|
Voting Rights In The United States
Voting rights, specifically Suffrage, enfranchisement and disenfranchisement of different groups, have been a moral and political issue throughout United States history. Eligibility to vote in the United States is governed by the United States Constitution and by federal and state laws. Several constitutional amendments (the Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Fifteenth, Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Nineteenth, and Twenty-sixth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Twenty-sixth specifically) require that voting rights of U.S. citizens cannot be abridged on account of race, color, previous condition of servitude, sex, or age (18 and older); the constitution as originally written did not establish any such rights during 1787–1870, except that if a state permitted a person to vote for the "most numerous branch" of its state legislature, it was required to permit that person to vote in elections for members of the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
At-large
At large (''before a noun'': at-large) is a description for members of a governing body who are elected or appointed to represent a whole membership or population (notably a city, county, state, province, nation, club or association), rather than a subset. In multi-hierarchical bodies, the term rarely extends to a tier beneath the highest division. A contrast is implied, with certain electoral districts or narrower divisions. It can be given to the associated territory, if any, to denote its undivided nature, in a specific context. Unambiguous synonyms are the prefixes of cross-, all- or whole-, such as cross-membership, or all-state. The term is used as a suffix referring to specific members (such as the U.S. congressional Representative/the Member/Rep. for Wyoming ''at large''). It figures as a generic prefix of its subject matter (such as Wyoming is an at-large U.S. congressional district, at present). It is commonly used when making or highlighting a direct contrast with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winner-take-all System
A winner-take-all (or winner-takes-all) electoral system is one where a voting bloc can win all seats in a legislature or electoral district, denying representation to any political minorities. Such systems are used in many major democracies. Such systems are sometimes called "majoritarian representation", though this term is a misnomer, as most such systems do not always elect majority preferred candidates and do not always produce winners who received majority of votes cast in the district, and they allow parties to take a majority of seats in the chamber with just a minority of the vote. Any election with only a single seat is a winner-take-all system (as it is impossible for the winner to take less than one seat). As a result, legislatures elected by single-member districts are often described as using "winner-take-all". However, winner-take-all systems do not necessarily mean the majority of voters are represented properly. A minority of voters across the country may take all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Electoral College
In the United States, the Electoral College is the group of presidential electors that is formed every four years for the sole purpose of voting for the President of the United States, president and Vice President of the United States, vice president in the United States presidential election, presidential election. This process is described in Article Two of the United States Constitution, Article Two of the Constitution. The number of electors from each U.S. state, state is equal to that state's United States congressional apportionment, congressional delegation which is the number of List of current United States senators, senators (two) plus the number of US Representatives, Representatives for that state. Each state Article II of the United States Constitution#Clause 2: Method of choosing electors, appoints electors using legal procedures determined by its State legislature (United States), legislature. Federal government of the United States, Federal office holders, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wesberry V
''Wesberry v. Sanders'', 376 U.S. 1 (1964), was a landmark U.S. Supreme Court case in which the Court ruled that districts in the United States House of Representatives must be approximately equal in population. Along with '' Baker v. Carr'' (1962) and ''Reynolds v. Sims'' (1964), it was part of a series of Warren Court cases that applied the principle of "one person, one vote" to U.S. legislative bodies. Article One of the United States Constitution requires members of the U.S. House of Representatives to be apportioned by population among the states, but it does not specify exactly how the representatives from each state should be elected. The case arose from a challenge to the unequal population of congressional districts in the state of Georgia. In his majority opinion, which was joined by five other justices, Associate Justice Hugo Black held that Article One required that "as nearly as practicable one man's vote in a congressional election is to be worth as much as anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baker V
A baker is a tradesperson who bakes and sometimes sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery. History Ancient history Since grains have been a staple food for millennia, the activity of baking is a very old one. Control of yeast, however, is relatively recent.Wayne Gisslen, ''Professional Baking'' (4th ed.: John Wiley & Sons, 2005), p. 4. By the fifth and sixth centuries BCE, the ancient Greeks used enclosed ovens heated by wood fires; communities usually baked bread in a large communal oven. Greeks baked dozens and possibly hundreds of types of bread; Athenaeus described seventy-two varieties. In ancient Rome several centuries later, the first mass production of breads occurred, and "the baking profession can be said to have started at that time." Ancient Roman bakers used honey and oil in their products, creating pastries rather than breads. In ancient Rome, bak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren Court
The Warren Court was the period in the history of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1953 to 1969 when Earl Warren served as the chief justice. The Warren Court is often considered the most liberal court in U.S. history. The Warren Court expanded civil rights, civil liberties, judicial power, and the federal power in dramatic ways. It has been widely recognized that the court, led by the liberal bloc, created a major " Constitutional Revolution" in U.S. history. The Warren Court brought "one man, one vote" to the United States through a series of rulings, and created the Miranda warning. In addition, the court was both applauded and criticized for bringing an end to ''de jure'' racial segregation in the United States, incorporating the Bill of Rights (i.e. including it in the 14th Amendment Due Process clause), and ending officially sanctioned voluntary prayer in public schools. The period is recognized as the most liberal point that judicial power had ever reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One Man, One Vote
"One man, one vote" or "one vote, one value" is a slogan used to advocate for the principle of equal representation in voting. This slogan is used by advocates of democracy and political equality, especially with regard to electoral reforms like universal suffrage, direct elections, and proportional representation. Metrics and definitions The violation of equal representation on a seat per vote basis in various electoral systems can be measured with the Loosemore–Hanby index, the Gallagher index, and other measures of disproportionality. History The phrase surged in English-language usage around 1880, thanks in part to British trade unionist George Howell, who used the phrase "one man, one vote" in political pamphlets. During the mid-to-late 20th-century period of decolonisation and the struggles for national sovereignty, this phrase became widely used in developing countries where majority populations sought to gain political power in proportion to their numbers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynolds V
Reynolds may refer to: Places Australia * Hundred of Reynolds, a cadastral unit in South Australia * Hundred of Reynolds (Northern Territory), a cadastral unit in the Northern Territory of Australia United States * Reynolds, Mendocino County, California, a former settlement * Reynolds, Georgia, a town in Taylor County * Reynolds, Illinois, a village in Mercer and Rock Island counties * Reynolds, Indiana, a town in White County * Reynolds, Dallas County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Reynolds, Reynolds County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Reynolds, Nebraska, a village in Jefferson County * Reynolds, North Dakota, a city * Reynolds Township, Lee County, Illinois, a town * Reynolds Township, Michigan, a civil township of Montcalm County * Reynolds Township, Minnesota, a town in Todd County * Reynolds County, Missouri, a county in southeast Missouri Outer space * Reynolds (crater), impact crater on Mars Business * Reynolds Brothers, a New Jersey clot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of The United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over State court (United States), state court cases that turn on questions of Constitution of the United States, U.S. constitutional or Law of the United States, federal law. It also has Original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of the United States, original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, specifically "all Cases affecting Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, and those in which a State shall be Party." In 1803, the Court asserted itself the power of Judicial review in the United States, judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statute for violating a provision of the Constitution via the landmark case ''Marbury v. Madison''. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim Crow Laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Jim Crow" being a pejorative term for an African American. The last of the Jim Crow laws were generally overturned Voting Rights Act of 1965, in 1965. Formal and informal racial segregation policies were present in other areas of the United States as well, even as several states outside the South had banned discrimination in public accommodations and voting. Southern laws were enacted by white-dominated state legislatures (Redeemers) to disenfranchise and remove political and economic gains made by African Americans during the Reconstruction era. Such continuing racial segregation was also supported by the successful Lily-white movement. In practice, Jim Crow laws mandated racial segregation in all public facilities in the states of the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
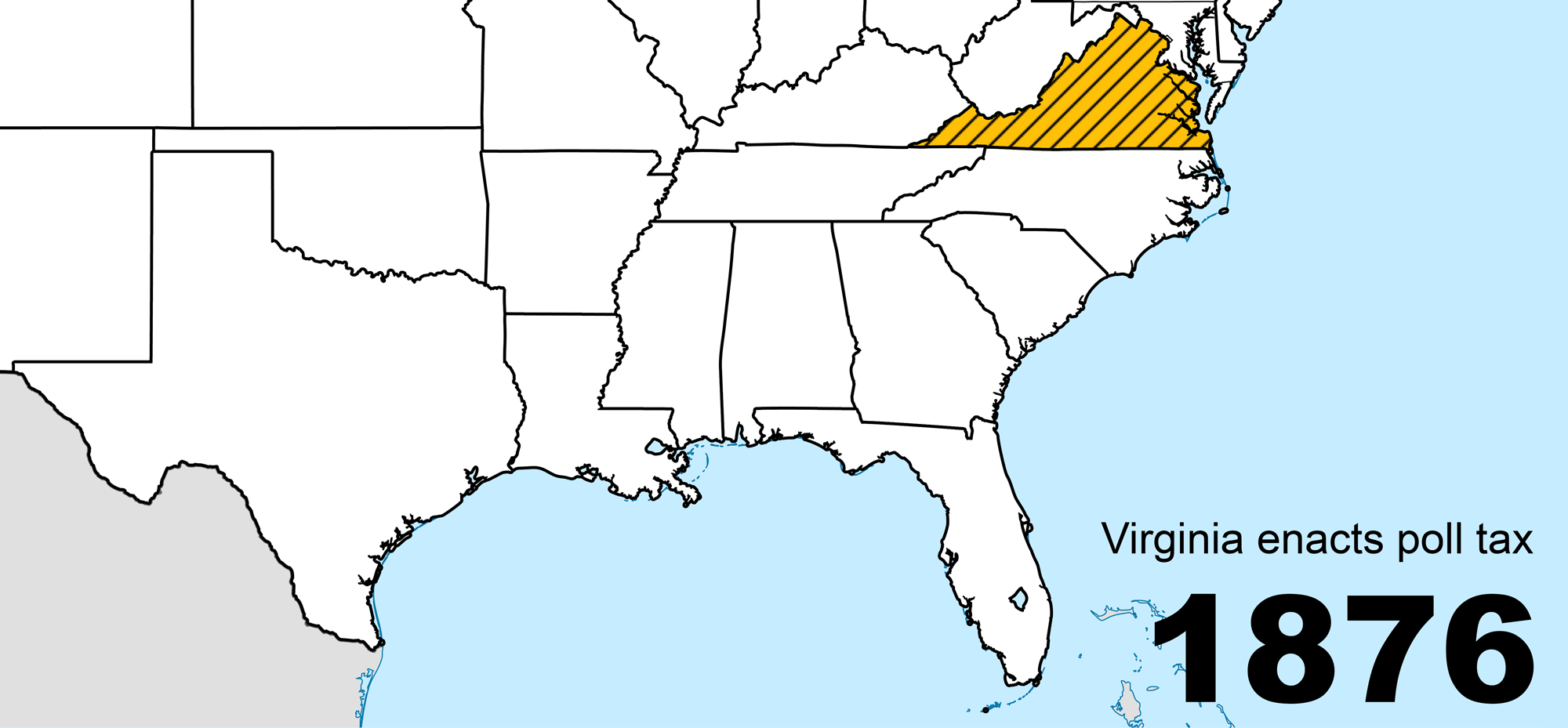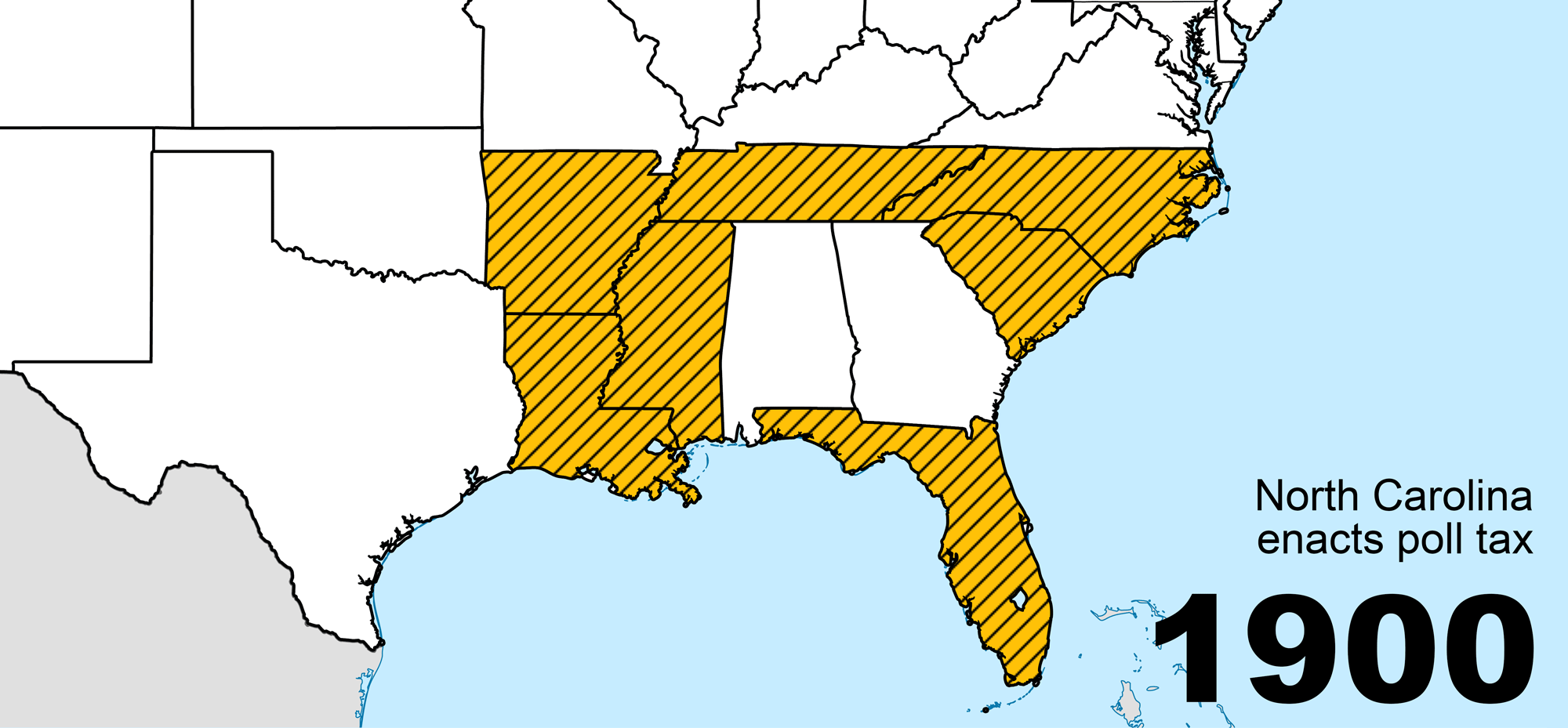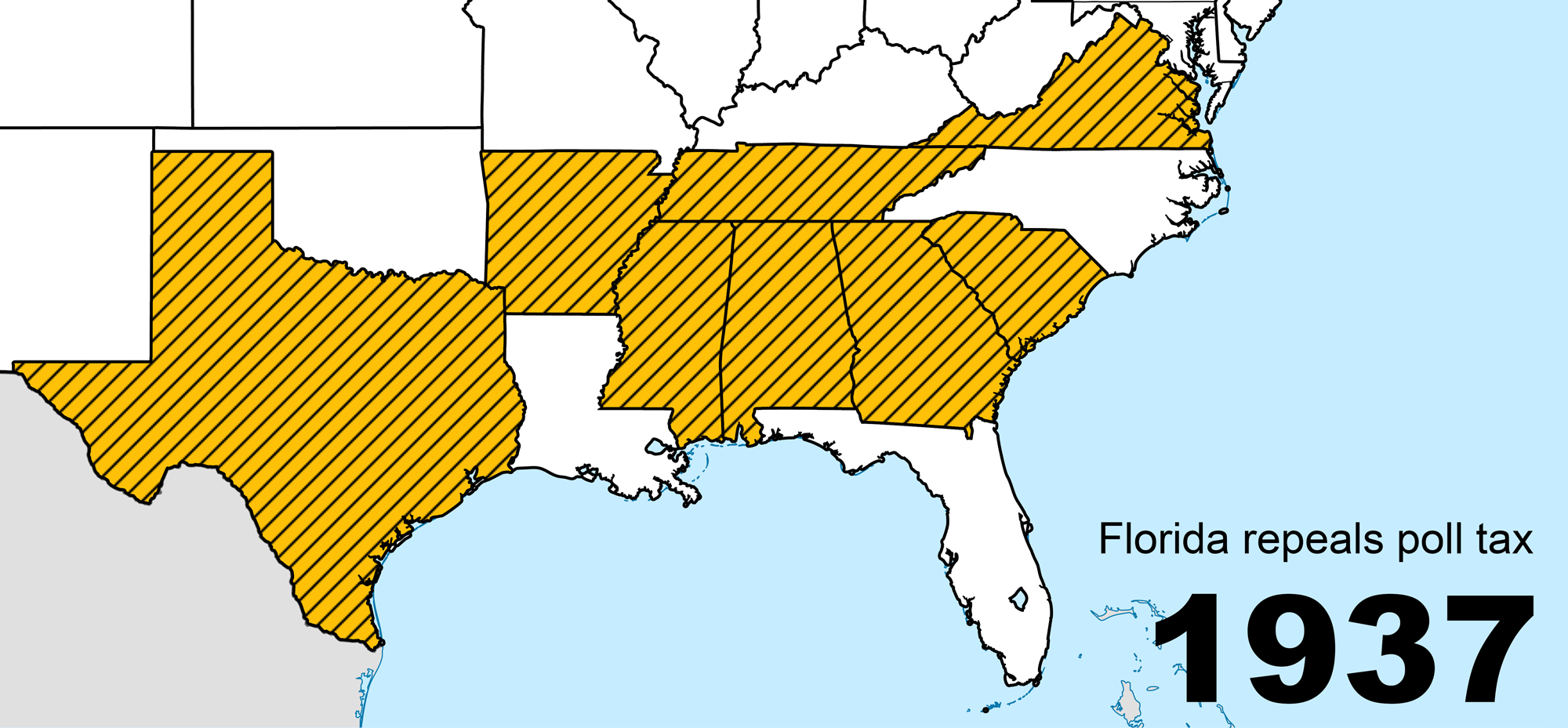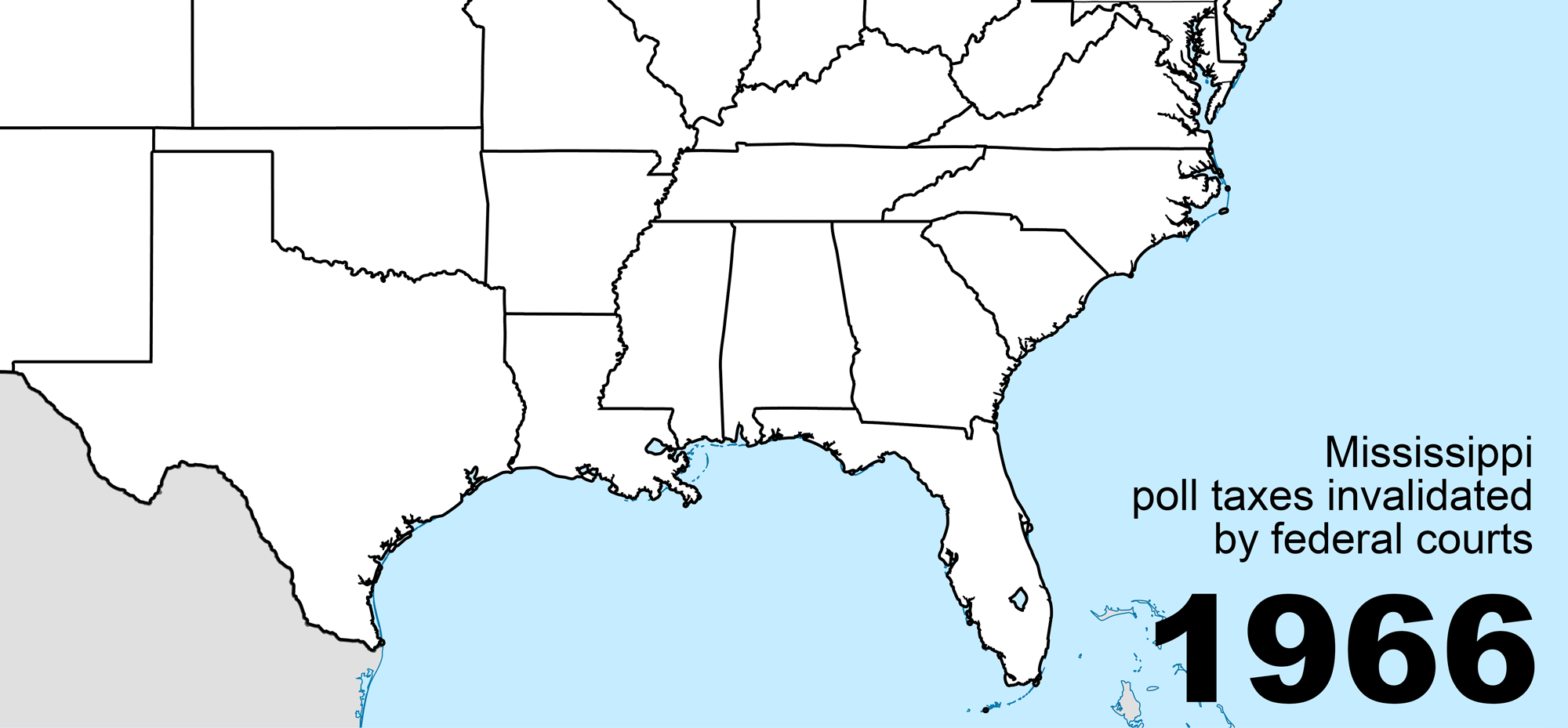
Poll Tax (United States)
Poll taxes were used in the United States until they were outlawed following the Voting Rights Act of 1965. Poll taxes (taxes of a fixed amount on every liable individual, regardless of their income) had also been a major source of government funding among the colonies and states which went on to form the United States. Poll taxes became a tool of disenfranchisement in the South during Jim Crow, following the end of Reconstruction. This form of disenfranchisement was common until the Voting Rights Act, which is considered one of the most monumental pieces of civil rights legislation ever passed. The Voting Rights Act followed the Twenty-fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which prohibited both Congress and the states from implementing poll taxes, but only for federal elections. Description A poll tax is a tax of a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. Various privileges of citizenship, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |