|
İpsala
İpsala (, ) is a town and district of Edirne Province in northwestern Turkey. It is the location of one of the main border checkpoints between Greece and Turkey. (The Greek town opposite İpsala is Kipoi.) The population is 8,332 (the city) and 30,112 (whole district). The state road (European route ) connects the border checkpoint İpsala with Tekirdağ at the coast of Marmara Sea. History In Roman and Byzantine times, this was the town of Cypsela, which belonged to the Roman province of Rhodope, whose capital and metropolitan see was Traianopolis. From the 7th century onward, the bishopric of Cypsela, initially a suffragan of Traianopolis, appears in the ''Notitiae Episcopatuum'' as an autocephalous archdiocese. Its bishops Georgius and Theophylactus were present respectively at the Second Council of Constantinople (553) and the Second Council of Nicaea (787). Stephanus was at both the Council of Constantinople (869) and the Council of Constantinople (879). No longe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kipoi, Evros
Kipoi or Kipi ( el, Κήποι) is a village in Feres municipal unit, Evros regional unit in northeastern Greece. A major motorway border crossing between Greece and Turkey is located here. The town on the Turkish side is İpsala. Kipoi was known as "Bahçeköy" ("Garden Village") or "Alibeyçiftliği" ("Ali Bey's Farm") during Ottoman rule. The settlements was created with the migration of Arvanites from Turkey in 1923. They largely originate from the inhabitants of the villages of Qytezë and Sultanköy. Kipoi is located on the right bank of the river Evros which forms the border between Greece and Turkey. The Kipoi border crossing is the eastern starting/ending point of European route E90 European route E 90 is an A-Class West–East European route, extending from Lisbon in Portugal in the west to the Turkish– Iraqi border in the east. It is connected to the M5 of the Arab Mashreq International Road Network Itinerary ... which is also the Greek Motorway A2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypsela (Thrace)
Cypsela or Kypsela ( grc, Κυψέλα or Κύψελα), was an ancient Greek town on the river Hebrus in ancient Thrace, which was once an important place on the Via Egnatia The Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a contin .... Antiochus besieged Cypsela and its citizens surrendered and became allies with Antiochus. Its site is located near the modern İpsala. See also * Greek colonies in Thrace References Populated places in ancient Thrace Former populated places in Turkey Greek colonies in Thrace History of Edirne Province {{Edirne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
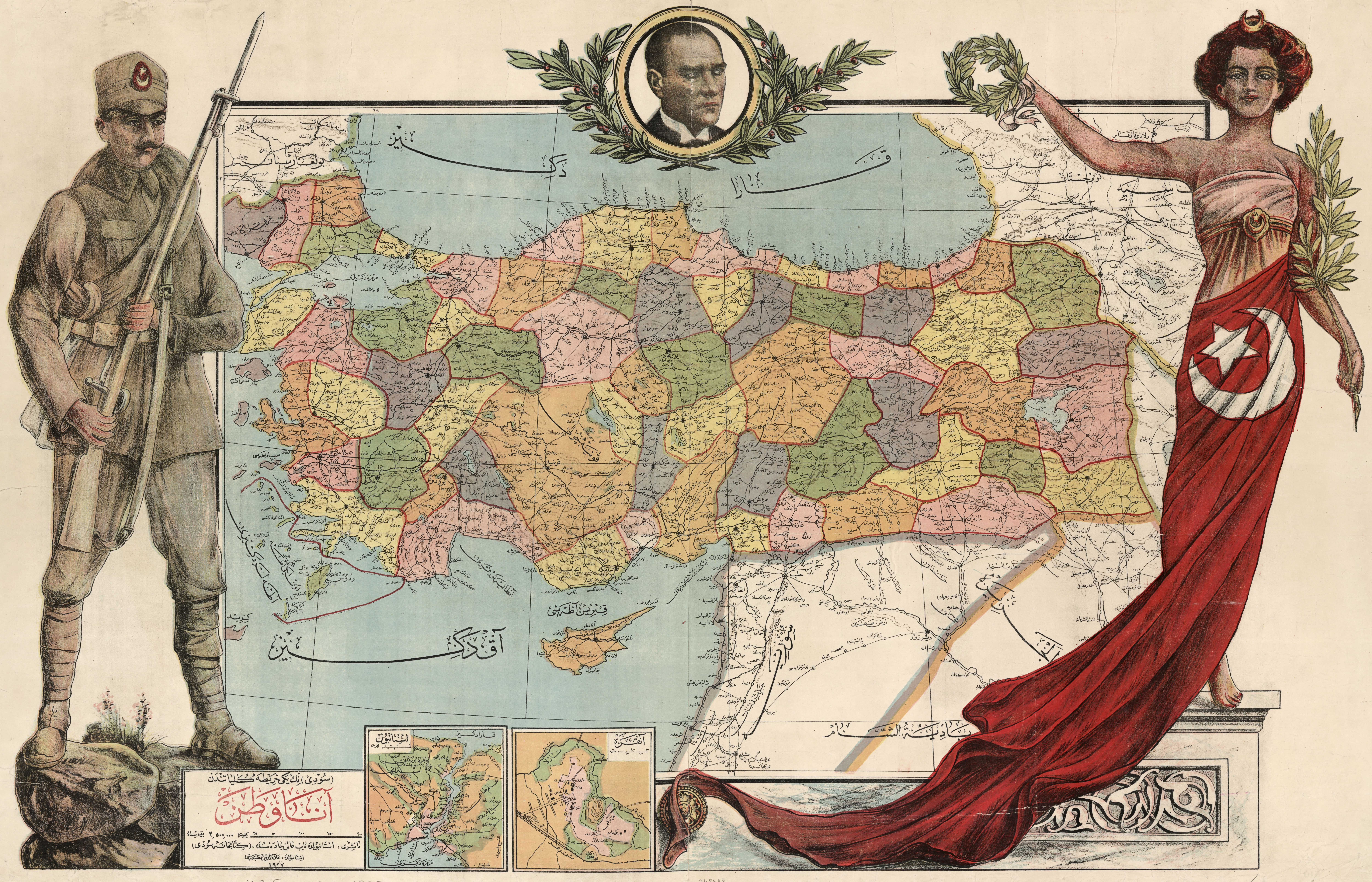
Edirne Province
Edirne Province ( tr, ) is a Turkish province located in East Thrace. Part of European Turkey, it is one of only three provinces located entirely within continental Europe. Edirne Province is bordered by Tekirdağ Province and Kırklareli Province to the east, and the Gallipoli peninsula of Çanakkale Province to the south-east. It shares international borders with Bulgaria (Haskovo and Yambol Provinces) to the north and Greece (Eastern Macedonia and Thrace) to the west. Edirne is the capital of the province, and the largest city. History Edirne, capital of the province is notable for serving as the third capital of the Ottoman Empire from 1363 to 1453. Edirne province was included in the Second Inspectorate General which was created on the 19 February 1934 and extended over the provinces of Edirne, Çanakkale, Kırklareli, Tekirdağ. It was ruled by an Inspector General, who had wide-ranging authorities over civilian, military and educational matters. The office of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Turkey
Turkey is divided into 81 provinces ( tr, il). Each province is divided into a number of districts (). Each provincial government is seated in the central district (). For non- metropolitan municipality designated provinces, the central district bears the name of the province (e.g. the city/district of Rize is the central district of Rize Province). Each province is administered by an appointed governor () from the Ministry of the Interior. List of provinces Below is a list of the 81 provinces of Turkey, sorted according to their license plate codes. Initially, the order of the codes matched the alphabetical order of the province names. After Zonguldak (code 67), the ordering is not alphabetical, but in the order of the creation of provinces, as these provinces were created more recently and thus their plate numbers were assigned after the initial set of codes had been assigned. Codes The province's ISO code suffix number, the first two digits of the vehicle regis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traianopolis (Thrace)
Traianoupoli ( el, Τραϊανούπολη) or Traianopolis or Trajanopolis was a medieval settlement in the 14th century in the Evros regional unit of East Macedonia and Thrace region, northeastern Greece, nowadays named Loutra Traianopouleos. Traianoupoli was also the name of a municipality which existed between 1997 and 2011 following the Kapodistrias Plan. Modern town Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Alexandroupoli, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 163.549 km2. Population 2,706 (2011). The seat of the municipality is in Antheia. Subdivisions The municipal unit Traianoupoli is subdivided into the following communities (''constituent villages given in parenthesis): * Antheia (Antheia, Aristino) * Doriko (Doriko, Aetochori) * Loutros (Loutros, Loutra Traianopouleos, Pefka) * Nipsa History The city was founded by the Roman emperor Trajan (r. 98–117) near the ancient town of Doriscus, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titular See
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbishop" (intermediary rank) or "titular bishop" (lowest rank), which normally goes by the status conferred on the titular see. Titular sees are dioceses that no longer functionally exist, often because the territory was conquered by Muslims or because it is schismatic. The Greek–Turkish population exchange of 1923 also contributed to titular sees. The see of Maximianoupolis along with the town that shared its name was destroyed by the Bulgarians under Emperor Kaloyan in 1207; the town and the see were under the control of the Latin Empire, which took Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade in 1204. Parthenia, in north Africa, was abandoned and swallowed by desert sand. Catholic Church During the Muslim conquests of the Middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies located List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Constantinople (879)
The Fourth Council of Constantinople was held in 879–880. It confirmed the reinstatement of Photius I as patriarch of Constantinople. The result of this council is accepted by some Eastern Orthodox as having the authority of an ecumenical council, who sometimes call it the eighth ecumenical council. Background The Council settled the dispute that had broken out after the deposition of Ignatius as Patriarch of Constantinople in 858. Ignatius, himself appointed to his office in an uncanonical manner, opposed Caesar Bardas, who had deposed the regent Theodora. In response, Bardas' nephew, the youthful Emperor Michael III engineered Ignatius's deposition and confinement on the charge of treason. The patriarchal throne was filled with Photius, a renowned scholar and kinsman of Bardas. The deposition of Ignatius without a formal ecclesiastical trial and the sudden promotion of Photios caused scandal in the church. Pope Nicholas I and the western bishops took up the cause of Igna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Constantinople (869)
The Fourth Council of Constantinople was the eighth ecumenical council of the Catholic Church held in Constantinople from October 5, 869, to February 28, 870. It was poorly attended, the first session by only 12 bishops and the number of bishops later never exceeded 103. In contrast the pro-Photian council of 879–80 was attended by 383 bishops. The Council met in ten sessions from October 869 to February 870 and issued 27 canons. The council was called by Emperor Basil I the Macedonian, with the support of Pope Hadrian II."Photius." Cross, F. L., ed. The Oxford dictionary of the Christian church. New York: Oxford University Press. 2005 It deposed Photius, a layman who had been appointed as Patriarch of Constantinople, and reinstated his predecessor Ignatius. The Council also reaffirmed the decisions of the Second Council of Nicaea in support of icons and holy images and required the image of Christ to have veneration equal with that of the gospel book.Steven Bigham, 1995 '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Council Of Nicaea
The Second Council of Nicaea is recognized as the last of the first seven ecumenical councils by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. In addition, it is also recognized as such by the Old Catholics, the Anglican Communion, and others. Protestant opinions on it are varied. It met in AD 787 in Nicaea (site of the First Council of Nicaea; present-day İznik, Bursa, in Turkey), to restore the use and veneration of icons (or holy images),Gibbon, p.1693 which had been suppressed by imperial edict inside the Byzantine Empire during the reign of Leo III (717–741). His son, Constantine V (741–775), had held the Council of Hieria to make the suppression official. Background The veneration of icons had been banned by Byzantine Emperor Constantine V and supported by his Council of Hieria (754 AD), which had described itself as the seventh ecumenical council. The Council of Hieria was overturned by the Second Council of Nicaea only 33 years later, and has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Council Of Constantinople
The Second Council of Constantinople is the fifth of the first seven ecumenical councils recognized by both the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. It is also recognized by the Old Catholics and others. Protestant opinions and recognition of it are varied. Some Protestants, such as Calvinists, recognize the first four councils, whereas Lutherans and most Anglo-Catholics accept all seven. Constantinople II was convoked by the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I under the presidency of Patriarch Eutychius of Constantinople. It was held from 5 May to 2 June 553. Participants were overwhelmingly Eastern bishops—only sixteen Western bishops were present, including nine from Illyricum and seven from Africa, but none from Italy—out of the 152 total. * (3 names, 3 bishops and 145 other, plus 1 pope, total 152) The main work of the council was to confirm the condemnation issued by edict in 551 by the Emperor Justinian against the Three Chapters. These were the Christo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

