in a Westminster-based parliamentary system. This article uses the term ''government'' as it is used in Parliamentary systems, i.e. meaning ''th ...
—the Conservatives, Bloc Québécois
The Bloc Québécois (, , BQ) is a centre-left politics, centre-left and list of federal political parties in Canada, federal political party in Canada devoted to Quebec nationalism, Quebecois nationalism, social democracy, and the promotion o ...
, and New Democratic Party
The New Democratic Party (NDP; , ) is a federal political party in Canada. Widely described as social democratic,The party is widely described as social democratic:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* The Editors of ''Encyclopædia Britann ...
(NDP)—and three of the four independents decided that the issue at hand was how to correct the Liberal corruption, and the motion of non-confidence passed 171–133.
Parties
 Most observers believed only the Liberals and the Conservatives were capable of forming a government in this election, although Canadian political history is not without examples of wholly unexpected outcomes, such as Ontario's provincial election in 1990. However, with the exception of the Unionist government of 1917 (which combined members of both the Conservatives and the Liberals), at the Federal stage, only Liberals or Conservatives have formed government. With the end of the campaign at hand, pollsters and pundits placed the Conservatives ahead of the Liberals.
Prime Minister Paul Martin's Liberals hoped to recapture their majority, and this appeared likely at one point during the campaign; but it would have required holding back Bloc pressure in
Most observers believed only the Liberals and the Conservatives were capable of forming a government in this election, although Canadian political history is not without examples of wholly unexpected outcomes, such as Ontario's provincial election in 1990. However, with the exception of the Unionist government of 1917 (which combined members of both the Conservatives and the Liberals), at the Federal stage, only Liberals or Conservatives have formed government. With the end of the campaign at hand, pollsters and pundits placed the Conservatives ahead of the Liberals.
Prime Minister Paul Martin's Liberals hoped to recapture their majority, and this appeared likely at one point during the campaign; but it would have required holding back Bloc pressure in Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
plus picking up some new seats there while also gaining seats in English Canada, most likely in rural Ontario and southwestern British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
. Towards the end of the campaign, even high-profile Liberals were beginning to concede defeat, and the best the Liberals could have achieved was a razor-thin minority.
Stephen Harper's Conservatives succeeded in bringing their new party into power in Canada. While continuing weaknesses in Quebec and urban areas rightfully prompted most observers to consider a Conservative majority government
A majority government is a government by one or more governing parties that hold an absolute majority of seats in a legislature. Such a government can consist of one party that holds a majority on its own, or be a coalition government of multi ...
to be mathematically difficult to achieve, early on, Harper's stated goal was to achieve one nonetheless. Though the Conservatives were ahead of the Liberals in Quebec, they remained far behind the Bloc Québécois, and additional gains in rural and suburban Ontario would have been necessary to meet Stephen Harper's goal. The polls had remained pretty well static over the course of December, with the real shift coming in the first few days of the New Year. That is when the Conservatives took the lead and kept it for the rest of the campaign.
Harper started off the first month of the campaign with a policy-per-day strategy, which included a GST reduction and a child-care allowance. The Liberals opted to hold any major announcements until after the Christmas holidays; as a result, Harper dominated media coverage for the first weeks of the campaign and was able to define his platform and insulate it from expected Liberal attacks. On December 27, 2005, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; , GRC) is the Law enforcement in Canada, national police service of Canada. The RCMP is an agency of the Government of Canada; it also provides police services under contract to 11 Provinces and terri ...
announced it was investigating allegations that Liberal Finance Minister
A ministry of finance is a ministry or other government agency in charge of government finance, fiscal policy, and financial regulation. It is headed by a finance minister, an executive or cabinet position .
A ministry of finance's portfoli ...
Ralph Goodale
Ralph Edward Goodale (born October 5, 1949) is a Canadian diplomat and retired politician who has served as the Canadian High Commissioner to the United Kingdom since April 19, 2021.
Goodale was first elected in 1974 as the member of Parliam ...
's office had engaged in insider trading
Insider trading is the trading of a public company's stock or other securities (such as bonds or stock options) based on material, nonpublic information about the company. In various countries, some kinds of trading based on insider informati ...
before making an important announcement on the taxation of income trust
An income trust is an investment that may hold equities, debt instruments, royalty interests or real properties. It is especially useful for financial requirements of institutional investors such as pension funds, and for investors such as retired ...
s. The RCMP indicated that they had no evidence of wrongdoing or criminal activity from any party associated with the investigation, including Goodale. However, the story dominated news coverage for the following week and prevented the Liberals from making their key policy announcements, allowing the Conservatives to refocus their previous attacks about corruption within the Liberal party. The Conservatives soon found themselves leading in the polls. By early January, they made a major breakthrough in Quebec, pushing the Liberals to second place.
As their lead solidified, media coverage
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Means of communication, tools and channels used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Interactive media, media that is inte ...
of the Conservatives was much more positive, while Liberals found themselves increasingly criticized for running a poor campaign and making numerous gaffes.
The NDP has claimed that last minute tactical voting
Strategic or tactical voting is voting in consideration of possible ballots cast by other voters in order to maximize one's satisfaction with the election's results.
Gibbard's theorem shows that no voting system has a single "always-best" stra ...
cost them several seats last time, as left-of-centre voters moved to the Liberals so that they could prevent a Harper-led government. Jack Layton avoided stating his party's goal was to win the election outright, instead calling for enough New Democrats to be elected to hold the balance of power in a Liberal or Conservative minority government. Political commentators have long argued that the NDP's main medium-term goal is to serve as junior partners to the Liberals in Canada's first-ever true coalition government
A coalition government, or coalition cabinet, is a government by political parties that enter into a power-sharing arrangement of the executive. Coalition governments usually occur when no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an ...
. NDP leader Jack Layton was concerned last time over people voting Liberal so that they could avoid a Conservative government. Over the course of the last week of the campaign, Jack Layton called on Liberal voters disgusted with the corruption to "lend" their votes to the NDP to elect more NDP members to the House and hold the Conservatives to a minority.
The Bloc Québécois had a very successful result in the 2004 election, with the Liberals reduced to the core areas of federalist support in portions of Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and the Outaouais
Outaouais (, ; also commonly called The Outaouais) is a region of western Quebec, Canada. It includes the city of Gatineau, the municipality of Val-des-Monts, the municipality of Cantley, Quebec, Cantley and the Papineau Regional County Municipal ...
. Oddly enough, this meant that there were comparatively few winnable Bloc seats left—perhaps eight or so—for the party to target. With provincial allies the Parti Québécois
The Parti Québécois (PQ; , ) is a sovereignist and social democratic provincial political party in Quebec, Canada. The PQ advocates national sovereignty for Quebec involving independence of the province of Quebec from Canada and establishi ...
widely tipped to regain power in 2007, a large sovereigntist contingent in the House could play a major role in reopening the matter of Quebec independence. The Bloc Québécois only runs candidates in the province of Quebec. However, Gilles Duceppe's dream of winning 50%+ of the popular vote was dashed when the polls broke after the New Year, and the Conservatives became a real threat to that vision in Quebec.
In addition to the four sitting parties, the Green Party of Canada
The Green Party of Canada () is a federal political party in Canada, founded in 1983 with a focus on green politics.
The Green Party is currently the fifth largest party in the House of Commons by seat count. It elected its first member of ...
ran candidates in all 308 federal ridings for the second consecutive election. Though the Greens had been an official party since the 1984 election, this campaign was the first in which they had stable financial support with which to campaign. After a breakthrough in the 2004 election, they exceeded the minimum 2% of the popular vote to receive federal funding. Supporters and sympathisers criticize that the party were not invited to the nationally televised debates even with its official status. The party has occasionally polled as high as 19% in British Columbia and 11% nationwide. Critics of the Green Party contend that, by drawing away left-of-centre votes, the Green Party actually assists the Conservative Party in some ridings. The Greens deny this.
Other parties are listed in the table of results above.
Events during the 38th Parliament
An early election seemed likely because the 2004 federal election, held on June 28, 2004, resulted in the election of a Liberalminority government
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in ...
. In the past, minority governments have had an average lifespan of a year and a half. Some people considered the 38th parliament to be particularly unstable. It involved four parties, and only very implausible ideological combinations (e.g., Liberals + Conservatives; Liberals + BQ; Conservatives + BQ + NDP) could actually command a majority of the seats, a necessity if a government is to retain power. From its earliest moments, there was some threat of the government falling as even the Speech from the Throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or their representative, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a Legislative session, session is opened. ...
almost resulted in a non-confidence vote.
Brinkmanship in the spring of 2005
The Liberal government came close to falling when testimony from theGomery Commission
The sponsorship scandal, AdScam or Sponsorgate, was a scandal in Canada that came as a result of a Government of Canada, federal government "Sponsor (commercial), sponsorship program" in the province of Quebec involving the Liberal Party of Can ...
caused public opinion to move sharply against the government. The Bloc Québécois were eager from the beginning to have an early election. The Conservatives announced they had also lost confidence in the government's moral authority
Moral authority is authority premised on principles, or fundamental truths, which are independent of written, or positive laws. As such, moral authority necessitates the existence of and adherence to truth. Because truth does not change the princip ...
. Thus, during much of spring 2005, there was a widespread belief that the Liberals would lose a confidence vote, prompting an election taking place in the spring or summer of 2005.
In a televised speech on April 21, Martin promised to request a dissolution of Parliament
The dissolution of a legislative assembly (or parliament) is the simultaneous termination of service of all of its members, in anticipation that a successive legislative assembly will reconvene later with possibly different members. In a democracy ...
and begin an election campaign within 30 days of the Gomery Commission's final report. The release date of that report would later solidify as February 1, 2006; Martin then clarified that he intended to schedule the election call so as to have the polling day in April 2006.
Later that week, the NDP, who had initially opposed the budget, opted to endorse Martin's proposal for a later election. The Liberals agreed to take corporate tax cuts out of the budget on April 26 in exchange for NDP support on votes of confidence, but even with NDP support the Liberals still fell three votes short of a majority. However, a surprise defection of former Conservative leadership candidate Belinda Stronach to the Liberal party on May 17 changed the balance of power in the House. Independents Chuck Cadman and Carolyn Parrish
Carolyn Parrish (born Karolina Janozeski; October 3, 1946) is a Canadian politician who has been the 7th and current mayor of Mississauga since June 24, 2024. Parrish previously served as a Member of Parliament (Canada), member of Parliament (MP ...
provided the last two votes needed for the Liberals to win the budget vote.
The deal turned out to be rather unnecessary, as the Conservatives opted to ensure the government's survival on the motion of confidence
A motion or vote of no confidence (or the inverse, a motion or vote of confidence) is a motion and corresponding vote thereon in a deliberative assembly (usually a legislative body) as to whether an officer (typically an executive) is deemed fi ...
surrounding the original budget, expressing support to the tax cuts and defence spending therein. When Parliament voted on second reading and referral of the budget and the amendment on May 19, the previous events kept the government alive. The original budget bill, C-43, passed easily, as expected, but the amendment bill, C-48, resulted in an equality of votes, and the Speaker of the House
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hung ...
broke the tie to continue the parliament. The government never got as close to falling after that date. Third reading of Bill C-48 was held late at night on an unexpected day, and several Conservatives being absent, the motion passed easily, guaranteeing there would be no election in the near future.
Aftermath of the first Gomery report
On November 1,John Gomery
John Howard Gomery (August 9, 1932 – May 18, 2021) was a Canadian jurist from Quebec. He was a Justice of the Quebec Superior Court from 1982 to 2007, and appointed Commissioner for the Royal Commission investigating the Sponsorship scandal ...
released his interim report, and the scandal returned to prominence. Liberal support again fell, with some polls registering an immediate ten percent drop. The Conservatives and Bloc thus resumed their push for an election before Martin's April date. The NDP stated that their support was contingent on the Liberals agreeing to move against the private provision of healthcare. The Liberals and NDP failed to come to an agreement, however, and the NDP joined the two other opposition parties in demanding an election.
However, the Liberals had intentionally scheduled the mandatory "opposition days" (where a specified opposition party controls the agenda) on November 15 (Conservative), November 17 (Bloc Québécois) and November 24 (NDP). These days meant that any election would come over the Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a Religion, religious and Culture, cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by coun ...
season, an unpopular idea. Following negotiations between the opposition parties, they instead issued an ultimatum to the Prime Minister to call an election immediately after the Christmas holidays or face an immediate non-confidence vote which would prompt a holiday-spanning campaign.
To that end, the NDP introduced a parliamentary motion demanding that the government drop the writ in January 2006 for a February 13 election date; however, only the prime minister has the authority to advise the Governor General on an election date, the government was therefore not bound by the NDP's motion. Martin had indicated that he remained committed to his April 2006 date, and would disregard the motion, which the opposition parties managed to pass, as expected, on November 21 by a vote of 167–129.
The three opposition leaders had agreed to delay the tabling of the no-confidence motion until the 24th, to ensure that a conference between the government and aboriginal leaders scheduled on the 24th would not be disrupted by the campaign. Parliamentary procedure dictated that the vote be deferred until the 28th. Even if the opposition had not put forward the non-confidence motion, the government was still expected to fall—there was to have been a vote on supplementary budget estimates on December 8, and if it had been defeated, loss of Supply
Loss of supply occurs where a government in a parliamentary democracy using the Westminster System or a system derived from it is denied a supply of treasury or exchequer funds, by whichever house or houses of parliament or head of state is cons ...
would have toppled the Liberals.
Conservative leader Stephen Harper
Stephen Joseph Harper (born April 30, 1959) is a Canadian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Canada from 2006 to 2015. He is to date the only prime minister to have come from the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada, ser ...
, the leader of the Opposition
The Leader of the Opposition is a title traditionally held by the leader of the Opposition (parliamentary), largest political party not in government, typical in countries utilizing the parliamentary system form of government. The leader of the ...
, introduced a motion of no confidence on November 24, which NDP leader Jack Layton
John Gilbert Layton (July 18, 1950 – August 22, 2011) was a Canadian politician and academic who served as the leader of the New Democratic Party (NDP) from 2003 to 2011 and leader of the Official Opposition in 2011. He previously sat on T ...
seconded. The motion was voted upon and passed in the evening of November 28, with all present MPs from the NDP, Bloc Québécois, and Conservatives and 3 Independents ( Bev Desjarlais, David Kilgour
David William Kilgour (February 18, 1941 – April 5, 2022) was a Canadian human rights activist, author, lawyer, and politician. He also served as a senior fellow to the Raoul Wallenberg Centre for Human Rights.
Kilgour earned a degree in ...
and Pat O'Brien), voting with a combined strength of 171 votes for the motion and 132 Liberals and one Independent (Carolyn Parrish
Carolyn Parrish (born Karolina Janozeski; October 3, 1946) is a Canadian politician who has been the 7th and current mayor of Mississauga since June 24, 2024. Parrish previously served as a Member of Parliament (Canada), member of Parliament (MP ...
) voting against. One Bloc Québécois MP was absent from the vote. It is the fifth time a Canadian government has lost the confidence of Parliament, but the first time this has happened on a straight motion of no confidence. The four previous instances have been due to loss of supply or votes of censure
A censure is an expression of strong disapproval or harsh criticism. In parliamentary procedure, it is a debatable main motion that could be adopted by a majority vote. Among the forms that it can take are a stern rebuke by a legislature, a sp ...
.
Martin visited Governor General
Governor-general (plural governors-general), or governor general (plural governors general), is the title of an official, most prominently associated with the British Empire. In the context of the governors-general and former British colonies, ...
Michaëlle Jean
Michaëlle Jean (; born September 6, 1957) is a Canadian former journalist who served as the 27th governor general of Canada from 2005 to 2010. She is the first Haitian Canadian and black person to hold this office.
Jean was the Organisation i ...
the following morning, where he formally advised her to dissolve Parliament and schedule an election for January 23. In accordance with Canadian constitutional practice, she consented (such a request has only been turned down once in Canadian history), officially beginning an election campaign that had been simmering for months.
Early on in the campaign, polls showed the Liberals with a solid 5–10 point lead over the Conservatives, and poised to form a strong minority government at worst. Around Christmas, after reports of an RCMP investigation into allegations of insider trading within the Finance department, this situation changed dramatically, leading to the opposition parties consistently attacking the Liberals on corruption. Almost at the same time, the Boxing Day shooting, an unusually violent gun fight between rival gangs on December 26 in downtown Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
(resulting in the death of 15-year-old Jane Creba, an innocent bystander), may have swayed some Ontario voters to support the more hardline CPC policies on crime. The Conservatives enjoyed a fairly significant lead in polls leading up to the election, but the gap narrowed in the last few days.
Issues
Several issues—some long-standing (notablyfiscal imbalance Fiscal imbalance is a mismatch in the revenue powers and expenditure responsibilities of a government.
Fiscal imbalances as differences in net fiscal benefits
A fiscal imbalance emerges when sub-national governments have different abilities to ra ...
, the gun registry, abortion
Abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. Abortions that occur without intervention are known as miscarriages or "spontaneous abortions", and occur in roughly 30–40% of all pregnan ...
, and Quebec sovereignty
The Quebec sovereignty movement (French: ''mouvement souverainiste du Québec'', ) is a political movement advocating for Quebec's independence from Canada. Proponents argue that Quebecers form a distinct nation with a unique culture, language, ...
), others recently brought forth by media coverage (including redressing the Chinese Canadian community for long-standing wrongs that forced both parties to back-track on their position in the national and ethnic media, particularly in key British Columbia and Alberta ridings), or court decisions (the sponsorship scandal
The sponsorship scandal, AdScam or Sponsorgate, was a scandal in Canada that came as a result of a federal government " sponsorship program" in the province of Quebec involving the Liberal Party of Canada, which was in power from 1993 to 2006.
...
, same-sex marriages
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same legal sex. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 38 countries, with a total population of 1.5 billion people (20% ...
, income trust
An income trust is an investment that may hold equities, debt instruments, royalty interests or real properties. It is especially useful for financial requirements of institutional investors such as pension funds, and for investors such as retired ...
s, or Canada–United States relations
Canada and the United States have a long and complex relationship that has had a significant impact on Canada's history, economy, and culture. The two countries have long considered themselves among the "closest allies". They share the longest b ...
)—took the fore in debate among the parties and also influenced aspects of the parties' electoral platforms.
Elections Canada
Elections Canada () is the non-partisan agency responsible for administering elections in Canada, Canadian federal elections and Referendums in Canada, referendums.
History
Elections Canada is an agency of the Parliament of Canada, and reports ...
later investigated improper election spending by the Conservative Party, which became widely known as the In and Out scandal. In 2011, charges against senior Conservatives were dropped in a plea deal that saw the party and its fundraising arm plead guilty and receive the maximum possible fines, totaling $52,000.
Opinion polls
 Prior to and during the election campaign,
Prior to and during the election campaign, opinion poll
An opinion poll, often simply referred to as a survey or a poll, is a human research survey of public opinion from a particular sample. Opinion polls are usually designed to represent the opinions of a population by conducting a series of qu ...
ing showed variable support for the governing Liberals and opposition Conservatives. In November 2005, the first report by Justice John Gomery was released to the public; subsequently, poll numbers for the Liberals again dropped. Just days later, polling showed the Liberals were already bouncing back; upon the election call, the Liberals held a small lead over the Conservatives and maintained this for much of December. Renewed accusations of corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
and impropriety at the end of 2005 – amid Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; , GRC) is the Law enforcement in Canada, national police service of Canada. The RCMP is an agency of the Government of Canada; it also provides police services under contract to 11 Provinces and terri ...
criminal probes of possible government leaks regarding income trust
An income trust is an investment that may hold equities, debt instruments, royalty interests or real properties. It is especially useful for financial requirements of institutional investors such as pension funds, and for investors such as retired ...
tax changes and advertising sponsorships – led to an upswing of Conservative support again and gave them a lead over the Liberals, portending a change in government. Ultimately this scandal was linked to a blackberry exchange to a banking official by Liberal candidate Scott Brison. Polling figures for the NDP increased slightly, while Bloc figures experienced a slight dip; figures for the Green Party did not change appreciably throughout the campaign.
Exit poll
An exit poll was carried out byIpsos Reid
Ipsos Reid was the name of a Canada-based research company, still existing under the name Ipsos as the Canadian arm of the global Ipsos Group. Founded in Winnipeg in 1979 as the Angus Reid Group, the company expanded across the country and was pu ...
polling firm. The poll overestimated the NDP's support and underestimated the Liberals' support. Here is a results breakdown by demographics:
Candidates
The election involved the same 308electoral districts
An electoral (congressional, legislative, etc.) district, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a geographical portion of a political unit, such as a country, state or province, city, or administrative region, created to provid ...
as in 2004, except in New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
, where the boundary between Acadie—Bathurst
Acadie—Bathurst (formerly known as Gloucester) is a federal electoral district (Canada), electoral district in New Brunswick, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1867.
Geography
The district includes ...
and Miramichi was ruled to be illegal. Many of the candidates were also the same: fewer incumbents chose to leave than if they had served a full term, and the parties have generally blocked challenges to sitting MPs for the duration of the minority government, although there had been some exceptions.
Gender breakdown of candidates
An ongoing issue in Canadian politics is the imbalance between the genders in selection by political parties of candidates. Although in the past some parties, particularly the New Democrats, have focused on the necessity of having equal gender representation in Parliament, no major party has ever nominated as many or more women than men in a given election. In 2006, the New Democrats had the highest percentage of female candidates (35.1%) of any party aside from the Animal Alliance, which only had one candidate, its leader, Liz White. The proportion of female New Democrats elected was greater than the proportion nominated, indicating female New Democrats were nominated in winnable ridings. 12.3% of Conservative candidates and 25.6% of Liberal candidates were female.Campaign slogans
The parties' campaign slogans for the 2006 election:Endorsements
Target ridings
Incumbent MPs who did not run for re-election
Electoral district changes
The following name changes were made to the electoral districts after the 2004 election: In 2005, further changes were made: :* Battle River and Kitchener—Wilmot—Wellesley—Woolwich reverted to their prior names, following passage of two private member's bills. :* A minor boundary adjustment was made betweenAcadie—Bathurst
Acadie—Bathurst (formerly known as Gloucester) is a federal electoral district (Canada), electoral district in New Brunswick, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1867.
Geography
The district includes ...
and Miramichi.
Results
The election was held on January 23, 2006. The first polls closed at 7:00 p.m. ET (0000UTC
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communica ...
); Elections Canada
Elections Canada () is the non-partisan agency responsible for administering elections in Canada, Canadian federal elections and Referendums in Canada, referendums.
History
Elections Canada is an agency of the Parliament of Canada, and reports ...
started to publish preliminary results on its website at 10:00 p.m. ET as the last polls closed. Harper was reelected in Calgary Southwest
Calgary Southwest was a federal electoral district in Alberta, Canada, that was represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1988 to 2015. The district was in the southwest part of the city of Calgary, south of Glenmore Trail and west of ...
, which he has held since 2002, ensuring that he had a seat in the new parliament. Shortly after midnight (ET) that night, incumbent Prime Minister Paul Martin
Paul Edgar Philippe Martin (born August 28, 1938), also known as Paul Martin Jr., is a Canadian lawyer and retired politician who served as the 21st prime minister of Canada and the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2003 to 2006.
Th ...
conceded defeat, and announced that he would resign as leader of the Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world.
The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left. For example, while the political systems ...
. At 9:30 a.m. on January 24, Martin informed Governor General
Governor-general (plural governors-general), or governor general (plural governors general), is the title of an official, most prominently associated with the British Empire. In the context of the governors-general and former British colonies, ...
Michaëlle Jean
Michaëlle Jean (; born September 6, 1957) is a Canadian former journalist who served as the 27th governor general of Canada from 2005 to 2010. She is the first Haitian Canadian and black person to hold this office.
Jean was the Organisation i ...
that he would not form a government and intended to resign as Prime Minister. Later that day, at 6:45 p.m., Jean invited Harper to form a government. Martin formally resigned and Harper was formally appointed and sworn in as Prime Minister on February 6.
Choosing not to take on the office of Leader of the Opposition
The Leader of the Opposition is a title traditionally held by the leader of the Opposition (parliamentary), largest political party not in government, typical in countries utilizing the parliamentary system form of government. The leader of the ...
, the first defeated Prime Minister who had retained his seat not to do so, Martin stepped down as parliamentary leader
A parliamentary leader is a political title or a descriptive term used in various countries to designate the person leading a parliamentary group or caucus in a legislature, legislative body, whether it be a national or sub-national legislature. ...
of his party on February 1, and the Liberal caucus appointed Bill Graham, MP for Toronto Centre and outgoing Defence Minister
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is the part of a government responsible for matters of defence and military forces, found in states where the government is divid ...
, as his interim successor. It was announced a month later that there would be a Liberal leadership convention later in the year, during which Stéphane Dion
Stéphane Maurice Dion (; ; born 28September 1955) is a Canadian diplomat, academic and former politician who has been the List of ambassadors of Canada to France, Canadian ambassador to France and Monaco since 2022 and special envoy to the Eu ...
won the leadership of the Liberal Party. Martin continued to sit as a Member of Parliament representing LaSalle—Émard
LaSalle—Émard was a federal electoral district in the Canadian province of Quebec that was represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1988 to 2015. Its population in 2001 was 99,767. The MP from 1988 to 2008 was Paul Martin, who serv ...
, the Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
-area riding he had held since 1988
1988 was a crucial year in the early history of the Internet—it was the year of the first well-known computer virus, the Morris worm, 1988 Internet worm. The first permanent intercontinental Internet link was made between the United State ...
, until his retirement in 2008.
Overall results
The elections resulted in a Conservative minority government with 124 seats in parliament with a Liberal opposition and a strengthened NDP. In his speech following the loss, Martin stated he would not lead the Liberal Party of Canada in another election. Preliminary results indicated that 64.9% of registered voters cast a ballot, a notable increase over 2004's 60.9%. The NDP won new seats in British Columbia and Ontario as their overall popular vote increased 2% from 2004. The Bloc managed to win almost as many seats as in 2004 despite losing a significant percentage of the vote. Most of the Conservatives' gains were in rural Ontario and Quebec as they took a net loss in the west, but won back the only remaining Liberal seat in Alberta. The popular vote of the Conservatives and Liberals were almost the mirror image of 2004, though the Conservatives were not able to translate this into as many seats as the Liberals did in 2004. A judicial recount was automatically scheduled in the Parry Sound-Muskoka riding, where early results showed ConservativeTony Clement
Tony Peter Clement ('' né'' Payani; born January 27, 1961) is a Canadian former politician in the federal and Ontario governments. He was Member of Parliament for Parry Sound-Muskoka and a federal cabinet minister in the Conservative Party ...
only 21 votes ahead of Liberal Andy Mitchell, because the difference of votes cast between the two leading candidates was less than 0.1%. Clement was confirmed as the winner by 28 votes.
Conservative candidate Jeremy Harrison, narrowly defeated by Liberal Gary Merasty
Gary Merasty (born September 22, 1964, in Winnipeg, Manitoba) is a Canadian politician and former Liberal Member of Parliament for Desnethé—Missinippi—Churchill River in northern Saskatchewan. A former two-time Grand Chief of the Prince ...
in the Saskatchewan riding of Desnethé—Missinippi—Churchill River by 72 votes, alleged electoral fraud but decided not to pursue the matter. A judicial recount was ordered in the riding, which certified Gary Merasty
Gary Merasty (born September 22, 1964, in Winnipeg, Manitoba) is a Canadian politician and former Liberal Member of Parliament for Desnethé—Missinippi—Churchill River in northern Saskatchewan. A former two-time Grand Chief of the Prince ...
the winner by a reduced margin of 68 votes.
Synopsis of results
: = went to a judicial recount : = Open seat : = turnout is above national average : = Incumbent had switched allegiance : = Previously incumbent in another riding : = Not incumbent; was previously elected to the House : = Incumbency arose from by-election gain : = other incumbents defeated : = changed allegiance immediately after election : = Multiple candidatesSummary analysis
Results by province

Notes
David Emerson, elected on January 23 as a Liberal in the British Columbia riding ofVancouver Kingsway
Vancouver Kingsway is a federal electoral district in British Columbia, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1953 to 1988 and since 1997. It is located in Vancouver.
Demographics
This riding's population is ...
, changed parties on February 6 to join the Conservatives before the new Parliament had taken office. He is reflected here as a Liberal.
André Arthur
André Arthur (December 21, 1943 – May 8, 2022) was a Canadian radio host and politician. He was the Independent politician, independent Parliament of Canada, Member of Parliament for the riding of Portneuf—Jacques-Cartier from 2006 to 2011. ...
was elected as an independent candidate in the Quebec riding of Portneuf—Jacques-Cartier
Portneuf—Jacques-Cartier (; formerly known as Portneuf) is a federal electoral district (Canada), electoral district in Quebec, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1867. Its population in 2001 was 87,141 ...
.
10 closest ridings
# Parry Sound-Muskoka, ON:Tony Clement
Tony Peter Clement ('' né'' Payani; born January 27, 1961) is a Canadian former politician in the federal and Ontario governments. He was Member of Parliament for Parry Sound-Muskoka and a federal cabinet minister in the Conservative Party ...
(Cons) def. Andy Mitchell (Lib) by 28 votes
# Desnethé—Missinippi—Churchill River, SK: Gary Merasty
Gary Merasty (born September 22, 1964, in Winnipeg, Manitoba) is a Canadian politician and former Liberal Member of Parliament for Desnethé—Missinippi—Churchill River in northern Saskatchewan. A former two-time Grand Chief of the Prince ...
(Lib) def. Jeremy Harrison (Cons) by 73 votes
# Winnipeg South
Winnipeg South () is a electoral district (Canada), Canadian federal electoral district in Manitoba, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1917 to 1979, and since 1988. It covers the southernmost part of the ...
, MB: Rod Bruinooge (Cons) def. Reg Alcock (Lib) by 111 votes
# Glengarry—Prescott—Russell, ON: Pierre Lemieux (Cons) def. René Berthiaume (Lib) by 203 votes
# Louis-Hébert, QC: Luc Harvey (Cons) def. Roger Clavet (BQ) by 231 votes
# St. Catharines
St. Catharines is the most populous city in Canada's Niagara Region, the eighth largest urban area in the province of Ontario. As of 2021, St. Catharines has an area of and 136,803 residents. It lies in Southern Ontario, south of Toronto ac ...
, ON: Rick Dykstra (Cons) def. Walt Lastewka (Lib) by 244 votes
# Tobique—Mactaquac
Tobique—Mactaquac is a federal electoral district in New Brunswick, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1997.
Political geography
The district includes the counties of Carleton and Victoria as well as ...
, NB: Mike Allen (Cons) def. Andy Savoy
Andy Savoy (born July 12, 1963) is a Canadian politician and engineer.
Early life
Savoy was raised in Victoria County in the Perth-Andover, New Brunswick area and educated at the University of New Brunswick in Fredericton where he earned a Bachel ...
(Lib) by 336 votes
# Thunder Bay—Superior North
Thunder is the sound caused by lightning. Depending upon the distance from and nature of the lightning, it can range from a long, low rumble to a sudden, loud crack. The sudden increase in temperature and hence pressure caused by the lightning pr ...
, ON: Joe Comuzzi
Joseph Robert Comuzzi, (April 5, 1933 – December 31, 2021) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as a cabinet minister under Prime Minister Paul Martin. He served as a Member of Parliament (MP) from 1988 to 2008, representing Thund ...
(Lib) def. Bruce Hyer (NDP) by 408 votes
# West Nova
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
, NS: Robert Thibault
Robert G. Thibault, (born September 29, 1959) is a Canadian politician.
Early life
Thibault was born in Digby, Nova Scotia in 1959. He is the grandson of former provincial politician, Joseph William Comeau.
Political career
Thibault served a ...
(Lib) def. Greg Kerr (Cons) by 511 votes
# Brant, ON: Lloyd St. Amand (Lib) def. Phil McColeman (Cons) by 582 votes
Results by region
* Results of the 2006 Canadian federal election by riding * Western Canada and Territories *Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
* Quebec and Atlantic Canada
See also
Articles on parties' candidates in this election: * Independents * Canadian Action *Communists
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, d ...
* Progressive Canadian Party
The Progressive Canadian Party (PC Party) () was a minor centre-right federal political party in Canada. It was registered with Elections Canada, the government's election agency, on March 29, 2004.
Under provisions of the Canada Elections Ac ...
* List of Canadian political scandals
* Libertarians
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according ...
* Marijuana Party
* Bloc Québécois
The Bloc Québécois (, , BQ) is a centre-left politics, centre-left and list of federal political parties in Canada, federal political party in Canada devoted to Quebec nationalism, Quebecois nationalism, social democracy, and the promotion o ...
* Conservatives
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilizati ...
* Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as environmentalism and social justice.
Green party platforms typically embrace Social democracy, social democratic economic policies and fo ...
* New Democrats
New Democrats may refer to:
* New Democratic Party, a social democratic party in Canada
* New Democrats (United States), the ideological centrist faction of the Democratic Party
** New Democrat Coalition, the related caucus in the United State ...
* Christian Heritage
* In and Out scandal
References
Further reading
* *External links
Election Prediction Project
– Vote by issue quiz
Government links
*Elections Canada
Elections Canada () is the non-partisan agency responsible for administering elections in Canada, Canadian federal elections and Referendums in Canada, referendums.
History
Elections Canada is an agency of the Parliament of Canada, and reports ...
br>nominations databaseNational media coverage
*First French Leaders' DebatWindows Media Video stream
Humour
by Graeme MacKay of ''The Hamilton Spectator''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Canadian federal election, 2006
2006
2006 was designated as the International Year of Deserts and Desertification.
Events
January
* January 1– 4 – Russia temporarily cuts shipment of natural gas to Ukraine during a price dispute.
* January 12 – A stampede during t ...
Federal
January 2006 in Canada