|
Đại Nam Thực Lục
''Đại Nam thực lục'' ( vi-hantu, 大南寔錄, lit. "Veritable Records of the Great South", "Annals of Đại Nam", "Chronicle of Greater Vietnam") was the official history of Nguyễn dynasty, Vietnam. It contained the royal records of the Nguyễn lords, and the imperial annals of Nguyễn dynasty emperors up until Khải Định. Just like other official histories, ''Đại Nam thực lục'' was written in Classical Chinese. The annals comprised 584 volumes. At first the records were called "''Đại Nam thật lục''" "". During Thiệu Trị's reign however, "" was changed to "", and its pronunciation changed to "thực", because "實" was against the naming taboo of Empress Tá Thiên, Thiệu Trị's mother. ''Đại Nam thực lục'' was the most important primary source regarding the Nguyễn dynasty. It was an important reference of Cao Xuân Dục's ''Quốc triều chính biên toát yếu'' and Trần Trọng Kim's ''Việt Nam sử lược''. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quốc Sử Quán
Quốc is a Vietnamese given name. Notable people with the name include: * Nguyễn Quốc Cường (born 1982), Vietnamese politician * Quốc Thiên (born 1988), Vietnamese singer * Trần Quốc Khang (1237–1300), Vietnamese prince * Trần Quốc Tảng (died 1313), Vietnamese general * Trần Quốc Toản (1267–1285), Vietnamese marquis * Trần Quốc Tuấn (1228–1300), Vietnamese general {{DEFAULTSORT:Quoc Vietnamese names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minh Mạng
Minh Mạng () or Minh Mệnh (, vi-hantu, 明 命, lit. "the bright favour of Heaven"; 25 May 1791 – 20 January 1841; born Nguyễn Phúc Đảm, also known as Nguyễn Phúc Kiểu) was the second emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty of Vietnam, reigning from 14 February 1820 until his death, on 20 January 1841. He was the fourth son of Emperor Gia Long, whose eldest son, Nguyễn Phúc Cảnh, had died in 1801. He was well known for his opposition to French involvement in Vietnam and his rigid Confucian orthodoxy. Early years Born Nguyễn Phúc Đảm at Gia Định in the middle of the Second Tây Sơn – Nguyễn War, Minh Mạng was the fourth son of lord Nguyễn Phúc Ánh – future Emperor Gia Long. His mother was Gia Long's second wife Trần Thị Đang (historically known as Empress Thuận Thiên). At the age of three, under the effect of a written agreement made by Gia Long with his first wife Tống Thị Lan (Empress Thừa Thiên), he was taken in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Khoát
Nguyễn Phúc Khoát (26 September 1714 – 7 July 1765) was one of the Nguyễn lords who ruled over the southern portion of Vietnam from the 16th–18th centuries. Also known as Chúa Võ (主武) or Võ vương (武王) (roughly ''Martial Prince''), he continued the southern expansion undertaken by his predecessor as lord, Nguyễn Phúc Trú. Provinces and districts originally belonging to Cambodia were taken by Vo Vuong. The Vietnamese-Cambodian border established by the end of his reign remains the border today. In 1747, Vo Vuong sent a number of Vietnamese warriors to aid rebel princes of Cambodia against the newly crowned Cambodian King Ang Tong. These forces seized Sóc Trăng and then moved towards Oudong, then royal capital of Cambodia. Ang Tong requested aid from Mạc Thiên Tứ, who secured a truce with the Nguyễn lord, in exchange for a few more provinces, namely Gò Công and Tân An. Ten years later, the Cambodian throne was seized by Outey II, with the help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Chú
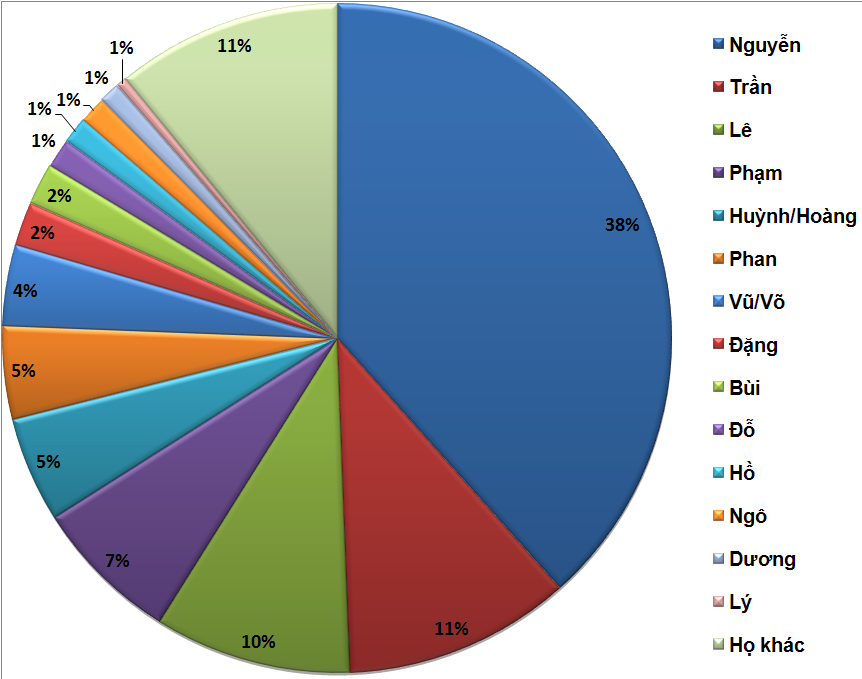
Nguyễn () is the most common Vietnamese surname. Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as Nguyen. Nguyên (元)is a different word and surname. By some estimates 39 percent of Vietnamese people bear this surname.Lê Trung Hoa, ''Họ và tên người Việt Nam'', NXB Khoa học - Xã hội, 2005 Origin and usage "Nguyễn" is the spelling of the Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation of the Han character 阮 (, ). The same Han character is often romanized as ''Ruǎn'' in Mandarin, ''Yuen'' in Cantonese, ''Gnieuh'' or ''Nyoe¹'' in Wu Chinese, or ''Nguang'' in Hokchew. . Hanja reading ( Korean) is 완 (''Wan'') or 원 (''Won'') and in Hiragana, it is げん (''Gen''), old reading as け゚ん (Ngen). The first recorded mention of a person surnamed Nguyen is a 317 CE description of a journey to Giao Châu undertaken by Eastern Jin dynasty (, ) officer and his family. Many events in Vietnamese history have contributed to the name's prominence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Chu
Nguyễn Phúc Chu ( vi-hantu, , 1675 – 1 June 1725) was one of the Nguyễn lords who ruled southern Vietnam (Dang Trong) from 1691 to 1725.Anh Thư Hà, Hồng Đức Trần ''A Brief Chronology of Vietnam's History'' 2000 Page 163 "Nguyễn Phúc Tăn was previously wrongly referred to as Nguyễn Phúc Trãn6. Lord Nguyễn Phúc Chu (Quốc Chúa) (1691-1725) Nguyễn Phúc Chu was born in 1675. He was the eldest son of Nguyễn Phúc Thái." During his time in power, he had to deal with a Champa rebellion and the first major war against the Cambodians. Nguyễn Phúc Chu was the eldest son of Nguyễn Phúc Trăn. He gained the throne on his father's early death, at just 15 years old. He took for himself the title ''Tong Quan-Cong'' (Duke of Tong). Early in his reign the Champa ruler of Panduranga (in present-day Ninh Thuận), Po Sot, began a rebellion against the Nguyễn. The revolt was at first unsuccessful and after the Nguyễn army put down the revolt there was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Thái
Nguyễn () is the most common Vietnamese surname. Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as Nguyen. Nguyên (元)is a different word and surname. By some estimates 39 percent of Vietnamese people bear this surname.Lê Trung Hoa, ''Họ và tên người Việt Nam'', NXB Khoa học - Xã hội, 2005 Origin and usage "Nguyễn" is the spelling of the Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation of the Han character 阮 (, ). The same Han character is often romanized as ''Ruǎn'' in Mandarin, ''Yuen'' in Cantonese, ''Gnieuh'' or ''Nyoe¹'' in Wu Chinese, or ''Nguang'' in Hokchew. . Hanja reading ( Korean) is 완 (''Wan'') or 원 (''Won'') and in Hiragana, it is げん (''Gen''), old reading as け゚ん (Ngen). The first recorded mention of a person surnamed Nguyen is a 317 CE description of a journey to Giao Châu undertaken by Eastern Jin dynasty (, ) officer and his family. Many events in Vietnamese history have contributed to the name's prominence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Tần
Nguyễn Phúc Tần (; 18 July 1620 – 30 April 1687) was one of the Nguyễn lords who ruled south Vietnam from the city of Phú Xuân (modern-day Huế) from 1648 to 1687. During his rule, the Trịnh–Nguyễn War came to an end. During his reign, he annexed nearly all the remaining Champa lands. Phuc Tan was the second son of Nguyễn Phúc Lan. Lan died just before Trịnh Tráng made yet another effort to conquer the southern provinces. Phuc Lan took the title ''Duong Quan-Cong'' (Duke of Duong). Biography Shortly after his father's death, Trịnh Tráng launched his final offensive against the Nguyễn. But in a climactic battle, called Truong Duc, the Royal (Trịnh) army was destroyed. At the same time the Lê Emperor (Lê Chan Tông) died, possibly as a result of being at the battle. This defeat was devastating for the Trịnh and the Nguyễn clan's generals planned to further the success and conquer the Imperial Capital. Four years after the battle, the Nguyễn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Lan
Nguyễn Phúc Lan (; 13 August 1601 – 19 March 1648) was one of the Nguyễn lords who ruled south Vietnam from the city of Phú Xuân (modern-day Huế) from 1635 to 1648. During his rule the Trịnh–Nguyễn War continued. Nguyễn Phúc Lan was the second son of Nguyễn Phúc Nguyên. His father died in the midst of the war by Trịnh Tráng to conquer the southern provinces. Unwilling to make peace, Nguyễn Phúc Lan continued his father's policies of maintaining a strong defensive position on the great walls while continuing friendly relations with the Portuguese and expanding south into Cambodian and Champa territory. Following after his grandfather, he took the title of Vuong (Prince/Lord), calling himself ''Cong-Thuong Vuong''. In 1640, famed Jesuit missionary Alexandre de Rhodes returned to Vietnam, this time to the Nguyễn court at Phú Xuân. He had been forced to leave the court at Hanoi ten years earlier but now he was back, reasoning correctly that rules a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Nguyên
Nguyễn Phúc Nguyên (阮福源; 16 August 1563 – 19 November 1635) was an early Nguyễn lord who ruled the southern Vietnam from the city of Phú Xuân (modern-day Huế) from 1613 to 1635. During his rule, the Nguyễn established a city at modern-day Saigon. Later, his refusal to pay tribute to the court in Hanoi sparked the Trịnh–Nguyễn War. Biography Nguyễn Phúc Nguyên was the sixth son of Nguyễn Hoàng. Upon the death of his father, Nguyễn Phúc Nguyên took over the rule of the southern provinces of Vietnam. He continued his father's policy of refusing to submit to the authority of the court in Hanoi, dominated at this time by his cousin, Trịnh Tùng. Unlike his father he did not take the title Vuong but instead called himself ''Nhon Quoc-Cong'' (roughly Duke of the Southern Provinces). Encourage foreign trade Starting as early as 1615, Nguyễn Phúc Nguyên allowed Portuguese merchants to set up a trading post at Faifo (modern-day Hội An).Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Hoàng
Nguyễn Hoàng (28 August 1525 – 20 July 1613) was the first of the Nguyễn lords who ruled the southern provinces of Vietnam between 1558 and 1613, from a series of cities: Ai Tu (1558–70), Tra Bat (1570–1600), and Dinh Cat (modern-day Huế) (1600–13). Early life He was the second son of Nguyễn Kim. When his father was assassinated by a Mạc supporter, his brother-in-law Trịnh Kiểm took command of the Lê royalist army. Sometime after his older brother (Nguyễn Uông) died (believed to have been poisoned), Nguyễn Hoàng requested his brother in law, and was appointed to govern the southernmost province of Vietnam. This land was formerly Champa territory which had been conquered by emperor Lê Thánh Tông and at the time was under control of Mạc force. Nguyễn Hoàng defeated the enemy commander Duke Lập and took over the province in 1558. In 1573 he was given the title Grand Master (Thái phó) by Emperor Lê Thế Tông. Later he was given the title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Censorship
Political censorship exists when a government attempts to conceal, fake, distort, or falsify information that its citizens receive by suppressing or crowding out political news that the public might receive through news outlets. In the absence of neutral and objective information, people will be unable to dissent with the government or political party in charge. The term also extends to the systematic suppression of views that are contrary to those of the government in power. The government often possesses the power of the army and the secret police, to enforce the compliance of journalists with the will of the authorities to spread the story that the ruling authorities want people to believe. At times this involves bribery, defamation, imprisonment, and even assassination. The word censorship comes from the Latin word censor, the job of two Romans whose duty was to supervise public behaviour and morals, hence 'censoring' the way people acted. Journalist prison census Accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Shilu
The ''Ming Shilu'' () contains the imperial annals of the emperors of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). It is the single largest historical source for the dynasty. According to modern historians, it "plays an extremely important role in the historical reconstruction of Ming society and politics." After the fall of the Ming dynasty, the ''Ming Shilu'' was used as a primary source for the compilation of the ''History of Ming'' by the Qing dynasty. Historical sources The Veritable Records (''shilu'') for each emperor was composed after the emperor's death by a History Office appointed by the Grand Secretariat The Grand Secretariat (; Manchu: ''dorgi yamun'') was nominally a coordinating agency but ''de facto'' the highest institution in the imperial government of the Chinese Ming dynasty. It first took shape after the Hongwu Emperor abolished the o ... using different types of historical sources such as: # "The Qiju zhu (), or 'Diaries of Activity and Repose'. These were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |