đÜđá1858đĺđť1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The U880 is an
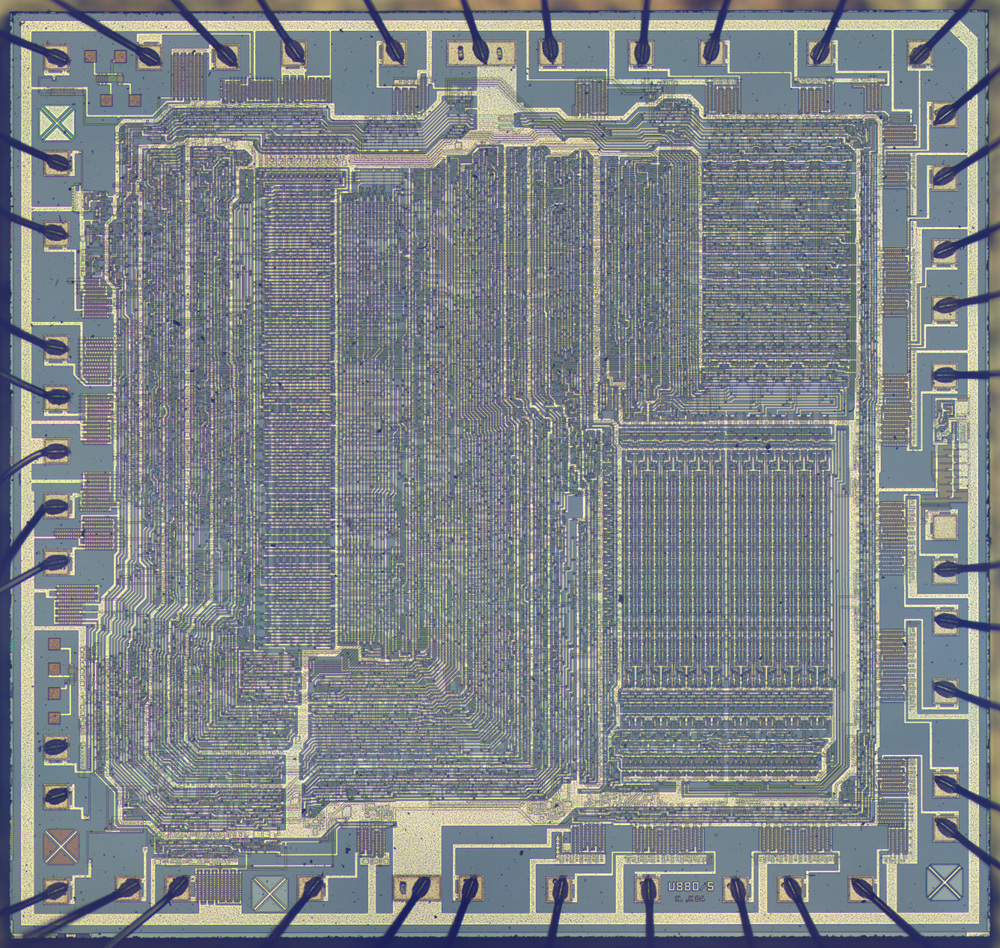 The U880 was manufactured in NMOS technology and encased in a plastic DIL40 package with a pin spacing of 2.5 mm (export versions had the Western pin spacing of 2.54 mm; Russian variants also came in a ceramic package).
The military version of the U880 has an additional "MEK 4" marking.
The U880 was manufactured in NMOS technology and encased in a plastic DIL40 package with a pin spacing of 2.5 mm (export versions had the Western pin spacing of 2.54 mm; Russian variants also came in a ceramic package).
The military version of the U880 has an additional "MEK 4" marking.
Image:Robotron UA880D MME 1.jpg, UA880D (1986)
Image:Robotron UB880D MME S1 1.jpg, UB880D S1 hobbyist version (1989)
Image:Robotron UB880D MME MEK4 1.jpg, UB880D with military "MEK 4" marking (1989)
Image:Robotron VB880D MME 1.jpg, VB880D industrial temperature version (1990)
Image:Robotron 80A CPU MME 1.jpg, 80A-CPU marking for export
Image:U880DC08 C3 FWE-L.jpg, U880DC08 (1992)
 VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" also manufactured a number of support chips for the U880. The prefixes UA, UB, VB, 80, and 80A correspond to the same temperature ranges and clock rates as for the processor variants above. Likewise, the suffix S1 indicates the out-of-spec, hobbyist version.
VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" also manufactured a number of support chips for the U880. The prefixes UA, UB, VB, 80, and 80A correspond to the same temperature ranges and clock rates as for the processor variants above. Likewise, the suffix S1 indicates the out-of-spec, hobbyist version.
 Following the example of Zilog where the Z80 was succeeded by the 16-bit processors Z8001 / Z8002, VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" produced the U8001 / U8002. And just like its Western counterpart, the U8001 / U8002 saw far less use than the U880. When
Following the example of Zilog where the Z80 was succeeded by the 16-bit processors Z8001 / Z8002, VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" produced the U8001 / U8002. And just like its Western counterpart, the U8001 / U8002 saw far less use than the U880. When
U880 Processors: images and descriptions from cpu-collection.de
{{Zilog Science and technology in East Germany Kombinat Mikroelektronik microprocessors 8-bit microprocessors
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data bu ...
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
that was manufactured by VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital (political), capital and largest city of the Central Germany (cultural area), Central German state of Thuringia, with a population of around 216,000. It lies in the wide valley of the Gera (river), River Gera, in the so ...
(abbreviated as MME; part of Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt
VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt was an important manufacturer of active electronic components in East Germany. It should not be confused with the more well-known VEB Kombinat Robotron Dresden which used integrated circuits from Kombinat ...
) in the German Democratic Republic
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
. Production of the U880 started in 1980 at VEB Funkwerk Erfurt (abbreviated as FWE; the plant was renamed to VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" in 1983). The U880 is an unlicensed clone of the Zilog
Zilog, Inc. is an American manufacturer of microprocessors, microcontrollers, and application-specific embedded System on a chip, system-on-chip (SoC) products.
The company was founded in 1974 by Federico Faggin and Ralph Ungermann, who were soo ...
Z80
The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog that played an important role in the evolution of early personal computing. Launched in 1976, it was designed to be software-compatible with the Intel 8080, offering a compelling altern ...
microprocessor, also supporting illegal opcodes and bugs, except for very minor differences like not setting the CY flag for the command (when L goes zero).
Processor variants
 The U880 was manufactured in NMOS technology and encased in a plastic DIL40 package with a pin spacing of 2.5 mm (export versions had the Western pin spacing of 2.54 mm; Russian variants also came in a ceramic package).
The military version of the U880 has an additional "MEK 4" marking.
The U880 was manufactured in NMOS technology and encased in a plastic DIL40 package with a pin spacing of 2.5 mm (export versions had the Western pin spacing of 2.54 mm; Russian variants also came in a ceramic package).
The military version of the U880 has an additional "MEK 4" marking.
Support chips
 VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" also manufactured a number of support chips for the U880. The prefixes UA, UB, VB, 80, and 80A correspond to the same temperature ranges and clock rates as for the processor variants above. Likewise, the suffix S1 indicates the out-of-spec, hobbyist version.
VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" also manufactured a number of support chips for the U880. The prefixes UA, UB, VB, 80, and 80A correspond to the same temperature ranges and clock rates as for the processor variants above. Likewise, the suffix S1 indicates the out-of-spec, hobbyist version.
Applications
The U880 was by far the most widely used microprocessor in the German Democratic Republic. Examples are: * office computersA 5120
The A 5120 was an office computer produced by VEB Robotron in Karl-Marx-Stadt (now Chemnitz), East Germany starting in 1982. The system featured an 8-bit microprocessor, the U880. It was built for office work and had minimal graphics and sound cap ...
, PC 1715
The PC 1715 was an office computer produced by VEB Robotron in East Germany starting in 1985. The system featured an 8-bit microprocessor, the U880, a clone of the Zilog Z80. It was built for office work and education, but was also put to some sp ...
(both by VEB Robotron
VEB Kombinat Robotron () (or simply Robotron) was the largest East German electronics manufacturer. It was headquartered in Dresden and employed 68,000 people in 1989. Its products included personal computers, SM EVM minicomputers, the ESER m ...
), the 1715 used a second U880 just for the keyboard.
* home computers KC 85
The KC 85 ('KC' meaning "Kleincomputer", or "small computer") were models of microcomputers (KC 85/2, KC 85/3 and KC 85/4) built in East Germany by VEB Mikroelektronik "Wilhelm Pieck" M├╝hlhausen. The first model in the series, the HC 900, origi ...
, KC compact (both by VEB Mikroelektronik "Wilhelm Pieck" M├╝hlhausen), KC 87, Z1013 (both by VEB Robotron), LC80 by Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt
VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt was an important manufacturer of active electronic components in East Germany. It should not be confused with the more well-known VEB Kombinat Robotron Dresden which used integrated circuits from Kombinat ...
* arcade game Poly Play
''Poly-Play'' is an arcade cabinet developed in East Germany in 1985 in video gaming, 1985; it is the only such machine to originate in the GDR. It was created by VEB Polytechnik and contained a number of games, including a ''Pac-Man'' clone.
A ...
(by VEB Polytechnik
VEB Polytechnik was a company from the German Democratic Republic (GDR) located in Chemnitz (then called Karl-Marx-Stadt). In the GDR, it was mainly known for producing overhead projector
An overhead projector (often abbreviated to OHP), lik ...
)
At the time the U880 was the most advanced 8-bit processor available in the Eastern Bloc. Only clones of the Intel 8080
The Intel 8080 is Intel's second 8-bit computing, 8-bit microprocessor. Introduced in April 1974, the 8080 was an enhanced successor to the earlier Intel 8008 microprocessor, although without binary compatibility.'' Electronic News'' was a week ...
were manufactured in Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and the Soviet Union. As the Z80 replaced the Intel 8080 in the West, the U880 was used throughout the Eastern Bloc. Examples are:
* Poland: home computers Mera-Elzab Meritum, , Elwro 800 Junior,
* Czechoslovakia: home computers Didaktik Gama
The Didaktik was a series of 8-bit home computers based on the clones of Intel 8080 and Zilog Z80 processors produced by Didaktik in Skalica, in the former Czechoslovakia.
Initially the company produced PMD 85 compatible machines aimed at schools ...
, Tesla Ondra
* Hungary: home computer
* Romania: home computers Electromagnetica JET, , , Feper Junior
* Bulgaria: office computer
* Soviet Union: home computer Dubna 48K
Further development
 Following the example of Zilog where the Z80 was succeeded by the 16-bit processors Z8001 / Z8002, VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" produced the U8001 / U8002. And just like its Western counterpart, the U8001 / U8002 saw far less use than the U880. When
Following the example of Zilog where the Z80 was succeeded by the 16-bit processors Z8001 / Z8002, VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" produced the U8001 / U8002. And just like its Western counterpart, the U8001 / U8002 saw far less use than the U880. When MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
emerged as the dominant operating system for personal computers, in the Eastern Bloc the only available clone of the Intel 8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit computing, 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-b ...
was the Soviet K1810VM86
The K1810VM86 () is a Soviet 16-bit microprocessor, a clone of the Intel 8086 CPU with which it is binary and pin compatible. It was developed between 1982 and 1985. The original K1810VM86 supported a clock frequency of up to 5 MHz while up ...
. VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" then proceeded to develop a clone of the Intel 80286
The Intel 80286 (also marketed as the iAPX 286 and often called Intel 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor that was introduced on February 1, 1982. It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non- multiplexed address and data buses and also the f ...
, the U80601
The U80601 was a 16-bit microprocessor made in 1989-1990 by Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt in the former German Democratic Republic of East Germany. It was manufactured in NMOS technology and encased in a PLCC or ceramic (CLCC) package (firs ...
. Furthermore, a CMOS version of the Z80 was developed with the designation U84C00. Due to the economic changes following the German reunification
German reunification () was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single sovereign state, which began on 9 November 1989 and culminated on 3 October 1990 with the dissolution of the East Germany, German Democratic Republic and the int ...
in 1990, neither project proceeded beyond pilot production. VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" (MME) was privatized in 1990 under the name ERMIC GmbH, a large part of which became Thesys Gesellschaft f├╝r Mikroelektronik mbH in 1992. Both ERMIC and Thesys continued to manufacture the NMOS version of the U880, ERMIC still with the MME name and logo, Thesys under its new name. A die shrink
The term die shrink (sometimes optical shrink or process shrink) refers to the List of semiconductor scale examples, scaling of metalÔÇôoxideÔÇôsemiconductor (MOS) devices. The act of shrinking a Die (integrated circuit), die creates a somewhat ...
chip with the marking U880/6 had been developed in 1990 and went into production some time after that. The smaller chip allowed clock rates up to 8 MHz for the U880DC08 and Thesys Z80H. While Zilog likely could have taken up legal action against the successors of VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" for copyright infringement, they recruited Thesys as a Zilog distributor instead.
From about 1991 until 1993, bare U880 chips were sold to Russian and Ukrainian companies and packaged there. Initially the U880/5 chip revision was labelled as 80A-CPU and (). Later integrated circuits with U880/6 chips inside received the official designation () for the plastic package and KM1858VM1 () for the ceramic package. Manufacturers include Angstrem Zelenograd
Zelenograd (, , ) is a city and administrative okrug of Moscow, Russia. The city of Zelenograd and the territory under its jurisdiction form the Zelenogradsky Administrative Okrug (ZelAO), an exclave located within Moscow Oblast, north-west ...
, Kvazar Kiev, and VZPP Voronesh.
References
Further reading
External links
U880 Processors: images and descriptions from cpu-collection.de
{{Zilog Science and technology in East Germany Kombinat Mikroelektronik microprocessors 8-bit microprocessors